Cost-Effectiveness of Pertussis Vaccination Schedule in Israel
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
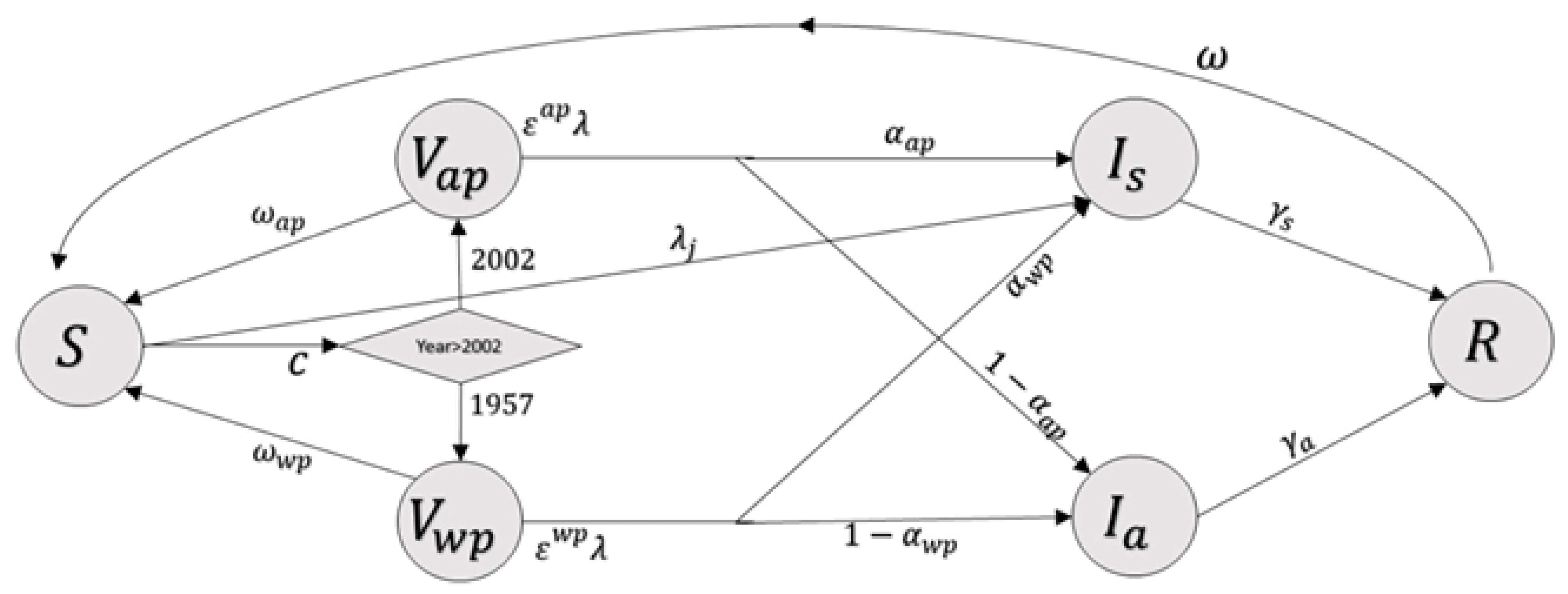
2.1. Transmission Model
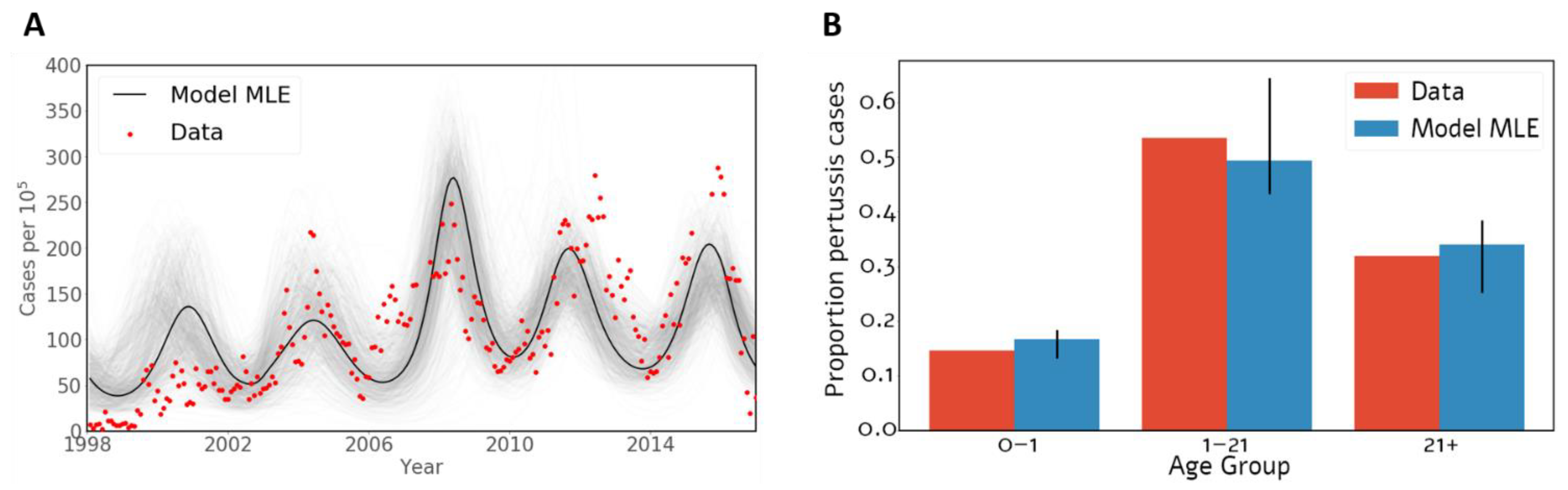
2.1.1. Calibration of Unknown Parameters
2.1.2. Model Projections
2.2. Clinical Outcomes
2.3. Quality of Life and Costs
2.4. Policy Optimization and Cost-Effectiveness Analysis
2.5. Sensitivity Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Model of Pertussis Transmission
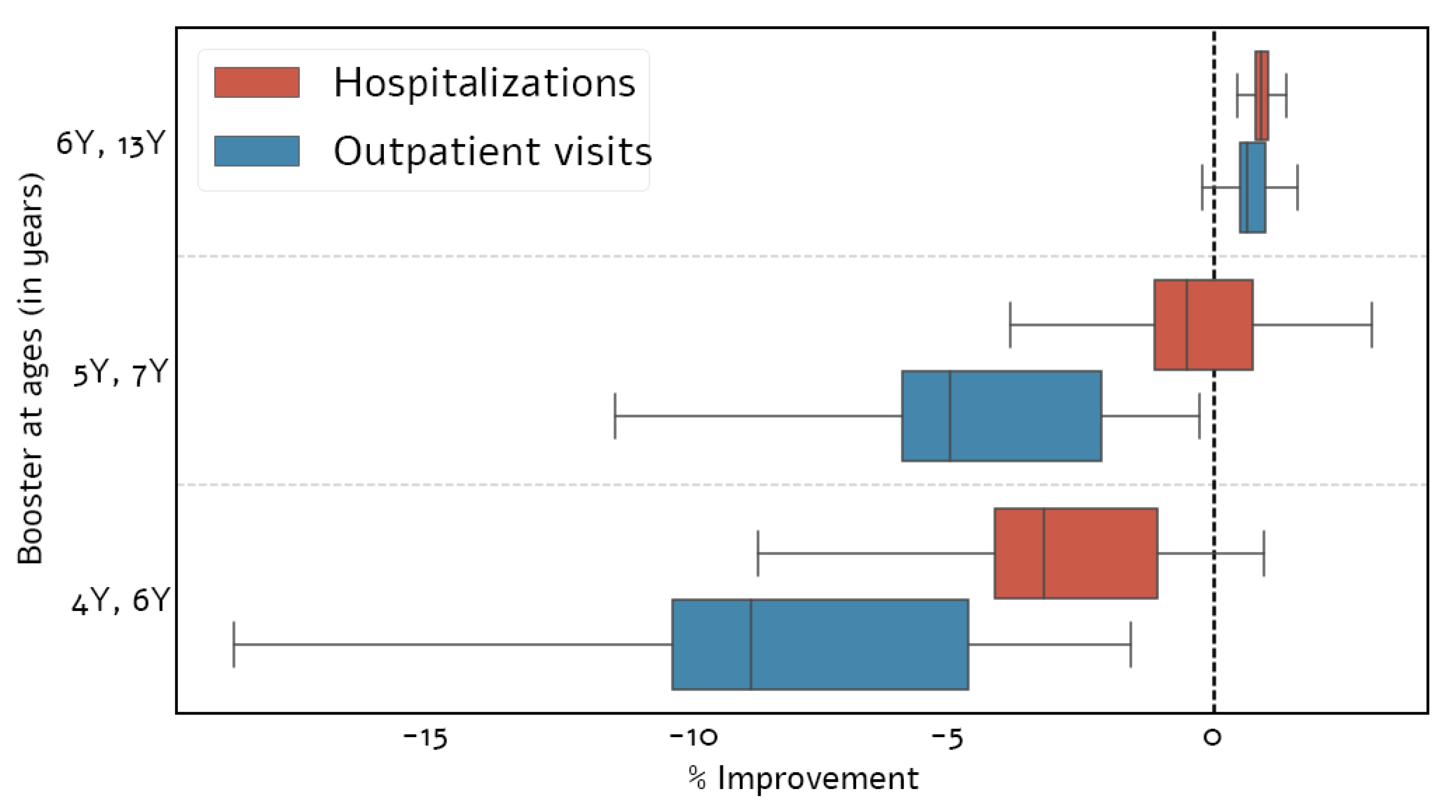
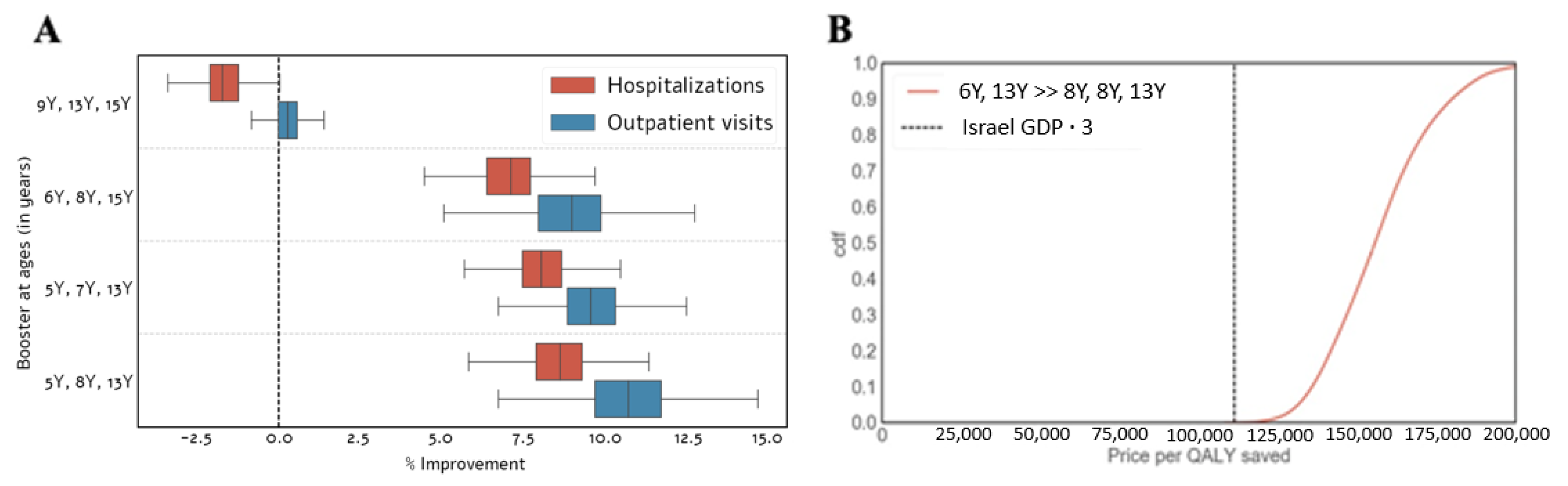
3.2. Optimal Vaccination Schedule
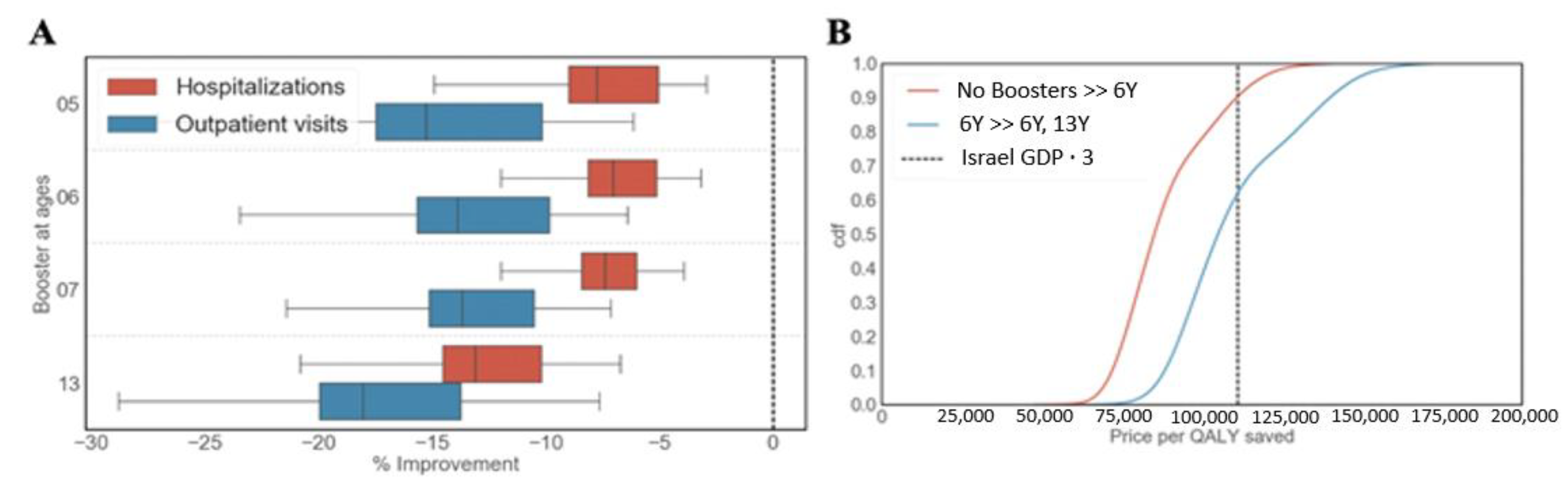
3.3. Cost-Effectiveness Analysis
3.3.1. Existing Booster Doses
3.3.2. Adding a Booster Dose
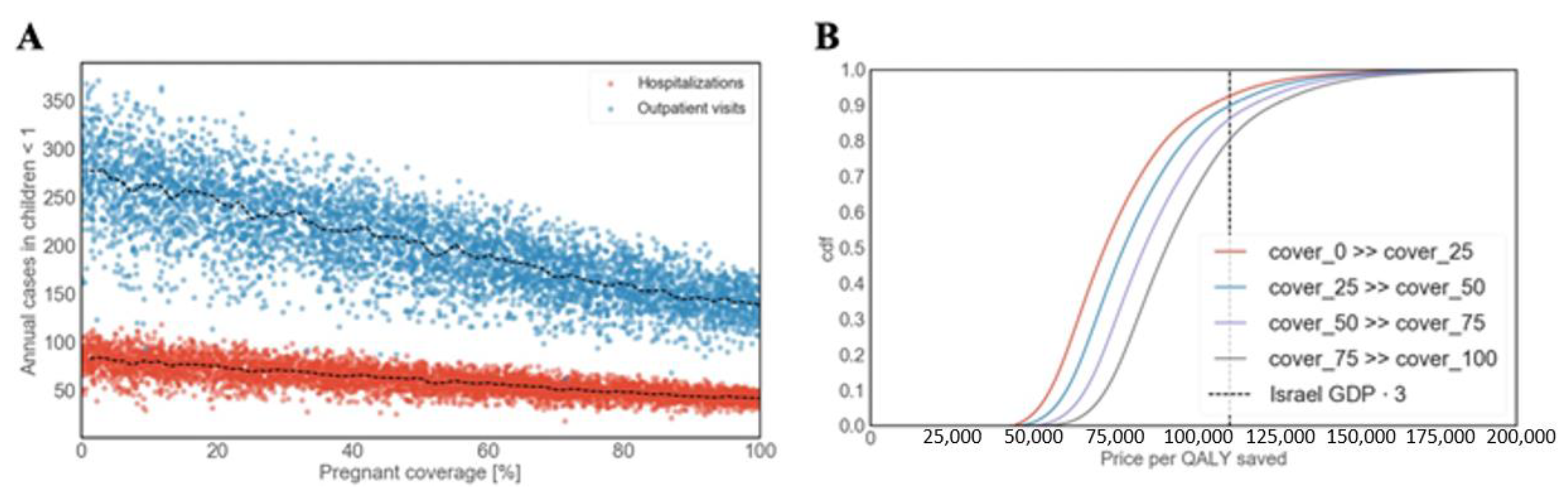
3.3.3. Maternal Vaccination
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cohn, A.C.; Cohn, A.C.; Clark, T.A.; Messonnier, N.E.; Martin, S.W. Early Impact of the US Tdap Vaccination Program on Pertussis Trends. Arch. Pediatr. Adolesc. Med. 2012, 166, 344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rohani, P.; Drake, J.M. The decline and resurgence of pertussis in the US. Epidemics 2011, 3, 183–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, Y.H.; Campbell, H.; Amirthalingam, G.; van Hoek, A.J.; Miller, E. Investigating the pertussis resurgence in England and Wales, and options for future control. BMC Med. 2016, 14, 