Permeate Flux in Ultrafiltration Processes—Understandings and Misunderstandings
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Fundamentals
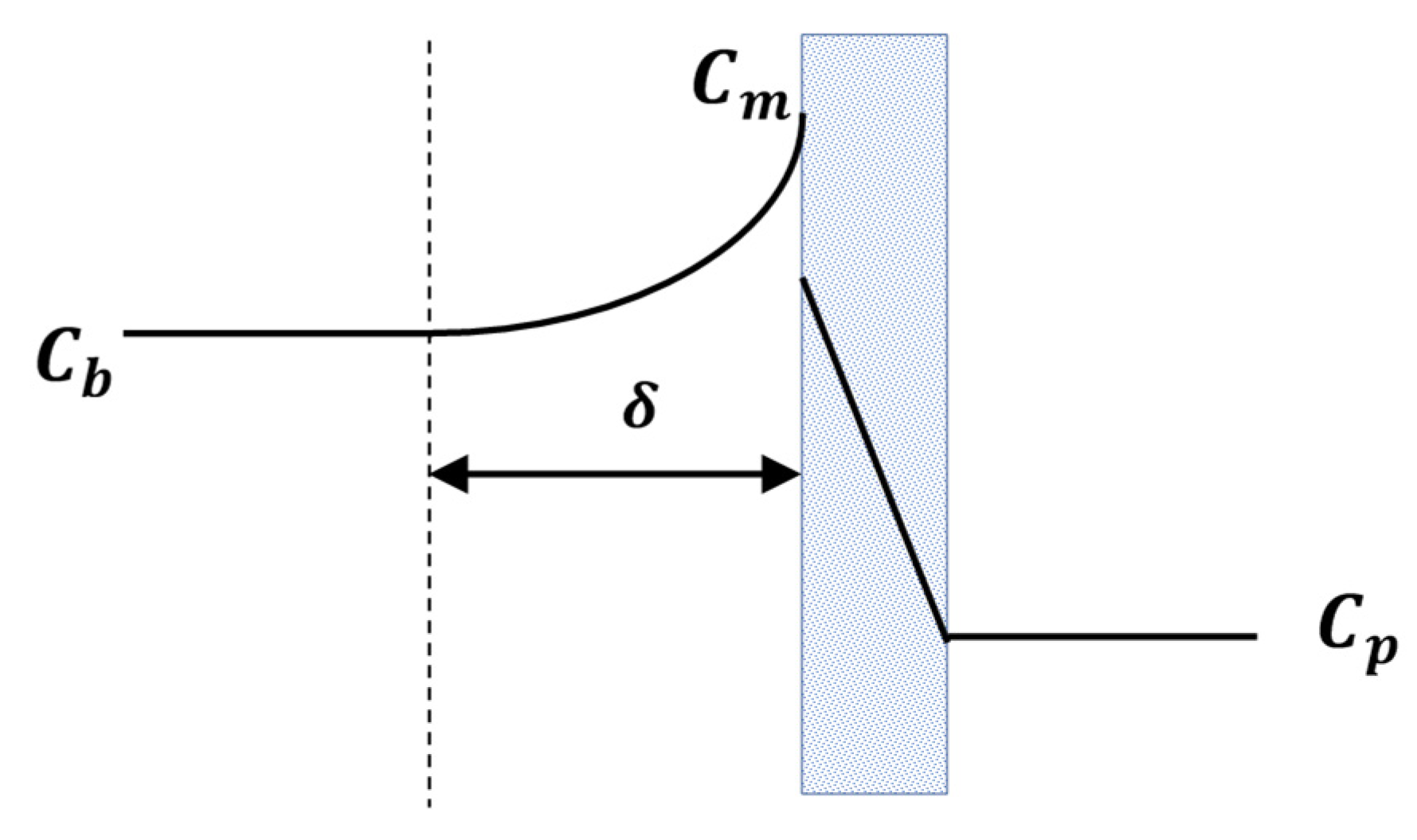
2.1. Is Concentration Polarisation Distinct from Fouling?
2.2. Is Concentration Polarisation the Primary Reason for Flux Decline during the Initial Period of Operation?
2.3. Can Gel Theory Explain Flux Decline?
2.4. Can the Effect of Viscosity upon Mass Transfer Explain a Limiting Flux?
2.5. Can the Effect of Osmotic Pressure Explain a Limiting Flux?
2.6. What Is the Flux Paradox?
3. Modelling of Flux Decline
3.1. What Is an Appropriate Classification for Flux Decline Models?
3.2. What Is the Appropriate Viscosity in the Resistance-In-Series Model?
3.3. When Is It Appropriate to Include a Concentration Polarisation Resistance Term?
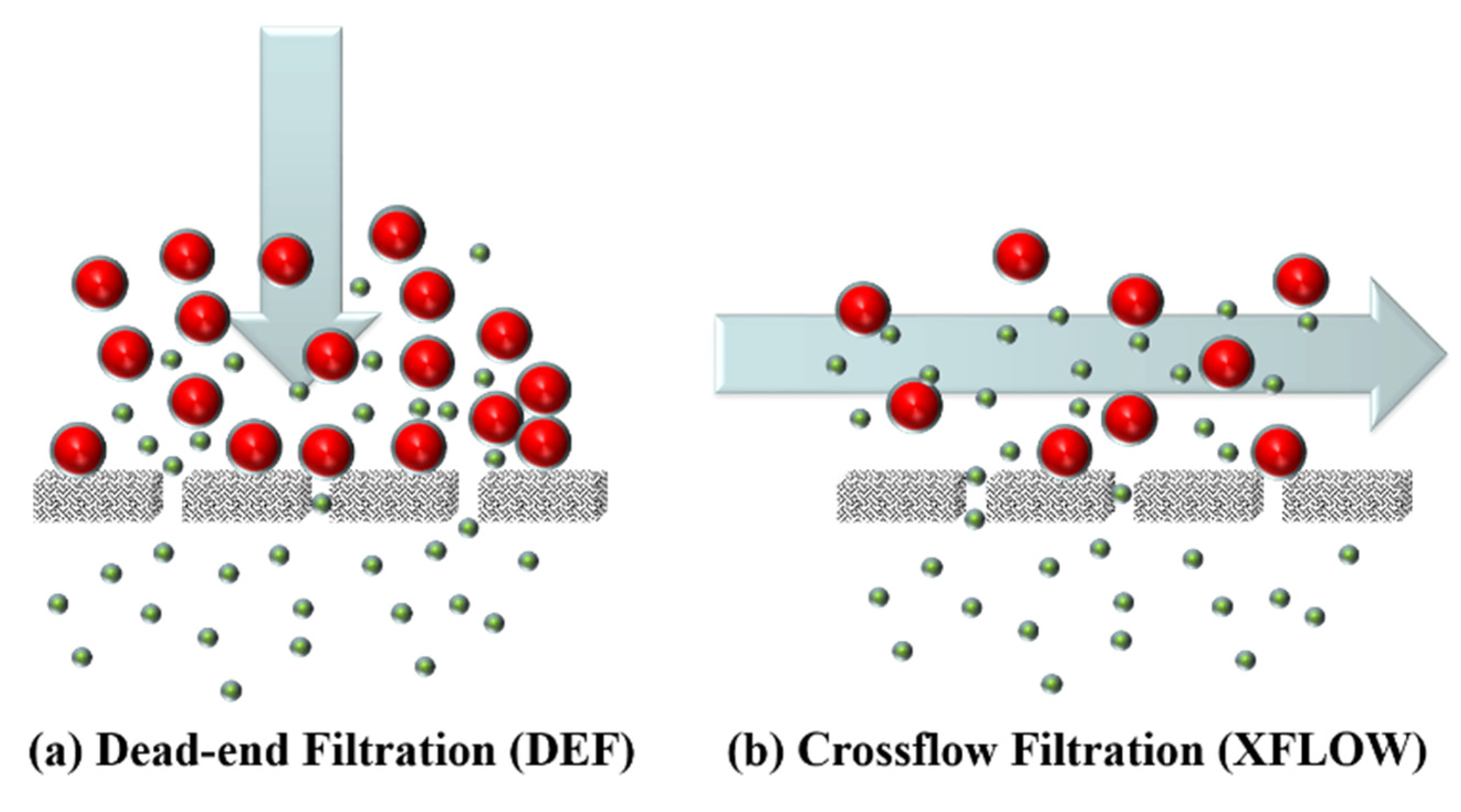
3.4. Is There a Robust Methodology for Fouling Analysis of Crossflow Systems?
3.5. Can One Make Permeate Flux Predictions?
3.6. What Differences Are Observed in Operation under Constant Flux?
4. Design
Is Pilot Plant Evaluation Essential?
5. Concluding Remarks
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations and Nomenclature
| ARIMA | Autoregressive integrated moving average |
| CP | Concentration polarisation |
| ln | natural logarithm |
| Pe | Boundary layer Peclet number |
| TMP | Transmembrane Pressure |
| UF | Ultrafiltration |
| A | area of membrane |
| C | concentration |
| D | diffusivity |
| F | net driving force |
| J or J(t) | volumetric flux |
| Kn | constant dependent upon the mode of blockage (Equation (11)) |
| k | boundary layer mass transfer coefficient |
| kn | constant dependent upon the mode of blockage (Equation (9)) |
