Abstract
Objective: This study estimates the cost-effectiveness of vaccination with the 13-valent pneumococcal conjugate vaccine (PCV13) among infants in Beijing, Shanghai, Shenzhen, Chengdu, Karamay, Qingdao, and Suzhou. Methods: A previously published cost-effectiveness model comparing vaccination with PCV13 to no vaccination was localized to the included Chinese cities. A systematic literature review was undertaken to identify age-specific incidence rates for pneumococcal bacteremia, pneumococcal meningitis, pneumonia, and otitis media (AOM). Age-specific direct medical costs of treating the included pneumococcal diseases were taken from the Chinese Health Insurance Association database. The base case analysis evaluated vaccine efficacy using direct effect and indirect effects (DE+ IDE). A subsequent scenario analysis evaluated the model outcomes if only DE was considered. A vaccination rate of 70% was used. The model reported outcomes over a one-year period after it was assumed the vaccine effects had reached a steady state (5–7 years after vaccine introduction) to include the direct and indirect effects of vaccination. Health outcomes were discounted at 5% during the steady-state period. Results: Vaccination with PCV13 was cost-effective in the base case analysis for all included cities with the incremental cost-effectiveness ratio (ICER) ranging from 1145 CNY(Shenzhen) to 15,422 CNY (Qingdao) per quality-adjusted life-year (QALY) gained. PCV13 was the dominant strategy in Shanghai with lower incremental costs and higher incremental QALYs. PCV13 remained cost-effective in the DE-only analysis with all ICERs falling below a cost-effectiveness threshold of three times GDP per capita in each city. Conclusions: Vaccination with PCV13 was a cost-effective strategy in the analyzed cities for both the DE-only and DE + IDE analyses. PCV13 became very cost-effective when a vaccination rate was reached where IDE is observed.
1. Introduction
Invasive pneumococcal diseases (IPD) caused by Streptococcus pneumoniae (S. pneumonia) include meningitis and bacteremia. S. pneumonia can also cause non-invasive pneumococcal infections such as pneumonia and acute otitis media (AOM). The World Health Organization (WHO) has estimated 1 million children die from pneumococcal disease each year, with the majority in developing countries [1]. Patients with pneumococcal diseases also experience decreased quality of life and incur significant direct and indirect costs due to medical healthcare resource utilization, absenteeism, and presenteeism [2].
The burden of pneumococcal diseases in China is significant, with an estimated 12% of global cases occurring in China [3]. In China lower respiratory infections including pneumonia were the 12th leading cause of overall deaths and premature deaths (years of life lost) in 2017 [4]. Pneumococcal diseases pose a significant burden in China where there are an estimated 30,000 deaths per year [3,5]. In 2000, it was estimated there were 22 million cases of pneumonia among children younger than five years of age in China [6]. Of patients dying of pneumonia, it is estimated that nearly 50% are attributable to S. pneumonia [7].
Pneumococcal conjugate vaccines (PCVs) have been proven to be safe and effective interventions to prevent pneumococcal diseases. The first PCV available on the market was Prevenar 7®, a 7-valent pneumococcal conjugate vaccine (PCV7) in the United States (U.S.), which was introduced in February 2000. PCV7 protects against seven pneumococcal serotypes (4, 6B, 9V, 14, 18C, 19F, and 23F), Prevenar 13®, a 13-valent pneumococcal conjugate vaccine (PCV13), which was introduced to the U.S. market in 2010, protects against thirteen pneumococcal serotypes (1, 3, 4, 5, 6A, 6B, 7F, 9V, 14, 19A, 19F, 18C, and 23F) starting at two months of age. PCVs (including PCV13 and PCV10) are recommended to be included in all childhood immunization programs according to the WHO [8].
The introduction of PCV7 and subsequently PCV13 has led to significant declines in invasive pneumococcal disease, pneumonia, and otitis media in settings with universal vaccination programs [9,10,11,12,13]. The effectiveness of vaccination has been felt through both the direct effect and through the indirect effect of vaccination [14].
The immunogenicity and safety of PCV13 in infants was studied in a Phase 3 clinical trial conducted in China [15]. The double-blind study compared PCV13 with PCV7 among two or more month old infants in China [15]. The study showed PCV13 was non-inferior to PCV7 among the seven common serotypes, and PCV13 offered additional protection and immune response to the six additional serotypes without any additional safety concerns [15]. Prevenar 13® was licensed in China in 2016 and is approved for a 3 + 1 dosing schedule. This analysis considers cost and effectiveness data specifically for Prevenar 13®, which have been derived from the literature. Several PCV13 vaccinations have been launched in China but due to differences in the production technique and ingredients, further studies are needed to provide more context to their long-term safety and effectiveness compared to Prevenar 13®.
PCV13 has been shown to be cost-effective compared to the standard of care (either no vaccination or PCV7) in different global settings [16]. In China, there have been four studies published examining the cost-effectiveness of PCV13 [17,18,19,20]. All four studies compared PCV to no vaccination, and in all cases, PCV13 was cost-effective using a cost-effectiveness threshold of 3× GDP per capita. However, there have not been any studies assessing the cost-effectiveness of PCV13 in specific Chinese cities. As vaccine funding in China is based on cities, this analysis selected a sample of cities ranging from first- to fifth-tier with varying socioeconomic and geographic characteristics.
The objective of this study was to estimate the cost-effectiveness of 70% vaccination with PCV13 compared to no vaccination in Beijing, Shanghai, Shenzhen, Suzhou, Chengdu, Karamay, and Qingdao.
