Quantitative Evaluations of Hydrogen Diffusivity in V-X (X = Cr, Al, Pd) Alloy Membranes Based on Hydrogen Chemical Potential
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Procedure
2.2. First Principle Calculation
3. Results
3.1. Experimental Results
3.2. First Principle Calculations
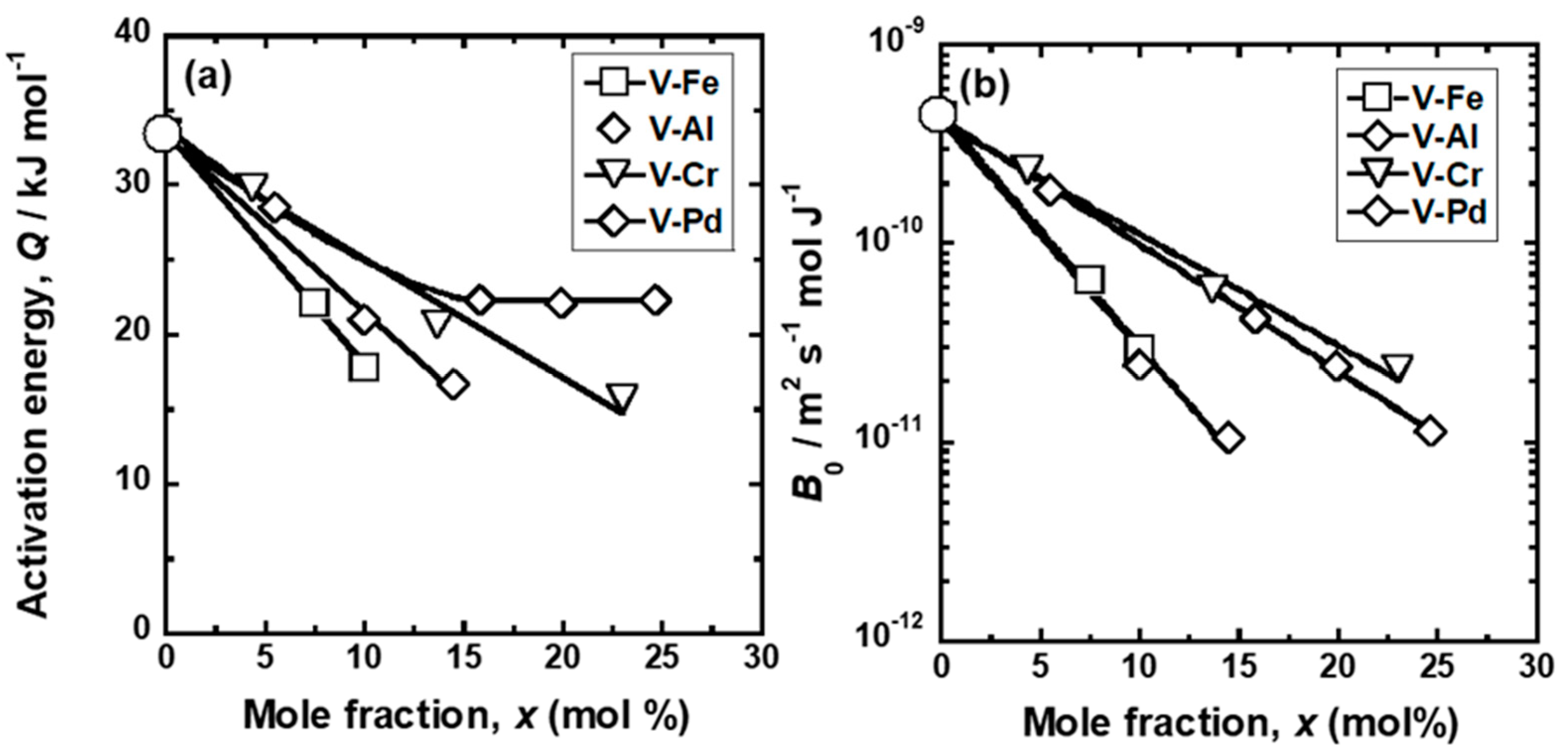
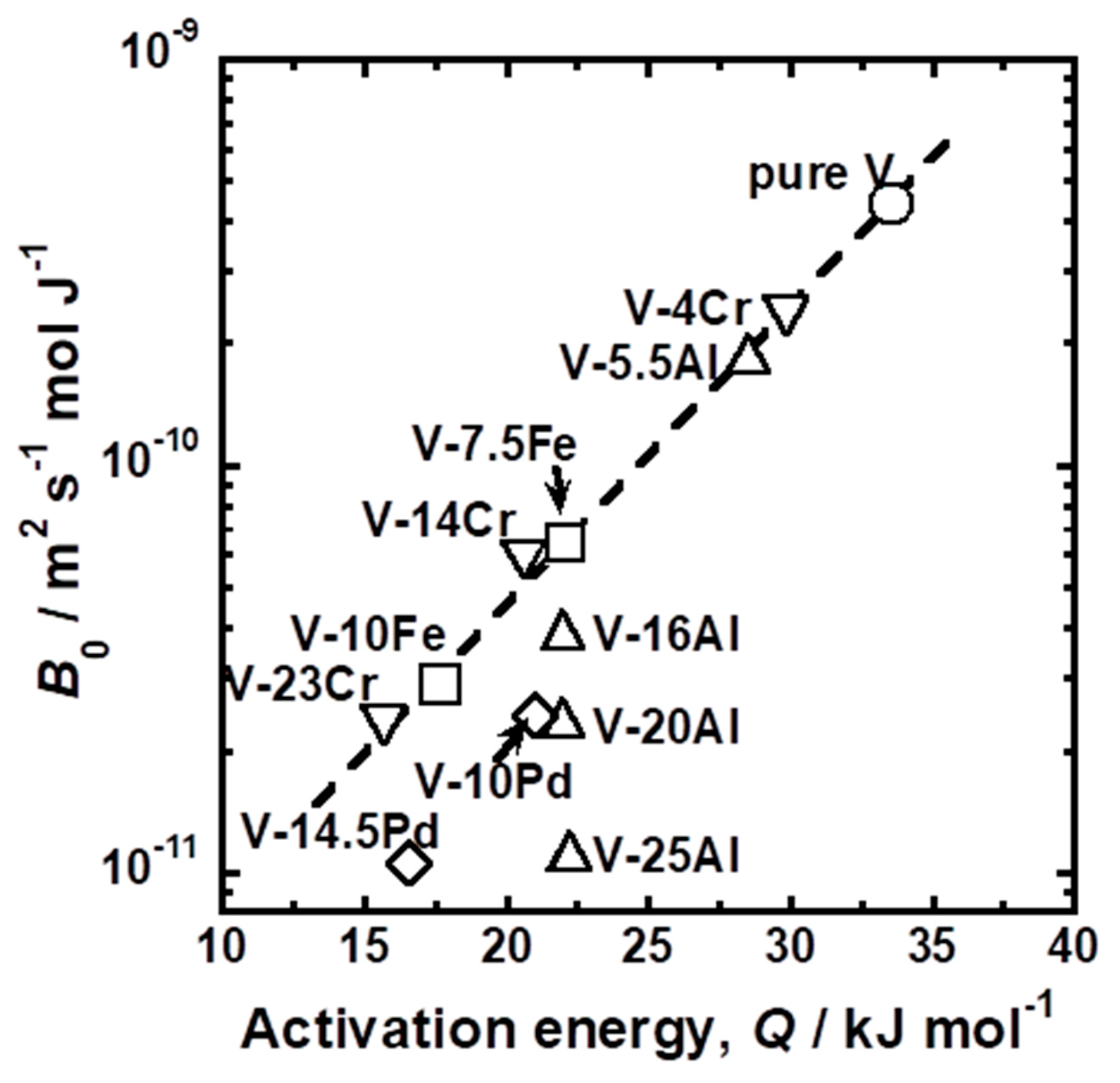
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Valente, A.; Iribarren, D.; Galvez-Martos, J.-L.; Dufour, J. Robust eco-efficiency assessment of hydrogen from biomass gasification as an alternative to conventional hydrogen: A life-cycle study with and without external costs. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 650, 1465–1475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, X.; Shi, Z.; Glass, N.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, J.; Song, D.; Liu, Z.-S.; Wang, H.; Shen, J. A review of PEM hydrogen fuel cell contamination: Impacts, mechanisms, and mitigation. J. Power Sources 2007, 165, 739–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knapton, A.G. Palladium Alloys for Hydrogen Diffusion Membranes a Review of High Permeability Materials. Platin. Met. Rev. 1977, 21, 44–50. [Google Scholar]
- Serra, E.; Kemali, M.; Perujo, A.; Ross, D.K. Metall. Hydrogen and deuterium in Pd-25 pct Ag alloy: Permeation, diffusion, solubilization, and surface reaction. Metall. Mater. Sci. A 1998, 29, 1023–1028. [Google Scholar]
