A Paradigm Shift in End-of-Life Membrane Recycling: From Conventional to Emerging Techniques
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Recyclability in Membrane Technology
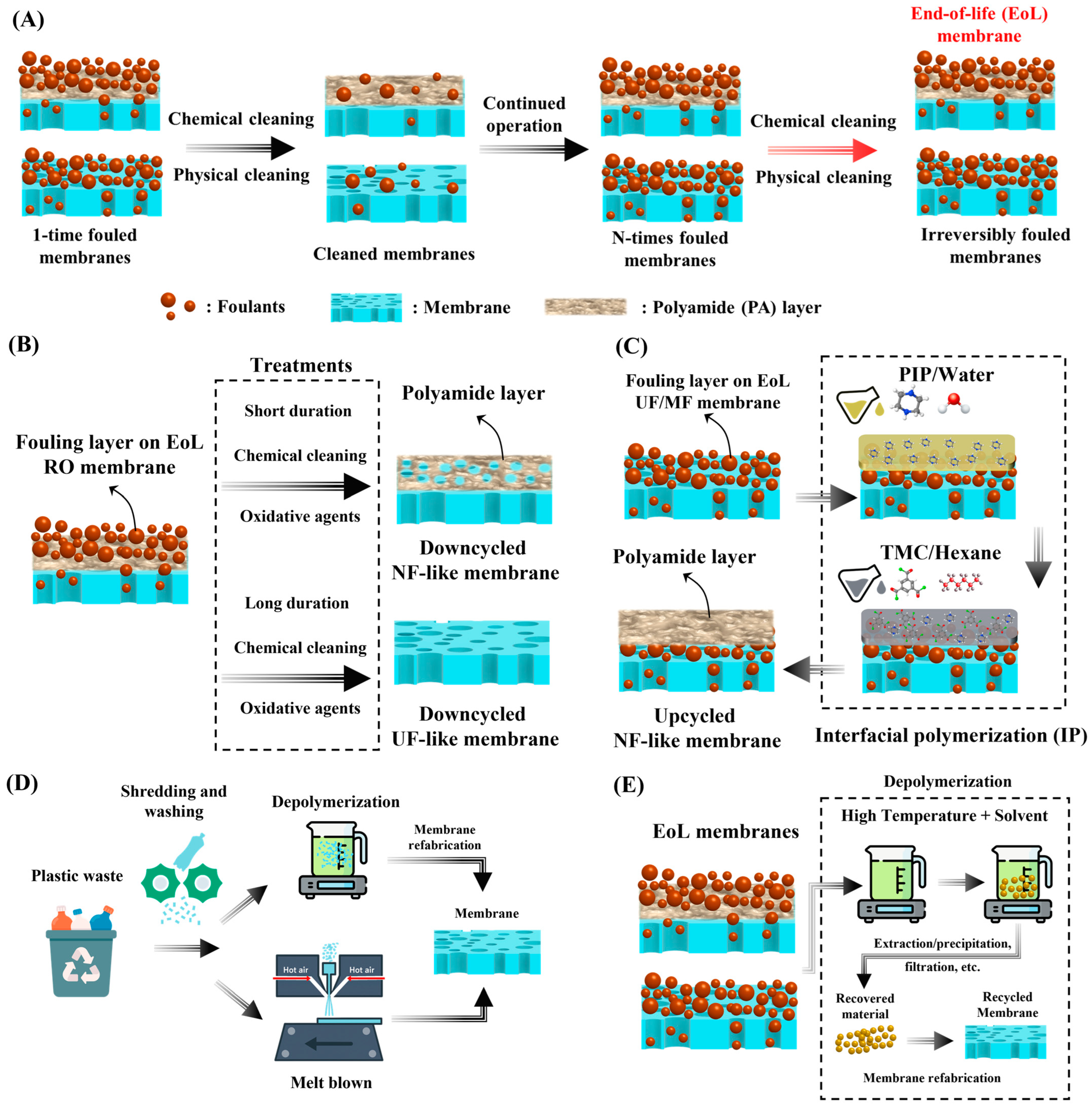
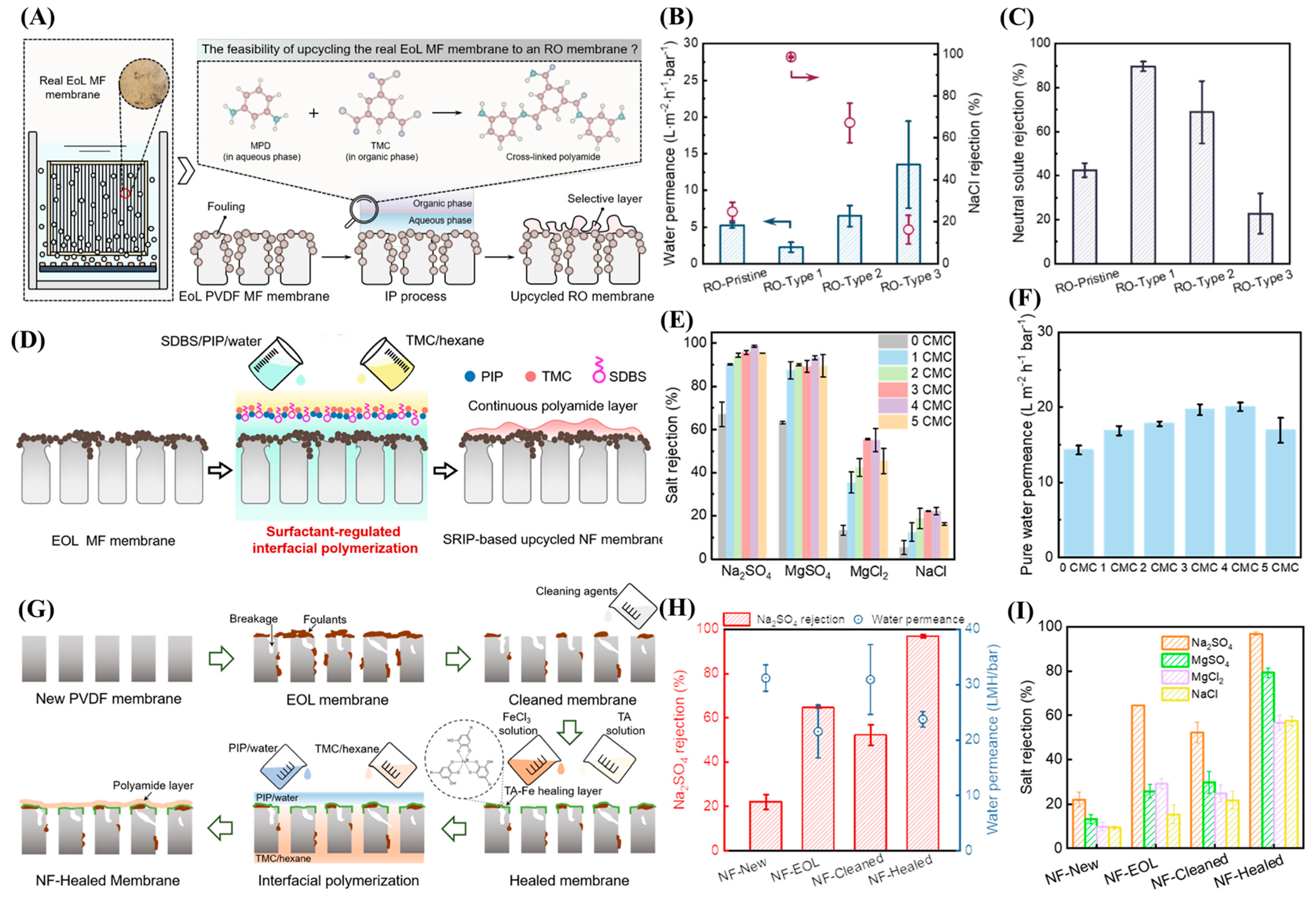
2.1. Down- and Upcycling of Fouled EoL Membranes
2.2. Recycling of Plastic Waste for Membrane Fabrication
