Computational Insights into the Interaction of the Conserved Cysteine-Noose Domain of the Human Respiratory Syncytial Virus G Protein with the Canonical Fractalkine Binding site of Transmembrane Receptor CX3CR1 Isoforms
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Molecular Modeling of the Transmembrane Receptor CX3CR1 Isoforms
2.2. Molecular Docking of the cndG with CX3CR1 Isoforms
2.3. Molecular Dynamics Simulations of the CX3CR1/cndG Complexes
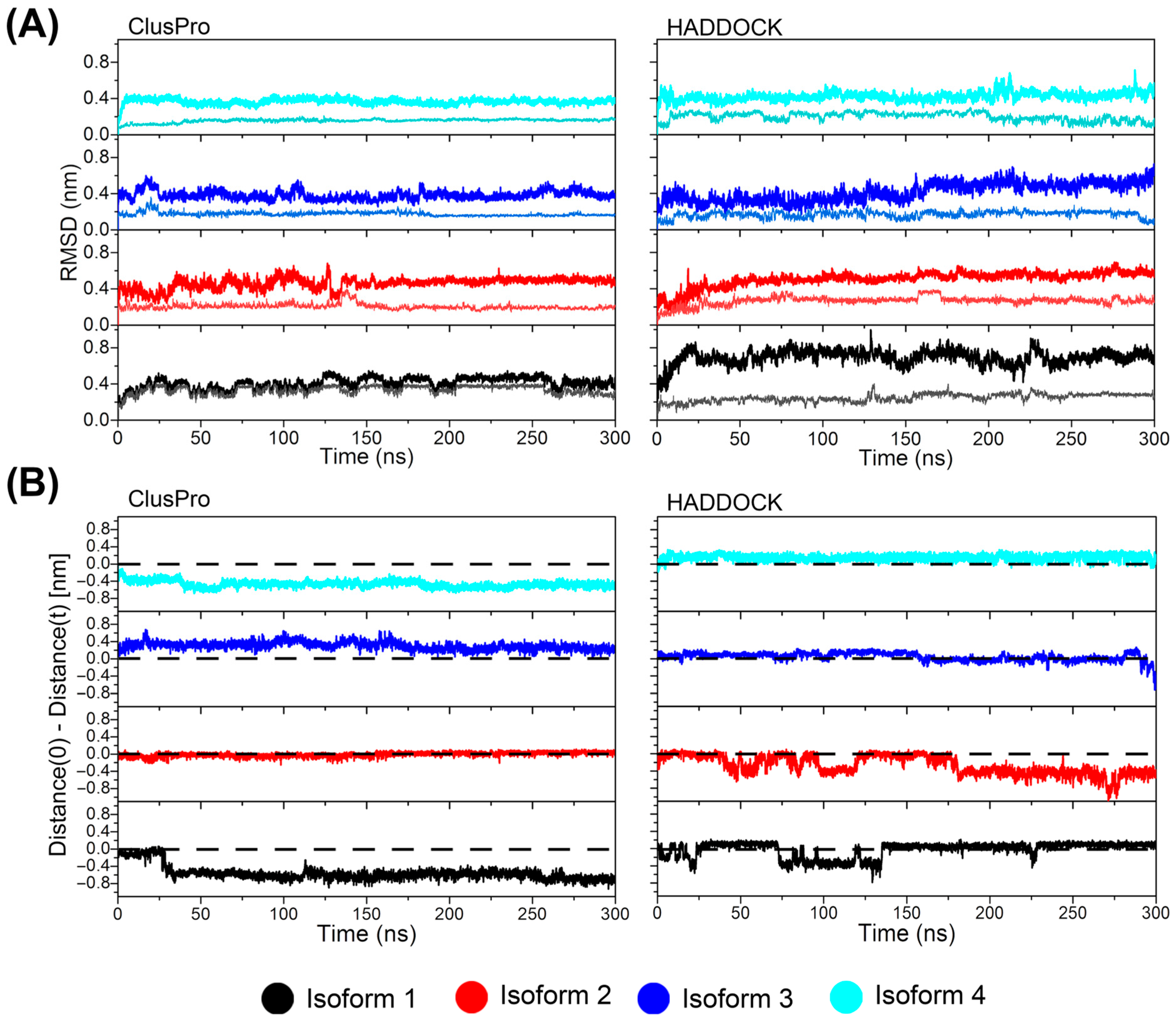
3. Results and Discussion
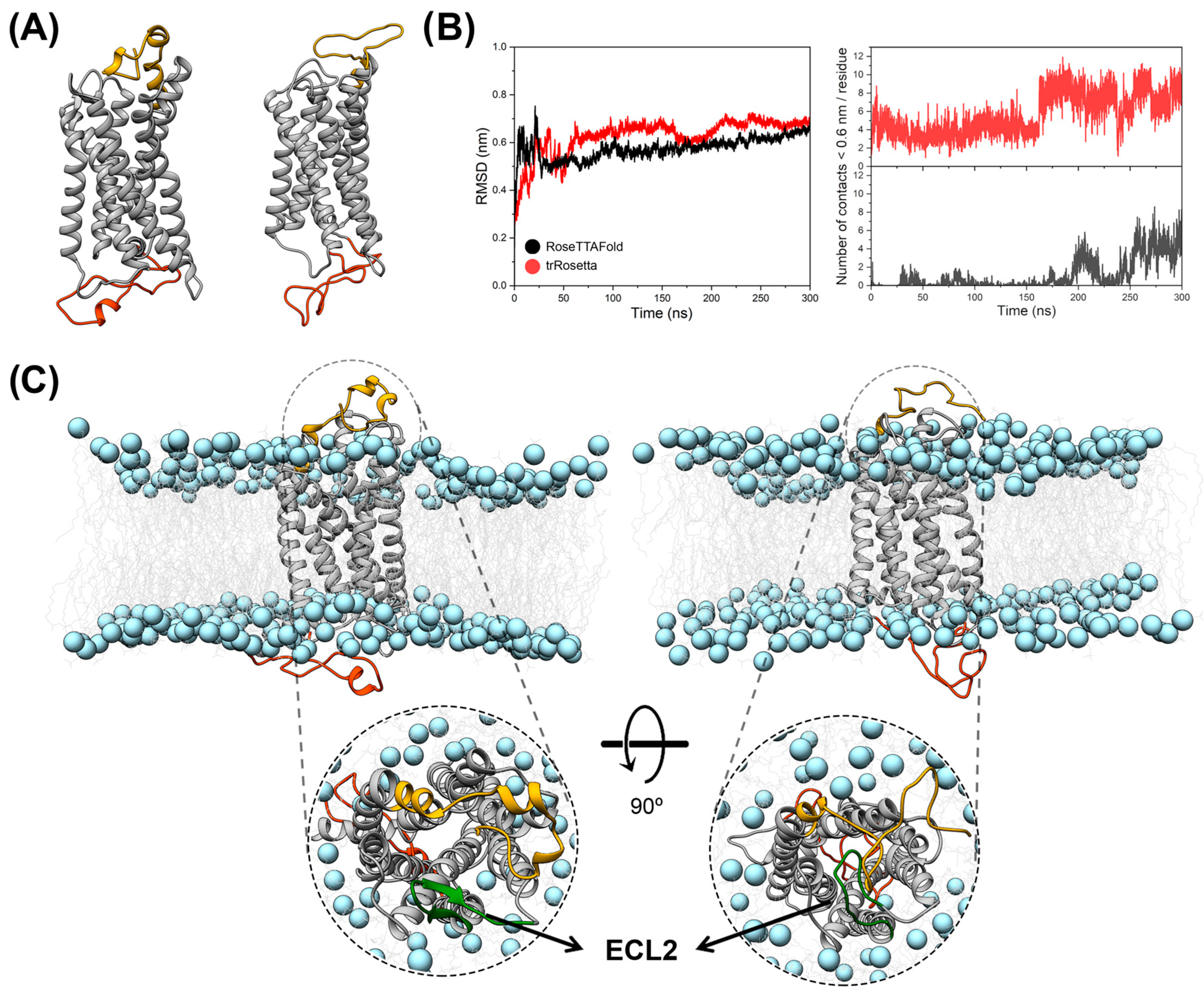
3.1. Molecular Modeling and MD Simulations of Structural Models of the CX3CR1 Isoforms Embedded in POPC Lipid Bilayer
3.2. Docking and MD Simulations of the Interaction of cndG with the Canonical Fractalkine Binding Site in the CX3CR1 Isoforms
3.3. Identification of Key Residues for Stabilization of the CX3CR1/cndG Interaction from Hydrogen Bonds and MM-GBSA Analysis
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Collins, P.L.; Fearns, R.; Graham, B.S. Respiratory Syncytial Virus: Virology, Reverse Genetics, and Pathogenesis of Disease. Curr. Top. Microbiol. Immunol. 2013, 372, 3–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Glezen, W.P.; Taber, L.H.; Frank, A.L.; Kasel, J.A. Risk of Primary Infection and Reinfection with Respiratory Syncytial Virus. Am. J. Dis. Child. 1986, 140, 543–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, T.; McAllister, D.A.; O’Brien, K.L.; Simoes, E.A.F.; Madhi, S.A.; Gessner, B.D.; Polack, F.P.; Balsells, E.; Acacio, S.; Aguayo, C.; et al. Global, Regional, and National Disease Burden Estimates of Acute Lower Respiratory Infections Due to Respiratory Syncytial Virus in Young Children in 2015: A Systematic Review and Modelling Study. Lancet 2017, 390, 946–958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falsey, A.R.; Hennessey, P.A.; Formica, M.A.; Cox, C.; Walsh, E.E. Respiratory Syncytial Virus Infection in Elderly and High-Risk Adults. N. Engl. J. Med. 2005, 352, 1749–1759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raboni, S.M.; Nogueira, M.B.; Tsuchiya, L.R.V.; Takahashi, G.A.; Pereira, L.A.; Pasquini, R.; Siqueira, M.M. Respiratory Tract Viral Infections in Bone Marrow Transplant Patients. Transplantation 2003, 76, 142–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, W.W.; Shay, D.K.; Weintraub, E.; Cox, N.; Anderson, L.J.; Fukuda, K. Mortality Associated With Influenza and Respiratory Syncytial Virus in the United States. JAMA 2003, 289, 179–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Topalidou, X.; Kalergis, A.M.; Papazisis, G. Respiratory Syncytial Virus Vaccines: A Review of the Candidates and the Approved Vaccines. Pathogens 2023, 12, 1259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papi, A.; Ison, M.G.; Langley, J.M.; Lee, D.