- Buxbaum, R.E.; Kinney, A.B. Hydrogen transport through tubular membranes of palladium-coated tantalum and niobium. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 1996, 35, 530–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dolan, M.D. Non-Pd BCC alloy membranes for industrial hydrogen separation. J. Membr. Sci. 2010, 362, 12–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gahr, S.; Birnbaum, H.K. Hydrogen embrittlement of niobium-III. High temperature behavior. Acta Metall. 1978, 26, 1781–1788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsumoto, Y.; Yukawa, H.; Nambu, T. Quantitative evaluation of hydrogen embrittlement of metal membrane defected by in-situ small punch test under hydrogen permeation. Met. J. 2010, LXIII, 74–78. [Google Scholar]
- Matsumoto, Y.; Yukawa, H.; Nambu, T. Determination of Ductile-to-Brittle Transition Hydrogen Concentrations for V and Nb Alloys using in-situ Small Punch Test. In Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference Small Sample Test Technics (SSTT2012); Matocha, K., Hurst, R., Sun, W., Eds.; OCELOT s.r.o.: Ostrava, Czech Republic, 2012; pp. 132–137. [Google Scholar]
- Amano, M.; Komaki, M.; Nishimura, C. Hydrogen permeation characteristics of palladium-plated V-Ni alloy membranes. J. Less Common Met. 1991, 172–174, 727–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dolan, M.D.; Mclennan, K.G.; Way, J.D. Diffusion of atomic hydrogen through V-Ni alloy membranes under nondilute conditions. J. Phys. Chem. C 2012, 16, 1512–1518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dolan, M.D.; Kellam, M.E.; Mclennan, K.G.; Liang, D.; Song, G. Hydrogen transport properties of several vanadium-based binary alloys. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2013, 38, 9794–9799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishimura, C.; Ozaki, T.; Komaki, M.; Zhang, Y. Hydrogen permeation and transmission electron microscope observations of V-Al alloys. J. Alloys Compd. 2003, 356, 295–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alimov, V.N.; Busnyuk, A.O.; Notkin, M.E.; Peredistov, E.Y.; Livshits, A.I. Hydrogen transport through V–Pd alloy membranes: Hydrogen solution, permeation and diffusion. J. Membr. Sci. 2015, 481, 54–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, A.; Yukawa, H.; Nambu, T.; Matsumoto, Y.; Murata, Y. Quantitative Evaluation of Hydrogen Solubility and Diffusivity of V-Fe Alloys toward the Design of Hydrogen Permeable Membrane for Low Operative Temperature. Mater. Trans. 2016, 57, 1823–1831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yukawa, H.; Nambu, T.; Matsumoto, Y. V-W alloy membranes for hydrogen purification. J. Alloys Compd. 2011, 509, S881–S884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yukawa, H.; Nambu, T.; Matsumoto, Y. Hydrogen solubility and permeability of V-W-Mo alloy membrane for hydrogen separation and purification. J. Alloys Compd. 2013, 580, S386–S390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, A.; Yukawa, H.; Nambu, T.; Matsumoto, Y.; Murata, Y. Consistent description of hydrogen permeability through metal membrane based on hydrogen chemical potential. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2014, 39, 7919–7924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okamoto, H. Supplemental Literature Review of Binary Phase Diagrams: Ag-Li, Ag-Sn, Be-Pu, C-Mn, C-Si, Ca-Li, Cd-Pu, Cr-Ti, Cr-V, Cu-Li, La-Sc, and Li-Sc. J. Phase Equilibria Diffus. 