2. Methods
2.1. Approach
A previously published cost-effectiveness model assessing the cost-effectiveness of implementing a PCV13 program was localized to seven cities in China [19,21,22,23,24,25]. The seven cities included Beijing, Chengdu, Karamay, Qingdao, Shanghai, Shenzhen, and Suzhou. These cities were chosen according to their geographical distribution and as representative of the socioeconomics and healthcare patterns of their respective regions. The details of the model structure and design have been well published [19,21,22,23,24,25]. Patients (infants) first enter the model and are assigned vaccine protection based on the vaccine uptake, which was assumed to be 70% in this analysis.
There are a total of eight health states within the model, two each for invasive pneumococcal diseases (IPD), pneumonia (PNE), and acute otitis media (AOM), in addition to no illness and death. Within IPD there are the pneumococcal bacteremia and pneumococcal meningitis states, within PNE there are the inpatient and outpatient states, and within AOM there are the mild and moderate/severe states.
A decision analytic model (Figure 1) is used to determine the outcomes (recovery, sequelae, or death) associated with the IPD, PNE, and AOM health states.
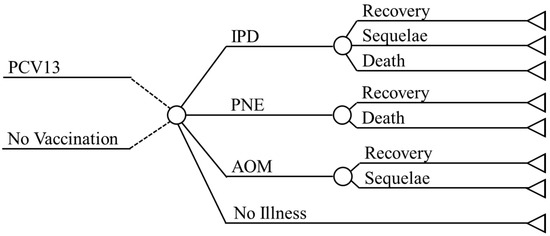
Figure 1.
Model Design. Abbreviations: PCV = Pneumococcal conjugate vaccine; IPD = Invasive pneumococcal diseases; PNE = Pneumonia; AOM = Acute otitis media.
The model took a payer perspective for each city, and outcomes were calculated over a one-year time horizon after a steady-state period was reached, which was assumed to take 5–7 years, to include the direct and indirect effects of vaccination. Outcomes were recorded for each arm in the model (vaccination and no vaccination) and included the number of cases and deaths for each health state, the number of quality-adjusted life-years lost due to death, sequelae, and acute disease, vaccination costs, and treatment-related costs of the included health states. Life-years were estimated over a lifetime time horizon, by using the conditional expected remaining life-years according to each age group in the model. Lifetime health outcomes were discounted at a rate of 5%, and costs were expressed in CNY. Per the approved vaccination schedule of Prevenar 13® in China, children were to receive a 3 + 1 schedule, which included a total of 4 doses in the base case analysis. A separate analysis explored the impact of a 2 + 1 dosing schedule on the results of the base case analysis.
2.2. Demographic Inputs
Key demographic data was included for each of the analyzed cities in China and included the total population, the percentage of patients under one year of age, and the age distribution [26].
2.3. Epidemiologic Inputs
The model considers age-based incidence rates for pneumococcal meningitis, pneumococcal bacteremia, pneumonia (inpatient and outpatient), otitis media (mild and moderate/severe), and sequelae (Table 1). Incidence rates were calculated based on rates retrieved from a systematic literature review and the results from an analysis of the Chinese Health Insurance and Research Association Database (CHIRA) (Supplementary Materials: Table S1.). The CHIRA database includes data from a sample (2–10%) of Tier 1 municipalities, capital cities of each province (Tier 2), prefecture-level cities (Tier 3), and country-level cities (Tier 4). The methodology used to collect the data for CHIRA has been well described by Shen et al. [19].

Table 1.
Clinical Model Inputs.
To better understand the context of the incidence rates retrieved from the CHIRA database and compare them to others that have been used in China, a systematic literature review (SLR) was undertaken. The objective of the SLR was to identify economic evaluations of PCVs for mainland China between 1/1/2006 and 10/11/2016. Of the 1012 records identified there were seven studies of PCVs focusing on mainland China [17,18,19,20,27,28,29,33].
Each of the studies identified in the SLR was analyzed to extract the age-based incidence rates for bacteremia, meningitis, pneumonia, and otitis media, as well as the source(s) for the incidence rates. The rates and sources are shown in Supplementary Material Table S1.
Bacteremia and meningitis incidence rate sources included CHIRA [19], Taiwan’s Health Insurance Research Database (HIRD) [18,20], Chen et al. [27,28], and studies using surveillance data from the literature [17,29].
Incidence rates for inpatient pneumonia were identified from CHIRA [19], the HIRD [18,20], and studies using the literature [27,28]. Outpatient pneumonia incidence rates included CHIRA [19], and the HIRD [18,20]. Otitis media incidence rates for both mild and moderate/severe cases were identified in the CHIRA 2013–2015 database, the HIRD [18,20], and using the literature [19].
Within each of the diseases, age-based incidence rates were calculated for each source by taking the average across all studies using the data source. Point estimates for each disease were calculated by then taking an average across all of the sources. This method ensures that sources not weighted by their frequency of use in economic evaluations.
The results of the SLR and subsequent data extraction did find that CHIRA may overestimate the incidence of inpatient pneumonia. The point estimates for meningitis, bacteremia, pneumonia, and AOM developed through an average of all available sources were utilized in the model (Table 1).
The model also considered disease sequelae for cases of pneumococcal meningitis. Sequelae included neurological impairment (7.0%) and hearing loss (13.0%) [35].
