Flexibility in the Insulin Receptor Ectodomain Enables Docking of Insulin in Crystallographic Conformation Observed in a Hormone-Bound Microreceptor
Abstract
:1. Introduction


2. Methods
2.1. Molecular Dynamics Flexible Fitting
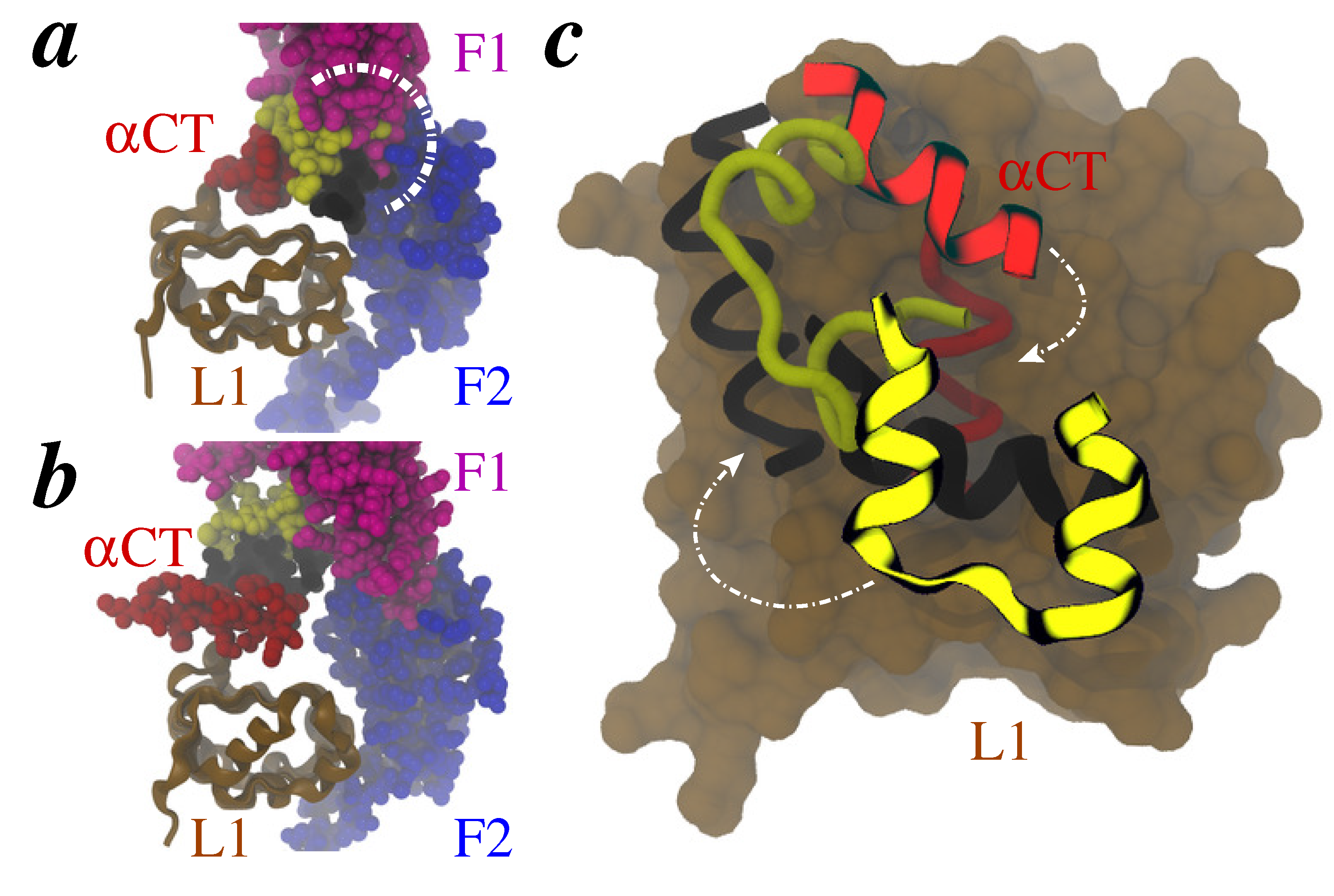
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. MDFF Fitting

3.2. MDFF-Generated Model: Key Features



4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Steiner, D. Adeventures with insulin in the Islets of Langerhans. J. Biol. Chem. 2011, 286, 17399–17421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ullrich, A.; Bell, J.R.; Chen, E.Y.; Herrera, R.; Petruzzelli, L.M.; Dull, T.J.; Gray, A.; Coussens, L.; Liao, Y.C.; Tsubokawa, M.; et al. Human insulin receptor and its relationship to the tyrosine kinase family of oncogenes. Nature 1985, 313, 756–761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Meyts, P.; Whittaker, J. Structural biology of insulin and IGF1 receptors: implications for drug design. Nat. Rev. Drug. Discov. 2002, 1, 769–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Meyts, P. Insulin and its receptor: structure, function and evolution. BioEssays 2004, 26, 1351–1362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Meyts, P. The insulin receptor: A prototype for dimeric, allosteric membrane receptors? Trends Biochem. Sci. 2008, 33, 376–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adams, M.J.; Blundell, T.; Dodson, E.; Dodson, G.; Vijayan, M.; Baker, E.; Harding, M.; Hodgkin, D.; Rimmer, B.; Sheat, S. Structure of rhombohedral 2 zinc insulin crystals. Nature 1969, 224, 491–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKern, N.; Lawrence, M.; Streltsov, V.; Lou, M.; Adams, T.; Lovrecz, G.; Elleman, T.; Richards, K.; Bentley, J.; Pilling, P.; et al. Structure of the insulin receptor ectodomain reveals a folded-over conformation. Nature 2006, 443, 218–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, B.; Huang, K.; Kong, G.; Chan, S.; Nakagawa, S.; Menting, J.; Hu, S.; Whittaker, J.; Steiner, D.; Katsoyannis, P.; et al. Structural resolution of a tandem hormone-binding element in the insulin receptor and its implications for design of peptide agonists. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 6771–6776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lou, M.; Garrett, T.; McKern, N.; Hoyne, P.; Epa, V.; Bentley, J.; Lovrecz, G.; Cosgrove, L.; Frenkel, M.; Ward, C. The first three domains of the insulin receptor differ structurally from the insulin-like growth factor 1 receptor in the regions governing ligand specificity. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 12429–12434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Meyts, P. The structural basis of insulin and insulin-like growth factor-I receptor binding and negative co-operativity, and its relevance to mitogenic versus metabolic signalling. Diabetologia 1994, 37, S135–S148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ward, C.W.; Garrett, T.P. The relationship between the L1 and L2 domains of the insulin and epidermal growth factor receptors and leucine-rich repeat modules. BMC Bioinformatics 2001, 2, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ward, C.; Lawrence, M.; Streltsov, V.; Adams, T.; McKern, N. The insulin and EGF receptor structures: new insights into ligand-induced receptor activation. Trends Biochem. Sci. 2007, 32, 129–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ward, C.; Lawrence, M.; Streltsov, V.; Garrett, T.; McKern, N.; Lou, M.; Lovrecz, G.; Adams, T. Structural insights into ligand-induced activation of the insulin receptor. Acta Physiol. 