Membranes for Redox Flow Battery Applications
Abstract
:1. Introduction
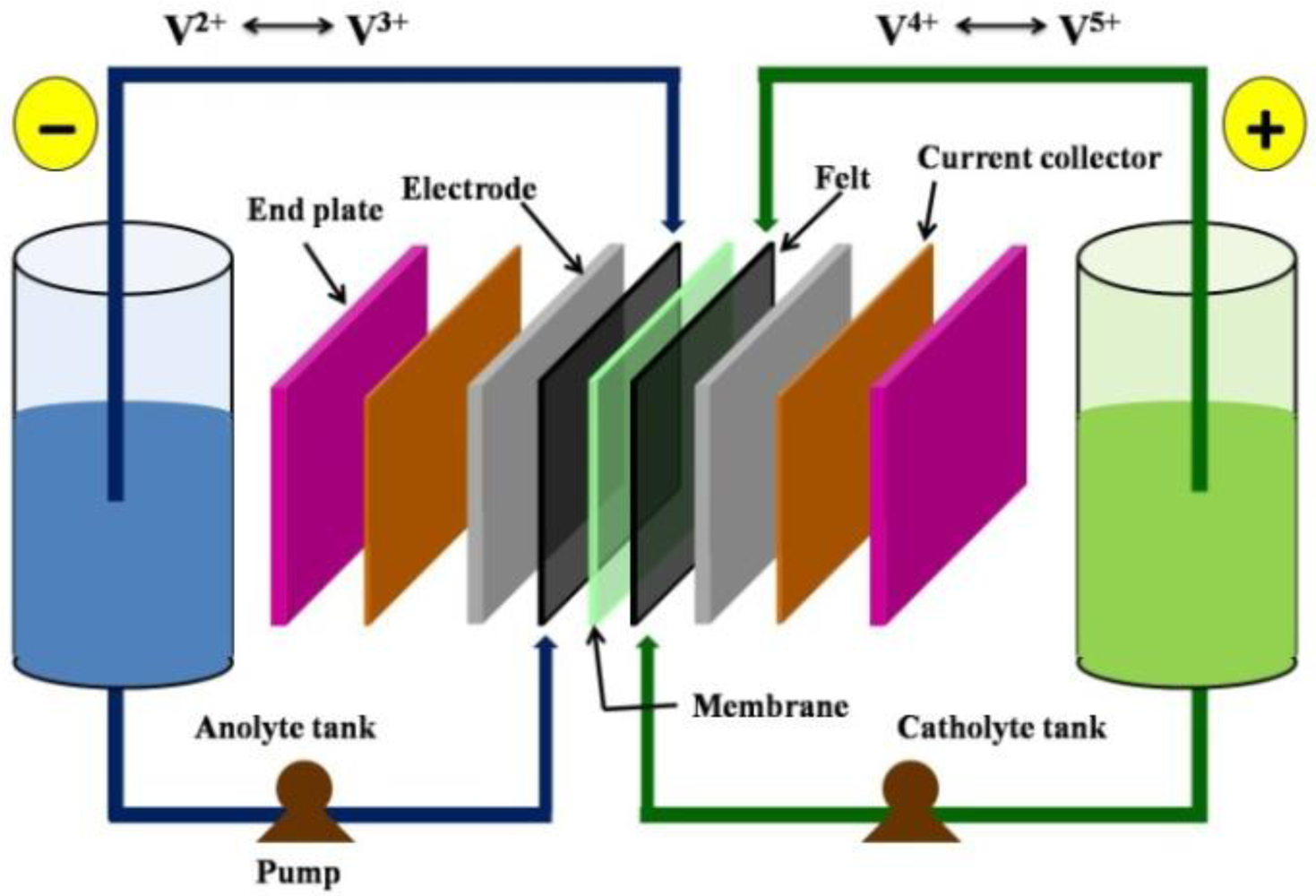
2. Ion Exchange Membranes
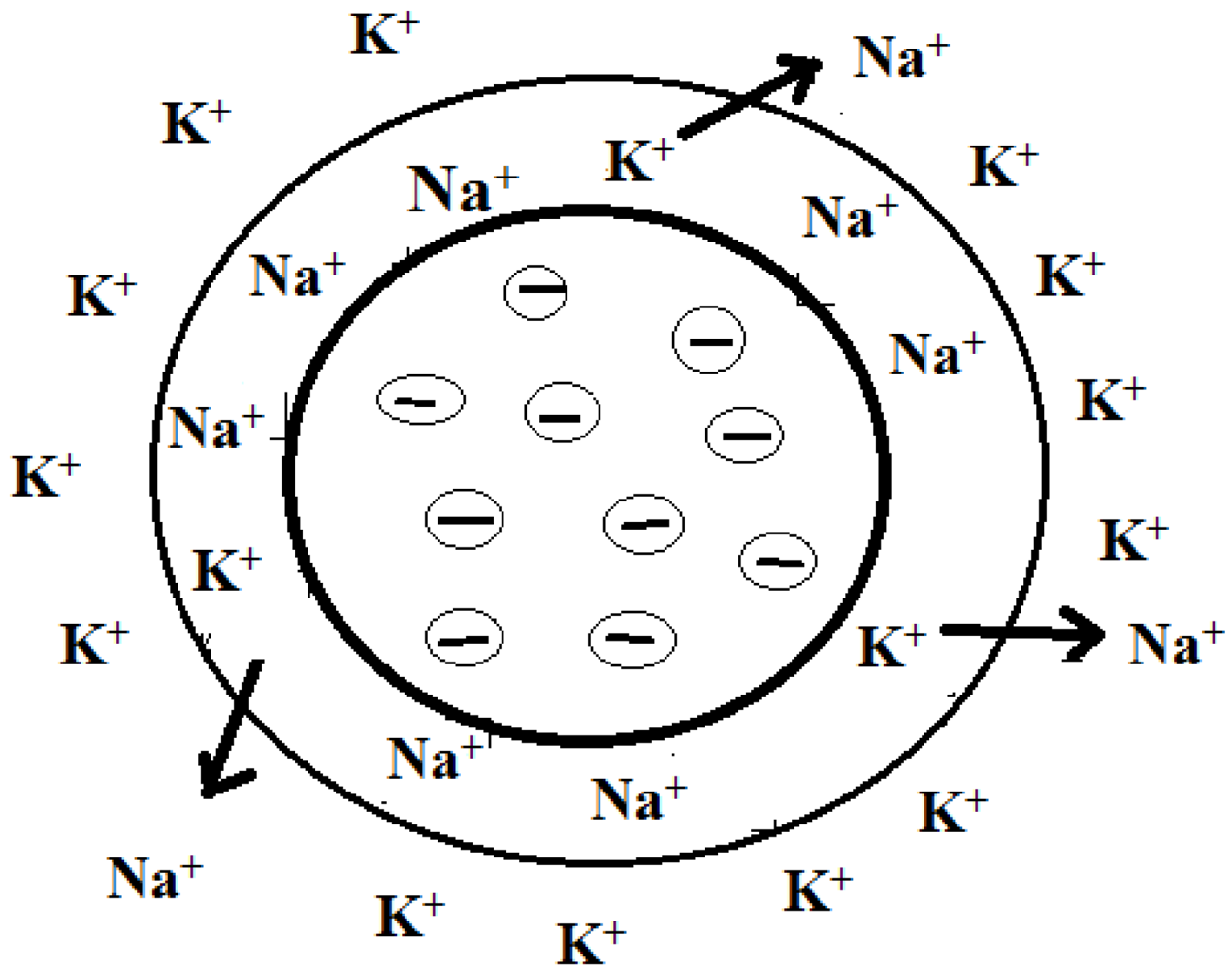
3. Types of Ion Exchange Membranes

4. Preparation of Membranes
4.1. Method of Production of Ion Exchange Membranes

4.2. Fabrication of Microporous Separators
5. Research Progress on Membranes for Redox Flow Batteries
5.1. Membrane Evaluation Methods
5.1.1. Vanadium Ion Permeability Measurements


5.1.2. Ion Exchange Capacity, Ionic Conductivity and Area Resistance Measurements

5.1.3. Chemical Stability Measurements
5.1.4. Water Transport Measurements
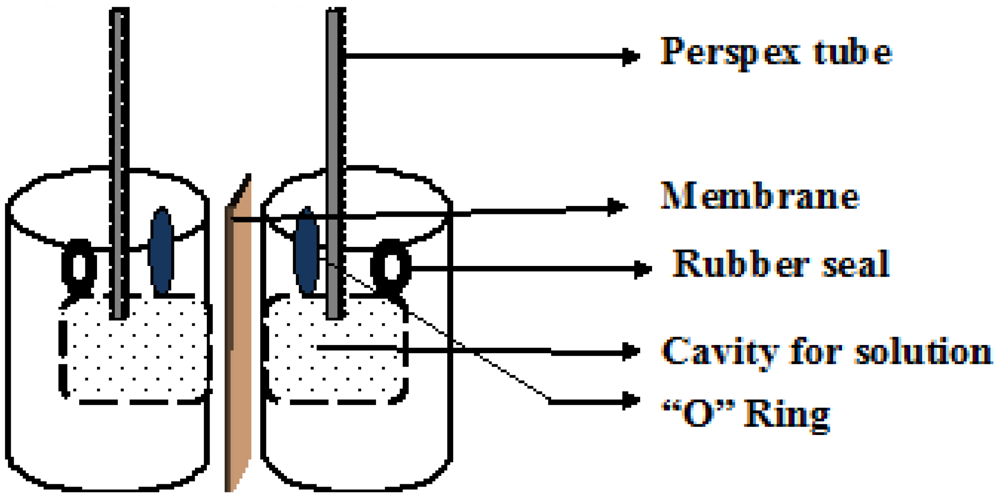
5.1.5. Cell Performance Tests
5.2. Daramic (Microporous Separator)
5.3. Nafion (Perfluorinated Membrane)
5.3.1. Coating Nafion with Charged Substances (Polycations and Polyanions)
5.3.2. Blocking Nafion with Inorganic Materials
5.3.3. Polymer Blending with Polyvinylidene Fluoride (PVDF)
5.4. Other Perfluorinated Membranes (PVDF as Backbone)
5.5. Non Fluorinated Membranes
5.6. Other Hydrocarbon Based Cation Exchange Membranes
5.7. Anion Exchange Membranes
5.8. Amphoteric Ion Exchange Membranes in VRB
6. Water Transfer Studies
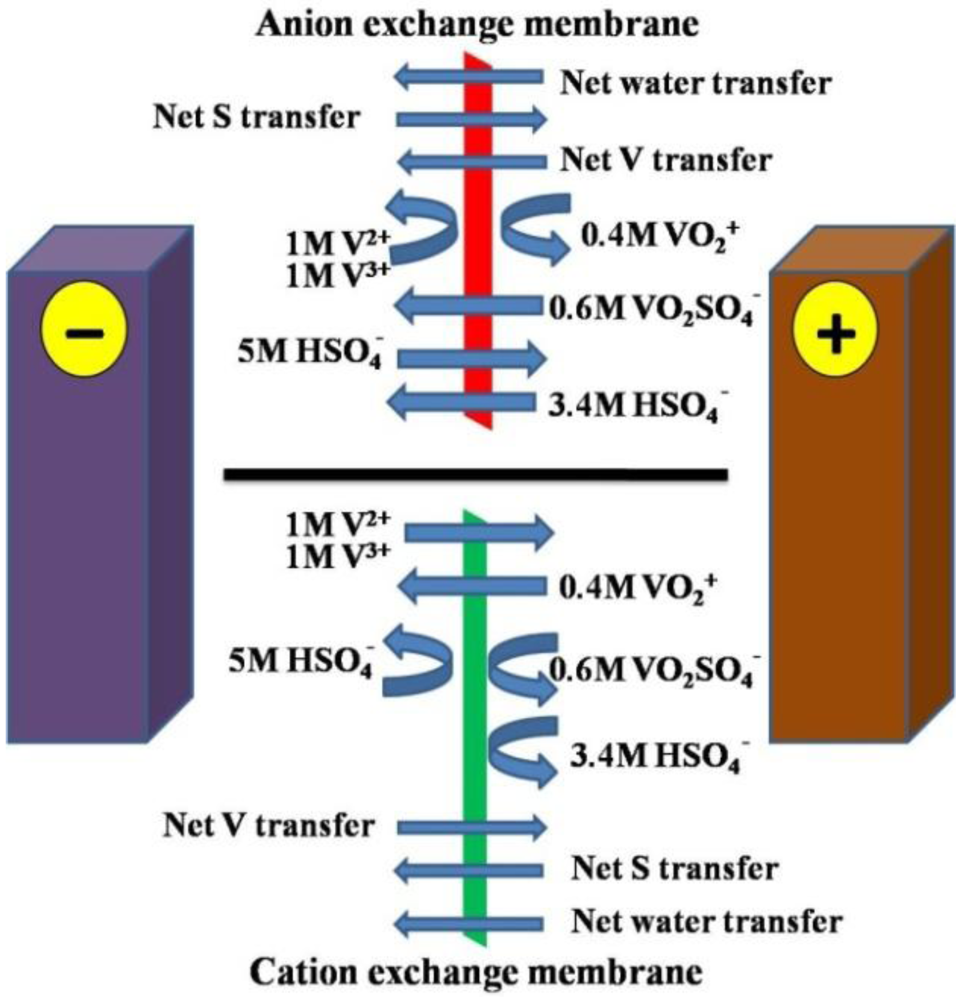
7. Vanadium Ion Transfer Studies
| Membrane | Diffusivity /cm min−1 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| V(II) | V(III) | V(IV) | V(V) | |
| AMV | 2.01 × 10−6 | l.11 × 10−6 | 3.17 × 10−5 | 5.67 × 10−5 |
| CMV | 1.01 × 10−5 | 1.34 × 10−5 | 2.65 × 10−5 | 2.14 × 10−4 |
| Nafion 117 | 4.63 × 10−5 | 4.24 × 10−5 | 1.94 × 10−4 | 1.41 × 10−4 |
| Daramic (0.15mm) | 6.21 × 10−4 | 7.09 × 10−4 | 1.46 × 10−3 | >1 × 10−2 |
| Composite membrane (0.23mm) | 1.26 × 10−4 | 1.34 × 10−4 | 3.64 × 10−4 | 2.92 × 10−3 |
8. Stability Studies of Membranes in Vanadium Solutions
9. Conclusions
References
- The Electricity Storage Association Homepage. Available online: http://www.electricitystorage.org/technology/technology_applications/applications_overview (accessed on 15 December 2011). [Green Version]
- Rahman, F.; Skyllas-Kazacos, M. Vanadium redox battery: Positive half-cell electrolyte studies. J. Power Sources 2009, 189, 1212–1219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skyllas-Kazacos, M.; Chakrabarti, M.H.; Hajimolana, S.A.; Mjalli, F.S.; Saleem, M. Progress in flow battery research and development. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2011, 158, R55–R79. [Google Scholar]
- Skyllas-Kazacos, M.; Bankstown, R.M.; Lindfield, R.R. All-Vanadium Redox Battery. U.S. Patent 4,786,567, 22 November 1988. [Google Scholar] [Green Version]
- Skyllas-Kazacos, M.; Kasherman, D.; Hong, D.R.; Kazacos, M. Characteristics and performance of 1 kW UNSW vanadium redox battery. J. Power Sources 1991, 35, 399–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, S.; Skyllas-Kazacos, M. Electrochemical behaviour of vanadium(V)/vanadium(IV) redox couple at graphite electrodes. J. Power Sources 1992, 39, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Largent, R.L.; Skyllas-Kazacos, M.; Chieng, J. Improved PV system performance using vanadium batteries. In Proceedings of the Photovoltaic Specialists ConferenceConference Record of the Twenty Third IEEE, Louisville, KY, USA, 10 May–14 May 1993; pp. 1119–1124. [Green Version]
- Menictas, C.; Hong, D.R.; Yan, Z.H.; Wilson, J.; Kazacos, M.; Skyllas-Kazacos, M. Status of the vanadium battery development programme. In Proceedings of the Electrical Engineering Congress, Sydney, Australia, 1994. [Green Version]