| n | index characteristic of a particular mode of blocking |
| Rf | foulant resistance (m−1) |
| Rm | hydraulic resistance of the membrane (m–1) |
| Rt | overall resistance (m−1) |
| t | time |
| V | filtrate volume |
| v | specific volume |
| thickness of mass transfer boundary layer | |
| μ | viscosity |
| viscosity of the permeate | |
| ΔP | transmembrane pressure difference |
| osmotic pressure difference across the membrane ( |
Subscripts
| 0 | initial |
| b | bulk |
| cp | concentration polarisation |
| gel | gel |
| lim | limit |
| m | upstream membrane surface |
| p | permeate |
| R | removal term |
References
- Field, R.W.; She, Q.; Siddiqui, F.A.; Fane, A.G. Reverse osmosis and forward osmosis fouling: A comparison. Discov. Chem. Eng. 2021, 1, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fane, A.G.; Fell, C.J.; Waters, A.G. The relationship between membrane surface pore characteristics and flux for ultrafiltration membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 1981, 9, 245–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baker, R.J.; Fane, A.G.; Fell, C.J.; Yoo, B.H. Factors affecting flux in crossflow filtration. Desalination 1985, 53, 81–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Field, R.W.; Wu, J.J. On boundary layers and the attenuation of driving forces in forward osmosis and other membrane processes. Desalination 2018, 429, 167–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aimar, P.; Howell, J.A.; Clifton, M.J.; Sanchez, V. Concentration polarisation build-up in hollow fibers: A method of measurement and its modelling in ultrafiltration. J. Membr. Sci. 1991, 59, 81–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velicangil, O.; Howell, J.A. Self-cleaning membranes for ultrafiltration. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 1981, 23, 843–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koros, W.J.; Ma, Y.H.; Shimidzu, T. Terminology for membranes and membrane processes (IUPAC Recommendations 1996). Pure Appl. Chem. 1996, 68, 1479–1489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berg, G.V.D.; Smolders, C. Flux decline in ultrafiltration processes. Desalination 1990, 77, 101–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Quezada, C.; Estay, H.; Cassano, A.; Troncoso, E.; Ruby-Figueroa, R. Prediction of Permeate Flux in Ultrafiltration Processes: A Review of Modeling Approaches. Membranes 2021, 11, 368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zydney, A.L. Stagnant film model for concentration polarization in membrane systems. J. Membr. Sci. 1997, 130, 275–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasan, S.S.; Field, R.W. On maintaining consistency between the film model and the profile of the concentration polarisation layer. J. Membr. Sci. 2006, 279, 434–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qaid, S.; Zait, M.; El Kacemi, K.; El Midaoui, A.; El Hajjil, H.; Taky, M. Ultrafiltration for clarification of Valencia orange juice: Comparison of two flat sheet membranes on quality of juice production. J. Mater. Environ. Sci. 2017, 8, 1186–1194. [Google Scholar]
- Denisov, G.A. Theory of concentration polarization in cross-flow ultrafiltration: Gel-layer model and osmotic-pressure model. J. Membr. Sci. 1994, 91, 173–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Field, R.; Aimar, P. Ideal limiting fluxes in ultrafiltration: Comparison of various theoretical relationships. J. Membr. Sci. 1993, 80, 107–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porter, M.C. Concentration