2008, 192, 3–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ward, C.W.; Lawrence, M.C. Ligand-induced activation of the insulin receptor: A multi-step process involving structural changes in both the ligand and the receptor. Bioessays 2009, 31, 422–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lawrence, M.; McKern, N.; Ward, C. Insulin receptor structure and its implications for the IGF-1 receptor. Curr. Opin. Struct. Biol. 2007, 17, 699–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ward, C.W.; Lawrence, M.C. Landmarks in insulin research. Front. Endocrin. 2011, 2, 76. [Google Scholar]
- Ward, C.; Lawrence, M. Similar but different: ligand-induced activation of the insulin and epidermal growth factor receptor families. Curr. Opin. Struct. Biol. 2012, 22, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ward, C.W.; Menting, J.G.; Lawrence, M.C. The insulin receptor changes conformation in unforeseen ways on ligand binding: sharpening the picture of insulin receptor activation. BioEssays 2013, 35, 945–954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hubbard, S.R. Structural biology: Insulin meets its receptor. Nature 2013, 493, 171–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ullrich, A.; Gray, A.; Tam, A.W.; Yangfeng, T.; Tsubokawa, M.; Collins, C.; Henzel, W.; Lebon, T.; Kathuria, S.; Chen, E.; et al. Insulin-like growth factor-I receptor primary structure-Comparison with insulin-receptor suggests structural determinants that define functional specificity. EMBO J. 1986, 5, 2503–2512. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Whitten, A.; Smith, B.; Menting, J.; Margetts, M.; McKern, N.; Lovrecz, G.; Adams, T.; Richards, K.; Bentley, J.; Trewhella, J.; et al. Solution structure of ectodomains of the insulin receptor family: the ectodomain of the Type 1 insulin-like growth factor receptor displays asymmetry of ligand binding accompanied by limited conformational change. J. Mol. Biol. 2009, 394, 878–892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pullen, R.; Lindsay, D.; Wood, S.; Tickle, I.; Blundell, T.; Wollmer, A.; Krail, G.; Brandenburg, D.; Zahn, H.; Gliemann, J.; et al. Receptor-binding region of insulin. Nature 1976, 259, 369–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Meyts, P.; Obberghen, E.; Roth, J.; Wollmer, A.; Brandenburg, D. Mapping of the residues responsible for the negative cooperativity of the receptor-binding region of insulin. Nature 1978, 273, 504–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kristensen, C.; Kjeldsen, T.; Wiberg, F.; Schäffer, L.; Hach, M.; Havelund, S.; Bass, J.; Steiner, D.; Andersen, A. Alanine scanning mutagenesis of insulin. J. Biol. Chem. 1997, 272, 12978–12983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, H.; Shi, M.; Guo, Z.; Tang, Y.; Qiao, Z.; Liang, Z.; Feng, Y. Four new monomeric insulins obtained by alanine scanning the dimer-forming surface of the insulin molecule. Protein Eng. 2000, 13, 779–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakamura, T.; Takahashi, H.; Takahashi, M.; Shimba, N.; Suzuki, E.i.; Shimada, I. Direct determination of the insulin-insulin receptor interface using transferred cross-saturation experiments. J. Med. Chem. 2010, 