Generation of Nano-Bubbles by NaHCO3 for Improving the FO Membrane Performance
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Membrane Preparation
2.3. Membranes Characterization
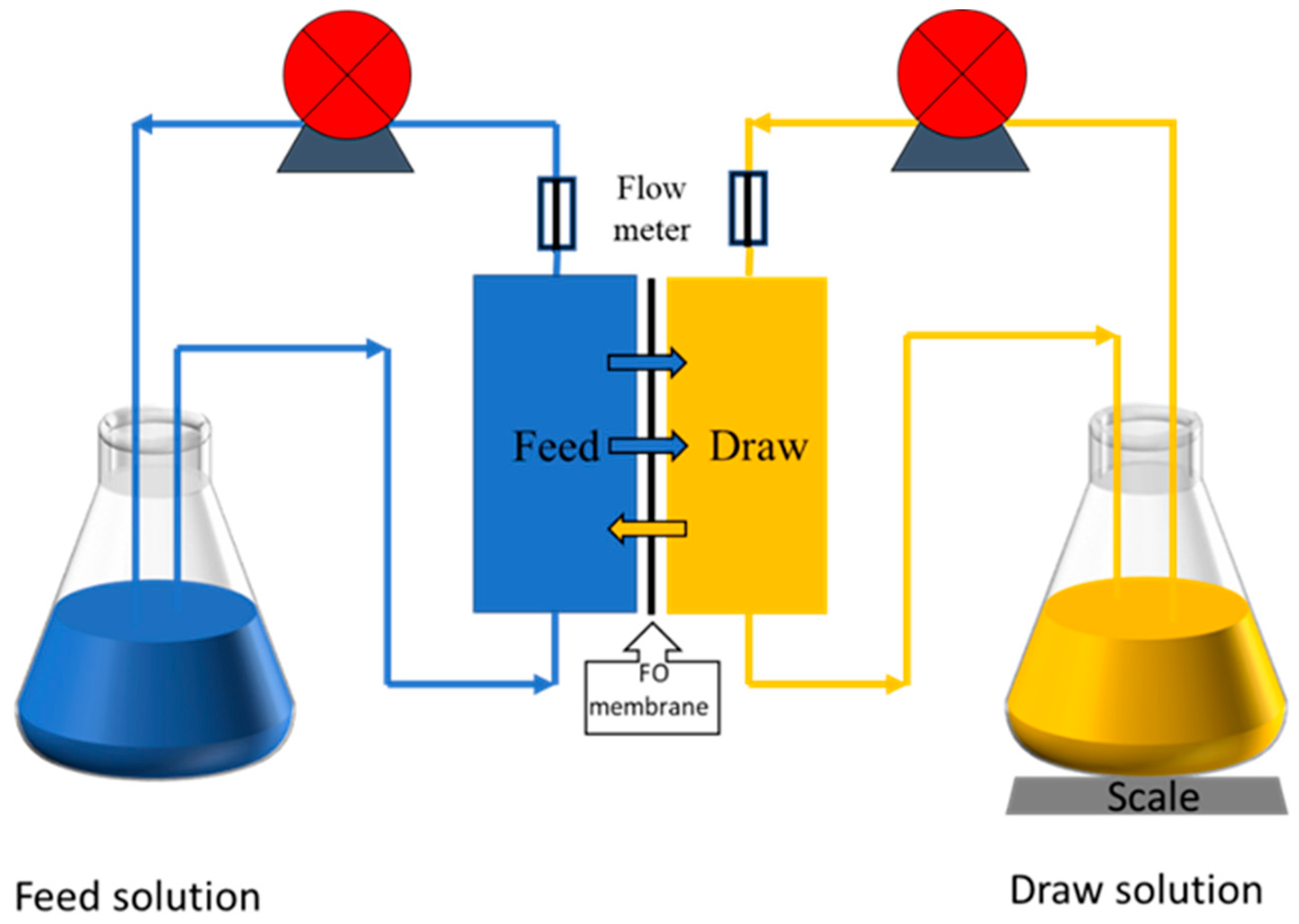
2.4. Filtration Experiments
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Nanobubbles Regulate the Surface Structure
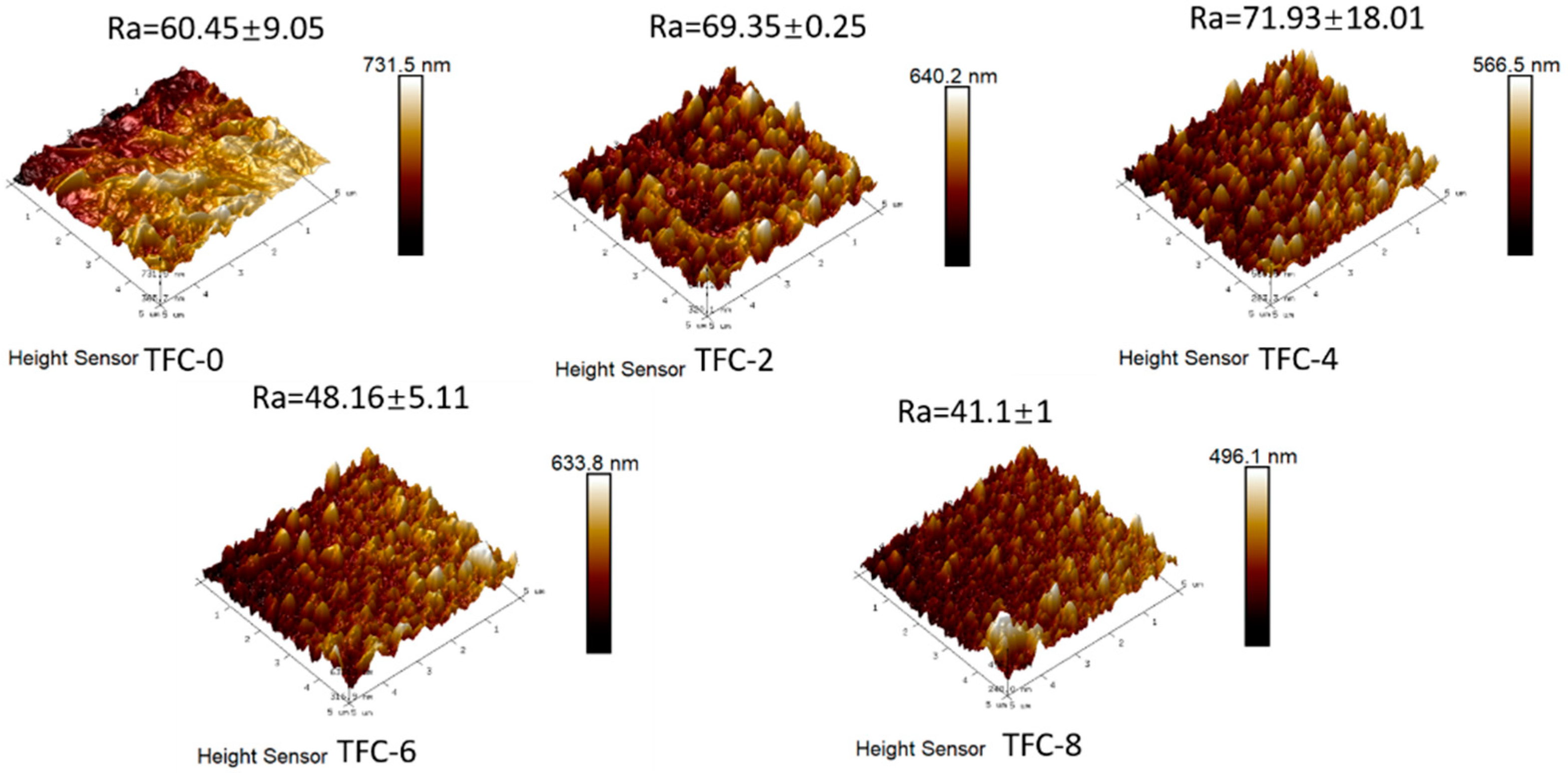
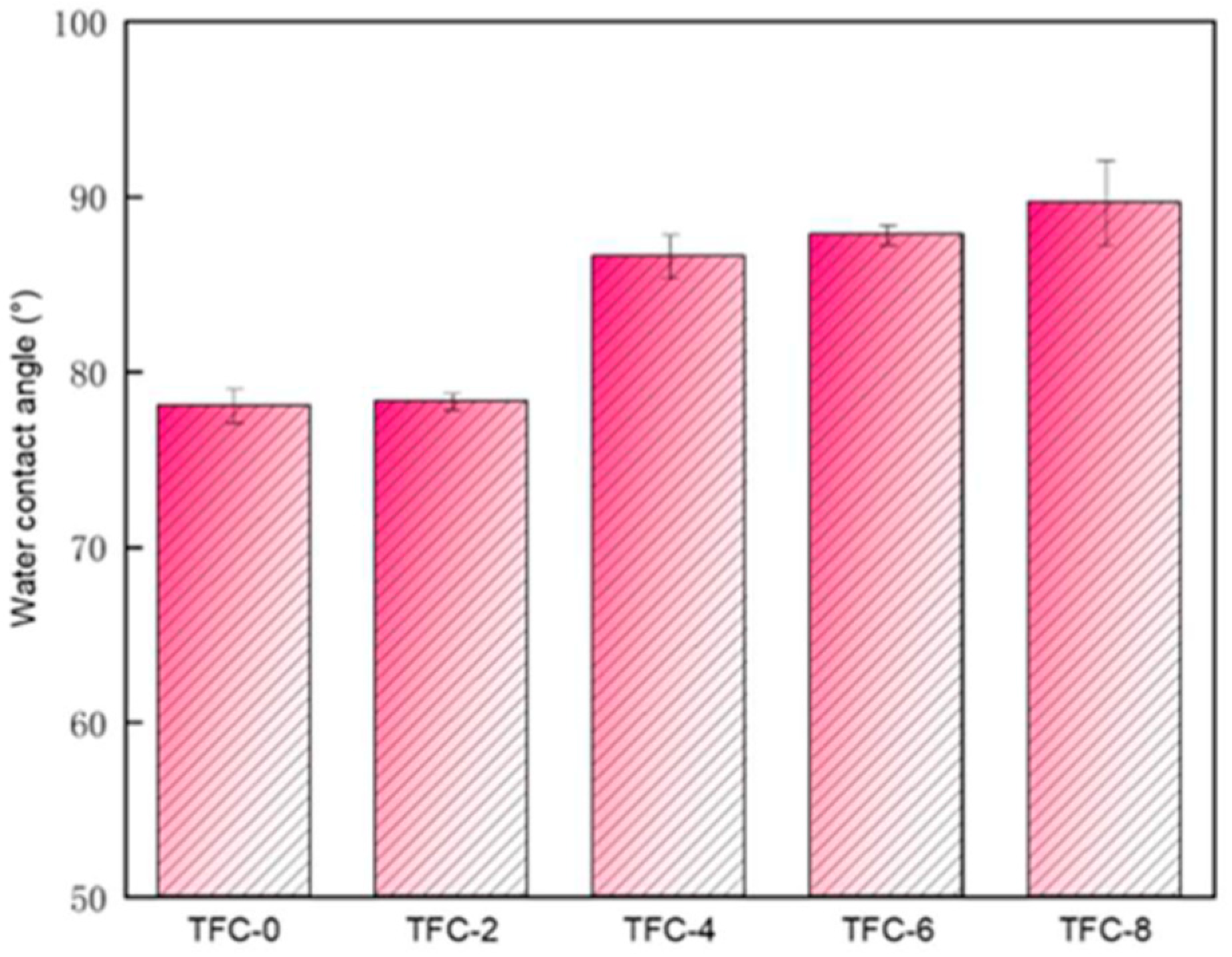
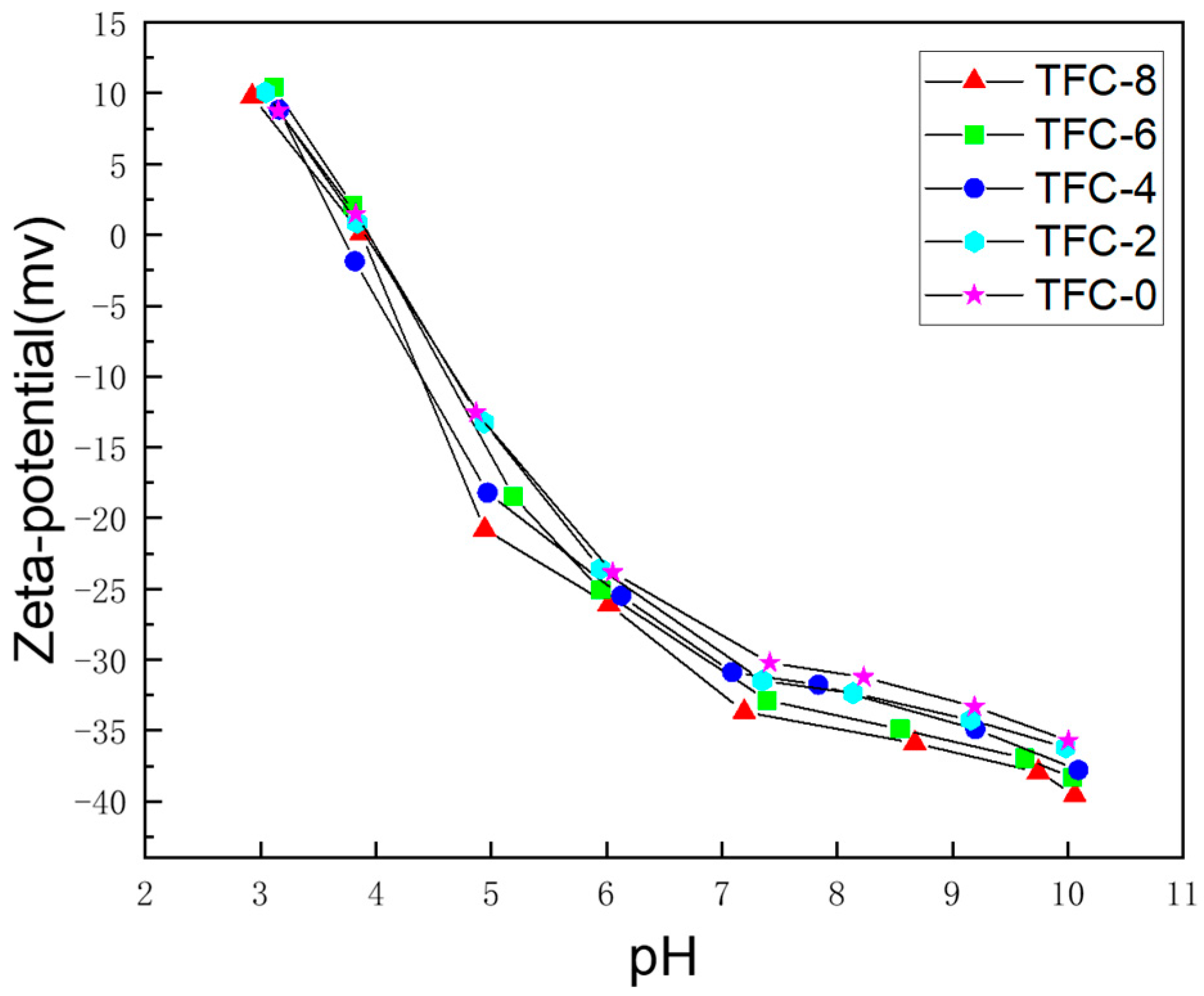
3.2. Effect of Sodium Hydrogen Acid on the Roughness
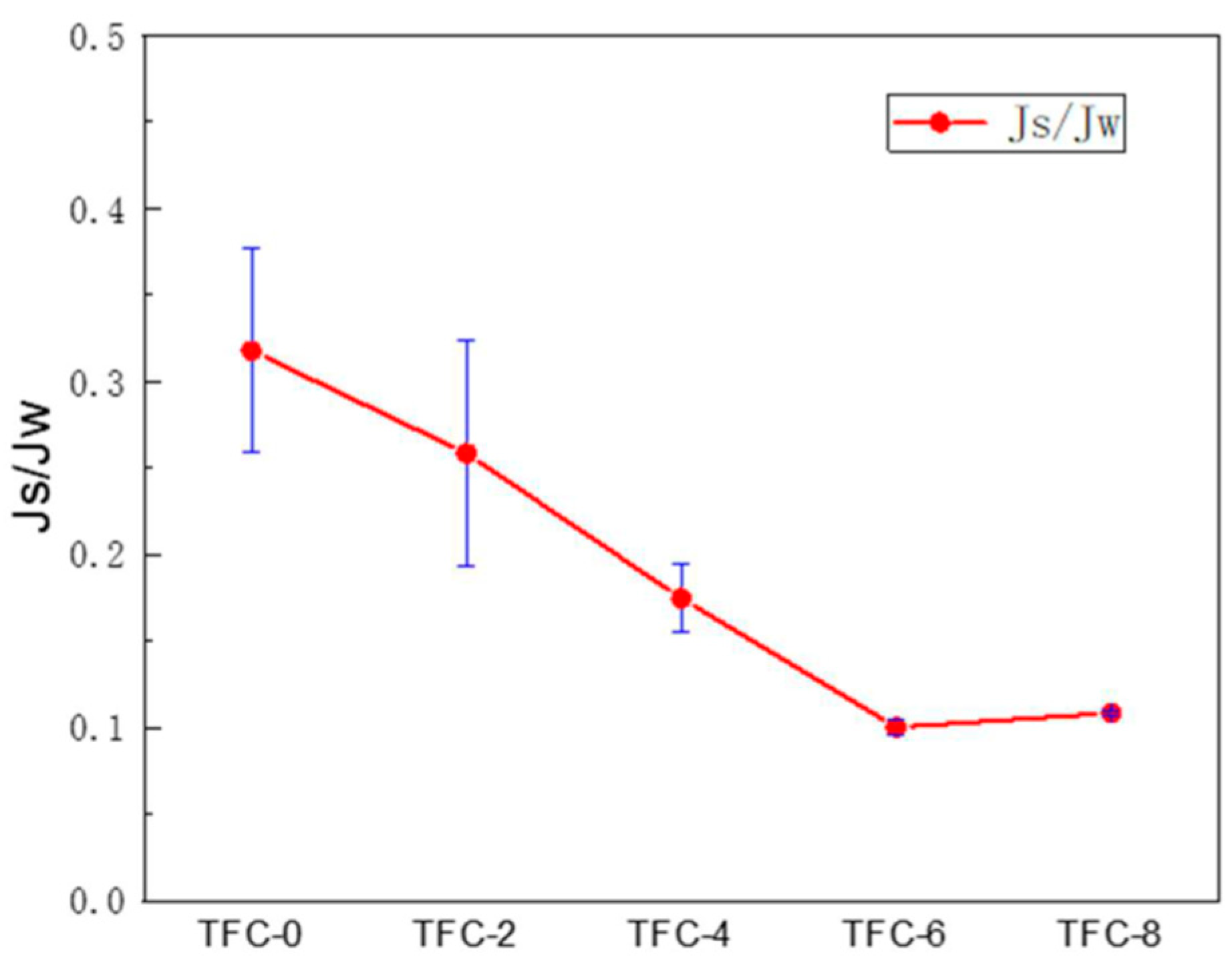
3.3. Effect of Roughness on the Performance of FO Membranes
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wu, X.; Kohl, T.M.; Tsanaktsidis, J.; Xie, Z. Improved performance and mitigated internal concentration polarization of thin-film composite forward osmosis membrane with polysulfone/polyaniline substrate. ACS Appl. Polym. Mater. 2021, 3, 5758–5766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGinnis, R.L.; Elimelech, M. Energy requirements of ammonia–carbon dioxide forward osmosis desalination. Desalination 2007, 207, 370–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, M.-J.; Nam, S.