Prediction of CO2 Permeance across ZIF-L@PDMS/PES Composite Membrane
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals
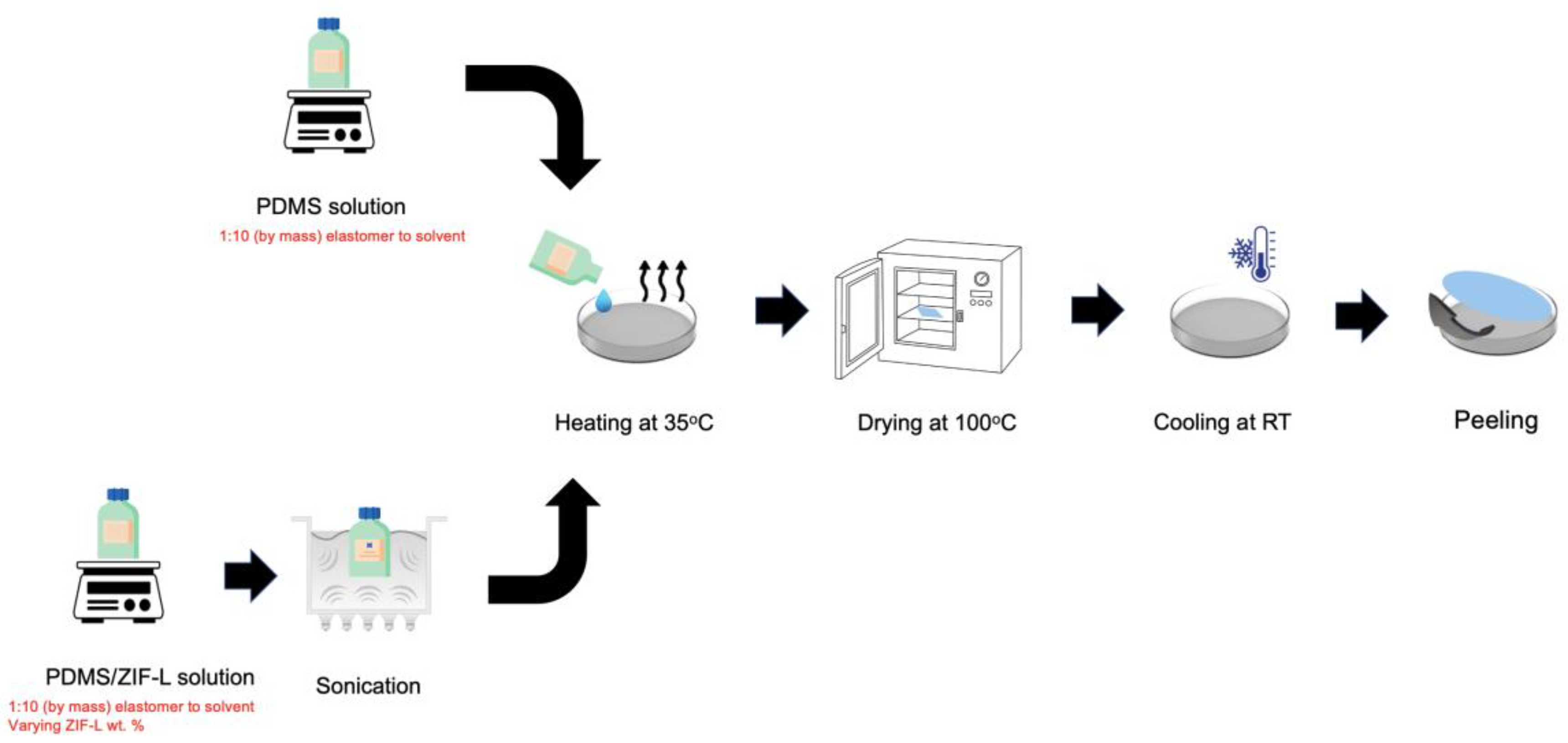
2.2. PDMS and ZIF-L@PDMS Flat Sheet Membrane Fabrication
2.3. PES Hollow Fiber Membrane Fabrication
2.4. PDMS/PES and ZIF-L@PDMS/PES Composite Membrane Fabrication
2.5. Single Gas Permeation
2.6. Sample Characterization
3. Results and Discussion
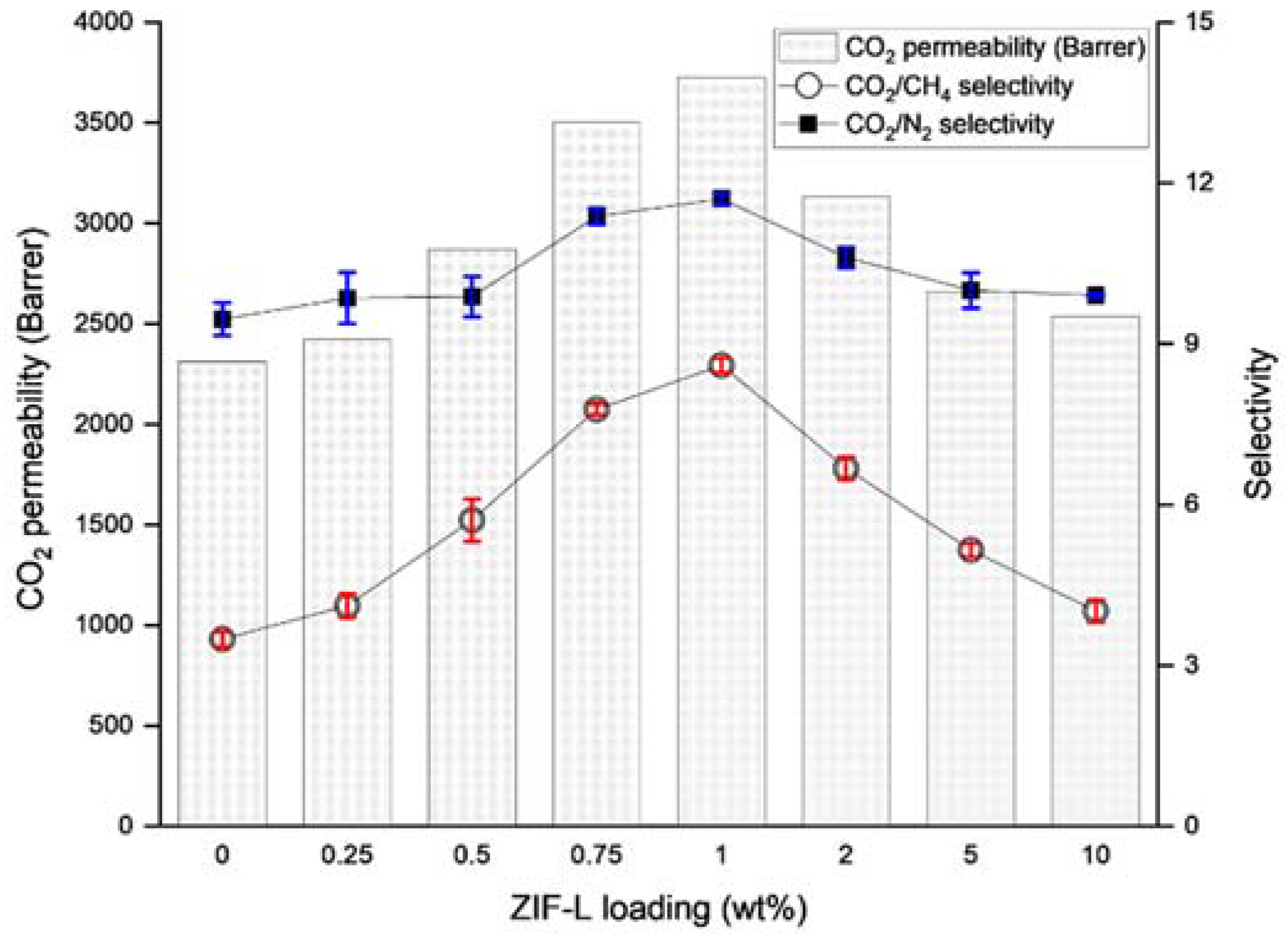
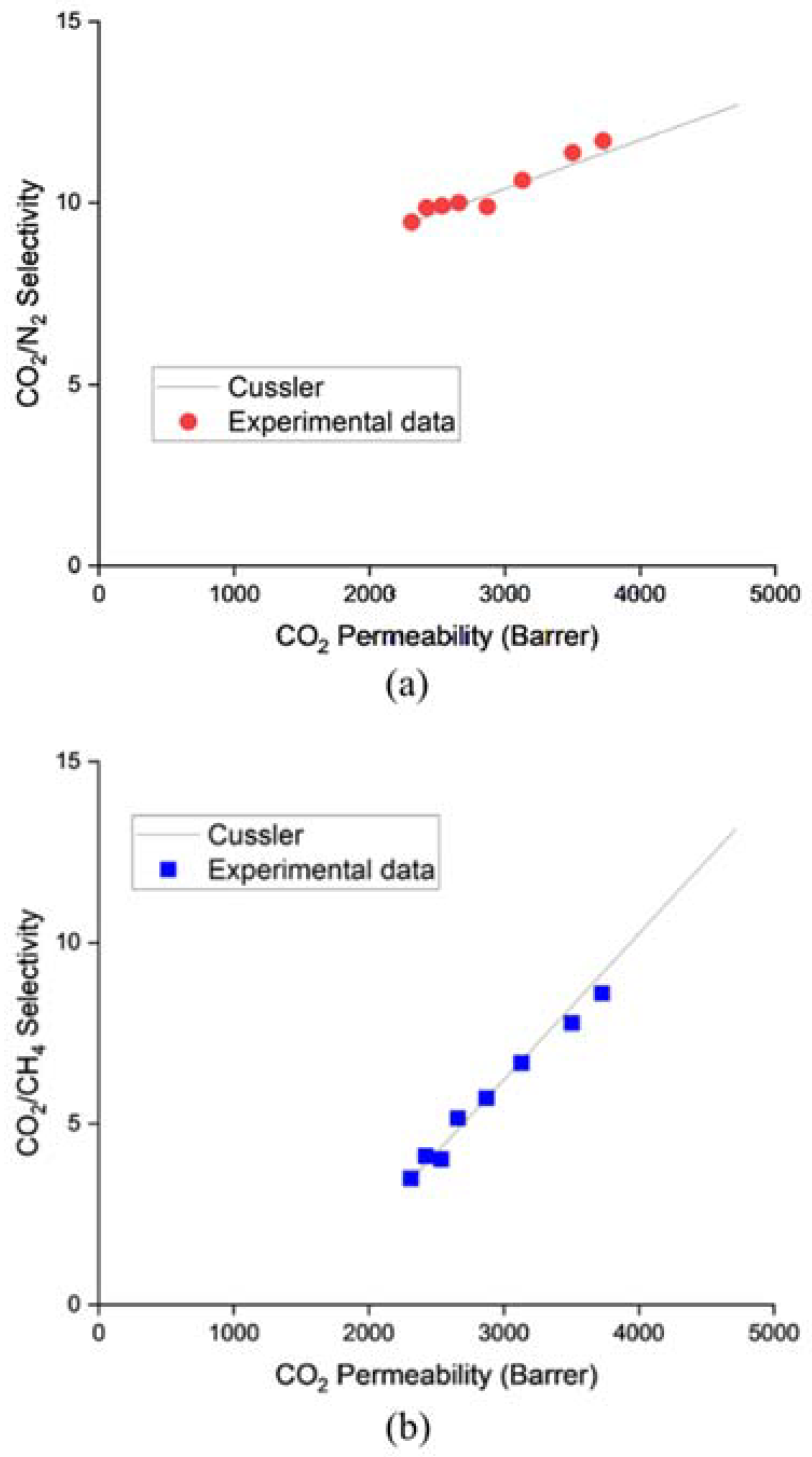
3.1. ZIF-L@PDMS Membrane Performance
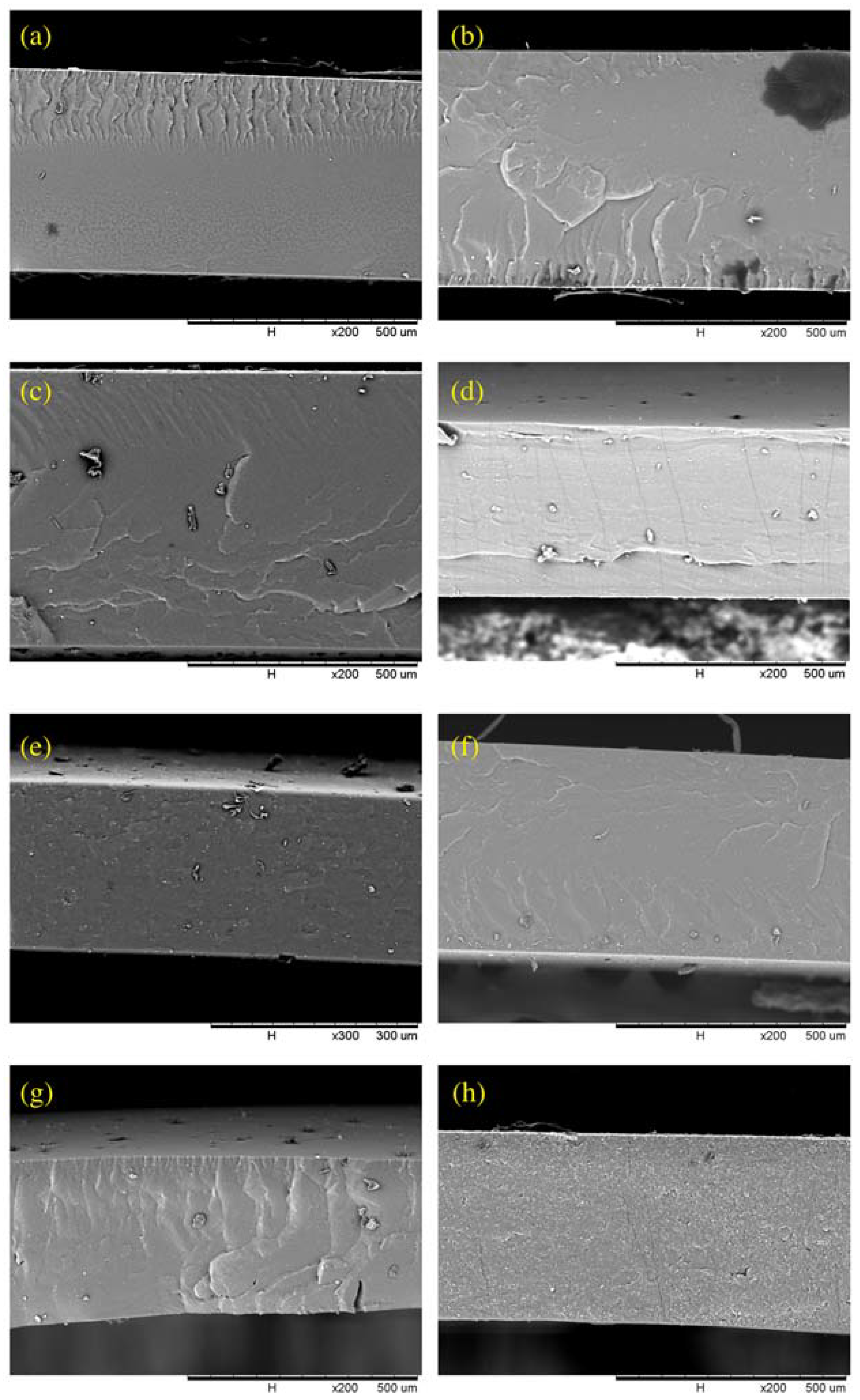
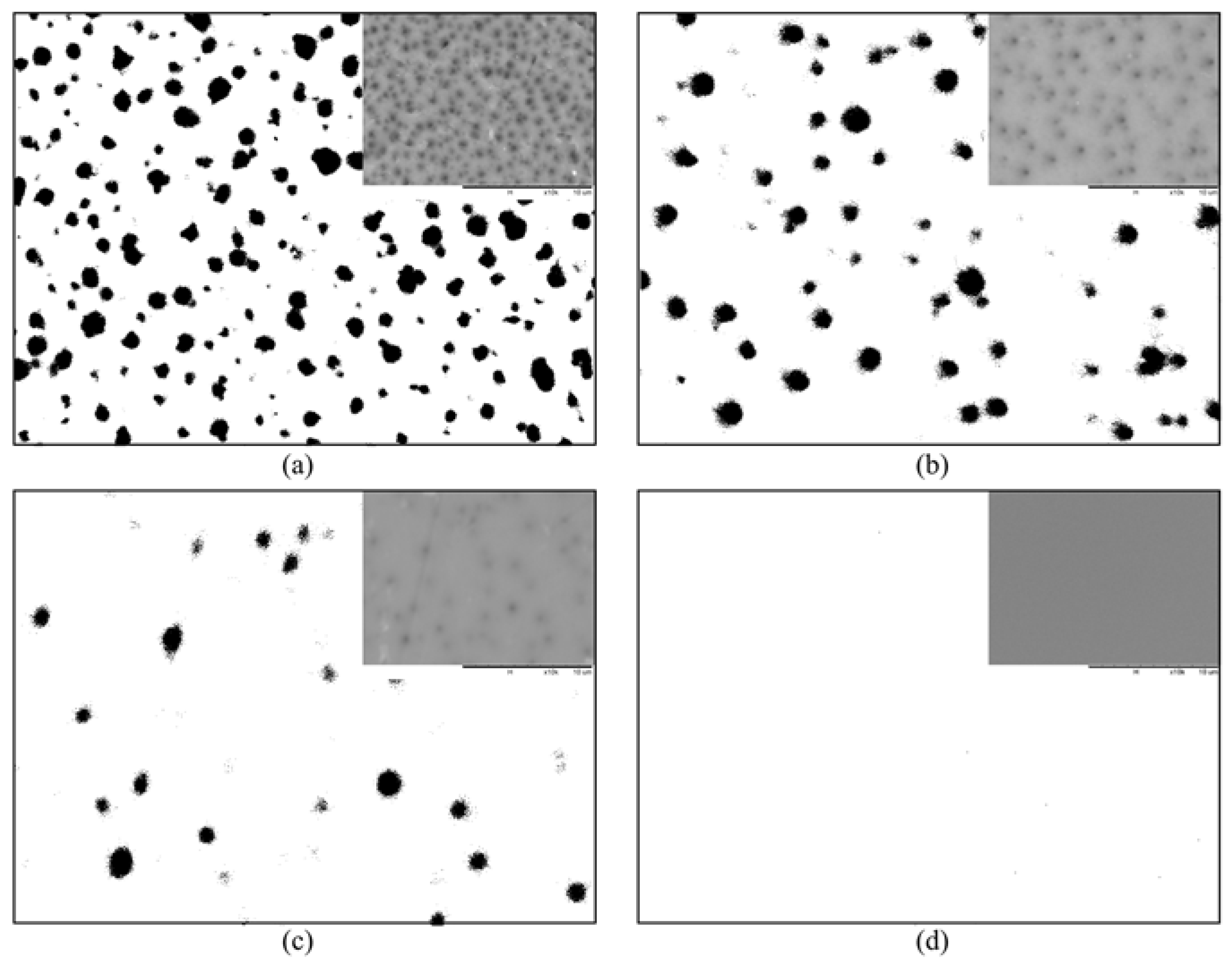
3.2. PDMS/PES Composite Membrane
| PES (wt.%) | Surface Porosity (ε) | Mean Surface Pore Size (nm) | PDMS Layer Thickness (cm) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 21 | 0.230 | 231.05 | 0.00065 |
| 25 | 0.052 | 233.38 | 0.00061 |
| 27 | 0.020 | 253.05 | 0.00059 |
| 29 | 0.000092 1 | - | 0.00033 |
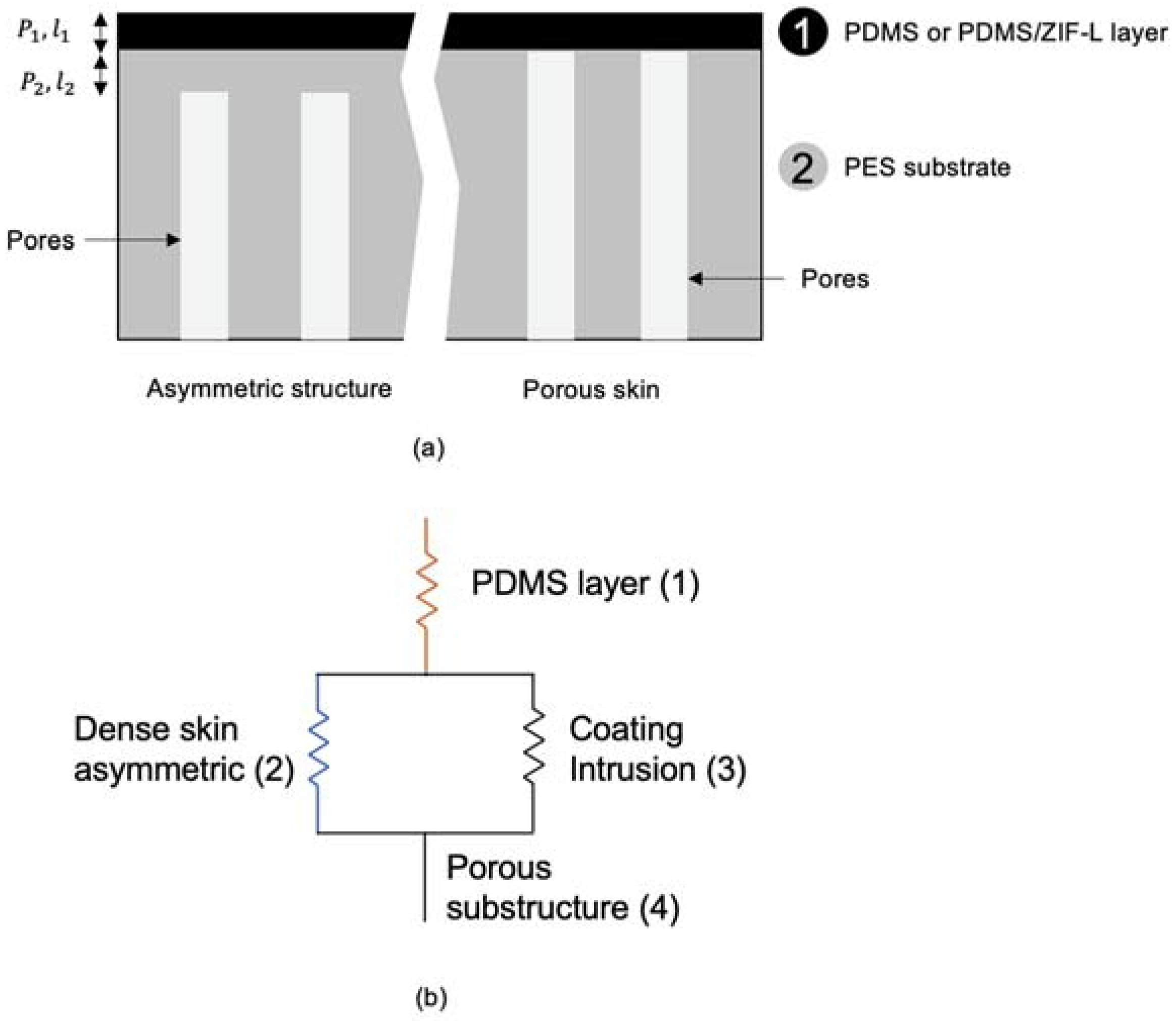
