Hydrophilic Dual Layer Hollow Fiber Membranes for Ultrafiltration
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
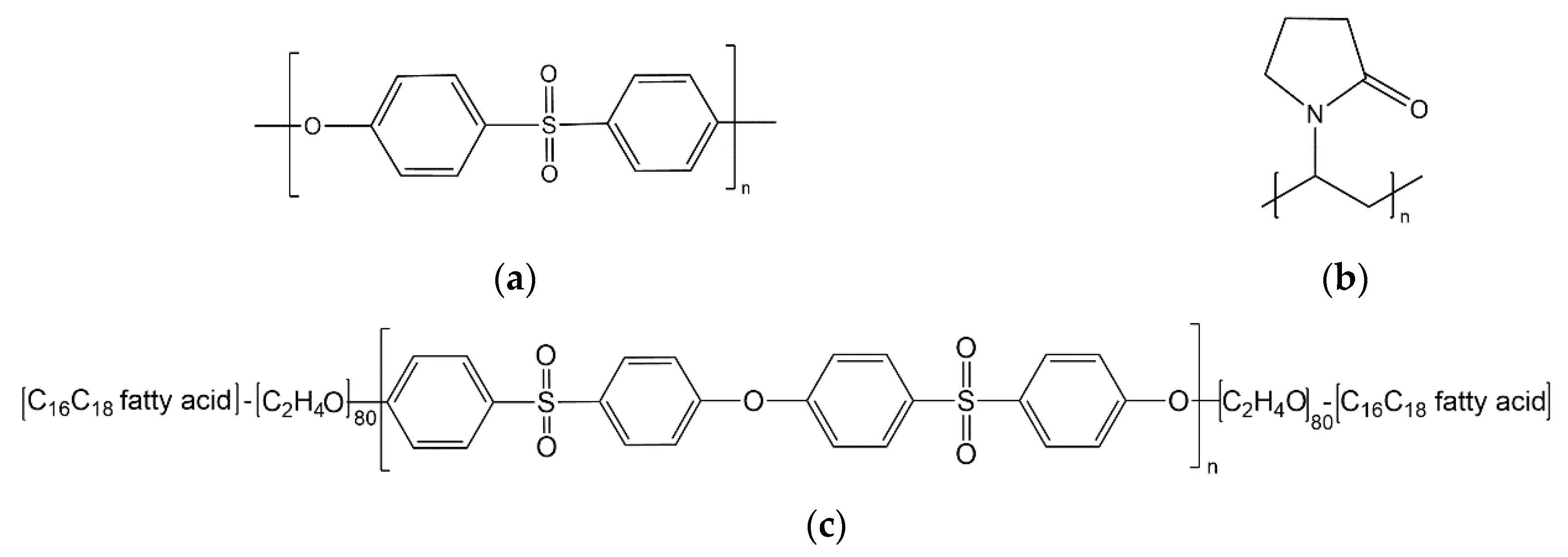
2.2. Additive Synthesis
2.3. Preparation of Dope and Additive Solutions
2.4. Viscoelastic, Diffusion and Precipitation Behaviour of the Solutions
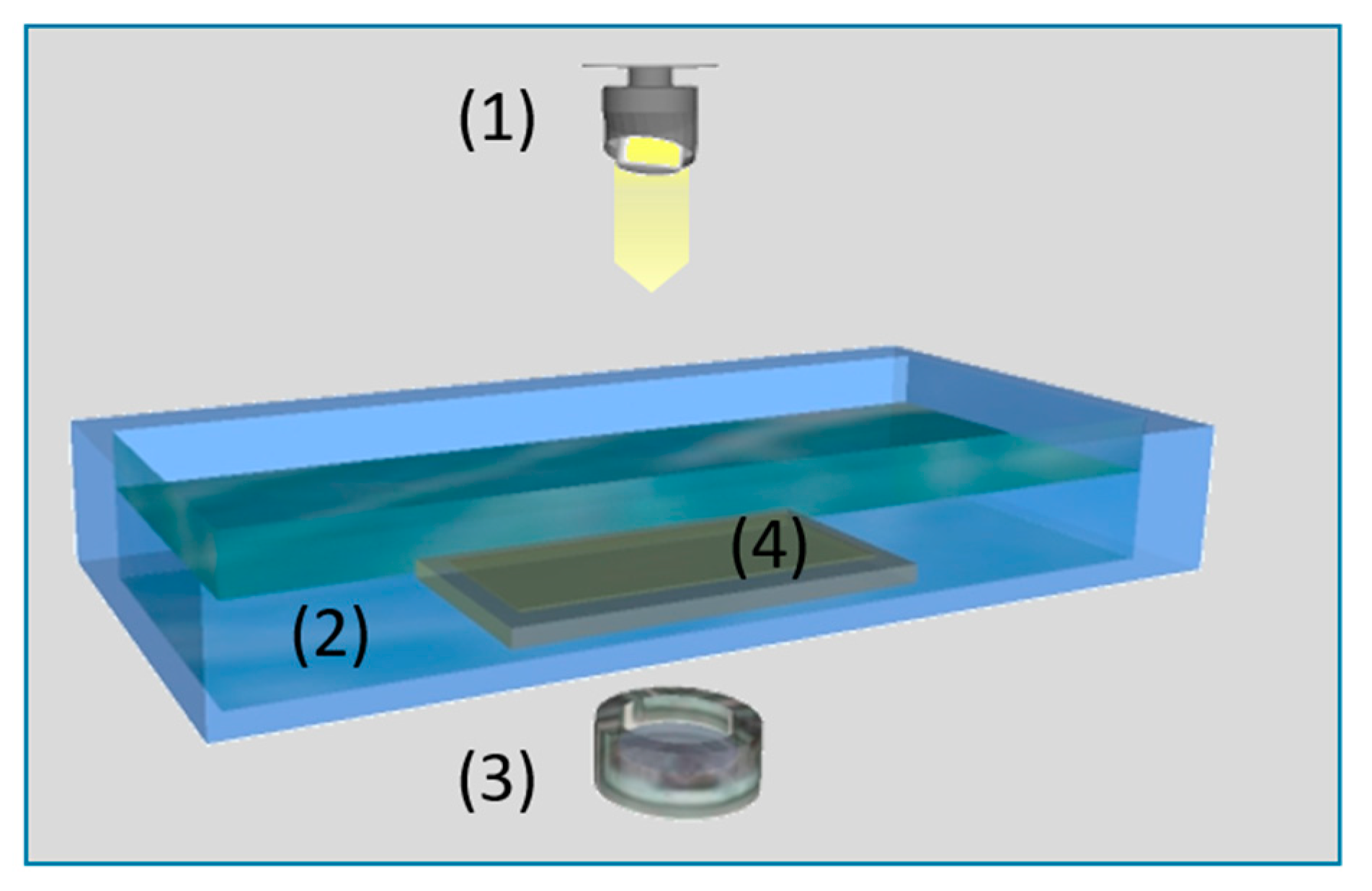
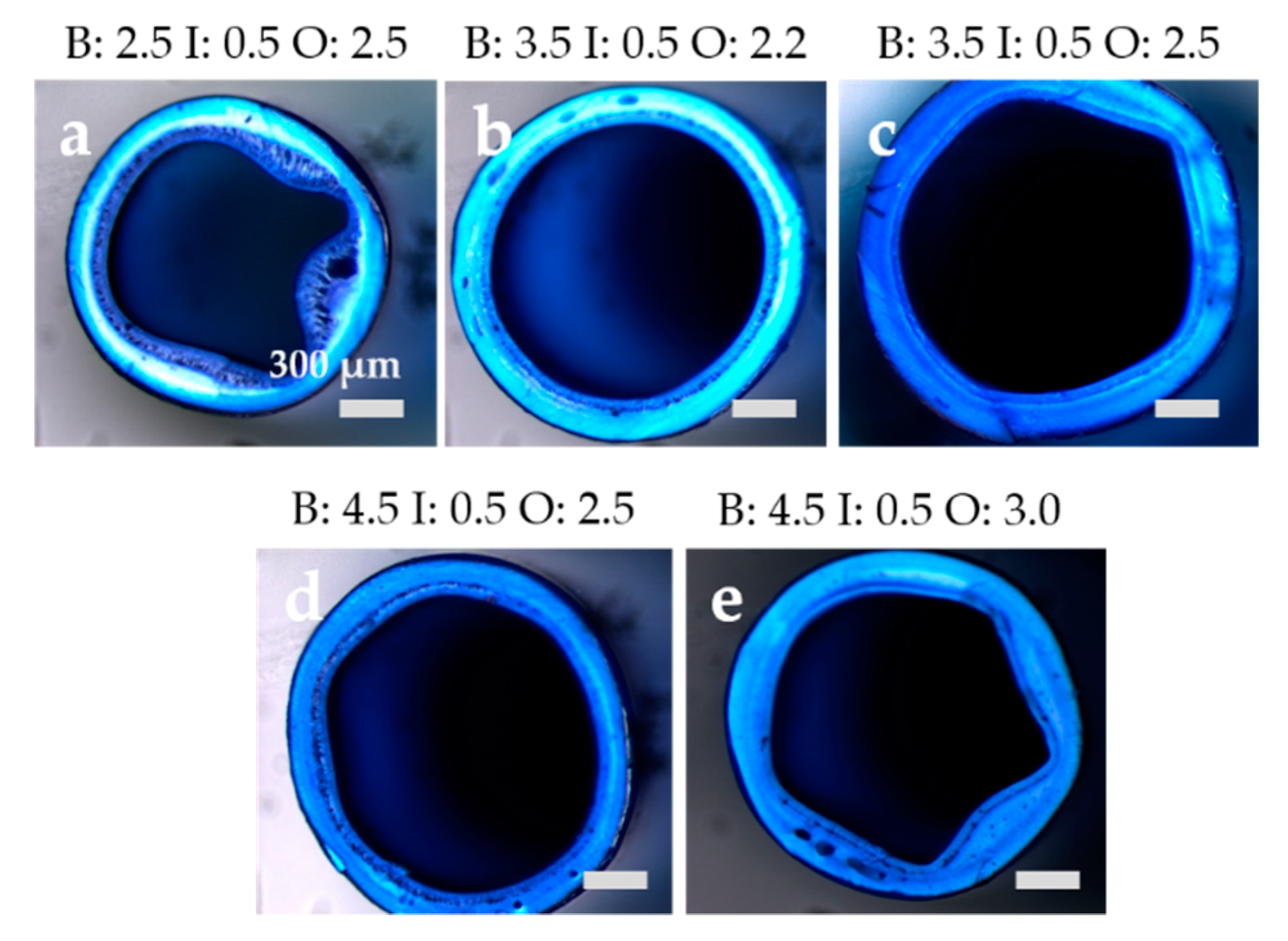
2.5. Preparation of Hollow Fiber Membranes
2.6. Degree of Hydrophilicity
2.7. Membrane Morphology and Performance
3. Results
3.1. Characterisation of Solutions
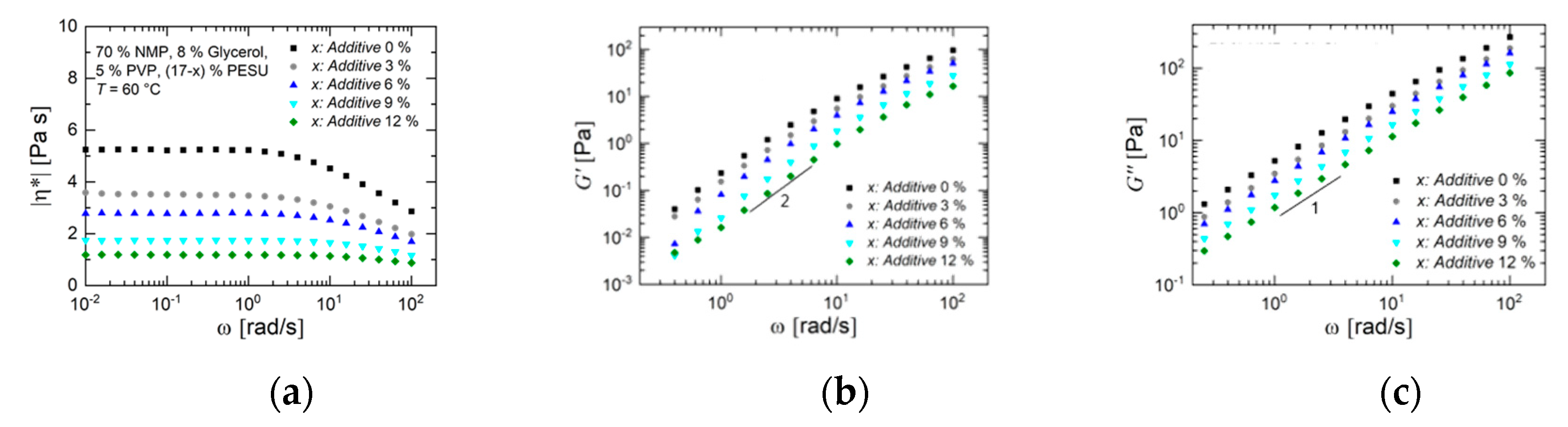
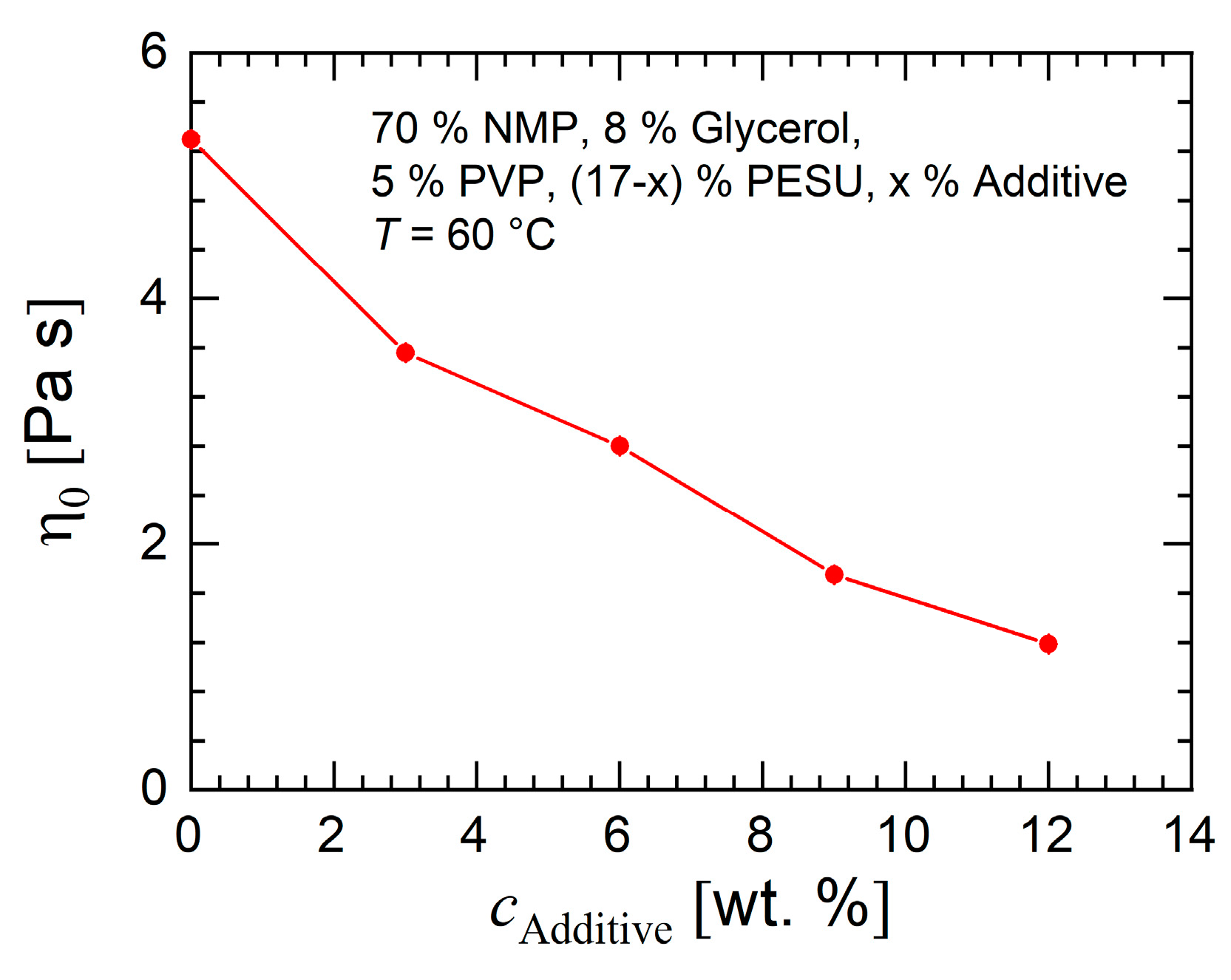
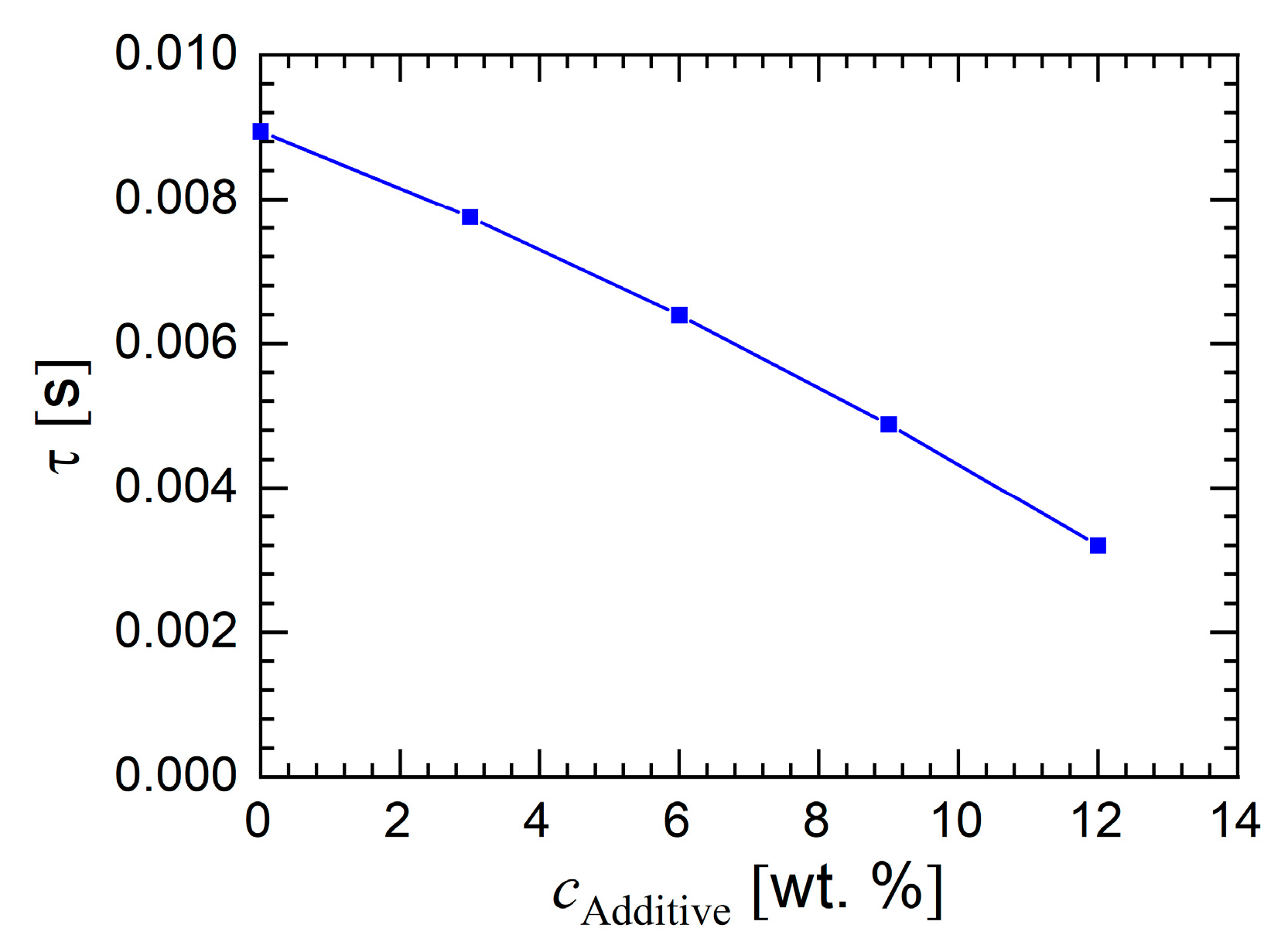
3.1.1. Rheology
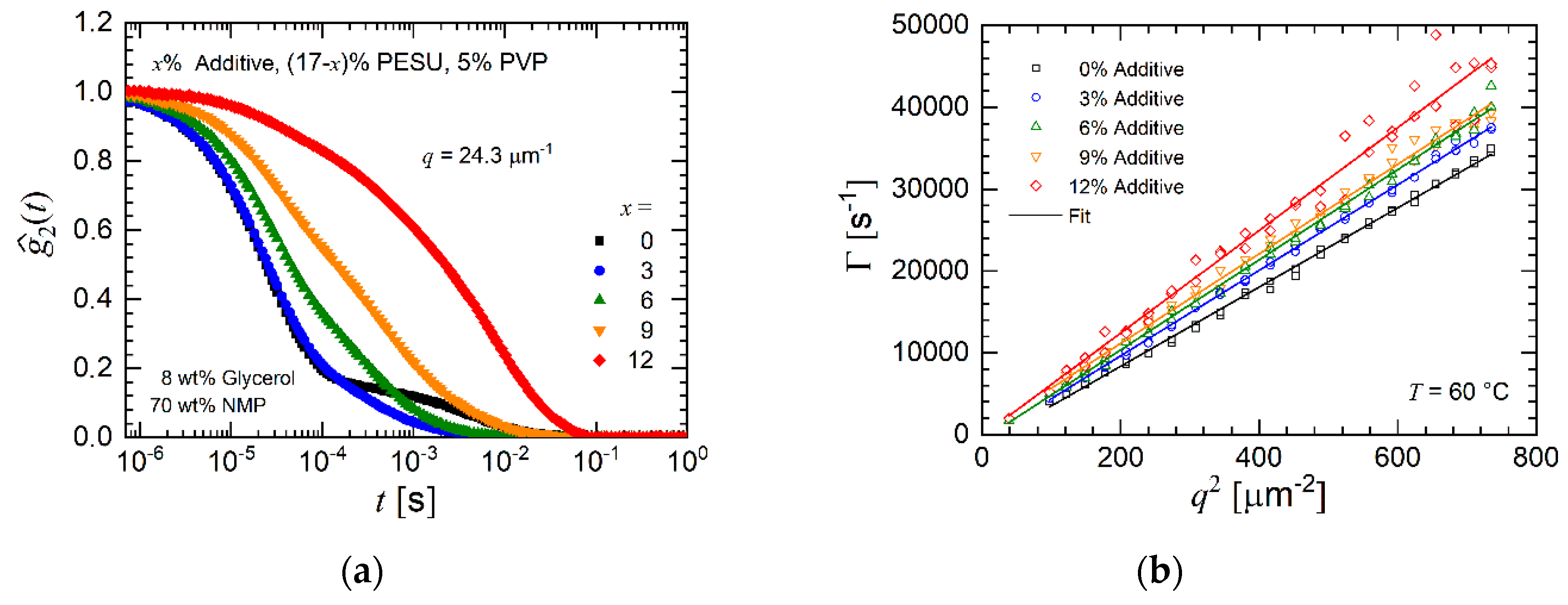
3.1.2. Dynamic Light Scattering
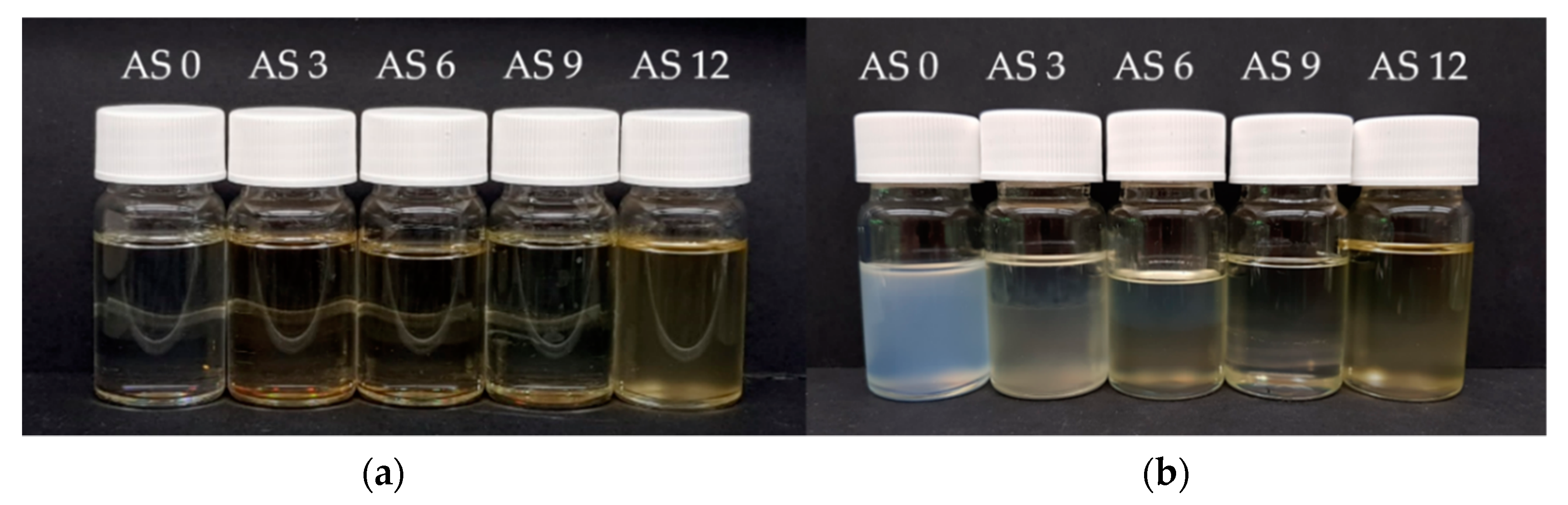
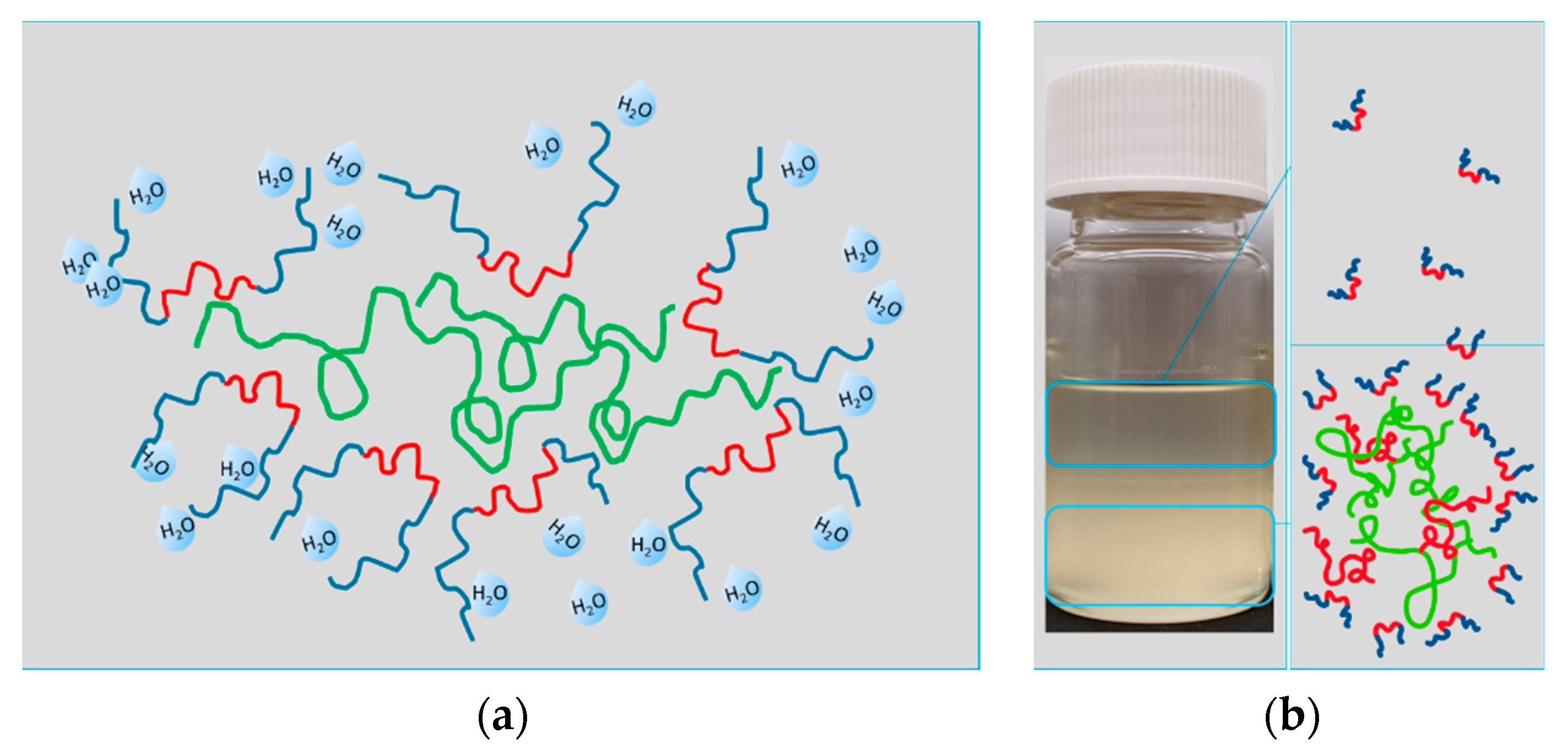
3.1.3. Cloud Point Determination
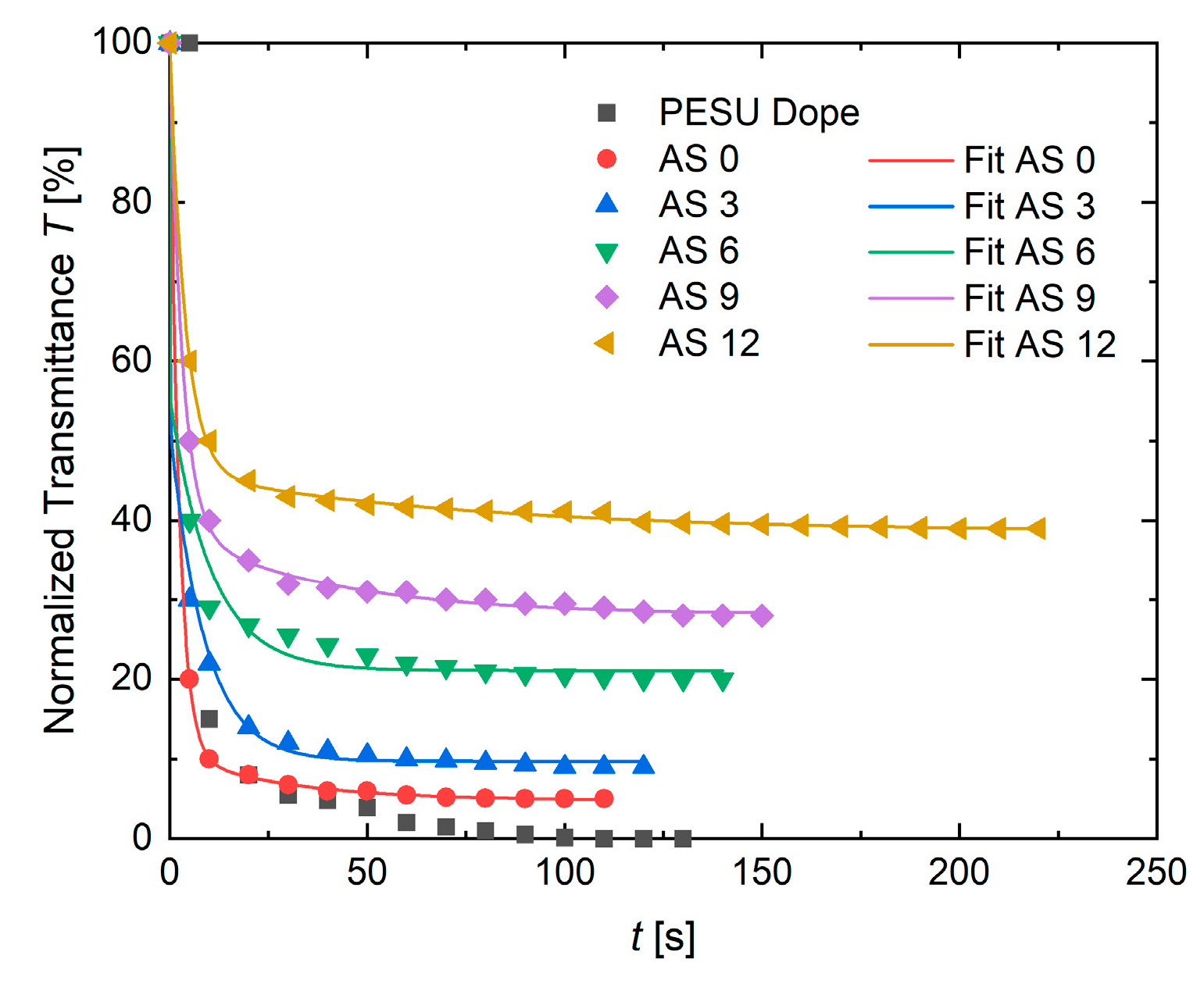
3.1.4. Precipitation Experiments
3.2. Characterisation of Membranes
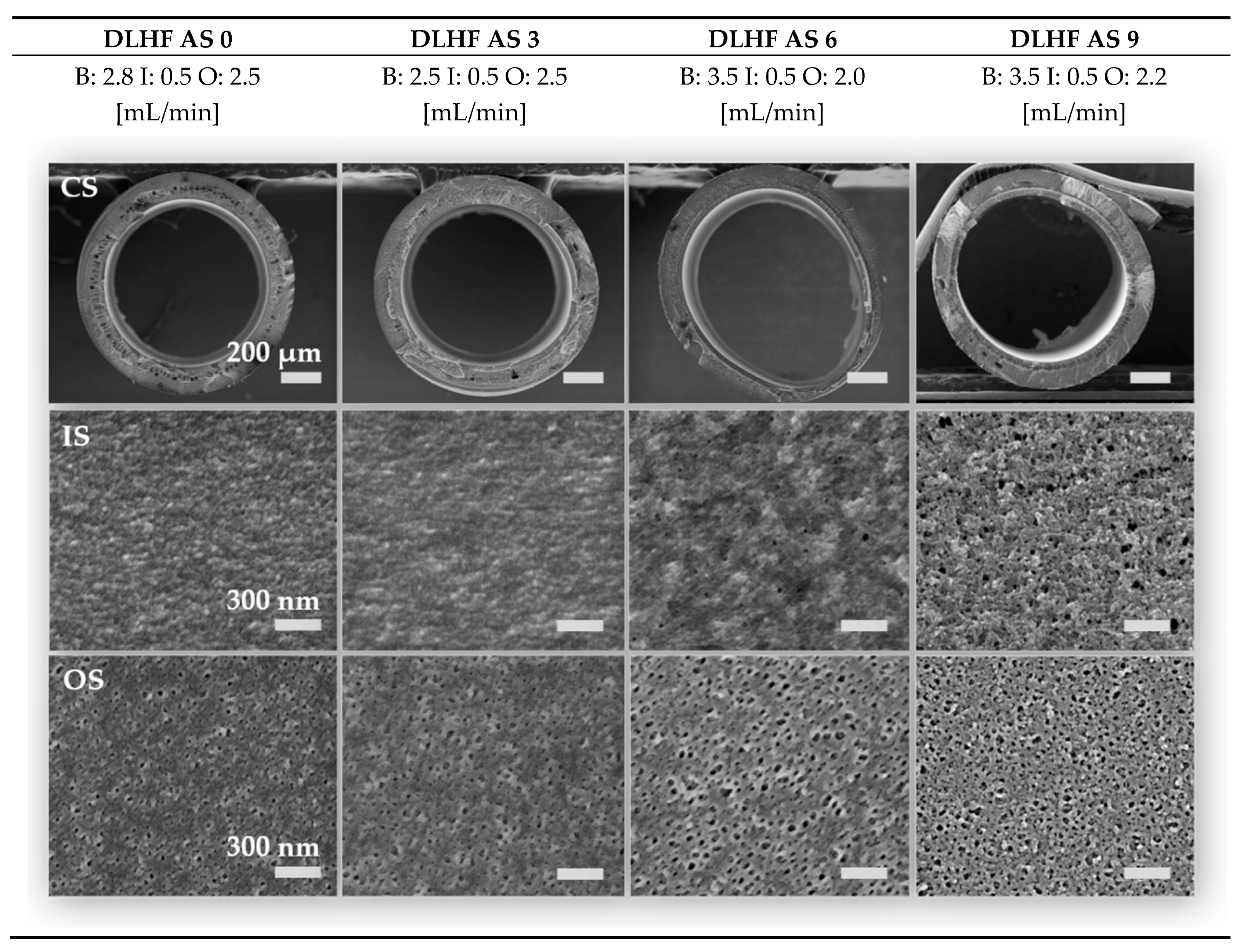
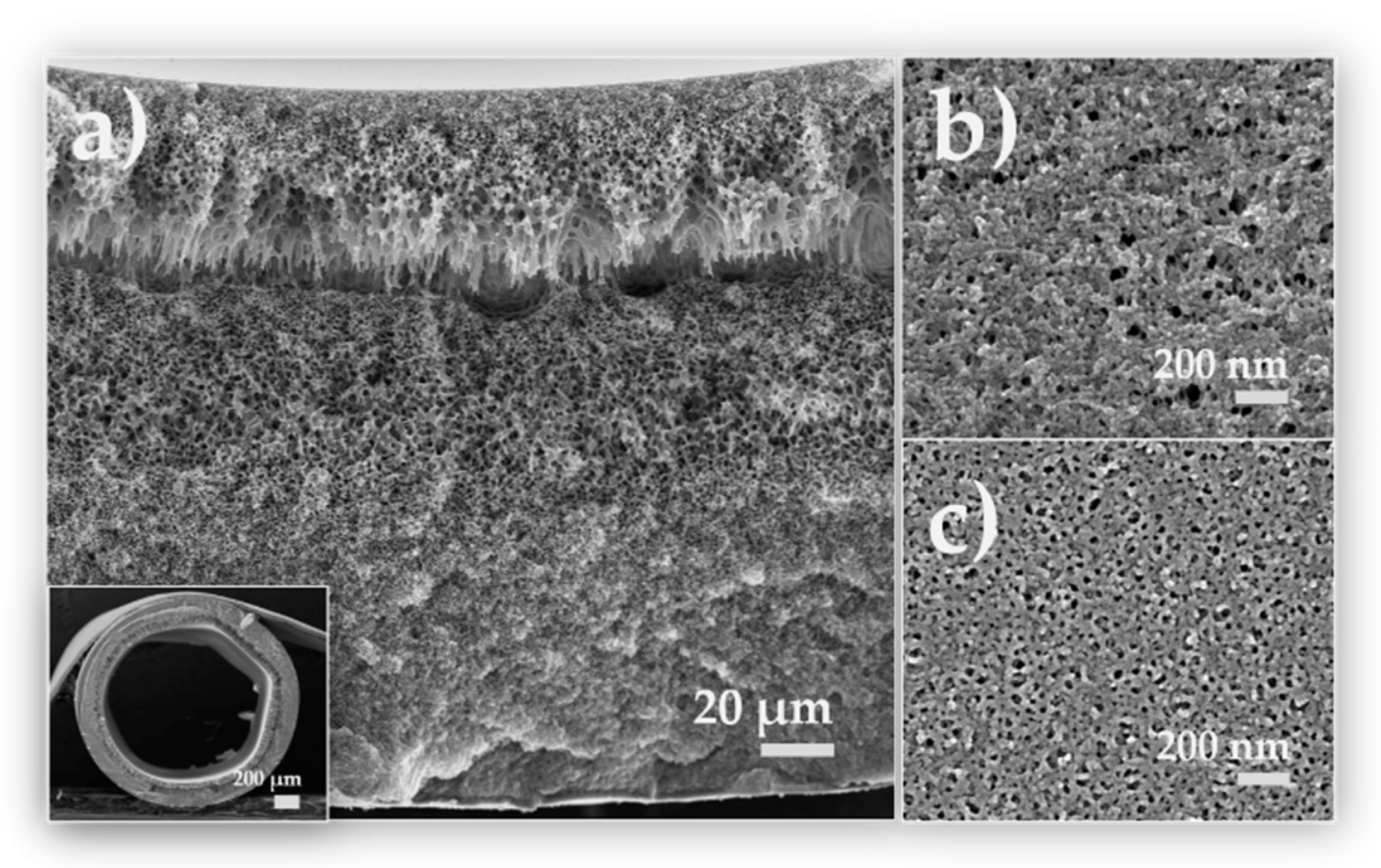
3.2.1. Membrane Morphology
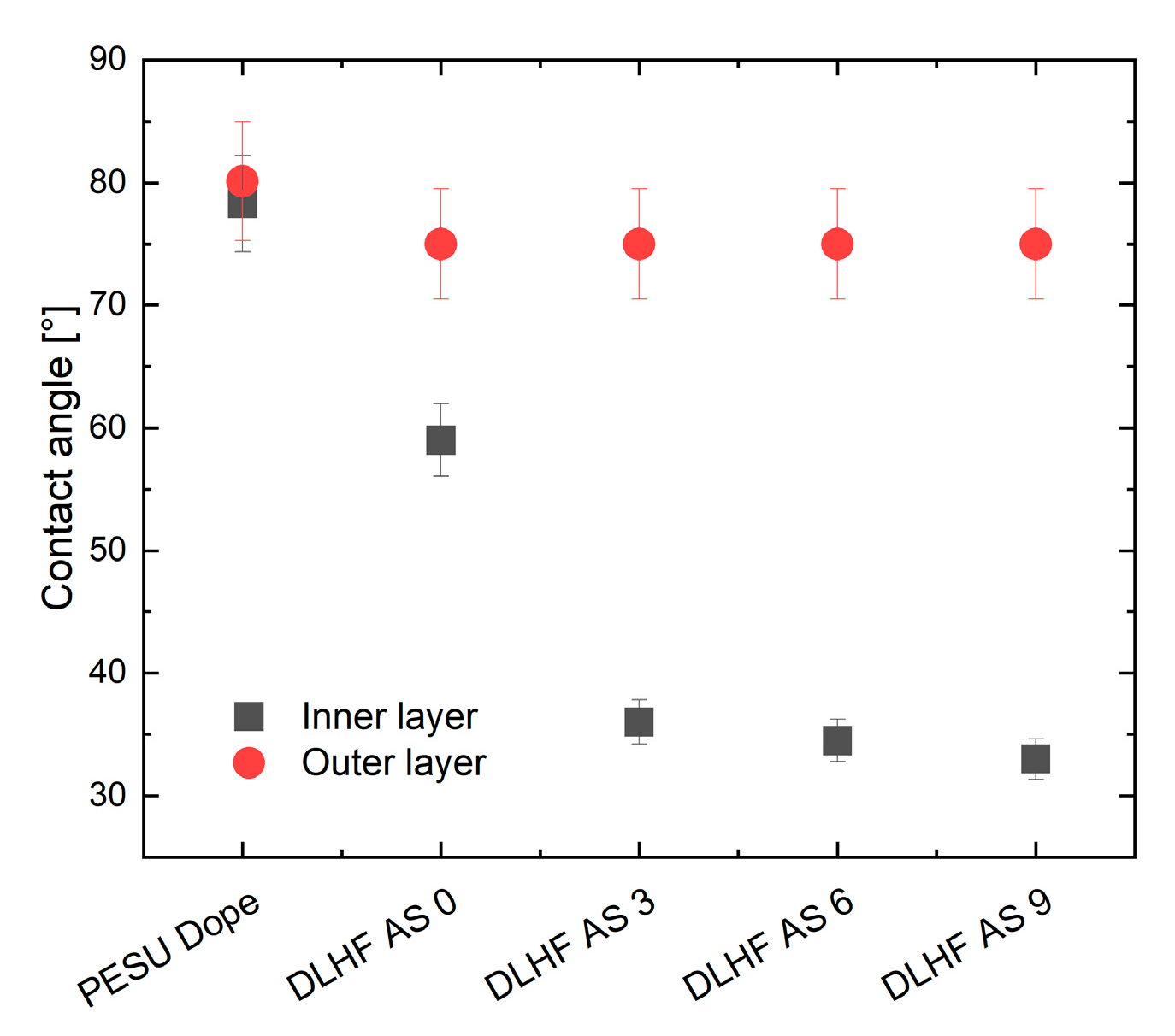
3.2.2. Membrane Hydrophilicity
3.2.3. Membrane Performance
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Xu, Y.M.; Tang, Y.P.; Chung, T.-S.; Weber, M.; Maletzko, C. Polyarylether membranes for dehydration of ethanol and methanol via pervaporation. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2018, 193, 165–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gronwald, O.; Weber, M. Agnique amd 3l as green solvent for polyethersulfone ultrafiltration membrane preparation. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2020, 137, 48419–48430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prulho, R.; Therias, S.; Rivaton, A.; Gardette, J.-L. Ageing of polyethersulfone/polyvinylpyrrolidone blends in contact with bleach water. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2013, 98, 1164–1172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Regula, C.; Carretier, E.; Wyart, Y.; Sergent, M.; Gésan-Guiziou, G.; Ferry, D.; Vincent, A.; Boudot, D.; Moulin, P. Ageing of ultrafiltration membranes in contact with sodium hypochlorite and commercial oxidant: Experimental designs as a new ageing protocol. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2013, 103, 119–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nunes, S.P.; Peinemann, K.V. Ultrafiltration membranes from pvdf/pmma blends. J. Membr. Sci. 1992, 73, 25–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Y.; Han, G.; Zhang, L.; Chen, S.-B.; Chung, T.-S.; Weber, M.; Staudt, C.; Maletzko, C. Rheology and phase inversion behavior of polyphenylenesulfone (ppsu) and sulfonated ppsu for membrane formation. Polymer 2016, 99, 72–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishino, T.; Nabata, N.; Maeoka, T. Process of Making a Porous Ptfe Membrane. US5910277A, 17 May 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, D.; Li, K.; Teo, W. Porous pvdf asymmetric hollow fiber membranes prepared with the use of small molecular additives. J. Membr. Sci. 2000, 178, 13–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banerjee, I.; Pangule, R.C.; Kane, R.S. Antifouling coatings: Recent developments in the design of surfaces that prevent fouling by proteins, bacteria, and marine organisms. Adv. Mater. 