-G.; Leroux-Roels, I.; Martinon-Torres, F.; Schwarz, T.F.; van Zyl-Smit, R.N.; Campora, L.; Dezutter, N.; et al. Respiratory Syncytial Virus Prefusion F Protein Vaccine in Older Adults. N. Engl. J. Med. 2023, 388, 595–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walsh, E.E.; Pérez Marc, G.; Zareba, A.M.; Falsey, A.R.; Jiang, Q.; Patton, M.; Polack, F.P.; Llapur, C.; Doreski, P.A.; Ilangovan, K.; et al. Efficacy and Safety of a Bivalent RSV Prefusion F Vaccine in Older Adults. N. Engl. J. Med. 2023, 388, 1465–1477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kampmann, B.; Madhi, S.A.; Munjal, I.; Simões, E.A.F.; Pahud, B.A.; Llapur, C.; Baker, J.; Pérez Marc, G.; Radley, D.; Shittu, E.; et al. Bivalent Prefusion F Vaccine in Pregnancy to Prevent RSV Illness in Infants. N. Engl. J. Med. 2023, 388, 1451–1464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Day, N.D.; Branigan, P.J.; Gutshall, L.L.; Sarisky, R.T.; Del Vecchio, A.M. Relationship between the Loss of Neutralizing Antibody Binding and Fusion Activity of the F Protein of Human Respiratory Syncytial Virus. Virol. J. 2007, 4, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morris, S.K.; Dzolganovski, B.; Beyene, J.; Sung, L. A Meta-Analysis of the Effect of Antibody Therapy for the Prevention of Severe Respiratory Syncytial Virus Infection. BMC Infect. Dis. 2009, 9, 106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nokes, J.D.; Cane, P.A. New Strategies for Control of Respiratory Syncytial Virus Infection. Curr. Opin. Infect. Dis. 2008, 21, 639–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shan, J.; Britton, P.N.; King, C.L.; Booy, R. The Immunogenicity and Safety of Respiratory Syncytial Virus Vaccines in Development: A Systematic Review. Influenza Other Respi. Viruses 2021, 15, 539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Melero, J.A.; Moore, M.L. Influence of Respiratory Syncytial Virus Strain Differences on Pathogenesis and Immunity. Curr. Top. Microbiol. Immunol. 2013, 372, 59–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ngwuta, J.O.; Chen, M.; Modjarrad, K.; Joyce, M.G.; Kanekiyo, M.; Kumar, A.; Yassine, H.M.; Moin, S.M.; Killikelly, A.M.; Chuang, G.Y.; et al. Prefusion F-Specific Antibodies Determine the Magnitude of RSV Neutralizing Activity in Human Sera. Sci. Transl. Med. 2015, 7, 309ra162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anderson, L.J.; Jadhao, S.J.; Paden, C.R.; Tong, S. Functional Features of the Respiratory Syncytial Virus G Protein. Viruses 2021, 13, 1214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeong, K.I.; Piepenhagen, P.A.; Kishko, M.; DiNapoli, J.M.; Groppo, R.P.; Zhang, L.; Almond, J.; Kleanthous, H.; Delagrave, S.; Parrington, M. CX3CR1 Is Expressed in Differentiated Human Ciliated Airway Cells and Co-Localizes with Respiratory Syncytial Virus on Cilia in a G Protein-Dependent Manner. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0130517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anderson, C.S.; Chu, C.Y.; Wang, Q.; Mereness, J.A.; Ren, Y.; Donlon, K.; Bhattacharya, S.; Misra, R.S.; Walsh, E.E.; Pryhuber, G.S.; et al. CX3CR1 as a Respiratory Syncytial Virus Receptor in Pediatric Human Lung. Pediatr. Res. 2019, 87, 862–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collins, P.L.; Graham, B.S. Viral and Host Factors in Human Respiratory Syncytial Virus Pathogenesis. J. Virol. 2008, 82, 2040–2055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chirkova, T.; Lin, S.; Oomens, A.G.P.; Gaston, K.A.; Boyoglu-Barnum, S.; Meng, J.; Stobart, C.C.; Cotton, C.U.; Hartert, T.V.; Moore, M.L.; et al. CX3CR1 Is an Important Surface Molecule for Respiratory Syncytial Virus Infection in Human Airway Epithelial Cells. J. Gen. Virol. 2015, 96, 2543–2556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Che, Y.; Gribenko, A.V.; Song, X.; Handke, L.D.; Efferen, K.S.; Tompkins, K.; Kodali, S.; Nunez, L.; Prasad, A.K.; Phelan, L.M.; et al. Rational Design of a Highly Immunogenic Prefusion-Stabilized F Glycoprotein Antigen for a Respiratory Syncytial Virus Vaccine. Sci. Transl. Med. 2023, 15, eade6422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cockerill, G.S.; Angell, R.M.; Bedernjak, A.; Chuckowree, I.; Fraser, I.; Gascon-Simorte, J.; Gilman, M.S.A.; Good, J.A.D.; Harland, R.; Johnson, S.M.; et al. Discovery of Sisunatovir (RV521), an Inhibitor of Respiratory Syncytial Virus Fusion. J. Med. Chem. 2021, 64, 3658–3676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gilman, M.S.A.; Furmanova-Hollenstein, P.; Pascual, G.; van ‘t Wout, A.B.; Langedijk, J.P.M.; McLellan, J.S. Transient Opening of Trimeric Prefusion RSV F Proteins. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 2105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukhamedova, M.; Wrapp, D.; Shen, C.H.; Gilman, M.S.A.; Ruckwardt, T.J.; Schramm, C.A.; Ault, L.; Chang, L.; Derrien-Colemyn, A.; Lucas, S.A.M.; et al. Vaccination with Prefusion-Stabilized Respiratory Syncytial Virus Fusion Protein Induces Genetically and Antigenically Diverse Antibody Responses. Immunity 2021, 54, 769–780.e6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McLellan, J.S.; Ray, W.C.; Peeples, M.E. Structure and Function of RSV Surface Glycoproteins. Curr. Top. Microbiol. Immunol. 