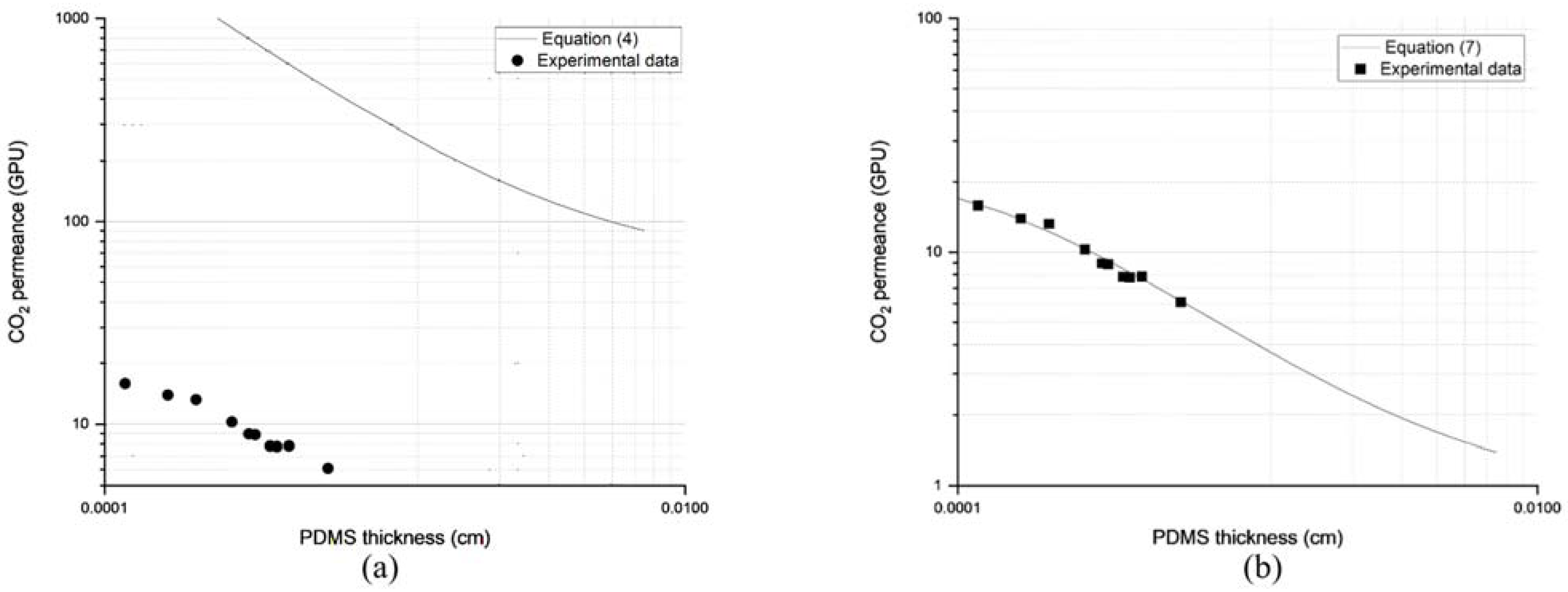
3.3. Prediction via Resistance in Series Model
3.4. ZIF-L@PDMS/PES Composite Membrane
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ahmad, A.L.; Zainuddin, M.I.F.; Shah Buddin, M.M.H.; Mohd Shafie, Z.M.H. Poly(4-methyl-1-pentene) Membrane for CO2 Separation: Performance Comparison of Dense and Anisotropic Membrane. Arab. J. Sci. Eng. 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henis, J.M.S.; Tripodi, M.K. Composite hollow fiber membranes for gas separation: The resistance model approach. J. Membr. Sci. 1981, 8, 233–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Chung, T.-S. Determination of pore sizes and surface porosity and the effect of shear stress within a spinneret on asymmetric hollow fiber membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 2001, 188, 29–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, F.; Liu, J.; Li, J. Analysis of the gas transport performance through PDMS/PS composite membranes