Electrochemical Sensor Based on the Hierarchical Carbon Nanocomposite for Highly Sensitive Ciprofloxacin Determination
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Measuring Apparatus
- thermal treatment of non-woven carbon in a tubular furnace;
- fragmentation of the obtained composite in a mortar;
- mixing the powder with the DMF to obtain a suspension with a concentration of 1 mg mL−1;
- homogenization of the suspension on the ultrasonic washer (Intersonic, IS-1K, Olsztyn, Poland) for 15 min;
- preparation of the GC electrode surface by polishing with an alumina slurry with a particle size of 0.3 µm (Buehler Micropolish II, Chicago, IL, USA);
- rinsing the leftovers of the alumina slurry with double-distilled water and methanol;
- application of 7.5 µL of modifier suspension to the surface of the GC electrode surface with an automatic pipette (Eppendorf, Hamburg, Germany)
- drying electrodes for about 12 h at room temperature.
2.2. Chemicals
2.3. Sample Preparation
2.3.1. Pharmaceutical Samples Preparation
2.3.2. Antibiotic Disc
2.3.3. Urine Preparation
2.3.4. Plasma Preparation
2.4. Standard Procedure of Measurements
3. Results
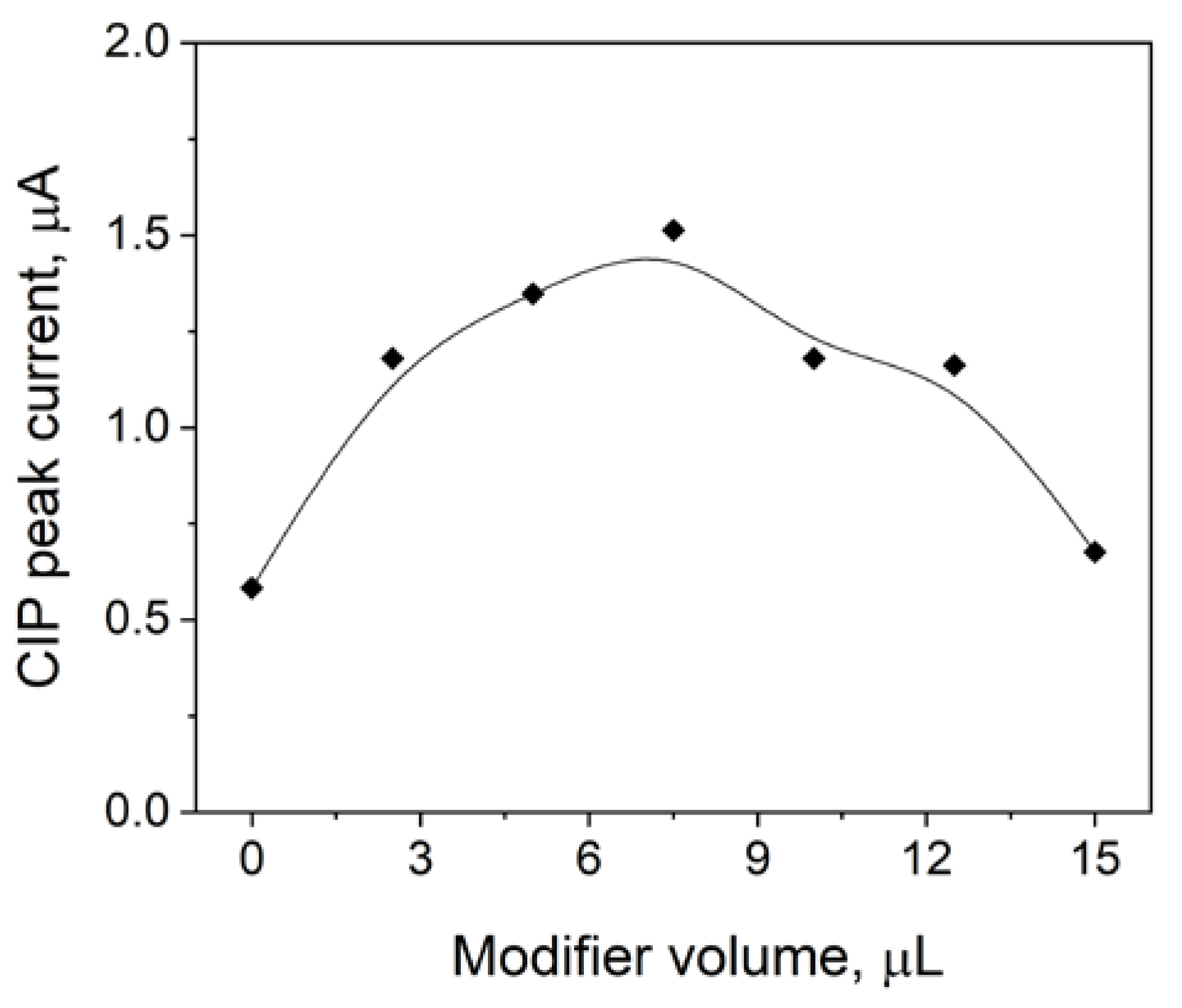
3.1. Influence of the Volume of eCNF/CNT/NiCo Layer on the Glassy Carbon Electrode on the Ciprofloxacin Peak
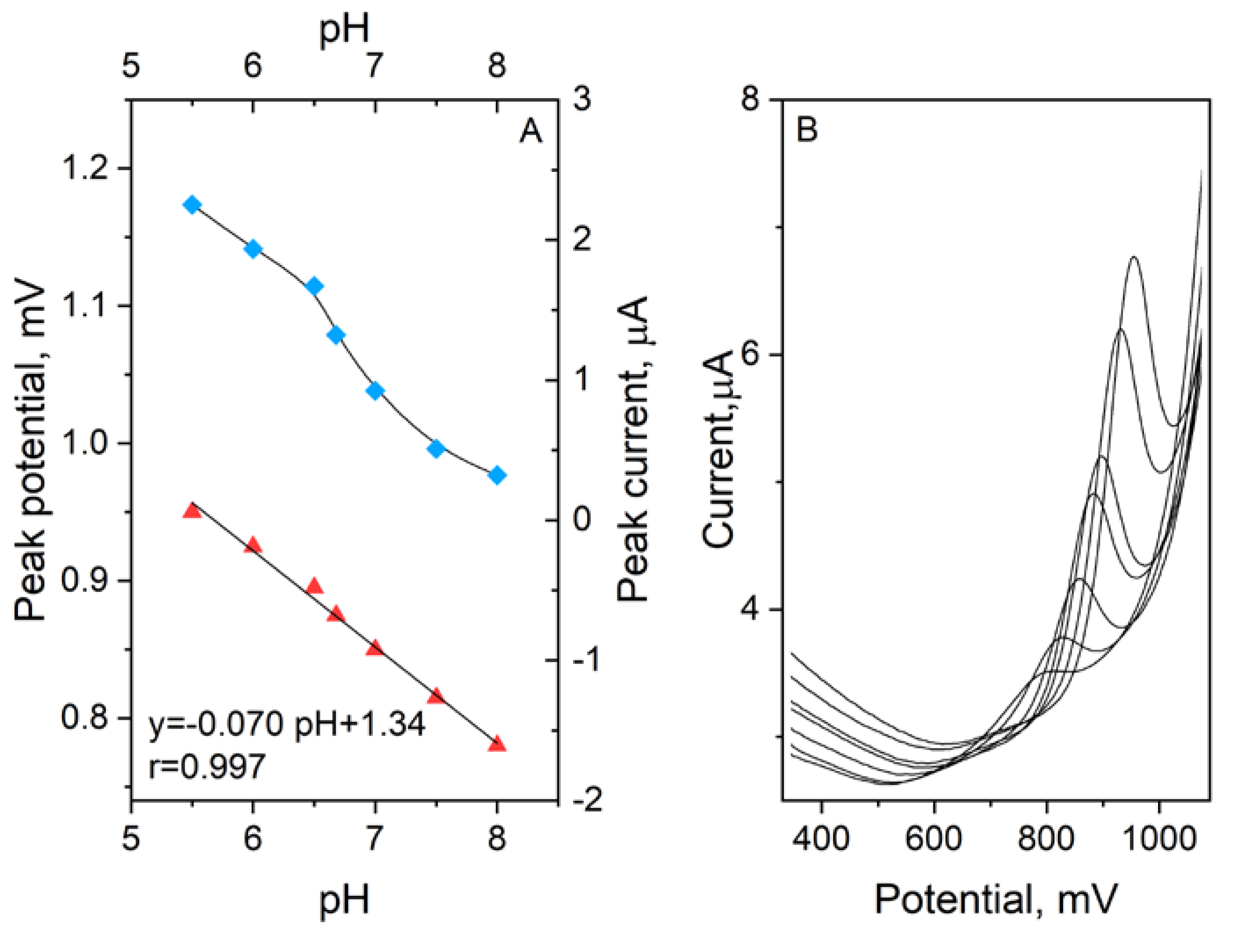
3.2. Influence of the Supporting Electrolyte Composition on the Ciprofloxacin Peak
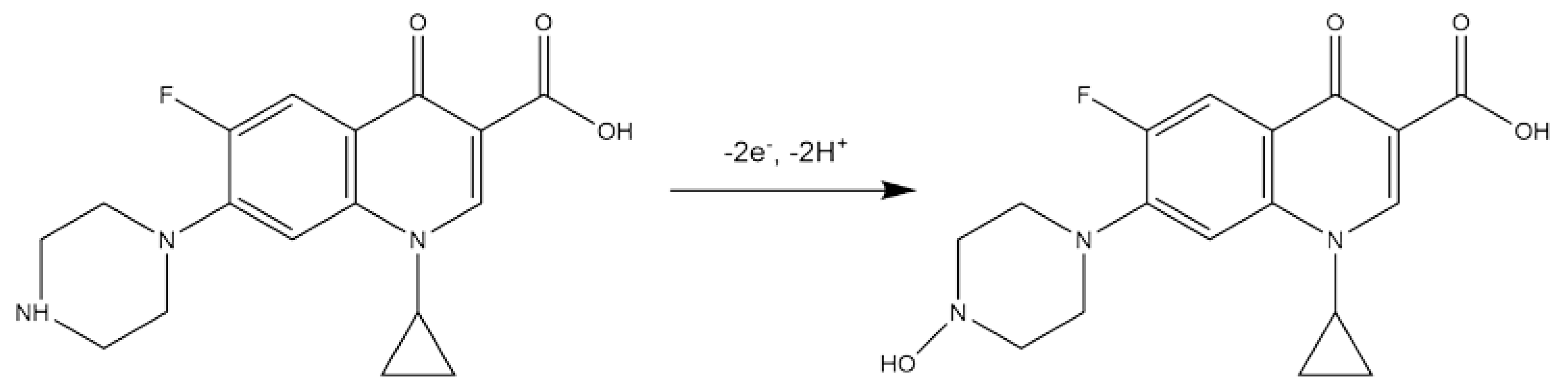
3.3. Voltammetric Behaviour of Ciprofloxacin on eCNF/CNT/NiCo/GC Electrode
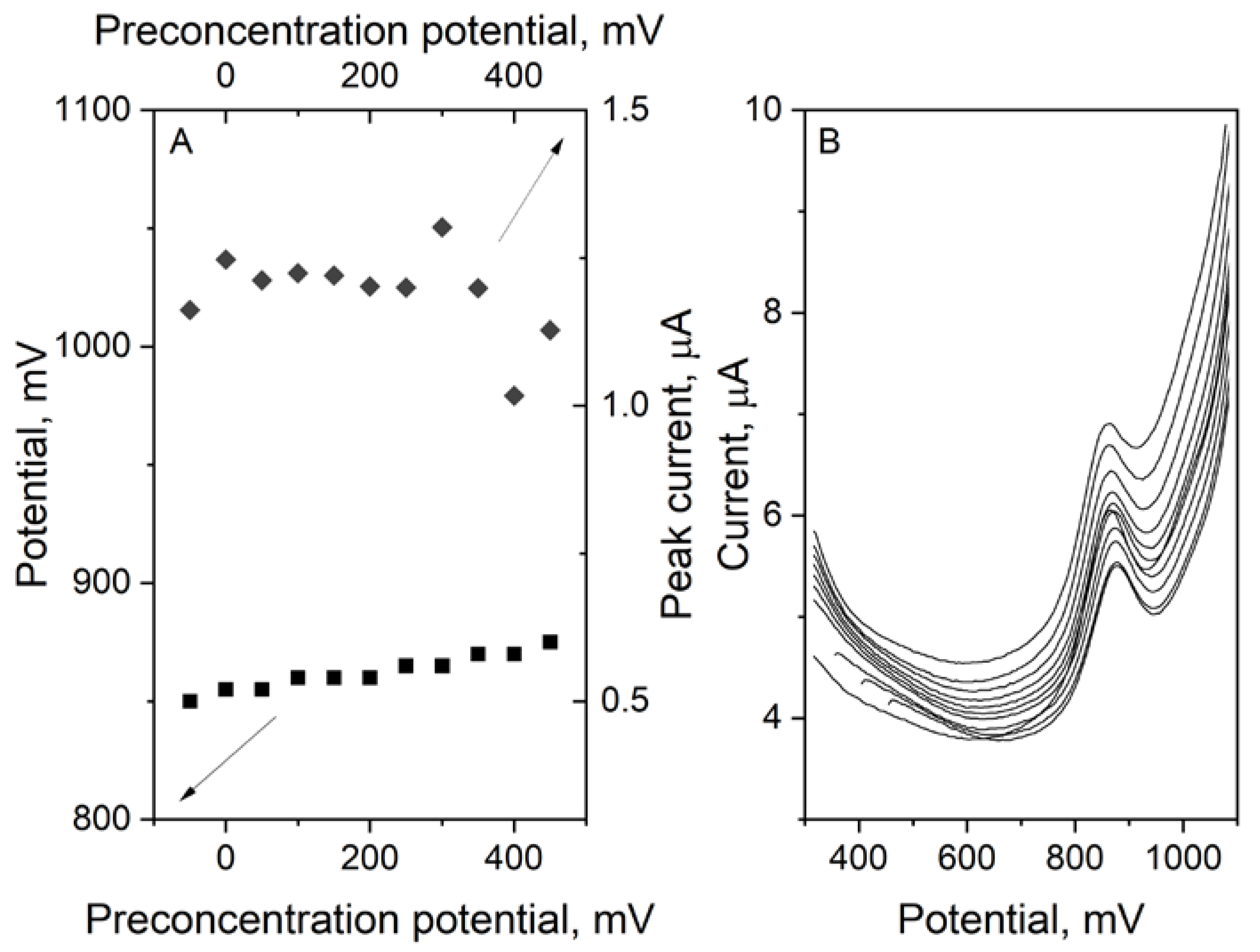
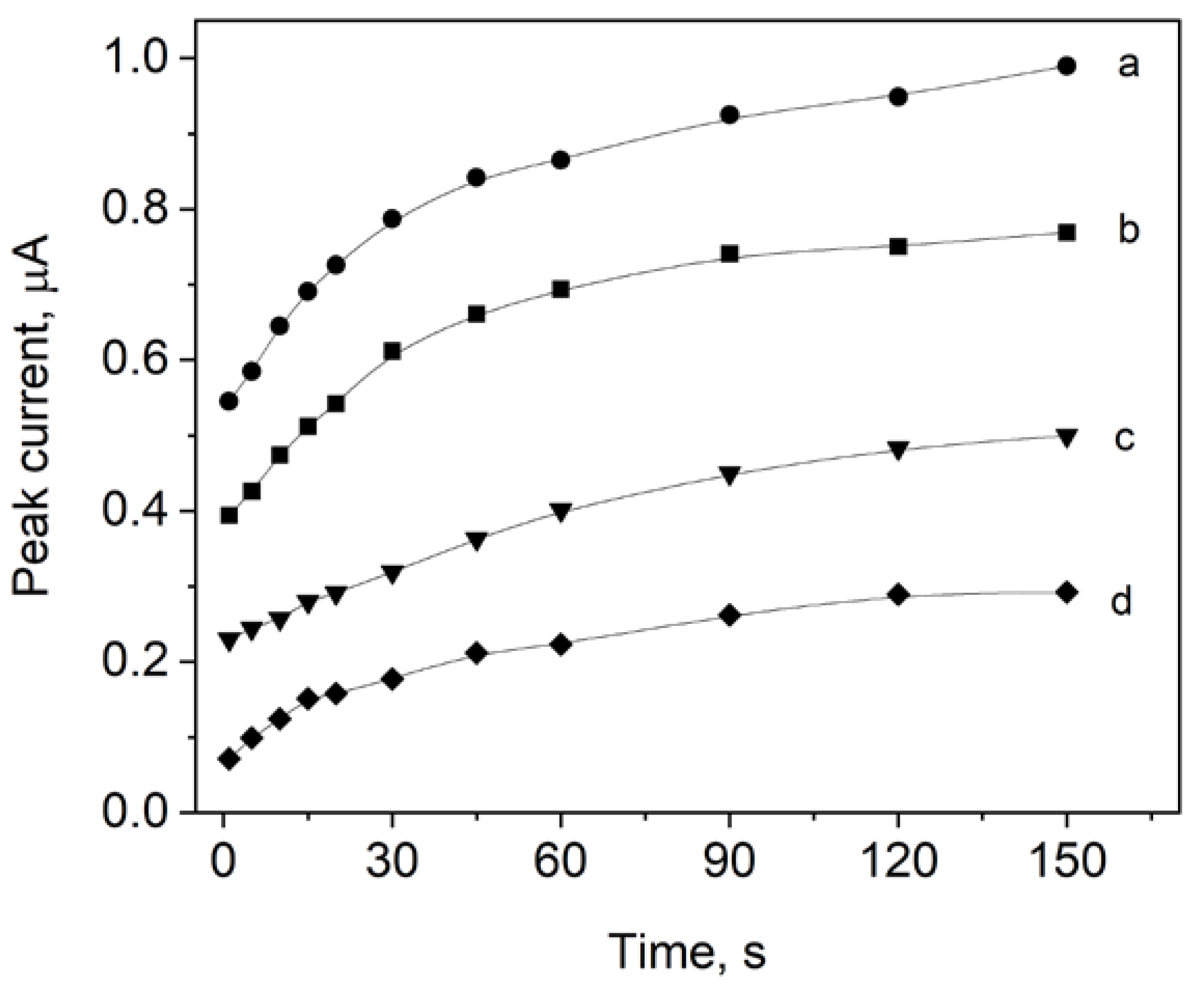
3.4. Preconcentration Time and Potential Influence on the Ciprofloxacin Peak
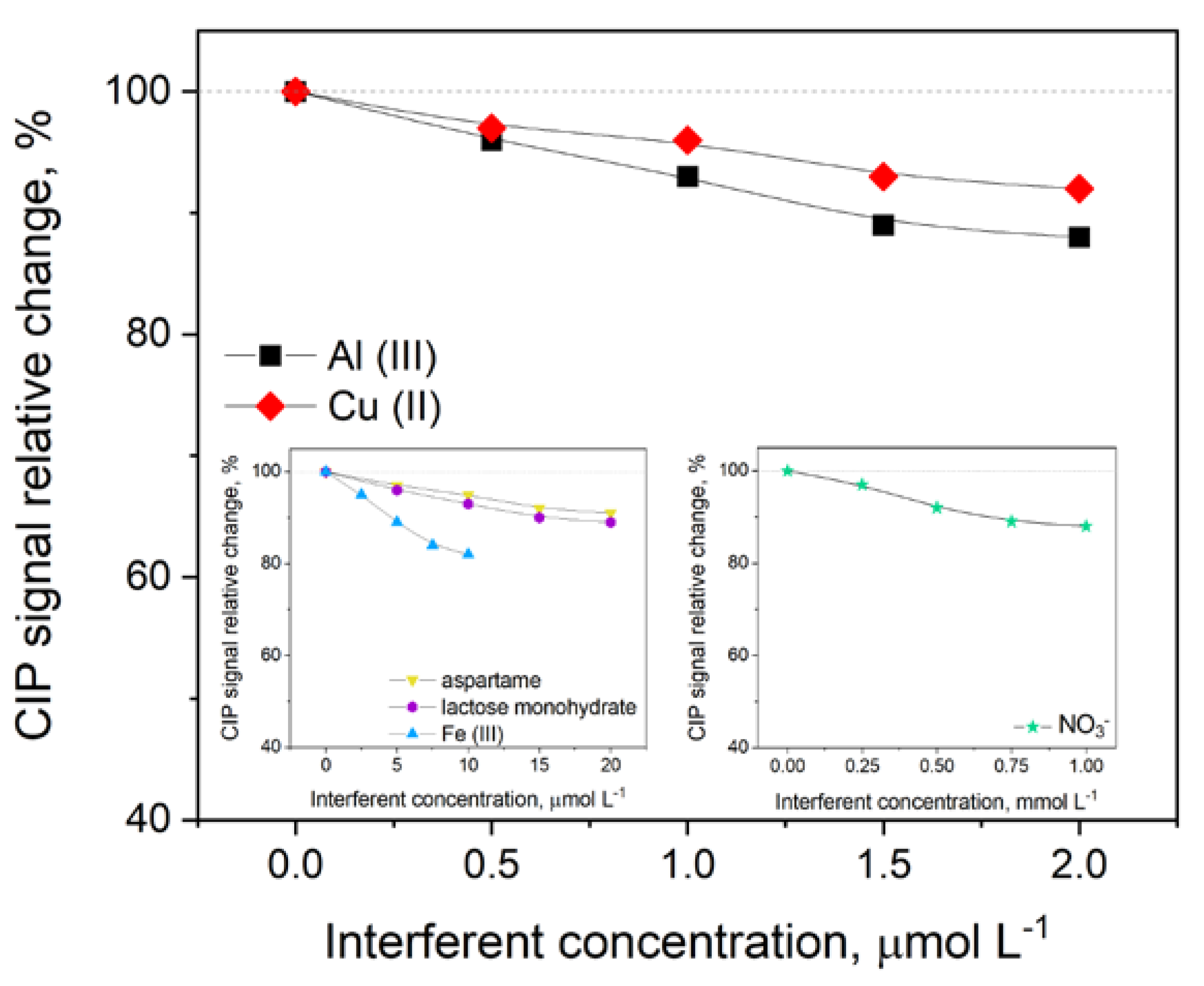
3.5. Interferences
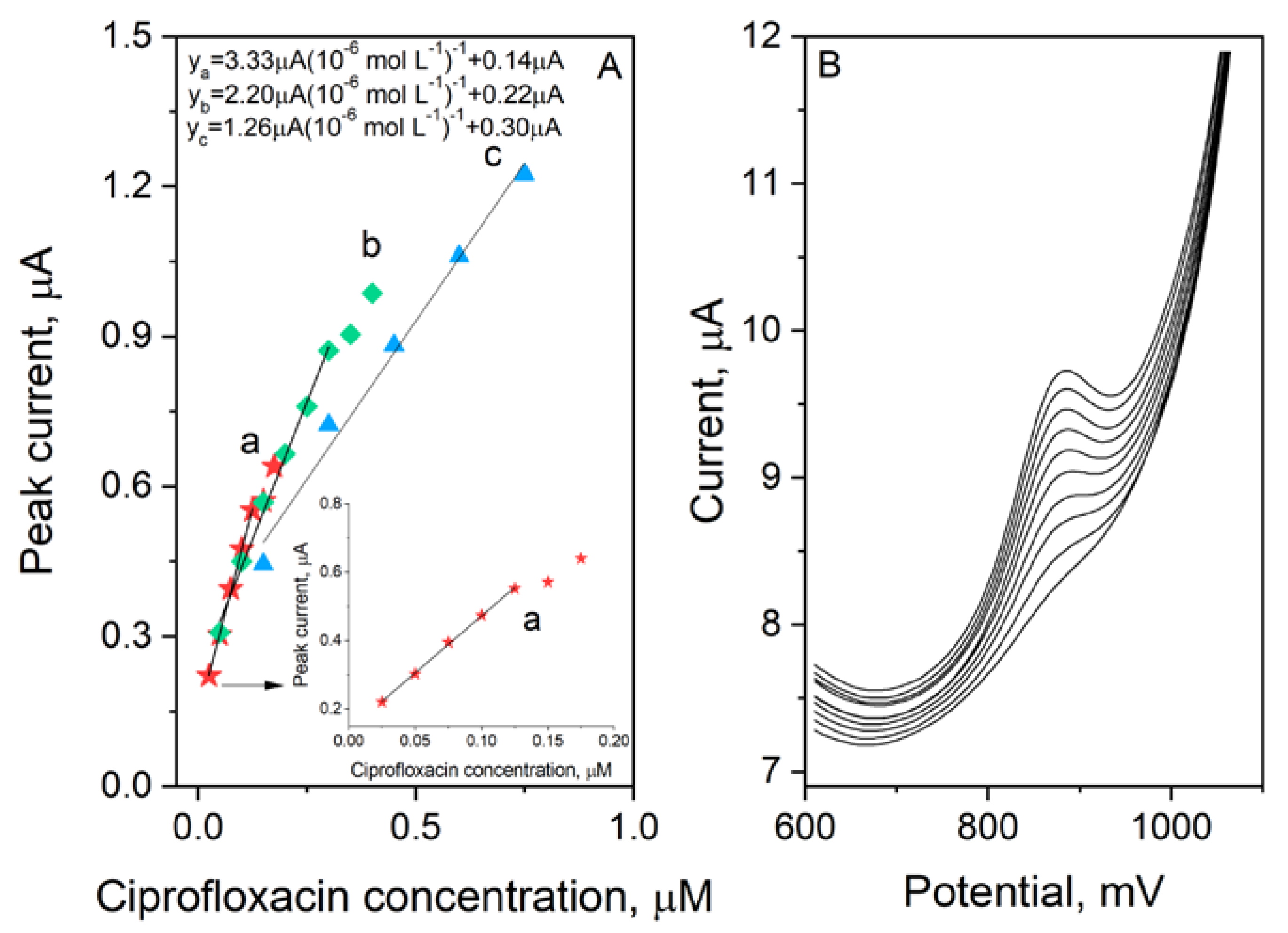
3.6. Analytical Performance
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mucklow, J.C. Martindale: The Complete Drug Reference; Pharmaceutical Press: London, UK, 2009; ISBN 853694990. [Google Scholar]
- Brunton, L.L.; Lazo, J.S.; Parker, K.L. Goodman and Gilman’s The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics; McGraw-Hill Professional: New York, NY, USA, 2005; ISBN 0071354697. [Google Scholar]
