Third-Phase Formation in Rare Earth Element Extraction with D2EHPA: Key Factors and Impact on Liquid Membrane Extraction Performance
Abstract
1. Introduction
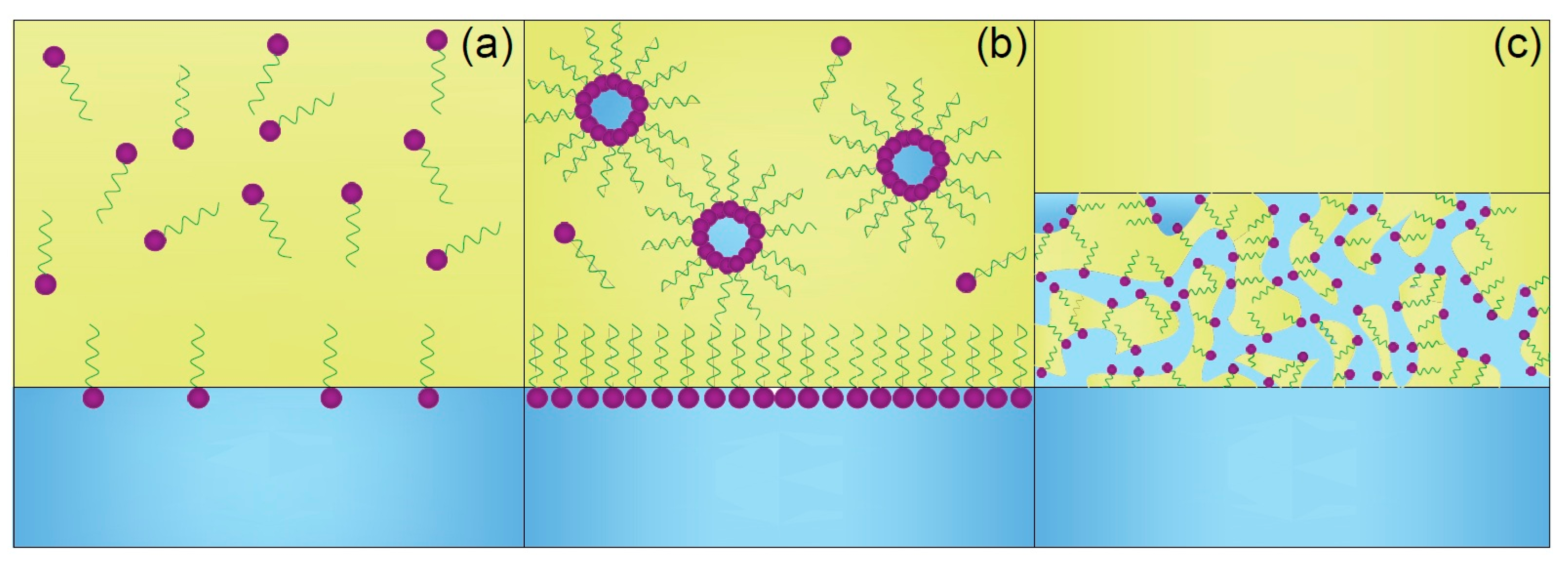
1.1. The Mechanism Behind Third-Phase Formation
1.2. Third-Phase Formation in REE Extraction with D2EHPA
2. Experimental Procedure
2.1. Reagents and Materials
2.2. Analytical Methods
2.3. Experimental Procedure
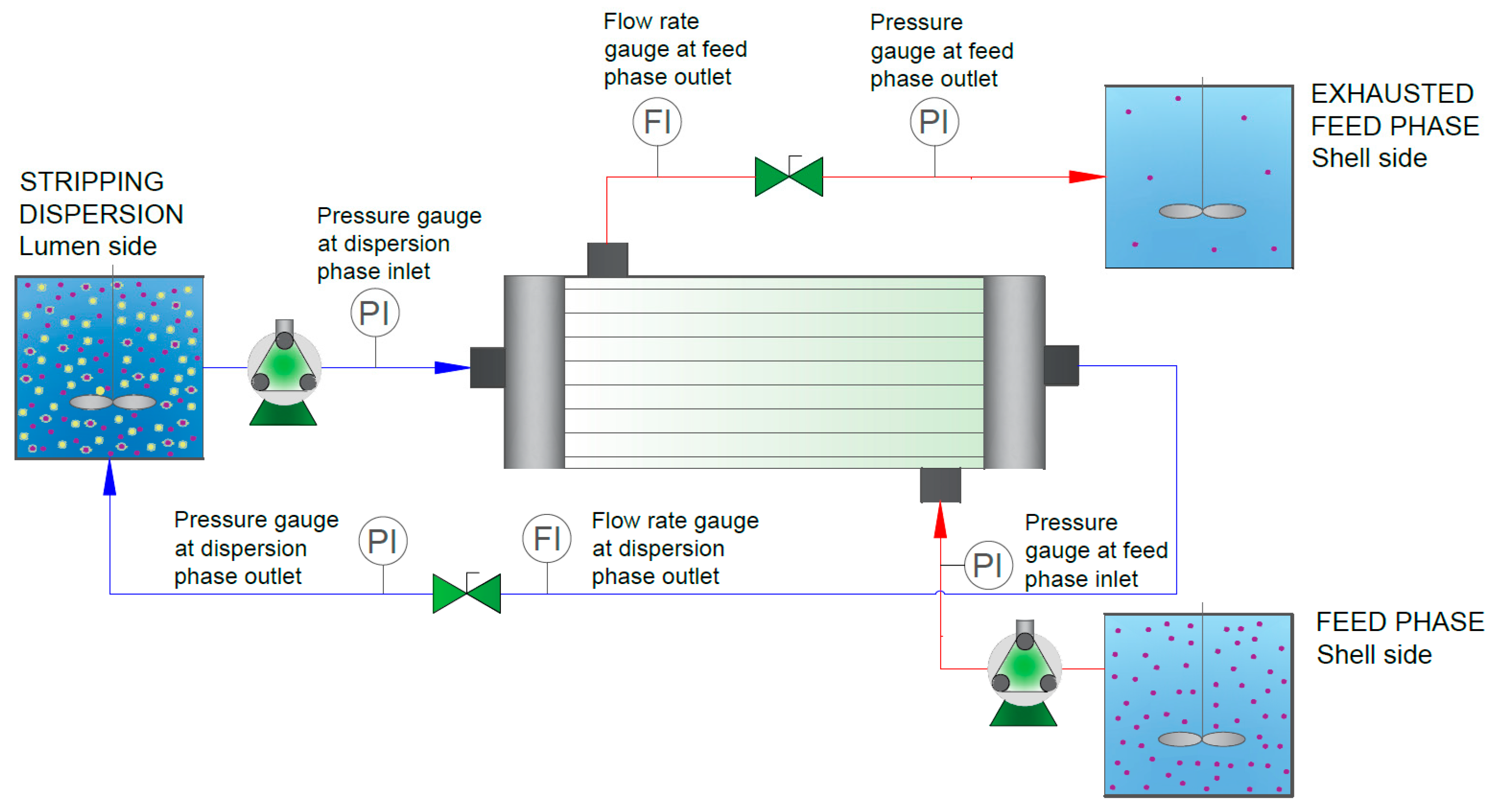
2.3.1. Evaluation of Third-Phase Formation in the HFRLM System
2.3.2. Determination of the Equilibrium Distribution Coefficient
2.3.3. Evaluation of the Limiting Organic Concentration (LOC)
2.3.4. Determination of Interactions in the Organic Phase: FT-IR Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. HFRLM Evaluation
3.2. Determination of the Limiting Organic Concentration (LOC)
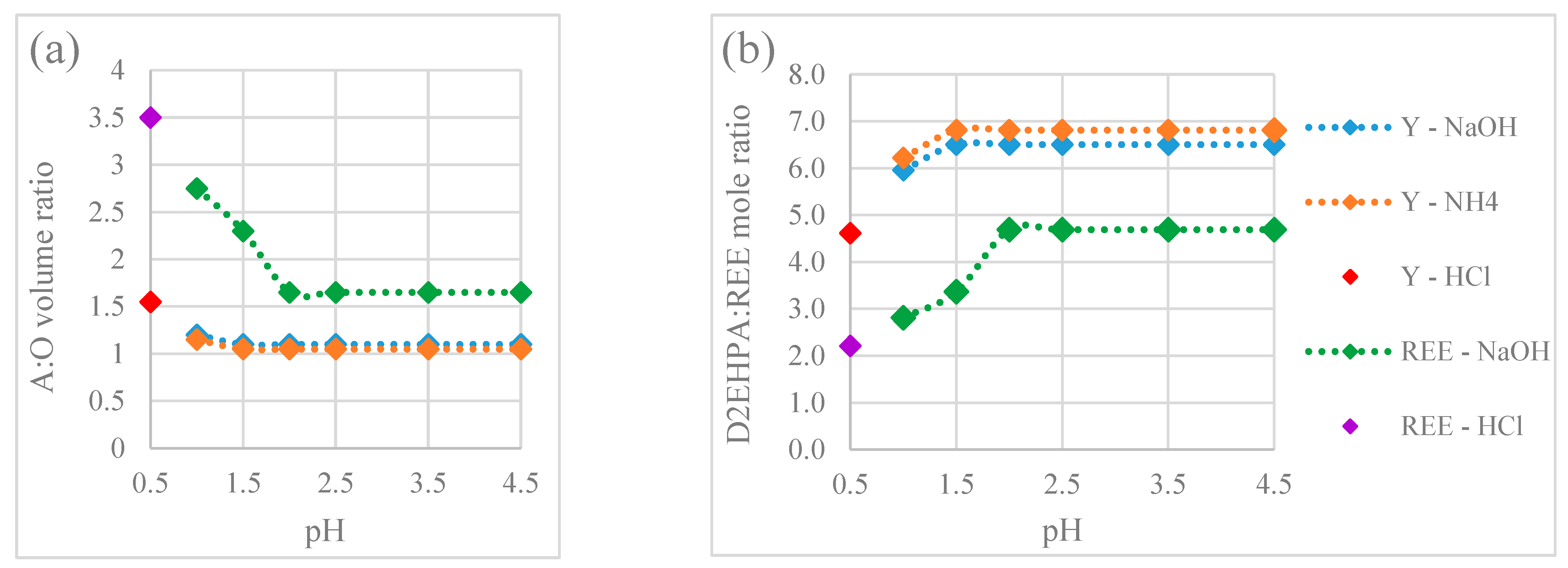
3.2.1. Effect of Ions and pH in the Feed Aqueous Phase
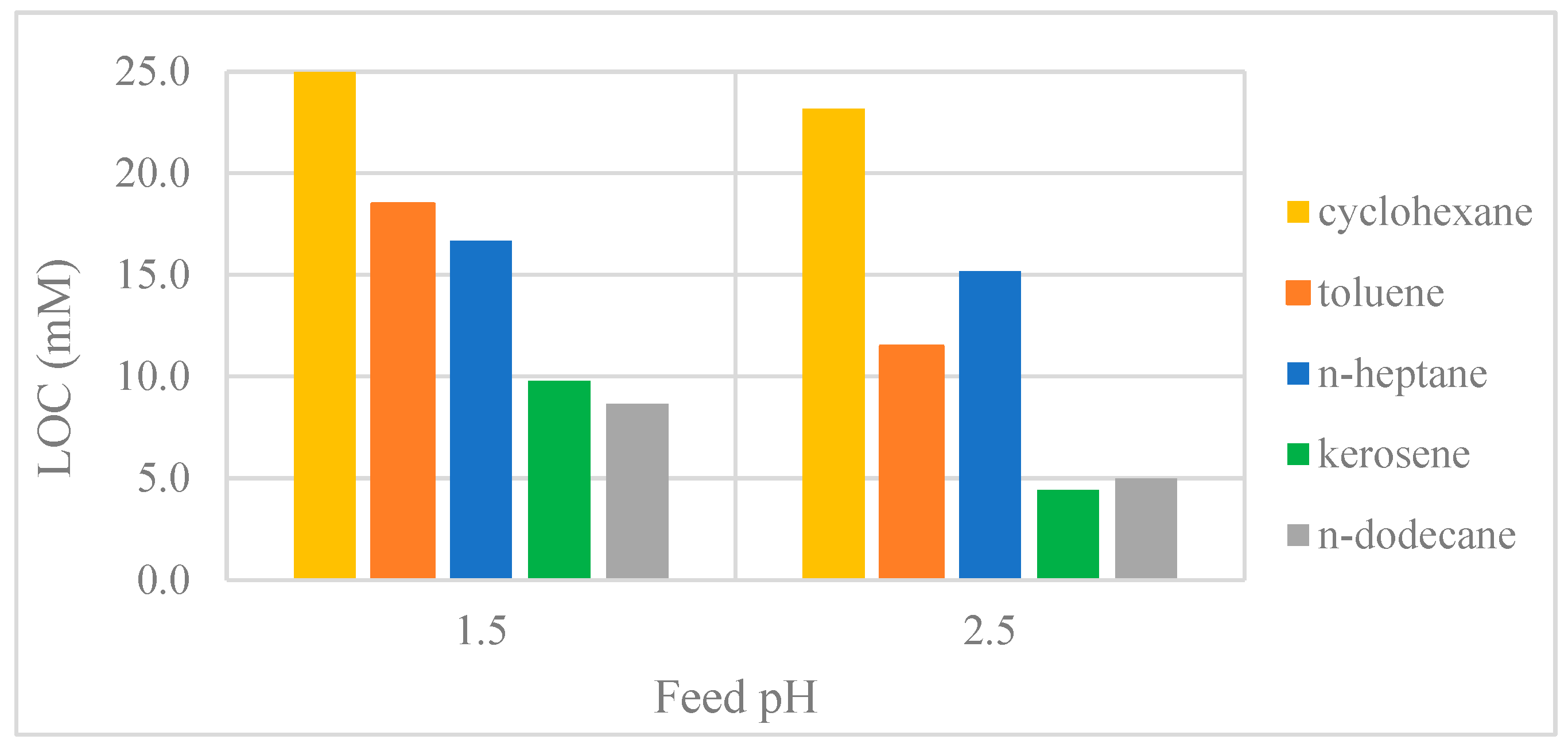
3.2.2. Effect of Organic Diluent
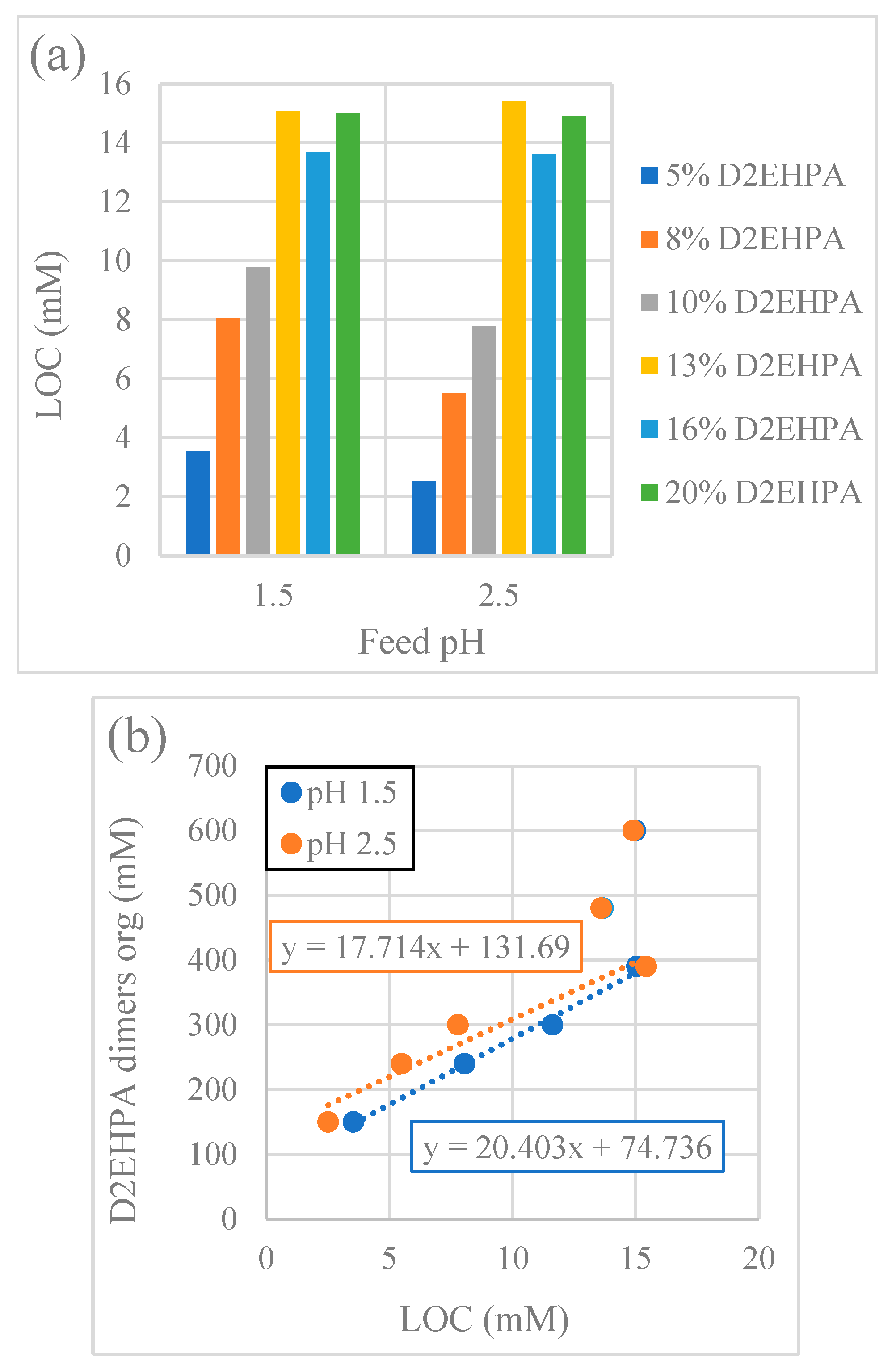
3.2.3. Effect of Extractant Concentration
3.2.4. The Effect of Adding a Modifier
The Effect of Tri-N-Butyl Phosphate Addition
The Effect of the Addition of 1-Decanol
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhang, J.; Zhao, B.; Schreiner, B. Separation Hydrometallurgy of Rare Earth Elements; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2016; ISBN 978-3-319-28233-6. [Google Scholar]
- Communication from the Commission to the European Parliament, the Council, the European Economic and Social Committee and the Committee of the Regions. Critical Raw Materials Resilience: Charting a Path Towards Greater Security and Sustaina-bility. Brussels. 2020. Available online: https://ec.europa.eu/docsroom/documents/42849 (accessed on 16 June 2024).
- Lucas, J.; Lucas, P.; Mercier, T.L.; Rollat, A.; Davenport, W.G. Chapter 5: Rare earths purification, separation, precipitation and calcination. In Science, Technology, Production and Use; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2015; pp. 69–91. ISBN 978-0-444-62735-3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prasad, R.; Sirkar, K.K. Chapter 41: Membrane-based solvent extraction. In Membrane Handbook; Springer Science + Business Media: New York, NY, USA, 1992; Volume I, pp. 727–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aguilar, M.; Cortina, J.L. Chapter 4: Hollow fiber membrane-based separation technology performance and design perspectives. In Solvent Extraction and Liquid Membranas: Fundamentals and Applications in New Materials; Taylor & Francis Group: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2008; pp. 91–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Román, M.F.S.; Ortiz, I.; Ibañez, R.; Bringas, E. Liquid membrane technology: Fundamentals and review of its applications. