Receptor-Binding Domain Proteins of SARS-CoV-2 Variants Elicited Robust Antibody Responses Cross-Reacting with Wild-Type and Mutant Viruses in Mice
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Mice and Ethical Approval
2.2. Preparation of Recombinant RBD Proteins
2.3. SDS-PAGE and Western Blot
2.4. Mouse Immunization and Sample Collection
2.5. ELISA
2.6. Generation of Wild-Type and Mutant SARS-CoV-2 Pseudoviruses and Neutralization Experiment
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
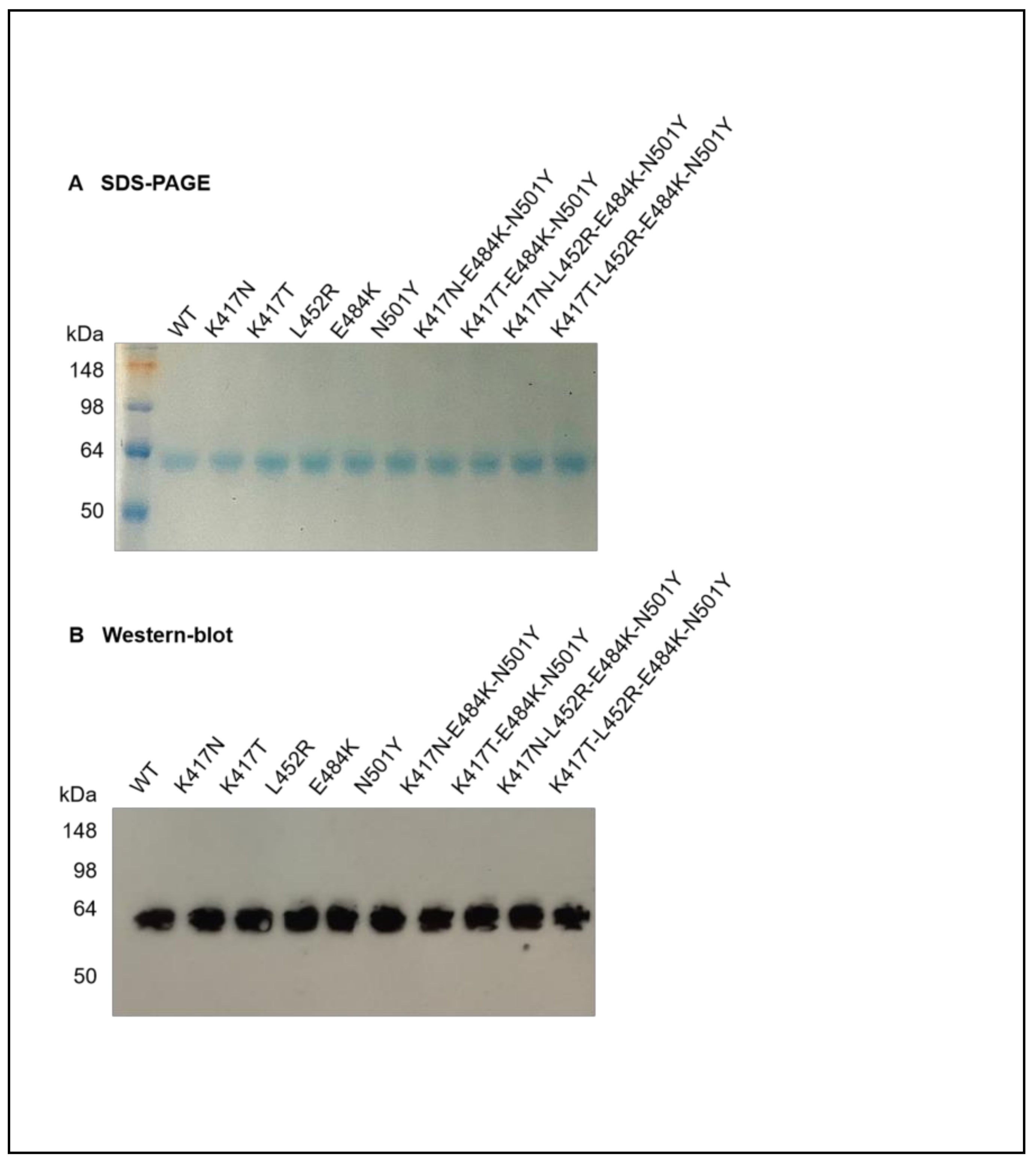
3.1. Characterization of Recombinant Mutant RBD-Fc Proteins of SARS-CoV-2
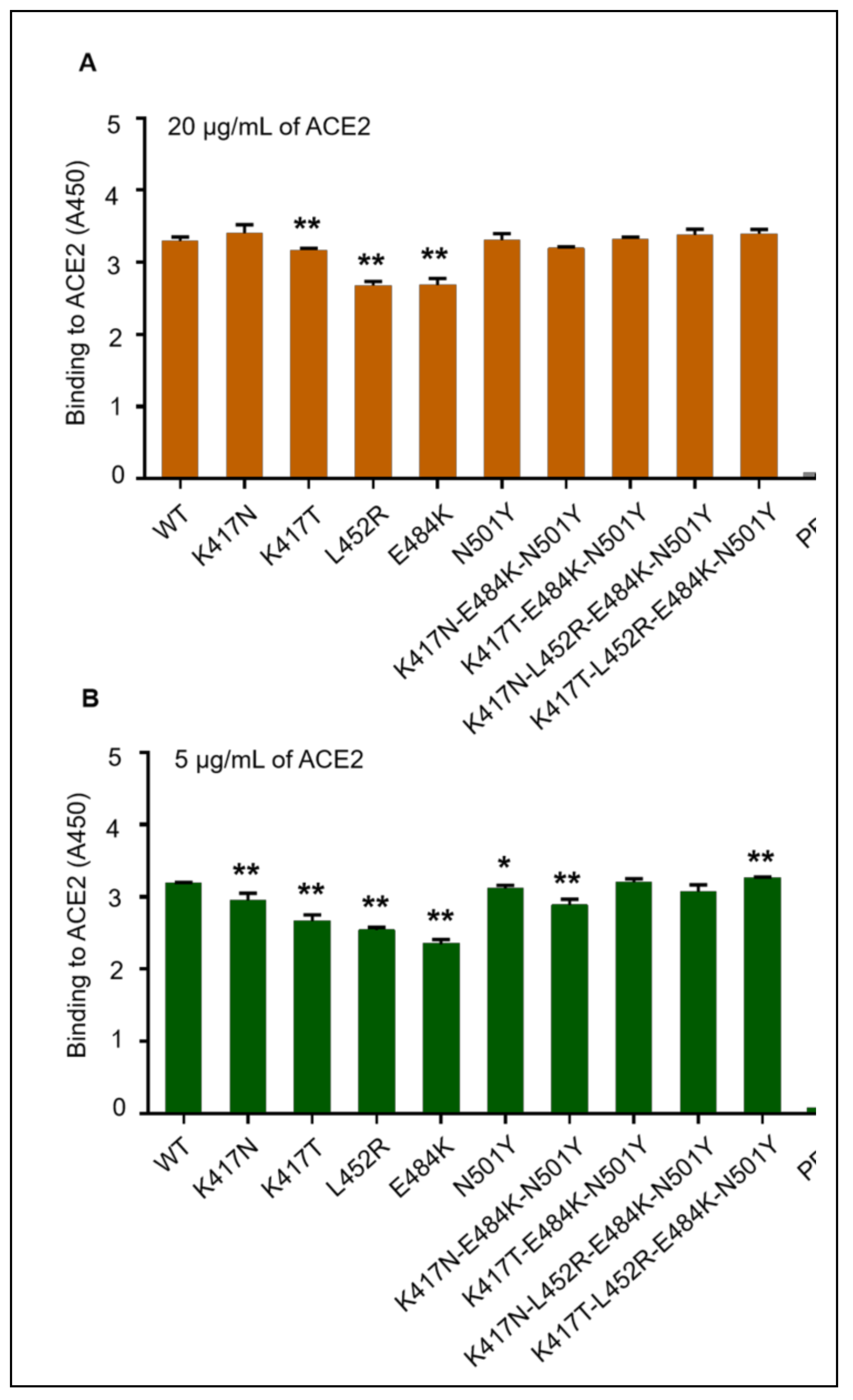
3.2. Binding Affinity of Mutant SARS-CoV-2 RBD-Fc Proteins with hACE2
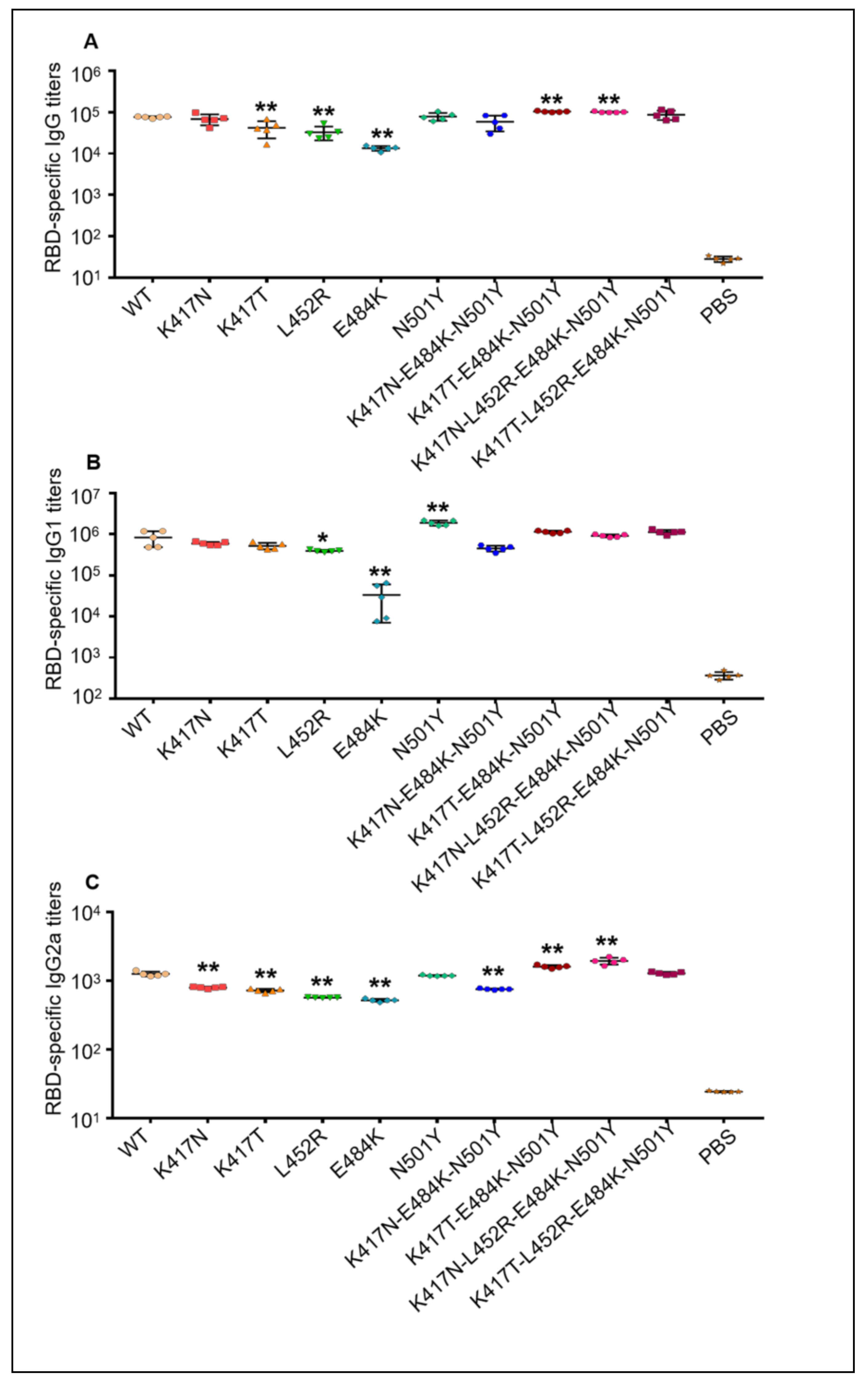
3.3. Mutant RBD-Fc Proteins of SARS-CoV-2 Elicited Robust Antibody Responses in Mice
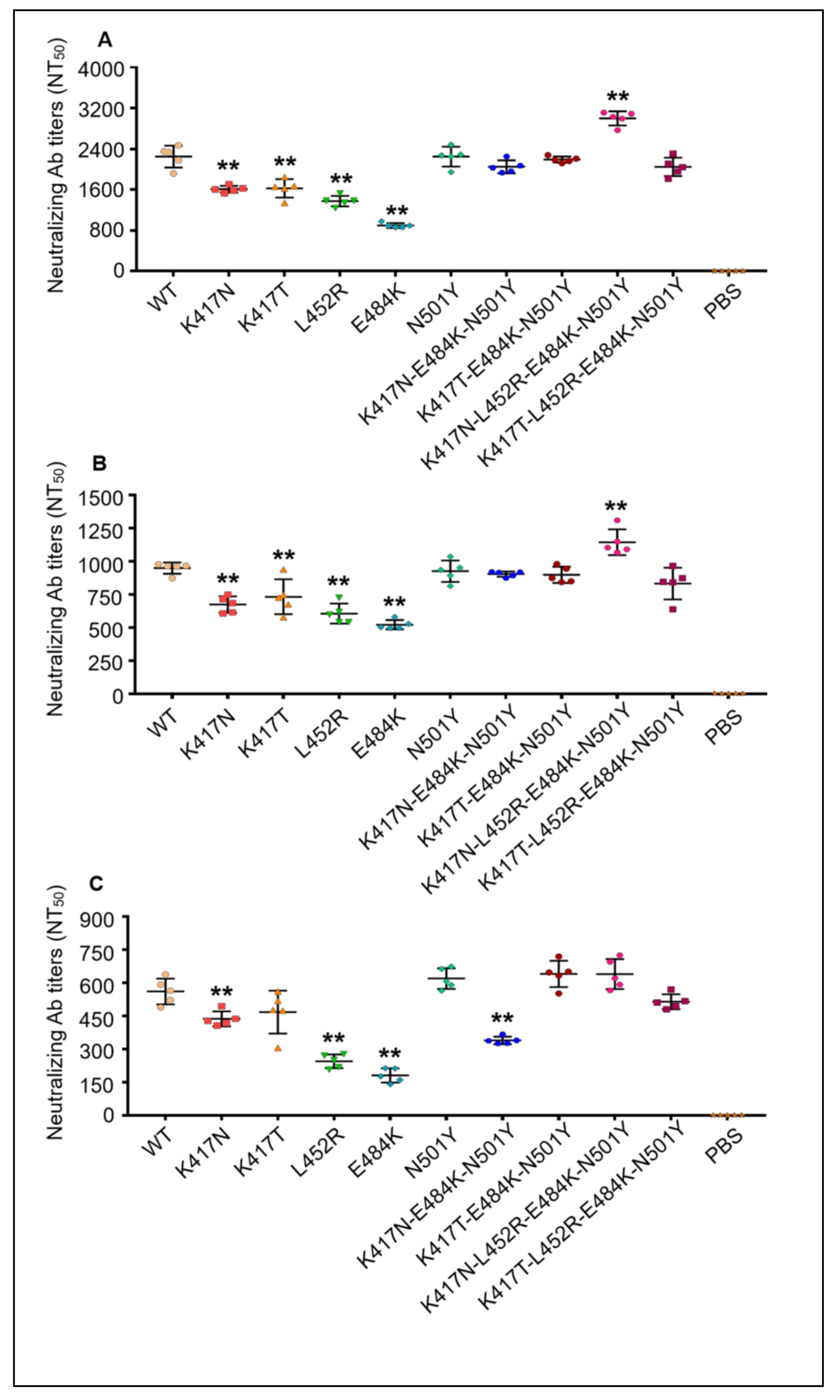
3.4. Mutant RBD-Fc Proteins of SARS-CoV-2 Induced High-Level Cross-Neutralizing Antibodies Production in Mice
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| COVID-19 | Coronavirus Disease 2019 |
| SARS-CoV-2 | Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus-2 |
| VOCs | Variants of concern |
| RBD | Receptor-binding domain |
| hACE2 | Human angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 |
| HRP | Horseradish peroxidase |
| MPL | Monophosphoryl lipid A |
| DMEM | Dulbecco’s Modified Eagle Medium |
| NT50 | Neutralizing antibody titer needed to neutralize 50% of viral infectivity. |
References
