Cyanuric Chloride with the s-Triazine Ring Fabricated by Interfacial Polymerization for Acid-Resistant Nanofiltration
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. General Materials
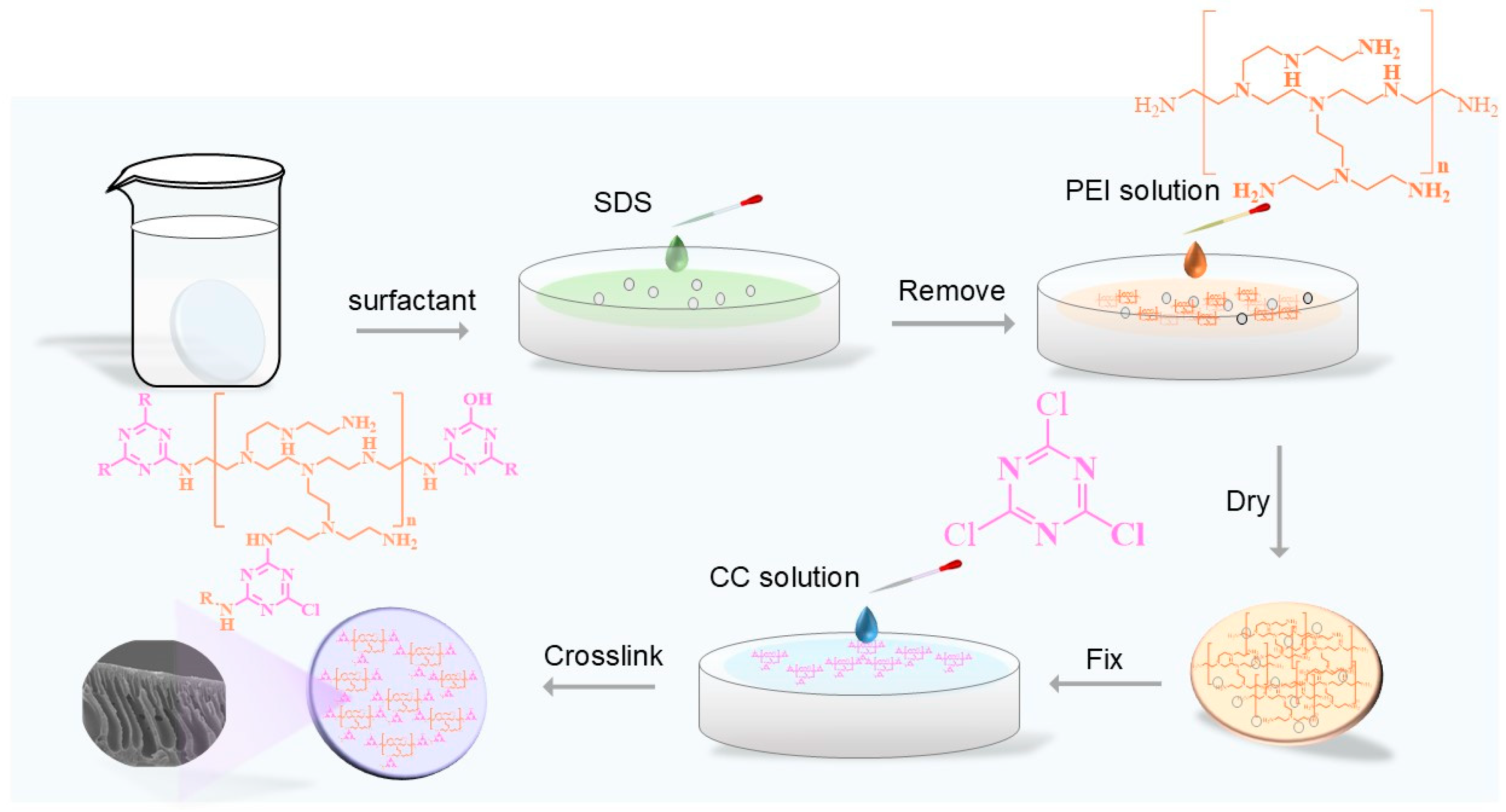
2.2. Membrane Fabrication
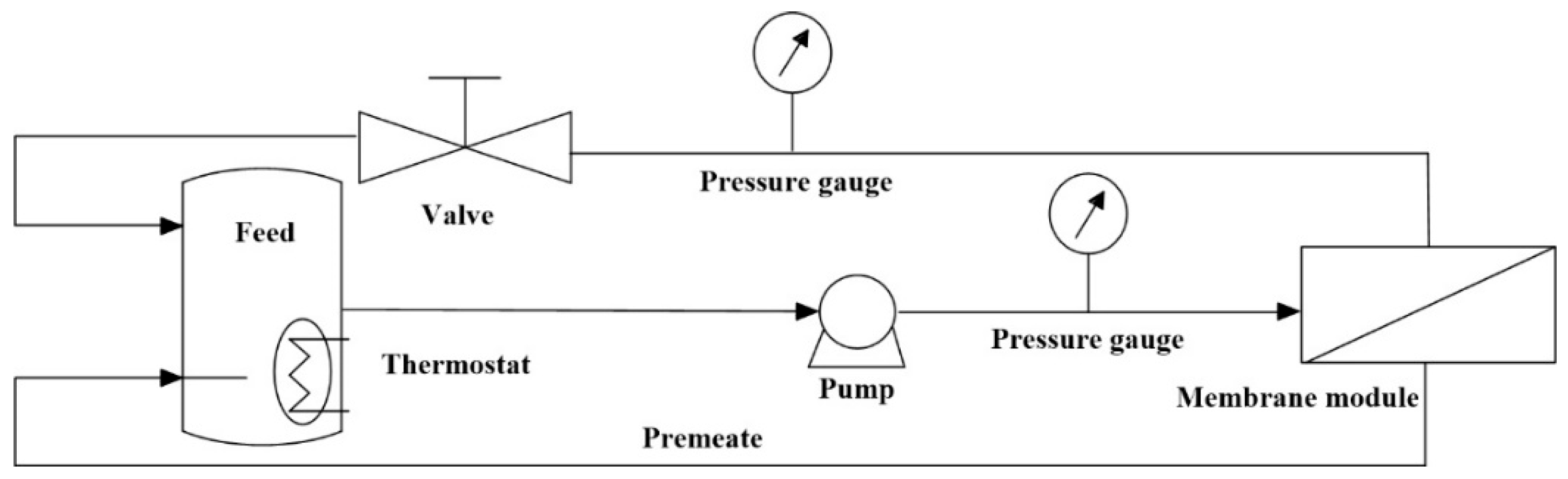
2.3. Characterization
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Effect of Fabrication Conditions on Membrane Performance
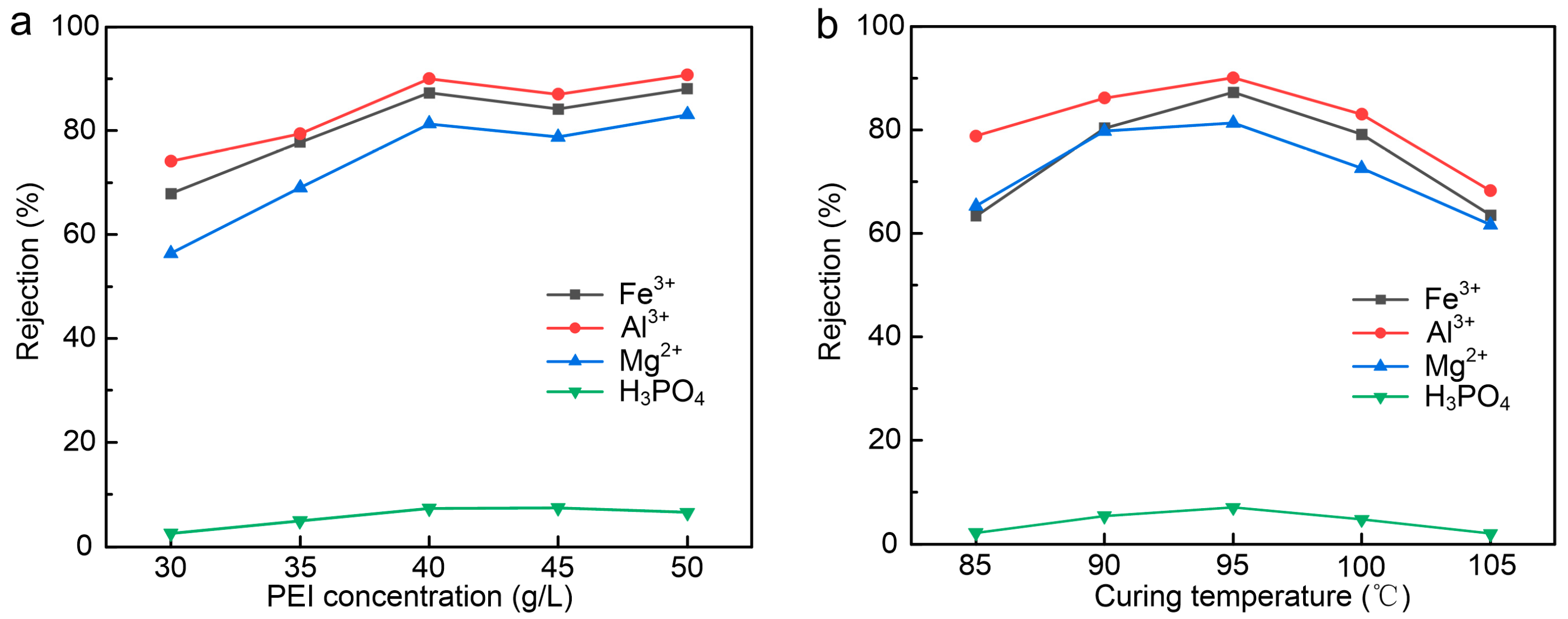
3.2. Effect of PEI Concentration and Curing Temperature
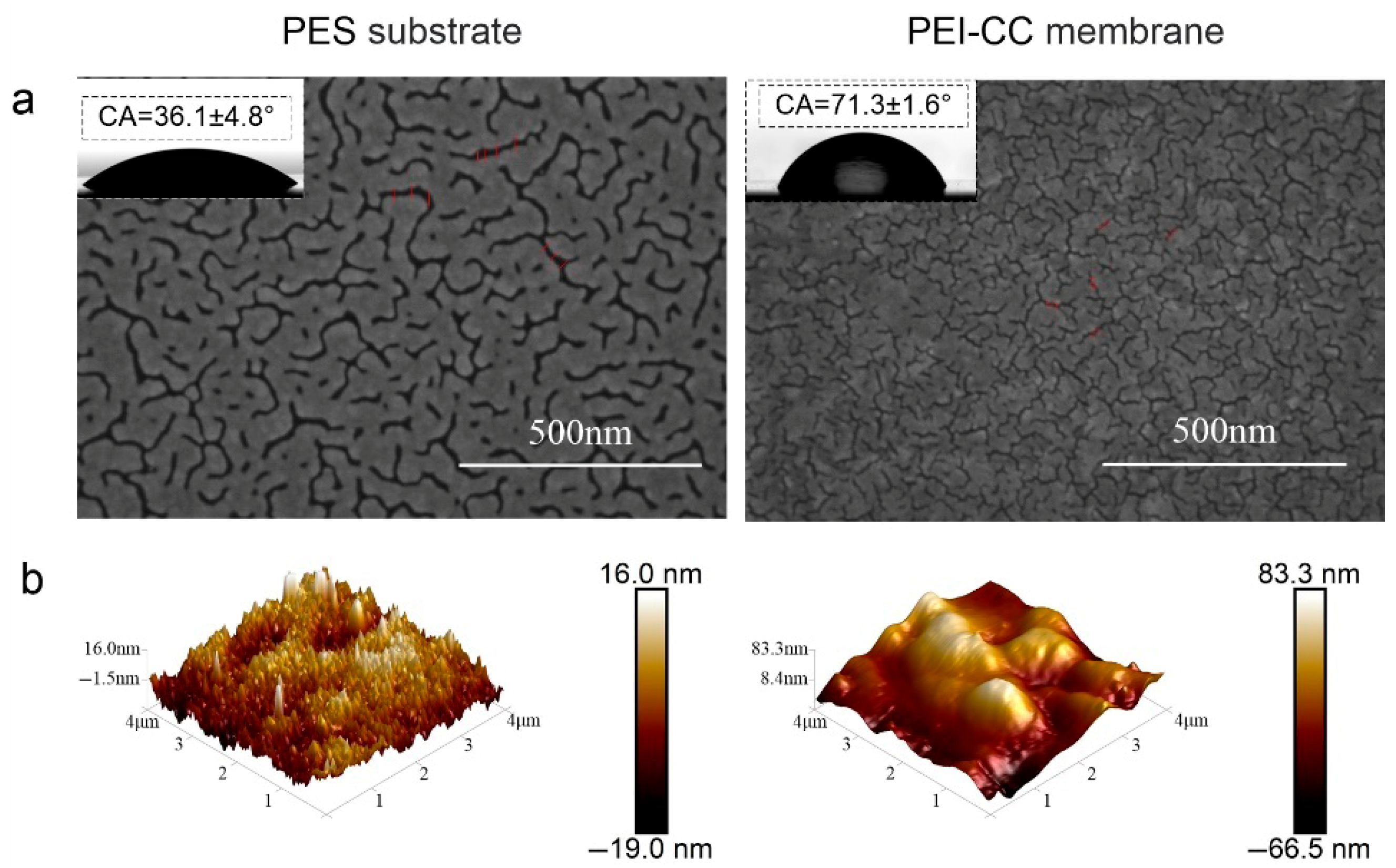
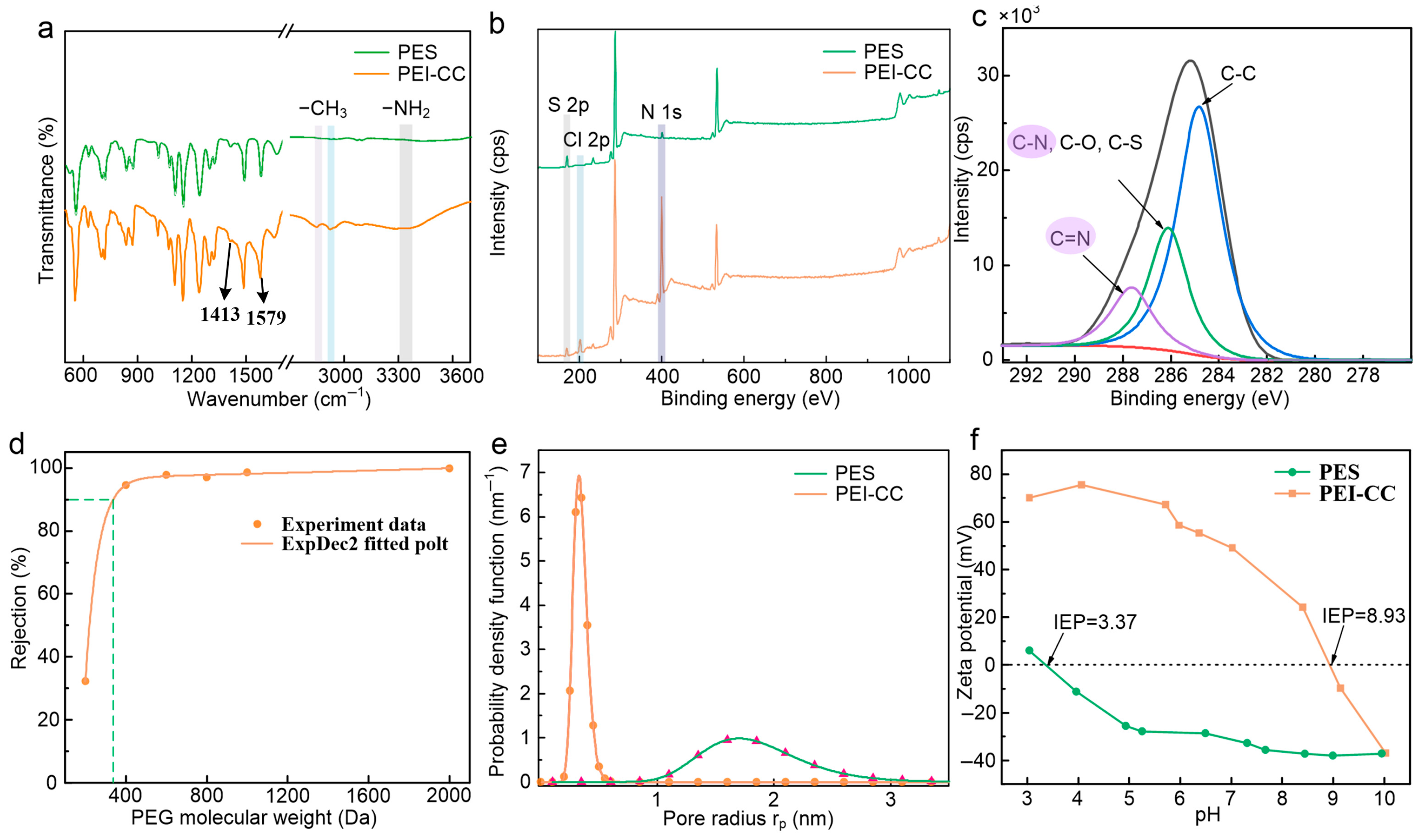
3.3. Surface Morphology and Composition
3.4. Separation Performance
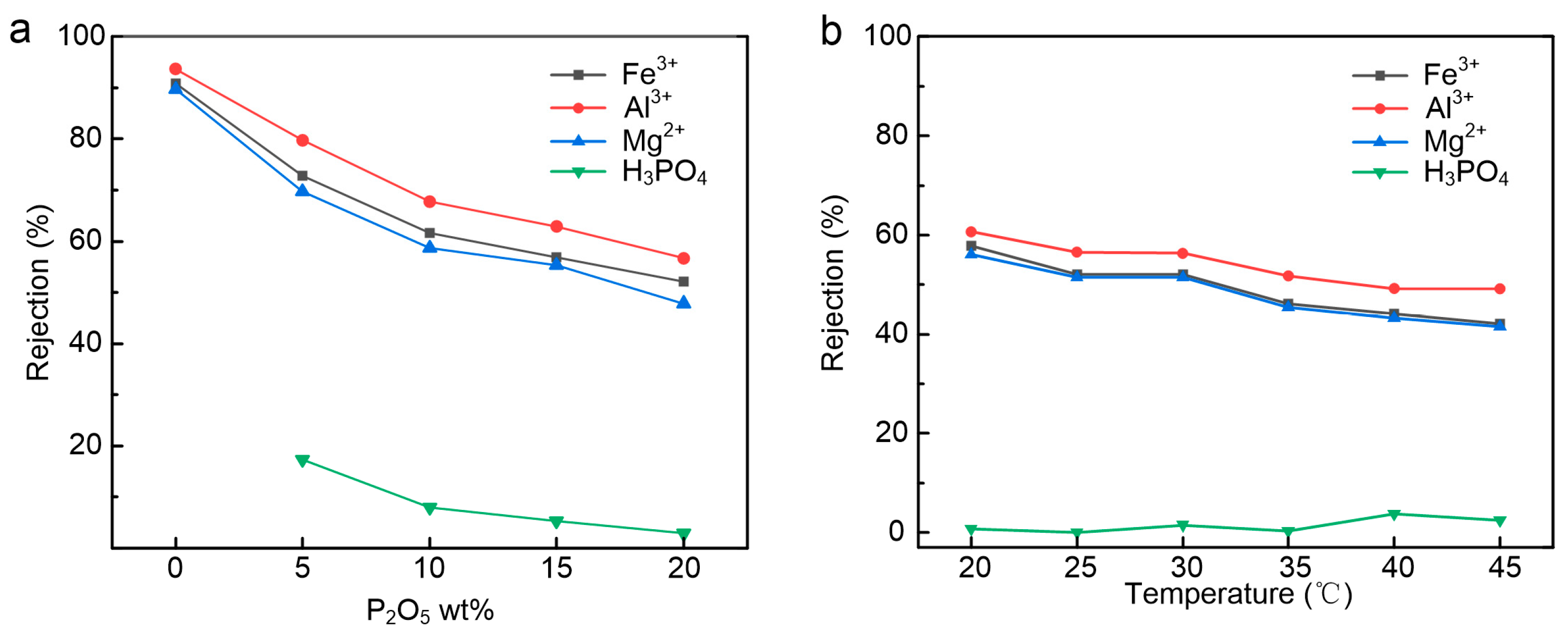
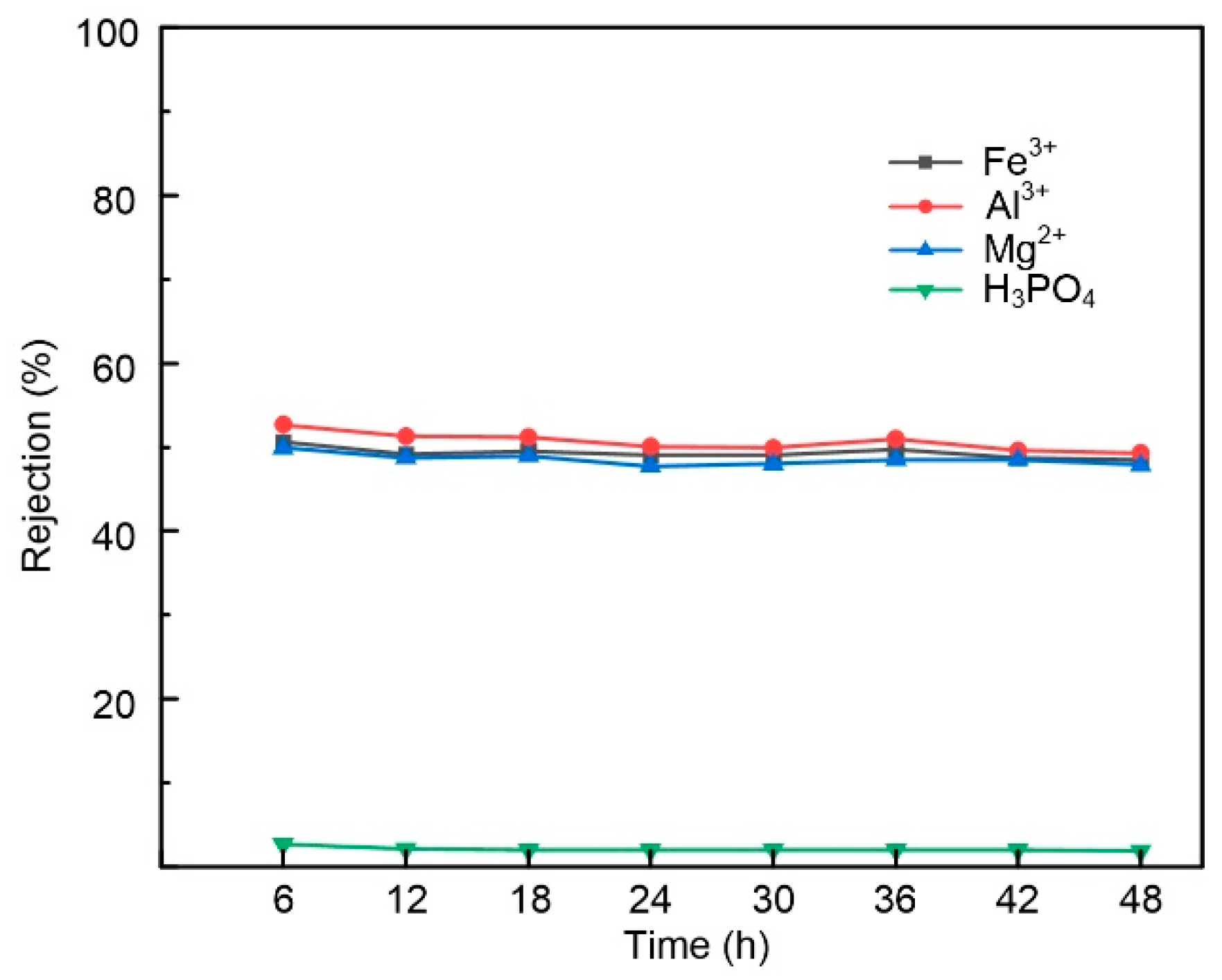
3.5. Acid Stability Evaluation of the Membrane
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wang, R.; Alghanayem, R.; Lin, S. Multipass nanofiltration for lithium separation with high selectivity and recovery. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2023, 57, 14464–14471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gouveia, T.I.A.; Alves, A.; Santos, M.S.F. Theoretical rejection of fifty-four antineoplastic drugs by different nanofiltration membranes. Environ Sci. Pollut. R. 2023, 30, 106099–106111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, S.; Patel, R.; Woo, Y.C. Polyester-based thin-film composite membranes for nanofiltration of saline water: A review. Desalination 2024, 572, 117138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, H.; Li, X.; Yang, W.; Yao, Z.; Mei, Y.; Peng, L.E.; Yang, Z.; Shao, S.; Tang, C.Y. Nanofiltration for drinking water treatment: A review. Front. Chem. Sci. Eng. 2022, 16, 681–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ricci, B.C.; Ferreira, C.D.; Marques, L.S.; Martins, S.S.; Reis, B.G.; Amaral, M.C.S. Assessment of the chemical stability of nanofiltration and reverse osmosis membranes employed in treatment of acid gold mining effluent. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2017, 174, 301–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, K.P.; Zheng, J.; Bargeman, G.; Kemperman, A.J.B.; Benes, N.E. pH stable thin film composite polyamine nanofiltration membranes by interfacial polymerisation. J. Membr. Sci. 2015, 478, 75–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, L.; Zhang, Y.; Xu, L.; Liu, Q.; Borjigin, B.; Hou, D.; Xiang, J.; Wang, J. One step prepared Janus acid-resistant nanofiltration membranes with opposite surface charges for acidic wastewater treatment. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2020, 250, 117245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, Y.; Wang, L.; Zhang, L.; Yu, J.Q. An acid resistant nanofiltration membrane prepared from a precursor of poly(s-triazine-amine) by interfacial polymerization. J. Membr. Sci. 2018, 546, 225–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, K.P.; Bargeman, G.; de Rooij, R.; Kemperman, A.J.B.; Benes, N.E. Interfacial polymerization of cyanuric chloride and monomeric amines: pH resistant thin film composite polyamine nanofiltration membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 2017, 523, 487–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, D.; Huang, Y.; Yu, S.; Lawless, D.; Feng, X. Thin film composite nanofiltration membranes assembled layer-by-layer via interfacial polymerization from polyethylenimine and trimesoyl chloride. J. Membr. Sci. 2014, 472, 141–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Wei, Z.; Wang, H.; Jiang, H.; Li, Y.; Wu, C. An acid-stable positively charged polysulfonamide nanofiltration membrane prepared by interfacial polymerization of polyallylamine and 1,3-benzenedisulfonyl chloride for water treatment. RSC Adv. 2019, 9, 