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 2010, 85, 2–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, Y.; Cui, C.; Ren, Z.; Zhang, W.; Liu, Y. New liquid membrane technology for simultaneous extraction and stripping of copper(II) from wastewater. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2007, 62, 6090–6101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minuchehr, A.; Charkhi, A.; Allahyari, S.A.; Ahmadi, S.J. Thorium pertraction through hollow fiber renewal liquid membrane (HFRLM) using Cyanex 272 as carrier. Prog. Nucl. Energy 2017, 100, 209–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, Y.; Lin, J.; Hu, K.; Liu, Y.; Chen, T.; Li, X.; Zhang, W.; Xu, Q. Towards clean sustainable yttrium separation strategy using hollow fiber renewal supported liquid membrane with [N1888][CA12]. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2023, 320, 124132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez, J.; Alemrajabi, M.; Ricknell, J.; Samak, S.; Varela, R.R.; Rasmuson, Å.C.; Forsberg, K.; Hedman, F. Separation of Rare-Earth Elements Using Supported Liquid Membrane Extraction in Pilot Scale. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2022, 61, 18475–18491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadollahi, A.; Zahakifar, F.; Charkhi, A.; Saberyan, K.; Torab-Mostaedi, M. Intensification of zirconium and hafnium separation through the hollow fiber renewal liquid membrane technique using synergistic mixture of TBP and Cyanex-272 as extractant. Chin. J. Chem. Eng. 2019, 27, 1817–1827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadollahi, A.; Davarkhah, R.; Zahakifar, F.; Charkhi, A.; Torab-Mostaedi, M. Effect of surfactants on the performance of hollow fiber renewal liquid membrane (HFRLM): A case study of uranium transfer. J. Radioanal. Nucl. Chem. 2018, 318, 973–983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davarkhah, R.; Charkhi, A.; Zahakifar, F.; Torab-Mostaedi, M. Performance evaluation of hollow fiber renewal liquid membrane for extraction of uranium(VI) from acidic sulfate solution. Radiochim. Acta 2018, 106, 181–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, H.; Zhou, C.; Wang, X. Enrichment of Rare Earth Through the Hollow Fiber Dispersion Liquid Membrane. Chin. J. Appl. Chem. 2017, 34, 971–976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charkhi, A.; Allahyari, S.A.; Ahmadi, S.J.; Minuchehr, A. Th(IV) transport from nitrate media through hollow fiber renewal liquid membrane. J. Membr. Sci. 2016, 520, 374–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Wang, H.; Liu, J.; Ren, Z.; Zhang, W. Modeling study on the mass transfer of hollow fiber renewal liquid membrane: Effect of the hollow fiber module scale. J. Membr. Sci. 2013, 439, 28–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.M.; Pei, L.; Guo, W. Stripping dispersion hollow fiber liquid membrane containing carrier PC-88A and HNO3 for the extraction of