- World Health Organization (WHO). Tracking SARS-CoV-2 Variants. Available online: https://www.who.int/en/activities/tracking-SARS-CoV-2-variants/ (accessed on 15 October 2021).
- Cascella, M.; Rajnik, M.; Aleem, A.; Dulebohn, S.C.; Di Napoli, R. Features, Evaluation, and Treatment of Coronavirus (COVID-19); StatPearls: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Galloway, S.E.; Paul, P.; MacCannell, D.R.; Johansson, M.A.; Brooks, J.T.; MacNeil, A.; Slayton, R.B.; Tong, S.; Silk, B.J.; Armstrong, G.L.; et al. Emergence of SARS-CoV-2 B.1.1.7 Lineage—United States, December 29, 2020–January 12, 2021. MMWR. Morb. Mortal. Wkly. Rep. 2021, 70, 95–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Volz, E.; Mishra, S.; Chand, M.; Barrett, J.C.; Johnson, R.; Geidelberg, L.; Hinsley, W.R.; Laydon, D.J.; Dabrera, G.; O’Toole, Á.; et al. Assessing transmissibility of SARS-CoV-2 lineage B.1.1.7 in England. Nature 2021, 593, 266–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tegally, H.; Wilkinson, E.; Giovanetti, M.; Iranzadeh, A.; Fonseca, V.; Giandhari, J.; Doolabh, D.; Pillay, S.; San, E.J.; Msomi, N.; et al. Detection of a SARS-CoV-2 variant of concern in South Africa. Nature 2021, 592, 438–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Faria, N.R.; Mellan, T.A.; Whittaker, C.; Claro, I.M.; Candido, D.D.S.; Mishra, S.; Crispim, M.A.E.; Sales, F.C.; Hawryluk, I.; McCrone, J.T.; et al. Genomics and Epidemiology of a Novel SARS-CoV-2 Lineage in Manaus, Brazil. MedRxiv 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cele, S.; Africa, N.F.G.S.I.S.; Gazy, I.; Jackson, L.; Hwa, S.