Cardiorespiratory Events Following the Second Routine Immunization in Preterm Infants: Risk Assessment and Monitoring Recommendations
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Recruitment
2.2. Data Acquisition and Analysis
2.3. Statistical Analyses
2.4. Ethics
3. Results
CREs
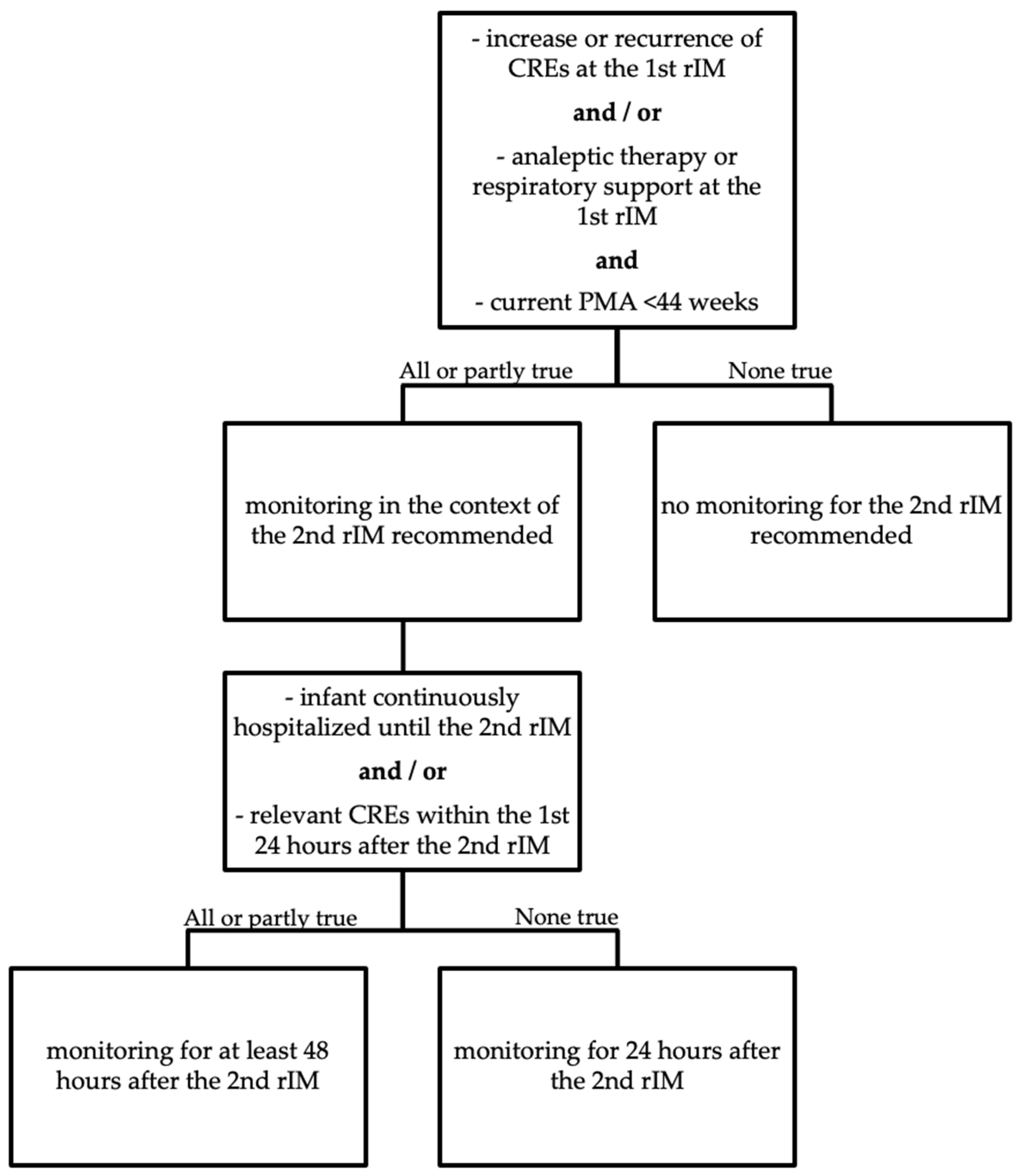
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ständige Impfkommission: Empfehlungen der Ständigen Impfkommission (STIKO) am Robert Koch-Institut (RKI). Epidemiol. Bull. 2019, 34, 313–364. [CrossRef]
- Public Health England. The UK Immunization Schedule: The Green Book, Chapter 11. January 2020. Available online: http://www.gov.uk/government/publications/immunisation-schedule-the-green-book-chapter-11 (accessed on 28 May 2021).
