Humoral Immunity against Measles in Mother–Infant Pairs during the First Year of Life in Greece: A Cross-Sectional Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Study Population and Methods
3. Statistical Analysis
4. Results
4.1. Demographic and Epidemiological Data
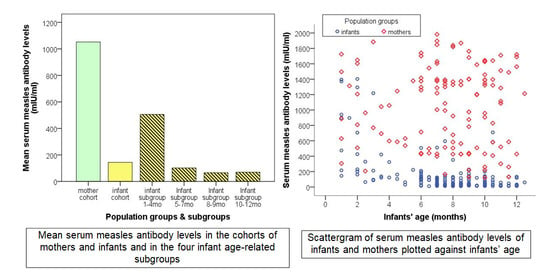
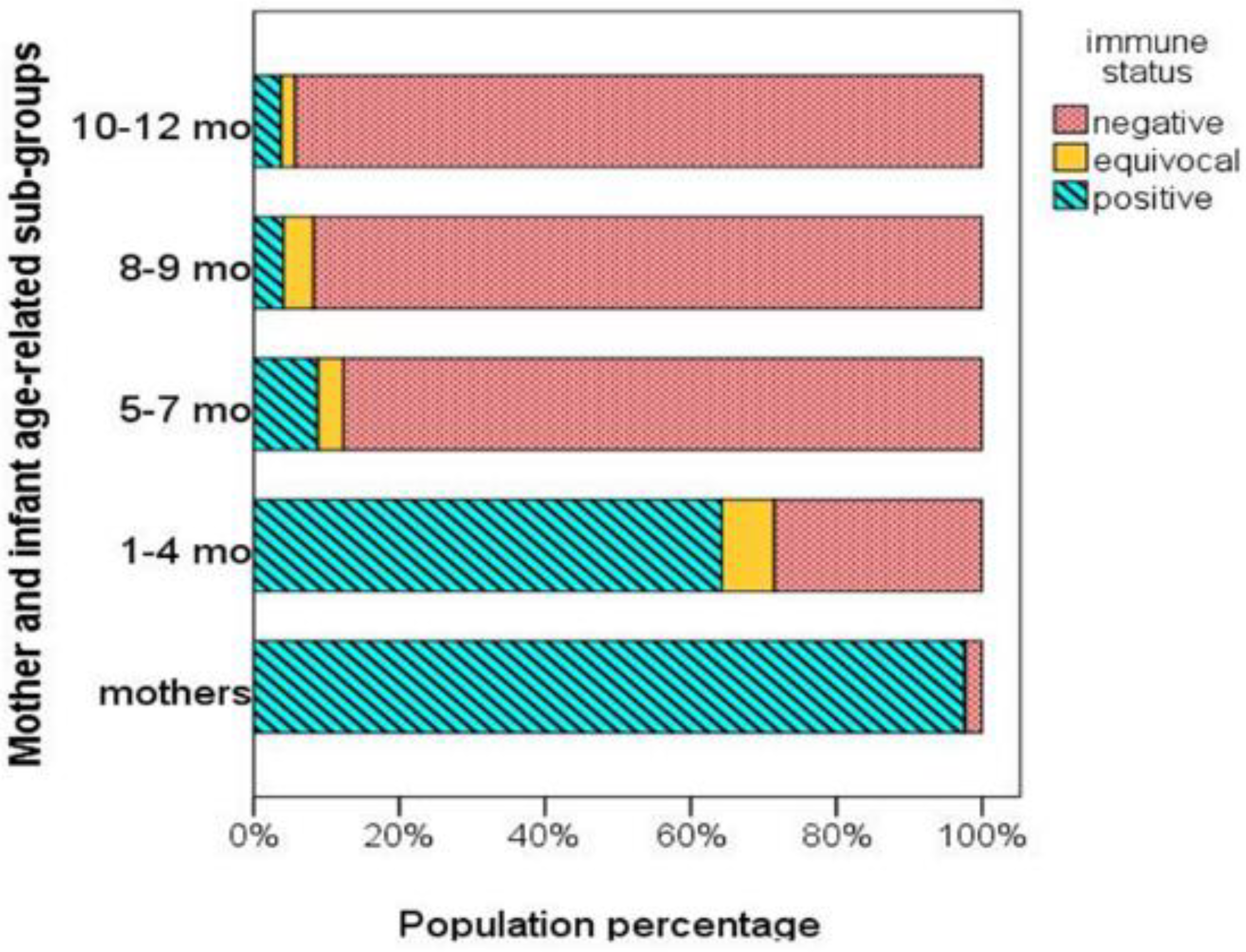
4.2. Humoral Immunity against Measles in Mothers and Infants
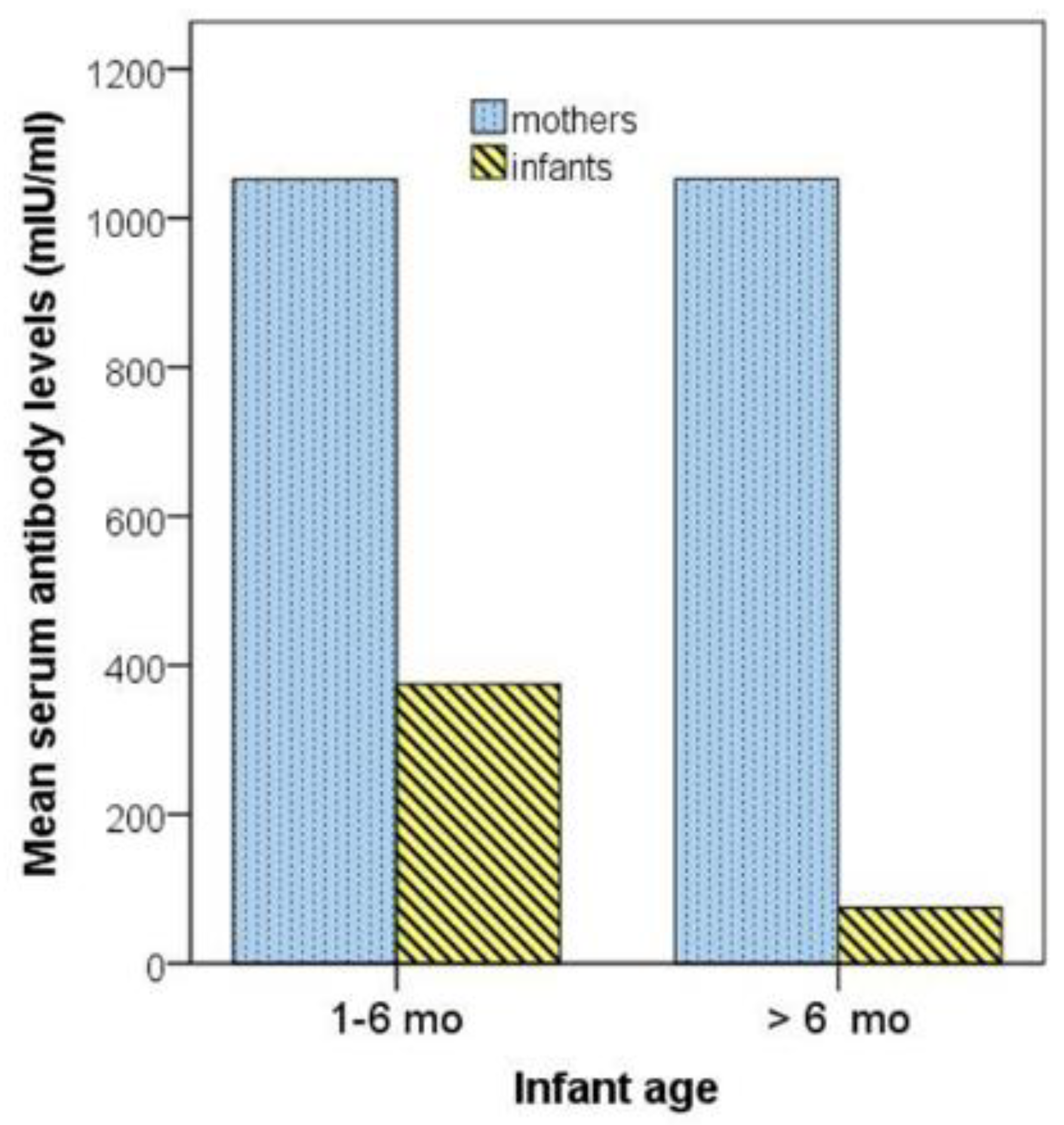
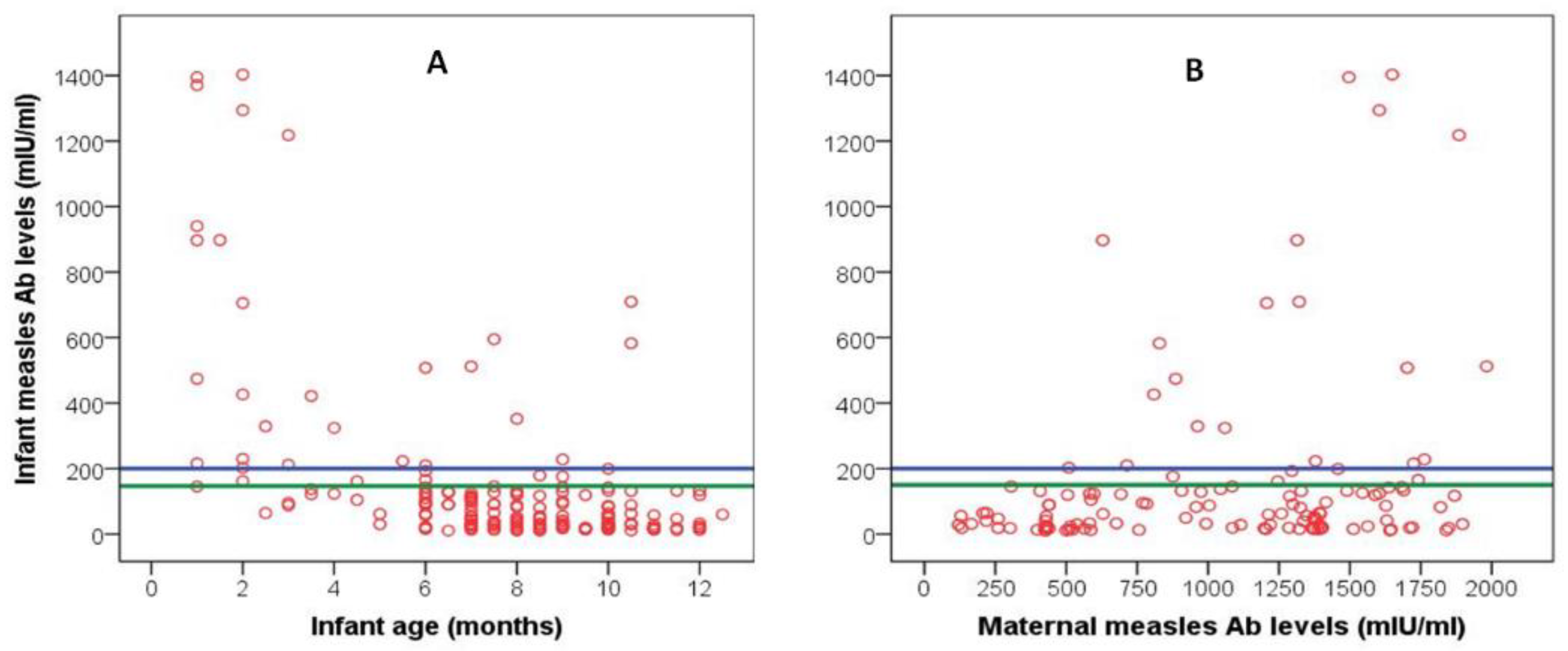
4.3. Infant Measles Passive Immunity in Relation to Infant Age
4.4. Multiple Regression Analysis
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- World Health Organization [WHO]. Global Measles and Rubella Strategic Plan 2012–2020; WHO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2012; Available online: http://apps.who.int/iris/bitstream/10665/44855/1/9789241503396_eng.pdf (accessed on 31 March 2020).
