Multiepitope Proteins for the Differential Detection of IgG Antibodies against RBD of the Spike Protein and Non-RBD Regions of SARS-CoV-2
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Patient Samples and Ethical Approval
2.2. B-Linear Epitope Mapping
2.3. Gene Synthesis, Protein Expression, and Purification
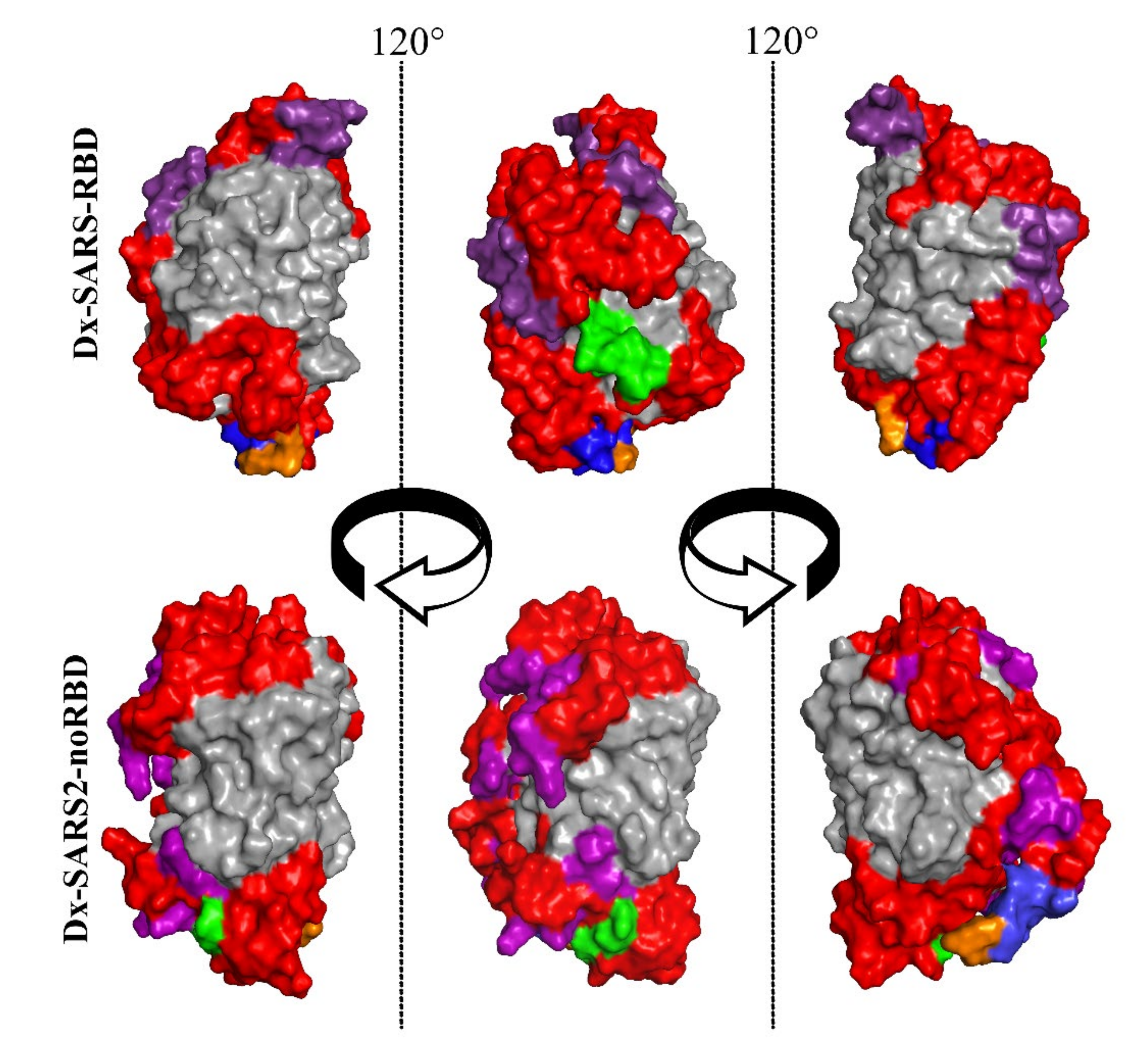
2.4. Molecular Modeling
2.5. In-House ELISAs
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Bioengineering Multiepitope Proteins Specific for SARS-CoV-2
3.2. Performance of Dx-SARS2-RBD and Dx-SARS2-noRBD in Serodiagnosis
3.3. Screening of Individuals with Suspected Contact with COVID-19
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
6. Patents
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gao, G.F. From “A”IV to “ZIKV”: Attacks from emerging and re-emerging pathogens. Cell 2018, 172, 1157–1159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, G.; Fan, Y.; Lai, Y.; Han, T.; Li, Z.; Zhou, P.; Pan, P.; Wang, W.; Hu, D.; Liu, X.; et al. Coronavirus infections and immune responses. J. Med. Virol. 2020, 92, 424–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.R.; Cao, Q.D.; Hong, Z.S.; Tan, Y.Y.; Chen, S.D.; Jin, H.J.; Tan, K.S.; Wang, D.Y.; Yan, Y. The origin, transmission, and clinical therapies on coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) outbreak—An update on the status. Mil. Med. Res. 2020, 7, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Du, Z.; Xu, X.; Wu, Y.; Wang, L.; Cowling, B.J.; Meyers, L.A. Serial interval of COVID-19 among publicly reported confirmed cases. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2020, 26, 1341–1343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tindale, L.C.; Stockdale, J.E.; Coombe, M.; Garlock, E.S.; Lau, W.Y.V.; Saraswat, M.; Zhang, L.; Chen, D.; Wallinga, J.; Colijn, C. Evidence for transmission of COVID-19 before symptom onset. Elife 2020, 9, e57149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tosta, E. Transmission of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 through asymptomatic carriers and aerosols: A major public health challenge. Rev. Soc. Bras. Med. Trop. 2020, 53, e20200669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, A.; Peng, Y.; Huang, B.; Ding, X.; Wang, X.; Niu, P.; Meng, J.; Zhu, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Jiangyuan, W.; et al. Genome Composition and divergence of the novel coronavirus (2019-nCoV) originating in China. Cell Host Microbe 2020, 27, 325–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wang, H.; Li, X.; Li, T.; Zhang, S.; Wang, L.; Wu, X.; Liu, J. The genetic sequence, origin, and diagnosis of SARS-CoV-2. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2020, 39, 1629–1635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, W.J.; Ni, Z.Y.; Hu, Y.; Liang, W.H.; Ou, C.Q.; He, J.X.; Liu, L.; Shan, H.; Lei, C.L.; Hui, D.S.C.; et al. Clinical characteristics of coronavirus disease 2019 in China. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 382, 1708–1720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teymouri, M.; Mollazadeh, S.; Mortazavi, H.; Naderi Ghale-Noie, Z.; Keyvani, V.; Aghababaei, F.; Hamblin, M.R.; Abbaszadeh-Goudarzi, G.; Pourghadamyari, H.; Hashemian, S.M.R.; et al. Recent advances and challenges of RT-PCR tests for the diagnosis of COVID-19. Pathol. Res. Pract. 2021, 221, 153443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, Y.; Wan, Z.; Li, L.; Li, P.; Li, C.; Ma, Q.; Cao, C. Antibody responses against SARS-coronavirus and its nucleocapsid in SARS patients. J. Clin. Virol. 2004, 31, 66–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, K.; Ko, H.L.; Lee, E.Y.; Park, H.J.; Kim, Y.S.; Kim, Y.S.; Cho, N.H.; Park, M.S.; Lee, S.M.; Kim, J.; et al. Development of a diagnostic system for detection of specific antibodies and antigens against middle east respiratory syndrome coronavirus. Microbiol. Immunol. 2018, 62, 574–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dowlatshahi, S.; Shabani, E.; Abdekhodaie, M.J. Serological assays and host antibody detection in coronavirus-related disease diagnosis. Arch. Virol. 2021, 166, 715–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, F.R.; Napoleão-Pego, P.; De-Simone, S.G. Identification of linear B epitopes of pertactin of Bordetella pertussis induced by immunization with whole and acellular vaccine. Vaccine 2014, 32, 6251–6258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- De Simone, S.G.; Gomes, L.R.; Napoleão-Pêgo, P.; Lechuga, G.C.; Pina, J.C.; Silva, F.R. Identification of linear B epitopes liable for the protective immunity of diphtheria toxin. Vaccines 2021, 9, 313. [Google Scholar]
- Lechuga, G.C.; Napoleão-Pêgo, P.; Bottino, C.C.G.; Pinho, R.T.; Provance, D.W., Jr.; De-Simone, S.G. Trypanosoma cruzi presenilin-like transmembrane aspartyl protease: Characterization and cellular localization. Biomolecules 2020, 10, 1564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y. I-TASSER server for protein 3D structure prediction. BMC Bioinform. 2008, 9, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Roy, A.; Kucukural, A.; Zhang, Y. I-TASSER: A unified platform for automated protein structure and function prediction. Nat. Protoc. 2010, 5, 725–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Close, D.W.; Paul, C.D.; Langan, P.S.; Wilce, M.C.; Traore, D.A.; Halfmann, R.; Rocha, R.C.; Waldo, G.S.; Payne, R.J.; Rucker, J.B.; et al. Thermal green protein, an extremely stable, nonaggregating fluorescent protein created by structure-guided surface engineering. Proteins 2015, 83, 1225–1237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jiang, X.; Rayner, S.; Luo, M.H. Does SARS-CoV-2 has a longer incubation period than SARS and MERS. J. Med. Virol. 2020, 92, 476–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omori, R.; Matsuyama, R.; Nakata, Y. The age distribution of mortality from novel coronavirus disease (COVID-19) suggests no large difference of susceptibility by age. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 16642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, C.Y.; Park, H.; Kim, D.W.; Choi, Y.J.; Kim, S.W.; Chang, T.I. Clinical characteristics of asymptomatic patients with COVID-19: A Nationwide cohort study in South Korea. Int. J. Infect. Dis. 2020, 99, 266–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corman, V.M.; Landt, O.; Kaiser, M.; Molenkamp, R.; Meijer, A.; Chu, D.K.; Bleicker, T.; Brünink, S.; Schneider, J.; Schmidt, M.L.; et al. Detection of 2019 novel coronavirus (2019-nCoV) by real-time RT-PCR. Euro Surveill. 2020, 25, 2000045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mohammadi, A.; Esmaeilzadeh, E.; Li, Y.; Bosch, R.J.; Li, J. SARS-CoV-2 detection in different respiratory sites: A systematic review and meta-analysis. EBioMedicine 2020, 59, 102903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- To, K.K.; Tsang, O.T.; Yip, C.; Chan, K.H.; Wu, T.C.; Chan, J.M.; Leung, W.S.; Chik, T.S.; Choi, C.Y.; Kandamby, D.H.; et al. Consistent detection of 2019 novel coronavirus in saliva. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2020, 71, 841–843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pan, Y.; Zhang, D.; Yang, P.; Poon, L.L.M.; Wang, Q. Viral load of SARS-CoV-2 in clinical samples. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2020, 20, 411–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, L.; Ruan, F.; Huang, M.; Liang, L.; Huang, H.; Hong, Z.; Yu, J.; Kang, M.; Song, Y.; Xia, J.; et al. SARS-CoV-2 viral load in upper respiratory specimens of infected patients. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 382, 1177–1179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, P.; Yang, X.L.; Wang, X.G.; Hu, B.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, W.; Si, H.R.; Zhu, Y.; Li, B.; Huang, C.L.; et al. A pneumonia outbreak associated with a new coronavirus of probable bat origin. Nature 2020, 579, 270–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Liu, R.; Han, H.; Liu, F.; Lv, Z.; Wu, K.; Liu, Y.; Feng, Y.; Zhu, C. Positive rate of RT-PCR detection of SARS-CoV-2 infection in 4880 cases from one hospital in Wuhan, China, from Jan to Feb 2020. Clin. Chim. Acta 2020, 505, 172–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Xu, Y.; Gao, R.; Lu, R.; Han, K.; Wu, G.; Tan, W. Detection of SARS-CoV-2 in different types of clinical specimens. JAMA 2020, 323, 1843–1844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Han, H.; Luo, Q.; Mo, F.; Long, L.; Zheng, W. SARS-CoV-2 RNA more readily detected in induced sputum than in throat swabs of convalescent COVID-19 patients. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2020, 20, 655–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wölfel, R.; Corman, V.M.; Guggemos, W.; Seilmaier, M.; Zange, S.; Müller, M.A.; Niemeyer, D.; Jones, T.C.; Vollmar, P.; Rothe, C.; et al. Virological assessment of hospitalized patients with COVID-2019. Nature 2020, 581, 465–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wang, Y.; Zhang, L.; Sang, L.; Ye, F.; Ruan, S.; Zhong, B.; Song, T.; Alshukairi, A.N.; Chen, R.; Zhang, Z.; et al. Kinetics of viral load and antibody response in relation to COVID-19 severity. J. Clin. Investig. 