53, 1917–1922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Williams, P.; Mynarcik, D.; Yu, G.; Whittaker, J. Mapping of an NH2-terminal ligand binding site of the insulin receptor by alanine scanning mutagenesis. J. Biol. Chem. 1995, 270, 3012–3016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Whittaker, J.; Whittaker, L. Characterization of the functional insulin binding epitopes of the full-length insulin receptor. J. Biol. Chem. 2005, 280, 20932–20936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mynarcik, D.; Williams, P.; Schaffer, L.; Yu, G.; Whittaker, J. Analog binding properties of insulin receptor mutants. J. Biol. Chem. 1997, 272, 2077–2081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schaefer, E.; Siddle, K.; Ellis, L. Deletion analysis of the human insulin receptor ectodomain reveals independently folded soluble subdomains and insulin binding by a monomeric α-subunit. J. Biol. Chem. 1990, 265, 13248–13253. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kristensen, C.; Andersen, A.; Hach, M.; Wiberg, F.; Schäffer, L.; Kjeldsen, T. A single-chain insulin-like growth factor I/insulin hybrid binds with high affinity to the insulin receptor. Biochem. J. 1995, 305, 981–986. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Schlein, M.; Havelund, S.; Kristensen, C.; Dunn, M.; Kaarsholm, N. Ligand-induced conformational change in the minimized insulin receptor. J. Mol. Biol. 2000, 303, 161–169. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Brandt, J.; Andersen, A.; Kristensen, C. Dimeric fragment of the insulin receptor α-subunit binds insulin with full holoreceptor affinity. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 12378–12384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Surinya, K.; Molina, L.; Soos, M.; Brandt, J.; Kristensen, C.; Siddle, K. Role of insulin receptor dimerization domains in ligand binding, cooperativity, and modulation by anti-receptor antibodies. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 16718–16725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kristensen, C.; Andersen, A.; Østergaard, S.; Hansen, P.; Brandt, J. Functional reconstitution of insulin receptor binding site from non-binding receptor fragments. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 18340–18345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kurose, T.; Pashmforoush, M.; Yoshimasa, Y.; Carroll, R.; Schwartz, G.; Burke, G.; Katsoyannis, P.; Steiner, D. Cross-linking of a B25 Azidophenylalanine insulin derivative to the carboxyl-terminal regions of the α-subunit of the insulin receptor. J. Biol. Chem. 1994, 269, 29190–29197. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Mynarcik, D.; Yu, G.; Whittaker, J. Alanine-scanning mutagenesis of a C-terminal ligand binding domain in the insulin receptor α subunit. J. Biol. Chem. 1996, 271, 2439–2442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kristensen, C.; Wiberg, F.; Andersen, A. Specificity of insulin and insulin-like growth factor I receptors investigated using chimeric mini-receptors. J. Biol. Chem. 1999, 274, 37351–37356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Molina, L.; Marino-Buslje, C.; Quinn, D.; Siddle, K. Structural domains of the insulin receptor and IGF receptor required for dimerization and ligand binding. FEBS Lett. 2000, 467, 226–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Whittaker, L.; Hao, C.; Fu, W.; Whittaker, J. High-affinity insulin binding: insulin interacts with two receptor ligand binding sites. Biochemistry 2008, 47, 12900–12909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, B.; Roth, R. A region of the insulin receptor important for ligand binding (residues 450-601) is recognized by patients’ autoimmune antibodies and inhibitory monoclonal antibodies. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1991, 88, 9858–9862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fabry, M.; Schaefer, E.; Ellis, L.; Kojro, E.; Fahrenholz, F.; Brandenburg, D. Detection of a new hormone contact site within the insulin receptor ectodomain by the use of a novel photoreactive insulin. J. Biol. Chem. 1992, 267, 8950–8956. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Schumacher, R.; Soos, M.; Schlessinger, J.; Brandenburg, D.; Siddle, K.; Ullrich, A. Signaling-competent receptor chimeras allow mapping of major insulin receptor binding domain determinants. J. Biol. Chem. 1993, 268, 1087–1094. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hao, C.; Whittaker, L.; Whittaker, J. Characterization of a second ligand binding site of the insulin receptor. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2006, 347, 334–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benyoucef, S.; Surinya, K.; Hadaschik, D.; Siddle, K. Characterization of insulin/IGF hybrid receptors: contributions of the insulin receptor L2 and Fn1 domains and the alternatively spliced exon 11 sequence to ligand binding and receptor activation. Biochem. J. 2007, 403, 603–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Renteria, M.; Gandhi, H.; Vinuesa, P.; Helmerhorst, E.; Mancera, R. A comparative structural bioinformatics analysis of the insulin receptor family ectodomain based on phylogenetic information. PLoS One 2008, 3, e3667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hua, Q.X.; Shoelson, S.E.; Kochoyan, M.; Weiss, M. Receptor-binding redefined by a structural switch in a mutant human insulin. Nature 1991, 354, 238–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ludvigsen, S.; Olsen, H.; Kaarsholm, N. A structural switch in a mutant insulin exposes key residues for receptor binding. J. Mol. Biol. 1998, 279, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wan, Z.L.; Huang, K.; Xu, B.; Hu, S.Q.; Wang, S.H.; Chu, Y.C.; Katsoyannis, P.G.; Weiss, M.A. Diabetes-associated mutations in human insulin: Crystal structure and photo-cross-linking studies of A-chain variant insulin Wakayama. Biochemistry 2005, 44, 5000–5016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiracek, J.; Zakova, L.; Antolikova, E.; Watson, C.J.; Turkenburg, J.P.; Dodson, G.G.; Brzozowski, A.M. Implications for the active form of human insulin based on the structural convergence of highly active hormone analogues. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 1966–1970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pillutla, R.C.; Hsiao, K.C.; Beasley, J.R.; Brandt, J.; Ostergaard, S.; Hansen, P.H.; Spetzler, J.C.; Danielsen, G.M.; Andersen, A.S.; Brissette, R.E.; et al. Peptides identify the critical hotspots involved in the biological activation of the insulin receptor. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 22590–22594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schaffer, L.; Brissette, R.E.; Spetzler, J.C.; Pillutla, R.C.; Ostergaard, S.; Lennick, M.; Brandt, J.; Fletcher, P.W.; Danielsen, G.M.; Hsiao, K.C. ;et al. Assembly of high-affinity insulin receptor agonists and antagonists from peptide building blocks. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2003, 100, 4435–4439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, K.; Xu, B.; Hu, S.; Chu, Y.; Hua, Q.; Qu, Y.; Li, B.; Wang, S.; Wang, R.; Nakagawa, S.; et al. How insulin binds: The B-chain α-helix contacts the L1 β-helix of the insulin receptor. J. Mol. Biol. 2004, 341, 529–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, K.; Chan, S.; Hua, Q.; Chu, Y.; Wang, R.; Klaproth, B.; Jia, W.; Whittaker, J.; De Meyts, P.; Nakagawa, S.; et al. The A-chain of insulin contacts the insert domain of the insulin receptor. J. Biol. Chem. 2007, 282, 35337–35349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, B.; Huang, K.; Chu, Y.C.; Hu, S.Q.; Nakagawa, S.; Wang, S.; Wang, R.Y.; Whittaker, J.; Katsoyannis, P.G.; Weiss, M. Decoding the cryptic active conformation of a protein by synthetic photoscanning: Insulin inserts a detachable arm between receptor domains. J. Biol. Chem. 2009, 284, 14597–14608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Menting, J.; Ward, C.; Margetts, M.; Lawrence, M. A thermodynamic study of ligand binding to the first three domains of the human insulin receptor: relationship between the receptor alpha-chain C-terminal peptide and the site-1 insulin mimetic peptides. Biochemistry 2009, 48, 5492–5500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Whittaker, J.; Whittaker, L.; Roberts, C., Jr; Phillips, N.; Ismail-Beigi, F.; Lawrence, M.; Weiss, M. α-Helical element at the hormone-binding surface of the insulin receptor functions as a signaling element to activate its tyrosine kinase. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 11166–11171. [Google Scholar]
- Menting, J.G.; Whittaker, J.; Margetts, M.B.; Whittaker, L.J.; Kong, G.K.W.; Smith, B.J.; Watson, C.J.; Žáková, L.; Kletvíková, E.; Jirácˇek, J.; et al. How insulin engages its primary binding site on the insulin receptor. Nature 2013, 493, 241–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Menting, J.G.; Yang, Y.; Chan, S.J.; Phillips, N.B.; Smith, B.J.; Whittaker, J.; Wickramasinghe, N.P.; Whittaker, L.J.; Pandyarajan, V.; Wan, Z.l.; et al. Protective hinge in insulin opens to enable its receptor engagement. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, E3395–E3404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kiselyov, V.; Versteyhe, S.; Gauguin, L.; De Meyts, P. Harmonic oscillator model of the insulin and IGF1 receptors’ allosteric binding and activation. Mol. Syst. Biol. 2009, 5, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vashisth, H.; Abrams, C.F. All-atom structural models of insulin binding to the insulin receptor in the presence of a tandem hormone-binding element . Proteins 2013, 81, 1017–1030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vashisth, H.; Abrams, C.F. Docking of insulin to a structurally equilibrated insulin receptor ectodomain. Proteins 2010, 78, 1531–1543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vashisth, H.; Abrams, C.F. All-atom structural models for complexes of insulin-like growth factors IGF1 and IGF2 with their cognate receptor. J. Mol. Biol. 2010, 400, 645–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trabuco, L.G.; Villa, E.; Mitra, K.; Frank, J.; Schulten, K. Flexible fitting of atomic structures into electron