2017, 38, 70–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murray, J.L. AI-V (Aluminum-Vanadium). Bull. Alloy Phase Diagr. 1989, 10, 351–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, J.F. Pd-V (Palladium-Vanadium). Bin. Alloy Phase Diagr. 1990, 3, 3062–3065. [Google Scholar]
- Nambu, T.; Shimizu, N.; Ezaki, H.; Yukawa, H.; Morinaga, M. Hydrogen Permeation of Pure Niobium Metal in Highly Soluble Hydrogen State. J. Jpn. Inst. Met. 2005, 69, 841–847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Kawai, R.; Yukawa, H.; Suzuki, A.; Nambu, T.; Murata, Y. Alloying effects of Fe and Al on formation and decomposition temperatures of vanadium hydride, V2H. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2017, 42, 22564–22574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Segall, M.D.; Lindan, P.J.D.; Probert, M.J.; Pickard, C.J.; Hasnip, P.J.; Clark, S.J.; Payne, M.C. First-principles simulation: Ideas, illustrations and the CASTEP code. J. Phys. Condens. Matt. 2002, 14, 2717–2744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukai, Y. The Metal-Hydrogen System; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1993; pp. 95–100. [Google Scholar]
- Vanmal, H.H.; Buschow, K.H.J.; Miedema, A.R. Hydrogen Absorption in LaNi5 and Related Compounds: Experimental Observations and Their Explanation. J. Less Common Met. 1974, 35, 65–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, A.; Yukawa, H. Review for