2042–2054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, X.; Hong, J.; Zhu, S.; Chen, J.; Lv, B. Structure–performance study of polyamide composite nanofiltration membranes prepared with polyethyleneimine. J. Mater. Sci. 2017, 52, 11701–11714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khaless, K.; Chanouri, H.; Amal, S.; Ouaattou, A.; Mounir, E.M.; Haddar, H.; Benhida, R. Wet process phosphoric acid purification using functionalized organic nanofiltration membrane. Separations 2022, 9, 100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lasisi, K.H.; Liu, M.; Tao, B.; Shao, S.; Meng, W.; Zhang, K.; Field, R.W. Fabrication of additive-free polyamine-based membranes by facile copolymerization of salt-functionalized poly(allylamine hydrochloride) and branched polyethyleneimine towards high performance nanofiltration. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2025, 375, 133835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, L.; Li, Z.; Peng, Z.; Zhao, Y.; Yang, H.; Wang, M. Fabrication of a novel acid-resistant nanofiltration membrane with dual-charged functional layer for metal ions recovery. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2023, 11, 111410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalwani, M.; Benes, N.E.; Bargeman, G.; Stamatialis, D.; Wessling, M. Effect of pH on the performance of polyamide/polyacrylonitrile based thin film composite membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 2011, 372, 228–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabde, A.D.; Trivedi, M.K.; Ramachandhran, V.; Hanra, M.S.; Misra, B.M. Casting and characterization of cellulose acetate butyrate based UF membranes. Desalination 1997, 114, 223–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Ren, Y.; Zhang, H.; Luo, J.; Woodley, J.M.; Wan, Y. Targeted modification of polyamide nanofiltration membrane