Electrodialytic Transport Properties of Anion-Exchange Membranes Prepared from Poly(vinyl alcohol) and Poly(vinyl alcohol-co-methacryloyl aminopropyl trimethyl ammonium chloride)
Abstract
:1. Introduction

2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Water Content as a Function of Cpc
2.2. IEC of the AEMs
2.3. The Effective Charge Density of the Membranes as a Function of Cpc

| Sample | Cpc (mol %) | IEC (meq/g dry-CEM) |
|---|---|---|
| RPA-1 | 3.0 | 0.22 (0.60 a) |
| RPA-2 | 4.2 | 0.27 (0.81) |
| RPA-3 | 4.8 | 0.30 (0.90) |
| RPA-4 | 6.0 | 0.39 (1.09) |
| AMX a | – | 1.4 |
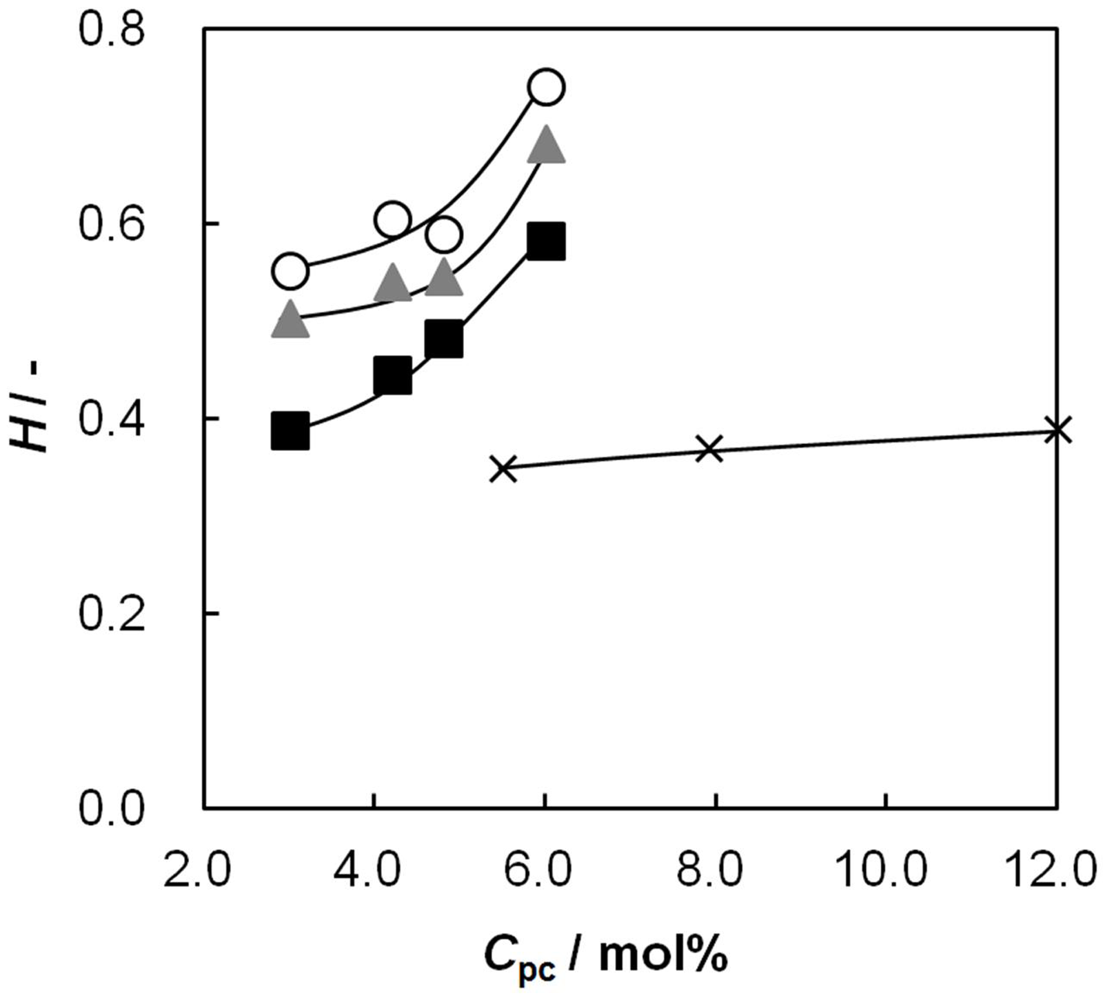

2.4. Membrane Resistance as a Function of Cpc
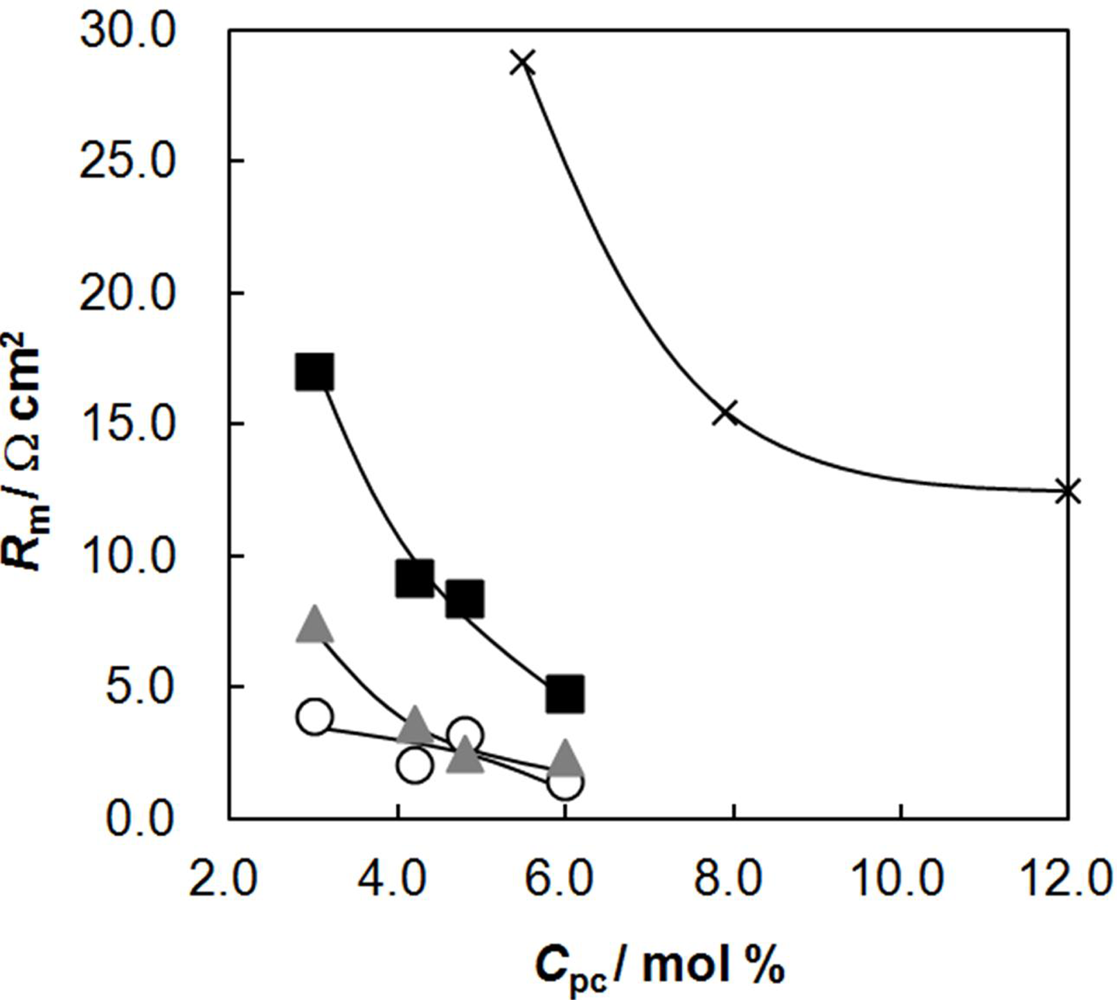
2.5. Membrane Resistance as a Function of Water Content


2.6. Dynamic State Transport Number of the AEMs as a Function of Cpc
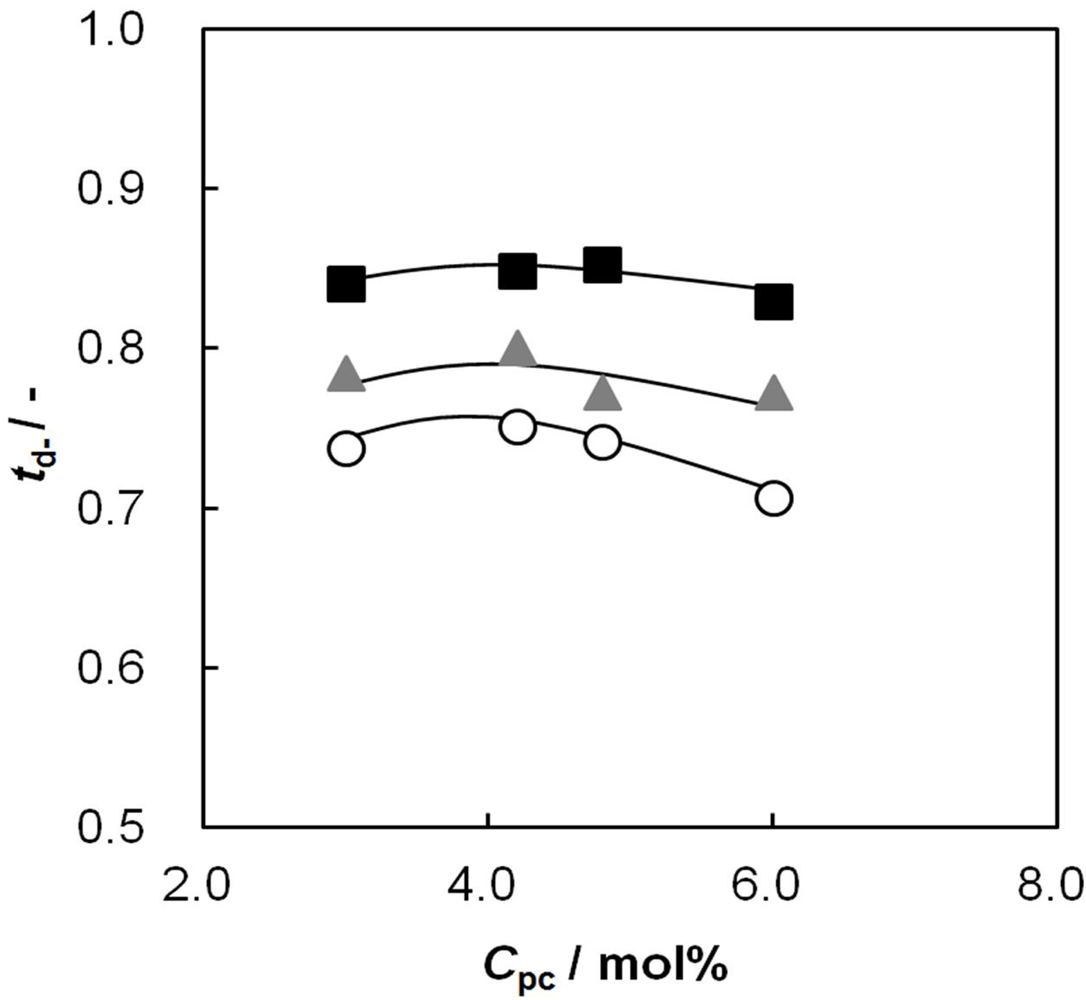
2.7. Relationship between Membrane Resistance and Dynamic State Transport Number

2.8. Relationship between Dynamic State Transport Number and Effective Charge Density