Sm3+. Chin. Chem. Lett. 2012, 23, 101–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pei, L.; Wang, L.; Guo, W. Separation of trivalent samarium through facilitated stripping dispersion hollow fiber liquid membrane using p204 as mobile carrier. Chin. J. Chem. 2011, 29, 1233–1238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, N.; Pei, L.; Wang, L.; Guo, W. Stripping dispersion hollow fiber liquid membrane containing PC-88A as carrier and HCl for transport behavior of trivalent dysprosium. J. Membr. Sci. 2011, 378, 520–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, H.; Liu, J.; Ren, Z.; Zhang, W.; Wang, S. Extraction separation of Cu(II) and Co(II) from sulfuric solutions by hollow fiber renewal liquid membrane. J. Membr. Sci. 2010, 365, 260–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Cui, C.; Zhang, W. Mass Transfer of Copper(II) in Hollow Fiber Renewal Liquid Membrane with Different Carriers. Chin. J. Chem. Eng. 2010, 18, 346–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, Y.; Cui, C.; Meng, H.; Ren, Z.; Zhang, W. Simultaneous removal and recovery of copper(II) from acidic wastewater by hollow fiber renewal liquid membrane with LIX984N as carrier. Chem. Eng. J. 2010, 157, 230–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Yao, B.; Pei, L. Transport of Tm(III) through dispersion supported liquid membrane containing PC-88A in kerosene as the carrier. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2009, 65, 220–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Dai, Y.; Hao, Z.; Ren, Z.; Zhang, W. Modeling of effect of pH on mass transfer of copper(II) extraction by hollow fiber renewal liquid membrane. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2008, 47, 4256–4262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paatero, E.; Sjöblom, J. Phase behaviour in metal extraction systems. Hydrometallurgy 1990, 25, 231–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Li, D.; Li, H.; Meng, S.; Guo, F. Reversed micelle formation in a model liquid–liquid extraction system. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2008, 322, 605–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eicke, H.F. Surfactants in Nonpolar Solvents. Aggregation and Micellization. In Micelles; Topics in Current Chemistry; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1980; Volume 87, pp. 85–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warr, G.G.; Blom, A.; Wanless, E.J. Morphology Transitions in Nonionic Surfactant Adsorbed Layers near Their Cloud Points. Langmuir 2005, 21, 11850–11855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zemb, T.; Madic, C.; Erlinger, C.; Belloni, L. Attractive Interactions between Reverse Aggregates and Phase Separation in Concentrated Malonamide Extractant Solutions. Langmuir 1999, 15, 2290–2300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Testard, F.; Martinet, L.; Madic, C.; Zemb, T.; Berthon, L. Influence