- Kazacos, M.; Cheng, M.; Skyllas-Kazacos, M. Vanadium redox cell electrolyte optimization studies. J. Appl. Electrochem. 1990, 20, 463–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skyllas-Kazacos, M.; Menictas, C.; Kazacos, M. Thermal stability of concentrated V(V) electrolytes in the vanadium redox cell. J. Electrochem. Soc. 1996, 143, L86–L88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liyu, L.; Soowhan, K.; Wei, W.; Vijayakumar, M.; Zimin, N.; Baowei, C.; Jianlu, Z.; Guanguang, X.; Hu, J.; Gordon, G.; Jun, L.; Zhenguo, Y. A stable vanadium redox-flow battery with high energy density for large-scale energy storage. Adv. Energy Mater 2011, 1, 394–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwenzer, B.; Zhang, J.; Kim, S.; Li, L.; Liu, J.; Yang, Z. Membrane development for vanadium redox flow batteries. Chem. Sus. Chem 2011, 4, 1388–1406. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.; Zhang, H.; Mai, Z.; Zhang, H.; Vankelecom, I. Ion exchange membranes for vanadium redox flow battery (VRB) applications. Energ. Environ. Sci. 2011, 4, 1147–1160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skyllas-Kazacos, M.; Milne, N.A.; Kazacos, G.C. Membrane properties and behaviour in the Generation 2 Vanadium Bromide Redox Flow batteries. In Proceedings of the 16th International Federation for Heat Treatment and Surface Engineering Congress, Brisbane, QLD, Australia, 30 October–2 November 2007; pp. 72–77. [Green Version]
- Sukkar, T.; Skyllas Kazacos, M. Modification of membranes using polyelectrolytes to improve water transfer properties in the vanadium redox battery. J. Membr. Sci. 2003, 222, 249–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammadi, T.; Skyllas-Kazacos, M. Characterisation of novel composite membrane for redox flow battery applications. J. Membr. Sci. 1995, 98, 77–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vafiadis, H.; Skyllas-Kazacos, M. Evaluation of membranes for the novel vanadium bromine redox flow cell. J. Membr. Sci. 2006, 279, 394–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohya, H.; Kuromoto, M.; Matsumoto, H.; Matsumoto, K.; Negishi, Y. Electrical resistivities and permeabilities of composite membranes based on a cation exchange membrane for a redox flow battery. J. Membr. Sci. 1990, 51, 201–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, T. Ion exchange membranes: State of their development and perspective. J. Membr. Sci. 2005, 263, 1–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paterson, R. An Introduction to Ion Exchange.; Heyden and Son, Ltd.: London, UK, 1970. [Google Scholar] [Green Version]
- Nagarale, R.K.; Gohil, G.S.; Shahi, V.K. Recent developments on ion-exchange membranes and electro-membrane processes. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2006, 119, 97–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kunin, R.; Myers, R.J. Ion Exchange Resins; John Wiley & Sons Inc: New York, NY, USA, 1950. [Google Scholar] [Green Version]
- Dorfner, K. Ion Exchangers: Properties and Applications; Ann Arbor Science Publishers: Ann Arbor, MI, USA, 1972. [Google Scholar] [Green Version]
- Donnan, F.G. The theory of membrane equilibrium in presence of a non-dialyzable electrolyte. Z. Electrochem. 1911, 17, 572–581. [Google Scholar]
- Juda, M.; McRae, W.A. Coherent ion-exchange gels and membranes. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1950, 72, 1044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacobson, K.S.; Drew, D.M.; He, Z. Efficient salt removal in a continuously operated upflow microbial desalination cell with an air cathode. Bioresour. Technol. 2011, 102, 376–380. [Google Scholar]
- Strathmann, H. Synthetic membranes and their preparation. In Proceedings of the NATO Advanced Study Institute on Synthetic Membranes: ScienceEngineeringand Applications, Alcabideche, Portugal, 26 June–8 July 1983; Bungay, P.M., Lonsdale, H.K., de Pinho, M.N., Eds.; Reidel Publishing Company: Dordrecht, the Netherlands, 1986. [Google Scholar] [Green Version]