- Georgakopoulou, T.; Horefti, E.; Vernardaki, A.; Pogka, V.; Gkolfinopoulou, K.; Triantafyllou, E.; Tsiodras, S.; Theodoridou, M.; Mentis, A.; Panagiotopoulos, T. Ongoing measles outbreak in Greece related to the recent European-wide epidemic. Epidemiol. Infect. 2018, 146, 1692–1698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dabbagh, A.; Patel, M.K.; Dumolard, L.; Gacic-Dobo, M.; Mulders, M.N.; Okwo-Bele, J.-M.; Kretsinger, K.; Papania, M.J.; Rota, P.A.; Goodson, J.L. Progress Toward Regional Measles Elimination—Worldwide, 2000–2016. MMWR. Morb. Mortal. Wkly. Rep. 2017, 66, 1148–1153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muscat, M.; Bang, H.; Wohlfahrt, J.; Glismann, S.; Mølbak, K. Measles in Europe: An epidemiological assessment. Lancet 2009, 373, 383–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control [ECDC]. Monthly Measles and Rubella Surveillance—2017; ECDC: Stockholm, Switzerland, 2018; Available online: https://ecdc.europa.eu/en/publications-data/annual-Measles-and-Rubella-monitoring-report-2017 (accessed on 31 March 2020).
- European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control. Monthly Measles and Rubella Monitoring Report, June 2018; ECDC: Stockholm, Switzerland, 2018; Available online: https://www.ecdc.europa.eu/en/publications-data/monthly-measles-and-rubella-monitoring-report-june-2018 (accessed on 31 May 2020).
- Savage, R.; Severini, A.; McLachlan, E.; Hughes, S.L.; Arnold, C.; Richardson, S.; Crowcroft, N.; Deeks, S.; Halperin, S.; Brown, K.; et al. Measles Antibody Levels in Young Infants. Pediatrics 2019, 144, e20190630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dagan, R.; Slater, P.E.; Duvdevani, P.; Golubev, N.; Mendelson, E. Decay of maternally derived measles antibody in a highly vaccinated population in southern Israel. Pediatr. Infect. Dis. J. 1995, 14, 965–968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maldonado, Y.A.; Lawrence, E.C.; DeHovitz, R.; Hartzell, H.; Albrecht, P. Early loss of passive measles antibody in infants of mothers with vaccine-induced immunity. Pediatrics 1995, 96, 447–450. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Brugha, R.; Ramsay, M.; Forsey, T.; Brown, D. A study of maternally derived measles antibody in infants born to naturally infected and vaccinated women. Epidemiology Infect. 1996, 117, 519–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leuridan, E.; Van Damme, P. Passive transmission and persistence of naturally acquired or vaccine-induced maternal antibodies against measles in newborns. Vaccine 2007, 25, 6296–6304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leuridan, E.; Hens, N.; Hutse, V.; Ieven, M.; Aerts, M.; Van Damme, P. Early waning of maternal measles antibodies in era of measles elimination: Longitudinal study. BMJ 2010, 340, c1626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Waaijenborg, S.; Hahné, S.J.M.; Mollema, L.; Smits, G.P.; Berbers, G.A.M.; Van Der Klis, F.R.M.; De Melker, H.E.; Wallinga, J. Waning of Maternal Antibodies Against Measles, Mumps, Rubella, and Varicella in Communities With Contrasting Vaccination Coverage. J. Infect. Dis. 2013, 208, 10–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boulton, M.L.; Wang, X.; Wagner, A.L.; Zhang, Y.; Carlson, B.F.; Gillespie, B.W.; Ding, Y. Measles Antibodies in Mother-Infant Dyads in Tianjin, China. J. Infect. Dis. 2017, 216, 1122–1129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guerra, F.M.; Crowcroft, N.S.; Friedman, L.; Deeks, S.L.; Halperin, S.A.; Severini, A.; Hatchette, T.F.; Bolotin, S. Waning of measles maternal antibody in infants in measles elimination settings—A systematic literature review. Vaccine 2018, 36, 1248–1255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cilleruelo, M.J.; Fernández-García, A.; Villaverde, S.; Echevarría, J.; Marín, M.