2011, 23, 690–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, T.; Li, X.; Wan, C.; Chung, T.-S. Zwitterionic polymers grafted poly(ether sulfone) hollow fiber membranes and their antifouling behaviors for osmotic power generation. J. Membr. Sci. 2016, 497, 142–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.-H.; Shao, X.-S.; Zhou, Q.; Li, M.-Z.; Zhang, Q.-Q. The double effects of silver nanoparticles on the pvdf membrane: Surface hydrophilicity and antifouling performance. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2013, 265, 663–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Zhong, Z.; Ma, R.; Zhang, W.; Li, J. Development of high-antifouling ppsu ultrafiltration membrane by using compound additives: Preparation, morphologies, and filtration resistant properties. Membranes 2016, 6, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, M.; Su, Y.; Mu, C.; Jiang, Z. Improved antifouling property of pes ultrafiltration membranes using additive of silica− pvp nanocomposite. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2010, 49, 790–796. [Google Scholar]
- Navarro, E.; Piccapietra, F.; Wagner, B.; Marconi, F.; Kaegi, R.; Odzak, N.; Sigg, L.; Behra, R. Toxicity of silver nanoparticles to chlamydomonas reinhardtii. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2008, 42, 8959–8964. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, H.; Zhang, Y.; Sadam, H.; Ma, J.; Bai, Y.; Shen, X.; Kim, J.