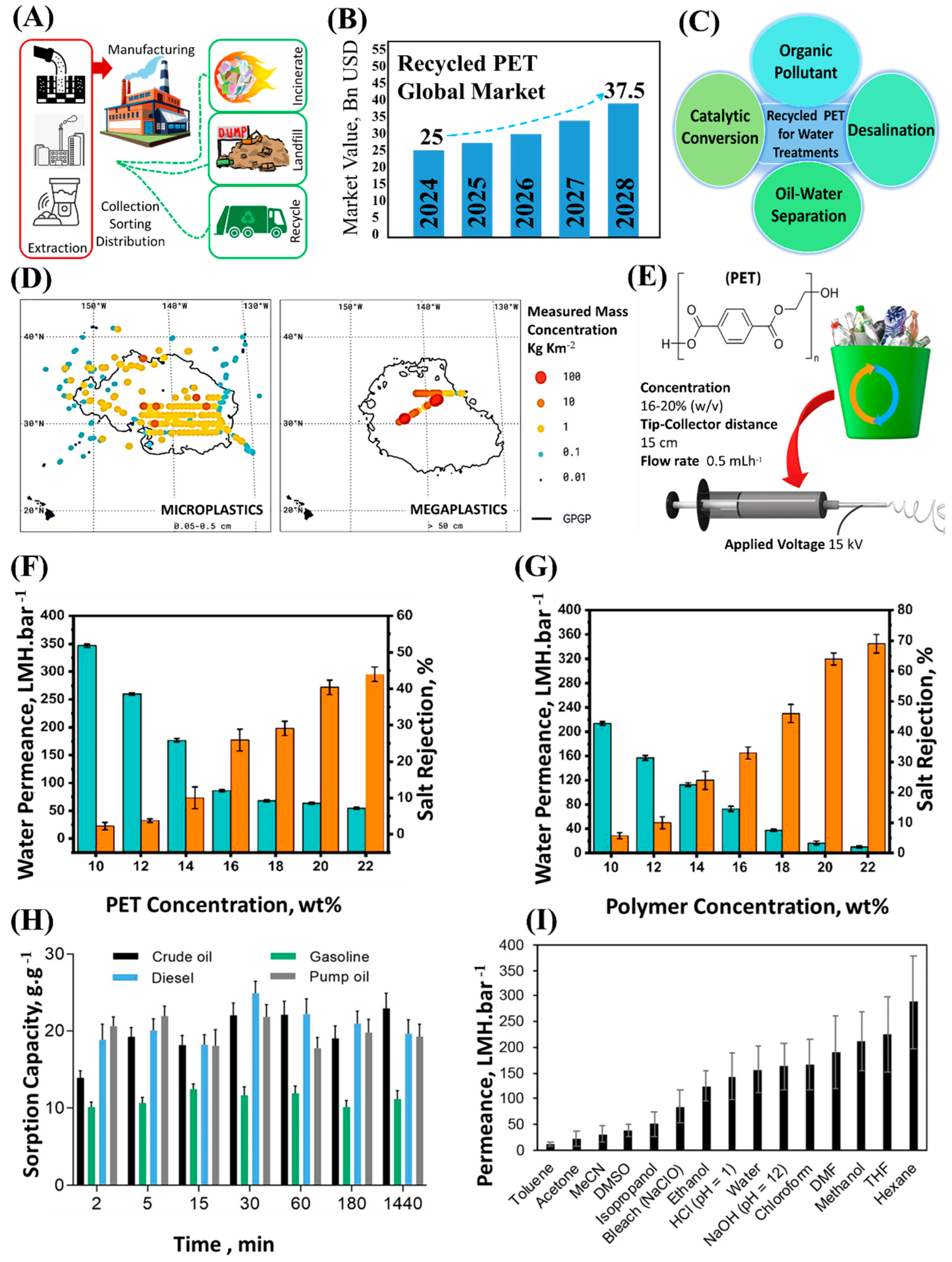
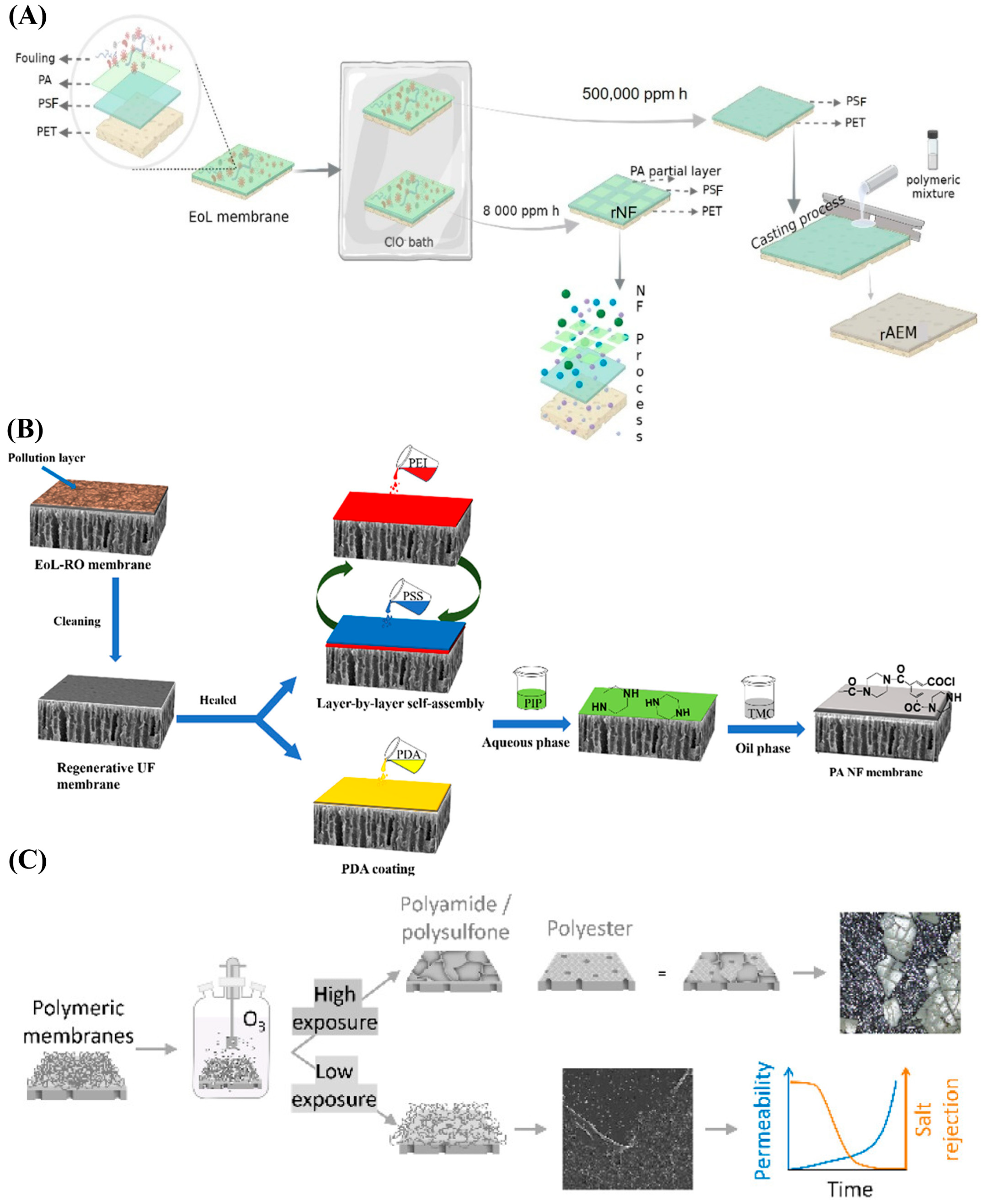
2.3. Emerging Techniques in Membrane Recycling
3. Conclusions and Future Recommendations
- Closed-loop design and reprocessable materials should remain a central focus of future research. Developing membranes with reversible or healable chemistries will allow multiple regeneration cycles without performance degradation, thereby reducing polymer waste and dependence on virgin feedstocks. Equally important is the advancement of green solvent systems capable of low-temperature depolymerization and integrated recovery processes that simplify recycling, minimize energy use, and enable truly sustainable membrane regeneration.