- Australian Technical Advisory Group on Immunisation (ATAGI). Australian Immunisation Handbook; Australian Government Department of Health: Canberra, Australia, 2018. Available online: http://immunisationhandbook.health.gov.au (accessed on 28 May 2021).
- Ezeanolue, E.; Harriman, K.; Hunter, P.; Kroger, A.; Pellegrini, C.; National Center for Immunization and Respiratory Diseases. General Best Practice Guidelines for Immunization. Best Practices Guidance of the Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices (ACIP). Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/vaccines/hcp/acip-recs/general-recs/downloads/general-recs.pdf (accessed on 28 May 2021).
- Immunization of Infants Born Prematurely: Canadian Immunization Guide. Part 3: Vaccination of Specific Populations. Available online: https://www.canada.ca/en/public-health/services/publications/healthy-living/canadian-immunization-guide-part-3-vaccination-specific-populations/page-5-immunization-infants-born-prematurely.html (accessed on 28 May 2021).
- Klein, N.P.; Abu-Elyazeed, R.; Cheuvart, B.; Janssens, W.; Mesaros, N. Immunogenicity and safety following primary and booster vaccination with a hexavalent diphtheria, tetanus, acellular pertussis, hepatitis B, inactivated poliovirus andHaemophilus influenzaetype b vaccine: A randomized trial in the United States. Hum. Vaccines Immunother. 2019, 15, 809–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinón-Torres, F.; Czajka, H.; Center, K.J.; Wysocki, J.; Majda-Stanislawska, E.; Omeñaca, F.; Iturbe, E.B.; Gamero, D.B.; Concheiro-Guisan, A.; Gimenez-Sanchez, F.; et al. 13-Valent Pneumococcal Conjugate Vaccine (PCV13) in Preterm Versus Term Infants. Pediatrics 2015, 135, e876–e886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kent, A.; Ladhani, S.N.; Andrews, N.J.; Scorrer, T.; Pollard, A.J.; Clarke, P.; Hughes, S.M.; Heal, C.; Menson, E.; Chang, J.; et al. Schedules for pneumococcal vaccination of preterm infants: An RCT. Pediatrics 2016, 138, e20153945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Robinson, J.L.; Spady, D.W. Frequency of apnea, bradycardia, and desaturations following first diphtheria-tetanus-pertussis-inactivated polio-Haemophilus influenzae type B immunization in hospitalized preterm infants. BMC Pediatr. 