-T. Thermodynamic and rheological variation in polysulfone solution by PVP and its effect in the preparation of phase inversion membrane. J. Membr. Sci. 2002, 202, 55–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ridgway, H.F.; Orbell, J.; Gray, S. Molecular simulations of polyamide membrane materials used in desalination and water reuse applications: Recent developments and future prospects. J. Membr. Sci. 2017, 524, 436–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cadotte, J.E. Evolution of composite reverse osmosis membranes. Mater. Sci. Synth. Membr. 1985, 486, 273–294. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, M.; Yu, S.; Tao, J.; Gao, C. Preparation, structure characteristics and separation properties of thin-film composite polyamide-urethane seawater reverse osmosis membrane. J. Membr. Sci. 2008, 325, 947–956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alihemati, Z.; Hashemifard, S.; Matsuura, T.; Ismail, A.; Hilal, N. Current status and challenges of fabricating thin film composite forward osmosis membrane: A comprehensive roadmap. Desalination 2020, 491, 114557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, F.; Wang, J.; Yao, Z.; Zhang, L.; Chen, H. Polydopamine nanoparticles modified nanofiber supported thin film composite membrane with enhanced adhesion strength for forward osmosis. J. Membr. Sci. 2021, 618, 118673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Lai, G.S.; Chong, J.Y.; Wang, R. Dissecting the structure-compaction-performance relationship of thin-film composite polyamide membranes with different structure features. J. Membr. Sci. 2022, 654, 120553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, A.A.; Cho, Y.H.; Choi, H.