Case fatality ratios for bacteremia, meningitis, and inpatient pneumonia and serotype coverage parameters were derived from Shen et al. [19]. Case fatality ranged 1–6% depending on age in bacteremia, 0–14% for meningitis, and 1–16% for inpatient pneumonia [17,33]. Pneumococcal bacteremia and pneumococcal meningitis were assumed to have 87.1% of cases caused by PCV13 serotypes [30]. Estimates of 92.3% and 81.5% were used for the serotype coverage of pneumonia and otitis media, respectively [31,32].
2.4. Vaccine Effectiveness
The direct and indirect effects of vaccination are both considered in this model. The derivation of the effectiveness rates for PCV13 was previously described in Shen et al., [14,19,34,35,36,37,38]. The direct effect of PCV13 refers to the reduction of disease in children that are vaccinated, while indirect effect refers to the herd effect or the reduction in disease for unvaccinated individuals. Herd effect within PCV13 has been well documented in the literature [14,37,38]. It has been estimated that the herd effect is observed with vaccination rates starting at 54% [14].
A scenario analysis examined a 2 + 1 vaccination schedule, which has been previously studied, and is suited for situations with high uptake in a national immunization program [39]; a 3 + 1 schedule is recommended in low uptake settings to maximize individual protection. A recent study comparing 3 + 1 and 2 + 1 vaccination schedules in China reported IgG geometric mean concentrations and OPA geometric mean titers trended numerically higher with 3 + 1 versus 2 + 1 dose schedules after the 3 priming doses versus 2 priming doses, respectively, in the first year of life [40]. However, no significant differences in immunogenicity were observed between the 3 + 1 versus 2 + 1 dose schedules after the toddler dose [40]. PCV13 was well-tolerated across all schedules [40]. Therefore, while direct protection in the first year of life may differ, we assumed 3 + 1 and 2 + 1 vaccination schedules had similar effectiveness when uptake in the infant population was greater than 70%.
2.5. Direct Costs
Direct treatment-related costs for pneumococcal meningitis, pneumococcal bacteremia, inpatient and outpatient pneumonia, and mild and moderate/severe otitis media were included in the model (Table 2). Costs were sourced from the CHIRA database, which provided costs for Tier 1 cities and national costs. In cases where data was not available specifically for Tier 1 cities, the national cost data was used. Treatment-related costs were assumed to include all of the direct medical costs for the treatment of a case and were specific to each age group.

Table 2.
Cost Inputs.
A cost of 698 CNY was used for each dose of PCV13 for all included cities. Costs related to the service fee of the vaccination and transportation were only considered if they were direct costs. Service and transportation fees per dose, sourced from provincial governments or based on assumptions, were applied to Shanghai (5.5 CNY) (Assumption), Suzhou (20 CNY) [41], Shenzhen (25 CNY) [42], Beijing (25 CNY) [43], Chengdu (30 CNY) [44], and Qingdao (34 CNY) [45,46].
2.6. Quality of Life
Utility values were assigned to patients in the model to calculate the health-related quality of life. The general population of healthy patients was assumed to have a utility of 0.9. Disutility values through QALY decrements were applied to patients with bacteremia (0.008), meningitis (0.023), inpatient pneumonia (0.006), outpatient pneumonia (0.004), and acute otitis media (0.005) [47]. These QALY decrements were applied once for each observed case, which aimed to represent the short-term impact of the disease.
Patients with long-term sequelae were assigned separate utilities, which were applied to life-years to calculate QALYs. Neurological impairment and hearing loss due to pneumococcal meningitis carried utilities of 0.60 and 0.80, respectively [48].
2.7. Analysis
The base case analysis considered both DE and IDE and compared the costs and health outcomes of vaccination with PCV13 with no vaccination. For each arm of the model, the total number of QALYs and costs are reported and the incremental values for all outcomes between the PCV13 vaccination and no vaccination arms are calculated. The incremental cost-effectiveness ratio (ICER) is calculated by dividing the incremental total costs by incremental total QALYs to determine the cost per additional QALY for vaccination compared to no vaccination. China has not published an explicit cost-effectiveness threshold for the willingness to pay for an additional QALY. The China Guidelines for Pharmacoeconomic Evaluations, published in 2020, endorse the use of GDP per capita to calculate the willingness to payer threshold [49]. Interventions with ICERs less than GDP per capita income are considered “very cost-effective” and ICERs between 1–3x GDP per capita are considered “cost-effective”.
A one-way sensitivity analysis was performed by using the known confidence intervals of parameters or varying the parameters by +/− 10%. The minimum and maximum values of the disease incidence rates were used as the low/high values. Furthermore, an analysis of the incidence rates was undertaken to address the uncertainty within the point estimates of the incidence rates. For all included disease states the minimum and maximum values for each point estimate found either in the CHIRA database or the literature were recorded. A “minimum” and “maximum” scenario analysis were undertaken where all of the minimum values were used simultaneously in the minimum scenario and all of the maximum values were used in the maximum scenario.
Lastly, a scenario analysis evaluated the outcomes of the model when only DE was considered.
3. Results
3.1. Base Case Results
Table 3 shows the results of the base case analysis. Compared with no vaccination, PCV13 reduced the number of pneumococcal disease cases (thousands) by 46.33 (Beijing), 46.30 (Shanghai), 33.92 (Chengdu), 22.91 (Shenzhen), 21.72 (Qingdao), 21.30 (Suzhou), and 1.10 (Karamay). The reduction in pneumococcal disease cases resulted in QALYs saved (thousands) of 14.83 (Shanghai), 12.01 (Beijing), 9.71 (Chengdu), 7.66 (Shenzhen), 6.87 (Suzhou), 5.43 (Qingdao), and 0.27 (Karamay).