121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.; Zhu, T.; Gao, C.; Gao, Z.; Liu, Y.; Ding, Y.; Sun, J.; Guo, L.; Liu, P.; Chen, D.; et al. Epidemiological features of pertussis resurgence based on community populations with high vaccination coverage in China. Epidemiol. Infect. 2015, 143, 1950–1956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GORDON, J.E.; HOOD, R.I. Whooping cough and its epidemiological anomalies. Am. J. Med. Sci. 1951, 222, 333-61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeung, K.H.T.; Duclos, P.; Nelson, E.A.S.; Hutubessy, R.C.W. An update of the global burden of pertussis in children younger than 5 years: A modelling study. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2017, 17, 974–980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skoff, T.H.; Hadler, S.; Hariri, S. The Epidemiology of Nationally Reported Pertussis in the United States, 2000–2016. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, T.A. Changing Pertussis Epidemiology: Everything Old is New Again. J. Infect. Dis. 2014, 209, 978–981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pichichero, M.E.; Blatter, M.M.; Kennedy, W.A.; Hedrick, J.; Descamps, D.; Friedland, L.R. Acellular pertussis vaccine booster combined with diphtheria and tetanus toxoids for adolescents. Pediatrics 2006, 117, 1084–1093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pichichero, M.E.; Rennels, M.B.; Edwards, K.M.; Blatter, M.M.; Marshall, G.S.; Bologa, M.; Wang, E.; Mills, E. Combined tetanus, diphtheria, and 5-component pertussis vaccine for use in adolescents and adults. J. Am. Med. Assoc. 