-H.; Tegally, H.; Lustig, G.; Giandhari, J.; Pillay, S.; Wilkinson, E.; et al. Escape of SARS-CoV-2 501Y.V2 from neutralization by convalescent plasma. Nature 2021, 593, 142–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Casner, R.G.; Nair, M.S.; Wang, M.; Yu, J.; Cerutti, G.; Liu, L.; Kwong, P.D.; Huang, Y.; Shapiro, L.; et al. Increased resistance of SARS-CoV-2 variant P.1 to antibody neutralization. Cell Host Microbe 2021, 29, 747–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gidari, A.; Sabbatini, S.; Bastianelli, S.; Pierucci, S.; Busti, C.; Monari, C.; Pasqua, B.L.; Dragoni, F.; Schiaroli, E.; Zazzi, M.; et al. Cross-neutralization of SARS-CoV-2 B.1.1.7 and P.1 variants in vaccinated, convalescent and P.1 infected. J. Infect. 2021, 83, 467–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Ginn, H.M.; Dejnirattisai, W.; Supasa, P.; Wang, B.; Tuekprakhon, A.; Nutalai, R.; Zhou, D.; Mentzer, A.J.; Zhao, Y.; et al. Reduced neutralization of SARS-CoV-2 B.1.617 by vaccine and convalescent serum. Cell 2021, 184, 4220–4236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benton, D.J.; Wrobel, A.G.; Xu, P.; Roustan, C.; Martin, S.R.; Rosenthal, P.B.; Skehel, J.J.; Gamblin, S.J. Receptor binding and priming of the spike protein of SARS-CoV-2 for membrane fusion. Nature 2020, 588, 327–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, H.T.; Zhang, S.; Wang, Q.; Anang, S.; Wang, J.; Ding, H.; Kappes, J.C.; Sodroski, J. Spike Glycoprotein and Host Cell Determinants of SARS-CoV-2 Entry and Cytopathic Effects. J. Virol. 