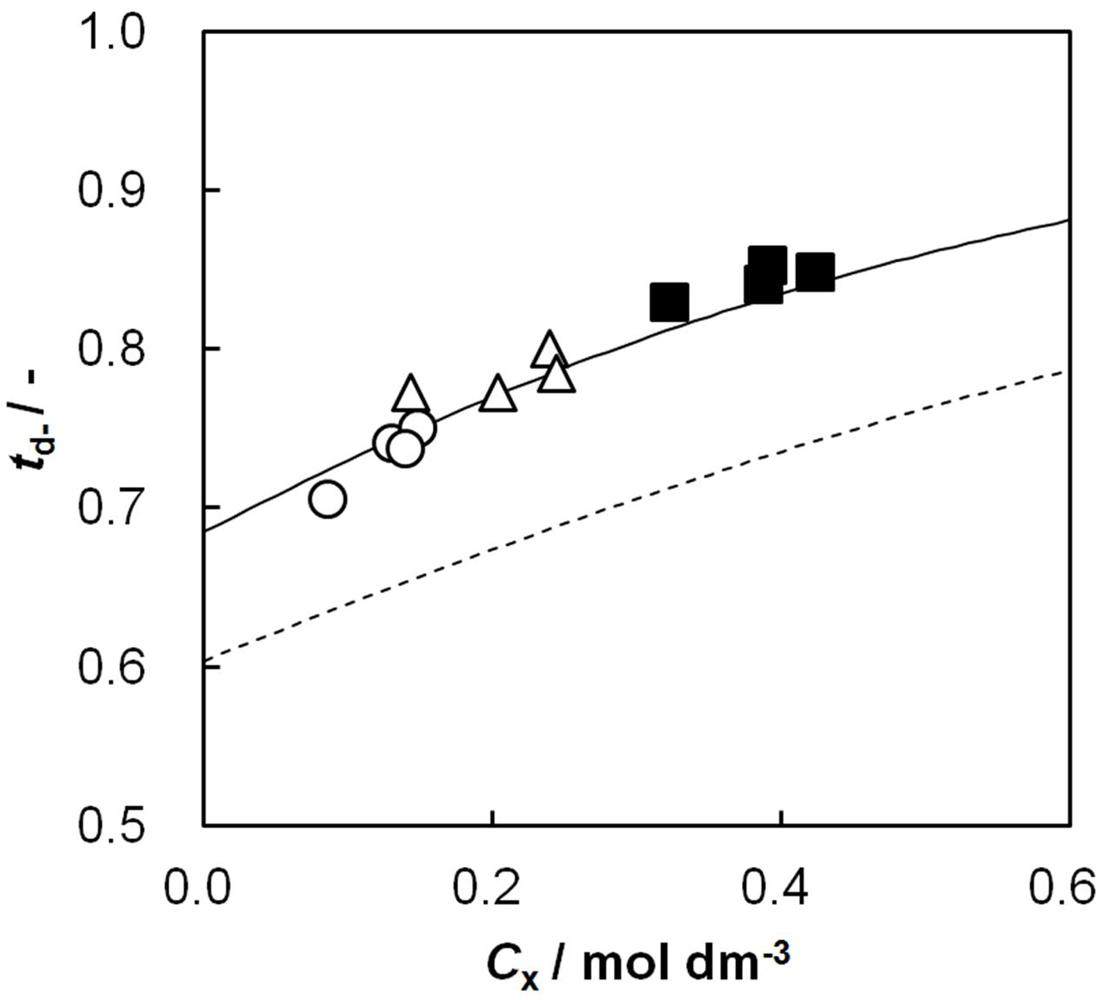




 and γi are the corresponding activity coefficients in the membrane and the solution. The values of the mobility of Na+ and Cl− ions in an aqueous solution are 5.4 × 10−13 mol m2 J−1 s−1 and 7.9 × 10−13 mol m2 J−1 s−1, respectively [21]. Hence, the ratio of wNa to wCl is 0.66. In the case of assuming that αNa/αCl = 1 and QNa/QCl = 1, the calculation of β = 0.66 is lower than the experiments as shown in the broken curve in Figure 7. The calculation of β = 0.46 as shown in the solid curve is in good agreement with the experiments. This means that the ratio of the correction factor, αNa/αCl, and/or the ratio, QNa/QCl, is less than 1.0. The correction factor of the highly hydrated ion Ca2+ in PVA-based membranes is smaller than that of the Cl− (αCa = 0.60, αCl = 0.94) [21]. The radius of the hydrated Na+ is lower than that of the Cl−. Hence, αNa/αCl is lower than 1.0. The result indicates that the transport number can be estimated from the value of the effective charge density.