2005, 293, 3003–3011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Hendrikx, L.H.; Öztürk, K.; de Rond, L.G.H.; Veenhoven, R.H.; Sanders, E.A.M.; Berbers, G.A.M.; Buisman, A.M. Identifying long-term memory B-cells in vaccinated children despite waning antibody levels specific for Bordetella pertussis proteins. Vaccine 2011, 29, 1431–1437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palazzo, R.; Carollo, M.; Bianco, M.; Fedele, G.; Schiavoni, I.; Pandolfi, E.; Villani, A.; Tozzi, A.E.; Mascart, F.; Ausiello, C.M. Persistence of T-cell immune response induced by two acellular pertussis vaccines in children five years after primary vaccination. New Microbiol. 2016, 39, 45–57. [Google Scholar]
- MOOI, F.R.; VAN DER MAAS, N.A.T.; De MELKER, H.E. Pertussis resurgence: Waning immunity and pathogen adaptation – two sides of the same coin. Epidemiol. Infect. 2014, 142, 685–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koepke, R.; Eickhoff, J.C.; Ayele, R.A.; Petit, A.B.; Schauer, S.L.; Hopfensperger, D.J.; Conway, J.H.; Davis, J.P. Estimating the Effectiveness of Tetanus-Diphtheria-Acellular Pertussis Vaccine (Tdap) for Preventing Pertussis: Evidence of Rapidly Waning Immunity and Difference in Effectiveness by Tdap Brand. J. Infect. Dis. 2014, 210, 942–953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Misegades, L.K.; Winter, K.; Harriman, K.; Talarico, J.; Messonnier, N.E.; Clark, T.A.; Martin, S.W. Association