Role of Ligand Distribution in the Cytoskeleton-Associated Endocytosis of Ellipsoidal Nanoparticles
Abstract
1. Introduction
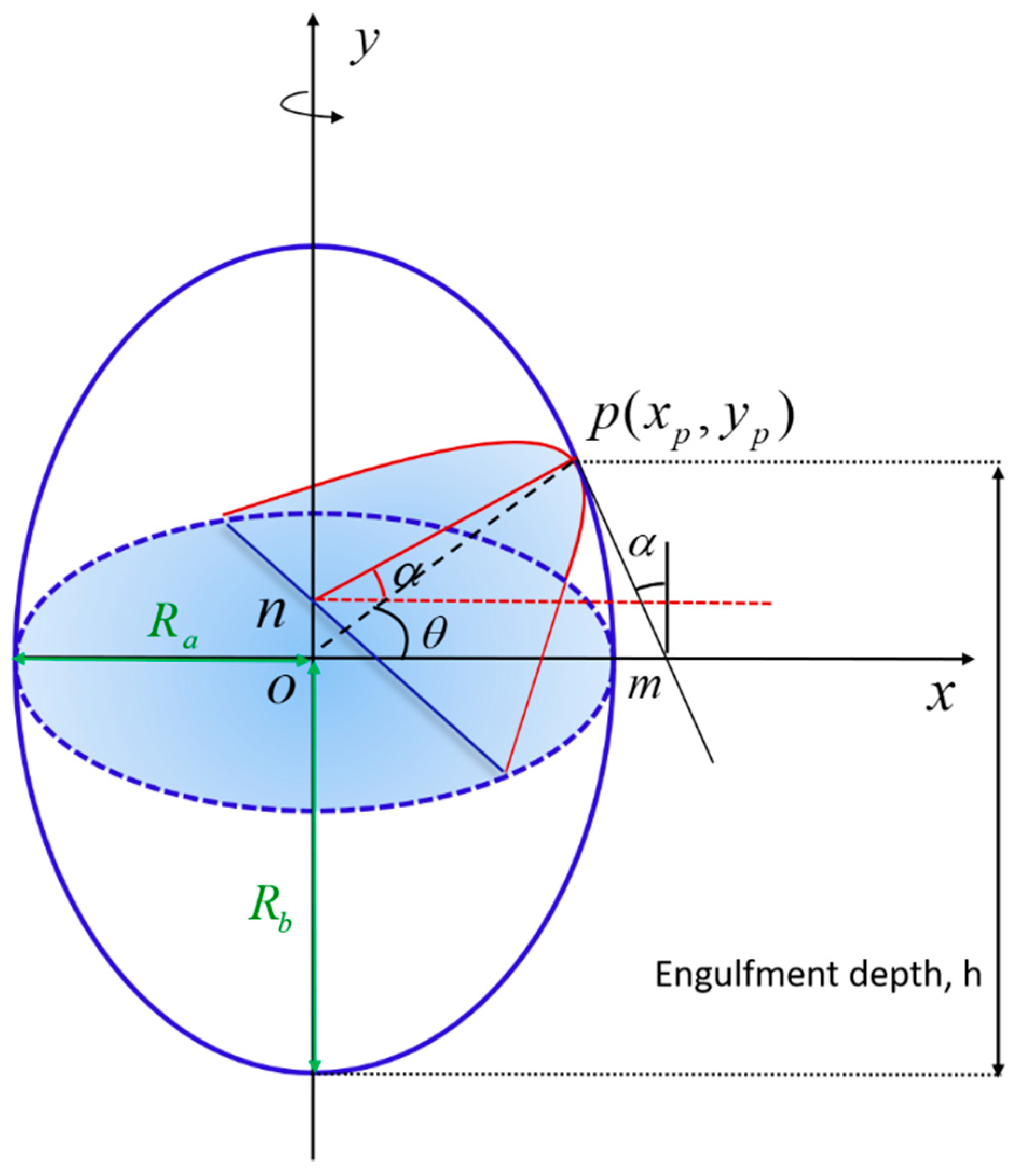
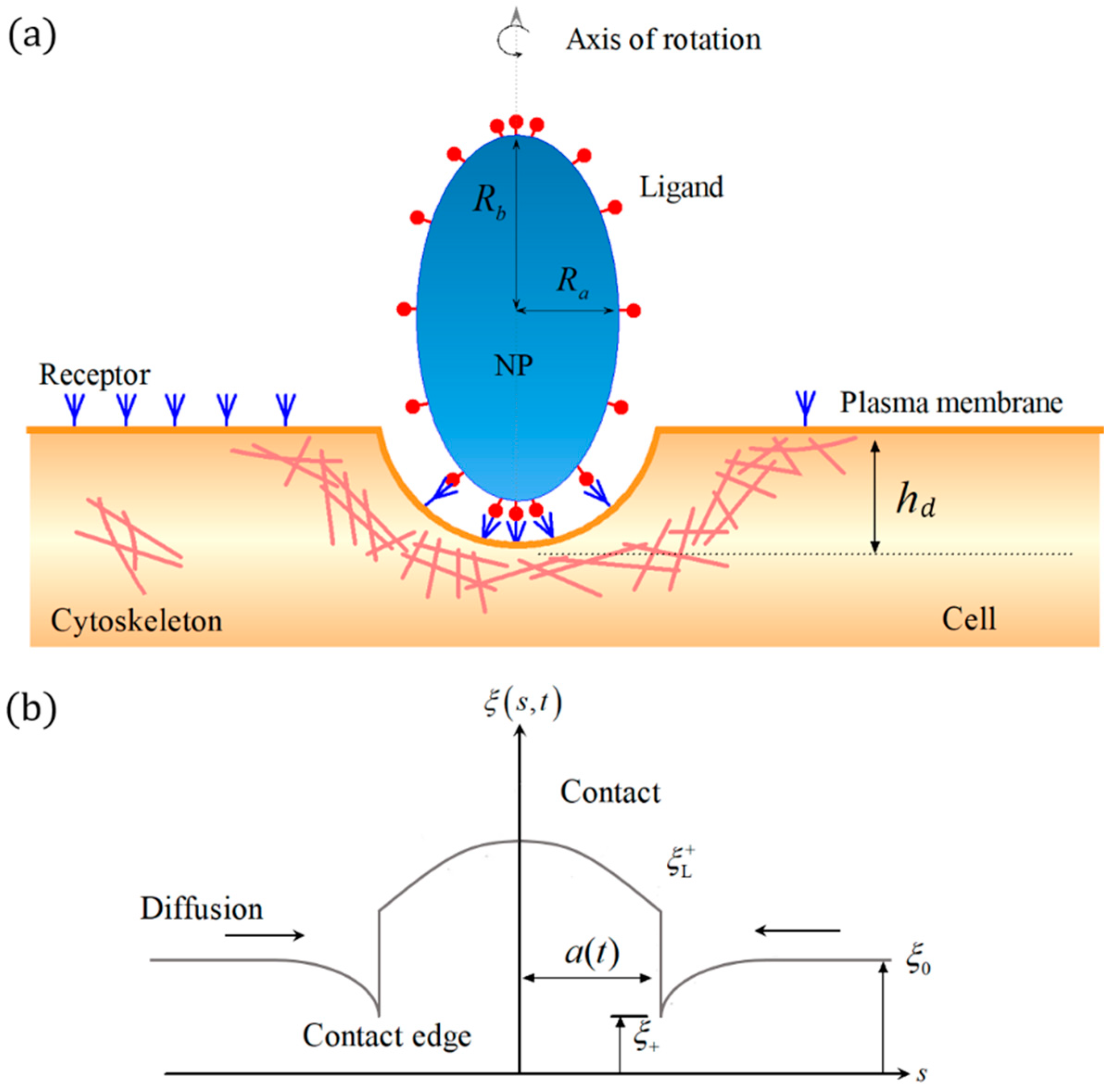
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
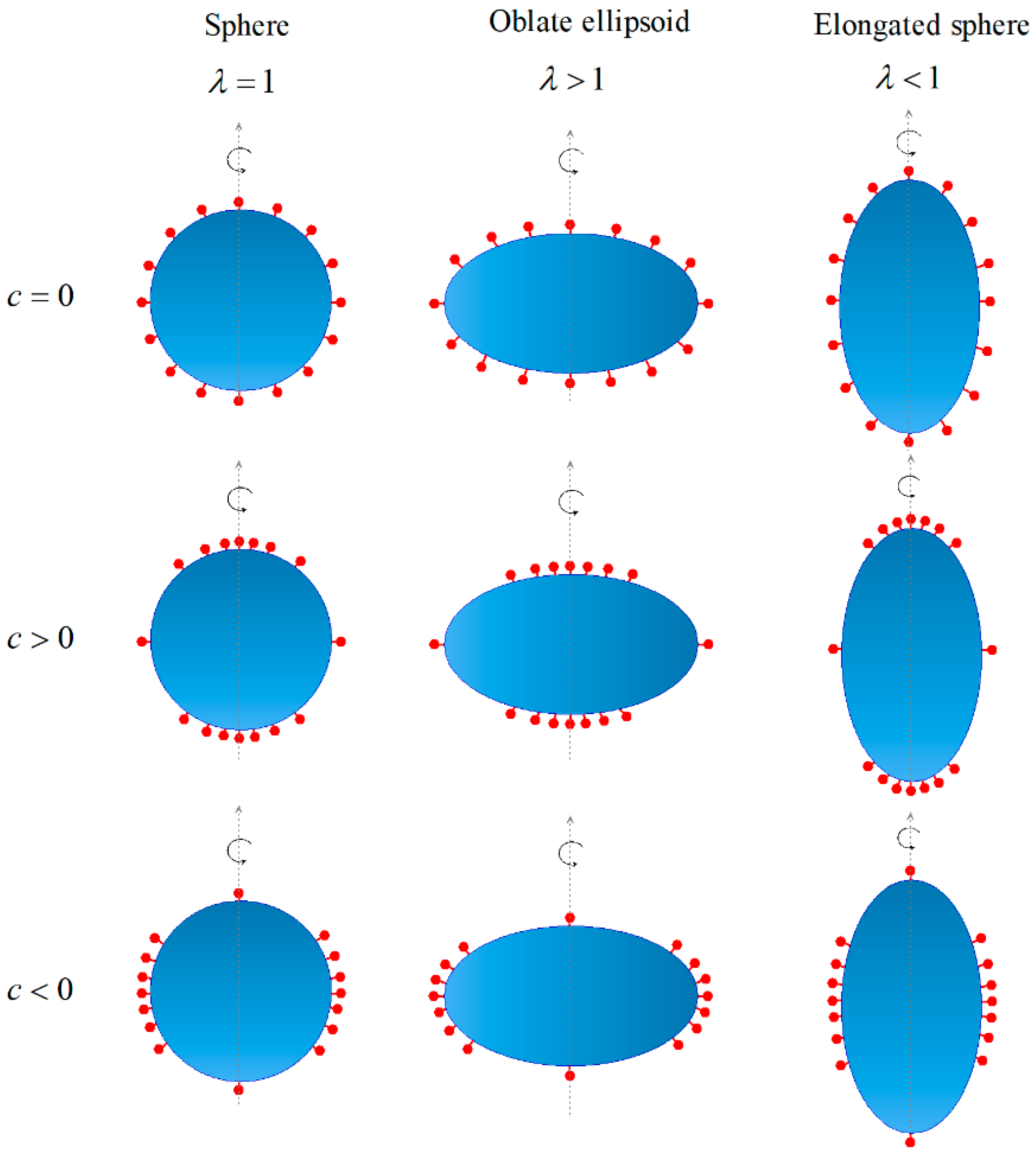
3.1. Influence of Ligand Distribution on the Cellular Uptake of NPs with Different Shapes
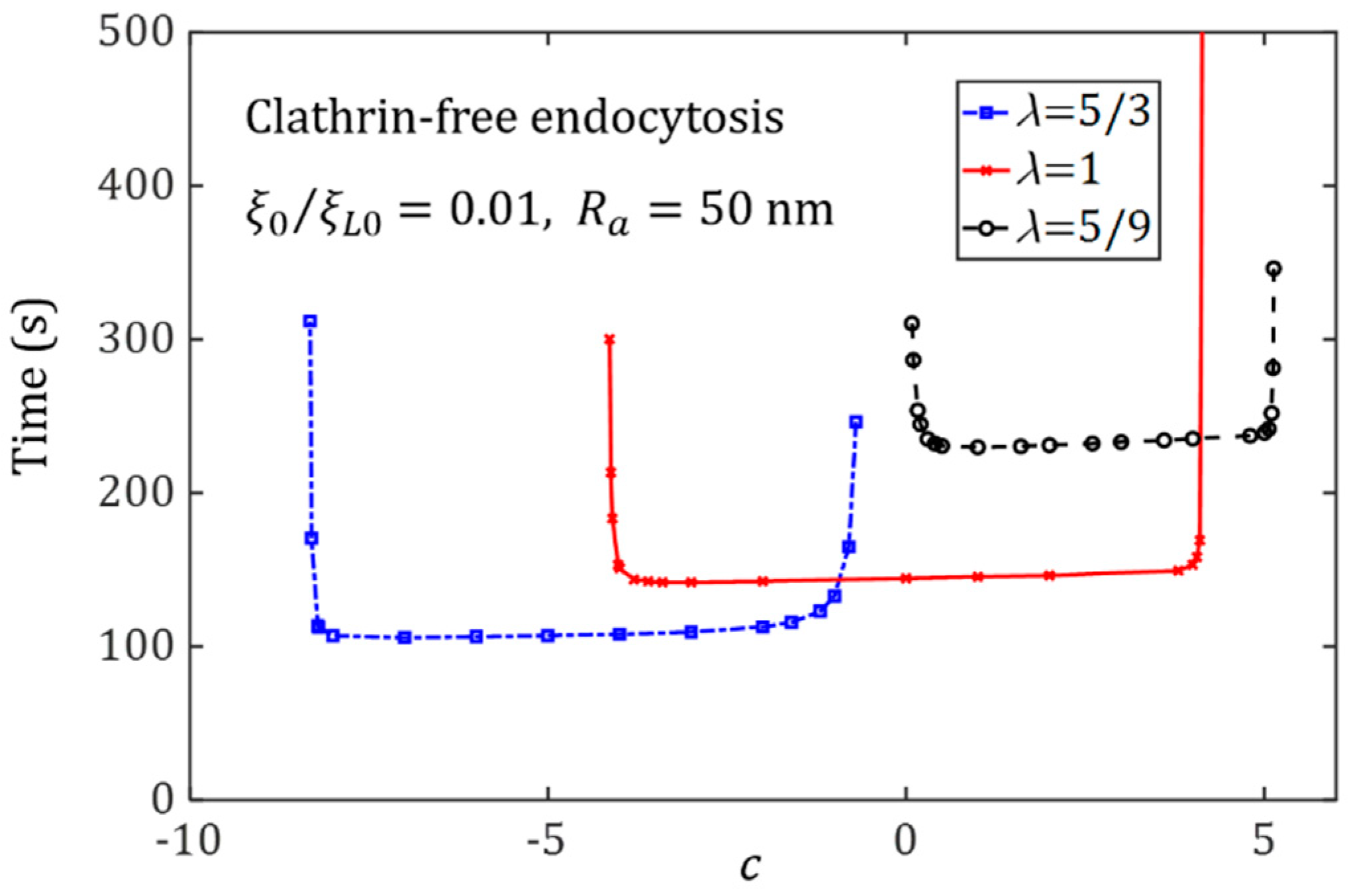
3.2. Effect of Ligand Distribution on the Cytoskeleton-Associated Endocytosis
3.3. Effect of Ligand Distribution on the Cellular Uptake of NPs under Different Initial Receptor Densities
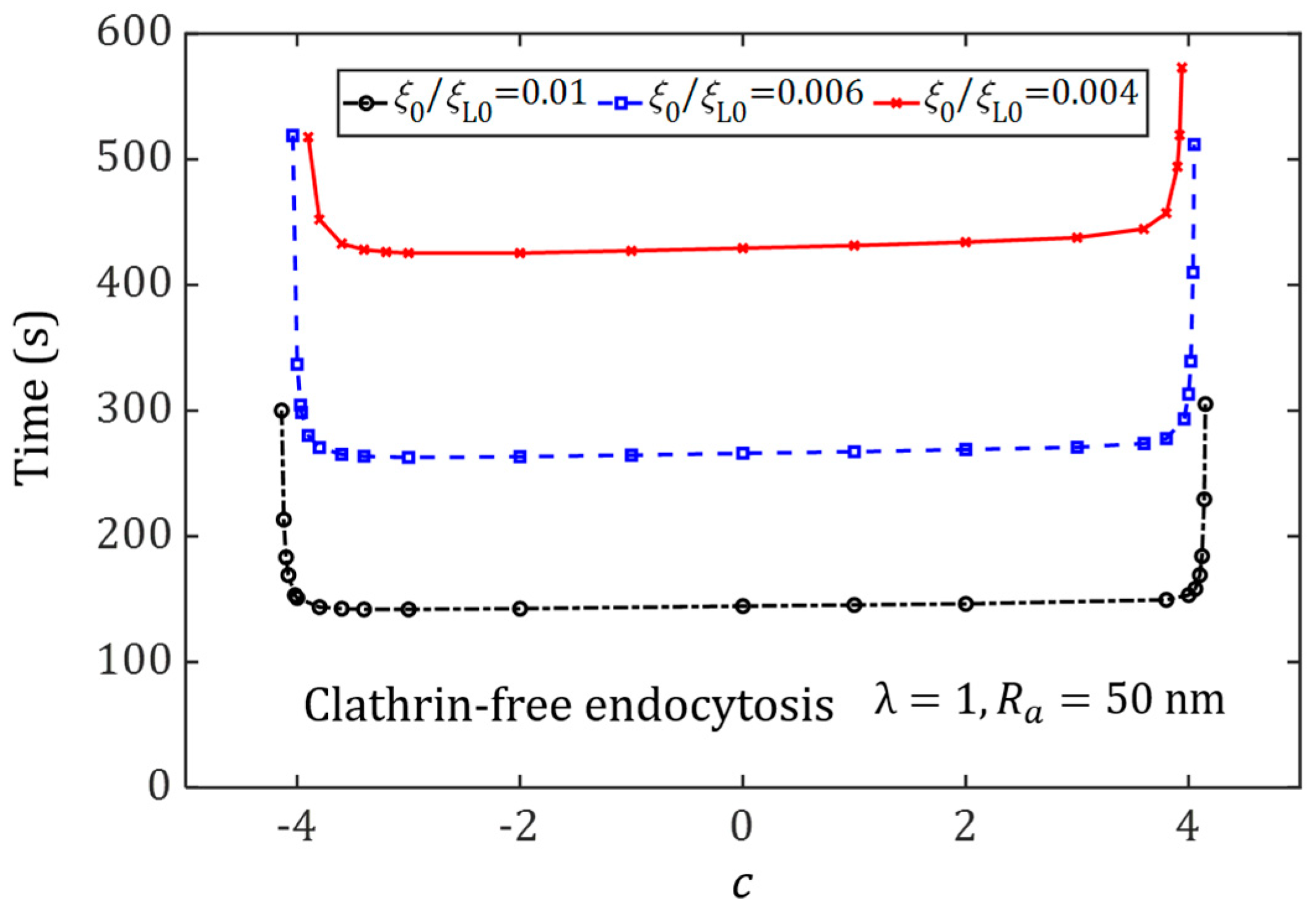
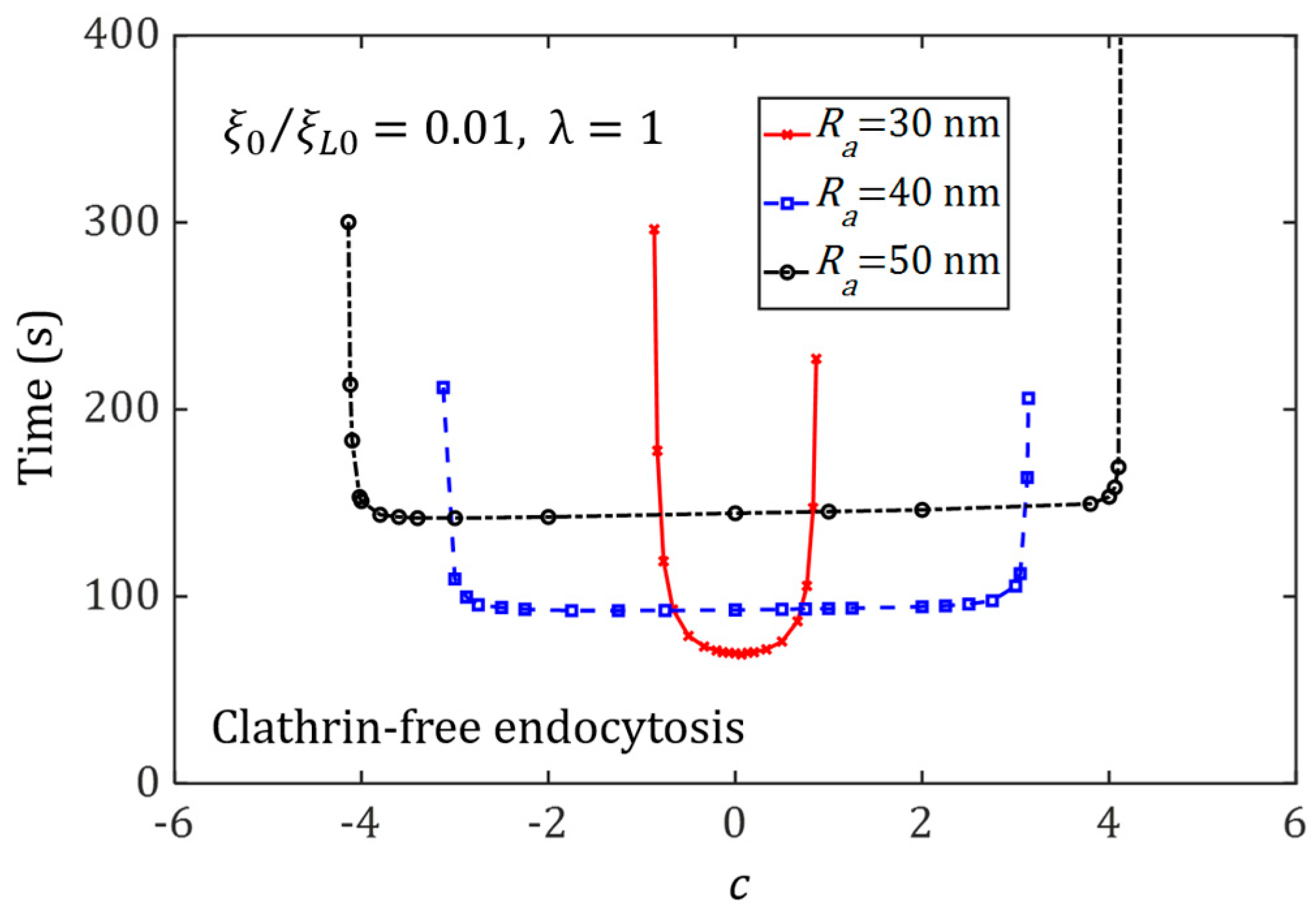
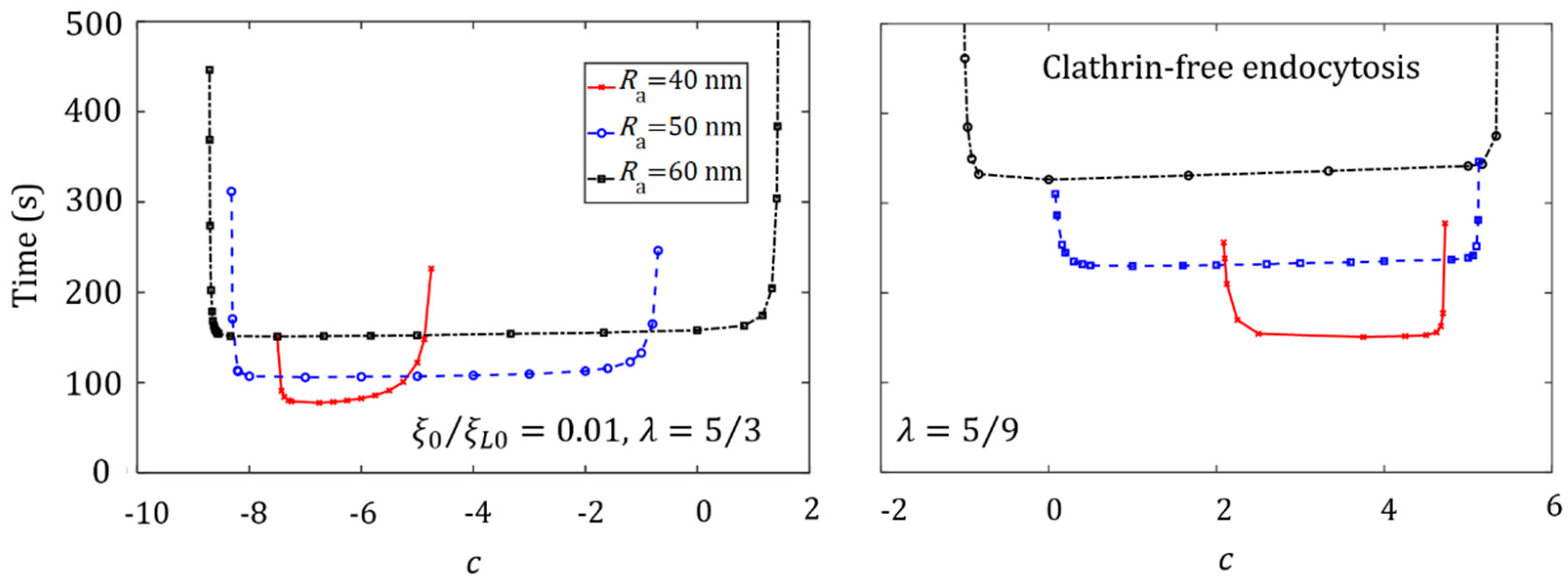
3.4. Effect of Ligand Distribution on the Cellular Uptake of NP with Different Sizes
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
Appendix B
References
- Bao, G.; Bazilevs, Y.; Chung, J.-H.; Decuzzi, P.; Espinosa, H.D.; Ferrari, M.; Gao, H.; Hossain, S.S.; Hughes, T.J.R.; Kamm, R.D.; et al. USNCTAM perspectives on mechanics in medicine. J. R. Soc. Interface 2014, 11, 20140301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poland, C.A.; Duffin, R.; Kinloch, I.; Maynard, A.; Wallace, W.A.H.; Seaton, A.; Stone, V.; Brown, S.; MacNee, W.; Donaldson, K. Carbon nanotubes introduced into the abdominal cavity of mice show asbestos-like pathogenicity in a pilot study. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2008, 3, 423–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sahay, G.; Alakhova, D.Y.; Kabanov, A.V. Endocytosis of nanomedicines. J. Control. Release 2010, 145, 182–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, H.; Shi, W.; Freund, L.B. Mechanics of receptor-mediated endocytosis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 9469–9474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, W.; Wang, J.; Fan, X.; Gao, H. Size