2013, 372, 83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melero, J.A.; Mas, V.; McLellan, J.S. Structural, Antigenic and Immunogenic Features of Respiratory Syncytial Virus Glycoproteins Relevant for Vaccine Development. Vaccine 2017, 35, 461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Langedijk, J.P.M.; Schaaper, W.M.M.; Meloen, R.H.; Van Oirschot, J.T. Proposed Three-Dimensional Model for the Attachment Protein G of Respiratory Syncytial Virus. J. Gen. Virol. 1996, 77 Pt 6, 1249–1257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tripp, R.A.; Jones, L.P.; Haynes, L.M.; Zheng, H.Q.; Murphy, P.M.; Anderson, L.J. CX3C Chemokine Mimicry by Respiratory Syncytial Virus G Glycoprotein. Nat. Immunol. 2001, 2, 732–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garin, A.; Tarantino, N.; Faure, S.; Daoudi, M.; Lécureuil, C.; Bourdais, A.; Debré, P.; Deterre, P.; Combadiere, C. Two Novel Fully Functional Isoforms of CX3CR1 Are Potent HIV Coreceptors. J. Immunol. 2003, 171, 5305–5312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, M.; Zhao, W.; Han, S.; Lin, X.; Xu, T.; Tan, Q.; Wang, M.; Yi, C.; Chu, X.; Yang, W.; et al. Activation of the Human Chemokine Receptor CX3CR1 Regulated by Cholesterol. Sci. Adv. 2022, 8, 8048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burg, J.S.; Ingram, J.R.; Venkatakrishnan, A.J.; Jude, K.M.; Dukkipati, A.; Feinberg, E.N.; Angelini, A.; Waghray, D.; Dror, R.O.; Ploegh, H.L.; et al. Structural Basis for Chemokine Recognition and Activation of a Viral G Protein-Coupled Receptor. Science 2015, 347, 1113–1117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferretti, E.; Pistoia, V.; Corcione, A. Role of Fractalkine/CX3CL1 and Its Receptor in the Pathogenesis of Inflammatory and Malignant Diseases with Emphasis on B Cell Malignancies. Mediators Inflamm. 2014, 2014, 480941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wojdasiewicz, P.; Turczyn, P.; Dobies-Krzesniak, B.; Frasunska, J.; Tarnacka, B. Role of CX3CL1/CX3CR1 Signaling Axis Activity in Osteoporosis. Mediators Inflamm. 2019, 2019, 7570452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, M.; Lee, Y.; Song, J.; Lee, J.; Chang, S.Y. Tissue-Specific Role of CX3CR1 Expressing Immune Cells and Their Relationships with Human Disease. Immune Netw. 2018, 18, e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baek, M.; DiMaio, F.; Anishchenko, I.; Dauparas, J.; Ovchinnikov, S.; Lee, G.R.; Wang, J.; Cong, Q.; Kinch, L.N.; Dustin Schaeffer, R.; et al. Accurate Prediction of Protein Structures and Interactions Using a Three-Track Neural Network. Science 2021, 373, 871–876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Anishchenko, I.; Park, H.; Peng, Z.; Ovchinnikov, S.; Baker, D. Improved Protein Structure Prediction Using Predicted Interresidue Orientations. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2020, 117, 1496–1503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jumper, J.; Evans, R.; Pritzel, A.; Green, T.; Figurnov, M.; Ronneberger, O.; Tunyasuvunakool, K.; Bates, R.; Žídek, A.; Potapenko, A.; et al. Highly Accurate Protein Structure Prediction with AlphaFold. Nature 2021, 596, 583–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Yan, R.; Roy, A.; Xu, D.; Poisson, J.; Zhang, Y. The I-TASSER Suite: Protein Structure and Function Prediction. Nat. Methods 2015, 12, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelley, L.A.; Mezulis, S.; Yates, C.M.; Wass, M.N.; Sternberg, M.J.E. The Phyre2 Web Portal for Protein Modeling, Prediction and Analysis. Nat. Protoc. 2015, 10, 845–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laskowski, R.A.; MacArthur, M.W.; Moss, D.S.; Thornton, J.M. PROCHECK: A Program to Check the Stereochemical Quality of Protein Structures. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 1993, 26, 283–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desta, I.T.; Porter, K.A.; Xia, B.; Kozakov, D.; Vajda, S. Performance and Its Limits in Rigid Body Protein-Protein Docking. Structure 2020, 28, 1071–1081.e3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Honorato, R.V.; Koukos, P.I.; Jiménez-García, B.; Tsaregorodtsev, A.; Verlato, M.; Giachetti, A.; Rosato, A.; Bonvin, A.M.J.J. Structural Biology in the Clouds: The WeNMR-EOSC Ecosystem. Front. Mol. Biosci. 2021, 8, 729513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiménez-García, B.; Pons, C.; Fernández-Recio, J. PyDockWEB: A Web Server for Rigid-Body Protein-Protein Docking Using Electrostatics and Desolvation Scoring. Bioinformatics 2013, 29, 1698–1699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pierce, B.G.; Hourai, Y.; Weng, Z. Accelerating Protein Docking in ZDOCK Using an Advanced 3D Convolution Library. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e24657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Y.; Zhang, D.; Zhou, P.; Li, B.; Huang, S.Y. HDOCK: A Web Server for Protein–Protein and Protein–DNA/RNA Docking Based on a Hybrid Strategy. Nucleic Acids Res. 2017, 45, W365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, P.; Jin, B.; Li, H.; Huang, S.Y. HPEPDOCK: A Web Server for Blind Peptide-Protein Docking Based on a Hierarchical Algorithm. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018, 46, W443–W450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, X.; Yan, C.; Zou, X. MDockPeP: An Ab-Initio Protein–Peptide Docking Server. J. Comput. Chem. 2018, 39, 2409–2413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fedechkin, S.O.; George, N.L.; Wolff, J.T.; Kauvar, L.M.; DuBois, R.M. Structures of Respiratory Syncytial Virus G Antigen Bound to Broadly Neutralizing Antibodies. Sci. Immunol. 2018, 3, 3534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmid, N.; Eichenberger, A.P.; Choutko, A.; Riniker, S.; Winger, M.; Mark, A.E.; Van Gunsteren, W.F. Definition and Testing of the GROMOS Force-Field Versions 54A7 and 54B7. Eur. Biophys. J. 2011, 40, 843–856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berger, O.; Edholm, O.; Jähnig, F. Molecular Dynamics Simulations of a Fluid Bilayer of Dipalmitoylphosphatidylcholine at Full Hydration, Constant Pressure, and Constant Temperature. Biophys. J. 1997, 72, 2002–2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jorgensen, W.L.; Chandrasekhar, J.; Madura, J.D.; Impey, R.W.; Klein, M.L. Comparison of Simple Potential Functions for Simulating Liquid Water. J. Chem. Phys. 1983, 79, 926–935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brooks, B.R.; Brooks, C.L.; Mackerell, A.D.; Nilsson, L.; Petrella, R.J.; Roux, B.; Won, Y.; Archontis, G.; Bartels, C.; Boresch, S.; et al. CHARMM: The Biomolecular Simulation Program. J. Comput. Chem. 2009, 30, 1545–1614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, E.L.; Cheng, X.; Jo, S.; Rui, H.; Song, K.C.; Dávila-Contreras, E.M.; Qi, Y.; Lee, J.; Monje-Galvan, V.; Venable, R.M.; et al. CHARMM-GUI Membrane Builder toward Realistic Biological Membrane Simulations. J. Comput. Chem. 2014, 35, 1997–2004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olsson, M.H.M.; SØndergaard, C.R.; Rostkowski, M.; Jensen, J.H. PROPKA3: Consistent Treatment of Internal and Surface Residues in Empirical p K a Predictions. J. Chem. Theory Comput. 2011, 7, 525–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pronk, S.; Páll, S.; Schulz, R.; Larsson, P.; Bjelkmar, P.; Apostolov, R.; Shirts, M.R.; Smith, J.C.; Kasson, P.M.; Van Der Spoel, D.; et al. GROMACS 4.5: A High-Throughput and Highly Parallel Open Source Molecular Simulation Toolkit. Bioinformatics 2013, 29, 845–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daura, X.; Gademann, K.; Jaun, B.; Seebach, D.; van Gunsteren, W.F.; Mark, A.E.; Rigault, A.; Siegel, J.; Harrowfield, J.; Chevrier, B.; et al. Peptide Folding: When Simulation Meets Experiment; Duke University: Durham, NC, USA, 1998; Volume 31. [Google Scholar]
- Lemkul, A.J. Scripts and Programs, OSF. Available online: https://osf.io/bafn4/ (accessed on 13 June 2020).