-K.; Shao, L. Novel mussel-inspired zwitterionic hydrophilic polymer to boost membrane water-treatment performance. J. Membr. Sci. 2019, 582, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koehler, J.A.; Ulbricht, M.; Belfort, G. Intermolecular forces between a protein and a hydrophilic modified polysulfone film with relevance to filtration. Langmuir 2000, 16, 10419–10427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marshall, A.; Munro, P.; Trägårdh, G. The effect of protein fouling in microfiltration and ultrafiltration on permeate flux, protein retention and selectivity: A literature review. Desalination 1993, 91, 65–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buzea, C.; Pacheco, I.I.; Robbie, K. Nanomaterials and nanoparticles: Sources and toxicity. Biointerphases 2007, 2, MR17–MR71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gronwald, O.; Frost, I.; Ulbricht, M.; Kouchaki Shalmani, A.; Panglisch, S.; Grünig, L.; Handge, U.A.; Abetz, V.; Heijnen, M.; Weber, M. Hydrophilic poly(phenylene sulfone) membranes for ultrafiltration. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2020, 250, 117107–117117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panglisch, S.; Kouchaki Shalmani, A.; Weber, M.; Gronwald, O.; Berg, P.; Heijnen, M.; Krug, M.; Koti, M.; Nahrstedt, A.; Abetz, V.; et al. Material selection box for the production of advanced polymer membranes for water treatment. Chem. Ing. Tech. 2019, 91, 1162–1167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Handge, U.A.; Gronwald, O.; Weber, M.; Hankiewicz, B.; Abetz, V. Phase behavior and dynamics of pluronic®-based additives in semidilute solutions of poly(ethersulfone) and poly(n-vinyl pyrrolidone): Rheological