2006, 6, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mialet-Marty, T.; Beuchée, A.; Ben Jmaa, W.; N’Guyen, N.; Navarro, X.; Poree, F.; Nuyt, A.M.; Pladys, P. Possible Predictors of Cardiorespiratory Events after Immunization in Preterm Neonates. Neonatology 2013, 104, 151–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pourcyrous, M.; Korones, S.B.; Arheart, K.L.; Bada, H.S. Primary Immunization of Premature Infants with Gestational Age < 35 Weeks: Cardiorespiratory Complications and C-Reactive Protein Responses Associated with Administration of Single and Multiple Separate Vaccines Simultaneously. J. Pediatr. 2007, 151, 167–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeMeo, S.D.; Raman, S.R.; Hornik, C.P.; Wilson, C.C.; Clark, R.; Smith, P.B. Adverse Events After Routine Immunization of Extremely Low-Birth-Weight Infants. JAMA Pediatr. 2015, 169, 740–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gottlob, S.; Gille, C.; Poets, C.F. Randomized Controlled Trial on the Effects of Morning versus Evening Primary Vaccination on Episodes of Hypoxemia and Bradycardia in Very Preterm Infants. Neonatology 2019, 116, 315–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaudelus, J.; Lefèvre-Akriche, S.; Roumegoux, C.; Bolie, S.; Belasco, C.; Letamendia-Richard, E.; Lachassinne, É. Vaccination du prematuré. Arch. Pédiatr. 2007, 14, S24–S30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saari, T.N. Committee on Infectious Diseases. Immunization of Preterm and Low Birth Weight Infants. Pediatrics 2003, 112, 193–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heininger, U.; Bartmann, P.; Huppertz, H.J.; Kinet, M.; Klein, R.; Korenke, C.; Gahr, M.; Deutsche Akademie für Kinder- und Jugendmedizin e.V. Aktualisierte Stellungnahme der Kommission für Infektionskrankheiten und Impffragen der DAKJ. Überwachung der Atmung bei ehemaligen Frühgeborenen (<28 Schwangerschaftswochen) im Rahmen der Grundimmunisierung. Juli 2013. Mon. Kinderheilkd. 2013, 161, 946–949. Available online: https://www.dakj.de/stellungnahmen/ueberwachung-der-atmung-bei-ehemaligen-fruehgeborenen/#:~:text=Bei%20sehr%20unreifen%20Fr%C3%BChgborenen%20%5B%3C28,48%E2%80%9372%20h%20zu%20%C3%BCberwachen (accessed on 13 August 2021). [CrossRef]