of the extracted solute on the aggregation of malonamide extractant in organic phases: Consequences for phase stability. Comptes Rendus Chim. 2010, 13, 1326–1334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zemb, T.; Martinet, L.; Madic, C.; Testard, F.; Berthon, L. Solvent penetration and sterical stabilization of reverse aggregates based on the DIAMEX process extracting molecules: Conse-quences for the third phase formation. Solvent Extr. Ion Exch. 2007, 25, 545–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moyer, B.A. Chapter 7, Third-Phase Formation in Liquid/Liquid Extraction: A Colloidal Approach. In Ion Exchange and Solvent Extraction: A Series of Advances, 1st ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2009; Volume 19, pp. 381–427. [Google Scholar]
- Steytler, D.C.; Robinson, B.H.; Eastoe, J.; Heenan, R.K.; Jenta, T.R. Structure of reversed micelles formed by metal salts of bis(ethylhexyl) phosphoric acid. Langmuir 1996, 12, 1483–1489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cote, G. The supramolecular speciation: A key for improved understanding and modelling of chemical reactivity in complex systems. Radiochim. Acta 2003, 91, 639–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, D. Chapter 2. Extractants used in solvent extraction-separation of rare earths: Extraction mechanism, properties, and features. In Hydrometallurgy of Rare Earths: Extraction and Separation; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2018; pp. 187–289. ISBN 978-0-12-813920-2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gannaz, B. Spéciations Moléculaire et Supramoléculaire de Systèmes D’extraction Liquide-Liquide à base de Malonamide et/ou d’acides Dialkylphosphoriques Pour La Séparation An(III)/Ln(III). Ph.D. Thesis, University of Paris XI, Orsay, France, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Peppard, D.; Mason, G.; Driscoll, W.; Maier, J. Fractional extraction of the lanthanides as their di-alkyl orthophosphates. J. Inorg. Nucl. Chem. 1957, 4, 334–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masana, A.; Iglesias, M.; Valiente, M.; Salvadó, V.; Anticó, E. Effect of Y(III) distribution between aqueous nitrate and organic D2EHPA solutions on the Y(III) precipitation stripping using oxalic acid. Solvent Extr. Ion Exch. 1999, 17, 277–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masana, A.; Iglesias, M.; Valiente, M.; Salvadó, V.; Hidalgo, M.; Anticó, E. Solvent extraction of yttrium from chloride media by di(2-ethylhexyl)phosphoric acid in kerosene. Speciation studies and gel formation. Anal. Chim. Acta 1996, 327, 267–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harada, T.; Smutz, M. Extraction of yttrium in the system YCI3-HCl-H20 di(2-ethylhexyl) phosphoric acid. J. Inorg. Nucl. Chem. 1970, 32, 649–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harada, T.; Bautista, R.G.; Smutz, M. Characterization