2020, 130, 5235–5244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, W.; Lu, Y.; Zhang, J.; Wang, J.; Dan, Y.; Tan, Z.; He, X.; Qian, C.; Sun, Q.; Hu, Q.; et al. Viral kinetics and antibody responses in patients with COVID-19. medRxiv 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Okba, N.M.A.; Müller, M.A.; Li, W.; Wang, C.; GeurtsvanKessel, C.H.; Corman, V.M.; Lamers, M.M.; Sikkema, R.S.; de Bruin, E.; Chandler, F.D.; et al. Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2−specific antibody responses in coronavirus disease patients. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2020, 26, 1478–1488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lou, B.; Li, T.D.; Zheng, S.F.; Su, Y.Y.; Li, Z.Y.; Liu, W.; Yu, F.; Ge, S.X.; Zou, Q.D.; Yuan, Q.; et al. Serology characteristics of SARS-CoV-2 infection after exposure and post-symptom onset. Eur. Respir. J. 2020, 56, 2000763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haveri, A.; Smura, T.; Kuivanen, S.; Österlund, P.; Hepojoki, J.; Ikonen, N.; Pitkäpaasi, M.; Blomqvist, S.; Rönkkö, E.; Kantele, A.; et al. Serological and molecular findings during SARS-CoV-2 infection: The first case study in Finland, January to February 2020. Euro Surveill. 2020, 25, 2000266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, F.; Wang, A.; Liu, M.; Wang, Q.; Chen, J.; Xia, S.; Ling, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Xun, J.; Lu, L.; et al. Neutralizing antibody responses to SARS-CoV-2 in a COVID-19 recovered patient cohort and their implications. medRxiv 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grayson, K.J.; Anderson, J.L.R. Designed for life: Biocompatible de novo designed proteins and components. J. R. Soc. Interface 2018, 15, 20180472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.; Sesterhenn, F.; Bonet, J.; van Aalen, E.A.; Scheller, L.; Abriata, L.A.; Cramer, J.T.; Wen, X.; Rosset, S.; Georgeon, S.; et al. Bottom-up de novo design of functional proteins with complex structural features. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2021, 17, 492–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crameri, A.; Whitehorn, E.A.; Tate, E.; Stemmer, W.P. Improved green fluorescent protein by molecular evolution using DNA shuffling. Nat. Biotechnol. 1996, 14, 315–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fisher, A.C.; DeLisa, M.P. Laboratory evolution of fast-folding green fluorescent protein using secretory pathway quality control. PLoS ONE 2008, 3, e2351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ormö, M.; Cubitt, A.B.; Kallio, K.; Gross, L.A.; Tsien, R.Y.; Remington, S.J. Crystal structure of the Aequorea victoria green fluorescent protein. Science 1996, 273, 1392–1395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pédelacq, J.D.; Cabantous, S.; Tran, T.; Terwilliger, T.C.; Waldo, G.S. Engineering and characterization of a super folder green fluorescent protein. Nat. Biotechnol. 