Á.; Sanz, J.C.; López, A.; Royuela, A.; Antoran, B.R.; De Ory, F. Duration of immunity to measles, rubella and mumps during the first year of life. Vaccine 2019, 37, 4164–4171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Plans-Rubió, P. Are the Objectives Proposed by the WHO for Routine Measles Vaccination Coverage and Population Measles Immunity Sufficient to Achieve Measles Elimination from Europe? Vaccines 2020, 8, 218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Georgakopoulou, T.; Menegas, D.; Katsioulis, A.; Theodoridou, M.; Kremastinou, J.; Hadjichristodoulou, C. A cross-sectional vaccination coverage study in preschool children attending nurseries-kindergartens: Implications on economic crisis effect. Hum. Vaccines Immunother. 2017, 13, 190–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Markowitz, L.E.; Albrecht, P.; Rhodes, P.; Demonteverde, R.; Swint, E.; Maes, E.F.; Powell, C.; Patriarca, P.A. Changing levels of measles antibody titers in women and children in the United States: Impact on response to vaccination. Kaiser Permanente Measles Vaccine Trial Team. Pediatrics 1996, 97, 53–58. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kumar, M.L.; Johnson, C.E.; Chui, L.W.; Whitwell, J.K.; Staehle, B.; Nalin, D. Immune response to measles vaccine in 6-month-old infants of measles seronegative mothers. Vaccine 1998, 16, 2047–2051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gans, H.; Yasukawa, L.; Rinki, M.; DeHovitz, R.; Forghani, B.; Beeler, J.; Audet, S.; Maldonado, Y.; Arvin, A.M. Immune responses to measles and mumps vac-cinations of infants at 6,9 and 12 months. J. Infect. Dis. 2001, 184, 817–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gans, H.; DeHovitz, R.; Forghani, B.; Beeler, J.; Maldonado, Y.; Arvin, A.M. Measles and mumps vaccination as a model to investigate the developing immune system: Passive and active immunity during the first year of life. Vaccine 2003, 21, 3398–3405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Redd, S.C.; King, G.E.; Heath, J.L.; Forghani, B.; Bellini, W.J.; Markowitz, L.E. Comparison of Vaccination with Measles-Mumps-Rubella Vaccine at 9, 12, and 15 Months of Age. J. Infect. Dis. 2004, 189, S116–S122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Shirayama, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Ba, W.; Ikeda, N.; Mori, R.; Shibuya, K. Duration of maternally derived antibody against measles: A seroepidemiological study of infants aged under 8 months in Qinghai, China. Vaccine 2012, 30, 752–757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gagneur, A.; Pinquier, D. Early waning of maternal measles antibodies: Why immunization programs should be adapted over time. Expert Rev. Anti-infective Ther. 2010, 8, 1339–1343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Montalti, M.; Kawalec, A.; Leoni, E.; Dallolio, L. Measles Immunization Policies and Vaccination Coverage in EU/EEA Countries over the Last Decade. Vaccines 2020, 8, 86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| 1. Inclusion criteria |
|
|
|
|
| 2. Exclusion criteria |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Total Population | Maternal National Origin | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Greek | Non-Greek | p | ||
| N | 187 | 136 | 51 | |
| Infant age [months; median (IQR)] | 8.0 (4.0) | 8 (3.5) | 8 (3.5) | 0.235 |
| Male sex [n (%)] | 112 (59.9) | 80 (58.8) | 32 (62.7) | 0.738 |
| Maternal age [years; median (IQR)] | 31.0 (8.0) | 32.0 (8.0) | 29.0 (6.0) | 0.003 |
| Maternal measles history | 0.320 | |||