using the resistances-in-series model. J. Membr. Sci. 2003, 222, 225–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramon, G.Z.; Wong, M.C.Y.; Hoek, E.M.V. Transport through composite membrane, part 1: Is there an optimal support membrane? J. Membr. Sci. 2012, 415–416, 298–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wijmans, J.G.; Hao, P. Influence of the porous support on diffusion in composite membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 2015, 494, 78–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghadimi, A.; Norouzbahari, S.; Lin, H.; Rabiee, H.; Sadatnia, B. Geometric restriction of microporous supports on gas permeance efficiency of thin film composite membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 2018, 563, 643–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, P.; Wijmans, J.G.; He, Z.; White, L.S. Effect of pore location and pore size of the support membrane on the permeance of composite membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 2020, 594, 117465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, I.U.; Othman, M.H.D.; Ismail, A.F.; Ismail, N.; Jaafar, J.; Hashim, H.; Rahman, M.A.; Jilani, A. Structural transition from two-dimensional ZIF-L to three-dimensional ZIF-8 nanoparticles in aqueous room temperature synthesis with improved CO2 adsorption. Mater. Charact. 2018, 136, 407–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tyler, B.J.; Hook, A.; Pelster, A.; Williams, P.; Alexander, M.; Arlinghaus, H.F. Development and characterization of a stable adhesive bond between a poly(dimethylsiloxane) catheter material and a bacterial biofilm resistant acrylate polymer coating. Biointerphases 2017, 12, 02C412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.; Shamsaei, E.; Lin, X.; Hu, Y.; Simon, G.P.; Seong, J.G.; Kim, J.S.; Lee, W.H.; Lee, Y.M.; Wang, H. The enhanced hydrogen separation performance of mixed matrix membranes by incorporation of two-dimensional