2021, 95, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walls, A.C.; Park, Y.-J.; Tortorici, M.A.; Wall, A.; McGuire, A.T.; Veesler, D. Structure, Function, and Antigenicity of the SARS-CoV-2 Spike Glycoprotein. Cell 2020, 181, 281–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dai, L.; Gao, G.F. Viral targets for vaccines against COVID-19. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2021, 21, 73–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ura, T.; Yamashita, A.; Mizuki, N.; Okuda, K.; Shimada, M. New vaccine production platforms used in developing SARS-CoV-2 vaccine candidates. Vaccine 2021, 39, 197–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, L.; Guo, P.; Zhang, X.; Yu, Z.; Zhang, W.; Sun, H. SARS-CoV-2 vaccine candidates in rapid development. Hum. Vaccines Immunother. 2021, 17, 644–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Russell, R.L.; Pelka, P.; Mark, B.L. Frontrunners in the race to develop a SARS-CoV-2 vaccine. Can. J. Microbiol. 2021, 67, 189–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Wang, W.; Chen, Z.; Lu, S.; Yang, F.; Bi, Z.; Bao, L.; Mo, F.; Li, X.; Huang, Y.; et al. A vaccine targeting the RBD of the S protein of SARS-CoV-2 induces protective immunity. Nature 2020, 586, 572–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Xu, W.; Xia, S.; Gu, C.; Wang, X.; Wang, Q.; Zhou, J.; Wu, Y.; Cai, X.; Qu, D.; et al. RBD-Fc-based COVID-19 vaccine candidate induces highly potent SARS-CoV-2 neutralizing antibody response. Signal. Transduct. Target. Ther. 2020, 5, 282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, H.; Chen, Q.; Yang, G.; He, L.; Fan, H.; Deng, Y.