of Childhood Pertussis With Receipt of 5 Doses of Pertussis Vaccine by Time Since Last Vaccine Dose, California, 2010. JAMA 2012, 308, 2126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wendelboe, A.M.; Van Rie, A.; Salmaso, S.; Englund, J.A. Duration of immunity against pertussis after natural infection or vaccination. Pediatr. Infect. Dis. J. 2005, 24, S58–S61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edwards, K.M. Unraveling the challenges of pertussis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 575-6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Warfel, J.M.; Zimmerman, L.I.; Merkel, T.J. Acellular pertussis vaccines protect against disease but fail to prevent infection and transmission in a nonhuman primate model. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 787–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Althouse, B.M.; Scarpino, S.V. Asymptomatic transmission and the resurgence of Bordetella pertussis. BMC Med. 2015, 13, 146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amirthalingam, G.; Andrews, N.; Campbell, H.; Ribeiro, S.; Kara, E.; Donegan, K.; Fry, N.K.; Miller, E.; Ramsay, M. Effectiveness of maternal pertussis vaccination in England: An observational study. Lancet 2014, 384, 1521–1528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaccination guidance in Israel; Ministry of Health Israel: Jerusalem, Israel, 2014.
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), M.; Liang, J.L.; Messonnier, N.; Clark, T.A. Updated recommendations for use of tetanus toxoid, reduced diphtheria toxoid, and acellular pertussis vaccine (Tdap) in pregnant women--Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices (ACIP), 2012. MMWR. Morb. Mortal. Wkly. Rep. 2013, 62, 131-5. [Google Scholar]
- Putri, W.C.W.S.; Muscatello, D.J.; Stockwell, M.S.; Newall, A.T. Economic burden of seasonal influenza in the United States. Vaccine 2018, 36, 3960–3966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Langsam, D.; Anis, E.; Haas, E.J.; Gosinov, R.; Yechezkel, M.; Grotto, I.; Shmueli, E.; Yamin, D. Tdap vaccination during pregnancy interrupts a twenty-year increase in the incidence of pertussis. Vaccine 2020, 38, 2700–2706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Broutin, H.; Viboud, C.; Grenfell, B.T.; Miller, M.A.; Rohani, P. Impact of vaccination and birth rate on the epidemiology of pertussis: A comparative study in 64 countries. Proc. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2010, 277, 3239–3245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keeling, M.J.; Rohani, P. Modeling Infectious Diseases in Humans and Animals; Princeton University Press: Princeton, NJ, USA, 2011; ISBN 9781400841035. [Google Scholar]
- Yechezkel, M.; Ndeffo Mbah, M.L.; Yamin, D. Optimizing antiviral treatment for seasonal influenza in the USA: a mathematical modeling analysis. BMC Med. 2021, 19, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeAngelis, H.; Scarpino, S.V.; Fitzpatrick, M.C.; Galvani, A.P.; Althouse, B.M. Epidemiological and Economic Effects of Priming With the Whole-Cell Bordetella pertussis Vaccine. JAMA Pediatr. 