and dynamic light scattering experiments. Rheol. Acta 2019, 58, 591–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weber, M.; Janssen, N.; Voss, H.; Malisz, J.; Heijnen, M.; Menozzi, E. Process for Making Membranes. WO2016023765A1, 18 February 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Handge, U.A.; Gronwald, O.; Weber, M.; Koll, J.; Abetz, C.; Hankiewicz, B.; Abetz, V. Fabrication of membranes of polyethersulfone and poly(n-vinyl pyrrolidone): Influence of glycerol on processing and transport properties. Polym. Int. 2020, 69, 502–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Provencher, S.W. A constrained regularization method for inverting data represented by linear algebraic or integral equations. Comput. Phys. Commun. 1982, 27, 213–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guillen, G.R.; Ramon, G.Z.; Kavehpour, H.P.; Kaner, R.B.; Hoek, E.M. Direct microscopic observation of membrane formation by nonsolvent induced phase separation. J. Membr. Sci. 2013, 431, 212–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Chung, T.-S.; Wang, R. Morphological aspects and structure control of dual-layer asymmetric hollow fiber membranes formed by a simultaneous co-extrusion approach. J. Membr. Sci. 2004, 243, 155–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lodge, T. Dynamic light scattering from multicomponent polymer solutions. Int. J. Polym. Anal. Charact. 1996, 2, 323–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandit, N.K.; Kanjia, J. Phase behavior of nonionic surfactant solutions in the presence of polyvinylpyrrolidone. Int. J. Pharm. 