Consistent Analysis of Hydrogen Permeability through Dense Metallic Membranes. Membranes 2020, 10, 120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, A.; Yukawa, H. Analysis of Reverse Temperature Dependence of Hydrogen Permeability through Pd-X (X=Y, Ho Ni) Alloy Membranes Based on Hydrogen Chemical Potential. Membranes 2020, 10, 123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yelon, A.; Movaghar, B.; Branz, H.M. Origin and consequences of the compensation (Meyer-Neldel) law. Phys. Rev. B 1992, 46, 12244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, A.; Yukawa, H.; Nambu, T.; Matsumoto, Y.; Murata, Y. Analysis of hydrogen mobility in Nb-based alloy membranes in view of new description of hydrogen permeability based on hydrogen chemical potential. J. Alloys Compd. 2015, 645, S107–S111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.X.; Yukawa, H.; Nambu, T.; Matsumoto, Y.; Morinaga, M. Alloying effects of Ru and W on hydrogen diffusivity during hydrogen permeation through Nb-based hydrogen permeable membranes. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2010, 35, 1245–1249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.S.; Ouyang, C.; Suh, J.-Y.; Fleury, E.; Cho, Y.W.; Shim, J.-H. Role of alloying elements in vanadium-based binary alloy membranes for hydrogen separation. J. Memb. Sci. 2012, 423–424, 332–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, A.; Yukawa, H.; Nambu, T.; Matsumoto, Y.; Murata, Y. Analysis of pressure-composition-isotherms for design of non-Pd-based alloy membranes with high hydrogen permeability and strong resistance to hydrogen-induced embrittlement. J. Memb. Sci. 2016, 503, 110–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