- Choi, J.-H.; Kim, S.-H.; Moon, S.-H. Heterogeneity of ion-exchange membranes: the effects of membrane heterogeneity on transport properties. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2001, 241, 120–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kesting, R.E. Phase inversion membranes. In Materials Science of Synthetic Membranes; Lloyd, D.R., Ed.; American Chemical Society: Washington, DC, USA, 1985; pp. 131–164. [Google Scholar] [Green Version]
- Smitha, B.; Sridhar, S.; Khan, A.A. Solid polymer electrolyte membranes for fuel cell applications—A review. J. Membr. Sci. 2005, 259, 10–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kyu, T. Structure and properties of perfluorinated ion-exchange membranes. In Materials Science of Synthetic Membranes; Lloyd, D.R., Ed.; American Chemical Society: Washington, DC, USA, 1985; pp. 365–405. [Google Scholar] [Green Version]
- Bahar, B.; Hobson, A.R.; Kolde, J.A.; Zuckerbrod, D. Ultra-Thin Integral Composite Membrane. U.S. Patent 5,547,551, 20 August 1996. [Google Scholar] [Green Version]
- Desai, V.M.; Vafiadis (Prifti), H. Personal Communication. [Green Version]
- Meares, P. Ion exchange membranes: Principles, production and processes. In Ion Exchange: Science and Technology; Rodrigues, A.E., Ed.; Martinus Nijhoff Publishers: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 1986. [Google Scholar] [Green Version]
- Cabasso, I. Membranes. Encycl. Polym. Sci. Eng. 1987, 9, 509–579. [Google Scholar]
- Mizutani, Y.; Yamane, R.; Ihara, H.; Motomura, H. Studies of ion exchange membranes. XVI. The preparation of ion exchange membranes by the “paste method”. Bull. Chem. Soc. Jpn. 1963, 36, 361–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mizutani, Y.; Yamane, R.; Motomura, H. Studies of ion exchange membranes. XXII. Semicontinuous preparation of ion exchange membranes by the “paste method”. Bull. Chem. Soc. Jpn. 1965, 38, 689–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mizutani, Y. Structure of ion exchange membranes. J. Membrane Sci. 1990, 49, 121–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carretta, N.; Tricoli, V.; Picchioni, F. Ionomeric membranes based on partially sulfonated poly(styrene): Synthesis, proton conduction and methanol permeation. J. Membrane Sci. 2000, 166, 189–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Material Safety Data Sheet: Chloromethyl Methyl Ether, Sigma-Aldrich: New South Wales, Australia; 11 February 2006. [Green Version]
- Tongwen, X.; Weihua, Y. Fundamental studies of a new series of anion exchange membranes: membrane preparation and characterization. J. Membrane Sci. 2001, 190, 159–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Govindan, K.P.; Narayanan, P.K. Improvements in or Relating to the Preparation of Interpolymer Compositions and Ion-Exchange Membranes. Indian Patent 124573, December 1969. [Google Scholar] [Green Version]
- Adhikary, S.K.; Dave, N.J.; Narayanan, P.K.; Harkare, W.P.; Joshi, B.S.; Govindan, K.P. Studies on interpolymer membranes. Part III. Cation-exchange membranes. React. Polym. Ion Exch., Sorbents 1983, 1, 197–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Metayer, M.; Ould M'Bareck, C. Semi-interpenetrating networks (sIPN). Preparation of ion-exchange membranes, using a gaseous crosslinking reagent. React. Funct. Polym. 1997, 33, 311–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rautenbach, R.; Albrecht, R. Membrane Processes; John Wiley & Sons Ltd: Chichester, UK, 1989. [Google Scholar] [Green Version]
- Cadotte, J.E. Evolution of composite reverse osmosis membranes. In Materials Science of Synthetic Membranes; Lloyd, D.R., Ed.; American Chemical Society: Washington, DC, USA, 1985; pp. 273–294. [Google Scholar] [Green Version]
- D’Agostino, V.; Lee, J.; Lu, E. Modifying membranes to meet industrial needs. In Proceedings of the Symposium on Ion Exchange Transport and Interfacial Properties; The Electrochemical Society: Honolulu, HI, USA, 1981; 81-82, pp. 81–82. [Google Scholar]