Polarization with Membrane Ultrafiltration. Prod. RD 1972, 11, 234–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wijmans, J.; Nakao, S.; Smolders, C. Flux limitation in ultrafiltration: Osmotic pressure model and gel layer model. J. Membr. Sci. 1984, 20, 115–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mondal, S.; Cassano, A.; Conidi, C.; De, S. Modeling of gel layer transport during ultrafiltration of fruit juice with non-Newtonian fluid rheology. Food Bioprod. Process. 2016, 100, 72–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gill, W.N.; Wiley, D.E.; Fell, C.J.; Fane, A.G. Effect of viscosity on concentration polarization in ultrafiltration. AIChE J. 1988, 34, 1563–1567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aimar, P.; Field, R. Limiting flux in membrane separations: A model based on the viscosity dependency of the mass transfer coefficient. Chem. Eng. Sci. 1992, 47, 579–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aimar, P.; Sanchez, V. A novel approach to transfer-limiting phenomena during ultrafiltration of macromolecules. Ind. Eng. Chem. Fundam. 1986, 25, 789–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kozinski, A.A.; Lightfoot, E.N. Protein ultrafiltration: A general example of boundary layer filtration. AIChE J. 1972, 18, 1030–1040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gekas, V.; Ölund, K. Mass transfer in the membrane concentration polarization layer under turbulent cross flow: II. Application to the characterization of ultrafiltration membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 1988, 37, 145–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pritchard, M.; Howell, J.A.; Field, R.W. The ultrafiltration of viscous fluids. J. Membr. Sci. 1995, 102, 223–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, R.; Probstein, R. Colloidal fouling of reverse osmosis membranes. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 1986, 114, 194–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bacchin, P.; Aimar, P.; Sanchez, V. Model for colloidal fouling of membranes. AIChE J. 1995, 41, 368–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bacchin, P.; Aimar, P.; Field, R. Critical and sustainable fluxes: Theory, experiments and applications. J. Membr. Sci. 2006, 281, 42–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
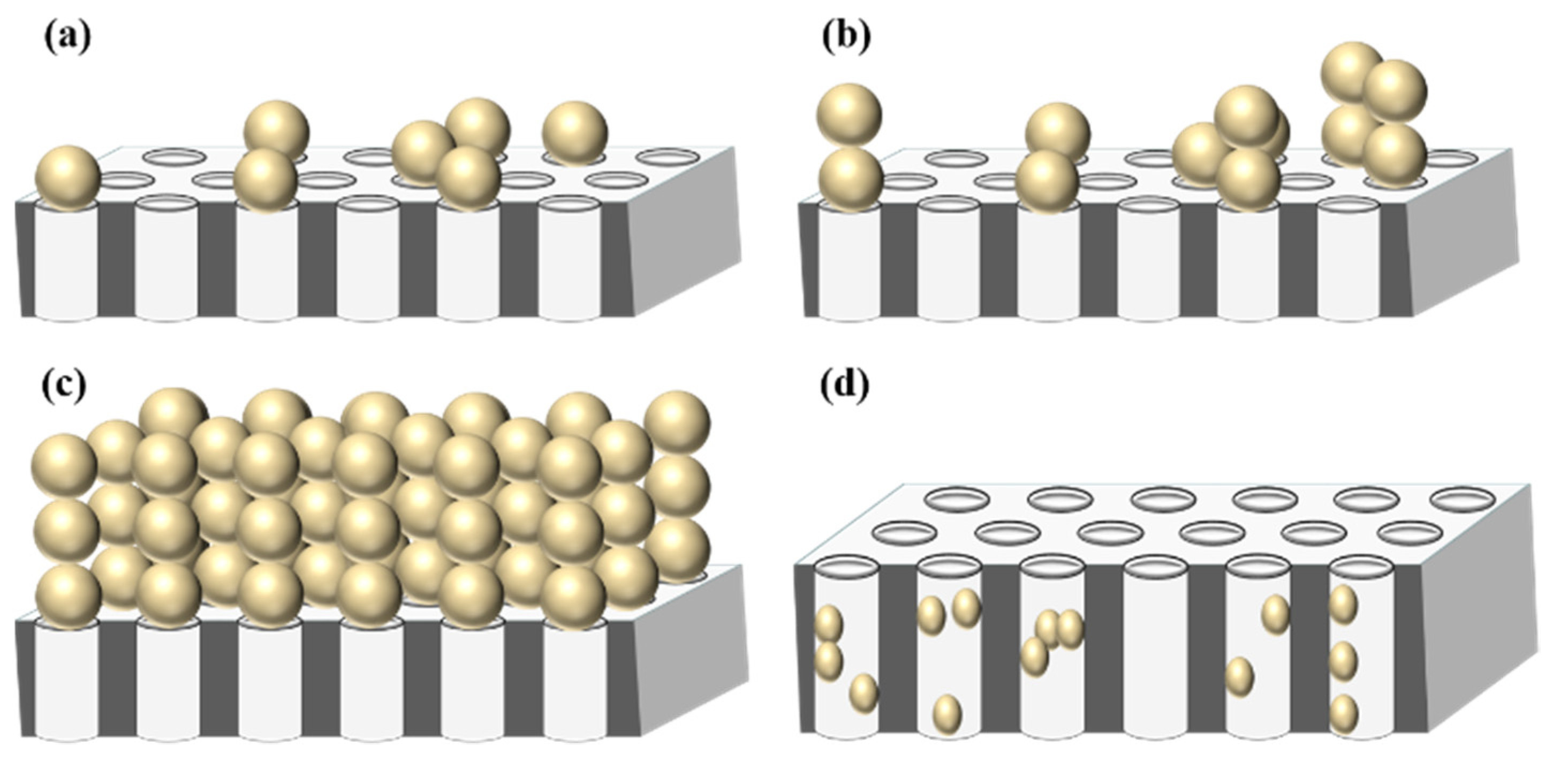
- Davis, R.H. Modeling of Fouling of Crossflow Microfiltration Membranes. Sep. Purif. Methods 1992, 21, 75–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belfort, G.; Davis, R.H.; Zydney, A.L. The behavior of suspensions and macromolecular solutions in crossflow microfiltration. J. Membr. Sci. 1994, 96, 1–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hermia, J. Constant pressure blocking filtration laws—Application to power-law non-Newtonian fluids. Trans. IChemE. 1982, 60, 183–187. [Google Scholar]
- Field, R.; Wu, D.; Howell, J.; Gupta, B. Critical flux concept for microfiltration fouling. J. Membr. Sci. 1995, 100, 259–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Razi, B.; Aroujalian, A.; Fathizadeh, M. Modeling of fouling layer deposition in cross-flow microfiltration during tomato juice clarification. Food Bioprod. Processing 2012, 90, 841–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ochando-Pulido, J.M.; Martinez-Ferez, A. Fouling modelling on a reverse osmosis membrane in the purification of pretreated olive mill wastewater by