- Valdés-Tresanco, M.S.; Valdés-Tresanco, M.E.; Valiente, P.A.; Moreno, E. Gmx_MMPBSA: A New Tool to Perform End-State Free Energy Calculations with GROMACS. J. Chem. Theory Comput. 2021, 17, 6281–6291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brelot, A.; Heveker, N.; Montes, M.; Alizon, M. Identification of Residues of CXCR4 Critical for Human Immunodeficiency Virus Coreceptor and Chemokine Receptor Activities. J. Biol. Chem. 2000, 275, 23736–23744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karlström, S.; Nordvall, G.; Sohn, D.; Hettman, A.; Turek, D.; Åhlin, K.; Kers, A.; Claesson, M.; Slivo, C.; Lo-Alfredsson, Y.; et al. Substituted 7-Amino-5-Thio-Thiazolo[4,5-d]Pyrimidines as Potent and Selective Antagonists of the Fractalkine Receptor (CX3CR1). J. Med. Chem. 2013, 56, 3177–3190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, F.; Zhang, Y.; Jernigan, D.L.; Feng, X.; Yan, J.; Garcia, F.U.; Meucci, O.; Salvino, J.M.; Fatatis, A. Novel Small-Molecule CX3CR1 Antagonist Impairs Metastatic Seeding and Colonization of Breast Cancer Cells. Mol. Cancer Res. 2016, 14, 518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wakita, H.; Yanagawa, T.; Kuboi, Y.; Imai, T. E6130, a Novel CX3C Chemokine Receptor 1 (CX3CR1) Modulator, Attenuates Mucosal Inflammation and Reduces CX3CR1+ Leukocyte Trafficking in Mice with Colitis. Mol. Pharmacol. 2017, 92, 502–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cederblad, L.; Rosengren, B.; Ryberg, E.; Hermansson, N.O. AZD8797 Is an Allosteric Non-Competitive Modulator of the Human CX3CR1 Receptor. Biochem. J. 2016, 473, 641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Low, S.; Wu, H.; Jerath, K.; Tibolla, A.; Fogal, B.; Conrad, R.; MacDougall, M.; Kerr, S.; Berger, V.; Dave, R.; et al. VHH Antibody Targeting the Chemokine Receptor CX3CR1 Inhibits Progression of Atherosclerosis. mAbs 2020, 12, 1709322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Piloto, J.V.; Dias, R.V.R.; Mazucato, W.S.A.; Fossey, M.A.; de Melo, F.A.; Almeida, F.C.L.; de Souza, F.P.; Caruso, I.P. Computational Insights into the Interaction of the Conserved Cysteine-Noose Domain of the Human Respiratory Syncytial Virus G Protein with the Canonical Fractalkine Binding site of Transmembrane Receptor CX3CR1 Isoforms. Membranes 2024, 14, 84. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes14040084
Piloto JV, Dias RVR, Mazucato WSA, Fossey MA, de Melo FA, Almeida FCL, de Souza FP, Caruso IP. Computational Insights into the Interaction of the Conserved Cysteine-Noose Domain of the Human Respiratory Syncytial Virus G Protein with the Canonical Fractalkine Binding site of Transmembrane Receptor CX3CR1 Isoforms. Membranes. 2024; 14(4):84. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes14040084
Chicago/Turabian StylePiloto, João Victor, Raphael Vinicius Rodrigues Dias, Wan Suk Augusto Mazucato, Marcelo Andres Fossey, Fernando Alves de Melo, Fabio Ceneviva Lacerda Almeida, Fatima Pereira de Souza, and Icaro Putinhon Caruso. 2024. "Computational Insights into the Interaction of the Conserved Cysteine-Noose Domain of the Human Respiratory Syncytial Virus G Protein with the Canonical Fractalkine Binding site of Transmembrane Receptor CX3CR1 Isoforms" Membranes 14, no. 4: 84. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes14040084
APA StylePiloto, J. V., Dias, R. V. R., Mazucato, W. S. A., Fossey, M. A., de Melo, F. A., Almeida, F. C. L., de Souza, F. P., & Caruso, I. P. (2024). Computational Insights into the Interaction of the Conserved Cysteine-Noose Domain of the Human Respiratory Syncytial Virus G Protein with the Canonical Fractalkine Binding site of Transmembrane Receptor CX3CR1 Isoforms. Membranes, 14(4), 84. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes14040084