microscopy maps using molecular dynamics. Structure 2008, 16, 673–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trabuco, L.G.; Villa, E.; Schreiner, E.; Harrison, C.B.; Schulten, K. Molecular dynamics flexible fitting: A practical guide to combine cryo-electron microscopy and X-ray crystallography. Methods 2009, 49, 174–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trabuco, L.G.; Schreiner, E.; Gumbart, J.; Hsin, J.; Villa, E.; Schulten, K. Applications of the molecular dynamics flexible fitting method. J. Struct. Biol. 2011, 173, 420–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schreiner, E.; Trabuco, L.G.; Freddolino, P.L.; Schulten, K. Stereochemical errors and their implications for molecular dynamics simulations. BMC Bioinform. 2011, 12, 190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, K.Y.; Gumbart, J.; McGreevy, R.; Watermeyer, J.M.; Sewell, B.T.; Schulten, K. Symmetry-restrained flexible fitting for symmetric EM maps. Structure 2011, 19, 1211–1218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gumbart, J.; Trabuco, L.G.; Schreiner, E.; Villa, E.; Schulten, K. Regulation of the protein-conducting channel by a bound ribosome. Structure 2009, 17, 1453–1464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsin, J.; Gumbart, J.; Trabuco, L.G.; Villa, E.; Qian, P.; Hunter, C.N.; Schulten, K. Protein-induced membrane curvature investigated through molecular dynamics flexible fitting. Biophys. J. 2009, 97, 321–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, W.; Trabuco, L.G.; Schulten, K.; Frank, J. Molecular dynamics of EF-G during translocation. Proteins 2011, 79, 1478–1486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trabuco, L.G.; Schreiner, E.; Eargle, J.; Cornish, P.; Ha, T.; Luthey-Schulten, Z.; Schulten, K. The role of L1 stalk-tRNA interaction in the ribosome elongation cycle. J. Mol. Biol. 2010, 402, 741–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sener, M.; Hsin, J.; Trabuco, L.G.; Villa, E.; Qian, P.; Hunter, C.N.; Schulten, K. Structural model and excitonic properties of the dimeric RC-LH1-Pufx complex from Rhodobacter sphaeroides. Chem. Phys. 2009, 357, 188–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Armache, J.P.; Jarasch, A.; Anger, A.M.; Villa, E.; Becker, T.; Bhushan, S.; Jossinet, F.; Habeck, M.; Dindar, G.; Franckenberg, S.; et al. Cryo-EM structure and rRNA model of a translating eukaryotic 80S ribosome at 5.5 Å resolution. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 19748–19753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Armache, J.P.; Jarasch, A.; Anger, A.M.; Villa, E.; Becker, T.; Bhushan, S.; Jossinet, F.; Habeck, M.; Dindar, G.; Franckenberg, S.; et al. Localization of eukaryote-specific ribosomal proteins in a 5.5 Å cryo-EM map of the 80S eukaryotic ribosome. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 19754–19759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agirrezabala, X.; Schreiner, E.; Trabuco, L.G.; Lei, J.; Ortiz-Meoz, R.F.; Schulten, K.; Green, R.; Frank, J. Structural insights into cognate versus near-cognate discrimination during decoding. EMBO J. 2011, 30, 1497–1507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Strunk, B.S.; Loucks, C.R.; Su, M.; Vashisth, H.; Cheng, S.; Schilling, J.; Brooks, C.L., III.; Karbstein, K.; Skiniotis, G. Ribosome assembly factors prevent premature translation initiation by 40S assembly intermediates. Science 2011, 333, 