and shape effects on diffusion and absorption of colloidal particles near a partially absorbing sphere: Implications for uptake of nanoparticles in animal cells. Phys. Rev. E 2008, 78, 061914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, S.; Li, J.; Lykotrafitis, G.; Bao, G.; Suresh, S. Size-Dependent Endocytosis of Nanoparticles. Adv. Mater. 2009, 21, 419–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dasgupta, S.; Auth, T.; Gompper, G. Shape and Orientation Matter for the Cellular Uptake of Nonspherical Particles. Nano Lett. 2014, 14, 687–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Decuzzi, P.; Ferrari, M. The Receptor-Mediated Endocytosis of Nonspherical Particles. Biophys. J. 2008, 94, 3790–3797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niikura, K.; Matsunaga, T.; Suzuki, T.; Kobayashi, S.; Yamaguchi, H.; Orba, Y.; Kawaguchi, A.; Hasegawa, H.; Kajino, K.; Ninomiya, T.; et al. Gold Nanoparticles as a Vaccine Platform: Influence of Size and Shape on Immunological Responses in Vitro and in Vivo. ACS Nano 2013, 7, 3926–3938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, X.; von Dem Bussche, A.; Hurt, R.H.; Kane, A.B.; Gao, H. Cell entry of one-dimensional nanomaterials occurs by tip recognition and rotation. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2011, 6, 714–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yi, X.; Gao, H. Phase diagrams and morphological evolution in wrapping of rod-shaped elastic nanoparticles by cell membrane: A two-dimensional study. Phys. Rev. E 2014, 89, 062712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richards, D.M.; Endres, R.G. Target shape dependence in a simple model of receptor-mediated endocytosis and phagocytosis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, 6113–6118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.; Zhang, Y.; Yuan, H.; Gao, H.; Zhang, S. Role