Table 3.
Base Case Results—Total Cases and Costs with and without the PCV13 Program.
In Shanghai the cost of vaccination (295,111,028) was fully offset by savings in pneumococcal disease costs of 323,757,862 CNY, resulting in total cost savings of 28,646,835 CNY. In the other analyzed cities, the cost of vaccination was reduced by savings in pneumococcal disease-related costs, resulting in incremental total costs of 8764,793 CNY (Shenzhen), 4062,450 CNY (Karamay), 49,163,176 CNY (Beijing), 60,918,974 CNY (Suzhou), 83,713,944 CNY (Qingdao), and 113,549,270 CNY (Chengdu).
Vaccination with PCV13 dominated the no vaccination strategy in Shanghai with lower incremental costs and higher incremental QALYs. In the remaining cities, ICERs ranged from 1145 CNY in Shenzhen to 15,422 CNY in Qingdao. All ICERs were below 1× GDP per capita in each city.
The base case scenario was further analyzed by the total number of vaccination doses, a 2 + 1 (three total doses) vaccination schedule was evaluated along with the base case 3 + 1 (four total doses) (Table 4). Vaccination with PCV13 remained cost-effective across both vaccination schedules.

Table 4.
Base Case Results—Analysis of Dosing Schedule.
One-way sensitivity analysis was performed on the base case (DE + IDE) analysis for each city (Figure 2). The top ten most influential parameters according to the spread between the high and low results, for each comparison and city were recorded. The incidence of inpatient pneumonia in those aged 18 to 34, 2 to 4, and 0 to less than 2 were the three most influential parameters. The total direct vaccine cost and the discount rate, which was varied between 3% and 7%, were the fourth and fifth most influential parameters, respectively.
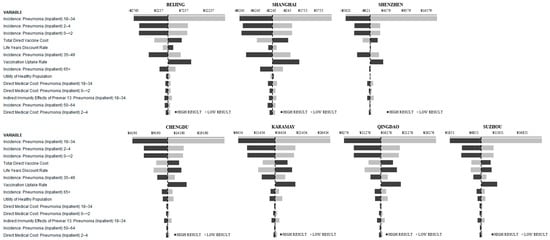
Figure 2.
IDE + DE: One-Way Sensitivity Analysis Results (Tornado Diagrams).
3.2. Incidence Rate Analysis
The results for the scenario analysis comparing the minimum and maximum pneumococcal disease incidence rates for IPD, pneumonia, and otitis media are shown in Figure 3. Vaccination with PCV13 dominated the no vaccination strategy when the maximum incidence rate values were used and increased to between 47,890 CNY (Shanghai) and 98,971 CNY (Chengdu) when all the minimum incidence rate values were used, both remaining below the 1× GDP per capita threshold.
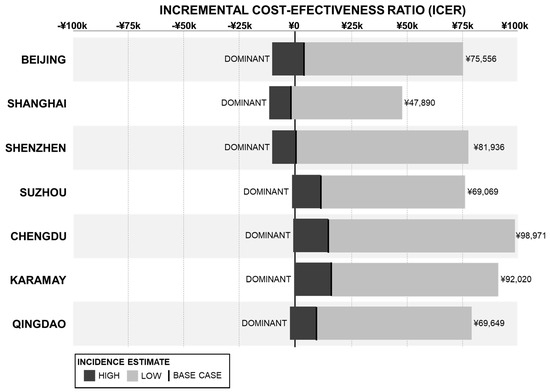
Figure 3.
Scenario Analysis of Disease Incidence Rates—ICER Results.
3.3. DE-Only Scenario
The results of the DE-only scenario analysis are shown in Table 5. The total number of pneumococcal disease cases (thousands) avoided with PCV13 vaccination was 26.03, 23.85, and 11.73 in the cities of Beijing, Shanghai, and Shenzhen, respectively. In the other analyzed cities, the number of pneumococcal disease cases (thousands) avoided was 0.64 in Karamay, 11.01 in Suzhou, 12.38 in Qingdao, and 18.41 in Chengdu. Vaccination with PCV13 provided higher incremental QALYs (thousands) of 1.59 (Beijing), 1.46 (Shanghai), 1.13 (Chengdu), 0.76 (Qingdao), 0.72 (Shenzhen), 0.67 (Suzhou), and 0.04 (Karamay) compared to no vaccination. Incremental total costs including direct medical and vaccination costs were higher for the PCV13 vaccination program compared to no-vaccination. The ICERs for vaccination with PCV13 were 161,237 CNY (Shenzhen), 155,625 CNY (Shanghai), 161,237 CNY (Beijing), 161,710 CNY (Karamay), 167,466 CNY (Suzhou), 170,345 CNY (Chengdu), and 171,496 CNY (Qingdao). All ICERs fell below the threshold of three times GDP per capita in the respective city.

Table 5.
DE-Only Scenario Results—Total Cases and Costs with and without the PCV13 Program.