adapted crossflow blocking mechanisms. J. Membr. Sci. 2017, 544, 108–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, H.; Zhang, K.; Dionysiou, D.D.; Oerther, D.; Sorial, G.A. Effect of permeate flux and tangential flow on membrane fouling for wastewater treatment. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2005, 45, 68–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wijmans, J.; Nakao, S.; Berg, J.V.D.; Troelstra, F.; Smolders, C. Hydrodynamic resistance of concentration polarization boundary layers in ultrafiltration. J. Membr. Sci. 1985, 22, 117–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ko, M.K.; Pellegrino, J.J. Determination of osmotic pressure and fouling resistance and their effects of performance of ultrafiltration membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 1992, 74, 141–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Field, R.W.; Wu, J.J. Modelling of permeability loss in membrane filtration: Re-examination of fundamental fouling equations and their link to critical flux. Desalination 2011, 283, 68–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirschner, A.Y.; Cheng, Y.H.; Paul, D.R.; Field, R.W.; Freeman, B.D. Fouling mechanisms in constant flux crossflow ultrafiltration. J. Membr. Sci. 2019, 574, 65–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wu, J.J. Improving membrane filtration performance through time series analysis. Discov. Chem. Eng. 2021, 1, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grenier, A.; Meireles, M.; Aimar, P.; Carvin, P. Analysing flux decline in dead-end filtration. Chem. Eng. Res. Des. 2008, 86, 1281–1293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vela, M.C.; Blanco, S.