of iron and rare-earth polymers of di(2-ethylhexyl)phosphoric acid. J. Chem. Eng. Data 1972, 17, 203–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hrdlička, A.; Doležal, J.; Moreno, C.; Valiente, M. Selective transport of lanthanides through supported liquid membranes containing non-selective extractant, di-(2-ethylhexyl)phosphoric acid, as a carrier. J. Membr. Sci. 2000, 168, 175–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Datsenko, A.M.; Murashova, N.M.; Yurtov, E.V. Gel formation in extraction of terbium by bis(2-ethylhexyl) hydrogen phosphate. Russ. J. Inorg. Chem. 2006, 51, 670–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murashova, N.M.; Yurtov, E.V. Gels, emulsions, and liquid crystals in extraction systems with Di(2-ethylhexyl)phosphoric acid. Theor. Found. Chem. Eng. 2007, 41, 737–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asano, T.; Sano, N.; Imai, S.; Kanki, T.; Tomita, A. On the mechanism of the interfacial reaction in extraction of rare earth metals by D2EHPA. Dev. Chem. Eng. Miner. Process. 2003, 11, 539–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peppard, D.; Ferraro, J.; Mason, G. Hydrogen bonding in organophosphoric acids. J. Inorg. Nucl. Chem. 1958, 7, 231–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peppard, D.; Mason, G.; Driscoll, W.; Sironen, R. Acidic esters of orthophosphoric acid as selective extractants for metallic cations—Tracer studies. J. Inorg. Nucl. Chem. 1958, 7, 276–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zemb, T.; Testard, F.; Martinet, L.; Bauduin, P.; Madic, C.; Abécassis, B.; Berthon, L. Self-assembling properties of malonamide extractants used in separation processes. Radiochim. Acta 2008, 96, 265–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiarizia, R.; Rickert, P.G.; Kolarik, Z.; Borkowski, M.; Thiyagarajan, P.; Jensen, M.P. Extraction of zirconium nitrate by TBP in n-octane: Influence of cation type on third phase formation according to the “sticky spheres” model. Langmuir 2004, 20, 10798–10808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, D.W. Ionic hydration enthalpies. J. Chem. Educ. 1977, 54, 540–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammadi, M.; De La Cruz, J.M.; Rasmuson, Å.; Kloo, L.; Forsberg, K. Separation of ND(III), DY(III) and Y(III) by solvent extraction using D2EHPA and EHEHPA. Hydrometallurgy 2015, 156, 215–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Su, W.; Jing, Y. Aqueous partition mechanism of organophosphorus extractants in rare earths extraction. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2016, 55, 8424–8431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chagnes, A.; Stambouli, M.; Omelchuk, K. Investigation of aggregation and acid dissociation of new cationic exchangers for liquid-liquid extraction. J. Mol. Liq. 2018, 262, 111–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.