- Flatz-Jequier, A.; Posfay-Barbe, K.M.; Pfister, R.E.; Siegrist, C.-A. Recurrence of Cardiorespiratory Events following Repeat DTaP-Based Combined Immunization in Very Low Birth Weight Premature Infants. J. Pediatr. 2008, 153, 429–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, J.; Noori, K.; A Morris, S. Apnoea after the 2-month immunisation in extremely preterm infants: What happens with the 4-month immunisation? J. Paediatr. Child. Health 2013, 49, E217–E220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clifford, V.; Crawford, N.W.; Royle, J.; Lazzaro, T.; Danchin, M.; Perrett, K.P.; Lee, K.J.; Buttery, J.P. Recurrent apnoea post immunisation: Informing re-immunisation policy. Vaccine 2011, 29, 5681–5687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poets, C.F. Interventions for apnoea of prematurity: A personal view. Acta Paediatr. 2009, 99, 172–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rhein, L.; Simoneau, T.; Davis, J.; Correia, C.; Ferrari, D.; Monuteaux, M.; Gregory, M. Reference values of nocturnal oxygenation for use in outpatient oxygen weaning protocols in premature infants. Pediatr. Pulmonol. 2011, 47, 453–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, P.S.; Hakak, H.; Mohamed, A.; Shah, J.; Young, J.; Kelly, E. Oxygen saturation profile in late-preterm and term infants: A prospective cohort study. J. Perinatol. 2014, 34, 917–920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poets, C.F.; Stebbens, V.A.; Alexander, J.R.; Arrowsmith, W.A.; Salfield, S.A.; Southall, D.P. Arterial oxygen saturation in preterm infants at discharge from the hospital and six weeks later. J. Pediatr. 1992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poets, C.F.; A Stebbens, V.; Samuels, M.P.; Southall, D.P. The Relationship between Bradycardia, Apnea, and Hypoxemia in Preterm Infants. Pediatr. Res. 1993, 34, 144–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beresford, M.W.; Parry, H.; Shaw, N.J. Twelve-Month Prospective Study of Oxygen Saturation Measurements among Term and Preterm Infants. J. Perinatol. 2004, 25, 30–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Wellington, G.; Elder, D.; Campbell, A. 24-hour oxygen saturation recordings in preterm infants: Editing artefact. Acta Paediatr. 2018, 107, 1362–1369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wellington, G.; Campbell, A.J.; E Elder, D. Comparison of 12-hour and 24-hour oximetry recordings in preterm infants. J. Paediatr. Child Health 2018, 55, 938–942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bohnhorst, B.; Seidel, K.; Bohne, C.; Peter, C.; Pirr, S. Heart rate, respiratory rate, apnoeas and peripheral arterial oxygen saturation in healthy term neonates during quiet sleep. Acta Paediatr. 