-g.; Nam, S.-E.; Kim, J.F.; Kim, Y.; Park, Y.-I.; Park, H. Facile integration of halloysite nanotubes with bioadhesive as highly permeable interlayer in forward osmosis membranes. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2019, 73, 276–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, L.; Zhang, X.; Zuo, J.; Wang, Y. Performance enhancement of TFC FO membranes with polyethyleneimine modification and post-treatment. J. Membr. Sci. 2017, 534, 46–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Fang, F.; Zhang, B.; Wu, J.J.; Zhang, K. Biogenic silver nanoparticles-modified forward osmosis membranes with mitigated internal concentration polarization and enhanced antibacterial properties. NPJ Clean Water 2022, 5, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petersen, R.J. Composite reverse osmosis and nanofiltration membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 1993, 83, 81–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Guo, H.; Tang, C.Y. The upper bound of thin-film composite (TFC) polyamide membranes for desalination. J. Membr. Sci. 2019, 590, 117297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oreamuno, F.A.P.; Alberto, F. Microscopic Characterization of the Nanostructure of Polyamide Thin Films in Reverse Osmosis and Nanofiltration Membranes. Ph.D. Thesis, Stanford University, Stanford, CA, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Freger, V. Kinetics of film formation by interfacial polycondensation. Langmuir 2005, 21, 1884–1894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, X.; Gan, B.; Yang, Z.; Tang, C.Y.; Gao, C. Confined nanobubbles shape the surface roughness structures of thin film composite polyamide desalination membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 2019, 582, 342–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janssen, L.; Te Nijenhuis, K. Encapsulation by interfacial polycondensation. I. The capsule production and a model for wall growth. J. Membr. Sci. 1992, 65, 59–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karan, S.; Jiang, Z.; Livingston, A.G. Sub–10 nm polyamide nanofilms with ultrafast solvent transport for molecular separation. Science 2015, 348, 1347–1351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Z.; Karan, S.; Livingston, A.G. Water transport through ultrathin polyamide nanofilms used for reverse osmosis. Adv. Mater. 2018, 30, 1705973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.-H.; Yao, Z.-K.; Yang, Z.; Guo, H.; Xu, Z.