2006, 24, 79–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abedi, M.R.; Caponigro, G.; Kamb, A. Green fluorescent protein as a scaffold for intracellular presentation of peptides. Nucleic Acids Res. 1998, 26, 623–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kiss, C.; Fisher, H.; Pesavento, E.; Dai, M.; Valero, R.; Ovecka, M.; Nolan, R.; Phipps, M.L.; Velappan, N.; Chasteen, L.; et al. Antibody binding loop insertions as diversity elements. Nucleic Acids Res. 2006, 34, e132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavoor, T.V.; Cho, Y.K.; Shusta, E.V. Development of GFP-based biosensors possessing the binding properties of antibodies. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 11895–11900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhong, J.Q.; Freyzon, Y.; Ehrlich, D.J.; Matsudaira, P. Enhanced detection sensitivity using a novel solid-phase incorporated affinity fluorescent protein biosensor. Biomol. Eng. 2004, 21, 67–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ju, B.; Zhang, Q.; Ge, J.; Wang, R.; Sun, J.; Ge, X.; Yu, J.; Shan, S.; Zhou, B.; Song, S.; et al. Human neutralizing antibodies elicited by SARS-CoV-2 infection. Nature 2020, 584, 115–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Liu, S.; Kou, Z.; Li, W.; Farzan, M.; Jiang, S. Receptor-binding domain of SARS-CoV spike protein induces highly potent neutralizing antibodies: Implication for developing subunit vaccine. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2004, 324, 773–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.; Liu, Q.; Du, L.; Lu, L.; Jiang, S. Receptor-binding domain as a target for developing SARS vaccines. J. Thorac. Dis. 2013, 5 (Suppl. S2), S142–S148. [Google Scholar]
- Yan, G.; Lee, C.K.; Lam, L.T.M.; Yan, B.; Chua, Y.X.; Lim, A.Y.N.; Phang, K.F.; Kew, G.S.; Teng, H.; Ngai, C.H.; et al. Covert COVID-19 and false-positive dengue serology in Singapore. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2020, 20, 536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fiorentini, S.; Messali, S.; Zani, A.; Caccuri, F.; Giovanetti, M.; Ciccozzi, M.; Caruso, A. First detection of SARS-CoV-2 spike protein N501 mutation in Italy in August 2020. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2021, 21, e147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Zhang, Q.; Wei, P.; Chen, Z.; Aviszus, K.; Yang, J.; Downing, W.; Jiang, C.; Liang, B.; Reynoso, L.; et al. The basis of a more contagious 501Y.V1 variant of SARS-CoV-2. Cell Res. 2021, 1, 720–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Epitope | Origin | AAs 1 | Balancer 2 | AA in TGP 3 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dx-SARS2-RBD | FERDISTEIYQAGST | RBD of Spike | 464–479 | N/A | -NH2 |
| 4 /GSTPCNGVEGFNCYF | RBD of Spike 5 | 476–491 | GSSGEAAKEAAK/ | 50,58 | |
| NSNNLDSKVGGNYNY | RBD of Spike | 437–451 | N/A | 126,140 | |
| FERDISTEIYQAGST/ | RBD of Spike | 464–479 | /GGSGTSYWKGS | 168,172 | |
| GSTPCNGVEGFNCYF | RBD of Spike 5 | 476–491 | N/A | 184,193 | |
| YFPLQSYGFQPTNGV/ | RBD of Spike | 490–504 | /GSSGEAAKEAAK | 204,210 | |