2018, 108, 231–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonafide, C.P.; Brady, P.W.; Keren, R.; Conway, P.H.; Marsolo, K.; Daymont, C. Development of Heart and Respiratory Rate Percentile Curves for Hospitalized Children. Pediatrics 2013, 131, e1150–e1157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Javorka, K.; Lehotska, Z.; Kozar, M.; Uhrikova, Z.; Kolarovszki, B.; Zibolen, M. Heart Rate Variability in Newborns. Physiol. Res. 2017, 66, S203–S214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perlman, J.M.; Volpe, J.J. Episodes of apnea and bradycardia in the preterm newborn: Impact on cerebral circulation. Pediatrics 1985, 76, 333–338. [Google Scholar]
- Poets, C.; Bohnhorst, B.; Kerst, G. Therapie idiopathischer Apnoen, Bradykardien und Hypoxämien bei Früh- und Reifgeborenen. AWMF-Leitlinie Nr. 024-013, 02/2020. Available online: https://gnpi.de/wp-content/uploads/2020/07/024-013l_S2k_Idiopathische_Apnoen_Bradykardien_Hypoxaemien_Fruehgeborene_2020-06.pdf (accessed on 28 May 2021).
- Ng, D.K.; Chan, C.-H. A Review of Normal Values of Infant Sleep Polysomnography. Pediatr. Neonatol. 2013, 54, 82–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schluter, B.; Buschatz, D.; Trowitzsch, E. Polysomnographic Reference Curves for the First and Second Year of Life. Perzentilkurven polysomnographischer Parameter fur das erste und zweite Lebensjahr. Somnologie 2001, 5, 3–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cerar, L.K.; Scirica, C.V.; Gantar, I.S.; Osredkar, D.; Neubauer, D.; Kinane, T.B. A Comparison of Respiratory Patterns in Healthy Term Infants Placed in Car Safety Seats and Beds. Pediatrics 2009, 124, e396–e402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramanathan, R.; Corwin, M.; Hunt, C.E.; Lister, G.; Tinsley, L.R.; Baird, T.; Silvestri, J.M.; Crowell, D.H.; Hufford, D.; Martin, R.J.; et al. Cardiorespiratory Events Recorded on Home MonitorsComparison of Healthy Infants with Those at Increased Risk for SIDS. JAMA 2001, 285, 2199–2207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sen, S.; Cloete, Y.; Hassan, K.; Buss, P. Adverse events following vaccination in premature infants. Acta Paediatr. 2001, 90, 916–920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pfister, R.; Aeschbach, V.; Niksic-Stuber, V.; Martin, B.C.; Siegrist, C.