- Davis, R.; Markham, A.; Balfour, J.A. Ciprofloxacin An Updated Review of Its Pharmacology, Therapeutic Efficacy and Tolerability. Drugs 1996, 51, 1019–1074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Effa, E.E.; Lassi, Z.S.; Critchley, J.A.; Garner, P.; Sinclair, D.; Olliaro, P.L.; Bhutta, Z.A. Fluoroquinolones for Treating Typhoid and Paratyphoid Fever (Enteric Fever). Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2011, 10, 1–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hendricks, K.A.; Wright, M.E.; Shadomy, S.V.; Bradley, J.S.; Morrow, M.G.; Pavia, A.T.; Rubinstein, E.; Holty, J.-E.C.; Messonnier, N.E.; Smith, T.L.; et al. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention Expert Panel Meetings on Prevention and Treatment of Anthrax in Adults. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2014, 20, e130687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cazedey, E.; Salgado, H. Spectrophotometric Determination of Ciprofloxacin Hydrochloride in Ophthalmic Solution. Adv. Anal. Chem. 2012, 2, 74–79. [Google Scholar]
- Pascual-Reguera, M.I.; Parras, G.P.; Díaz, A.M. Solid-Phase UV Spectrophotometric Method for Determination of Ciprofloxacin. Microchem. J. 2004, 77, 79–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mostafa, S.; El-Sadek, M.; Alla, E.A. Spectrophotometric Determination of Ciprofloxacin, Enrofloxacin and Pefloxacin through Charge Transfer Complex Formation. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2002, 27, 133–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navalon, A.; Ballesteros, O.; Blanc, R.; Vilchez, J.L. Determination of Ciprofloxacin in Human Urine and Serum Samples by Solid-Phase Spectrofluorimetr. Talanta 2000, 52, 845–852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fratini, L.; Schapoval, E.E.S. Ciprofloxacin Determination by Visible Light Spectrophotometry Using Iron(III)Nitrate. Int. J. Pharm. 1996, 127, 279–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Y.L.; Dong, C. Simultaneous Determination of Trace Ofloxacin, Ciprofloxacin, and Sparfloxacin by Micelle TLC-Fluorimetry. J. Chromatogr. Sci. 2004, 42, 474–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murillo Pulgarín, J.A.; Alañón Molina, A.; Muñoz Fernández, L. Determination of Ciprofloxacin, the Major Metabolite of Enrofloxacin, in Milk by Isopotential Fluorimetry. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2008, 56, 8838–8843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrón, D.; Jiménez-Lozano, E.; Cano, J.; Barbosa, J. Determination of Residues of Enrofloxacin and Its Metabolite Ciprofloxacin in Biological Materials by Capillary Electrophoresis. J. Chromatogr. B Biomed. Sci. Appl. 2001, 759, 73–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, X.; Liu, L.; Jia, Z.; Shu, Y. Determination of Enrofloxacin and Ciprofloxacin in Foods of Animal Origin by Capillary Electrophoresis with Field Amplified Sample Stacking-Sweeping Technique. Food Chem. 2015, 176, 219–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Michalska, K.; Pajchel, G.; Tyski, S. Determination of Ciprofloxacin and Its Impurities by Capillary Zone Electrophoresis. J. Chromatogr. A 2004, 1051, 267–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vella, J.; Busuttil, F.; Bartolo, N.S.; Sammut, C.; Ferrito, V.; Serracino-Inglott, A.; Azzopardi, L.M.; LaFerla, G. A Simple HPLC-UV Method for the Determination of Ciprofloxacin in Human Plasma. J. Chromatogr. B Anal. Technol. Biomed. Life Sci. 2015, 989, 80–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Szerkus, O.; Jacyna, J.; Gibas, A.; Sieczkowski, M.; Siluk, D.; Matuszewski, M.; Kaliszan, R.; Markuszewski, M.J. Robust HPLC–MS/MS Method for Levofloxacin and Ciprofloxacin Determination in Human Prostate Tissue. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2017, 132, 173–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vybíralová, Z.; Nobilis, M.; Zoulova, J.; Květina, J.; Petr, P. High-Performance Liquid Chromatographic Determination of Ciprofloxacin in Plasma Samples. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2005, 37, 851–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imre, S.; Dogaru, M.T.; Vari, C.E.; Muntean, T.; Kelemen, L. Validation of an HPLC Method for the Determination of Ciprofloxacin in Human Plasma. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2003, 33, 125–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamberi, M.; Tsutsumi, K.; Kotegawa, T.; Nakamura, K.; Nakano, S. Determination of Ciprofloxacin in Plasma and Urine by HPLC with Ultraviolet Detection. Clin. Chem. 1998, 44, 1251–1255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Dea, P.; Garcíc, A.C.; Ordieres, A.J.M.; Blanco, P.T.; Smyth, M.R. Comparison of Adsorptive Stripping Voltammetry at Mercury and Carbon Paste Electrodes for the Determination of Ciprofloxacin in Urine. Electroanalysis 1991, 3, 337–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Ghamdi, A.F.; Bani-Yaseen, A.D. Electrochemical Reduction of Ciprofloxacin at the Mercury Electrode and Its Voltammetric Determination in Tablet and Urine. Russ. J. Electrochem. 