Hydrogen Separation Performance of UiO-66-NH2 Membranes Grown via Liquid-Phase Epitaxy Layer-by-Layer Deposition and One-Pot Synthesis
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Synthesis Procedures
2.2.1. Surface Functionalization Process
2.2.2. Synthesis of UiO-66-NH2 on α-Al2O3
UiO-66-NH2 Layer-by-Layer Synthesis Procedure (U-LBL)
UiO-66-NH2 One-Pot Synthesis Procedure (U-OP)
2.3. Sample Characterization
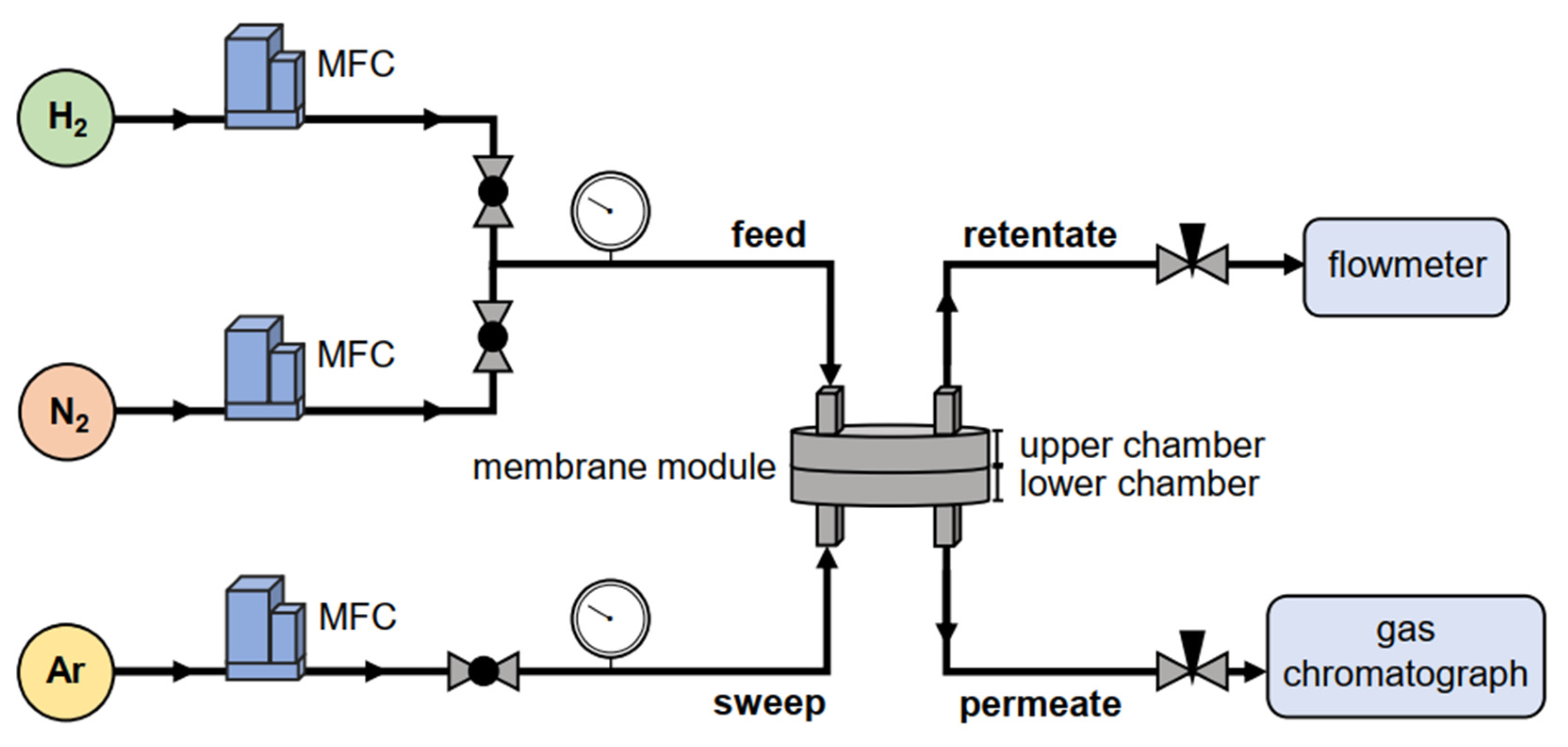
2.4. Permeation Tests
2.5. Gas Separation Experiments
3. Results
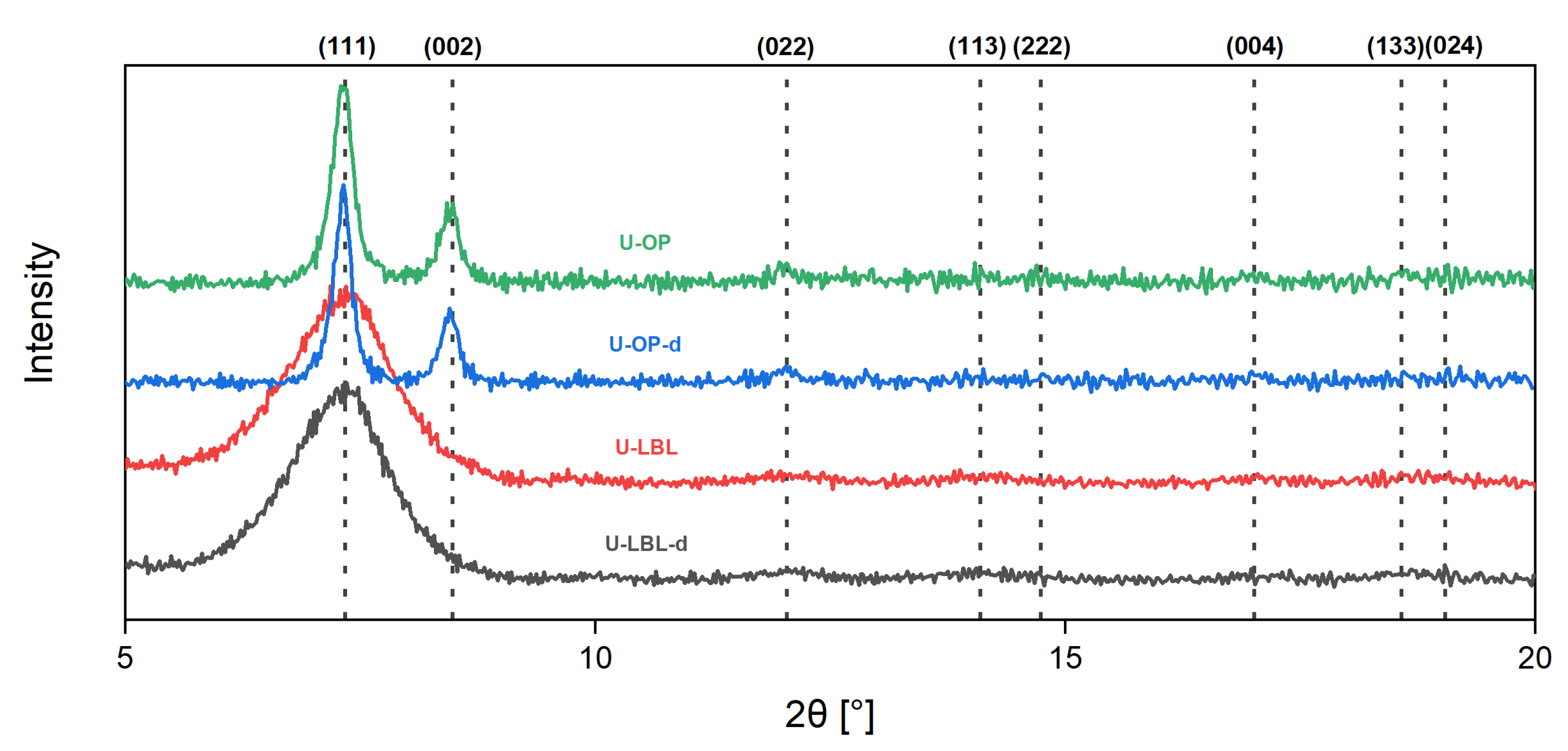
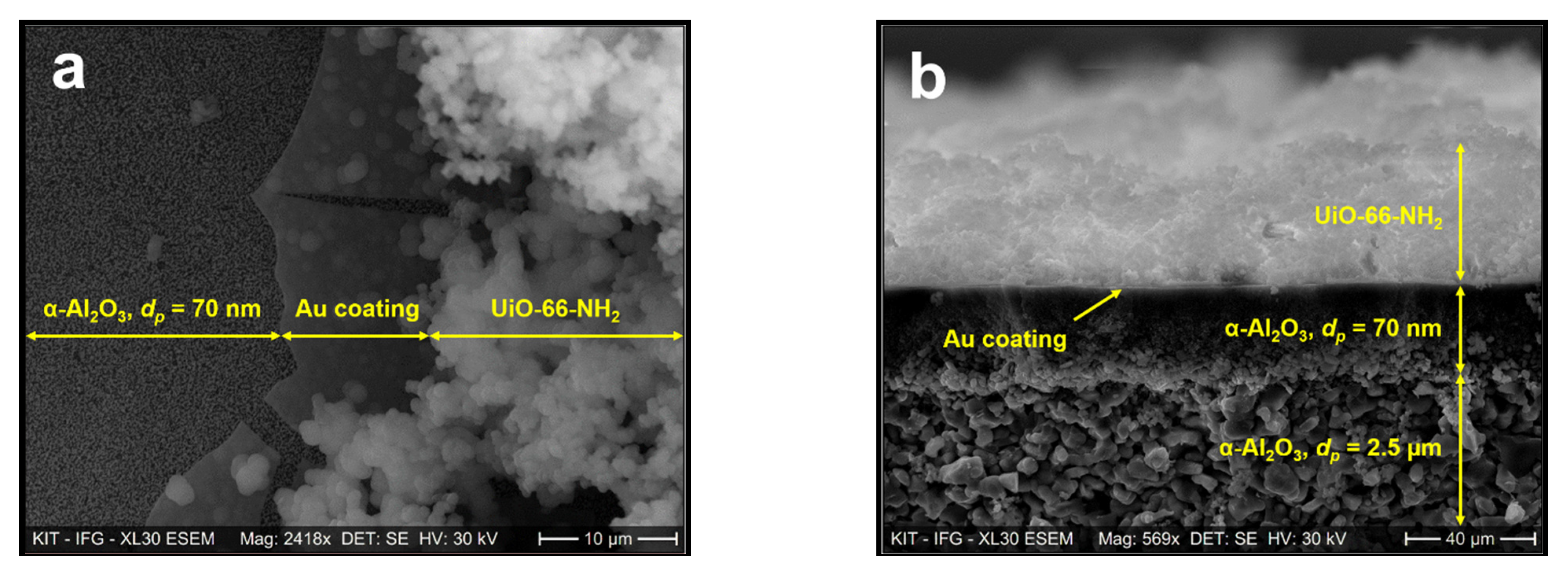
3.1. Sample Characterization
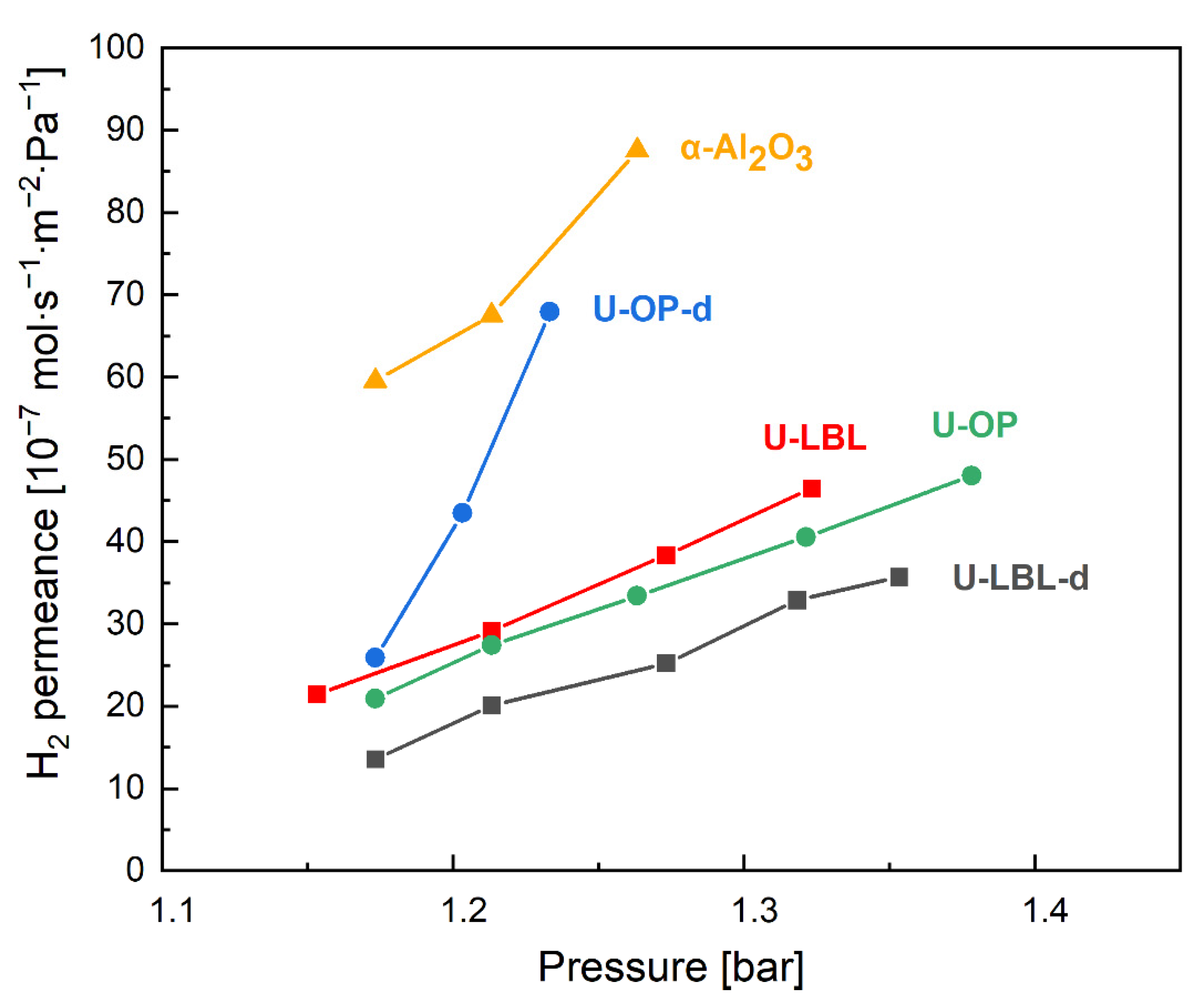
3.2. Permeation Tests
3.3. Gas Separation Experiments
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Directorate-General for Research and Innovation. Final Report of the High-Level Panel of the European Decarbonisation Pathways Initiative; European Commission: Brussels, Belgium, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Hydrogen Tools. International Hydrogen Fueling Stations. Available online: https://h2tools.org/hyarc/hydrogen-data/international-hydrogen-fueling-stations (accessed on 23 June 2021).
- U.S. Department of Energy. Hydrogen Fueling Station Locations. Available online: https://afdc.energy.gov/fuels/hydrogen_locations.html#/find/nearest?fuel=HY&country=US (accessed on 23 June 2021).