2016, 142, 672–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Atkins, K.E.; Fitzpatrick, M.C.; Galvani, A.P.; Townsend, J.P. Cost-Effectiveness of Pertussis Vaccination During Pregnancy in the United States. Am. J. Epidemiol. 2016, 183, 1159–1170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Magpantay, F.M.G.; Rohani, P. Dynamics of Pertussis Transmission in the United States. Am. J. Epidemiol. 2015, 181, 921–931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vynnycky, E.; White, R. Introduction. The basics: Infections, transmission and models. In An Introduction to Infectious Disease Modelling; Oxford University Press: New York, NY, USA, 2010; ISBN 978-0-19-856576-5. [Google Scholar]
- Fitzpatrick, M.C.; Wenzel, N.S.; Scarpino, S.V.; Althouse, B.M.; Atkins, K.E.; Galvani, A.P.; Townsend, J.P. Cost-effectiveness of next-generation vaccines: The case of pertussis. Vaccine 2016, 34, 3405–3411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rendi-Wagner, P.; Tobias, J.; Moerman, L.; Goren, S.; Bassal, R.; Green, M.; Cohen, D. The seroepidemiology of Bordetella pertussis in Israel--Estimate of incidence of infection. Vaccine 2010, 28, 3285-90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Central Bureau of Statistics. Available online: https://cbs.aw/wp/ (accessed on 2 June 2021).