4. Discussion
Vaccination with PCV13 at a rate of 70% was cost-effective in Beijing, Shanghai, Shenzhen, Suzhou, Chengdu, Karamay, and Qingdao. PCV13 remained cost-effective when a 2 + 1 dosing schedule was considered as well as in the separate sensitivity analysis of the disease incidence rates, when low incidence rate values were utilized, and became the dominant strategy with high incidence rate values. In the DE-only scenario, PCV13 was again cost-effective with all ICER falling below three times GDP per capita for each city. As vaccination with PCV13 was cost-effective in the DE-only and IDE + DE scenarios, it can be assumed to be cost-effective across all rates of vaccination, regardless of the presence of herd effect. While we assumed that a 3 + 1 and 2 + 1 schedule provide equivalent protection, it should be noted that a 3 + 1 schedule remains the preferable schedule where uptake of PCVs remains low [39,50]. Furthermore, while both schedules elicited equivalent immune responses following the booster dose, and we assumed similar protection, it has been hypothesized and modeled in the US that using two priming doses could result in incremental disease cases due to reduced protection in the first year of life, specifically when uptake is low and herd protection cannot be achieved [51].
The results of this study show that vaccination with PCV13 across all cities would avoid 2270 cases of IPD, 167,899 cases of pneumonia, and 23,407 cases of AOM in the base case analysis considering direct and indirect effects of vaccination. In the base case scenario, there were 3853 deaths avoided and an increase of 56,831 QALYs and 287,334,913 CNY in incremental total (vaccination and direct medical) costs.
Several other studies have assessed the cost-effectiveness of PCVs in China. PCV7 vs. no vaccination was examined by six studies [17,18,27,28,30,33], PCV10 vs. no vaccination by one [17], and PCV13 vs. no vaccination by four [17,18,19,20].
All four studies evaluating PCV13 vs. no vaccination found PCV13 to be cost-effective. The ICERs for PCV13 vs. no vaccination were 79,304 CNY (direct effect only), 76,551 CNY (direct effect and indirect effect for pneumonia only), and 3777 CNY (direct and indirect effect) in the study by Shen et al. These outcomes are similar to the ICERs in this analysis. Maurer et al. reported an ICER of 11,464 USD (CNY not reported), Mo et al., an ICER of 29,460 USD (182,652 CNY), and Zhou et al., 20,709 USD (140,821 CNY) for direct effect only and 18,483 USD (125,684 CNY) for direct and indirect effect. All of these ICERs fell below the threshold of 3× the current GDP per capita.
Incidence rates were highly influential parameters on the results of this study, and on the results of the cost-effectiveness studies in the literature. Studies using CHIRA data had significantly higher rates of inpatient pneumonia than those using HIRD data, local surveillance data, or other sources. Rather than focus on a single data source this study took an average of the point estimates for each source. Additionally, the low and high values observed in the literature for each point estimate were tested in the incidence rate analysis. While disease incidence did significantly influence the ICER for each city, PCV13 remained cost-effective when the low incidence rates were tested, and became the dominant strategy when the high incidence rates were tested.
The direct costs related to the vaccine and age distributions were the only parameters that varied from city to city, as all other parameters, including disease incidence rates, were consistent. As expected, lower direct vaccine and vaccine-related costs resulted in lower ICERs. Cities with younger populations tended to have lower ICERs as the vaccine’s effectiveness was higher in these younger populations. However, age distribution was only influential on the results in the base case scenario, which considered the indirect effects of the vaccine.
This study has several limitations. First, serotype coverage was assumed to be the same across all included cities. Large countries such as China can have considerable epidemiological differences between cities, especially those such as Karamay, with a smaller and demographically unique population. The model also did not consider serotype replacement in the long run. Second, the estimates of disease incidence vary considerably depending on the source for all included health states, especially inpatient pneumonia. These incidence rates are highly influential on the outcomes of the model as made evident by the one-way sensitivity analysis. Third, treatment costs were assumed across all tier 1 and non-tier 1 cities in the analysis. Costs are likely to vary from city to city within tier 1 and non-tier 1 cities. Lastly, the model may underestimate the benefit of vaccination with PCV as the number of patients carrying vaccine-serotype Streptococcus pneumoniae [52] and the prevalence of antimicrobial resistance [53] may decrease.
5. Conclusions
Vaccination with PCV13 is a cost-effective strategy for both the IDE + DE and DE-only scenarios in Beijing, Shanghai, Shenzhen, Suzhou, Chengdu, Karamay, and Qingdao. At vaccination rate levels where IDE are observed, PCV13 becomes very cost-effective with ICERs falling below GDP per capita in the respective cities. PCV13 remained cost-effective regardless of the dosing schedule and through an extended analysis of disease incidence. We estimate that vaccination with PCV13 will prevent a considerable number of cases of IPD, pneumonia, and AOM, as well as avoid mortality associated with IPD and pneumonia for both the vaccinated and unvaccinated population through the direct and indirect effect of the vaccine. This analysis can be used by policymakers when deciding on the allocation of resources in the studied cities.
Supplementary Materials
The following are available online at https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/vaccines9111368/s1, Table S1: Estimate of Incidence Rates
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, Y.L., H.W., W.F., B.C.M.W., P.D. and S.Z.; methodology, W.F., B.C.M.W., and S.Z.; formal analysis, W.F., B.C.M.W., P.D. and S.Z.; investigation, Y.L. and H.W.; writing—original draft preparation, W.F.; writing—review and editing, Y.L., H.W., W.F., B.C.M.W., P.D. and S.Z. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Data generated for this project come from proprietary models, which are described in detail in the manuscript.
Conflicts of Interest
W.F. and B.C.M.W. are paid consultants to Pfizer Investment Co., Ltd. P.D. and S.Z. are employees of Pfizer Investment Co., Ltd.
References
- World Health Organization. Estimated Hib and Pneumococcal Deaths for Children under 5 Years of Age. 2008. Available online: http://www.who.int/immunization/monitoring_surveillance/burden/estimates/Pneumo_hib/en/ (accessed on 23 April 2021).