- Module-level recycling and in situ regeneration approaches are needed to allow chemical modification and cleaning to occur directly within intact SWM modules. This includes designing controlled flow reactors or reagent circulation systems for such in situ processes to eliminate the need for destructive module disassembly and improve scalability.
- Mechanical reliability and long-term durability must be more rigorously assessed to ensure recycled membranes can withstand real operational pressures. Standardized testing for tensile strength, compaction resistance, and fatigue behavior should be incorporated into recyclability evaluations to guarantee structural stability and lifespan. Although there is no universally accepted benchmark or minimum dataset for mechanical robustness in membrane technology, given the variation in polymer types, fabrication methods, and applications, recycled or regenerated membranes should still be tested and should demonstrate mechanical properties comparable to commercial counterparts to ensure safe and durable operation in real-world applications.
- A comprehensive sustainability assessment should accompany every proposed recycling or upcycling approach. Detailed cost–benefit analyses, carbon footprint evaluations, and LCA are needed to validate claims of environmental advantage and identify the most impactful strategies.
- Recycling of plastic waste for membrane fabrication should focus more on the adoption of green solvent systems, efficient solvent recovery and reuse, and standardized purification protocols to ensure material safety, performance reproducibility, and genuine sustainability in large-scale membrane manufacturing.
- Cross-sector collaboration and policy integration are vital to bridge the gap between laboratory innovation and industrial adoption. Coordinated efforts among academia, industry, and regulatory bodies, along with incentives and certification frameworks, will be key to embedding circularity within the global membrane manufacturing sector.
- Developing green and energy-efficient recycling schemes remains a crucial research gap. Future studies should focus on integrating green solvent systems, improving solvent recovery and reuse, and exploring cross-industry practices that can be tailored to membrane recycling technologies.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rosa, L.; Sangiorgio, M. Global Water Gaps under Future Warming Levels. Nat. Commun. 2025, 16, 1192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, W.; Liu, W.; Wang, W.; Khanzada, N.K.; Guo, J.; Li, M.; Li, X.; Lao, J.-Y.; Jeong, S.Y.; Tso, C.Y.; et al. Facile Synthesis of Micro-Eggette Patterned Nanofiltration Membrane with Enhanced Anti-Fouling and Rejection Performance. Desalination 2023, 555, 116524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, J.A. Wastewater Treatment and Reuse for Sustainable Water Resources Management: A Systematic Literature Review. Sustainability 2023, 15, 10940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hilal, N.; Busca, G.; Hankins, N.; Mohammad, A.W. The Use of Ultrafiltration and Nanofiltration Membranes in the Treatment of Metal-Working Fluids. Desalination 2004, 167, 227–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, N.N.R.; Ang, W.L.; Teow, Y.H.; Mohammad, A.W.; Hilal, N. Nanofiltration Membrane Processes for Water Recycling, Reuse and Product Recovery within Various Industries: A Review. J. Water Process Eng. 2022, 45, 102478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khanzada, N.K.; Deka, B.J.; Kharraz, J.A.; Wong, P.W.; Jassby, D.; Rehman, S.; Leu, S.-Y.; Kumar, M.; An, A.K. Elucidating the Role of Graphene Oxide Layers in Enhancing N-Nitrosodimethylamine (NDMA) Rejection and Antibiofouling Property of RO Membrane Simultaneously. J. Membr. Sci. 2022, 643, 120043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torre-Celeizabal, A.; Russo, F.; Galiano, F.; Figoli, A.; Casado-Coterillo, C.; Garea, A. Green Synthesis of Cellulose Acetate Mixed Matrix Membranes: Structure–Function Characterization. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2025, 13, 1253–1270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Yu, Z.; Wang, J.; Ke, Z.; Tong, L.; Tang, X.; Bai, L.; Zhang, H.; Li, G.; Liang, H. A Review of Inland Nanofiltration and Reverse Osmosis Membrane Concentrates Management: Treatment, Resource Recovery and Future Development. Crit. Rev. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2025, 55, 649–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khanzada, N.K.; Farid, M.U.; Kharraz, J.A.; Choi, J.; Tang, C.Y.; Nghiem, L.D.; Jang, A.; An, A.K. Removal of Organic Micropollutants Using Advanced Membrane-Based Water and Wastewater Treatment: A Review. J. Membr. Sci. 2020, 598, 117672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richard Bowen, W.; Hilal, N.; Lovitt, R.W.; Williams, P.M. Visualisation of an Ultrafiltration Membrane by Non-Contact Atomic Force Microscopy at Single Pore Resolution. J. Membr. Sci. 1996, 110, 229–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minier-Matar, J.; Al-Maas, M.; Hussain, A.; Nasser, M.S.; Adham, S. Pilot-Scale Evaluation of Forward Osmosis Membranes for Volume Reduction of Industrial Wastewater. Desalination 2022, 531, 115689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adham, S.; Minier-Matar, J.; Hussain, A. Pilot Plant Evaluation of Membrane Distillation for