of Nanoparticle Geometry in Endocytosis: Laying Down to Stand Up. Nano Lett. 2013, 13, 4546–4550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Li, L. Coupled elasticity–diffusion model for the effects of cytoskeleton deformation on cellular uptake of cylindrical nanoparticles. J. R. Soc. Interface 2015, 12, 20141023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, X.; Shi, X.; Gao, H. A Universal Law for Cell Uptake of One-Dimensional Nanomaterials. Nano Lett. 2014, 14, 1049–1055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, J.; Zhang, L.; Wang, J.; Feng, Q.; Liu, D.; Yin, Q.; Xu, D.; Wei, Y.; Ding, B.; Shi, X.; et al. Tunable Rigidity of (Polymeric Core)-(Lipid Shell) Nanoparticles for Regulated Cellular Uptake. Adv. Mater. 2015, 27, 1402–1407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yi, X.; Gao, H. Cell membrane wrapping of a spherical thin elastic shell. Soft Matter 2015, 11, 1107–1115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, X.; Shi, X.; Gao, H. Cellular Uptake of Elastic Nanoparticles. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2011, 107, 098101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, F.; Wang, H.; Li, H.; Cheng, P.; Shi, X. Molecular simulation of diffusion of rigidity-tuned nanoparticles in biological hydrogels. Acta Mech. Sin. 2019, 35, 376–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Yang, H.; Liu, Y.; Gong, X.; Huang, H. Numerical study of clathrin-mediated endocytosis of nanoparticles by cells under tension. Acta Mech. Sin. 2019, 35, 691–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Liu, X.; Zhou, Y.; Wang, J. On Resistance to Virus Entry into Host Cells. Biophys. J. 2012, 102, 2230–2233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, S.X.; Wirtz, D. Mechanics of Enveloped Virus Entry into Host Cells. Biophys. J. 2006, 