- Helfferich, F.G. Ion Exchange; McGraw-Hill Book Company, Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 1962; pp. 339–420. [Google Scholar] [Green Version]
- Gupta, B.; Scherer, G.G. Proton exchange membranes by radiation-induced graft copolymerization of monomers into Teflon-FEP films. Chimia 1994, 48, 127–137. [Google Scholar]
- Kinoshita, K. Separators for batteries and fuel cells. In Proceedings of the Symposium on DiaphramsSeparators and Ion-Exchange Membranes, Boston, MA, USA, 1 October 1986; van Zee, J.W., White, R.E., Kinoshita, K., Burney, H.S., Eds.; The Electrochemical Society: Honolulu, HI, USA; 86-13. [Green Version]
- Hagedorn, N.H. The evolving NASA iron-chromium redox storage-system technology. J. Electrochem. Soc. 1983, 130, C304. [Google Scholar]
- Assink, R.A. Fouling mechanism of separator membranes for the iron/chromium redox battery. J. Membr. Sci. 1984, 17, 205–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perez, J.R.; Lopez-Atalaya, M.; Codina, G.; Vazquez, J.L.; Aldaz, A. Screening of advanced membranes for the iron/chromium redox flow battery in separated reactant operation. Bull. Electrochem. 1991, 7, 555–558. [Google Scholar]
- Lopez-Atalaya, M.; Codina, G.; Perez, J.R.; Vazquez, J.L.; Aldaz, A. Optimization studies on a Fe/Cr redox flow battery. J. Power Sources 1992, 39, 147–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swaminathan, P.; Disley, P.F.; Assender, H.E. Surface modification of ion exchange membrane using amines. J. Membrane Sci. 2004, 234, 131–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perez, J.R.; Lopez-Atalaya, M.; Codina, G.; Vazquez, J.L.; Aldaz, A. Screening of advanced membranes for the iron/chromium redox flow battery in separated reactant operation. Bull. Electrochem. 1991, 7, 555–558. [Google Scholar]
- Shibata, A.; Sato, K. Development of vanadium redox flow battery for electrical energy storage. Power Eng. J. 1999, 13, 130–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, P.; Zhang, H.; Zhou, H.; Chen, J.; Gao, S.; Yi, B. Characteristics and performance of 10 kW class all-vanadium redox-flow battery stack. J. Power Sources 2006, 162, 1416–1420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammadi, T.; Skyllas Kazacos, M. Modification of anion-exchange membranes for vanadium redox flow battery applications. J. Power Sources 1996, 63, 179–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammadi, T.; Chieng, S.C.; Kazacos, M.S. Water transport study across commercial ion exchange membranes in the vanadium redox flow battery. J. Membrane Sci. 1997, 133, 151–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammadi, T. Modification and Evaluation of Ion Exchange Membranes; The University of New South Wales: Sydney, Australia, 1995. [Google Scholar] [Green Version]
- Mohammadi, T.; Skyllas Kazacos, M. Evaluation of the chemical stability of some membranes in vanadium solution. J. Appl. Electrochem. 1997, 27, 153–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sukkar, T.; Skyllas Kazacos, M. Water transfer behaviour across cation exchange membranes in the vanadium redox battery. J. Membrane Sci. 2003, 222, 235–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grossmith, F.; Llewellyn, P.; Fane, A.G.; Skyllas-Kazacos, M. Evaluation of Membranes for All-Vanadium Redox Cell, Stationary Energy Storage, Load Levelling, and Remote Applications; The Electrochemical Society: Honolulu, HI, USA, 1988; pp. 363–373. [Google Scholar] [Green Version]
- Chieng, S.C. Membrane Processes and Membrane Modification for Redox Flow Battery Applications. PhD thesis, University of New South Wales, Sydney, Australia, 1993. [Google Scholar] [Green Version]