and γi are the corresponding activity coefficients in the membrane and the solution. The values of the mobility of Na+ and Cl− ions in an aqueous solution are 5.4 × 10−13 mol m2 J−1 s−1 and 7.9 × 10−13 mol m2 J−1 s−1, respectively [21]. Hence, the ratio of wNa to wCl is 0.66. In the case of assuming that αNa/αCl = 1 and QNa/QCl = 1, the calculation of β = 0.66 is lower than the experiments as shown in the broken curve in Figure 7. The calculation of β = 0.46 as shown in the solid curve is in good agreement with the experiments. This means that the ratio of the correction factor, αNa/αCl, and/or the ratio, QNa/QCl, is less than 1.0. The correction factor of the highly hydrated ion Ca2+ in PVA-based membranes is smaller than that of the Cl− (αCa = 0.60, αCl = 0.94) [21]. The radius of the hydrated Na+ is lower than that of the Cl−. Hence, αNa/αCl is lower than 1.0. The result indicates that the transport number can be estimated from the value of the effective charge density.3. Experimental Section
3.1. Materials
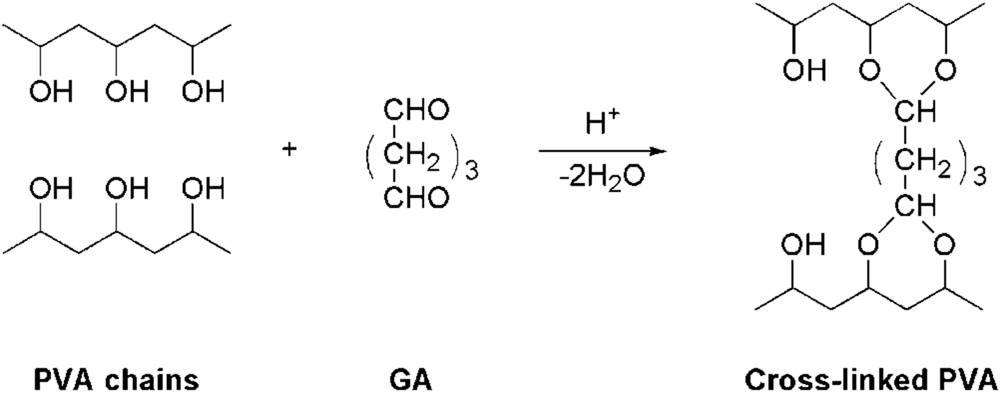
3.2. Preparation of Random-Type AEMs
3.3. Measurement of Membrane Water Content

3.4. Measurement of Ion-Exchange Capacity (IEC)

3.5. Determination of Membrane Effective Charge Density

3.6. Measurement of Membrane Resistance
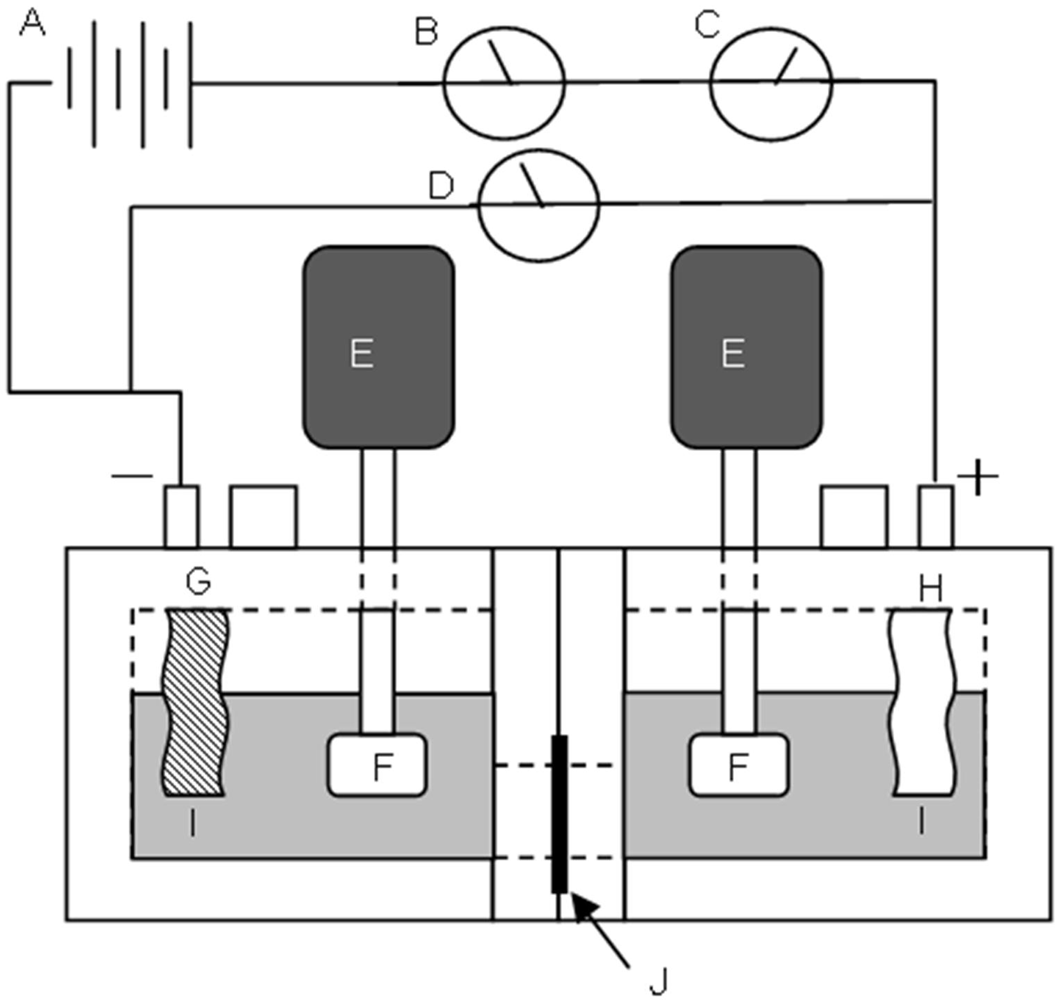
3.7. Measurement of Dynamic State Transport Number

4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Nomenclatures
| C | ionic concentration in a solution |
| Cpc | polycation content in the membrane |
| CGA | glutaraldehyde concentration |
| Cx | the charge density in an anion exchange membrane |
| F | Faraday’s constant |
| H | water content |
| IEC | Ion exchange capacity |
| q | the amount of electricity passing through a membrane during electrodialylsis |
| r | KCl concentration ratio between the high- and low-concentration chambers |
| R | gas constant |
| Ro | measured resistance without a sample membrane |
| Rs | measured resistance with a sample membrane |
| Rm | membrane resistance: Rm = Rs− Ro |
| t | transport number |
| T | absolute temperature |
| Wd | weight in dry state |
| Ww | weight in wet state |
Greek Symbols
| α | correction factor |
 | activity coefficients in the membrane |
| γ | activity coefficients in the solution |
| Δϕ | membrane potential |
| Δμ0 | standard chemical potential |
| w | ionic mobility |
Subscripts
| Cl | chloride ion |
| D | high-concentration chamber |
| K | potassium ion |
| Na | sodium ion |
| s | electrolyte solution |