1996, 141, 197–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chanamai, R.; McClements, D. Depletion flocculation of beverage emulsions by gum arabic and modified starch. J. Food Sci. 2001, 66, 457–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dickinson, E.; Golding, M. Depletion flocculation of emulsions containing unadsorbed sodium caseinate. Food Hydrocoll. 1997, 11, 13–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jenkins, P.; Snowden, M. Depletion flocculation in colloidal dispersions. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 1996, 68, 57–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuinier, R.; Rieger, J.; De Kruif, C. Depletion-induced phase separation in colloid–polymer mixtures. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2003, 103, 1–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boom, R.M. Membrane Formation by Immersion Precipitation: The Role of a Polymeric Additive. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Twente, Enschede, The Netherlands, 1992. [Google Scholar]
- Boom, R.M.; van den Boomgaard, T.; Smolders, C.a. Mass transfer and thermodynamics during immersion precipitation for a two-polymer system. J. Membr. Sci. 1994, 90, 231–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabasso, I.; Klein, E.; Smith, J.K. Polysulfone hollow fibers. I. Spinning and properties. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 1976, 20, 2377–2394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabasso, I.; Klein, E.; Smith, J.K. Polysulfone hollow fibers. Ii. Morphology. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 1977, 21, 165–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mixan, C.E.; Lambert, J.B. Esca [x-ray photoelectron spectroscopic] study of the sulfur-nitrogen bond in sulfimides. J. Org. Chem. 1973, 38, 1350–1353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chehimi, M.M.; Delamar, M. X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy of merocyanine dyes: Part viii. Partial charge and conjugation of heteroatoms in the electroattractor rings. J. Electron Spectrosc. Relat. Phenom. 1990, 50, C25–C32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yatsimirskii, K.; Nemoskalenko, V.; Aleshin, V.; Bratushko, Y.I.; Moiseenko, E. X-ray photoelectron spectra of mixed oxygenated cobalt (ii)-amino acid-imidazole complexes. Chem. Phys. Lett. 1977, 52, 481–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]







| Solution | Additive | PESU | PVP | Glycerol | NMP |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AS 0 | 0 | 17 | 5 | 8 | 70 |
| AS 3 | 3 | 14 | 5 | 8 | 70 |
| AS 6 | 6 | 11 | 5 | 8 | 70 |
| AS 9 | 9 | 8 | 5 | 8 | 70 |
| AS 12 | 12 | 5 | 5 | 8 | 70 |
| PESU Dope (outer) | 0 | 19 | 6 | 10 | 65 |
| Parameter | DLHF AS 0 | DLHF AS 3 | DLHF AS 6 | DLHF AS 9 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bore fluid | [mL/min] | 2.8 | 2.5 | 3.5 | 3.5 |
| Outer dope | [mL/min] | 2.5 | 2.0 | 2.0 | 2.2 |
| Additive solution | [mL/min] | 0.5 | 0.5 | 0.5 | 0.5 |
| Spinning temperature | [°C] | 60 | |||
| Distance to coagulation bath | [cm] | 15 | |||
| Solution | D [10−12 m2/s] |
|---|---|
| AS 0 | 48.4 ± 0.3 |
| AS 3 | 52.3 ± 0.3 |
| AS 6 | 55.1 ± 0.7 |
| AS 9 | 54.7 ± 0.7 |
| AS 12 | 62.8 ± 1.7 |