- Mohammadi, T.; Skyllas kazacos, M. Use of polyelectrolyte for incorporation of ion-exchange groups in composite membranes for vanadium redox flow battery applications. J. Power Sources 1995, 56, 91–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.Q.; Wang, B.B.; Yang, J.C. Adsorption and diffusion of VO2+ and VO2+ across cation membrane for all-vanadium redox flow battery. Solvent Extr. Ion Exch. 2009, 27, 312–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sukkar, T.; Skyllas Kazacos, M. Membrane stability studies for vanadium redox cell applications. J. Appl. Electrochem. 2004, 34, 137–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chieng, S.C.; Kazacos, M.; Skyllas-Kazacos, M. Preparation and evaluation of composite membrane for vanadium redox battery applications. J. Power Sources 1992, 39, 11–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammadi, T.; Skyllaskazacos, M. Preparation of sulfonated composite membrane for vanadium redox flow battery applications. J. Membrane Sci. 1995, 107, 35–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, B.; Yan, C.W.; Wang, F.H. Proton conducting composite membrane from Daramic/Nafion for vanadium redox flow battery. J. Membr. Sci. 2004, 234, 51–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mauritz, K.A.; Moore, R.B. State of understanding of Nafion. Chem. Rev. 2004, 104, 4535–4585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hickner, M.A.; Ghassemi, H.; Kim, Y.S.; Einsla, B.R.; McGrath, J.E. Alternative polymer systems for proton exchange membranes (PEMs). Chem. Rev. 2004, 104, 4587–4611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, S.P.; Liu, Z.; Tian, Z.Q. Layer-by-layer self-assembly of composite polyelectrolyte-nafion membranes for direct methanol fuel cells. Adv. Mater. 2006, 18, 1068–1072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Q.; Zhang, H.; Chen, J.; Qian, P.; Zhai, Y. Modification of nafion membrane using interfacial polymerization for vanadium redox flow battery applications. J. Membrane Sci. 2008, 311, 98–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, G.J.; Ohya, H. Preparation of cation exchange membrane as a separator for the all-vanadium redox flow battery. J. Membrane Sci. 1996, 120, 55–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, G.J.; Ohya, H. Crosslinking of anion exchange membrane by accelerated electron radiation as a separator for the all-vanadium redox flow battery. J. Membrane Sci. 1997, 132, 55–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, X.; Lu, Z.; Xi, J.; Wu, Z.; Zhu, W.; Chen, L.; Qiu, X. Influences of permeation of vanadium ions through PVDF-g-PSSA membranes on performances of vanadium redox flow batteries. J. Phys. Chem. B 2005, 109, 20310–20314. [Google Scholar]
- Miyake, N.; Wainright, J.S.; Savinell, R.F. Evaluation of a sol-gel derived nafion/silica hybrid membrane for proton electrolyte membrane fuel cell applications: I. Proton conductivity and water content. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2001, 148, A898–A904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyake, N.; Wainright, J.S.; Savinell, R.F. Evaluation of a sol-gel derived nafion/silica hybrid membrane for polymer electrolyte membrane fuel cell applications—II. Methanol uptake and methanol permeability. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2001, 148, A905–A909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Q.T.; Zhang, H.M.; Chen, J.; Qian, P.; Zhai, Y.F. Modification of nafion membrane using interfacial polymerization for vanadium redox flow battery applications. J. Membrane Sci. 2008, 311, 98–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xi, J.; Wu, Z.; Teng, X.; Zhao, Y.; Chen, L.; Qiu, X. Self-assembled polyelectrolyte multilayer modified nafion membrane with suppressed vanadium ion crossover for vanadium redox flow batteries. J. Mater. Chem. 2008, 18, 1232–1238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, J.; Jiang, C.P.; Wang, Y.H.; Chen, J.W.; Zhu, S.F.; Zhao, B.J.; Wang, R. Studies on polypyrrole modified nafion membrane for vanadium redox flow battery. Electrochem. Commun. 