| o | low-concentration chamber |
References
- Sata, T. Ion Exchange Membranes: Preparation, Characterization, Modification, and Application; Royal Society of Chemistry: London, UK, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Sata, T. Recent trends in ion exchange membrane research. Pure Appl. Chem. 1986, 58, 1613–1626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ray, P. Performance studies of heterogeneous ion exchange membranes in the removal of bivalent metal ions in an electrodialysis stack. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2009, 113, 1155–1164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merle, G.; Wessling, M.; Nijmeijer, K. Anion exchange membranes for alkaline fuel cells: A review. J. Membr. Sci. 2011, 377, 1–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melnik, L.; Vysotskaja, O.; Kornilovich, B. Boron behavior during desalination of sea and underground water by electrodialysis. Desalination 1999, 124, 125–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, E.-Y.; Bae, B.; Moon, S.-H. Control of the fixed charge distribution in an ion-exchange membrane via diffusion and the reaction rate of the monomer. J. Phys. Chem. B 2007, 111, 6383–6390. [Google Scholar]
- Miyazawa, T.; Asari, Y.; Miyoshi, K.; Umeno, D.; Saito, K.; Nagatani, T.; Yoshikawa, N. Development of novel ion-exchange membranes for electrodialysis of seawater by electron-beam-induced graft polymerization (II) graft polymerization of vinyl benzyltrimethylammonium chloride and sodium styrenesulfonate onto nylon-6 film. Bull. Soc. Sea Water Sci. Jpn. 2009, 63, 175–183. [Google Scholar]
- Uragami, T.; Nakamura, R.; Sugihara, M. Active and selective transport of alkali metal ions through crosslinked poly(styrenesulfonic acid) membrane. Makromol. Chem. Rapid Commun. 1982, 3, 467–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.S.; Park, H.B.; Rhim, J.W.; Lee, Y.M. Proton conductivity and methanol transport behavior of cross-linked PVA/PAA/silica hybrid membranes. Solid State Ionics 2005, 176, 117–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.S.; Yun, T.I.; Seo, M.Y.; Cho, H.I.; Lee, Y.M.; Nam, S.Y.; Rhim, J.W. Preparation of ion-exchange membranes for fuel cell based on crosslinked PVA/PSSA_MA/silica hybrid. Desalination 2006, 200, 634–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Higa, M.; Yamakawa, T. Design and preparation of a novel temperature-responsive ionic gel. 1. A fast and reversible temperature response in the charge density. J. Phys. Chem. B 2004, 