for efficient separation of monosaccharides and monovalent salt. J. Membr. Sci. 2021, 628, 119250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, J.; Wang, K.Y.; Chung, T.S. Design of nanofiltration (NF) hollow fiber membranes made from functionalized bore fluids containing polyethyleneimine (PEI) for heavy metal removal. J. Membr. Sci. 2020, 603, 118022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, K.; Pang, S.; Yang, B.; Ji, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Gao, C. Polyethyleneimine/4,4′-Bis(chloromethyl)-1,1′-biphenyl nanofiltration membrane for metal ions removal in acid wastewater. J. Membr. Sci. 2020, 614, 118497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freger, V. Kinetics of film formation by interfacial polycondensation. Langmuir 2005, 21, 1884–1894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghosh, A.K.; Jeong, B.H.; Huang, X.; Hoek, E.M.V. Impacts of reaction and curing conditions on polyamide composite reverse osmosis membrane properties. J. Membr. Sci. 2008, 311, 34–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wittbecker, E.L.; Morgan, P.W. Interfacial polycondensation. I. J. Polym. Sci. Pol. Chem. 1996, 34, 521–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mansourpanah, Y.; Alizadeh, K.; Madaeni, S.S.; Rahimpour, A.; Afarani, H.S. Using different surfactants for changing the properties of poly (piperazineamide) TFC nanofiltration membranes. Desalination 2011, 271, 169–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Z.; Xue, W.L.; Zeng, Z.X.; Gu, M.R. Kinetics of cyanuric chloride hydrolysis in aqueous solution. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2008, 47, 5318–5322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Just, G.; Pokorny, I.; Pritzkow, W. Kinetic studies on the reaction of cyanuric chloride with amines. J. Prakt. Chem./Chem.