2014, 50, 355–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garbellini, G.S.; Rocha-Filho, R.C.; Fatibello-Filho, O. Voltammetric Determination of Ciprofloxacin in Urine Samples and Its Interaction with DsDNA on a Cathodically Pretreated Boron-Doped Diamond Electrode. Anal. Methods 2015, 7, 3411–3418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stefano, J.S.; Cordeiro, D.S.; Marra, M.C.; Richter, E.M.; Munoz, R.A.A. Batch-Injection versus Flow-Injection Analysis Using Screen-Printed Electrodes: Determination of Ciprofloxacin in Pharmaceutical Formulations. Electroanalysis 2016, 28, 350–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, M.; Guo, P.; Liu, H.; Lu, J.; Xie, Q. Graphene Oxide Modified Screen-Printed Electrode for Highly Sensitive and Selective Electrochemical Detection of Ciprofloxacin Residues in Milk. J. Anal. Sci. Technol. 2021, 12, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsunaga, T.; Kondo, T.; Osasa, T.; Kotsugai, A.; Shitanda, I.; Hoshi, Y.; Itagaki, M.; Aikawa, T.; Tojo, T.; Yuasa, M. Sensitive Electrochemical Detection of Ciprofloxacin at Screen-Printed Diamond Electrodes. Carbon N. Y. 2020, 159, 247–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, H.; Li, C. Voltammetric Determination of Ciprofloxacin Based on the Enhancement Effect of Cetyltrimethylammonium Bromide (CTAB) at Carbon Paste Electrode. Russ. J. Electrochem. 2007, 43, 1377–1381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernández, P.; Aguilar-Lira, G.Y.; Islas, G.; Rodriguez, J.A. Development of a New Voltammetric Methodology for the Determination of Ciprofloxacin in Beef Samples Using a Carbon Paste Electrode Modified with Nafion and Fullerenes. Electroanalysis 2021, 33, 1539–1546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kingsley, M.P.; Kalambate, P.K.; Srivastava, A.K. Simultaneous Determination of Ciprofloxacin and Paracetamol by Adsorptive Stripping Voltammetry Using Copper Zinc Ferrite Nanoparticles Modified Carbon Paste Electrode. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 15101–15111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagheri, H.; Khoshsafar, H.; Amidi, S.; Hosseinzadeh Ardakani, Y. Fabrication of an Electrochemical Sensor Based on Magnetic Multi-Walled Carbon Nanotubes for the Determination of Ciprofloxacin. Anal. Methods 2016, 8, 3383–3390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chauhan, R.; Gill, A.A.S.; Nate, Z.; Karpoormath, R. Highly Selective Electrochemical Detection of Ciprofloxacin Using Reduced Graphene Oxide/Poly(Phenol Red) Modified Glassy Carbon Electrode. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2020, 871, 114254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diab, N.; Abu-Shqair, I.; Salim, R.; Al-Subu, M. The Behavior of Ciprofloxacin at a Dna Modified Glassy Carbon Electrodes. Int. J. Electrochem. Sci. 2014, 9, 1771–1783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gissawong, N.; Srijaranai, S.; Boonchiangma, S.; Uppachai, P.; Seehamart, K.; Jantrasee, S.; Moore, E.; Mukdasai, S. An Electrochemical Sensor for Voltammetric Detection of Ciprofloxacin Using a Glassy Carbon Electrode Modified with Activated Carbon, Gold Nanoparticles and Supramolecular Solvent. Microchim. Acta 2021, 188, 208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jalal, N.R.; Madrakian, T.; Afkhami, A.; Ghamsari, M. Polyethylenimine@Fe3O4@carbon Nanotubes Nanocomposite as a Modifier in Glassy Carbon Electrode for Sensitive Determination of Ciprofloxacin in Biological Samples. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2019, 833, 281–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebbesen, T.W. Carbon Nanotubes. Annu. Rev. Mater. Sci. 1994, 24, 235–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eletskii, A.V. Carbon Nanotubes. Phys.-Usp. 1997, 40, 899–924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Dai, H.; Hafner, J.H.; Colbert, D.T.; Smalley, R.E.; Tans, S.J.; Dekker, C. Fullerene “Crop Circles”. Nature 1997, 385, 780–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Liu, F.; Zhao, J. Curved Carbon Nanotubes: From Unique Geometries to Novel Properties and Peculiar Applications. Nano Res. 2014, 7, 626–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Zhao, J. Toroidal and Coiled Carbon Nanotubes. In Syntheses and Applications of Carbon Nanotubes and Their Composites; Suzuki, S., Ed.; IntechOpen: Rijeka, Croatia, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Purohit, R.; Purohit, K.; Rana, S.; Rana, R.S.; Patel, V. Carbon Nanotubes and Their Growth Methods. Procedia Mater. Sci. 2014, 6, 716–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tibbetts, G.G.; Lake, M.L.; Strong, K.L.; Rice, B.P. A Review of the Fabrication and Properties of Vapor-Grown Carbon Nanofiber/Polymer Composites. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2007, 67, 1709–1718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz-Cornejo, J.C.; Sebastián, D.; Lázaro, M.J. Synthesis and Applications of Carbon Nanofibers: A Review. Rev. Chem. Eng. 2020, 36, 493–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Zong, L.S.; Pan, Y.; Li, N.; Liu, Q.; Wang, J.; Jian, X. Preparation and Characterization of Branch-like Heteroatoms-Doped Ni@C Nanofibers for High-Performance Microwave Absorption with Thin Thickness. Compos. Part B Eng. 2021, 223, 109114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Górska, A.; Zambrzycki, M.; Paczosa-Bator, B.; Piech, R. New Electrochemical Sensor Based on Hierarchical Carbon Nanofibers with NiCo Nanoparticles and Its Application for Cetirizine Hydrochloride Determination. Materials 2022, 15, 3648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zambrzycki, M.; Piech, R.; Raga, S.R.; Lira-Cantu, M.; Fraczek-Szczypta, A. Hierarchical Carbon Nanofibers/Carbon Nanotubes/NiCo Nanocomposites as Novel Highly Effective Counter Electrode for Dye-Sensitized Solar Cells: A Structure-Electrocatalytic Activity Relationship Study. Carbon N. Y. 2023, 203, 97–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suhaimi, N.F.; Baharin, S.N.A.; Jamion, N.A.; Mohd Zain, Z.; Sambasevam, K.P. Polyaniline-Chitosan Modified on Screen-Printed Carbon Electrode for the Electrochemical Detection of Perfluorooctanoic Acid. Microchem. J. 2023, 188, 108502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galus, Z. Fundamentals of Electrochemical Analysis; Polish Scientific Publishing PWN: Warsaw, Poland, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Nicholson, R.S.; Shain, I. Theory of Stationary Electrode Polarography: Single Scan and Cyclic Methods Applied to Reversible, Irreversible, and Kinetic Systems. Anal. Chem. 1964, 36, 1212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tajik, S.; Beitollahi, H.; Zaeimbashi, R.; Sheikhshoaei, M.; Askari, M.B.; Salarizadeh, P. An Electrochemical Sensor Based on V2O5 Nanoparticles for the Detection of Ciprofloxacin. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 2021, 32, 17558–17567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Gu, S.; Ding, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Li, L. A Novel Sensor Based on Electropolymerization of β-Cyclodextrin and l-Arginine on Carbon Paste Electrode for Determination of Fluoroquinolones. Anal. Chim. Acta 2013, 770, 