Desalination of High-Salinity Brines. Appl. Water Sci. 2023, 13, 233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koutsonikolas, D.; Kaldis, S.; Lappas, A. Semi-Pilot Tests of Ethanol Dehydration Using Commercial Ceramic Pervaporation Membranes. J. Membr. Sci. Res. 2021, 7, 268–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galama, A.H.; Saakes, M.; Bruning, H.; Rijnaarts, H.H.M.; Post, J.W. Seawater Predesalination with Electrodialysis. Desalination 2014, 342, 61–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Surat’man, N.E.B.; Quek, X.L.; Wang, N.; Ye, E.; Xu, J.; Li, Z.; Li, B. Sustainable Nanofibrous Membranes for Air Filtration, Water Purification and Oil Removal. Nanoscale 2025, 17, 6427–6447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ibrahim, Y.; Naddeo, V.; Banat, F.; Hasan, S.W. Preparation of Novel Polyvinylidene Fluoride (PVDF)-Tin(IV) Oxide (SnO2) Ion Exchange Mixed Matrix Membranes for the Removal of Heavy Metals from Aqueous Solutions. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2020, 250, 117250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, Y.; Hilal, N. Enhancing Ultrafiltration Membrane Permeability and Antifouling Performance through Surface Patterning with Features Resembling Feed Spacers. Npj Clean Water 2023, 6, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdulkarem, E.; Ibrahim, Y.; Kumar, M.; Arafat, H.A.; Naddeo, V.; Banat, F.; Hasan, S.W. Polyvinylidene Fluoride (PVDF)-α-Zirconium Phosphate (α-ZrP) Nanoparticles Based Mixed Matrix Membranes for Removal of Heavy Metal Ions. Chemosphere 2021, 267, 128896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, Y.; Hilal, N. Integration of Porous and Permeable Poly(Ether Sulfone) Feed Spacer onto Membrane Surfaces via Direct 3D Printing. ACS Appl. Eng. Mater. 2024, 2, 1094–1109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Y.; Knauer, K.M. Trends and Future Outlooks in Circularity of Desalination Membrane Materials. Front. Membr. Sci. Technol. 2023, 2, 1169158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morales-Jiménez, M.; Palacio, D.A.; Palencia, M.; Meléndrez, M.F.; Rivas, B.L. Bio-Based Polymeric Membranes: Development and Environmental Applications. Membranes 2023, 13, 625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goh, P.S.; Othman, M.H.D.; Matsuura, T. Waste Reutilization in Polymeric Membrane Fabrication: A New Direction in Membranes for Separation. Membranes 2021, 11, 782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Candidate List of Substances of Very High Concern for Authorisation—ECHA. Available online: https://echa.europa.eu/candidate-list-table (accessed on 17 October 2025).
- Yadav, P.; Ismail, N.; Essalhi, M.; Tysklind, M.; Athanassiadis, D.; Tavajohi, N. Assessment of the Environmental Impact of Polymeric Membrane Production. J. Membr. Sci. 2021, 622, 118987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kapoor, D.D.; Madaan, P.; Kumar, J.; Tiwari, S.K.; Gupta, K.K.; Gupta, R.K. Transition towards Renewable and Biodegradable Polymers: A Comprehensive Review. J. Polym. Res. 2025, 32, 345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, R.; Han, H.; Wang, T.; Li, J.; Wu, Z.; Tang, C.Y.; Wang, Z. Cleaning–Healing–Interfacial Polymerization Strategy for Upcycling Real End-of-Life Polyvinylidene Fluoride Microfiltration Membranes. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2021, 9, 10352–10360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goh, P.S.; Zulhairun, A.K.; Ismail, A.F.; Hilal, N. Contemporary Antibiofouling Modifications of Reverse Osmosis Desalination Membrane: A Review. Desalination 2019, 468, 114072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, R.; Chen, J.; Han, H.; Zhou, H.; Wang, Z. Interfacial Wettability Regulation Enables One-Step Upcycling of the End-of-Life Polymeric Microfiltration Membrane. ACS EST Eng. 2023, 3, 479–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawler, W.; Bradford-Hartke, Z.; Cran, M.J.; Duke, M.; Leslie, G.; Ladewig, B.P.; Le-Clech, P. Towards New Opportunities for Reuse, Recycling and Disposal of Used Reverse Osmosis Membranes. Desalination 2012, 299, 103–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guclu, S.; Kizildag, N.; Dizman, B.; Unal, S. Solvent-Based Recovery of High Purity Polysulfone and Polyester from End-of-Life Reverse Osmosis Membranes. Sustain. Mater. Technol. 2022, 31, e00358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khoo, Y.S.; Lau, W.J.; Hasan, S.W.; Salleh, W.N.W.; Ismail, A.F. New Approach of Recycling End-of-Life Reverse Osmosis Membranes via Sonication for Microfiltration Process. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2021, 9, 106731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landaburu-Aguirre, J.; Molina, S. Circular Economy in Membrane Technology. Membranes 2023, 13, 784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loh, C.Y.; Burrows, A.D.; Xie, M. Sustainable Polymeric Membranes: Green Chemistry and Circular Economy Approaches. ACS EST Eng. 2025, 5, 1882–1906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khanzada, N.K.; Al-Juboori, R.A.; Khatri, M.; Ahmed, F.E.; Ibrahim, Y.; Hilal, N. Sustainability in Membrane Technology: Membrane Recycling and Fabrication Using Recycled Waste. Membranes 2024, 14, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Contreras-Martínez, J.; García-Payo, C.; Arribas, P.; Rodríguez-Sáez, L.; Lejarazu-Larrañaga, A.; García-Calvo, E.; Khayet, M. Recycled Reverse Osmosis Membranes for Forward Osmosis Technology. Desalination 2021, 519, 115312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Contreras-Martínez, J.; García-Payo, C.; Khayet, M. Electrospun Nanostructured Membrane Engineering Using Reverse Osmosis Recycled Modules: Membrane Distillation Application. Nanomaterials 2021, 11, 1601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tavares, T.; Tavares, J.; León-Zerpa, F.A.; Peñate-Suárez, B.; Ramos-Martín, A. Assessment of Processes to Increase the Useful Life and the Reuse of Reverse Osmosis Elements in Cape Verde and Macaronesia. Membranes 2022, 12, 613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Greenlee, L.F.; Lawler, D.F.; Freeman, B.D.; Marrot, B.; Moulin, P. Reverse Osmosis Desalination: Water Sources, Technology, and Today’s Challenges. Water Res. 2009, 43, 2317–2348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ziolkowska, J.R. Is Desalination Affordable?—Regional Cost and Price Analysis. Water Resour. Manag. 2015, 29, 1385–1397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pearce, G.K. The Case for UF/MF Pretreatment to RO in Seawater Applications. Desalination 2007, 203, 286–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abu Seman, M.N.; Khayet, M.; Hilal, N. Development of Antifouling Properties and Performance of Nanofiltration Membranes Modified by Interfacial Polymerisation. Desalination 2011, 273, 36–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, D.J.; Hilal, N. Nanocomposite Nanofiltration Membranes: State of Play and Recent Advances. Desalination 2022, 524, 115480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon, Y.-N.; Leckie, J.O. Hypochlorite Degradation of Crosslinked Polyamide Membranes: II. Changes in Hydrogen Bonding Behavior and Performance. J. Membr. Sci. 2006, 282, 456–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, G.-D.; Gao, C.-J.; Chen, W.-D.; Jie, X.-M.; Cao, Y.-M.; Yuan, Q. Study on Hypochlorite Degradation of Aromatic Polyamide Reverse Osmosis Membrane. J. Membr. Sci. 2007, 300, 165–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moradi, M.R.; Pihlajamäki, A.; Hesampour, M.; Ahlgren, J.; Mänttäri, M. End-of-Life RO Membranes Recycling: Reuse as NF Membranes by Polyelectrolyte Layer-by-Layer Deposition. J. Membr. Sci. 2019, 584, 300–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raval, H.D.; Chauhan, V.R.; Raval, A.H.; Mishra, S. Rejuvenation of Discarded RO Membrane for New Applications. Desalination Water Treat. 2012, 48, 349–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Pacheco, R.; Landaburu-Aguirre, J.; Molina, S.; Rodríguez-Sáez, L.; Teli, S.B.; García-Calvo, E. Transformation of End-of-Life RO Membranes into NF and UF Membranes: Evaluation of Membrane Performance. J. Membr. Sci. 2015, 495, 305–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Pacheco, R.; Landaburu-Aguirre, J.; Terrero-Rodríguez, P.; Campos, E.; Molina-Serrano, F.; Rabadán, J.; Zarzo, D.; García-Calvo, E. Validation of Recycled Membranes for Treating Brackish Water at Pilot Scale. Desalination 2018, 433, 199–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alkhouzaam, A.; Khraisheh, M. Towards Sustainable Management of End-of-Life Membranes: Novel Transformation of End of Life (EoL) Reverse Osmosis Membranes for Efficient Dye/Salt Separation. Desalination 2024, 571, 117104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreira, V.R.; Lebron, Y.A.R.; de Souza Santos, L.V.; Amaral, M.C.S. Low-Cost Recycled End-of-Life Reverse Osmosis Membranes for Water Treatment at the Point-of-Use. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 362, 132495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veza, J.M.; Rodriguez-Gonzalez, J.J. Second Use for Old Reverse Osmosis Membranes: Wastewater Treatment. Desalination 2003, 157, 65–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ambrosi, A.; Tessaro, I.C. Study on Potassium Permanganate Chemical Treatment of Discarded Reverse Osmosis Membranes Aiming Their Reuse. Sep. Sci. Technol. 2013, 48, 1537–1543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coutinho de Paula, E.; Gomes, J.C.L.; Amaral, M.C.S. Recycling of End-of-Life Reverse Osmosis Membranes by Oxidative Treatment: A Technical Evaluation. Water Sci. Technol. 2017, 76, 605–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zappulla-Sabio, B.; Jaurrieta, L.; Gernjak, W.; Balakrishnan, H.; Dumée, L.F.; Monclús, H.; Blandin, G. Membrane Recycling: Exploring Ozone as a Viable Alternative to Chlorine for Polymeric Membrane Transformation. ACS EST Eng. 2025, 5, 3183–3194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Xu, Y.; Ma, B.; Zou, W.; Zeng, J.; Dai, R.; Wang, Z. Alkaline Pre-Treatment Enables Controllable Downcycling of Si-Al Fouled End-of-Life RO Membrane to NF and UF Membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 2024, 690, 122209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pompa-Pernía, A.; Molina, S.; Lejarazu-Larrañaga, A.; Landaburu-Aguirre, J.; García-Calvo, E. Validation of Recycled Nanofiltration and Anion-Exchange Membranes for the Treatment of Urban Wastewater for Crop Irrigation. Membranes 2022, 12, 746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, J.; Chen, Y.; Guo, P.; Su, W.; Xu, L.; Zhang, Y. Recycling End-of-Life RO Membranes for NF Membranes via Layer-by-Layer Assembly and Interfacial Polymerization. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2023, 62, 9837–9848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreira, V.R.; Lebron, Y.A.R.; de Paula, E.C.; de Souza Santos, L.V.; Amaral, M.C.S. Recycled Reverse Osmosis Membrane Combined with Pre-Oxidation for Improved Arsenic Removal from High Turbidity Waters and Retrofit of Conventional Drinking Water Treatment Process. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 312, 127859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Dai, R.; Wu, Z.; Wang, Z. Upcycling End-of-Life Polyvinylidene Fluoride Membranes into Reverse Osmosis Membranes for Sustainable Water Purification. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2025, 59, 9849–9858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Han, H.; Zhou, H.; Wang, T.; Dai, R.; Wang, Z. Rapid Upcycling of End-of-Life Microfiltration Membrane Mediated by the Healing of Metal–Organic Complex. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2022, 10, 9841–9849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malaisamy, R.; Bruening, M.L. High-Flux Nanofiltration Membranes Prepared by Adsorption of Multilayer Polyelectrolyte Membranes on Polymeric Supports. Langmuir 2005, 21, 10587–10592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ng, L.Y.; Mohammad, A.W.; Ng, C.Y.; Leo, C.P.; Rohani, R. Development of Nanofiltration Membrane with High Salt Selectivity and Performance Stability Using Polyelectrolyte Multilayers. Desalination 2014, 351, 19–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, S.; Wang, Z. A Loose Nano-Filtration Membrane Prepared by Coating HPAN UF Membrane with Modified PEI for Dye Reuse and Desalination. J. Membr. Sci. 2017, 524, 214–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, N.; Walker, T.R. Plastic Recycling: A Panacea or Environmental Pollution Problem. Npj Mater. Sustain. 2024, 2, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alrazen, H.A.; Aminossadati, S.M.; Mahmood, H.A.; Hussein, A.K.; Ahmad, K.A.; Dol, S.S.; Jabbar, S.; Algayyim, S.J.M.; Konarova, M.; Fattah, I.M.R. A Review of the Pathways, Limitations, and Perspectives of Plastic Waste Recycling. Mater. Renew. Sustain. Energy 2025, 14, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Hu, Y.H. Advancements and Future Directions in Waste Plastics Recycling: From Mechanical Methods to Innovative Chemical Processes. Chem. Eng. J. 2024, 493, 152727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Recycled Plastics Market. Market.us. Available online: https://market.us/report/recycled-plastics-market/ (accessed on 18 October 2025).
- Umar, M.; Singdahl-Larsen, C.; Ranneklev, S.B. Microplastics Removal from a Plastic Recycling Industrial Wastewater Using Sand Filtration. Water 2023, 15, 896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stathatou, P.M.; Anglou, E.; Chang, Y.; Sweet, J.; Ganesan, A.; Yutthasaksunthorn, N.; Phillips, E.V.; Ragam, N.S.; Asensio, O.I.; Nair, S.; et al. Enabling Informed Decisions on Pyrolysis: A Key to Turn the Tide on Plastics Recycling. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2025, 13, 8496–8507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lebreton, L.; Slat, B.; Ferrari, F.; Sainte-Rose, B.; Aitken, J.; Marthouse, R.; Hajbane, S.; Cunsolo, S.; Schwarz, A.; Levivier, A.; et al. Evidence That the Great Pacific Garbage Patch Is Rapidly Accumulating Plastic. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 4666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senán-Salinas, J.; Landaburu-Aguirre, J.; Contreras-Martinez, J.; García-Calvo, E. Life Cycle Assessment Application for Emerging Membrane Recycling Technologies: From Reverse Osmosis into Forward Osmosis. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2022, 179, 106075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khatri, M.; Al-Juboori, R.A.; Khanzada, N.K.; Hilal, N. Recycled PET Conversion to High Efficiency Catalyst for 4-NP Reduction with Extended Reusability: Insights into Reduction Products and Kinetics. Chem. Eng. J. 2025, 505, 159304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pongmuksuwan, P.; Kitisatorn, W. Recycled Poly(Ethylene Terephthalate) for Membrane Material in Membrane Bioreactor. Mater. Today Proc. 2023, 77, 1154–1159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Topuz, F.; Oldal, D.G.; Szekely, G. Valorization of Polyethylene Terephthalate (PET) Plastic Wastes as Nanofibrous Membranes for Oil Removal: Sustainable Solution for Plastic Waste and Oil Pollution. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2022, 61, 9077–9086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehdi, M.; Mahar, F.K.; Qureshi, U.A.; Khatri, M.; Khatri, Z.; Ahmed, F.; Kim, I.S. Preparation of Colored Recycled Polyethylene Terephthalate Nanofibers from Waste Bottles: Physicochemical Studies. Adv. Polym. Technol. 2018, 37, 2820–2827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain, S.; Wadgama, M.H.; Khan, A.L.; Yasin, M.; Akhtar, F.H. Upcycling Poly(Ethylene Terephthalate) by Fabricating Membranes for Desalination. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2023, 11, 726–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pulido, B.A.; Habboub, O.S.; Aristizabal, S.L.; Szekely, G.; Nunes, S.P. Recycled Poly(Ethylene Terephthalate) for High Temperature Solvent Resistant Membranes. ACS Appl. Polym. Mater. 