90, L10–L12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Li, L.; Zhou, Y. Creep effect on cellular uptake of viral particles. Chin. Sci. Bull. 2014, 59, 2277–2281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Wang, N. Tissue cell differentiation and multicellular evolution via cytoskeletal stiffening in mechanically stressed microenvironments. Acta Mech. Sin. 2019, 35, 270–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, H.; Ye, H.; Zhang, H.; Zheng, Y. Wrapping of nanoparticles by the cell membrane: The role of interactions between the nanoparticles. Soft Matter 2015, 11, 8674–8683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Yao, H.; Shi, X. Cooperative entry of nanoparticles into the cell. J. Mech. Phys. Solids 2014, 73, 151–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bahrami, A.H.; Lipowsky, R.; Weikl, T.R. The role of membrane curvature for the wrapping of nanoparticles. Soft Matter 2016, 12, 581–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, H. Probing mechanical principles of cell–nanomaterial interactions. J. Mech. Phys. Solids 2014, 62, 312–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, A.; Sun, R. Role of interstitial flow in tumor migration through 3D ECM. Acta Mech. Sin. 2020, 36, 768–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huo, B.; Zhao, Y.; Bai, X.; Sun, Q.; Jiao, F. Regulation of substrate surface topography on differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells. Acta Mech. Sin. 2020, 36, 1158–1169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Li, X.; Li, Z.; Gao, H. Surface-structure-regulated penetration of nanoparticles across a cell membrane. Nanoscale 2012, 4, 3768–3775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, L.; Zhang, W.; Wang, J. A viscoelastic–stochastic model of the effects of cytoskeleton remodelling on cell adhesion. R. Soc. Open Sci. 2016, 3, 