108, 16703–16707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamakawa, T.; Ishida, S.; Higa, M. Transport properties of ions through temperature-responsive charged membranes prepared using poly(vinyl alcohol)/poly(N-isopropylacrylamide)/poly(vinyl alcohol-co-2-acrylamido-2-methylpropane sulfonic acid). J. Membr. Sci. 2005, 250, 61–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.S.; Park, H.B.; Rhim, J.W.; Lee, Y.M. Preparation and characterization of crosslinked PVA/SiO2 hybrid membranes containing sulfonic acid groups for direct methanol fuel cell applications. J. Membr. Sci. 2004, 240, 37–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.-C.; Chiu, S.-J.; Chien, W.-C. Development of alkaline direct methanol fuel cells based on crosslinked PVA polymer membranes. J. Power Sources 2006, 162, 21–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikolić, V.M.; Žugić, D.L.; Maksić, A.D.; Šaponjić, D.P.; Kaninski, M.P.M. Performance comparison of modified poly(vinyl alcohol) based membranes in alkaline fuel cells. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2011, 36, 11004–11010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Higa, M.; Sugita, M.; Maesowa, S.; Endo, N. Poly(vinyl alcohol)-based polymer electrolyte membranes for direct methanol fuel cells. Electrochim. Acta 2010, 55, 1445–1449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, J.; Fu, J.; Liu, L.; Liu, Y.; Sheng, J. Highly stable hydroxyl anion conducting membranes poly(vinyl alcohol)/poly(acrylamide-co-diallyldimethylammonium chloride) (PVA/PAADDA) for alkaline fuel cells: Effect of cross-linking. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2012, 37, 4580–4589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishimura, M.; Higa, M.; Akamine, K.; Masudaya, S. Preparation and characterization of anion-exchange membranes with a semi-interpenetrating network structure of poly(vinyl alcohol) and poly(allyl amine). Desalination 2008, 233, 157–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mackie, J.S.; Meares, P. The diffusion of electrolytes in a cation-exchange resin membrane. I. Theoretical. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. A 1955, 232, 498–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, N.; Nagase, M.; Higa, M. Preparation of aliphatic-hydrocarbon-based anion-exchange membranes and their anti-organic-fouling properties. J. Membr. Sci. 2011, 384, 27–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Higa, M.; Yamakawa, T. Design and preparation of a novel