- International Organization for Standardization. Hydrogen Fuel Quality—Product Specification; ISO 14687:2019; ISO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Mukundan, R.; Brosha, E.L.; Romero, C.J.; Poppe, D.; Rockward, T. Development of an electrochemical hydrogen contaminant detector. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2020, 167, 147507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bacquart, T.; Moore, N.; Hart, N.; Morris, A.; Aarhaug, T.A.; Kjos, O.; Aupretre, F.; Colas, T.; Haloua, F.; Gozlan, B.; et al. Hydrogen quality sampling at the hydrogen refuelling station—Lessons learnt on sampling at the production and at the nozzle. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2020, 45, 5565–5576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aarhaug, T.A.; Kjos, O.S.; Ferber, A.; Hsu, J.P.; Bacquart, T. Mapping of hydrogen fuel quality in Europe. Front. Energy Res. 2020, 8, 585334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basile, A.; Dalena, F.; Tong, J.; Veziroğlu, T.N. (Eds.) Hydrogen Production, Separation and Purification for Energy; IET Energy Engineering Series; The Institution of Engineering and Technology: London, UK, 2017; ISBN 978-1-78561-101-8. [Google Scholar]
- Sholl, D.S.; Lively, R.P. Seven chemical separations to change the world. Nature 2016, 532, 435–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, X.; Liu, D. Zeolitic imidazolate framework membranes for light olefin/paraffin separation. Crystals 2018, 9, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Robeson, L.M. The upper bound revisited. J. Membr. Sci. 2008, 320, 390–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Z.; Wang, K. The ‘Ideal Selectivity’ vs. ‘True Selectivity’ for permeation of gas mixture in nanoporous membranes. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2018, 323, 012002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Alique, D.; Martinez-Diaz, D.; Sanz, R.; Calles, J. Review of supported pd-based membranes preparation by electroless plating for ultra-pure hydrogen production. Membranes 2018, 8, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Phair, J.W.; Badwal, S.P.S. Materials for separation membranes in hydrogen and oxygen production and future power generation. Sci. Technol. Adv. Mater. 2006, 7, 792–805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Zhang, Y.; Li, Q.; Zhang, G. Metal−organic framework composite membranes: Synthesis and separation applications. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2015, 135, 232–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Q.; Su, Y.; Chi, C.; Cherian, C.T.; Huang, K.; Kravets, V.G.; Wang, F.C.; Zhang, J.C.; Pratt, A.; Grigorenko, A.N.; et al. Ultrathin graphene-based membrane with precise molecular sieving and ultrafast solvent permeation. Nat. Mater. 2017, 16, 1198–1202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- United States Department of Energy; Office of Energy Efficiency and Renewable Energy. Materials for Separation Technologies. Energy and Emission Reduction Opportunities; United States Department of Energy: Washington, DC, USA, 2005; p. 1218755. [Google Scholar]