2008, 10, 372–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwenzer, B.; Kim, S.; Vijayakumar, M.; Yang, Z.G.; Liu, J. Correlation of structural differences between nafion/polyaniline and nafion/polypyrrole composite membranes and observed transport properties. J. Membr. Sci. 2011, 372, 11–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xi, J.; Wu, Z.; Qiu, X.; Chen, L. Nafion/SiO2 hybrid membrane for vanadium redox flow battery. J. Power Sources 2007, 166, 531–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schulte, D.; Drillkens, J.; Schulte, B.; Sauer, D.U. Nafion hybrid membranes for use in redox flow batteries. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2010, 157, A989–A992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teng, X.G.; Zhao, Y.T.; Xi, J.Y.; Wu, Z.H.; Qiu, X.P.; Chen, L.Q. Nafion/organically modified silicate hybrids membrane for vanadium redox flow battery. J. Power Sources 2009, 189, 1240–1246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teng, X.; Zhao, Y.; Xi, J.; Wu, Z.; Qiu, X.; Chen, L. Nafion/organic silica modified TiO2 composite membrane for vanadium redox flow battery via in situ sol-gel reactions. J. Membrane Sci. 2009, 341, 149–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, N.; Peng, S.; Lu, D.; Liu, S.; Liu, Y.; Huang, K. Nafion/TiO2 hybrid membrane fabricated via hydrothermal method for vanadium redox battery. J. Solid State Electrochem. 2011, 16, 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Mai, Z.; Zhang, H.; Li, X.; Xiao, S. Nafion/polyvinylidene fluoride blend membranes with improved ion selectivity for vanadium redox flow battery application. J. Power Sources 2011, 196, 5737–5741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, J.; Zhao, L.; Zhai, M.; Ni, J.; Zhou, H.; Peng, J.; Li, J.; Wei, G. Pre-irradiation grafting of styrene and maleic anhydride onto PVDF membrane and subsequent sulfonation for application in vanadium redox batteries. J. Power Sources 2008, 177, 617–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linkous, C.A.; Anderson, H.R.; Kopitzke, R.W.; Nelson, G.L. Development of new proton exchange membrane electrolytes for water electrolysis at higher temperatures. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 1998, 23, 525–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lakshmi, R.; Meier-Haack, J.; Schlenstedt, K.; Vogel, C.; Choudhary, V.; Varma, I.K. Sulphonated poly(ether ether ketone) copolymers: Synthesis, characterisation and membrane properties. J. Membrane Sci. 2005, 261, 27–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, R.Y.; M. Shao, P.H.; Burns, C.M.; Feng, X. Sulfonation of poly(ether ether ketone)(PEEK): Kinetic study and characterization. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2001, 82, 2651–2660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaafar, J.; Ismail, A.F.; Mustafa, A. Physicochemical study of poly(ether ether ketone) electrolyte membranes sulfonated with mixtures of fuming sulfuric acid and sulfuric acid for direct methanol fuel cell application. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2007, 460–461, 475–484. [Google Scholar]