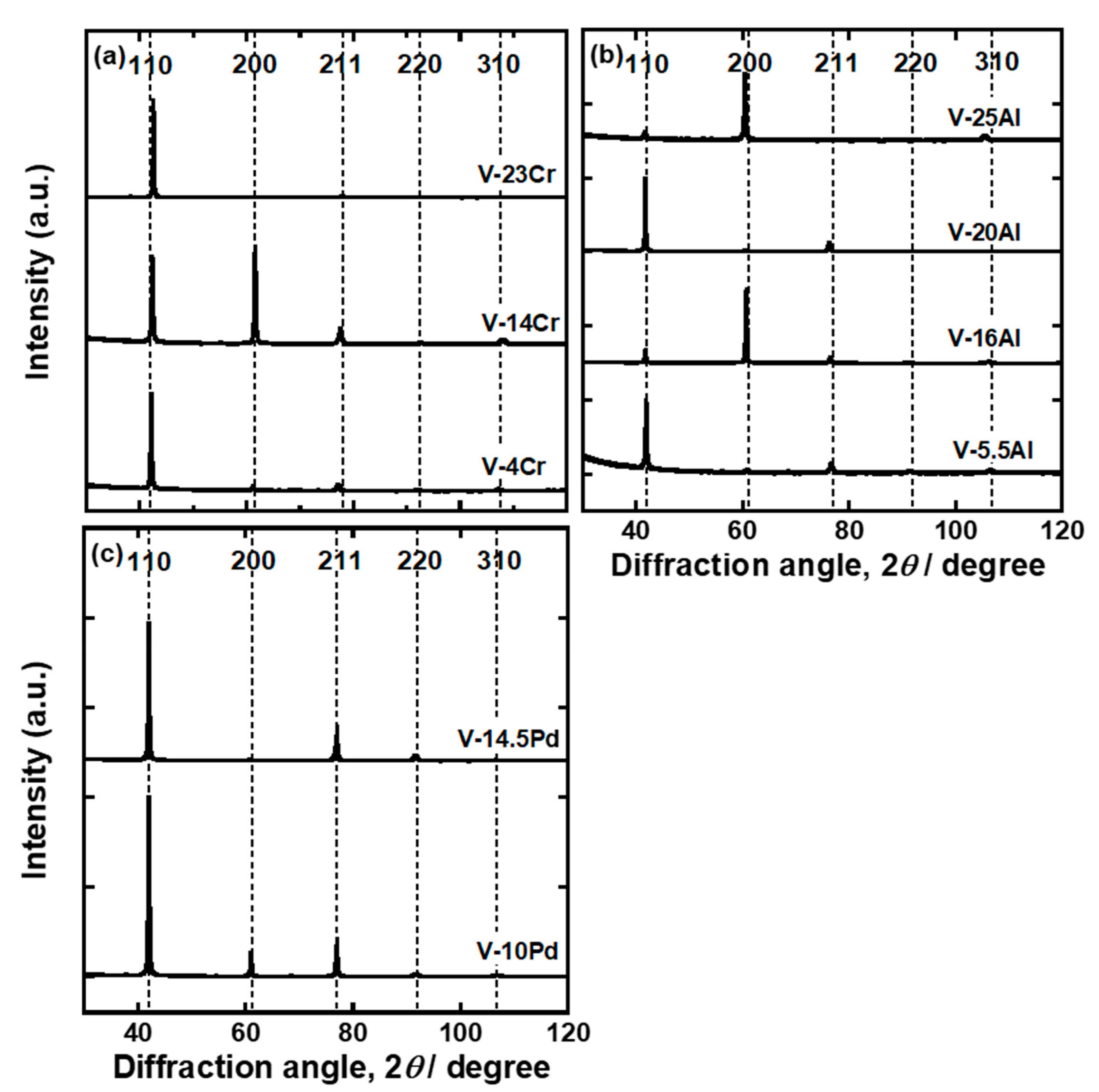
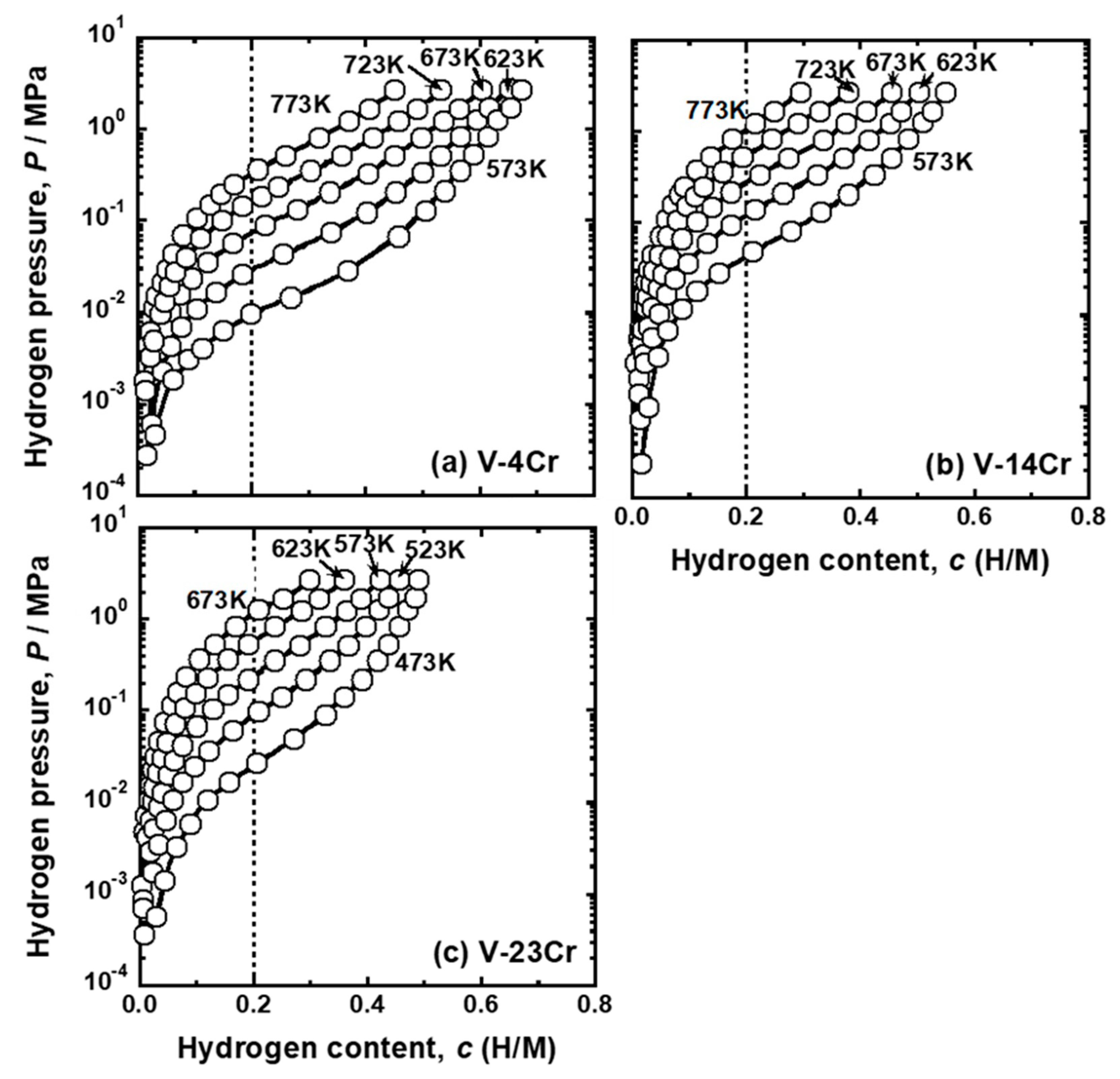
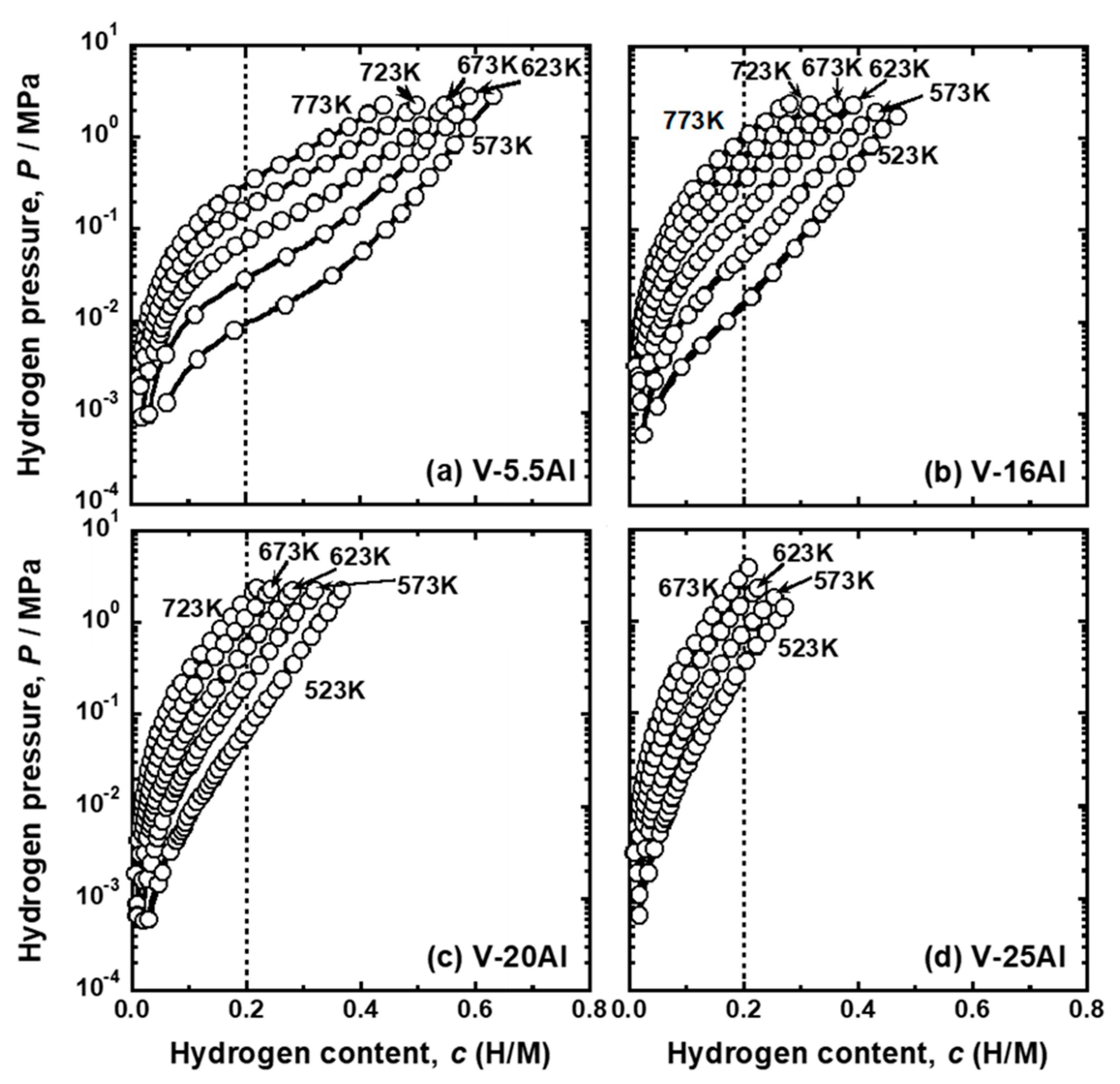
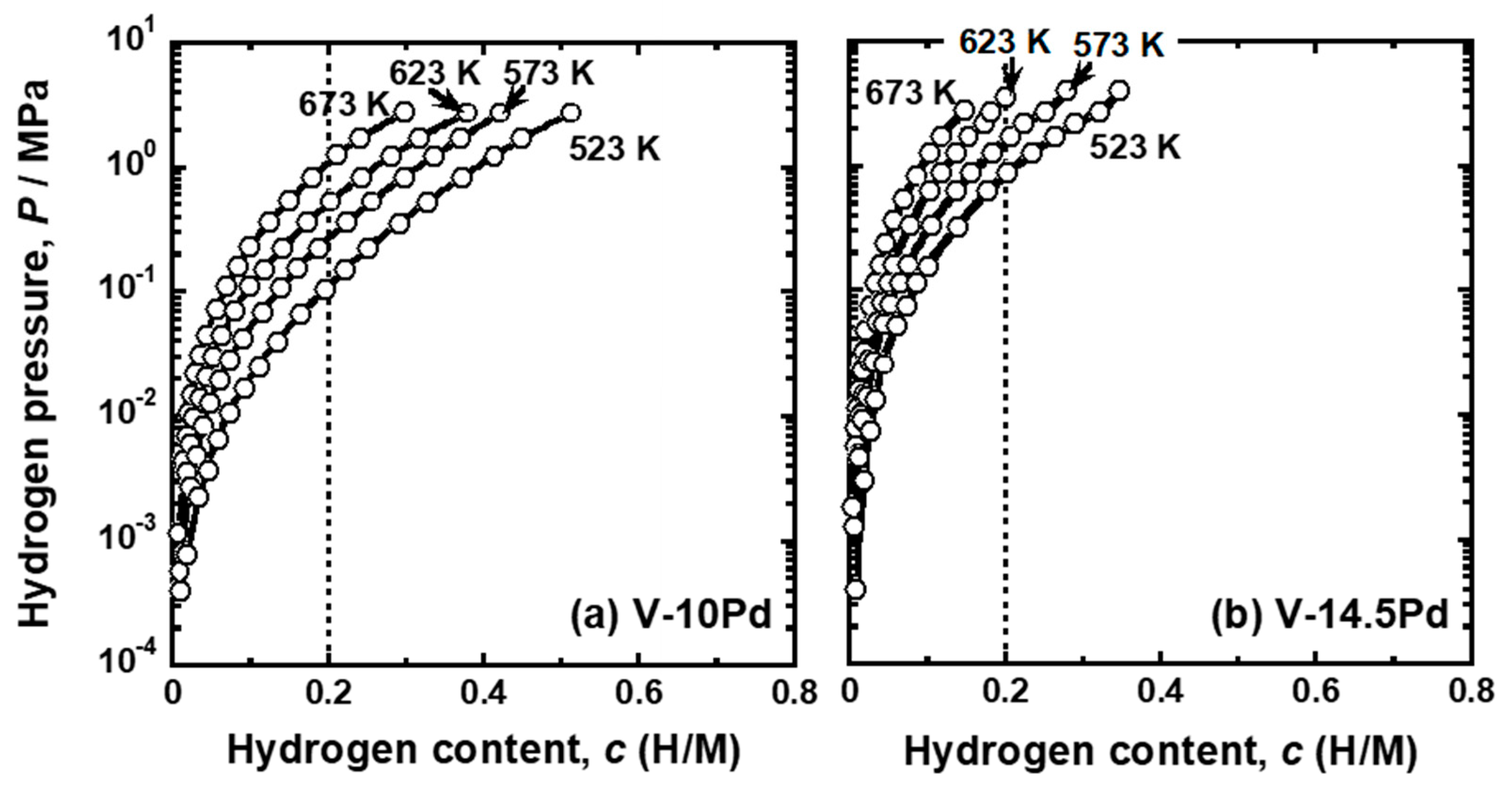
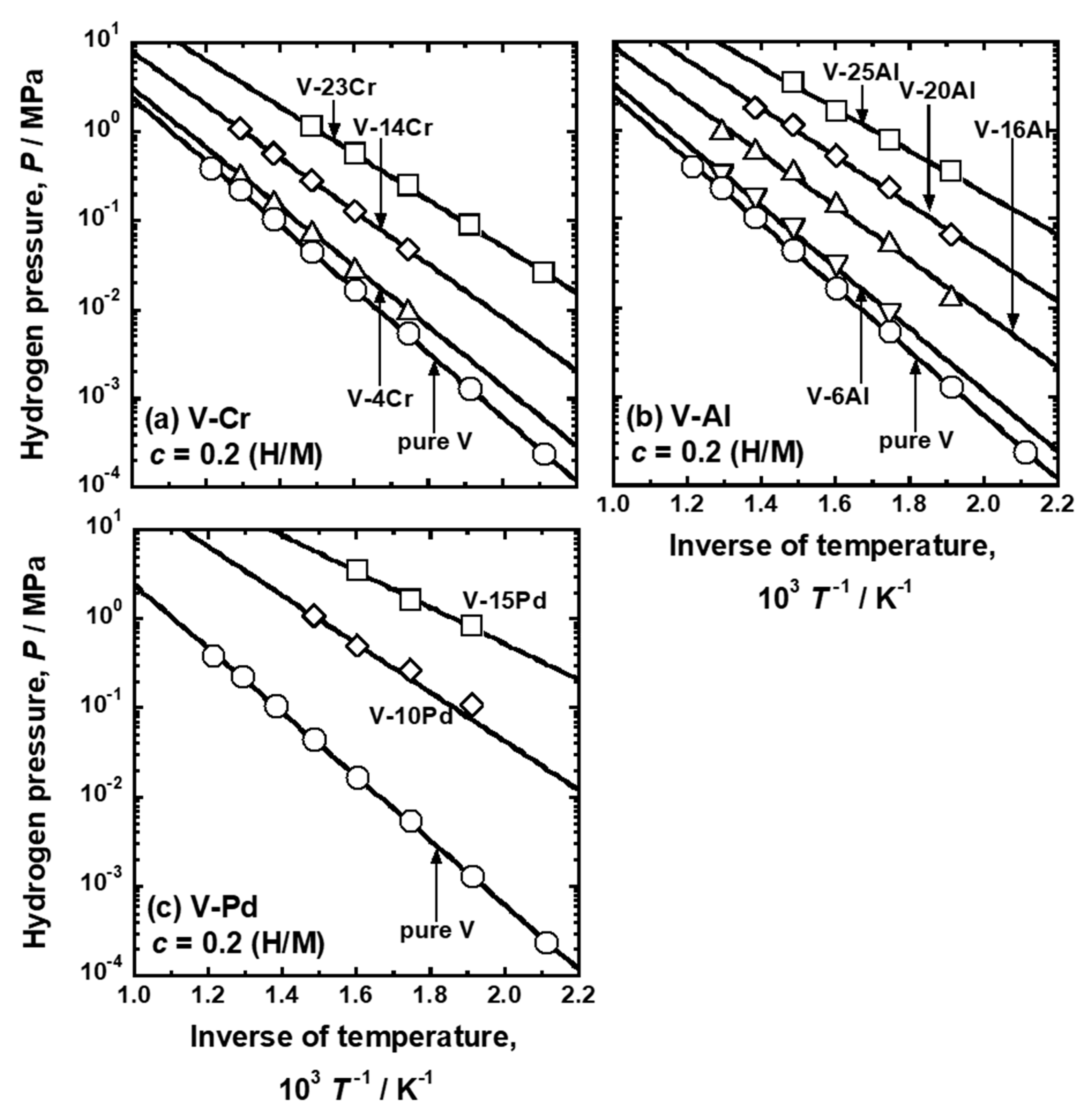
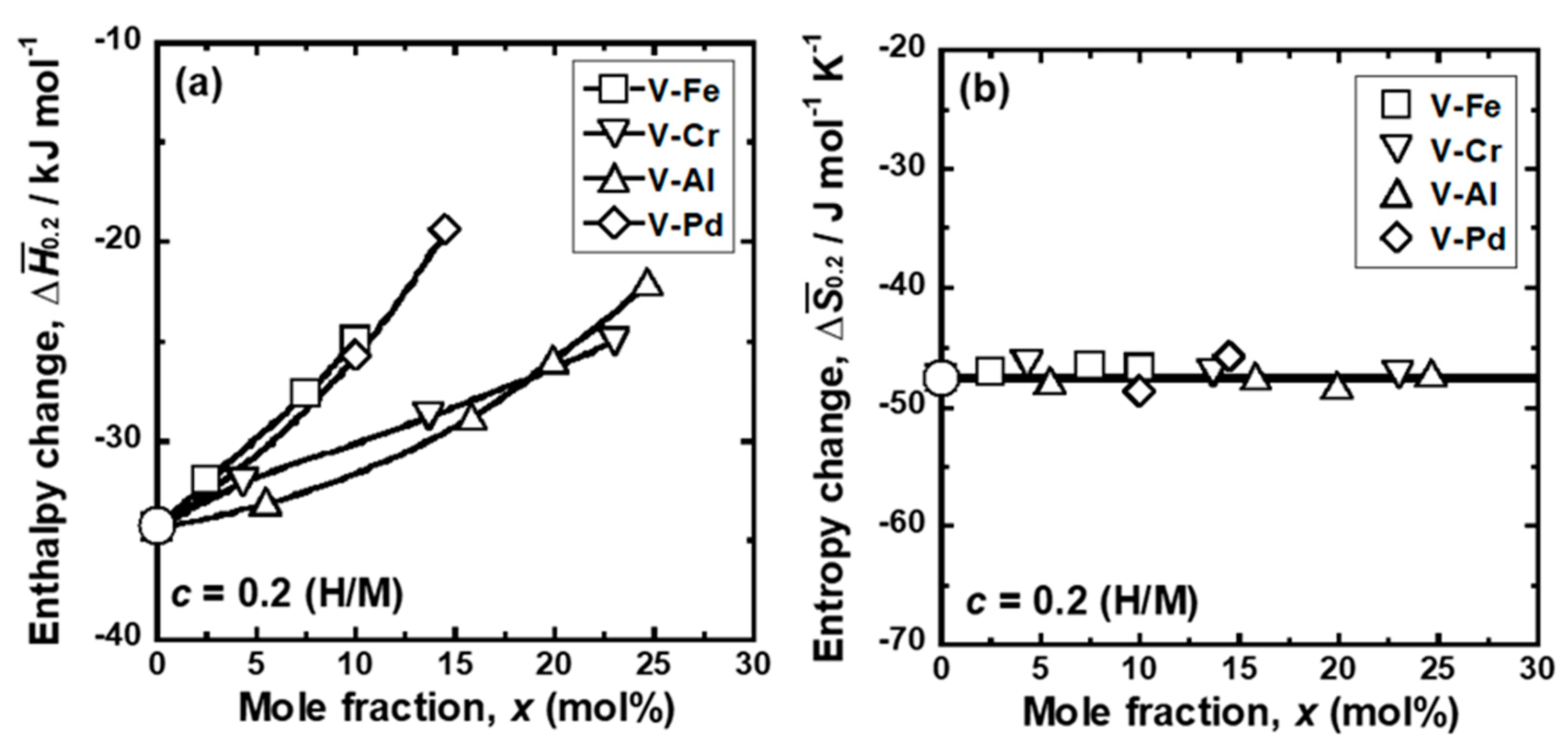
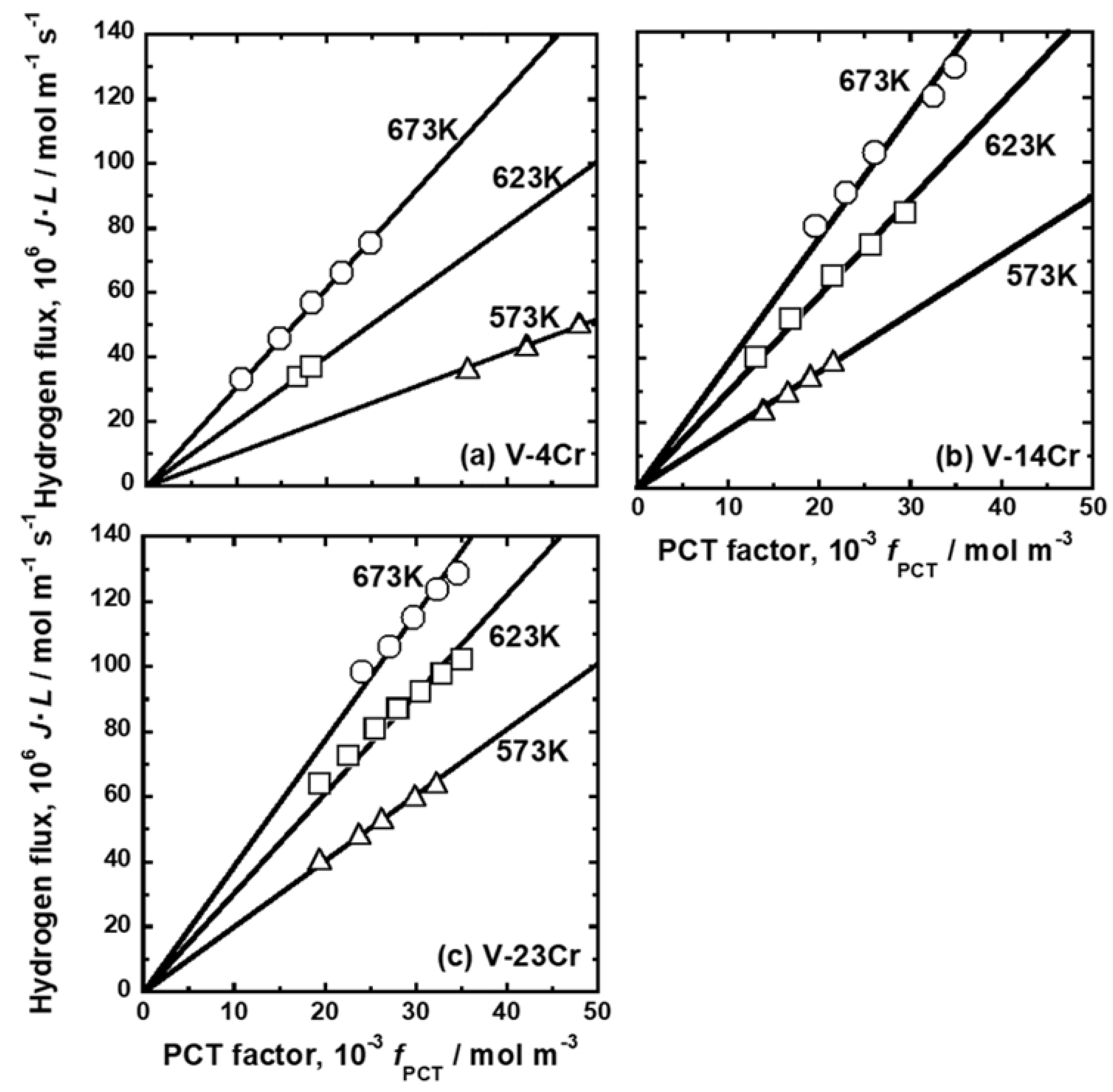
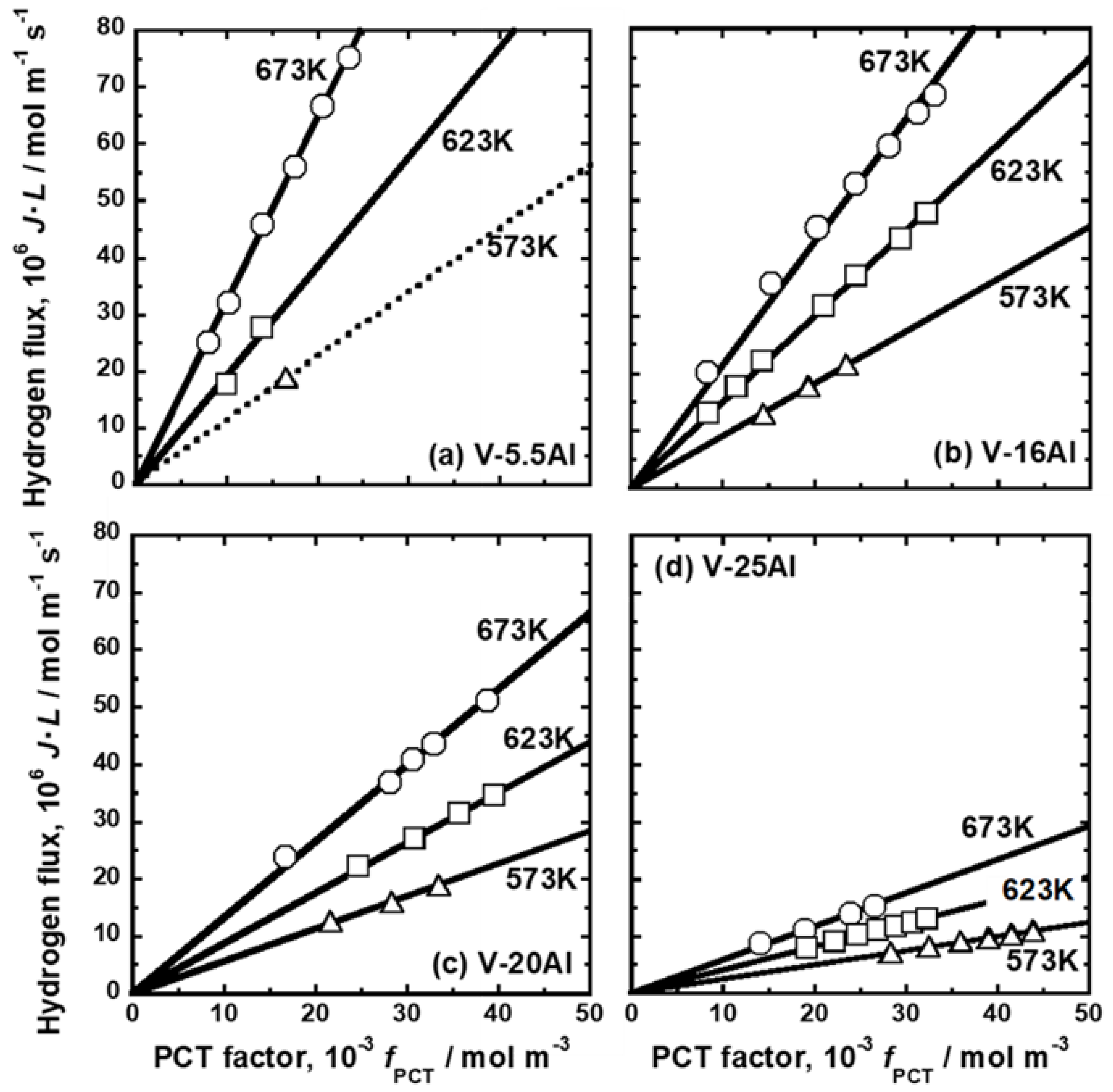
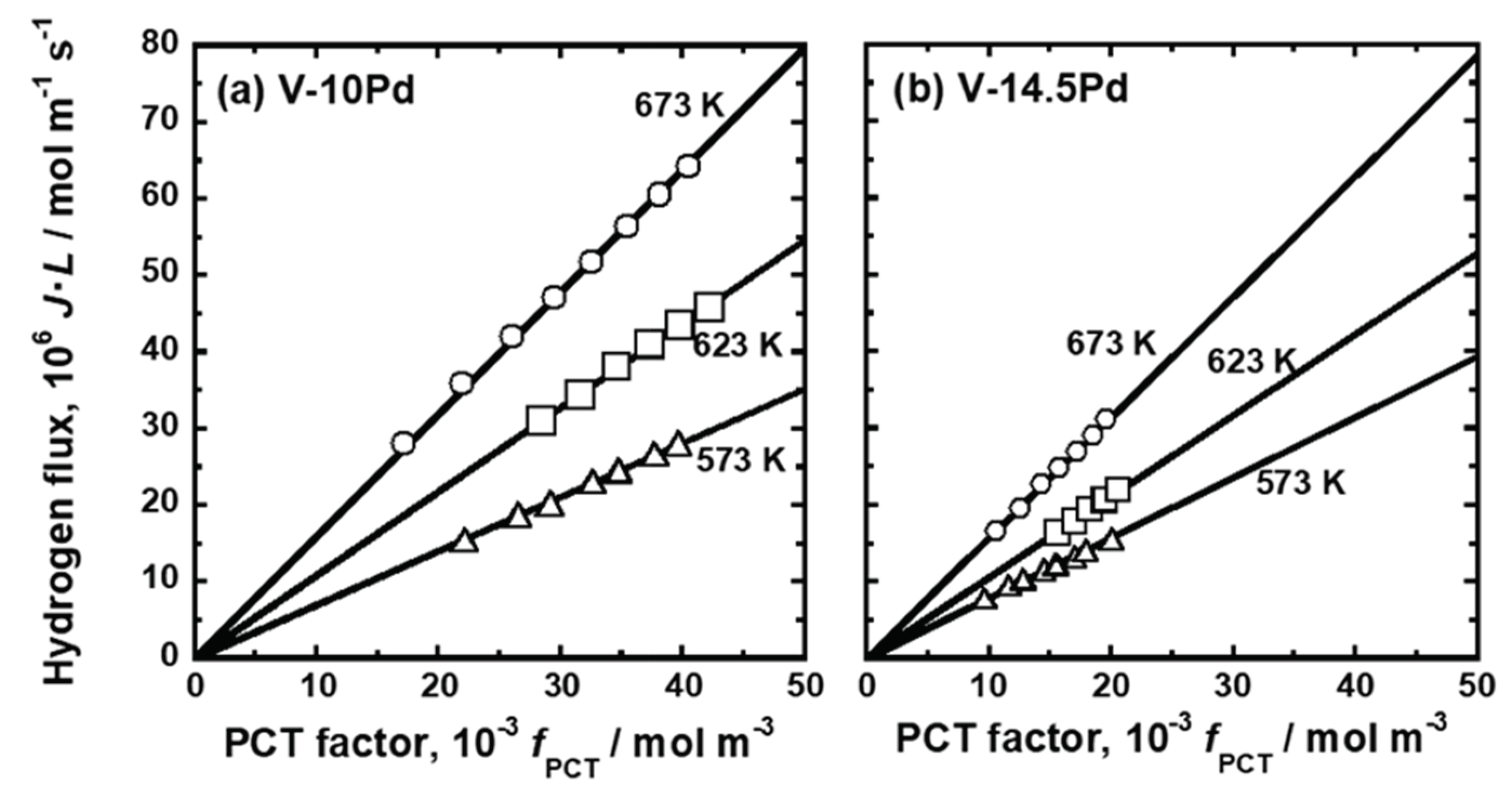
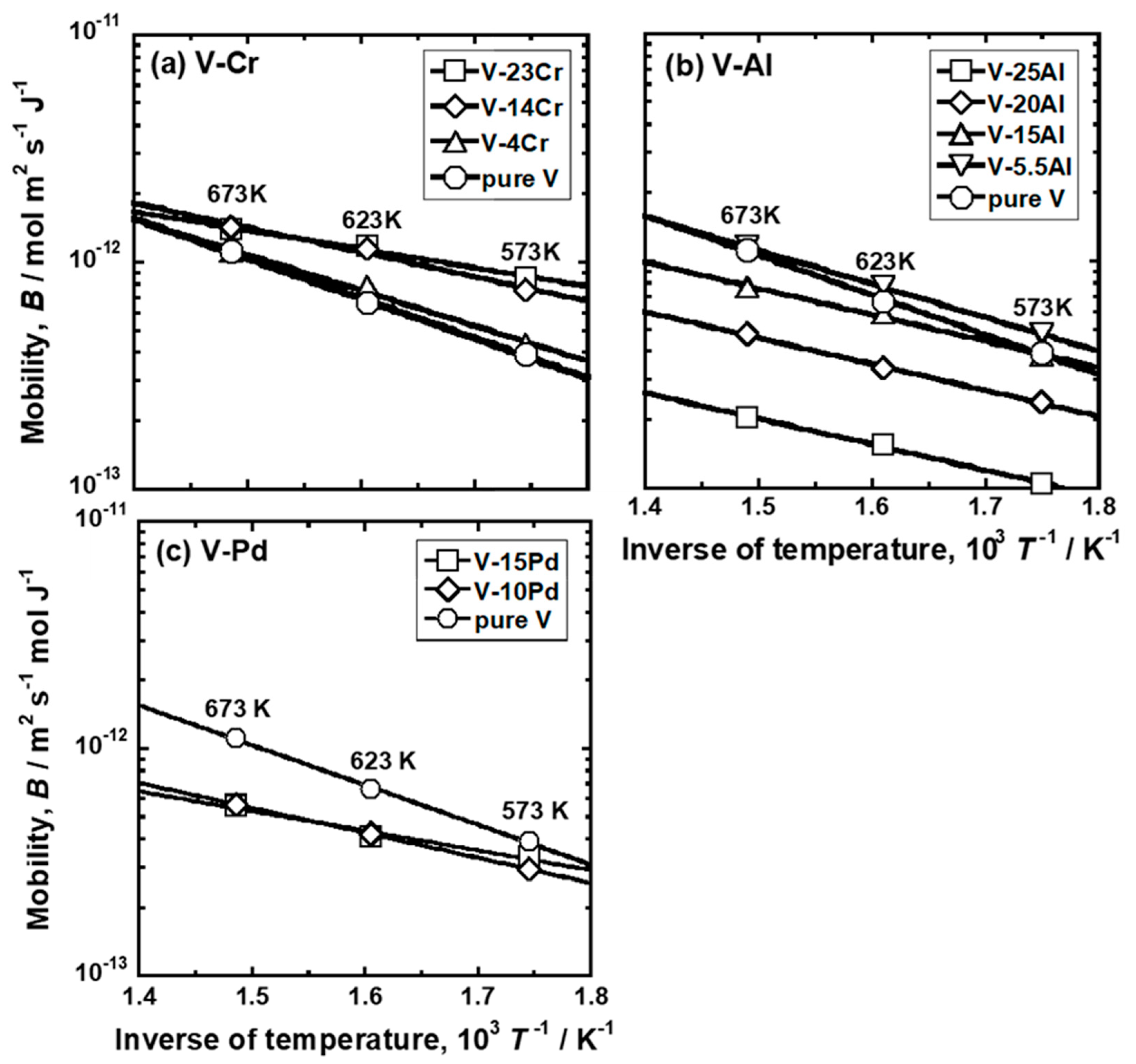
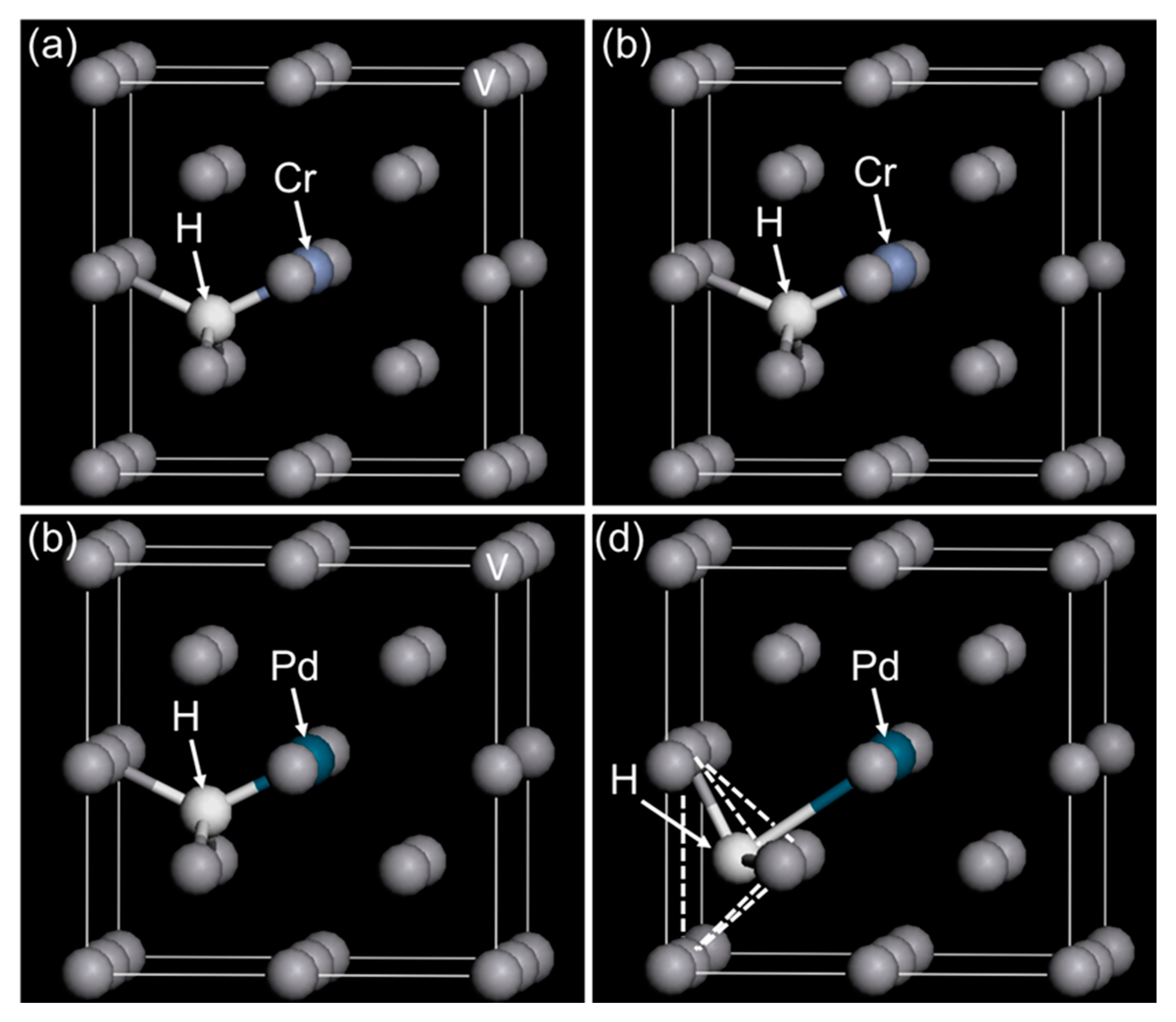
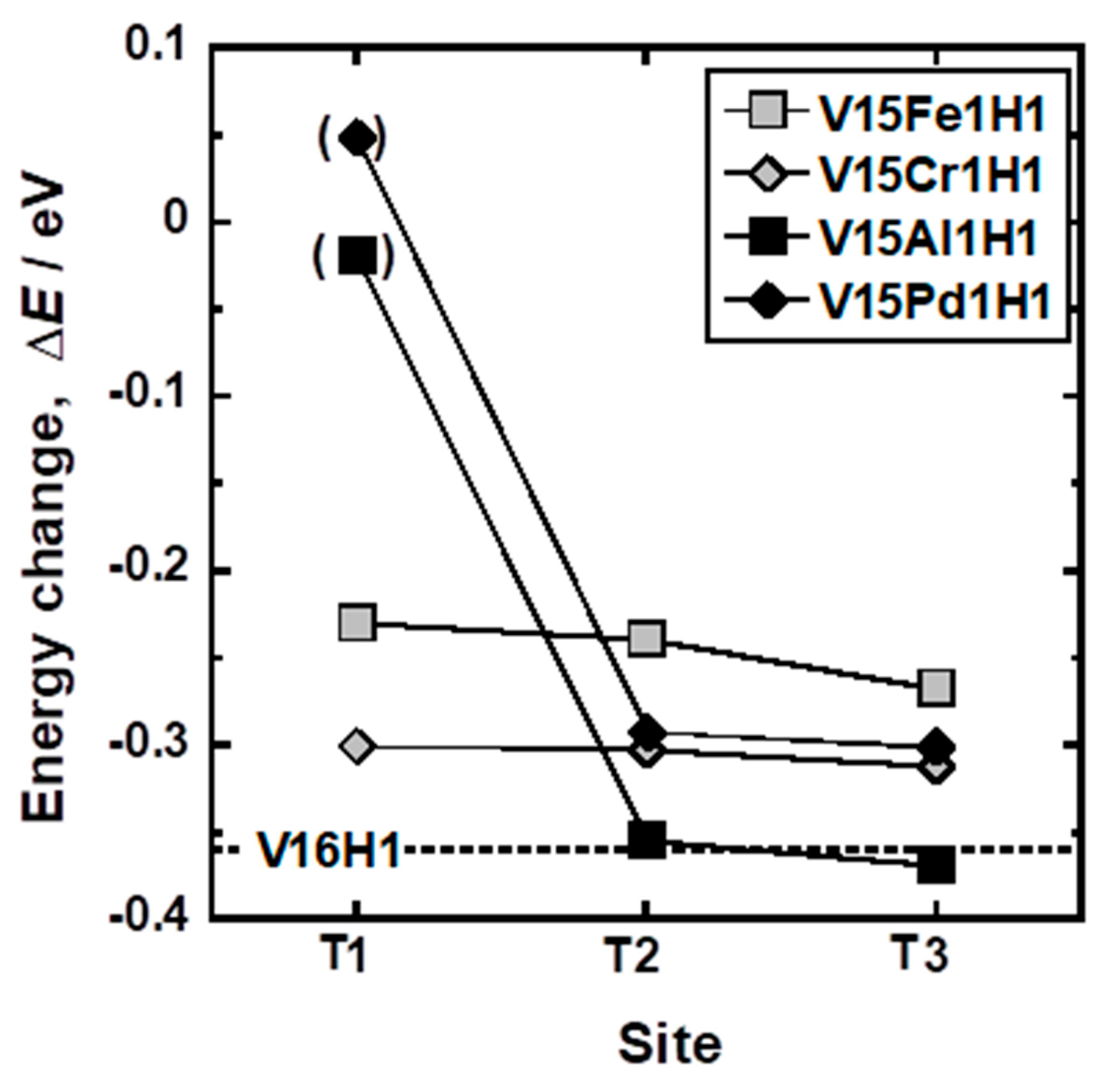
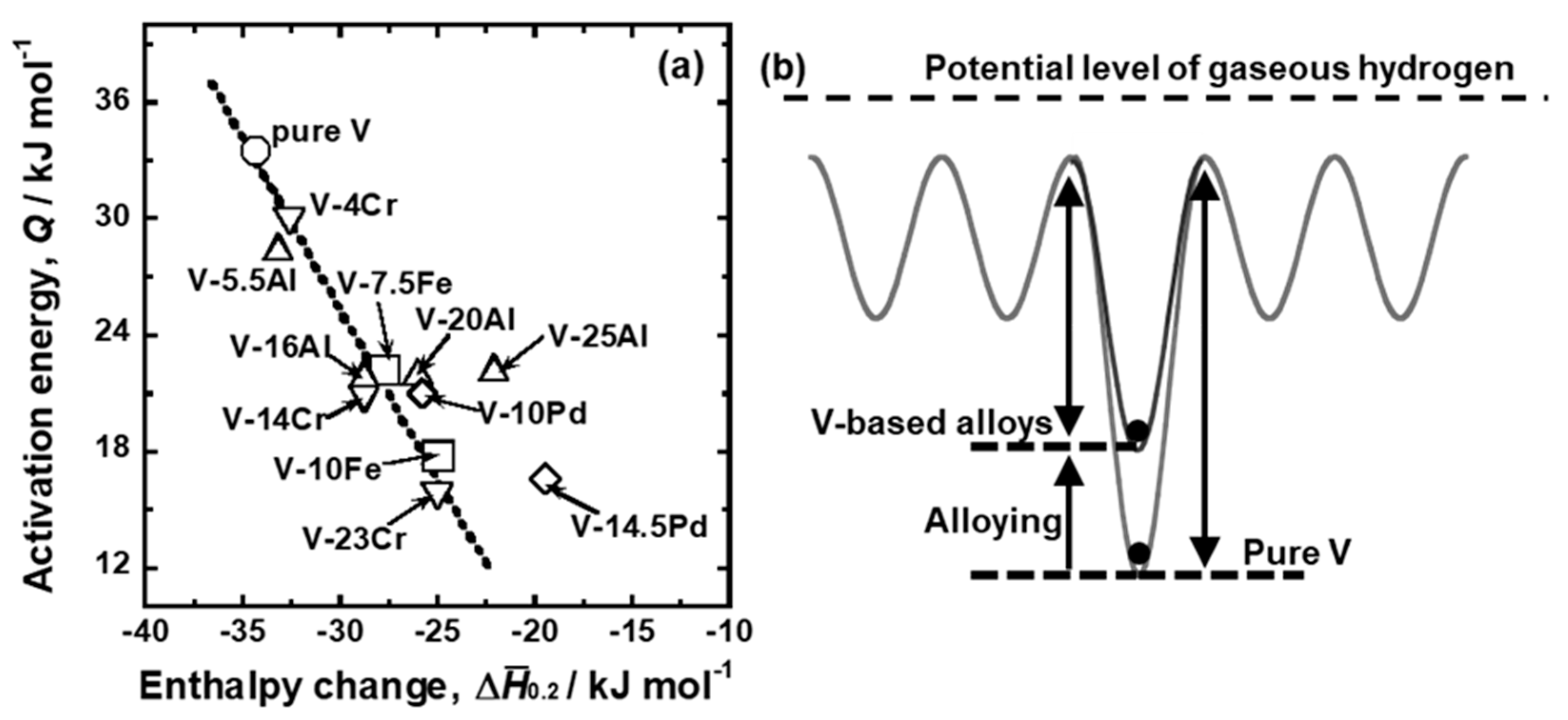
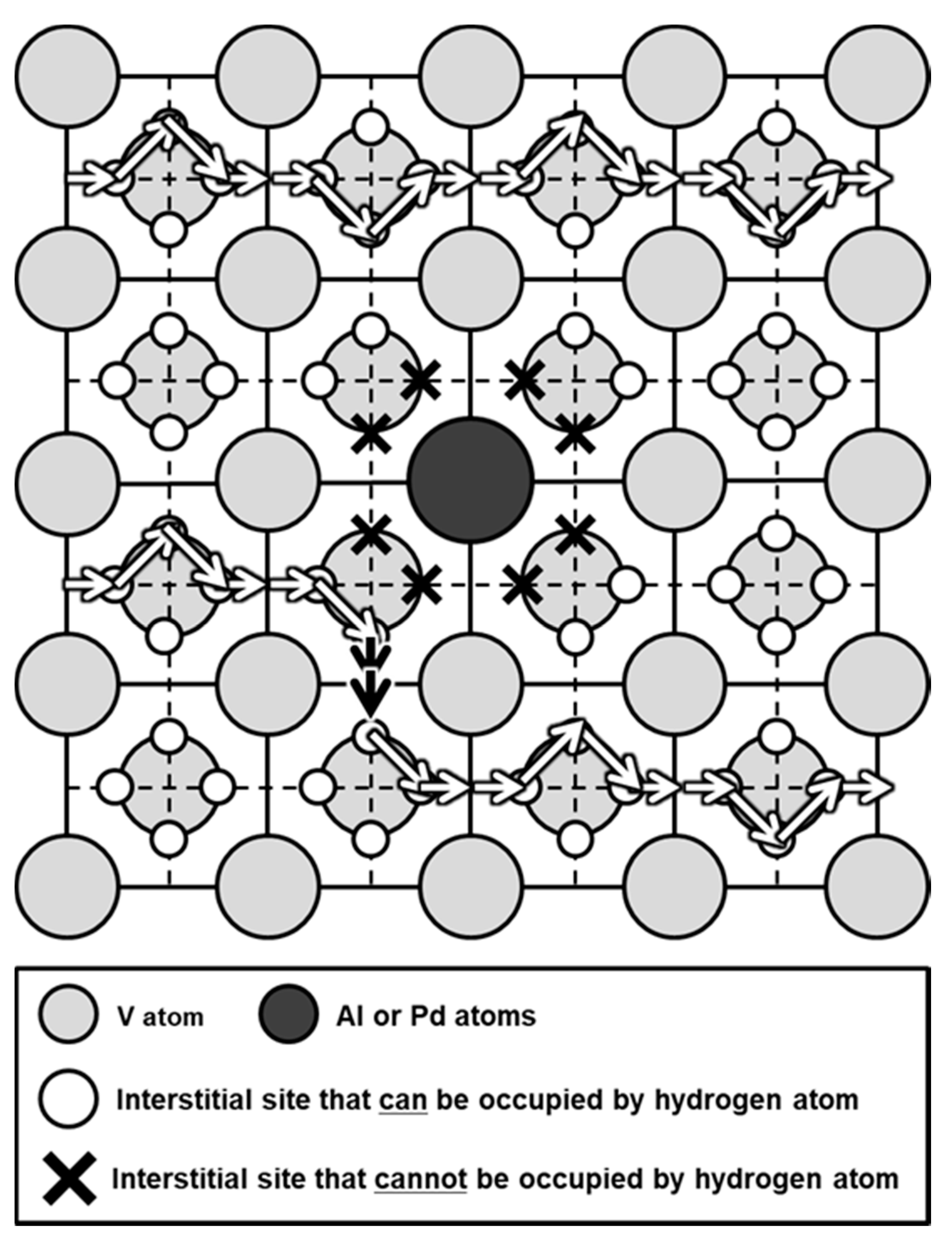
| Sample | Mole Fraction of Alloying Elements (mol%) |
|---|---|
| V-4Cr | 4.3 |
| V-14Cr | 13.7 |
| V-23Cr | 23.0 |
| V-5.5Al | 5.5 |
| V-16Al | 15.8 |
| V-20Al | 19.9 |
| V-25Al | 24.7 |
| V-10Pd | 9.8 |
| V-14.5Pd | 14.5 |
| Sample | Temperature, T/K | Hydrogen Pressure, P/kPa | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Feed | Permeate | ||
| V-4 Cr (L = 0.500 mm) | 573 | 30, 35, 40 | 10 |
| 623 | 28, 30 | ||
| 673 | 30, 40, 50, 60, 70 | ||
| V-14 Cr (L = 0.428 mm) | 573 | 30, 35, 40, 45 | |
| 623 | 45, 60, 80, 100, 120 | ||
| 673 | 120, 150, 180, 250, 280 | ||
| V-23 Cr (L = 0.521 mm) | 573 | 100, 130, 150, 180, 200 | |
| 623 | 200, 250, 300, 350, 400, 450, 500 | ||
| 673 | 500, 600, 700, 800, 900 | ||
| Sample | Temperature, T/K | Hydrogen Pressure, P/kPa | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Feed | Permeate | ||
| V-5.5 Al (L = 0.550 mm) | 573 | 20 | 10 |