- Ceyhan, M.; Ozsurekci, Y.; Aykac, K.; Hacibedel, B.; Ozbilgili, E. Economic burden of pneumococcal infections in children under 5 years of age. Hum. Vaccines Immunother. 2018, 14, 106–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- O'Brien, K.L.; Wolfson, L.J.; Watt, J.P.; Henkle, E.; Deloria-Knoll, M.; McCall, N.; Lee, E.; Mulholland, K.; Levine, O.S.; Cherian, T. Burden of disease caused by Streptococcus pneumoniae in children younger than 5 years: Global estimates. Lancet 2009, 374, 893–902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Institute for Health Metrics and Evaluation. China. Available online: http://www.healthdata.org/china (accessed on 14 April 2020).
- Yao, K.H.; Yang, Y.H. Streptococcus pneumoniae diseases in Chinese children: Past, present and future. Vaccine 2008, 26, 4425–4433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Deng, W.; Wang, S.-M.; Mo, Q.-M.; Jia, H.; Wang, Q.; Li, S.-G.; Li, X.; Yao, B.-D.; Liu, C.-J.; et al. Burden of pneumonia and meningitis caused by Streptococcus pneumoniae in China among children under 5 years of age: A systematic literature review. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e27333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rudan, I.; Boschi-Pinto, C.; Biloglav, Z.; Mulholland, K.; Campbell, H. Epidemiology and etiology of childhood pneumonia. Bull. World Health Organ. 2008, 86, 408–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mondiale de la Santé, O.; World Health Organization. Pneumococcal conjugate vaccines in infants and children under 5 years of age: WHO position paper–February 2019. Wkly. Epidemiol. Rec. 2019, 94, 85–104. [Google Scholar]
- Grijalva, C.; Nuorti, J.P.; Arbogast, P.G.; Martin, S.W.; Edwards, K.M.; Griffin, M.R. Decline in pneumonia admissions after routine childhood immunisation with pneumococcal conjugate vaccine in the USA: A time-series analysis. Lancet 2007, 369, 1179–1186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dinleyici, E.C.; Yargic, Z.A. Pneumococcal conjugated vaccines: Impact of PCV-7 and new achievements in the postvaccine era. Expert Rev. Vaccines 2008, 7, 1367–1394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, F.; Shefer, A.; Kong, Y.; Nuorti, J.P. Trends in acute otitis media-related health care utilization by privately insured young children in the United States, 1997–2004. Pediatrics 2008, 121, 253–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rose, M.; Zielen, S. Impact of infant immunization programs with pneumococcal conjugate vaccine in Europe. Expert Rev. Vaccines 2009, 8, 1351–1364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- PPilishvili, T.; Lexau, C.; Farley, M.M.; Hadler, J.; Harrison, L.H.; Bennett, N.M.; Reingold, A.; Thomas, A.; Schaffner, W.; Craig, A.S.; et al. Sustained reductions in invasive pneumococcal disease in the era of conjugate vaccine. J. Infect. Dis. 2010, 201, 32–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simonsen, L.; Taylor, R.J.; Schuck-Paim, C.; Lustig, R.; Haber, M.; Klugman, K.P. Effect of 13-valent pneumococcal conjugate vaccine on admissions to hospital 2 years after its introduction in the USA: A time series analysis. Lancet Respir. Med. 2014, 2, 387–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, F.; Hu, Y.; Li, J.; Ye, Q.; Young, M.M.; Zhou, X.; Chen, Z.; Yan, B.; Liang, J.Z.; Gruber, W.C.; et al. Immunogenicity and safety of 13-valent pneumococcal conjugate vaccine compared with 7-valent pneumococcal conjugate vaccine among healthy infants in China. Pediatric Infect. Dis. J. 2016, 35, 999–1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, D.B.C.; Chaiyakunapruk, N.; Chong, H.Y.; Beutels, P. Choosing between 7-, 10-and 13-valent pneumococcal conjugate vaccines in childhood: A review of economic evaluations (2006–2014). Vaccine 2015, 33, 1633–1658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maurer, K.A.; Chen, H.-F.; Wagner, A.L.; Hegde, S.T.; Patel, T.; Boulton, M.L.; Hutton, D.W. Cost-effectiveness analysis of pneumococcal vaccination for infants in China. Vaccine 2016, 34, 6343–6349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mo, X.; Tobe, R.G.; Liu, X.; Mori, R. Cost-effectiveness and health benefits of pediatric 23-valent pneumococcal polysaccharide vaccine, 7-valent pneumococcal conjugate vaccine and forecasting 13-valent pneumococcal conjugate vaccine in China. Pediatric Infect. Dis. J. 2016, 35, e353–e361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, K.; Wasserman, M.; Liu, D.; Yang, Y.H.; Yang, J.; Guzauskas, G.F.; Wang, B.C.; Hilton, B.; Farkouh, R. Estimating the cost-effectiveness of an infant 13-valent pneumococcal conjugate vaccine national immunization program in China. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0201245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.; He, J.; Wu, B.; Che, D. Cost-effectiveness analysis of routine 13-valent pneumococcal conjugate vaccinations in Chinese infants. Hum. Vaccines Immunother. 2018, 14, 1444–1452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Earnshaw, S.R.; McDade, C.L.; Zanotti, G.; Farkouh, R.A.; Strutton, D. Cost-effectiveness of 2 + 1 dosing of 13-valent and 10-valent pneumococcal conjugate vaccines in Canada. BMC Infect. Dis. 2012, 12, 101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Klok, R.M.; Lindkvist, R.-M.; Ekelund, M.; Farkouh, R.A.; Strutton, D.R. Cost-effectiveness of a 10- versus 13- valent pneumococcal conjugate vaccine in Denmark and Sweden. Clin. Ther. 2013, 35, 119–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mucino-Ortega, E.; Mould-Quevedo, J.F.; Farkouh, R.; Strutton, D. Economic evaluation of an infant immunization program in Mexico, based on 13-valent pneumococcal conjugated vaccines. Value Health 2011, 14 (5 Suppl. 1), S65–S70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Strutton, D.R.; Farkouh, R.A.; Earnshaw, S.R.; Hwang, S.; Theidel, U.; Kontodimas, S.; Klok, R.; Papanicolaou, S. Cost-effectiveness of 13-valent pneumococcal conjugate vaccine: Germany, Greece, and The Netherlands. J. Infect. 2012, 64, 54–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wasserman, M.; Mendoza, C.F.; Grajales, A.G.; Palacios, M.G.; Di Fusco, M. Cost-effectiveness of the 13-valent (PCV13) versus 10-valent (PCV10) pneumococcal conjugate vaccines as part of routine infant pneumococcal vaccination in Mexico. In Open Forum Infectious Diseases; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Brinkhoff T 2019 City Population—Population Statistics in Maps and Charts for Cities, Agglomerations and Administrative Divisions of All Countries of the World. Available online: https://citypopulation.de/ (accessed on 23 January 2020).