-L.; Tang, C.Y.; Elimelech, M. Nanofoaming of polyamide desalination membranes to tune permeability and selectivity. Environ. Sci. Technol. Lett. 2018, 5, 123–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, L.; Lopez, R.; Ramon, G.Z.; Coronell, O. Investigating the void structure of the polyamide active layers of thin-film composite membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 2016, 497, 365–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, X.; Qi, S.; Tang, C.Y.; Gao, C. Ultra-thin, multi-layered polyamide membranes: Synthesis and characterization. J. Membr. Sci. 2017, 540, 10–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chowdhury, M.R.; Steffes, J.; Huey, B.D.; McCutcheon, J.R. 3D printed polyamide membranes for desalination. Science 2018, 361, 682–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shah, A.A.; Choi, H.-g.; Nam, S.-E.; Park, A.; Lee, P.S.; Park, Y.-I.; Park, H. Optimization of polysulfone support layer for thin-film composite forward osmosis membrane. Desalin. Water Treat. 2017, 99, 155–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, X.; Wang, J.; Zhang, H.; Cao, Z.; Zhao, M.; Guan, Y.; Zhang, Y. Establishment of transport channels with carriers for water in reverse osmosis membrane by incorporating hydrotalcite into the polyamide layer. RSC Adv. 2018, 8, 12439–12448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, X.; Gan, B.; Qi, S.; Guo, H.; Tang, C.Y.; Zhou, Y.; Gao, C. Intrinsic nanoscale structure of thin film composite polyamide membranes: Connectivity, defects, and structure–property correlation. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2020, 54, 3559–3569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.; Yang, Z.; Yao, Z.; Guo, H.; Xu, Z.; Tang, C.Y. Tuning roughness features of thin film composite polyamide membranes for simultaneously enhanced permeability, selectivity and anti-fouling performance. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2019, 540, 382–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, H.; Miao, X.; Xu, J.; Pan, G.; Zhang, Y.; Shi, Y.; Guo, M.; Liu, Y. The porous structure of the fully-aromatic polyamide film in reverse osmosis membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 2015, 475, 504–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Kłosowski, M.M.; McGilvery, C.M.; Porter, A.E.; Livingston, A.G.; Cabral, J.T. Probing flow activity in polyamide layer of reverse osmosis membrane with nanoparticle tracers. J. Membr. Sci. 2017, 534, 9–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Hill, A.; Kentish, S. Formation of a thick aromatic polyamide membrane by interfacial polymerisation. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2013, 104, 276–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, C.Y.; Kwon, Y.-N.; Leckie, J.O. Fouling of reverse osmosis and nanofiltration membranes by humic acid—Effects of solution composition and hydrodynamic conditions. J. Membr. Sci. 2007, 290, 86–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Liu, C. Inhibiting the concentration polarization of FO membranes based on the wettable microporous supporting layer and the enhanced dense skin layer. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2017, 134, 45133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, X.; Zhang, Y.; Abdel-Ghafar, H.M.; Abdel-Aal, E.-S.A.; Huang, M.; Gul, S.; Jiang, H. Polyamide membrane with an ultrathin GO interlayer on macroporous substrate for minimizing internal concentration polarization in forward osmosis. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 412, 128607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Jin, W.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, N.; Wang, B.; Jiang, B. Sodium bicarbonate as novel additive for fabrication of composite nanofiltration membranes with enhanced permeability. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2018, 135, 46363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
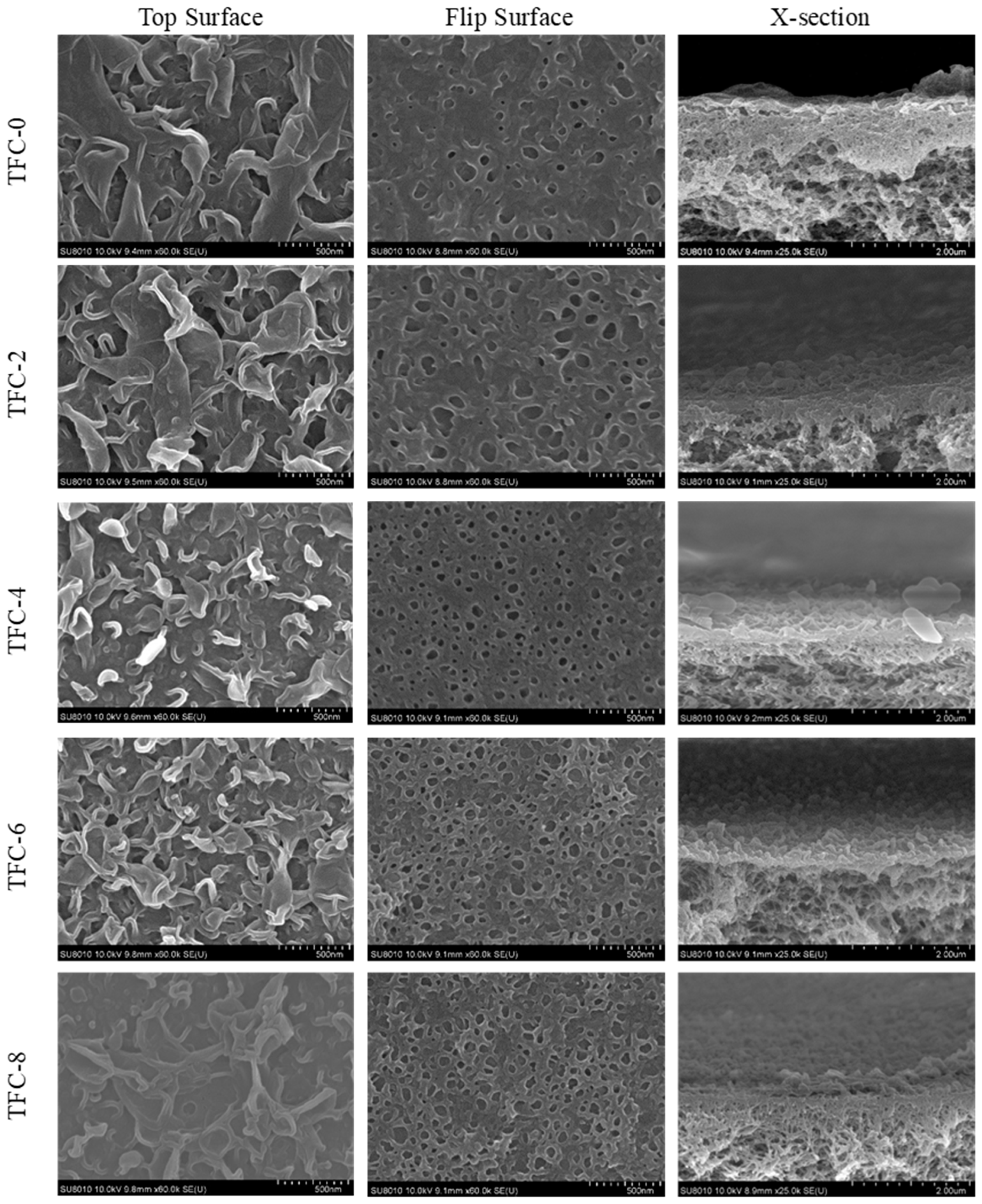
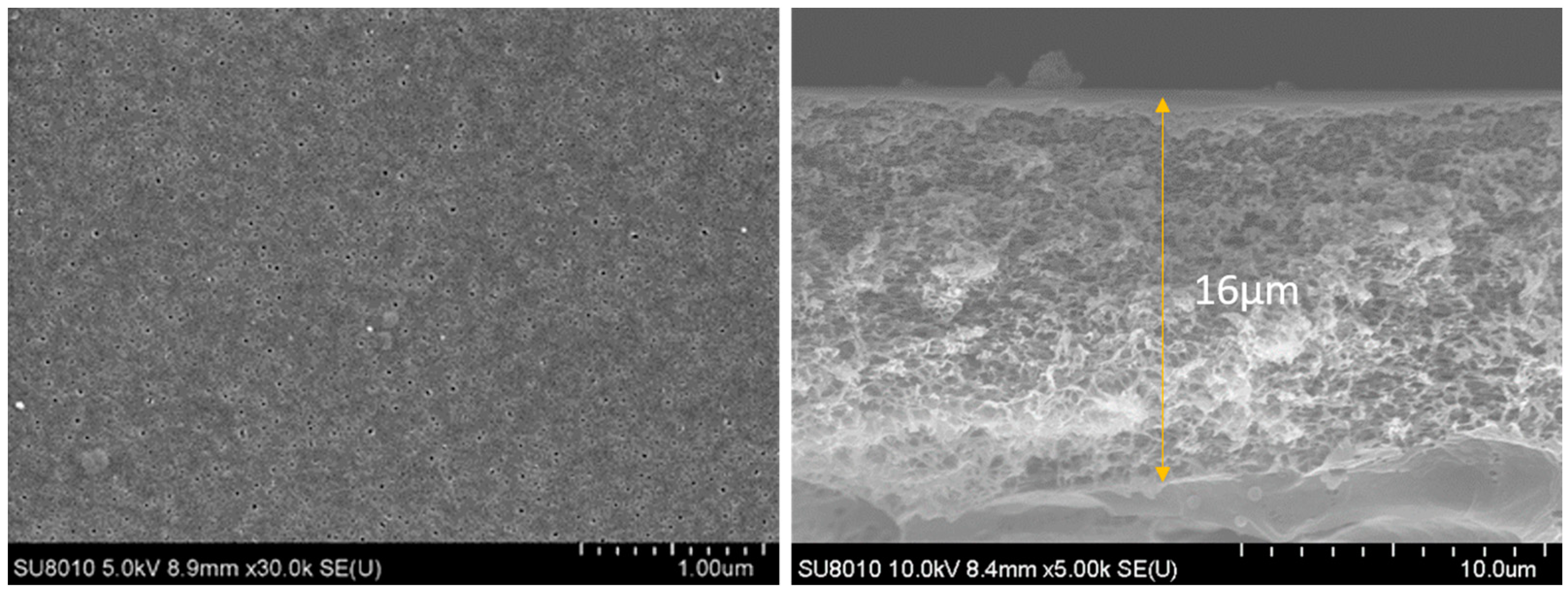

| Name | Number Density (Counts/μm2) | Diameter, dp (nm) |