2019, 1, 2379–2387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maeda, T.; Otsuka, H.; Takahara, A. Dynamic Covalent Polymers: Reorganizable Polymers with Dynamic Covalent Bonds. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2009, 34, 581–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kloxin, C.J.; Scott, T.F.; Adzima, B.J.; Bowman, C.N. Covalent Adaptable Networks (CANs): A Unique Paradigm in Cross-Linked Polymers. Macromolecules 2010, 43, 2643–2653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scheutz, G.M.; Lessard, J.J.; Sims, M.B.; Sumerlin, B.S. Adaptable Crosslinks in Polymeric Materials: Resolving the Intersection of Thermoplastics and Thermosets. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2019, 141, 16181–16196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Qi, Y.; Ulrich, S.; Barboiu, M.; Ramström, O. Dynamic Covalent Polymers for Biomedical Applications. Mater. Chem. Front. 2020, 4, 489–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Wang, S.; Loh, X.J.; Li, Z.; Chung, T.-S. Closed-Loop Recyclable Membranes Enabled by Covalent Adaptable Networks for Water Purification. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2023, 120, e2301009120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramírez-Martínez, M.; Aristizabal, S.; Upadhyaya, L.; Emwas, A.-H.; Hadjichristidis, N.; Nunes, S.P. Recyclable Membranes through Reversible and Dynamic Crosslinking. ACS Appl. Polym. Mater. 2024, 6, 13120–13131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hardian, R.; Ghaffar, A.; Shi, C.; Chen, E.Y.-X.; Szekely, G. Chemically Recyclable Nanofiltration Membranes Fabricated from Two Circular Polymer Classes of the Same Monomer Origin. J. Membr. Sci. Lett. 2024, 4, 100067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Qu, C.; Wang, S.; Yeo, J.C.C.; Surat’man, N.E.B.; Loh, X.J.; Li, Z.; Chung, T.-S. Closed-Loop Recyclable Dynamic Covalent Crosslinked Nanofibrous Membranes for Efficient Oil/Water Separation. J. Membr. Sci. 2024, 693, 122378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poniatowska, J.; Houben, M.; Borneman, Z.; Nijmeijer, K. Towards Organic Solvent Nanofiltration (OSN) Membrane Recyclability through Diels-Alder (DA) Dynamic Covalent Bonds. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2025, 362, 131812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, R.S.; Mandal, S.; Malakar, A.; Rege, S.; Islam, S.S.; Samanta, K.; Misra, A.; Bose, S. Graphene Oxide Offers Precise Molecular Sieving, Structural Integrity, Microplastic Removal, and Closed-Loop Circularity in Water-Remediating Membranes through a Covalent Adaptable Network. J. Mater. Chem. A 2023, 12, 321–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loh, C.Y.; Pang, T.; Zhang, D.; Burrows, A.D.; Xie, M. Dynamic Covalent Chemistry Enabled Closed-Loop Recycling of Thermally Modified Polymer Membrane. ACS Appl. Polym. Mater. 2025, 7, 7824–7835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Original Membrane * | Recycling Procedures | Performance of Membranes | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|
| EoL DOW® Fortilife™ XC70 RO membrane. | Multi-step treatment:
|
| [55] |
| EoL TM720-400 RO membrane |
|
| [56] |
| EoL TMH10A-400 RO membrane | Multi-step treatment:
|
| [57] |
| EoL FilmTec BW30 RO membrane | Multi-step treatment:
|
| [53] |
| EoL FilmTec TW30 RO membrane | Multi-step treatment:
|
| [50] |
| EoL BW RO membrane | Multi-step treatment:
|
| [48] |
| EoL FilmTec BW30-400 RO membrane | Multi-step treatment:
|
| [49] |
| EoL FilmTec BW30 RO membrane |
|
| [58] |
| EoL DOW FilmTec SW30 RO membrane | Multi-step treatment:
|
| [45] |
| Membrane | Recycling Conditions | Performance | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|
| Flat sheet cysteamine-crosslinked PEI (Ultem) membrane with reversible disulfide bonds. |
|
| [83] |
| Flat sheet furan-functionalized oligomer (FGE-D230) crosslinked with BMI in the presence of DMF and PEG. |
|
| [82] |
| Electrospun Copolymer poly[(furfuryl methacrylate)-co-(butyl methacrylate)] (FMA-co-HFBMA) membrane with BMI. |
|
| [85] |
| Flat sheet furfurylamine-modified poly(amide-imide) (PAI-FU) membrane crosslinked with BMI in acetone. |
|
| [86] |
| Flat sheet PVDF membrane with dopamine-anchored BMI-GO. |
|
| [87] |
| Electrospun Poly(FMA-co-BMA) (PFB) membrane with BMI. |
|
| [88] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Khanzada, N.K.; Ibrahim, Y.; Khatri, M.; Khayet, M.; Hilal, N. A Paradigm Shift in End-of-Life Membrane Recycling: From Conventional to Emerging Techniques. Membranes 2025, 15, 350. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes15120350
Khanzada NK, Ibrahim Y, Khatri M, Khayet M, Hilal N. A Paradigm Shift in End-of-Life Membrane Recycling: From Conventional to Emerging Techniques. Membranes. 2025; 15(12):350. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes15120350
Chicago/Turabian StyleKhanzada, Noman Khalid, Yazan Ibrahim, Muzamil Khatri, Mohamed Khayet, and Nidal Hilal. 2025. "A Paradigm Shift in End-of-Life Membrane Recycling: From Conventional to Emerging Techniques" Membranes 15, no. 12: 350. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes15120350
APA StyleKhanzada, N. K., Ibrahim, Y., Khatri, M., Khayet, M., & Hilal, N. (2025). A Paradigm Shift in End-of-Life Membrane Recycling: From Conventional to Emerging Techniques. Membranes, 15(12), 350. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes15120350