| AS 0 | AS 3 | AS 6 | AS 9 | AS 12 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | 89.20 | 47.01 | 43.39 | 60.79 | 53.85 |
| τ1 [s] | 2.30 | 0.09 | 0.06 | 3.16 | 3.88 |
| B | 6.00 | 42.32 | 34.47 | 11.06 | 7.48 |
| τ2 [s] | 27.85 | 8.69 | 10.47 | 38.25 | 73.08 |
| C | 4.80 | 9.72 | 21.09 | 28.12 | 38.61 |
| Membrane | PWP [L/(m2 h bar)] | MWCO [kDa] |
|---|---|---|
| DLHF AS 0 | 187 | 40 |
| DLHF AS 3 | 578 | 60 |
| DLHF AS 6 | 2040 | 200 |
| DLHF AS 9 | 2000 | 100 |
| PESU Dope | 1200 | 50 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Grünig, L.; Handge, U.A.; Koll, J.; Gronwald, O.; Weber, M.; Hankiewicz, B.; Scharnagl, N.; Abetz, V. Hydrophilic Dual Layer Hollow Fiber Membranes for Ultrafiltration. Membranes 2020, 10, 143. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes10070143
Grünig L, Handge UA, Koll J, Gronwald O, Weber M, Hankiewicz B, Scharnagl N, Abetz V. Hydrophilic Dual Layer Hollow Fiber Membranes for Ultrafiltration. Membranes. 2020; 10(7):143. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes10070143
Chicago/Turabian StyleGrünig, Lara, Ulrich A. Handge, Joachim Koll, Oliver Gronwald, Martin Weber, Birgit Hankiewicz, Nico Scharnagl, and Volker Abetz. 2020. "Hydrophilic Dual Layer Hollow Fiber Membranes for Ultrafiltration" Membranes 10, no. 7: 143. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes10070143
APA StyleGrünig, L., Handge, U. A., Koll, J., Gronwald, O., Weber, M., Hankiewicz, B., Scharnagl, N., & Abetz, V. (2020). Hydrophilic Dual Layer Hollow Fiber Membranes for Ultrafiltration. Membranes, 10(7), 143. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes10070143