-Ztg. 1995, 337, 133–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, W.; Wang, E.; Liu, S.; Su, B. Preparation of positively charged acid-resistant hollow fiber nanofiltration membrane with excellent separation performance by surface modification. Desalination 2025, 597, 118332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ismail, N.Q.; Azmi, N.A.; Shoparwe, N.F.; Ameram, N.; Yusoff, A.H. Characterization effect of polysulfone membranes with different molecular weight of polyethylene glycol additives. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2022, 1102, 012085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Z.; Miao, J.; He, Y.; Hong, X.; Tu, K.; Wang, X.; Chen, S.; Yang, H.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, R. A pH-stable positively charged composite nanofiltration membrane with excellent rejection performance. RSC Adv. 2019, 9, 37546–37555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Remmen, K.; Müller, B.; Köser, J.; Wessling, M.; Wintgens, T. Assessment of layer-by-layer modified nanofiltration membrane stability in phosphoric acid. Membranes 2020, 10, 61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duan, X.; Wang, C.-W.; Wang, T.; Xie, X.; Zhou, X.; Ye, Y. Removal of Metal Ions in Phosphoric Acid by Electro-Electrodialysis with Cross-Linked Anion-Exchange Membranes. ACS Omega 2021, 6, 32417–32430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bargeman, G.; Westerink, J.B.; Miguez, O.G.; Wessling, M. The effect of NaCl and glucose concentration on retentions for nanofiltration membranes processing concentrated solutions. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2014, 134, 46–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Escoda, A.; Fievet, P.; Lakard, S.; Szymczyk, A.; Déon, S. Influence of salts on the rejection of polyethyleneglycol by an NF organic membrane: Pore swelling and salting-out effects. J. Membr. Sci. 2010, 347, 174–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tansel, B. Significance of thermodynamic and physical characteristics on permeation of ions during membrane separation: Hydrated radius, hydration free energy and viscous effects. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2012, 86, 119–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Harahsheh, M.; Hussain, Y.A.; Al-Zoubi, H.; Batiha, M.; Hammouri, E. Hybrid precipitation-nanofiltration treatment of effluent pond water from phosphoric acid industry. Desalination 2017, 406, 88–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guastalli, A.R.; Labanda, J.; Llorens, J. Separation of phosphoric acid from an industrial rinsing water by means of nanofiltration. Desalination 2009, 243, 218–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diallo, H.; Rabiller-Baudry, M.; Khaless, K.; Chaufer, B. On the electrostatic interactions in the transfer mechanisms of iron during nanofiltration in high concentrated phosphoric acid. J. Membr. Sci. 2013, 427, 37–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González, M.P.; Navarro, R.; Saucedo, I.; Avila, M.; Revilla, J.; Bouchard, C. Purification of phosphoric acid solutions by reverse osmosis and nanofiltration. Desalination 2002, 147, 315–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Remmen, K.; Müller, B.; Köser, J.; Wessling, M.; Wintgens, T. Phosphorus recovery in an acidic environment using layer-by-layer modified membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 2019, 582, 254–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, S.; He, R.; Dong, C.; Sun, N.; Zhao, S.; He, H.; Yu, H.; Zhang, Y.-B.; He, T. Acid stable layer-by-layer nanofiltration membranes for phosphoric acid purification. J. Membr. Sci. 2022, 644, 120090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