|---|---|---|
| pores on substrate | 349 ± 26 | 14.71 ± 0.21 |
| TFC-0 | 22 ± 3 | 63.35 ± 12.4 |
| TFC-2 | 32 ± 4 | 88.31 ± 16.0 |
| TFC-4 | 73 ± 2.5 | 55.45 ± 10.5 |
| TFC-6 | 92 ± 3 | 64.86 ± 11.8 |
| TFC-8 | 94 ± 3.5 | 65.81 ± 9.5 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhou, S.; Zhou, Y.; He, J.; Lai, Y.; Li, Y.; Yan, W.; Zhou, Y.; Gao, C. Generation of Nano-Bubbles by NaHCO3 for Improving the FO Membrane Performance. Membranes 2023, 13, 404. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes13040404
Zhou S, Zhou Y, He J, Lai Y, Li Y, Yan W, Zhou Y, Gao C. Generation of Nano-Bubbles by NaHCO3 for Improving the FO Membrane Performance. Membranes. 2023; 13(4):404. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes13040404
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhou, Shilin, Yuzhe Zhou, Jin He, Yuwen Lai, Yanchun Li, Wentao Yan, Yong Zhou, and Congjie Gao. 2023. "Generation of Nano-Bubbles by NaHCO3 for Improving the FO Membrane Performance" Membranes 13, no. 4: 404. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes13040404
APA StyleZhou, S., Zhou, Y., He, J., Lai, Y., Li, Y., Yan, W., Zhou, Y., & Gao, C. (2023). Generation of Nano-Bubbles by NaHCO3 for Improving the FO Membrane Performance. Membranes, 13(4), 404. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes13040404