| YFPLQSYGFQPTNGV | RBD of Spike | 490–504 | N/A | -COOH | |
| /NSNNLDSKVGGNYNY | RBD of Spike | 437–451 | GGSGGGASG/ 6 | -COOH | |
| Dx-SARS2-noRBD | LGVYHKNNKSWMESEFRVY/ | Spike | 141–159 | /PAPAP | -NH2 |
| /FIYNKIVDEP | ORF3a | 231–240 | GGSGEAAK/ | 38,40 | |
| KNPLLYDANY | ORF3a | 136–145 | N/A | 50,58 | |
| AGNGGDAALALLLLD | Nucleoprotein | 221–225 | N/A | 77,90 | |
| RSYLTPGDSSS/ | Spike | 246–256 | /GGASG | 99,102 | |
| ADQLTPTWRV | Spike | 625–634 | N/A | 126,140 | |
| FIYNKIVDEP/ | ORF3a | 231–240 | /GGSGTSYWKGS | 168,172 | |
| KNPLLYDANY | ORF3a | 136–145 | N/A | 184,193 | |
| /RPQGLPNNTAS | Nucleoprotein | 41–50 | GGSGGEAAKG/ | 204,210 | |
| /LIRQGTDYKHWPQIA | Nucleoprotein | 291–305 | LAEILQKN/ | -COOH | |
| /GKIADYNYKL | Spike | 415–424 | GGSGG/ 5 | -COOH |
| Multiepitope Protein | 3× 1 | Absorbance | Sensitivity (%) | Specificity (%) | Likelihood |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dx-SARS2-RBD | 0.36 | 0.241 | 100 | 99.51 | 198.4 |
| 0.2658 | 100 | 100 | - | ||
| Dx-SARS2-noRBD | 0.24 | 0.2055 | 100 | 99.21 | 127 |
| 0.2385 | 100 | 100 | - |
| Multiepitope Protein | N (Positive) | N (Negative) | AUC | Std. Error | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dx-SARS2-RBD | 185 | 205 | 0.9984 | 0.0008596 | <0.0001 |
| Dx-SARS2-noRBD | 52 | 127 | 1 | 0 | <0.0001 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gomes, L.R.; Durans, A.M.; Napoleão-Pêgo, P.; Waterman, J.A.; Freitas, M.S.; De Sá, N.B.R.; Pereira, L.V.; Furtado, J.S.; Aquino, R.G.; Machado, M.C.R.; et al. Multiepitope Proteins for the Differential Detection of IgG Antibodies against RBD of the Spike Protein and Non-RBD Regions of SARS-CoV-2. Vaccines 2021, 9, 986. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines9090986
Gomes LR, Durans AM, Napoleão-Pêgo P, Waterman JA, Freitas MS, De Sá NBR, Pereira LV, Furtado JS, Aquino RG, Machado MCR, et al. Multiepitope Proteins for the Differential Detection of IgG Antibodies against RBD of the Spike Protein and Non-RBD Regions of SARS-CoV-2. Vaccines. 2021; 9(9):986. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines9090986
Chicago/Turabian StyleGomes, Larissa R., Andressa M. Durans, Paloma Napoleão-Pêgo, Jessica A. Waterman, Mariana S. Freitas, Nathalia B. R. De Sá, Lilian V. Pereira, Jéssica S. Furtado, Romário G. Aquino, Mario C. R. Machado, and et al. 2021. "Multiepitope Proteins for the Differential Detection of IgG Antibodies against RBD of the Spike Protein and Non-RBD Regions of SARS-CoV-2" Vaccines 9, no. 9: 986. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines9090986
APA StyleGomes, L. R., Durans, A. M., Napoleão-Pêgo, P., Waterman, J. A., Freitas, M. S., De Sá, N. B. R., Pereira, L. V., Furtado, J. S., Aquino, R. G., Machado, M. C. R., Fintelman-Rodrigues, N., Souza, T. M. L., Morel, C. M., Provance, D. W., & De-Simone, S. G. (2021). Multiepitope Proteins for the Differential Detection of IgG Antibodies against RBD of the Spike Protein and Non-RBD Regions of SARS-CoV-2. Vaccines, 9(9), 986. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines9090986