-S.; Li, Y.-S.; Lee, P.-C.; Chen, J.-Y.; Li, C.-W. Dissolution of D2EHPA in liquid–liquid extraction process: Implication on metal removal and organic content of the treated water. Water Res. 2011, 45, 5953–5958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zemb, T.N.; Bohinc, K.; Dufrêche, J.-F.; Špadina, M. Colloidal model for the prediction of the extraction of rare earths assisted by the acidic extractant. Langmuir 2019, 35, 3215–3230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ekberg, C.; Retegan, T.; Steenari, B.-M.; Gergoric, M. Separation of heavy rare-earth elements from light rare-earth elements via solvent extraction from a neodymium magnet leachate and the effects of diluents. J. Sustain. Met. 2017, 3, 601–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bauer, C. Metal Ion Extractant in Microemulsions: Where Solvent Extraction and Surfactant Science Meet. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Montpellier II, Montpellier, France, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Zemb, T.; Madic, C.; Testard, F.; Abécassis, B.; Berthon, L. Effect of n-Octanol on the Structure at the Supramolecular Scale of Concentrated Dimethyldioctylhexylethoxymalonamide Extractant Solutions. Langmuir 2003, 19, 6638–6644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bauer, D.; Bouvier, C.; Sabot, J.; Blondet, I.; Szymanowski, J.; Cote, G. Interfacial activity of bis(2-ethylhexyl) phosphoric acid in model liquid-liquid extraction systems. Hydrometallurgy 1997, 44, 163–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Ref. | Author | Year | Feed Phase | Organic Phase | Stripping Phase |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| [9] | K. Hu et al. | 2023 | Y(III) | [N1888] [CA12] in kerosene | HCl/Deionised water |
| [10] | M. Alemrajabi et al. | 2022 | Mixed REEs (La, Nd, Sm, Dy, Er, Y) in chloride media | D2EHPA in kerosene | HCl |
| [11] | A. Yadollahi et al. | 2019 | Zr/Hf in nitrate media | Mixture of TBP and Cyanex 272 | NH4F |
| [12] | F. Zahakifar et al. | 2018 | U(VI) in sulphate media | Alamine 336 in kerosene | NaCl, NH4Cl, NaHCO3 |
| [13] | F. Zahakifar et al. | 2018 | U(VI) in sulphate media | Alamine 336 in kerosene | NaCl, NH4Cl, NaNO3, NaF, Na2CO3, NaHCO3 |
| [14] | Cheng H. et al. | 2017 | Yb(III) in chloride media | EHEHPA in n-heptane | HCl |
| [8] | S.A. Allahyari et al. | 2017 | Th(IV) in nitrate media | Cyanex 272 in kerosene | H2SO4 |
| [15] | S.A. Allahyari et al. | 2016 | Th(IV) in nitrate media | TBP in kerosene | HNO3 |
| [16] | Z. Ren et al. | 2013 | CuSO4 | LIX984N in kerosene | H2SO4 |
| [17] | l. Pei et al. | 2012 | Sm(III) in acetate-buffered media | PC-88A/EHEHPA in kerosene | HNO3 |
| [18] | L. Pei et al. | 2011 | Sm(III) in acetate-buffered chloride media | P204/D2EHPA in kerosene | HCl |
| [19] | L. Pei et al. | 2011 | Dy(III) in acetate-buffered media | PC-88A/EHEHPA in kerosene | HCl |