ZIF-L into polyimide containing hydroxyl group. J. Membr. Sci. 2018, 549, 260–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah Buddin, M.M.H.; Ahmad, A.L.; Mohd Saufi, M.A.A. PES/ZIF-L mixed-matrix membrane for CO2 permeation: Influence of ionic liquid in pre- and post-modification treatment. Asia-Pac. J. Chem. Eng. 2022, e2853. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, R.; Yao, J.; Gu, Q.; Smeets, S.; Baerlocher, C.; Gu, H.; Zhu, D.; Morris, W.; Yaghi, O.M.; Wang, H. A two-dimensional zeolitic imidazolate framework with a cushion-shaped cavity for CO2 adsorption. Chem. Commun. 2013, 49, 9500–9502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheffel, J.A.; Tsapatsis, M. A semi-empirical approach for predicting the performance of mixed matrix membranes containing selective flakes. J. Membr. Sci. 2009, 326, 595–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah Buddin, M.M.H.; Ahmad, A.L. A review on metal-organic frameworks as filler in mixed matrix membrane: Recent strategies to surpass upper bound for CO2 separation. J. CO2 Util. 2021, 51, 101616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Kujawski, W.; Knozowska, K.; Kujawa, J. The Effects of PEI Hollow Fiber Substrate Characteristics on PDMS/PEI Hollow Fiber Membranes for CO2/N2 Separation. Membranes 2021, 11, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kapantaidakis, G.C.; Koops, G.H.; Wessling, M. Effect of spinning conditions on the structure and the gas permeation properties of high flux polyethersulfone—Polyimide blend hollow fibers. Desalination 2002, 144, 121–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pesek, S.C.; Koros, W.J. Aqueous quenched asymmetric polysulfone membranes prepared by dry/wet phase separation. J. Membr. Sci. 1993, 81, 71–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zulhairun, A.K.; Fachrurrazi, Z.G.; Nur Izwanne, M.; Ismail, A.F. Asymmetric hollow fiber membrane coated with polydimethylsiloxane–metal organic framework hybrid layer for gas separation. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2015, 146, 85–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.Y.; Kaliaguine, S.; Rodrigue, D. A Comparison between Several Commercial Polymer Hollow Fiber Membranes for Gas Separation. J. Membr. Sep. Technol. 2017, 6, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Francavilla, P.; Ferreira, D.P.; Araújo, J.C.; Fangueiro, R. Smart Fibrous Structures Produced by Electrospinning Using the Combined Effect of PCL/Graphene Nanoplatelets. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 1124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Permeance (GPU) | Selectivity | Error | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CO2/N2 | CO2/CH4 | Permeance | Selectivity | |||
| CO2/N2 | CO2/CH4 | |||||
| Predicted values | 9.62 GPU 1 801.21 GPU 2 | 9.98 | 3.82 | - | - | - |
| Experimental data | 9.69 GPU | 10.96 | 4.22 | 0.7% 98.8% | 8.9% | 9.4% |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Buddin, M.M.H.S.; Ahmad, A.L.; Zainuddin, M.I.F. Prediction of CO2 Permeance across ZIF-L@PDMS/PES Composite Membrane. Membranes 2023, 13, 134. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes13020134
Buddin MMHS, Ahmad AL, Zainuddin MIF. Prediction of CO2 Permeance across ZIF-L@PDMS/PES Composite Membrane. Membranes. 2023; 13(2):134. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes13020134
Chicago/Turabian StyleBuddin, Meor Muhammad Hafiz Shah, Abdul Latif Ahmad, and Muhd Izzudin Fikry Zainuddin. 2023. "Prediction of CO2 Permeance across ZIF-L@PDMS/PES Composite Membrane" Membranes 13, no. 2: 134. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes13020134
APA StyleBuddin, M. M. H. S., Ahmad, A. L., & Zainuddin, M. I. F. (2023). Prediction of CO2 Permeance across ZIF-L@PDMS/PES Composite Membrane. Membranes, 13(2), 134. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes13020134