- Gade, S.K.; Thoen, P.M.; Way, J.D. Unsupported palladium alloy foil membranes fabricated by electroless plating. J. Membr. Sci. 2008, 1–2, 112–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, J.; Matsumura, Y.; Suda, H.; Haraya, K. Thin and dense Pd/CeO2/MPSS composite membrane for hydrogen separation and steam reforming of methane. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2005, 46, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallucci, F.; Paturzo, L.; Famà, A.; Basile, A. Experimental study of the methane steam reforming reaction in a dense Pd/Ag membrane reactor. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2004, 43, 928–933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanz, R.; Calles, J.A.; Alique, D.; Furones, L.; Ordóñez, S.; Marín, P.; Corengia, P.; Fernandez, E. Preparation, testing and modelling of a hydrogen selective Pd/YSZ/SS composite membrane. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2011, 36, 15783–15793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rothenberger, K.; Cugini, A.; Howard, B.; Killmeyer, R.; Ciocco, M.; Morreale, B.; Enick, R.; Bustamante, F.; Mardilovich, I.; Ma, Y. High pressure hydrogen permeance of porous stainless steel coated with a thin palladium film via electroless plating. J. Membr. Sci. 2004, 244, 55–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavka, J.H.; Jakobsen, S.; Olsbye, U.; Guillou, N.; Lamberti, C.; Bordiga, S.; Lillerud, K.P. A new zirconium inorganic building brick forming metal organic frameworks with exceptional stability. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2008, 130, 13850–13851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, D.-W.; Ha, J.; Oruganti, Y.; Moon, H.R. Hydrogen separation and purification with MOF-based materials. Mater. Chem. Front. 2021, 5, 4022–4041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, Y.; Johnson, J.R.; Karvan, O.; Sholl, D.S.; Koros, W.J. Ultem®/ZIF-8 mixed matrix hollow fiber membranes for CO2/N2 separations. J. Membr. Sci. 2012, 401–402, 76–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Wei, J.; Liang, Y.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, X.; Shen, W.; Wang, H. Zeolitic imidazolate framework/graphene oxide hybrid nanosheets as seeds for the growth of ultrathin molecular sieving membranes. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2016, 55, 2048–2052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiggin, S. Classifying metal-organic frameworks MOFs for search and screening. Camb. Crystallogr. Data Cent. 2020. Available online: https://www.ccdc.cam.ac.uk/Community/blog/MOF-classification-search-screen/ (accessed on 23 June 2021).