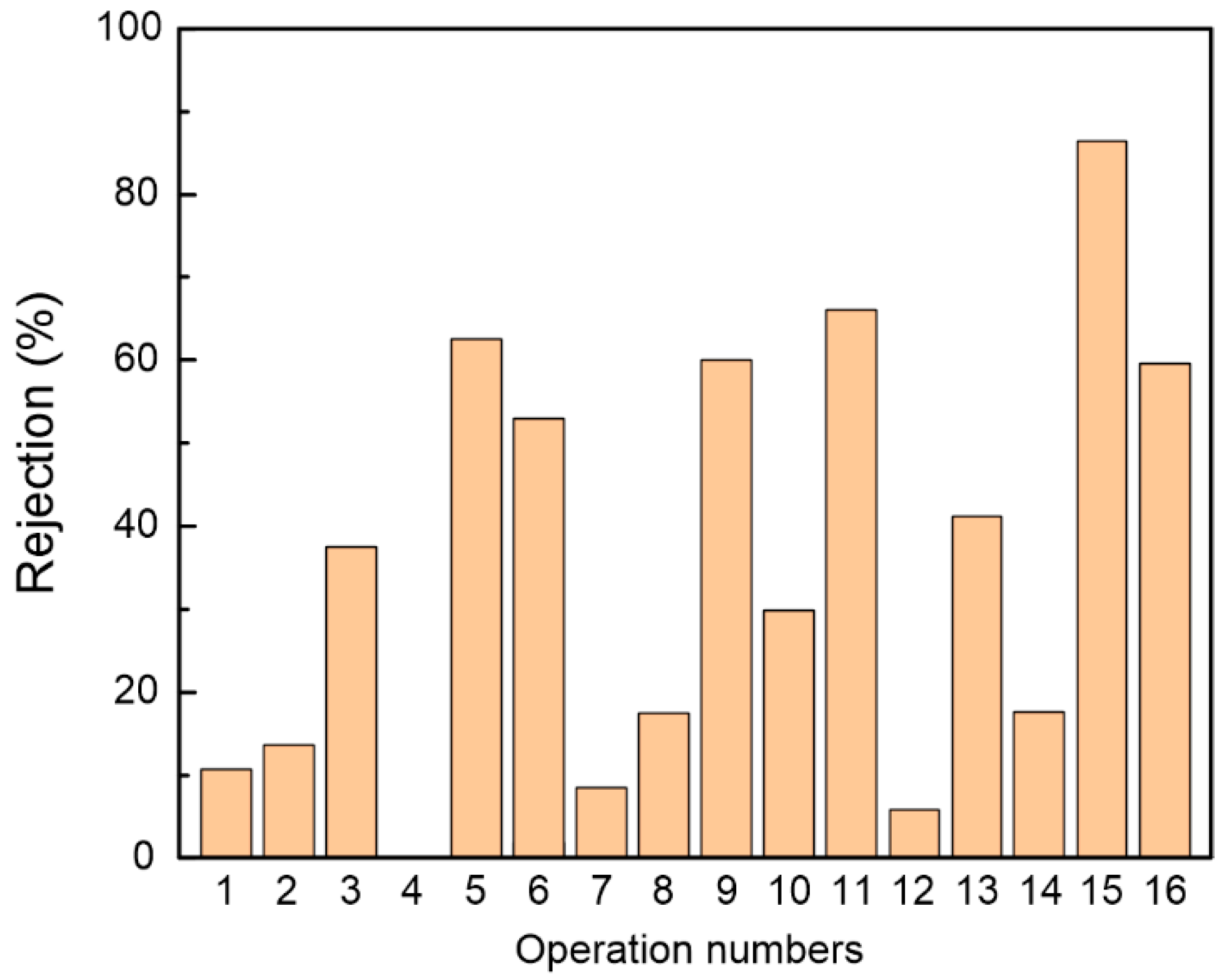
| Operation Numbers | Factors | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
PEI (g/L) |
CC (g/L) |
SDS (wt%) |
Curing Temperature (°C) |
Curing Time (min) | |
| N1 | 10 | 0.1 | 0 | 65 | 5 |
| N2 | 10 | 0.2 | 0.5 | 75 | 10 |
| N3 | 10 | 0.3 | 1 | 85 | 15 |
| N4 | 10 | 0.4 | 1.5 | 95 | 20 |
| N5 | 20 | 0.1 | 0.5 | 8 | 20 |
| N6 | 20 | 0.2 | 0 | 95 | 15 |
| N7 | 20 | 0.3 | 1.5 | 65 | 10 |
| N8 | 20 | 0.4 | 1 | 75 | 5 |
| N9 | 30 | 0.1 | 1 | 95 | 10 |
| N10 | 30 | 0.2 | 1.5 | 85 | 5 |
| N11 | 30 | 0.3 | 0 | 75 | 20 |
| N12 | 30 | 0.4 | 0.5 | 65 | 15 |
| N13 | 40 | 0.1 | 1.5 | 75 | 15 |
| N14 | 40 | 0.2 | 1 | 65 | 20 |
| N15 | 40 | 0.3 | 0.5 | 95 | 5 |
| N16 | 40 | 0.4 | 0 | 85 | 10 |
| Factors | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PEI (P) | CC (C) | SDS (S) | Temperature (T) | Time (t) | |
| Σ(1) | 0.6357 | 1.7436 | 1.8936 | 0.4260 | 1.4430 |
| Σ(2) | 1.4150 | 1.1400 | 1.6846 | 1.3837 | 1.4173 |
| Σ(3) | 1.6176 | 1.9860 | 1.3246 | 1.8934 | 1.3758 |
| Σ(4) | 2.0479 | 0.8467 | 0.8134 | 2.0131 | 1.4801 |
| K1 | 0.1589 | 0.4359 | 0.4734 | 0.1065 | 0.3608 |
| K2 | 0.3537 | 0.2850 | 0.4212 | 0.3459 | 0.3543 |
| K3 | 0.4044 | 0.4965 | 0.3311 | 0.4733 | 0.3440 |
| K4 | 0.5120 | 0.2117 | 0.2033 | 0.5033 | 0.3700 |
| R | 0.3530 | 0.2848 | 0.2700 | 0.3968 | 0.0261 |
| Optimum condition | 40 g/L | 0.3 g/L | 0 wt% | 95 °C | 20 min |
| 5 wt% P2O5 | 10 wt% P2O5 | 15 wt% P2O5 | 20 wt% P2O5 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| H3PO4 (%) | 90.6 | 93.4 | 94.7 | 95.5 |
| H2PO4− (%) | 9.4 | 6.6 | 5.3 | 4.5 |
| pH | 1.16 | 1.00 | 0.90 | 0.83 |
| Ions | Bare Radius (nm) | Hydrated Radius (nm) | Hydration Number (±1) | Diffusion Coefficient (10−9 m2/s, 25 °C) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fe3+ | 0.064 | 0.48 | 6 | 0.607 |
| Al3+ | 0.053 | 0.48 | 6 | 0.559 |
| Mg2+ | 0.072 | 0.428 | 6 | 0.705 |