- Li, L.; Zhang, J.; Wang, Y.X. Sulfonated poly(ether ether ketone) membranes for direct methanol fuel cell. J. Membrane Sci. 2003, 226, 159–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagarale, R.K.; Gohil, G.S.; Shahi, V.K. Sulfonated poly(ether ether ketone)/polyaniline composite proton-exchange membrane. J. Membrane Sci. 2006, 280, 389–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Liu, C.; Xu, D.; Zhao, C.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, G.; Na, H.; Xing, W. Preparation and properties of sulfonated poly(ether ether ketone)s (SPEEK)/polypyrrole composite membranes for direct methanol fuel cells. J. Power Sources 2006, 162, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, C.; Liu, J.; Yan, C. A significantly improved membrane for vanadium redox flow battery. J. Power Sources 2010, 195, 4380–4383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kreuer, K.D. On the development of proton conducting polymer membranes for hydrogen and methanol fuel cells. J. Membrane Sci. 2001, 185, 29–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Q.; Zhang, H.; Chen, J.; You, D.; Sun, C.; Zhang, Y. Preparation and characterization of Nafion/SPEEK layered composite membrane and its application in vanadium redox flow battery. J. Membr. Sci. 2008, 325, 553–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mai, Z.S.; Zhang, H.M.; Li, X.F.; Bi, C.; Dai, H. Sulfonated poly(tetramethydiphenyl ether ether ketone) membranes for vanadium redox flow battery application. J. Power Sources 2011, 196, 482–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, D.Y.; Wang, S.J.; Xiao, M.; Meng, Y.Z. Preparation and properties of sulfonated poly(fluorenyl ether ketone) membrane for vanadium redox flow battery application. J. Power Sources 2010, 195, 2089–2095. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, D.Y.; Wang, S.J.; Xiao, M.; Han, D.M.; Meng, Y.Z. Sulfonated poly (fluorenyl ether ketone) membrane with embedded silica rich layer and enhanced proton selectivity for vanadium redox flow battery. J. Power Sources 2010, 195, 7701–7708. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, S.; Yan, J.L.; Schwenzer, B.; Zhang, J.L.; Li, L.Y.; Liu, J.; Yang, Z.G.; Hickner, M.A. Cycling performance and efficiency of sulfonated poly(sulfone) membranes in vanadium redox flow batteries. Electrochem. Commun. 2010, 12, 1650–1653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.; Tighe, T.B.; Schwenzer, B.; Yan, J.L.; Zhang, J.L.; Liu, J.; Yang, Z.G.; Hickner, M.A. Chemical and mechanical degradation of sulfonated poly(sulfone) membranes in vanadium redox flow batteries. J. Appl. Electrochem. 2011, 41, 1201–1213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, D.Y.; Wang, S.J.; Xiao, M.; Meng, Y.Z. Synthesis and characterization of novel sulfonated poly(arylene thioether) ionomers for vanadium redox flow battery applications. Energ. Environ. Sci. 2010, 3, 622–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, D.Y.; Wang, S.J.; Xiao, M.; Meng, Y.Z. Synthesis and properties of novel sulfonated poly(arylene ether sulfone) ionomers for vanadium redox flow battery. Energ. Conv. Manage. 2010, 51, 2816–2824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, B.; Yan, C.W.; Wang, F.H. Modification and evaluation of membranes for vanadium redox battery applications. J. Appl. Electrochem. 2004, 34, 1205–1210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, J.Y.; Li, M.Y.; Ni, J.F.; Zhai, M.L.; Peng, J.; Xu, L.; Zhou, H.H.; Li, J.Q.; Wei, G.S. Preparation of ETFE-based anion exchange membrane to reduce permeability of vanadium ions in vanadium redox battery. J. Membrane Sci. 2007, 297, 174–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.H.; Yin, C.X.; Xing, D.B.; Yang, D.L.; Jian, X.G. Preparation of chloromethylated/quaternized poly(phthalazinone ether ketone) anion exchange membrane materials for vanadium redox flow battery applications. J. Membrane Sci. 2010, 363, 243–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, D.B.; Zhang, S.H.; Yin, C.X.; Zhang, B.G.; Jian, X.G. Effect of amination agent on the properties of quaternized poly(phthalazinone ether sulfone) anion exchange membrane