- Hu, S.; Shi, Q.; Chen, C.I.; Caldwell, R.; Wang, B.; Du, L.; He, J.; Roberts, C.S. Estimated public health impact of nationwide vaccination of infants with 7-valent pneumococcal conjugate vaccine (PCV7) in China. Int. J. Infect. Dis. 2014, 26, 116–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Caldwell, R.; Roberts, C.S.; An, Z.; Chen, C.I.; Wang, B. The health and economic impact of vaccination with 7-valent pneumococcal vaccine (PCV7) during an annual influenza epidemic and influenza pandemic in China. BMC Infect. Dis. 2015, 15, 284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Che, D.; Zhou, H.; He, J.; Wu, B. Modeling the impact of the 7-valent pneumococcal conjugate vaccine in Chinese infants: An economic analysis of a compulsory vaccination. BMC Health Serv. Res. 2014, 14, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Liu, Y.; Wang, H.; Chen, M.; Sun, Z.; Zhao, R.; Zhang, L.; Wang, H.; Zhang, H.; Wang, L.; Chu, Y.; et al. Serotype distribution and antimicrobial resistance patterns of Streptococcus pneumoniae isolated from children in China younger than 5 years. Diagn. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2008, 61, 256–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, K.H.; Wang, L.B.; Zhao, G.M.; Zheng, Y.J.; Deng, L.; Huang, J.F.; Wang, J.X.; Zhao, R.Z.; Deng, Q.L.; Hu, Y.H.; et al. Pneumococcal serotype distribution and antimicrobial resistance in Chinese children hospitalized for pneumonia. Vaccine 2011, 29, 2296–2301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hausdorff, W.P.; Yothers, G.; Dagan, R.; Kilpi, T.; Pelton, S.I.; Cohen, R.; Jacobs, M.R.; Kaplan, S.L.; Levy, C.; Lopez, E.L.; et al. Multinational study of pneumococcal serotypes causing acute otitis media in children. Pediatric Infect. Dis. J. 2002, 21, 1008–1016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, S.; Shi, Q.; Song, S.; Du, L.; He, J.; Chen, C.-I.; Caldwell, R.; Wang, B.; Roberts, C.S. Estimating the cost-effectiveness of the 7-valent pneumococcal conjugate vaccine in Shanghai, China. Value Health Reg. Issues 2014, 3, 197–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Black, S.B.; Shinefield, H.R.; Ling, S.; Hansen, J.; Fireman, B.; Spring, D.; Noyes, J.; Lewis, E.; Ray, P.; Lee, J.; et al. Effectiveness of heptavalent pneumococcal conjugate vaccine in children younger than five years of age for prevention of pneumonia. Pediatric Infect. Dis. J. 2002, 21, 810–815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ray, G.T.; Whitney, C.G.; Fireman, B.H.; Ciuryla, V.; Black, S.B. Cost-effectiveness of pneumococcal conjugate vaccine: Evidence from the first 5 years of use in the United States incorporating herd effects. Pediatric Infect. Dis. J. 2006, 25, 494–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fireman, B.; Black, S.B.; Shinefield, H.R.; Lee, J.; Lewis, E.; Ray, P. Impact of the pneumococcal conjugate vaccine on otitis media. Pediatric Infect. Dis. J. 2003, 22, 10–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moore, M.R.; Link-Gelles, R.; Schaffner, W.; Lynfield, R.; Lexau, C.; Bennett, N.M.; Petit, S.; Zansky, S.M.; Harrison, L.H.; Reingold, A.; et al. Effect of use of 13-valent pneumococcal conjugate vaccine in children on invasive pneumococcal disease in children and adults in the USA: Analysis of multisite, population-based surveillance. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2015, 15, 301–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Moore, M.R.; Link-Gelles, R.; Schaffner, W.; Lynfield, R.; Holtzman, C.; Harrison, L.H.; Zansky, S.M.; Rosen, J.B.; Reingold, A.; Scherzinger, K.; et al. Effectiveness of 13-valent pneumococcal conjugate vaccine for prevention of invasive pneumococcal disease in children in the USA: A matched case-control study. Lancet Respir. Med. 2016, 4, 399–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waight, P.A.; Andrews, N.J.; Ladhani, S.N.; Sheppard, C.L.; Slack, M.P.E.; Miller, E. Effect of the 13-valent pneumococcal conjugate vaccine on invasive pneumococcal disease in England and Wales 4 years after its introduction: An observational cohort study. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2015, 15, 535–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhu, F.; Hu, Y.; Li, J.; Ye, Q.; Young, M.M.; Liang, J.Z.; Gruber, W.C.; Giardina, P.C.; Scott, D.A. Immunogenicity and Safety of the 13-Valent Pneumococcal Conjugate Vaccine Administered in a 3+ 1 versus 2+ 1 Dose Schedule Among Infants in China. Pediatric Infect. Dis. J. 2019, 38, 1150–1158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiangsu Development and Reform Commission. Notice of the Provincial Development and Reform Commission of the Provincial Department of Finance on the Approval of Vaccination Service Fees. 2020. Available online: http://fzggw.jiangsu.gov.cn/art/2020/11/13/art_284_9578645.html (accessed on 9 November 2020).