| 623 | 20, 25 | ||
| 673 | 25, 30, 40, 50, 60, 70 | ||
| V-16 Al (L = 0.562 mm) | 573 | 30, 40, 50 | |
| 623 | 30, 40, 50, 80, 100, 130, 150 | ||
| 673 | 50, 100, 150, 180, 200, 250, 300, 350 | ||
| V-20 Al (L = 0.425 mm) | 573 | 100, 150, 200 | |
| 623 | 200, 300, 400, 500 | ||
| 673 | 200, 500, 600, 700, 1000 | ||
| V-25 Al (L = 0.504 mm) | 573 | 300, 400, 500, 600, 700, 800 | |
| 623 | 200, 300, 400, 500, 600, 700, 800, 900 | ||
| 673 | 300, 500, 800, 1000 | ||
| Sample | Temperature, T/K | Hydrogen Pressure, P/kPa | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Feed | Permeate | ||
| V-10 Pd (L = 0.521 mm) | 573 | 100, 130, 150, 180, 200, 230, 250 | 10 |
| 623 | 250, 300, 350, 400, 450, 500 | ||
| 673 | 200, 300, 400, 500, 600, 700, 800, 900 | ||
| V-14.5 Pd (L = 0.366 mm) | 573 | 100, 130, 150, 180, 200, 230, 250, 300 | |
| 623 | 300, 350, 400, 450, 500 | ||
| 673 | 300, 400, 500, 600, 700, 800, 900 | ||
| Sample | Temperature, T/K | Mobility, 1013 B/mol m2 s−1 J−1 |
|---|---|---|
| V-4 Cr | 673 | 11.0 |
| 623 | 7.8 | |
| 573 | 4.4 | |
| V-14 Cr | 673 | 14.3 |
| 623 | 11.4 | |
| 573 | 7.5 | |
| V-23 Cr | 673 | 13.8 |
| 623 | 11.7 | |
| 573 | 8.5 | |
| V-5.5 Al | 673 | 11.5 |
| 623 | 7.7 | |
| 573 | 4.8 | |
| V-16 Al | 673 | 7.6 |
| 623 | 5.8 | |
| 573 | 3.8 | |
| V-20 Al | 673 | 4.7 |
| 623 | 3.4 | |
| 573 | 2.4 | |
| V-25 Al | 673 | 2.0 |
| 623 | 1.6 | |
| 573 | 1.0 | |
| V-10 Pd | 673 | 5.7 |
| 623 | 4.2 | |
| 573 | 3.0 | |
| V-14.5 Pd | 673 | 5.6 |
| 623 | 4.1 | |
| 573 | 3.3 | |
| Pure Pd [28] | 673 | 10.0 |
| 573 | 6.0 | |
| Pd-23 Ag [28] | 673 | 8.3 |