- Jia, M.; Feng, Y.; Liu, S.; Qiu, J.; Yao, J. Graphene oxide gas separation membranes intercalated by UiO-66-NH2 with enhanced hydrogen separation performance. J. Membr. Sci. 2017, 539, 172–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Qin, W.; Li, Z.; Li, Y. Enhanced stability and CO2 affinity of a UiO-66 type metal–organic framework decorated with dimethyl groups. Dalton Trans. 2012, 41, 9283–9285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anjum, M.W.; Vermoortele, F.; Khan, A.L.; Bueken, B.; De Vos, D.E.; Vankelecom, I.F.J. Modulated UiO-66-based mixed-matrix membranes for CO2 separation. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2015, 7, 25193–25201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Q.; Wiersum, A.D.; Llewellyn, P.L.; Guillerm, V.; Serre, C.; Maurin, G. Functionalizing porous zirconium terephthalate UiO-66(Zr) for natural gas upgrading: A computational exploration. Chem. Commun. 2011, 47, 9603–9605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Q.; Wiersum, A.D.; Jobic, H.; Guillerm, V.; Serre, C.; Llewellyn, P.L.; Maurin, G. Understanding the thermodynamic and kinetic behavior of the CO2/CH4 gas mixture within the porous zirconium terephthalate UiO-66(Zr): A joint experimental and modeling approach. J. Phys. Chem. C 2011, 115, 13768–13774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kandiah, M.; Nilsen, M.H.; Usseglio, S.; Jakobsen, S.; Olsbye, U.; Tilset, M.; Larabi, C.; Quadrelli, E.A.; Bonino, F.; Lillerud, K.P. synthesis and stability of tagged UiO-66 Zr-MOFs. Chem. Mater. 2010, 22, 6632–6640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashem, T.; Ibrahim, A.H.; Wöll, C.; Alkordi, M.H. Grafting zirconium-based metal–organic framework UiO-66-NH2 nanoparticles on cellulose fibers for the removal of Cr(VI) ions and methyl orange from water. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 2019, 2, 5804–5808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashem, T.; Valadez Sánchez, E.P.; Weidler, P.G.; Gliemann, H.; Alkordi, M.H.; Wöll, C. Liquid-phase quasi-epitaxial growth of highly stable, monolithic UiO-66-NH2 MOF thin films on solid substrates. ChemistryOpen 2020, 9, 524–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shekhah, O.; Wang, H.; Kowarik, S.; Schreiber, F.; Paulus, M.; Tolan, M.; Sternemann, C.; Evers, F.; Zacher, D.; Fischer, R.A.; et al. Step-by-step route for the synthesis of metal−organic frameworks. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2007, 129, 15118–15119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chernikova, V.; Shekhah, O.; Eddaoudi, M. Advanced fabrication method for the preparation of MOF thin films: Liquid-phase epitaxy approach meets spin coating method. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 20459–20464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Arslan, H.K.; Shekhah, O.; Wohlgemuth, J.; Franzreb, M.; Fischer, R.A.; Wöll, C. High-throughput fabrication of uniform and homogenous MOF coatings. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2011, 21, 4228–4231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valadez Sánchez, E.P.; Gliemann, H.; Haas-Santo, K.; Ding, W.; Hansjosten, E.; Wohlgemuth, J.; Wöll, C.; Dittmeyer, R. α-Al2O3-supported ZIF-8 SURMOF membranes: Diffusion mechanism of ethene/ethane mixtures and gas separation performance. J. Membr. Sci. 2020, 594, 117421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valadez Sánchez, E.P.; Gliemann, H.; Haas-Santo, K.; Wöll, C.; Dittmeyer, R. ZIF-8 SURMOF Membranes synthesized by au-assisted liquid phase epitaxy for application in gas separation. Chem. Ing. Tech. 2016, 88, 1798–1805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kandiah, M.; Usseglio, S.; Svelle, S.; Olsbye, U.; Lillerud, K.P.; Tilset, M. Post-Synthetic modification of the metal–organic framework compound UiO-66. J. Mater. Chem. 2010, 20, 9848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, S.-L.; Yue, D.-M.; Li, X.-H.; Smith, T.J.; Li, N.; Zong, M.-H.; Wu, H.; Ma, Y.-Z.; Lou, W.-Y. Novel nano-/micro-biocatalyst: Soybean epoxide hydrolase immobilized on UiO-66-NH 2 MOF for efficient biosynthesis of enantiopure (R)-1, 2-Octanediol in deep eutectic solvents. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2016, 4, 3586–3595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burggraaf, A.J.; Vroon, Z.A.E.P.; Keizer, K.; Verweij, H. Permeation of single gases in thin zeolite MFI membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 1998, 144, 77–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friebe, S.; Geppert, B.; Steinbach, F.; Caro, J. Metal–organic framework UiO-66 layer: A highly oriented membrane with good selectivity and hydrogen permeance. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 12878–12885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vahidi, M.; Tavasoli, A.; Rashidi, A.M. Preparation of amine functionalized UiO-66, mixing with aqueous N–methyldiethanolamine and application on CO2 solubility. J. Nat. Gas Sci. Eng. 2016, 28, 651–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, A.X.; McEntee, M.; Browe, M.A.; Hall, M.G.; DeCoste, J.B.; Peterson, G.W. MOFabric: Electrospun nanofiber mats from PVDF/UiO-66-NH2 for chemical protection and decontamination. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 13632–13636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.-F.; Feng, Y.; Wang, Z.; Jia, M.; Yao, J. Fabrication of cellulose nanofibrils/UiO-66-NH2 composite membrane for CO2/N2 separation. J. Membr. Sci. 2018, 568, 10–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Y.; Zhang, H.; Song, F.; Huang, T.; Ji, J.; Zhong, Q.; Chu, W.; Xu, Q. UiO-66-NH2/GO composite: Synthesis, characterization and CO2 adsorption performance. Materials 2018, 11, 589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, S.-H.; Brunetti, A.; Drioli, E.; Barbieri, G. H2 separation from H2/N2 and H2/CO mixtures with Co-polyimide hollow fiber module. Sep. Sci. Technol. 2010, 46, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dechnik, J.; Sumby, C.J.; Janiak, C. Enhancing mixed-matrix membrane performance with metal–organic framework additives. Cryst. Growth Des. 2017, 17, 4467–4488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Venna, S.R.; Lartey, M.; Li, T.; Spore, A.; Kumar, S.; Nulwala, H.B.; Luebke, D.R.; Rosi, N.L.; Albenze, E. Fabrication of MMMs with improved gas separation properties using externally-functionalized MOF particles. J. Mater. Chem. A 2015, 3, 5014–5022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez, E.P.V. Thin Film MOFs (SURMOFs) for Application in Gas Separation; KIT Scientific Publishing: Karlsruhe, Germany, 2019; p. 180. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.; Chi, C.; Tao, J.; Peng, Y.; Ying, S.; Qian, Y.; Dong, J.; Hu, Z.; Gu, Y.; Zhao, D. Improving the hydrogen selectivity of graphene oxide membranes by reducing non-selective pores with intergrown ZIF-8 crystals. Chem. Commun. 2016, 52, 8087–8090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, A.; Liu, Q.; Wang, N.; Zhu, Y.; Caro, J. Bicontinuous zeolitic imidazolate framework ZIF-8@GO membrane with enhanced hydrogen selectivity. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2014, 136, 14686–14689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, S.; Falconer, J.L.; Noble, R.D.; Krishna, R. Modeling permeation of CO2/CH4, CO2/N2, and N2/CH4 mixtures across SAPO-34 membrane with the Maxwell−Stefan equations. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2007, 46, 3904–3911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Do, D.D.; Do, H.D. Cooperative and competitive adsorption of ethylene, ethane, nitrogen and argon on graphitized carbon black and in slit pores. Adsorption 2005, 11, 35–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, W.F.; Chung, T.-S.; Matsuura, T. Pervaporation study on the dehydration of aqueous butanol solutions: A comparison of flux vs. permeance, separation factor vs. selectivity. J. Membr. Sci. 2004, 245, 199–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drioli, E.; Giorno, L. (Eds.) Encyclopedia of Membranes; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2016; ISBN 978-3-662-44323-1. [Google Scholar]



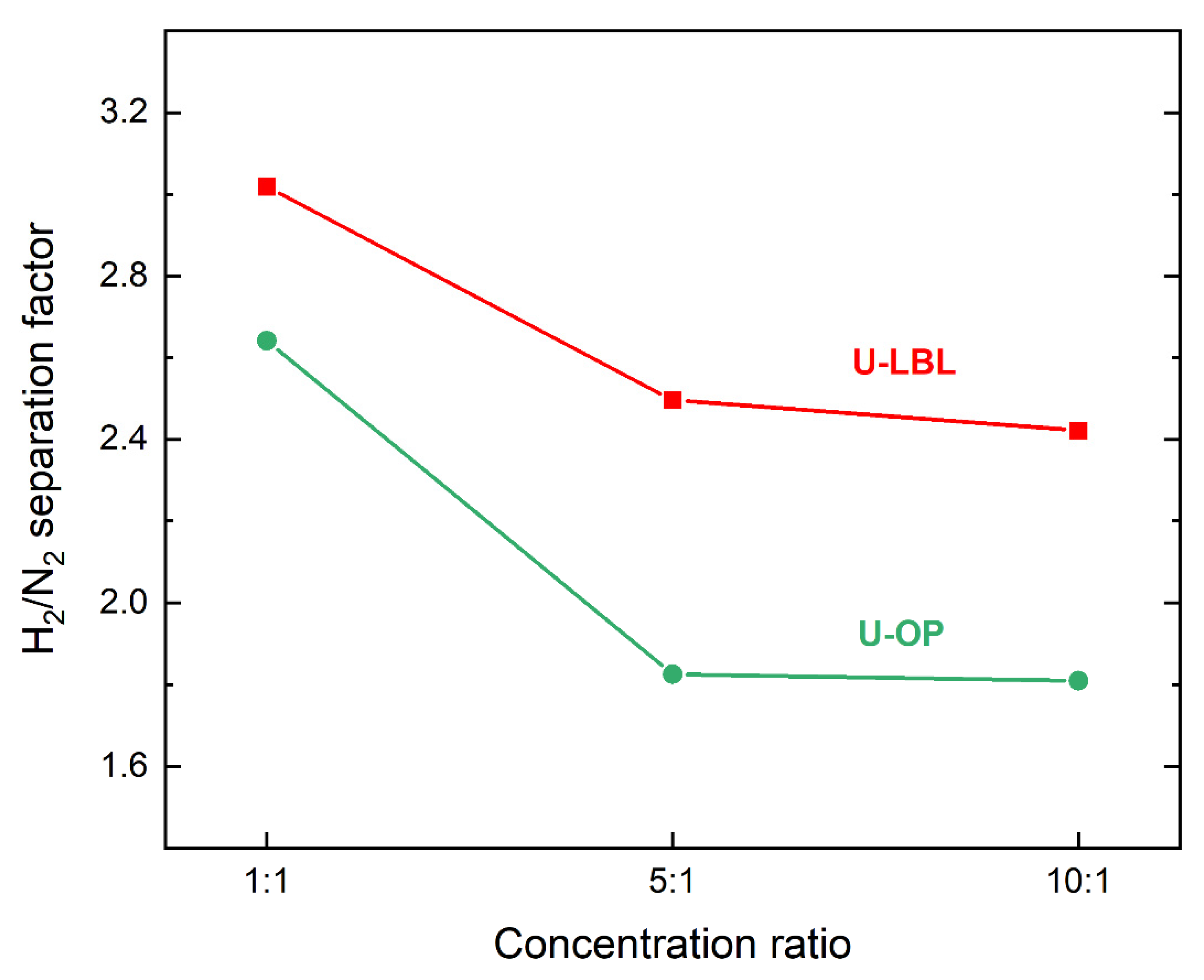
| Concentration Ratio | H2/N2 Separation Factor | H2 Permeance (10−7 mol⋅s−1⋅m−2⋅Pa−1) | N2 Permeance (10−7 mol⋅s−1⋅m−2⋅Pa−1) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| U-LBL | U-OP | U-LBL | U-OP | U-LBL | U-OP | |
| 1:1 | 3.02 | 2.64 | 119.5 | 196.9 | 27.7 | 49.4 |
| 5:1 | 2.50 | 1.83 | 162.0 | 180.2 | 45.5 | 72.5 |
| 10:1 | 2.42 | 1.81 | 157.5 | 177.7 | 45.9 | 72.6 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Micero, A.; Hashem, T.; Gliemann, H.; Léon, A. Hydrogen Separation Performance of UiO-66-NH2 Membranes Grown via Liquid-Phase Epitaxy Layer-by-Layer Deposition and One-Pot Synthesis. Membranes 2021, 11, 735. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes11100735
Micero A, Hashem T, Gliemann H, Léon A. Hydrogen Separation Performance of UiO-66-NH2 Membranes Grown via Liquid-Phase Epitaxy Layer-by-Layer Deposition and One-Pot Synthesis. Membranes. 2021; 11(10):735. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes11100735
Chicago/Turabian StyleMicero, Alessandro, Tawheed Hashem, Hartmut Gliemann, and Aline Léon. 2021. "Hydrogen Separation Performance of UiO-66-NH2 Membranes Grown via Liquid-Phase Epitaxy Layer-by-Layer Deposition and One-Pot Synthesis" Membranes 11, no. 10: 735. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes11100735
APA StyleMicero, A., Hashem, T., Gliemann, H., & Léon, A. (2021). Hydrogen Separation Performance of UiO-66-NH2 Membranes Grown via Liquid-Phase Epitaxy Layer-by-Layer Deposition and One-Pot Synthesis. Membranes, 11(10), 735. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes11100735