for vanadium redox flow battery application. J. Membrane Sci. 2010, 354, 68–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, J.Y.; Zhang, J.Z.; Chen, J.H.; Peng, J.; Xu, L.; Zhai, M.L.; Li, J.Q.; Wei, G.S. Amphoteric ion exchange membrane synthesized by radiation-induced graft copolymerization of styrene and dimethylaminoethyl methacrylate into PVDF film for vanadium redox flow battery applications. J. Membrane Sci. 2009, 334, 9–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, J.Y.; Zhai, M.L.; Chen, J.H.; Wang, Y.; Peng, J.; Xu, L.; Li, J.Q.; Wei, G.S. Performance of vanadium redox flow battery with a novel amphoteric ion exchange membrane synthesized by two-step grafting method. J. Membrane Sci. 2009, 342, 215–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kazacos, M.; Kazacos, M.S. High Energy Density Vanadium Electrolyte Solutions, Methods of Preparation Thereof and All-Vanadium Redox Cells and Batteries Containing High Energy Vanadium Electrolyte Solutions. U.S. Patent 6,468,688, 22 October 2002. [Google Scholar] [Green Version]
- Skyllas-Kazacos, M.; Goh, L. Modeling of vanadium ion diffusion across the ion exchange membrane in the vanadium redox battery. J. Membrane Sci. 2012, 399–400, 43–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, A.; Bao, J.; Skyllas-Kazacos, M. Dynamic modelling of the effects of ion diffusion and side reactions on the capacity loss for vanadium redox flow battery. J. Power Sources 2011, 196, 10737–10747. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, A.; Ting, S.; Bao, J.; Skyllas-Kazacos, M. Thermal modelling and simulation of the all-vanadium redox flow battery. J. Power Sources 2012, 203, 165–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, C.; Chen, J.; Zhang, H.; Han, X.; Luo, Q. Investigations on transfer of water and vanadium ions across Nafion membrane in an operating vanadium redox flow battery. J. Power Sources 2010, 195, 890–897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vijayakumar, M.; Bhuvaneswari, M.S.; Nachimuthu, P.; Schwenzer, B.; Kim, S.; Yang, Z.; Liu, J.; Graff, G.L.; Thevuthasan, S.; Hu, J. Spectroscopic investigations of the fouling process on Nafion membranes in vanadium redox flow batteries. J. Membrane Sci. 2011, 366, 325–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, A.; Bao, J.; Skyllas-Kazacos, M. Thermal modelling of battery configuration and self-discharge reactions in vanadium redox flow battery. J. Power Sources 2012. in submit. [Google Scholar] [Green Version]
- Bassett, D.; Chetland, J.; Kyte, A.B.; Marsden, H.M.; Roberts, P.N.; Summers, W.N.; Watkins, D.; Wylde, L.E. Introductory review. In Bromine Compounds: Chemistry and Applications; Price, D., Iddon, B., Wakefield, B.J., Eds.; Elsevier Science Publishers: Amsterdam, the Netherland, 1988; pp. 1–120. [Google Scholar] [Green Version]
© 2012 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Prifti, H.; Parasuraman, A.; Winardi, S.; Lim, T.M.; Skyllas-Kazacos, M. Membranes for Redox Flow Battery Applications. Membranes 2012, 2, 275-306. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes2020275
Prifti H, Parasuraman A, Winardi S, Lim TM, Skyllas-Kazacos M. Membranes for Redox Flow Battery Applications. Membranes. 2012; 2(2):275-306. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes2020275
Chicago/Turabian StylePrifti, Helen, Aishwarya Parasuraman, Suminto Winardi, Tuti Mariana Lim, and Maria Skyllas-Kazacos. 2012. "Membranes for Redox Flow Battery Applications" Membranes 2, no. 2: 275-306. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes2020275
APA StylePrifti, H., Parasuraman, A., Winardi, S., Lim, T. M., & Skyllas-Kazacos, M. (2012). Membranes for Redox Flow Battery Applications. Membranes, 2(2), 275-306. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes2020275