Á.; García, J.L.; Rodríguez, E.B. Analysis of membrane pore blocking models adapted to crossflow ultrafiltration in the ultrafiltration of PEG. Chem. Eng. J. 2009, 149, 232–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruby-Figueroa, R.; Saavedra, J.; Bahamonde, N.; Cassano, A. Permeate flux prediction in the ultrafiltration of fruit juices by ARIMA models. J. Membr. Sci. 2017, 524, 108–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Field, R.W.; Pearce, G.K. Critical, sustainable and threshold fluxes for membrane filtration with water industry applications. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2011, 164, 38–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Astudillo-Castro, C.; Cordova, A.; Oyanedel-Craver, V.; Soto-Maldonado, C.; Valencia, P.; Henriquez, P.; Jimenez-Flores, R. Prediction of the Limiting Flux and Its Correlation with the Reynolds Number during the Microfiltration of Skim Milk Using an Improved Model. Foods 2020, 9, 1621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hurt, E.; Adams, M.; Barbano, D. Microfiltration: Effect of retentate protein concentration on limiting flux and serum protein removal with 4-mm-channel ceramic microfiltration membranes. J. Dairy Sci. 2015, 98, 2234–2244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Field, R.; Lipnizki, F. Membrane Separation Processes: An Overview. In Engineering Aspects of Membrane Separation and Application in Food Processing; Field, R.W., Bekassy-Molnar, E., Lipnizki, F., Vatai, G., Eds.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2017; Chapter 1; pp. 3–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishna Kumar, N.; Yea, M.; Cheryan, M.; Kumar, N.K. Ultrafiltration of soy protein concentrate: Performance and modelling of spiral and tubular