-A. Safety of DTaP-based combined immunization in very-low-birth-weight premature infants: Frequent but mostly benign cardiorespiratory events. J. Pediatr. 2004, 145, 58–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Henderson-Smart, D. The effect of gestational age on the incidence and duration of recurrent apnoea in newborn babies. J. Paediatr. Child Health 1981, 17, 273–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eichenwald, E.C.; Committee on Fetus and Newborn, American Academy of Pediatrics. Apnea of Prematurity. Pediatrics 2015, 137, e20153757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amin, S.B.; Burnell, E. Monitoring Apnea of Prematurity: Validity of Nursing Documentation and Bedside Cardiorespiratory Monitor. Am. J. Perinatol. 2013, 30, 643–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brockmann, P.; Wiechers, C.; Pantalitschka, T.; Diebold, J.; Vagedes, J.; Poets, C.F. Under-recognition of alarms in a neonatal intensive care unit. Arch. Dis. Child. Fetal Neonatal Ed. 2013, 98, F524–F527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omeñaca, F.; Vázquez, L.; Garcia-Corbeira, P.; Mesaros, N.; Hanssens, L.; Dolhain, J.; Gómez, I.P.; Liese, J.; Knuf, M. Immunization of preterm infants with GSK’s hexavalent combined diphtheria-tetanus-acellular pertussis-hepatitis B-inactivated poliovirus-Haemophilus influenzae type b conjugate vaccine: A review of safety and immunogenicity. Vaccine 2018, 36, 986–996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiappini, E.; Petrolini, C.; Sandini, E.; Licari, A.; Pugni, L.; A Mosca, F.; Marseglia, G.L. Update on vaccination of preterm infants: A systematic review about safety and efficacy/effectiveness. Proposal for a position statement by Italian Society of Pediatric Allergology and Immunology jointly with the Italian Society of Neonatology. Expert Rev. Vaccines 2019, 18, 523–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
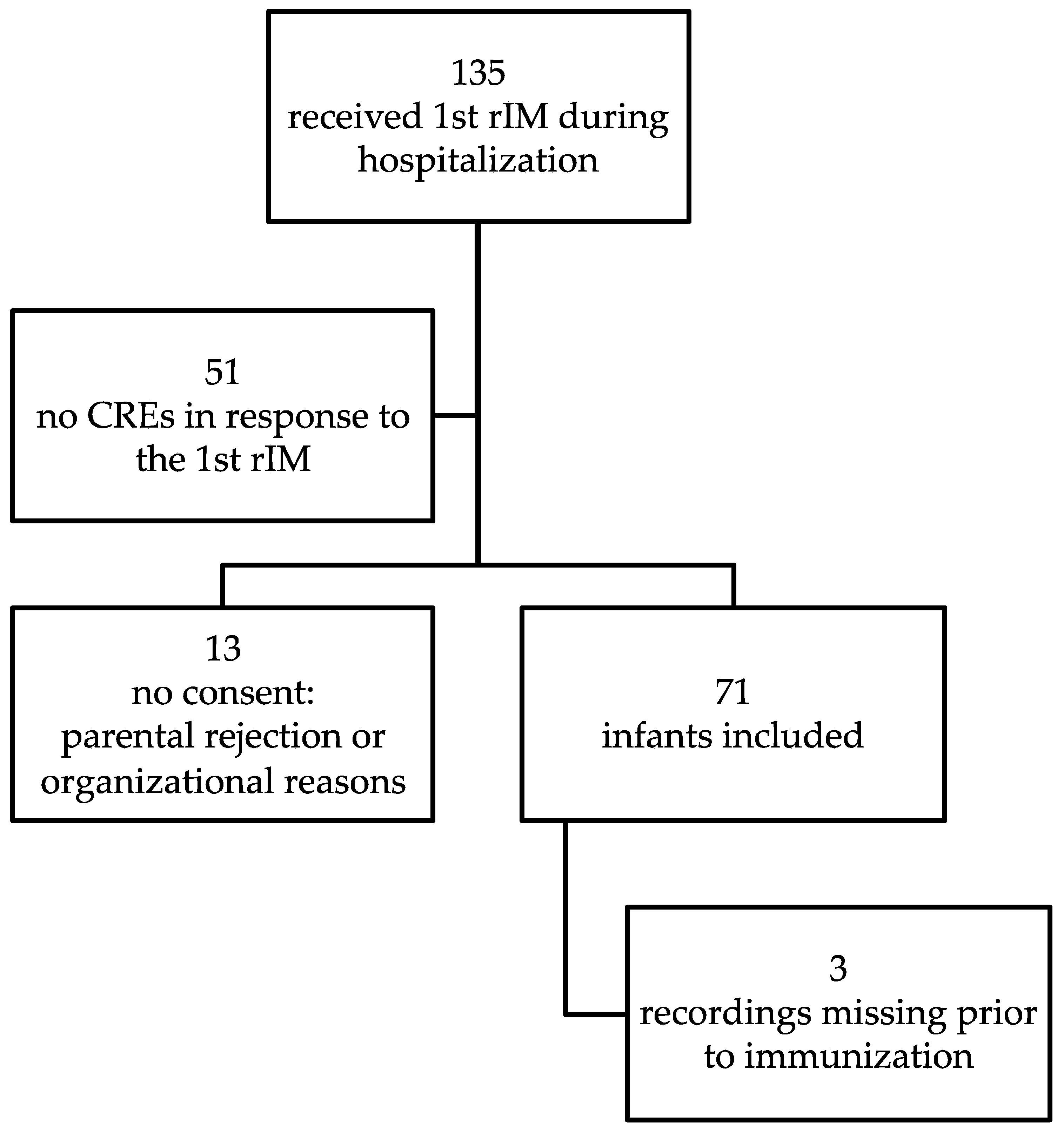
| Clinical Characteristics | Total n = 71 |
|---|---|
| GA at birth in weeks (median (range)) | 26.4 (22.7–30.9) |
| Birth weight in grams (median (range)) | 820 (480–1460) |
| Age at 2nd rIM in days (median (range)) | 94 (85–121) |
| GA at 2nd rIM in weeks (median (range)) | 40.0 (36.3–44.7) |
| Weight at 2nd rIM in grams (median (range)) | 2900 (1890–4080) |