| [20] | Z. Ren et al. | 2010 | Cu(II) and Co(II) in sulphate media | LIX984N in kerosene for Cu(II)/Cyanex 272 in kerosene for Co(II) | H2SO4 |
| [21] | W. Zhang | 2010 | CuSO4 in acetate buffer solution | D2EHPA or LIX984N in kerosene | H2SO4 |
| [22] | W. Zhang | 2010 | CuSO4 in sulphate media | LIX984N in kerosene | H2SO4 |
| [23] | L. Pei et al. | 2009 | Tm in acetate-buffered chloride media | PC-88A/EHEHPA in kerosene, n-heptane, methyl-isobutyl, ketone, butylacetate and benzene | HCl |
| [24] | Z. Ren et al. | 2008 | CuSO4 in acetate buffer solution | D2EHPA in kerosene | HCl, H3PO4, H2SO4, HNO3 |
| [7] | Z. Ren et al. | 2007 | CuSO4 | D2EHPA in kerosene | HCl |
| Provider | 3M |
|---|---|
| Contactor model | Liqui-Cel Extra-Flow 2.5 in × 8 in Celgard X50-215 Microporous Hollow Fibre Membrane Polypropylene Fibre |
| Effective surface area (m2) | 1.4 |
| Effective fibre length (cm) | 20.32 |
| Number of fibres | 11,000 |
| Outer fibre diameter (μm) | 300 |
| Inner fibre diameter (μm) | 220 |
| Fibre wall thickness (μm) | 40 |
| Fibre porosity | 0.4 |
| Pore tortuosity | 2.5 |
| Effective pore diameter (μm) | 0.04 |
| Exp. | [REE]feed (mM) | pHfeed | [D2EHPA]org (v/v%) | [TBP]org (v/v%) | [HNO3]strip (M) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | 1 | 3.75 | 1.5 | 10% | - | 3 |
| 2 | 3.75 | 2.5 | 10% | - | 3 | |
| 3 | 3.75 | 3.5 | 10% | - | 3 | |
| 4 | 3.75 | 4.5 | 10% | - | 3 | |
| B | 5 | 1.55 | 0.6 | 13% | 1% | 3 |
| 6 | 1.55 | 0.8 | 13% | 1% | 3 | |
| 7 | 1.55 | 1.0 | 13% | 1% | 3 | |
| 8 | 1.55 | 1.5 | 13% | 1% | 3 | |
| 9 | 1.55 | 1.75 | 13% | 1% | 3 | |
| 10 | 1.55 | 2.0 | 13% | 1% | 3 | |
| 11 | 1.55 | 2.5 | 13% | 1% | 3 |
| (a) Y(III) Solution | (b) REE Mixture | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Feed pH | pH Adjuster | LOC (mM) | L (%) | pH Adjuster | LOC (mM) | L (%) | pH Adjuster | LOC (mM) | L (%) |
| 0.5 | HCl | 9.3 | 18.4 | - | - | - | HCl | 25.6 | 50.7 |
| 1.0 | NaOH | 9.2 | 18.3 | NH4OH | 9.5 | 18.9 | NaOH | 39.1 | 77.6 |
| 1.5 | NaOH | 9.8 | 19.4 | NH4OH | 9.2 | 18.3 | NaOH | 36.7 | 71.7 |
| 2.0 | NaOH | 8.6 | 17.0 | NH4OH | 4.5 | 9.0 | NaOH | 28.2 | 55.9 |
| 2.5 | NaOH | 4.4 | 8.8 | NH4OH | 4.3 | 8.5 | NaOH | 27.5 | 54.6 |
| 3.5 | NaOH | 4.2 | 8.3 | NH4OH | 3.5 | 6.9 | NaOH | 26.7 | 53.0 |
| 4.5 | NaOH | 4.0 | 7.9 | NH4OH | 3.4 | 6.8 | NaOH | 25.3 | 50.1 |
| Feed pH | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| 1.5–2.5 | 1.5 | 2.5 | |
| Organic Phase | A:O Ratio | D2EHPA:Y Ratio | |
| 5 v/v% D2EHPA | <1 | - | - |
| 8 v/v% D2EHPA | <1 | - | - |
| 10 v/v% D2EHPA | 1.15 | 6.0 | 6.0 |
| 13 v/v% D2EHPA | 1.7 | 5.2 | 5.2 |
| 16 v/v% D2EHPA | 1.7 | 6.4 | 6.5 |
| 20 v/v% D2EHPA | 2.2 | 6.2 | 6.2 |
| pH 1.5 | pH 2.5 | pH 1.5–2.5 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| [TBP] (v/v%) | [TBP] (M) | LOC (mM) | EffectLOC (%) | L (%) | LOC (mM) | EffectLOC (%) | L (%) | A:O Ratio |