-Q.; Wang, Y.; Teng, Y.; Zhao, Z.; Cui, Y.; et al. Adaptation of SARS-CoV-2 in BALB/c mice for testing vaccine efficacy. Science 2020, 369, 1603–1607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chakraborty, S. Evolutionary and structural analysis elucidates mutations on SARS-CoV2 spike protein with altered human ACE2 binding affinity. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2021, 534, 374–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Y.; Wang, Z.; Wei, Z.; Schapiro, I.; Li, J. Binding affinity and mechanisms of SARS-CoV-2 variants. Comput. Struct. Biotechnol. J. 2021, 19, 4184–4191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boehm, E.; Kronig, I.; Neher, R.A.; Eckerle, I.; Vetter, P.; Kaiser, L. Novel SARS-CoV-2 variants: The pandemics within the pandemic. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2021, 27, 1109–1117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laffeber, C.; de Koning, K.; Kanaar, R.; Lebbink, J.H. Experimental Evidence for Enhanced Receptor Binding by Rapidly Spreading SARS-CoV-2 Variants. J. Mol. Biol. 2021, 433, 167058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmidt, F.; Weisblum, Y.; Muecksch, F.; Hoffmann, H.-H.; Michailidis, E.; Lorenzi, J.C.; Mendoza, P.; Rutkowska, M.; Bednarski, E.; Gaebler, C.; et al. Measuring SARS-CoV-2 neutralizing antibody activity using pseudotyped and chimeric viruses. J. Exp. Med. 2020, 217, e20201181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crawford, K.H.D.; Eguia, R.; Dingens, A.S.; Loes, A.N.; Malone, K.D.; Wolf, C.R.; Chu, H.Y.; Tortorici, M.A.; Veesler, D.; Murphy, M.; et al. Protocol and Reagents for Pseudotyping Lentiviral Particles with SARS-CoV-2 Spike Protein for Neutralization Assays. Viruses 2020, 12, 513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amanat, F.; Strohmeier, S.; Lee, W.-H.; Bangaru, S.; Ward, A.B.; Coughlan, L.; Krammer, F. Murine Monoclonal Antibodies against the Receptor Binding Domain of SARS-CoV-2 Neutralize Authentic Wild-Type SARS-CoV-2 as Well as B.1.1.7 and B.1.351 Viruses and Protect In Vivo in a Mouse Model in a Neutralization-Dependent Manner. MBio 2021, 12, e0100221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tada, T.; Dcosta, B.M.; Zhou, H.; Vaill, A.; Kazmierski, W.; Landau, N.R. Decreased neutralization of SARS-CoV-2 global variants by therapeutic anti-spike protein monoclonal antibodies. BioRxiv 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vidal, S.J.; Collier, A.-R.Y.; Yu, J.; McMahan, K.; Tostanoski, L.H.; Ventura, J.D.; Aid, M.; Peter, L.; Jacob-Dolan, C.; Anioke, T.; et al. Correlates of Neutralization against SARS-CoV-2 Variants of Concern by Early Pandemic Sera. J. Virol. 