1449–1453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vashisth, H.; Skiniotis, G.; Brooks, C.L., III. Using enhanced sampling and structural restraints to refine atomic structures into low-resolution electron microscopy maps. Structure 2012, 20, 1453–1462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vashisth, H.; Skiniotis, G.; Brooks, C.L., III. Enhanced sampling and overfitting analyses in structural refinement of nucleic acids into electron microscopy maps. J. Phys. Chem. B 2013, 117, 3738–3746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Phillips, J.; Braun, R.; Wang, W.; Gumbart, J.; Tajkhorshid, E.; Villa, E.; Chipot, C.; Skeel, R.; Kalé, L.; Schulten, K. Scalable molecular dynamics with NAMD. J. Comput. Chem. 2005, 26, 1781–1802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalé, L.; Skeel, R.; Bhandarkar, M.; Brunner, R.; Gursoy, A.; Krawetz, N.; Phillips, J.; Shinozaki, A.; Varadarajan, K.; Schulten, K. NAMD2: Greater scalability for parallel molecular dynamics. J. Comput. Phys. 1999, 151, 283–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacKerell, A.D., Jr.; Bashford, D.; Bellott, M.; Dunbrack, R.L., Jr.; Evanseck, J.D.; Field, M.J.; Fischer, S.; Gao, J.; Guo, H.; Ha, S.; et al. All-atom empirical potential for molecular modeling and dynamics studies of proteins. J. Phys. Chem. B 1998, 102, 3586–3616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- MacKerell, A.D., Jr.; Feig, M.; Brooks, C.L., III. Extending the treatment of backbone energetics in protein force fields: limitations of gas-phase quantum mechanics in reproducing protein conformational distributions in molecular dynamics simulations. J. Comput. Chem. 2004, 25, 1400–1415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chan, S.; Nakagawa, S.; Steiner, D. Complementation analysis demonstrates that insulin cross-links both α-subunits in a truncated insulin receptor dimer. J. Biol. Chem. 2007, 282, 13754–13758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thorsoe, K.S.; Schlein, M.; Steensgaard, D.B.; Brandt, J.; Schluckebier, G.; Naver, H. Kinetic evidence for the sequential association of insulin binding sites 1 and 2 to the insulin receptor and the influence of receptor isoform. Biochemistry 2010, 49, 6234–6246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2014 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Vashisth, H. Flexibility in the Insulin Receptor Ectodomain Enables Docking of Insulin in Crystallographic Conformation Observed in a Hormone-Bound Microreceptor. Membranes 2014, 4, 730-746. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes4040730
Vashisth H. Flexibility in the Insulin Receptor Ectodomain Enables Docking of Insulin in Crystallographic Conformation Observed in a Hormone-Bound Microreceptor. Membranes. 2014; 4(4):730-746. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes4040730
Chicago/Turabian StyleVashisth, Harish. 2014. "Flexibility in the Insulin Receptor Ectodomain Enables Docking of Insulin in Crystallographic Conformation Observed in a Hormone-Bound Microreceptor" Membranes 4, no. 4: 730-746. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes4040730
APA StyleVashisth, H. (2014). Flexibility in the Insulin Receptor Ectodomain Enables Docking of Insulin in Crystallographic Conformation Observed in a Hormone-Bound Microreceptor. Membranes, 4(4), 730-746. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes4040730