| Analeptic treatment at 1st rIM (n (%)) | 49 (69.0) |
| Respiratory support at 1st rIM (n (%)) | 47 (66.2) |
| Respiratory support at 2nd rIM (n (%)) | 28 (39.4) |
| Bronchopulmonary dysplasia, moderate or severe (n (%)) | 22 (31.0) |
| Intraventricular hemorrhage, >grade 2 (n (%)) | 10 (14.1) |
| 6 h Pre-Immunization n = 68 | 0–24 h Post-Immunization n = 71 | 24–48 h Post-Immunization n = 71 | p Value Pre- vs. Post-Immunization a | p Value 0–24 vs. 24–48 h Post-Immunization b | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bradycardias | |||||
| Number of infants, n (%) | 16 (23.5) | 38 (53.5) | 34 (47.9) | <0.0001 | n.s. |
| Number per hour, mean (SD) | 0.1 (0.2) | 0.15 (0.4) | 0.1 (0.2) | 0.1023 | n.s. |
| Lowest HR (bpm), mean (SD) | 68 (10) | 65 (10) | 64 (11) | 0.4185 | n.s. |
| Maximum duration (seconds), mean (SD) | 6.1 (5.1) | 12.4 (28.5) | 10.3 (9.9) | 0.5737 | n.s. |
| Hypoxemias | |||||
| Number of infants, n (%) | 49 (72.1) | 67 (94.4) | 61 (85.9) | 0.0002 | n.s. |
| Number per hour, mean (SD) | 1.6 (3.1) | 4.0 (7.8) | 1.7 (3.1) | <0.0001 | 0.0004 |
| Lowest SpO2 (%), mean (SD) | 64 (15) | 52 (21) | 57 (16) | 0.0023 | n.s. |
| Maximum duration (seconds), mean (SD) | 18.5 (30.4) | 33.5 (65.1) | 21.3 (21.6) | 0.1506 | n.s. |
| Apneas | |||||
| Number of infants, n (%) | 18 (26.5) | 44 (62.0) | 32 (45.1) | <0.0001 | 0.0320 |
| Number per hour, mean (SD) | 0.1 (0.3) | 0.3 (0.8) | 0.1 (0.2) | 0.0030 | 0.0076 |
| Maximum duration (seconds), mean (SD) | 10.9 (1.9) | 14.6 (7.3) | 13.5 (6.0) | 0.1124 | n.s. |
| CRE-ts | |||||
| Number of infants, n (%) | 3 (4.4) | 21 (29.6) | 12 (16.9) | <0.0001 | 0.0280 |
| Number per hour, mean (SD) | 0.01 (0.03) | 0.02 (0.05) | 0.01 (0.03) | 0.0034 | 0.0222 |
| 6 h Pre-Immunization | 0–24 h Post-Immunization | 24–48 h Post-Immunization | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Bradycardias | |||
| Number of infants, n | 16 | 38 | 34 |
| Number per hour, mean (SD) | 0.3 (0.3) | 0.3 (0.5) | 0.2 (0.3) |
| Hypoxemias | |||
| Number of infants, n | 49 | 67 | 61 |
| Number per hour, mean (SD) | 2.3 (3.5) | 4.1 (7.8) | 1.9 (3.2) |
| Apneas | |||
| Number of infants, n | 18 | 44 | 32 |
| Number per hour, mean (SD) | 0.4 (0.5) | 0.5 (0.9) | 0.2 (0.3) |
| CRE-ts | |||
| Number of infants, n | 3 | 21 | 12 |
| Number per hour, mean (SD) | 0.1 (0.1) | 0.1 (0.1) | 0.1 (0.04) |