2021, 95, e0040421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; VanBlargan, L.A.; Bloyet, L.M.; Rothlauf, P.W.; Chen, R.E.; Stumpf, S.; Zhao, H.; Errico, J.M.; Theel, E.S.; Liebeskind, M.J.; et al. Identification of SARS-CoV-2 spike mutations that attenuate monoclonal and serum antibody neutralization. Cell Host Microbe 2021, 29, 477–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shi, J.; Jin, X.; Ding, Y.; Liu, X.; Shen, A.; Wu, Y.; Peng, M.; Shen, C. Receptor-Binding Domain Proteins of SARS-CoV-2 Variants Elicited Robust Antibody Responses Cross-Reacting with Wild-Type and Mutant Viruses in Mice. Vaccines 2021, 9, 1383. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines9121383
Shi J, Jin X, Ding Y, Liu X, Shen A, Wu Y, Peng M, Shen C. Receptor-Binding Domain Proteins of SARS-CoV-2 Variants Elicited Robust Antibody Responses Cross-Reacting with Wild-Type and Mutant Viruses in Mice. Vaccines. 2021; 9(12):1383. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines9121383
Chicago/Turabian StyleShi, Juan, Xiaoxiao Jin, Yan Ding, Xiaotao Liu, Anran Shen, Yandan Wu, Min Peng, and Chuanlai Shen. 2021. "Receptor-Binding Domain Proteins of SARS-CoV-2 Variants Elicited Robust Antibody Responses Cross-Reacting with Wild-Type and Mutant Viruses in Mice" Vaccines 9, no. 12: 1383. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines9121383
APA StyleShi, J., Jin, X., Ding, Y., Liu, X., Shen, A., Wu, Y., Peng, M., & Shen, C. (2021). Receptor-Binding Domain Proteins of SARS-CoV-2 Variants Elicited Robust Antibody Responses Cross-Reacting with Wild-Type and Mutant Viruses in Mice. Vaccines, 9(12), 1383. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines9121383