| 623 | 6.4 | |
| 573 | 4.5 |
| Sample | Temperature Range | Pre-Exponential Factor, 1011 B0/mol m2 s−1 J−1 | Activation Energy, E/kJ mol−1 |
|---|---|---|---|
| V-4 Cr | 573~673 K | 23.3 | 29.8 |
| V-14 Cr | 5.9 | 20.6 | |
| V-23 Cr | 2.3 | 15.6 | |
| V-5.5 Al | 573~673 K | 18.9 | 28.5 |
| V-16 Al | 4.0 | 22.0 | |
| V-20 Al | 2.4 | 22.0 | |
| V-25 Al | 1.1 | 22.2 | |
| V-10 Pd | 573~673 K | 2.4 | 21.0 |
| V-14.5 Pd | 1.1 | 16.6 | |
| Pure Pd [28] | 423~673 K | 1.4 | 14.9 |
| Pd-23 Ag [28] | 373~673 K | 7.3 | 24.4 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Suzuki, A.; Yukawa, H. Quantitative Evaluations of Hydrogen Diffusivity in V-X (X = Cr, Al, Pd) Alloy Membranes Based on Hydrogen Chemical Potential. Membranes 2021, 11, 67. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes11010067
Suzuki A, Yukawa H. Quantitative Evaluations of Hydrogen Diffusivity in V-X (X = Cr, Al, Pd) Alloy Membranes Based on Hydrogen Chemical Potential. Membranes. 2021; 11(1):67. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes11010067
Chicago/Turabian StyleSuzuki, Asuka, and Hiroshi Yukawa. 2021. "Quantitative Evaluations of Hydrogen Diffusivity in V-X (X = Cr, Al, Pd) Alloy Membranes Based on Hydrogen Chemical Potential" Membranes 11, no. 1: 67. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes11010067
APA StyleSuzuki, A., & Yukawa, H. (2021). Quantitative Evaluations of Hydrogen Diffusivity in V-X (X = Cr, Al, Pd) Alloy Membranes Based on Hydrogen Chemical Potential. Membranes, 11(1), 67. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes11010067