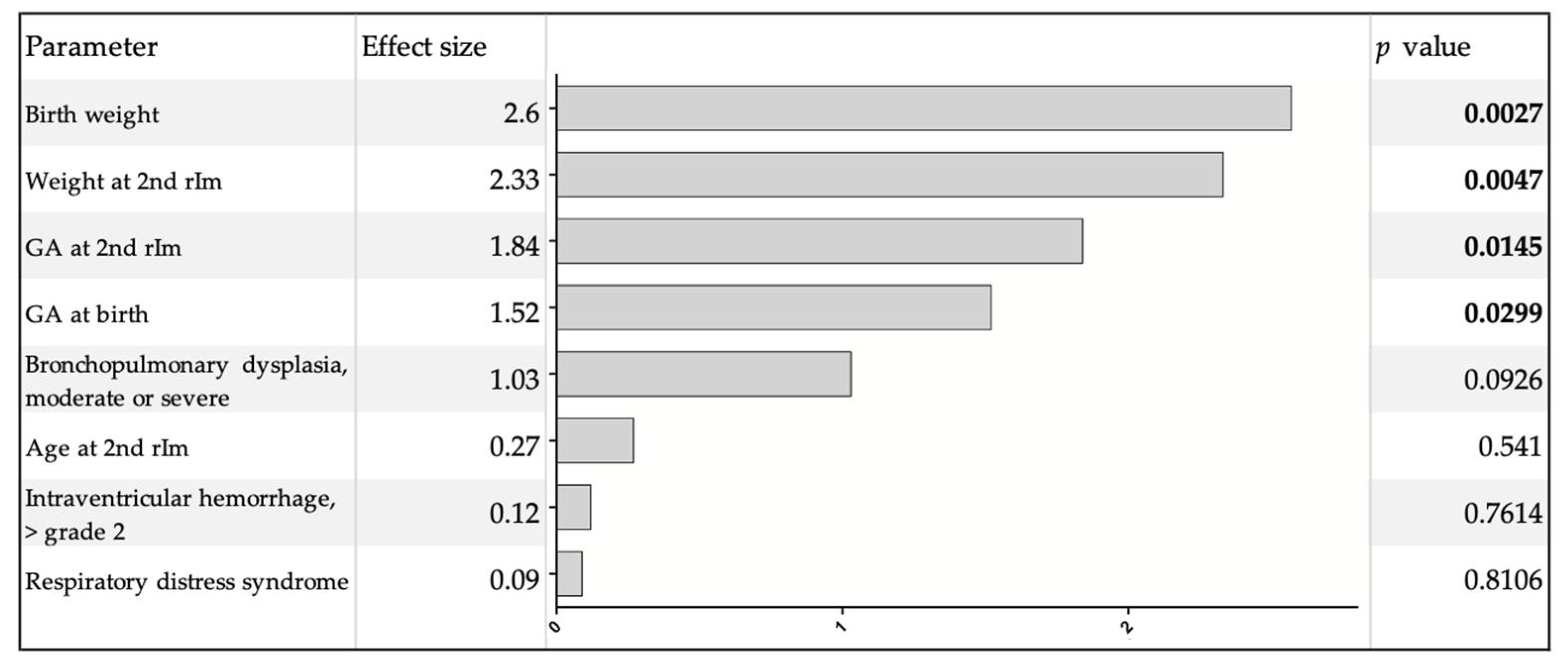
| Infants without CRE-ts n = 46 | Infants with CRE-ts n = 25 | p Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| GA at birth in weeks (median (range)) | 27.1 (23.6–30.9) | 25.4 (22.7–29.3) | 0.0024a |
| Birth weight in grams (median (range)) | 927.5 (480–1460) | 690 (520–1235) | 0.0022a |
| Age at 2nd rIM in days (median (range)) | 94 (88–121) | 94 (85–96) | 0.4483 b |
| GA at 2nd rIM in weeks (median (range)) | 40.9 (36.7–44.7) | 38.3 (36.3–42.6) | 0.0002a |
| Weight at 2nd rIM in grams (median (range)) | 3080 (1890–4080) | 2680 (2035–3770) | 0.0026a |
| Analeptic treatment at 1st rIM (n (%)) | 26 (56.5) | 23 (92.0) | 0.0022b |
| Respiratory support at 1st rIM (n (%)) | 25 (54.3) | 22 (88.0) | 0.0046b |
| Respiratory support at 2nd rIM (n (%)) | 10 (21.7) | 18 (72.0) | <0.0001b |
| Discharge home and readmission for 2nd rIM (n (%)) | 21 (45.7) | 2 (8.0) | 0.0013b |
| Bronchopulmonary dysplasia, moderate or severe (n (%)) | 12 (26.1) | 10 (40.0) | 0.2322 b |
| Intraventricular hemorrhage, >grade 2 (n (%)) | 4 (8.7) | 6 (24.0) | 0.0804 b |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bohnhorst, B.; Weidlich, C.; Peter, C.; Böhne, C.; Kattner, E.; Pirr, S. Cardiorespiratory Events Following the Second Routine Immunization in Preterm Infants: Risk Assessment and Monitoring Recommendations. Vaccines 2021, 9, 909. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines9080909
Bohnhorst B, Weidlich C, Peter C, Böhne C, Kattner E, Pirr S. Cardiorespiratory Events Following the Second Routine Immunization in Preterm Infants: Risk Assessment and Monitoring Recommendations. Vaccines. 2021; 9(8):909. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines9080909
Chicago/Turabian StyleBohnhorst, Bettina, Cornelia Weidlich, Corinna Peter, Carolin Böhne, Evelyn Kattner, and Sabine Pirr. 2021. "Cardiorespiratory Events Following the Second Routine Immunization in Preterm Infants: Risk Assessment and Monitoring Recommendations" Vaccines 9, no. 8: 909. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines9080909
APA StyleBohnhorst, B., Weidlich, C., Peter, C., Böhne, C., Kattner, E., & Pirr, S. (2021). Cardiorespiratory Events Following the Second Routine Immunization in Preterm Infants: Risk Assessment and Monitoring Recommendations. Vaccines, 9(8), 909. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines9080909