53–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faria, L.V.; Pereira, J.F.S.; Azevedo, G.C.; Matos, M.A.C.; Munoz, R.A.A.; Matos, R.C. Square-Wave Voltammetry Determination of Ciprofloxacin in Pharmaceutical Formulations and Milk Using a Reduced Graphene Oxide Sensor. J. Braz. Chem. Soc. 2019, 30, 1947–1954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ensafi, A.A.; Allafchian, A.R.; Mohammadzadeh, R. Characterization of MgFe2O4 Nanoparticles as a Novel Electrochemical Sensor: Application for the Voltammetric Determination of Ciprofloxacin. Anal. Sci. 2012, 28, 705–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ensafi, A.A.; Taei, M.; Khayamian, T.; Hasanpour, F. Simultaneous Voltammetric Determination of Enrofloxacin and Ciprofloxacin in Urine and Plasma Using Multiwall Carbon Nanotubes Modified Glassy Carbon Electrode by Least-Squares Support Vector Machines. Anal. Sci. 2010, 26, 803–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gayen, P.; Chaplin, B.P. Selective Electrochemical Detection of Ciprofloxacin with a Porous Nafion/Multiwalled Carbon Nanotube Composite Film Electrode. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 1615–1626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garrido, J.M.P.J.; Melle-Franco, M.; Strutyński, K.; Borges, F.; Brett, C.M.A.; Garrido, E.M.P.J. β–Cyclodextrin Carbon Nanotube-Enhanced Sensor for Ciprofloxacin Detection. J. Environ. Sci. Health Part A Toxic Hazard. Subst. Environ. Eng. 2017, 52, 313–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gill, A.A.S.; Singh, S.; Nate, Z.; Pawar, C.; Chauhan, R.; Thapliyal, N.B.; Karpoormath, R.; Patel, R. One-Pot Synthesis of β-Cyclodextrin Modified Silver Nanoparticles for Highly Sensitive Detection of Ciprofloxacin. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2021, 203, 114219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rani, R.; Deep, A.; Mizaikoff, B.; Singh, S. Copper Based Organic Framework Modified Electrosensor for Selective and Sensitive Detection of Ciprofloxacin. Electroanalysis 2020, 32, 2442–2451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Electrode | Technique | Linear Range | LOD, mol L−1 | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ds-DNA-BDD | SWV | 0.5–60 µM | 0.44·10−6 | [23] |
| rGO/PPR/GCE | DPV | 0.002–400 µM | 2.0·10−9 | [31] |
| SUPRAS-AuNPs/AC/GCE | DPV | 0.5–25 nM | 0.20·10−9 | [33] |
| PEI@Fe3O4@CNTS/GCE | DPV | 0.03–70.0 µM | 0.003·10−6 | [34] |
| V2O5/SPE | DPV | 0.04–365.0 µM | 0.01·10−6 | [49] |