| Infection [n (%)] | 29 (15.5) | 24 (17.6) | 5 (9.8) | |
| Vaccination [n (%)] | 110 (58.8) | 80 (58.8) | 30 (58.8) | |
| Unknown [n (%)] | 48 (25.7) | 32 (23.5) | 16 (31.4) | |
| Maternal protective immunity (n = 124) | 1.0 | |||
| Positive [n (%)] | 121 (97.6) | 82 (97.6) | 39 (97.5) | |
| Equivocal [n (%)] | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| Negative [n (%)] | 3 (2.4) | 2 (2.4) | 1 (2.5) | |
| Maternal antibody levels [mIU/mL, median (IQR)] | 1201 (868) | 1293 (736) | 640 (944) | 0.002 |
| Infant protective immunity | 0.534 | |||
| Positive [n (%)] | 27 (14.4) | 19 (14.0) | 8 (15.7) | |
| Equivocal [n (%)] | 7 (3.7) | 4 (2.9) | 3 (5.9) | |
| Negative [n (%)] | 153 (81.8) | 113 (83.1) | 40 (78.4) | |
| Infant antibody levels [mIU/mL, median (IQR)] | 56.9 (105) | 58.3 (102) | 54.2 (124) | 0.349 |
| Infant Age-Related Subgroups | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age 1–4 Months | Age 5–7 Months | Age 8–9 Months | Age 10–12 Months | p * | |
| Infants/mothers’ count | 28/21 | 57/37 | 49/31 | 53/35 | |
| Infant age range [months] | 1–4 | 5–7 | 8–9 | 10–12 m | |
| Infant age [months; median (IQR)] | 2.0 (2.3) | 7.0 (1.0) | 8.6 (1.0) | 10.5 (1.3) | <0.001 |
| Maternal age [years; median (IQR)] | 31.4 (4.8) | 31.5 (5.9) | 30.0 (5.3) | 30.9 (6) | 0.509 |
| Maternal history of measles | 0.07 | ||||
| Infection [n (%)] | 2 (7.1) | 15 (26.3) | 8 (16.3) | 4 (7.5) | |
| Vaccination [n (%)] | 16 (57.1) | 27 (47.4) | 29 (59.2) | 38 (58.8) | |
| Unknown [n (%)] | 10 (35.7) | 15 (26.3) | 12 (24.5) | 11 (20.8) | |
| Maternal antibody concentrations; [mIU/mL, median (IQR)] | 962.8 (791) | 1295.0 (823) | 921.5 (961) | 1285.0 (991) | 0.682 |
| Maternal protective immunity (n=121) | 0.419 | ||||
| Negative [n (%)] | 0 | 0 | 1 (3.2) | 2 (5.7) | |
| Equivocal [n (%)] | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| Positive [n (%)] | 21 (100) | 37 (100) | 30 (96.8) | 33 (94.3) | |
| Infant antibody concentrations [mIU/mL, median (IQR)] | 277.7 (758) | 87.4 (93) | 40 (76) | 29.7 (45) | <0.001 |
| Infants’ protective immunity | <0.001 | ||||
| Negative [n (%)] | 8 (28.6) | 50 (87.7) | 45 (91.8) | 50 (94.3) | |
| Equivocal [n (%)] | 2 (7.1) | 2 (3.5) | 2 (4.1) | 1 (1.9) | |
| Positive [n (%)] | 18 (64.3) | 5 (8.8) | 2 (1.1) | 2 (1.1) | |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kanakoudi-Tsakalidou, F.; Farmaki, E.; Papadimitriou, E.; Taparkou, A.; Agakidou, E.; Glykou, S.; Papachristou, F. Humoral Immunity against Measles in Mother–Infant Pairs during the First Year of Life in Greece: A Cross-Sectional Study. Vaccines 2021, 9, 143. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines9020143
Kanakoudi-Tsakalidou F, Farmaki E, Papadimitriou E, Taparkou A, Agakidou E, Glykou S, Papachristou F. Humoral Immunity against Measles in Mother–Infant Pairs during the First Year of Life in Greece: A Cross-Sectional Study. Vaccines. 2021; 9(2):143. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines9020143
Chicago/Turabian StyleKanakoudi-Tsakalidou, Florentia, Evangelia Farmaki, Eleni Papadimitriou, Anna Taparkou, Eleni Agakidou, Styliani Glykou, and Fotiοs Papachristou. 2021. "Humoral Immunity against Measles in Mother–Infant Pairs during the First Year of Life in Greece: A Cross-Sectional Study" Vaccines 9, no. 2: 143. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines9020143
APA StyleKanakoudi-Tsakalidou, F., Farmaki, E., Papadimitriou, E., Taparkou, A., Agakidou, E., Glykou, S., & Papachristou, F. (2021). Humoral Immunity against Measles in Mother–Infant Pairs during the First Year of Life in Greece: A Cross-Sectional Study. Vaccines, 9(2), 143. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines9020143