| 1 | 0.04 | 13.8 | +90.3 | 27.44 | 13.8 | +76.7 | 27.28 | 1.25 |
| 2 | 0.07 | 10.5 | +45.0 | 20.91 | 11.6 | +48.7 | 22.95 | 1.25 |
| 3 | 0.11 | 9.2 | +26.8 | 18.28 | 9.2 | +17.7 | 18.17 | 1.25 |
| 4 | 0.15 | 14.5 | +99.9 | 28.83 | 14.5 | +85.7 | 28.67 | 1.15 |
| 5 | 0.18 | 14.5 | +100.0 | 28.85 | 14.5 | +85.7 | 28.67 | 1.15 |
| 6 | 0.22 | 11.3 | +55.5 | 22.43 | 11.2 | +44.3 | 22.29 | 1.15 |
| Feed Phase | Organic Phase | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| pH | [Y]feed (mM) | [TBP] (v/v%) | DExtraction | DStripping |
| 1.5 | 41.11 | 0 | 91.1 | 0.27 |
| 1 | 318.9 | 0.46 | ||
| 3 | 130.2 | 0.37 | ||
| 5 | 51.6 | 0.32 | ||
| 2.5 | 41.05 | 0 | 96.3 | 0.31 |
| 1 | 546.9 | 0.45 | ||
| 3 | 175.6 | 0.41 | ||
| 5 | 106.74 | 0.34 | ||
| pH 1.5 | pH 2.5 | pH 1.5–2.5 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| [1-Dec] (v/v%) | [1-Dec] (M) | LOC (mM) | EffectLOC (%) | L (%) | LOC (mM) | EffectLOC (%) | L (%) | A:O Ratio |
| 1 | 0.05 | 4.8 | −33.8 | 9.55 | 5.2 | −32.7 | 10.39 | 1.25 |
| 2 | 0.10 | 5.7 | −22.2 | 11.22 | 4.6 | −40.9 | 9.13 | 1.15 |
| 3 | 0.15 | 5.7 | −22.2 | 11.22 | 6.8 | −13.3 | 13.39 | 1.15 |
| 4 | 0.21 | 6.3 | −13.0 | 12.54 | 6.3 | −19.2 | 12.47 | 1.0 |
| 5 | 0.26 | 5.9 | −18.9 | 11.70 | 5.9 | −24.6 | 11.64 | 1.0 |
| 6 | 0.31 | 6.3 | −13.1 | 12.53 | 5.5 | −29.4 | 10.91 | 1.0 |
| Feed Phase | Organic Phase | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| pH | [Y]feed (mM) | [1-Dec] (v/v%) | Dextraction | Dstripping |
| 1.5 | 41.11 | 0 | 91.1 | 0.27 |
| 1 | 17.2 | 0.18 | ||
| 3 | 14.4 | 0.13 | ||
| 5 | 9.3 | 0.11 | ||
| 2.5 | 41.05 | 0 | 96.3 | 0.31 |
| 1 | 29.7 | 0.19 | ||
| 3 | 26.3 | 0.16 | ||
| 5 | 17.9 | 0.11 | ||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rodríguez Varela, R.; Chagnes, A.; Forsberg, K. Third-Phase Formation in Rare Earth Element Extraction with D2EHPA: Key Factors and Impact on Liquid Membrane Extraction Performance. Membranes 2025, 15, 188. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes15070188
Rodríguez Varela R, Chagnes A, Forsberg K. Third-Phase Formation in Rare Earth Element Extraction with D2EHPA: Key Factors and Impact on Liquid Membrane Extraction Performance. Membranes. 2025; 15(7):188. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes15070188
Chicago/Turabian StyleRodríguez Varela, Raquel, Alexandre Chagnes, and Kerstin Forsberg. 2025. "Third-Phase Formation in Rare Earth Element Extraction with D2EHPA: Key Factors and Impact on Liquid Membrane Extraction Performance" Membranes 15, no. 7: 188. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes15070188
APA StyleRodríguez Varela, R., Chagnes, A., & Forsberg, K. (2025). Third-Phase Formation in Rare Earth Element Extraction with D2EHPA: Key Factors and Impact on Liquid Membrane Extraction Performance. Membranes, 15(7), 188. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes15070188