| P-β-CD-L-arg/CPE | DPV | 0.05–100 µM | 0.01·10−6 | [50] |
| CRGO/GCE | SWV | 6–40 µM | 0.21·10−6 | [51] |
| MgFe2O4-MWCNTs | CV | 0.10–1000 µM | 0.01·10−6 | [52] |
| MWCNT/GC | CV | 3–1200 µM | 0.9·10−6 | [53] |
| Porous-Nafion-MWCNT/BDD | DPV | 0.005–10 µM | 0.005·10−6 | [54] |
| PANI–β–CD/MWCNT/GCE | CV | 10–80 µM | 0.05·10−6 | [55] |
| Ag-β-CD/GCE | DPV | 0.1–50 nM | 0.028·10−9 | [56] |
| Cu-BTC | DPV | 10 nM–20 µM | 0.47·10−9 | [57] |
| eCNF/CNT/NiCo/GC | DPV | 0.025–0.3 µM | 6.0·10−9 | This work |
| Sample | Added, mg | Found, mg | Recovery, % |
|---|---|---|---|
| Tablet 1 | 0 | 521 | 104 |
| 500 | 1028 | 103 | |
| 1000 | 1508 | 101 | |
| 1500 | 1973 | 98 | |
| Tablet 2 | 0 | 513 | 103 |
| 500 | 1024 | 104 | |
| 1000 | 1535 | 103 | |
| 1500 | 1969 | 98 | |
| Producer declares 500 mg ciprofloxacin per tablet | |||
| Sample | Added, μg | Found, μg | Recovery, % |
| Antibiotic disc | 0 | 5.12 | 102 |
| 5 | 10.04 | 101 | |
| 10 | 14.92 | 99 | |
| Producer declares 5 μg ciprofloxacin per disc | |||
| Sample | Added, μmol L−1 | Found, μmol L−1 | Recovery, % |
| Urine (diluted 20×) | 0 | ND | - |
| 2 | 1.88 | 94 | |
| 4 | 4.04 | 101 | |
| 6 | 6.26 | 104 | |
| 8 | 7.80 | 97 | |
| Plasma (diluted 20×) | 0 | ND | - |
| 0.5 | 0.47 | 94 | |
| 1.0 | 1.04 | 104 | |
| 1.5 | 1.48 | 99 | |
| 2.0 | 1.93 | 97 | |
| ND—not detected | |||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Smajdor, J.; Paczosa-Bator, B.; Piech, R. Electrochemical Sensor Based on the Hierarchical Carbon Nanocomposite for Highly Sensitive Ciprofloxacin Determination. Membranes 2023, 13, 682. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes13070682
Smajdor J, Paczosa-Bator B, Piech R. Electrochemical Sensor Based on the Hierarchical Carbon Nanocomposite for Highly Sensitive Ciprofloxacin Determination. Membranes. 2023; 13(7):682. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes13070682
Chicago/Turabian StyleSmajdor, Joanna, Beata Paczosa-Bator, and Robert Piech. 2023. "Electrochemical Sensor Based on the Hierarchical Carbon Nanocomposite for Highly Sensitive Ciprofloxacin Determination" Membranes 13, no. 7: 682. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes13070682
APA StyleSmajdor, J., Paczosa-Bator, B., & Piech, R. (2023). Electrochemical Sensor Based on the Hierarchical Carbon Nanocomposite for Highly Sensitive Ciprofloxacin Determination. Membranes, 13(7), 682. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes13070682