temperature-responsive ionic gel. 2. Concentration modulation of specific ions in response to temperature changes. J. Phys. Chem. B 2005, 109, 11373–11378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Higa, M.; Nishimura, M.; Kinoshita, K.; Jikihara, A. Characterization of cation-exchange membranes prepared from poly(vinyl alcohol) and poly(vinyl alcohol-b-styrene sulfonic acid). Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2012, 37, 6161–6168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, R.L. Crystallographic Data and Melting Points for Various Polymers. In Polymer Handbook, 4th; Brandrup, J., Immergut, E.H., Grulke, E.A., Abe, A., Bloch, D.R., Eds.; Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 1999; p. 14. [Google Scholar]
- Teorell, T. Transport processes and electrical phenomena in ionic membranes. Prog. Biophys. Biophys. Chem. 1953, 3, 305–369. [Google Scholar]
- Meyer, K.H.; Sievers, J.-F. Permeability of membranes I. Theory of ionic permeability. Helv. Chim. Acta 1936, 19, 649–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2013 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Jikihara, A.; Ohashi, R.; Kakihana, Y.; Higa, M.; Kobayashi, K. Electrodialytic Transport Properties of Anion-Exchange Membranes Prepared from Poly(vinyl alcohol) and Poly(vinyl alcohol-co-methacryloyl aminopropyl trimethyl ammonium chloride). Membranes 2013, 3, 1-15. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes3010001
Jikihara A, Ohashi R, Kakihana Y, Higa M, Kobayashi K. Electrodialytic Transport Properties of Anion-Exchange Membranes Prepared from Poly(vinyl alcohol) and Poly(vinyl alcohol-co-methacryloyl aminopropyl trimethyl ammonium chloride). Membranes. 2013; 3(1):1-15. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes3010001
Chicago/Turabian StyleJikihara, Atsushi, Reina Ohashi, Yuriko Kakihana, Mitsuru Higa, and Kenichi Kobayashi. 2013. "Electrodialytic Transport Properties of Anion-Exchange Membranes Prepared from Poly(vinyl alcohol) and Poly(vinyl alcohol-co-methacryloyl aminopropyl trimethyl ammonium chloride)" Membranes 3, no. 1: 1-15. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes3010001
APA StyleJikihara, A., Ohashi, R., Kakihana, Y., Higa, M., & Kobayashi, K. (2013). Electrodialytic Transport Properties of Anion-Exchange Membranes Prepared from Poly(vinyl alcohol) and Poly(vinyl alcohol-co-methacryloyl aminopropyl trimethyl ammonium chloride). Membranes, 3(1), 1-15. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes3010001