160539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schubertová, V.; Martinez-Veracoechea, F.J.; Vácha, R. Influence of ligand distribution on uptake efficiency. Soft Matter 2015, 11, 2726–2730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Decuzzi, P. Facilitating the Clinical Integration of Nanomedicines: The Roles of Theoretical and Computational Scientists. ACS Nano 2016, 10, 8133–8138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, L.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, J. Effects of ligand distribution on receptor-diffusion-mediated cellular uptake of nanoparticles. R. Soc. Open Sci. 2017, 4, 170063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bahrami, A.H. Orientational changes and impaired internalization of ellipsoidal nanoparticles by vesicle membranes. Soft Matter 2013, 9, 8642–8646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vácha, R.; Martinez-Veracoechea, F.J.; Frenkel, D. Receptor-Mediated Endocytosis of Nanoparticles of Various Shapes. Nano Lett. 2011, 11, 5391–5395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaksonen, M.; Toret, C.P.; Drubin, D.G. Harnessing actin dynamics for clathrin-mediated endocytosis. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2006, 7, 404–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Engqvist-Goldstein, Å.E.Y.; Drubin, D.G. Actin Assembly and Endocytosis: From Yeast to Mammals. Annu. Rev. Cell Dev. Biol. 2003, 19, 287–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qualmann, B.; Kessels, M.M.; Kelly, R.B. Molecular Links between Endocytosis and the Actin Cytoskeleton. J. Cell Biol. 2000, 150, F111–F116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeng, R.L.; Welch, M.D. Cytoskeleton: Actin and endocytosis—No longer the weakest link. Curr. Biol. 2001, 11, R691–R694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, M.P.; Koyuncu, O.O.; Enquist, L.W. Subversion of the actin cytoskeleton during viral infection. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2011, 9, 427–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coller, K.E.; Berger, K.L.; Heaton, N.S.; Cooper, J.D.; Yoon, R.; Randall, G. RNA Interference and Single Particle Tracking Analysis of Hepatitis C Virus Endocytosis. PLoS Pathog. 2009, 5, e1000702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bettina, S.; Fackler, O.T. How hiv takes advantage of the cytoskeleton in entry and replication. Viruses 2011, 3, 293–311. [Google Scholar]
- Alberts, B.; Johnson, A.; Lewis, J.; Raff, M.; Roberts, K.; Walter, P. Studying gene expression and function. In Molecular Biology of the Cell, 4th ed.; Garland Science: New York, NY, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Kubo, Y.; Yoshii, H.; Kamiyama, H.; Tominaga, C.; Tanaka, Y.; Sato, H.; Yamamoto, N. Ezrin, Radixin, and Moesin (ERM) proteins function as pleiotropic regulators of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 infection. Virology 2008, 375, 130–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, Y.; Zhang, F.; Zhang, L.; Liu, S.; Cai, M.; Shan, Y.; Wang, X.; Wang, H.; Wang, H. The Process of Wrapping Virus Revealed by a Force Tracing Technique and Simulations. Adv. Sci. 2017, 4, 1600489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Obataya, I.; Nakamura, C.; Han, S.; Nakamura, N.; Miyake, J. Nanoscale Operation of a Living Cell Using an Atomic Force Microscope with a Nanoneedle. Nano Lett. 2005, 5, 27–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beard, J.D.; Guy, R.H.; Gordeev, S.N. Mechanical Tomography of Human Corneocytes with a Nanoneedle. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2013, 133, 1565–1571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, H.; Wen, J.; Xiao, Y.; Liu, J.; Hopyan, S.; Radisic, M.; Simmons, C.A.; Sun, Y. In Situ Mechanical Characterization of the Cell Nucleus by Atomic Force Microscopy. ACS Nano 2014, 8, 3821–3828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Helfrich, W. Elastic Properties of Lipid Bilayers: Theory and Possible Experiments. Z. Nat. C 1973, 28c, 693–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freund, L.; Lin, Y. The role of binder mobility in spontaneous adhesive contact and implications for cell adhesion. J. Mech. Phys. Solids 2004, 52, 2455–2472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicola, A.V.; Hou, J.; Major, E.O.; Straus, S.E. Herpes Simplex Virus Type 1 Enters Human Epidermal Keratinocytes, but Not Neurons, via a pH-Dependent Endocytic Pathway. J. Virol. 2005, 79, 7609–7616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, K.L. Contact Mechanics; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1987. [Google Scholar]
- Bell, G.I. Models for the Specific Adhesion of Cells to Cells. Science 1978, 200, 618–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Evans, E.; Rawicz, W. Entropy-driven tension and bending elasticity in condensed-fluid membranes. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1990, 64, 2094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sweeney, T.E.; Wong, H.R.; Khatri, P. Robust classification of bacterial and viral infections via integrated host gene expression diagnostics. Sci. Transl. Med. 2016, 8, 346ra91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, J.; Gastaminza, P.; Cheng, G.; Kapadia, S.; Kato, T.; Burton, D.R.; Wieland, S.F.; Uprichard, S.L.; Wakita, T.; Chisari, F.V. Robust hepatitis C virus infection in vitro. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 9294–9299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yi, X.; Gao, H. Kinetics of receptor-mediated endocytosis of elastic nanoparticles. Nanoscale 2016, 9, 454–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.Y.; Zhang, Y.W. Computational analysis of adhesion force in the indentation of cells using atomic force microscopy. Phys. Rev. E 2008, 77, 021912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, Q.H.; Liu, P.; Gao, H.J.; Zhang, Y.W. A computational modeling for micropipette-manipulated cell detachment from a substrate mediated by receptor–ligand binding. J. Mech. Phys. Solids 2009, 57, 205–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrari, R.; Lupi, M.; Colombo, C.; Morbidelli, M.; D’Incalci, M.; Moscatelli, D. Investigation of size, surface charge, PEGylation degree and concentration on the cellular uptake of polymer nanoparticles. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2014, 123, 639–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harris, W.F. Curvature of ellipsoids and other surfaces. Ophthalmic Physiol. Opt. 2006, 26, 497–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, Y.; Li, L.; Wang, J. Role of Ligand Distribution in the Cytoskeleton-Associated Endocytosis of Ellipsoidal Nanoparticles. Membranes 2021, 11, 993. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes11120993
Zhang Y, Li L, Wang J. Role of Ligand Distribution in the Cytoskeleton-Associated Endocytosis of Ellipsoidal Nanoparticles. Membranes. 2021; 11(12):993. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes11120993
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Yudie, Long Li, and Jizeng Wang. 2021. "Role of Ligand Distribution in the Cytoskeleton-Associated Endocytosis of Ellipsoidal Nanoparticles" Membranes 11, no. 12: 993. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes11120993
APA StyleZhang, Y., Li, L., & Wang, J. (2021). Role of Ligand Distribution in the Cytoskeleton-Associated Endocytosis of Ellipsoidal Nanoparticles. Membranes, 11(12), 993. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes11120993