- Development and Reform Commission of Shenzhen Municipality. Notice of the Guangdong Provincial Development and Reform Commission of the Guangdong Provincial Department of Finance on Extending the Fee Schedule of Vaccination Services for Non-Immunization Programs. 2021. Available online: http://fgw.sz.gov.cn/ztzl/zdlyxxgkzl/xzsyxsf/content/post_8577013.html (accessed on 9 November 2020).
- Beijing Price Monitoring Center. Notice of the Beijing Municipal Development and Reform Commission, the Beijing Municipal Health and Family Planning Commission and the Beijing Municipal Human Resources and Social Security Bureau on Setting the Price of the Second Type of Vaccination Service for Beijing Municipality (Beijing Municipal Development and Reform [2018] No. 362). 2018. Available online: http://www.beijingprice.cn/c/2018-03-06/502119.shtml (accessed on 9 November 2020).
- Sichuan Provincial Development and Reform Commission. Notice on the Fee Schedule of Vaccination Services and Its Related Issues (Sichuan Provincial Development and Reform [2018] No. 331). 2018. Available online: http://fgw.sc.gov.cn/sfgwsjd/c100030/2018/7/13/9878686f8a1744ca8f2b3257760b6c63.shtml (accessed on 9 November 2020).
- Qingdao Municipal Health Commission. Notice on Forwarding the “Notice of the Shandong Provincial Development and Reform Commission of the Shandong Provincial Department of Finance on the Fee Schedule of Vaccination Services for Non-Immunization Programs”. 2021. Available online: http://wsjkw.qingdao.gov.cn/n28356065/n32563139/n32563141/n32564190/210511193304387443.html (accessed on 10 November 2021).
- Qingdao Municipal Price Bureau. Notice of Qingdao Municipal Price Bureau and Qingdao Municipal Health and Family Planning Commission on Forwarding the “Notice of Shandong Provincial Price Bureau and Shandong Provincial Health and Family Planning Commission on Issues Concerning Storage and Transportation Fees for Type II Vaccines”. 2018. Available online: http://www.qingdao.gov.cn/n172/n24624151/n24629915/n24629929/n24629943/180126093021355736.html (accessed on 10 November 2021).
- Melegaro, A.; Edmunds, W. Cost-effectiveness analysis of pneumococcal conjugate vaccination in England and Wales. Vaccine 2004, 22, 4203–4214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morrow, A.; De Wals, P.; Petit, G.; Guay, M.; Erickson, L.J. The burden of pneumococcal disease in the Canadian population before routine use of the seven-valent pneumococcal conjugate vaccine. Can. J. Infect. Dis. Med Microbiol. 2007, 18, 121–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- China Guidelines for Pharmacoeconomic Evaluations Working Group. China Guidelines for Pharmacoeconomic Evaluations. December 2020. Available online: https://tools.ispor.org/PEguidelines/source/China-Guidelines-for-Pharmacoeconomic-Evaluations-2020.pdf (accessed on 5 November 2021).
- European Medicines Agency (EMA). Prevenar 13: EPAR–Product Information. 26 March 2020. Available online: https://www.ema.europa.eu/documents/product-information/prevenar-13-epar-product-information_en.pdf (accessed on 2 September 2020).
- Stoecker, C.; Hampton, L.M.; Link-Gelles, R.; Messonnier, M.L.; Zhou, F.; Moore, M.R. Cost-effectiveness of using 2 vs. 3 primary doses of 13-valent pneumococcal conjugate vaccine. Pediatrics 2013, 132, e324–e332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Davis, S.M.; Knoll, M.D.; Kassa, H.T.; O’Brien, K.L. Impact of pneumococcal conjugate vaccines on nasopharyngeal carriage and invasive disease among unvaccinated people: Review of evidence on indirect effects. Vaccine 2013, 32, 133–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Metcalf, B.J.; Gertz, R.E., Jr.; Gladstone, R.A.; Walker, H.; Sherwood, L.K.; Jackson, D.; Li, Z.; Law, C.; Hawkins, P.A.; Chochua, S.; et al. Strain features and distributions in pneumococci from children with invasive disease before and after 13 valent conjugate vaccine implementation in the United States. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2016, 22, 60.e9–60.e29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).