| Membranes | Rejections of | Acid Stability/H3PO4 | Rejection Decreased | Ref | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| H3PO4 | Fe3+ | Al3+ | Mg2+ | ||||
| NF270 | 66% | / | / | 93% | / | / | [35] |
| Desal-5 DK | 33% | / | 98% | / | 0.4 mol/L (soak for 7 weeks) | ≤5% | [36] |
| MPF34 | ~20% * | 80–90% | / | / | / | / | [37] |
| MPF34 | 9.2 | 26.9 | / | / | / | / | [38] |
| PDADMAC/PSS | / | / | / | 65–75% | 15 wt% (24 h) | ≤5% | [30] |
| PDADMAC/PSS | 5% | / | 93% | / | 10 wt% (60 min) | 2% | [39] |
| PSS/PAH | 10% | / | 97% | / | 10% (32 h) | <2% | [40] |
| This work | <3% | 58% | 60% | 56% | 20% P2O5 (48 h) | <5% | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tian, Z.; Yin, Y.; Wang, J.; Ao, X.; Liu, D.; Jin, Y.; Li, J.; Chen, J. Cyanuric Chloride with the s-Triazine Ring Fabricated by Interfacial Polymerization for Acid-Resistant Nanofiltration. Membranes 2025, 15, 231. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes15080231
Tian Z, Yin Y, Wang J, Ao X, Liu D, Jin Y, Li J, Chen J. Cyanuric Chloride with the s-Triazine Ring Fabricated by Interfacial Polymerization for Acid-Resistant Nanofiltration. Membranes. 2025; 15(8):231. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes15080231
Chicago/Turabian StyleTian, Zhuangzhuang, Yun Yin, Jiandong Wang, Xiuling Ao, Daijun Liu, Yang Jin, Jun Li, and Jianjun Chen. 2025. "Cyanuric Chloride with the s-Triazine Ring Fabricated by Interfacial Polymerization for Acid-Resistant Nanofiltration" Membranes 15, no. 8: 231. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes15080231
APA StyleTian, Z., Yin, Y., Wang, J., Ao, X., Liu, D., Jin, Y., Li, J., & Chen, J. (2025). Cyanuric Chloride with the s-Triazine Ring Fabricated by Interfacial Polymerization for Acid-Resistant Nanofiltration. Membranes, 15(8), 231. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes15080231