- Yamin, D.; Balicer, R.D.; Galvani, A.P. Cost-effectiveness of influenza vaccination in prior pneumonia patients in Israel. Vaccine 2014, 32, 4198–4205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Ginsberg, G.M.; Chemtob, D. Cost utility analysis of HIV pre exposure prophylaxis among men who have sex with men in Israel. BMC Public Health 2020, 20, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moshel, S.; Vexberg, M.H.; Shavit, O.; Toledano, Y. Economic Evaluation of Dapagliflozin as Add-On to Metformin in T2DM in the Israeli Health Care Setting. Diabetes 2018, 67, 1297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GitHub - DeanLa/israel_pertussis. Available online: https://github.com/DeanLa/israel_pertussis (accessed on 31 May 2021).
- Vaccines for Children Program (VFC) CDC Vaccine Price List Pediatric / VFC Vaccine Price List. Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/vaccines/programs/vfc/awardees/vaccine-management/price-list/archive.html (accessed on 2 June 2021).
- Price list, Ministry of Health Israel. Available online: https://www.health.gov.il/Subjects/Finance/Taarifon/Pages/PriceList.aspx (accessed on 31 May 2021).
- Bellido-Blasco, J.; Guiral-Rodrigo, S.; Míguez-Santiyán, A.; Salazar-Cifre, A.; González-Morán, F. A case–control study to assess the effectiveness of pertussis vaccination during pregnancy on newborns, Valencian community, Spain, 1 March 2015 to 29 February 2016. Eurosurveillance 2017, 22, 30545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Parameter | Description | Value | Justification |
|---|---|---|---|
| Birth rate | Time dependent, about 2% yearly | [34] | |
| Death rate | Time dependent | [34] | |
| Probability an infection is symptomatic given ACV | 1/e | ||
| Probability an infection is symptomatic given WCV | 1 | ||
| Waning from natural immunity | 30 years | [16] | |
| Loss of immunity ACV | 18 years | [16] | |
| Loss of immunity WCV | 30 years | [16] | |
| Population coverage | 95% | [21] | |
| Case report rate | 1.5% | [29,33] | |
| ACV efficacy | [29] | ||
| WCV efficacy | 99% | [29] | |
| Symptomatic infection healing rate | 25 days | [29] | |
| Asymptomatic infection healing rate | 8 days | [29] |
| Parameter | Prior Distribution | Posterior (Median Value, 95% HDI] |
|---|---|---|
| ) | ||
| U(0,0.5) | ||
| U(0,0.5) | ||
| U(0,0.5) |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Langsam, D.; Kahana, D.; Shmueli, E.; Yamin, D. Cost-Effectiveness of Pertussis Vaccination Schedule in Israel. Vaccines 2021, 9, 590. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines9060590
Langsam D, Kahana D, Shmueli E, Yamin D. Cost-Effectiveness of Pertussis Vaccination Schedule in Israel. Vaccines. 2021; 9(6):590. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines9060590
Chicago/Turabian StyleLangsam, Dean, Dor Kahana, Erez Shmueli, and Dan Yamin. 2021. "Cost-Effectiveness of Pertussis Vaccination Schedule in Israel" Vaccines 9, no. 6: 590. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines9060590
APA StyleLangsam, D., Kahana, D., Shmueli, E., & Yamin, D. (2021). Cost-Effectiveness of Pertussis Vaccination Schedule in Israel. Vaccines, 9(6), 590. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines9060590