polymeric modules. J. Membr. Sci. 2004, 244, 235–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Da Costa, A.R.; Fane, A.G.; Wiley, D.E. Spacer characterization and pressure drop modelling in spacer-filled channels for ultrafiltration. J. Membr. Sci. 1994, 87, 79–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Field, R.W.; Siddiqui, F.A.; Ang, P.; Wu, J.J. Analysis of the influence of module construction upon forward osmosis performance. Desalination 2018, 431, 151–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
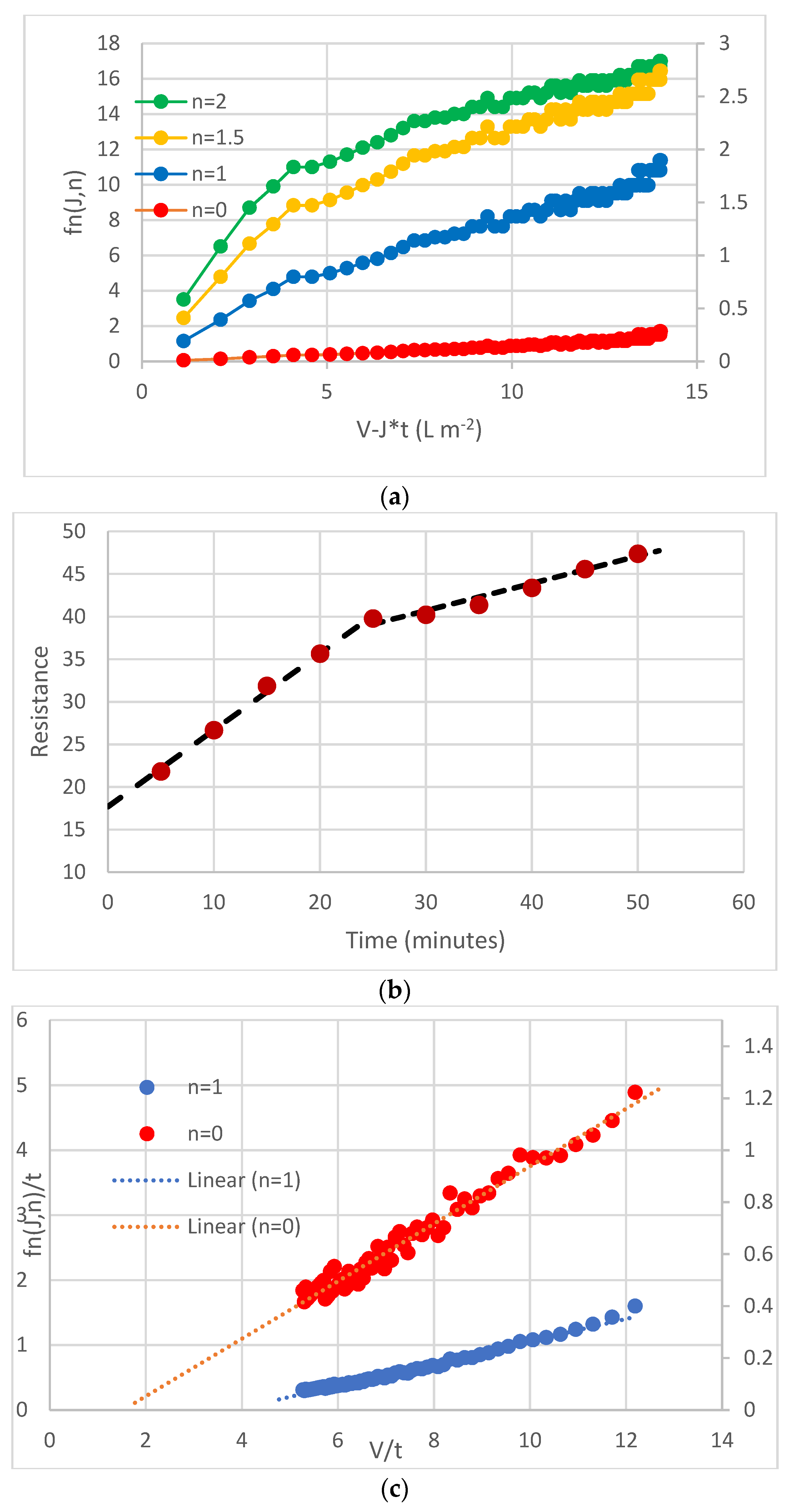
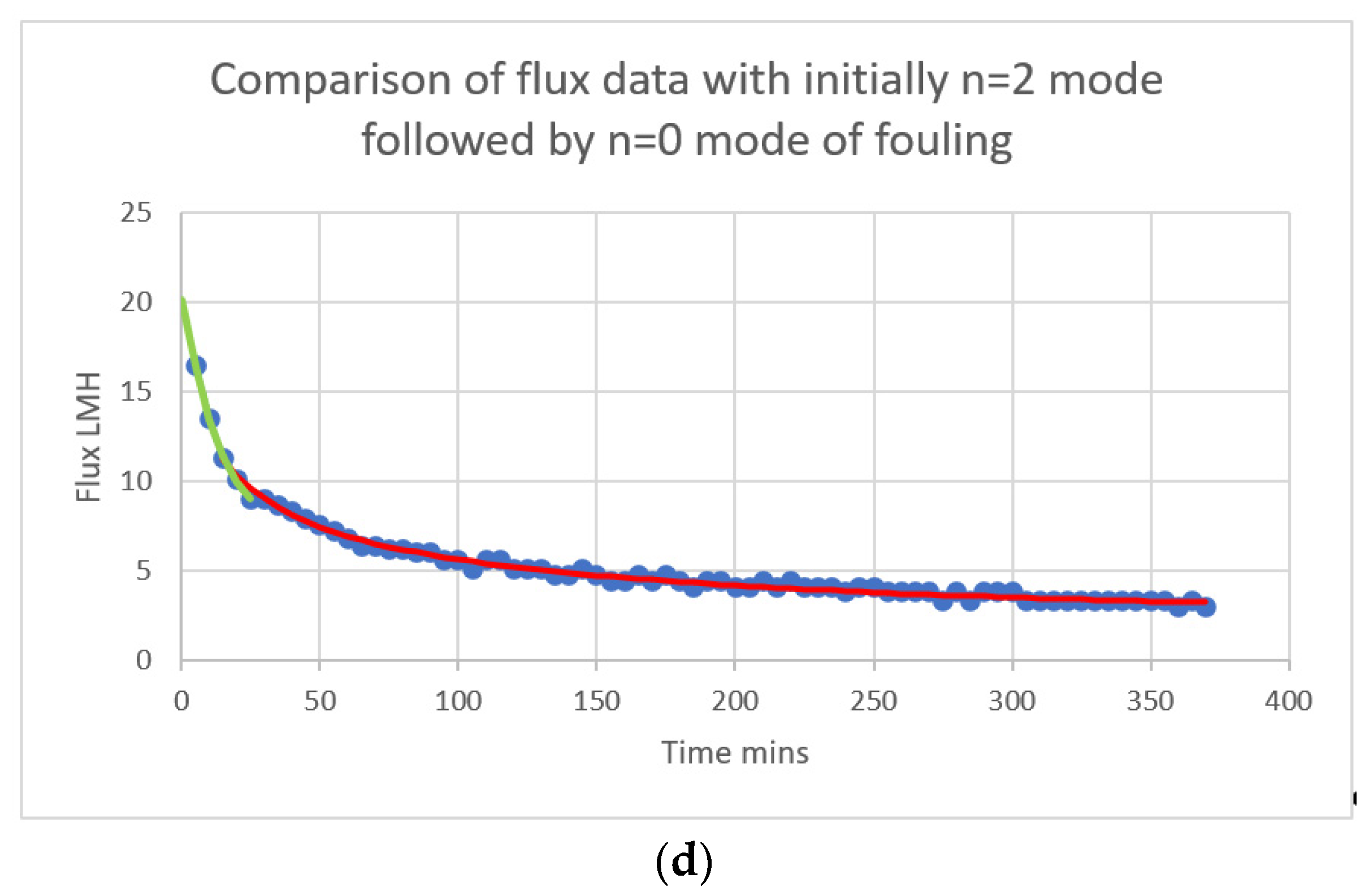
| Complete pore blocking with allowance for crossflow removal | (12a) | ||
| Pore filling mechanism (1) | (12b) | ||
| Intermediate pore blocking with allowance for crossflow removal | (12c) | ||
| Cake formation with allowance for crossflow removal | (12d) |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Field, R.W.; Wu, J.J. Permeate Flux in Ultrafiltration Processes—Understandings and Misunderstandings. Membranes 2022, 12, 187. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes12020187
Field RW, Wu JJ. Permeate Flux in Ultrafiltration Processes—Understandings and Misunderstandings. Membranes. 2022; 12(2):187. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes12020187
Chicago/Turabian StyleField, Robert W., and Jun Jie Wu. 2022. "Permeate Flux in Ultrafiltration Processes—Understandings and Misunderstandings" Membranes 12, no. 2: 187. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes12020187
APA StyleField, R. W., & Wu, J. J. (2022). Permeate Flux in Ultrafiltration Processes—Understandings and Misunderstandings. Membranes, 12(2), 187. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes12020187






