Robust SARS-CoV-2 Antibody Responses in Asian COVID-Naïve Subjects 180 Days after Two Doses of BNT162b2 mRNA COVID-19 Vaccine
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Participants
2.2. Methods and Materials
2.3. Statistical Analysis
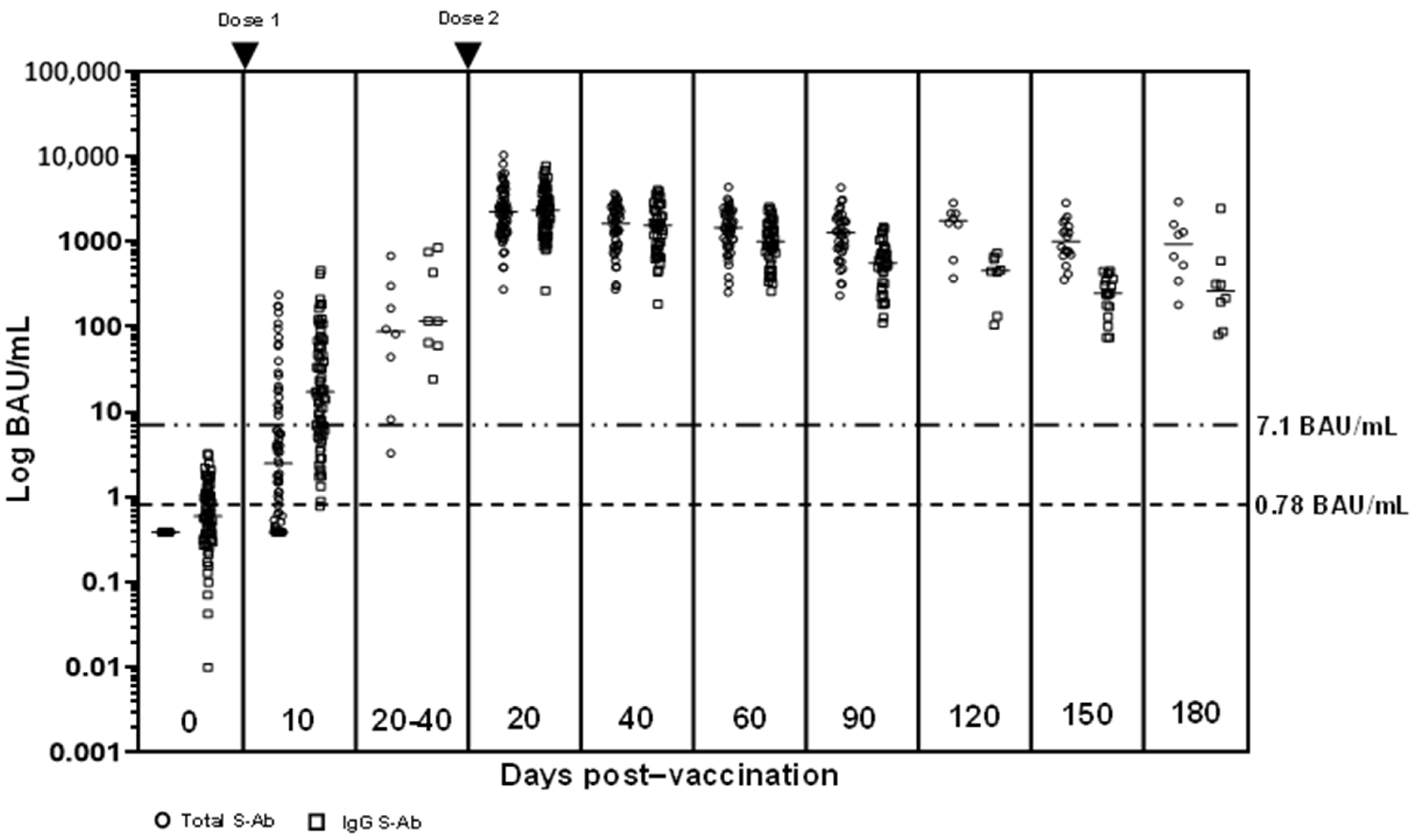
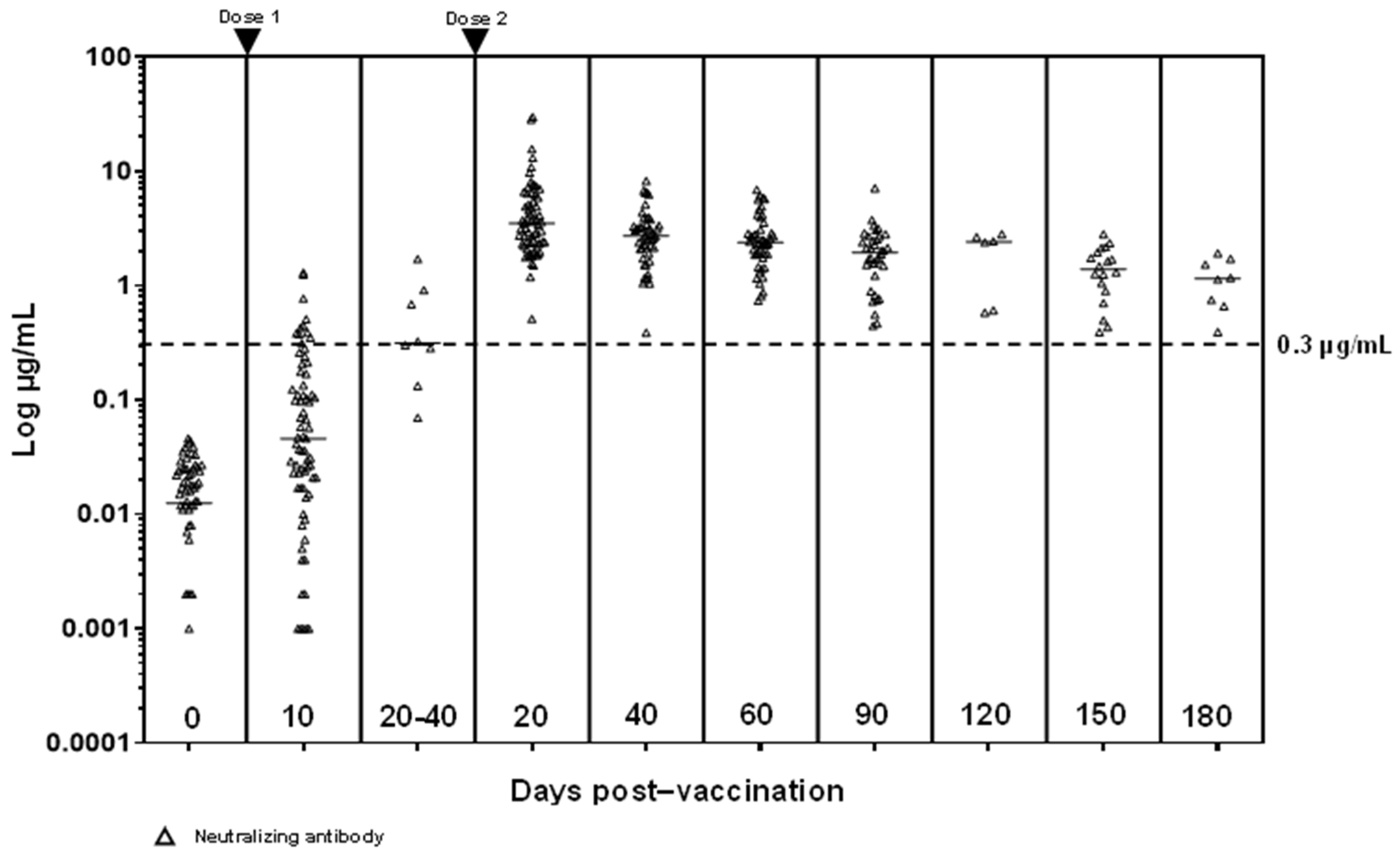
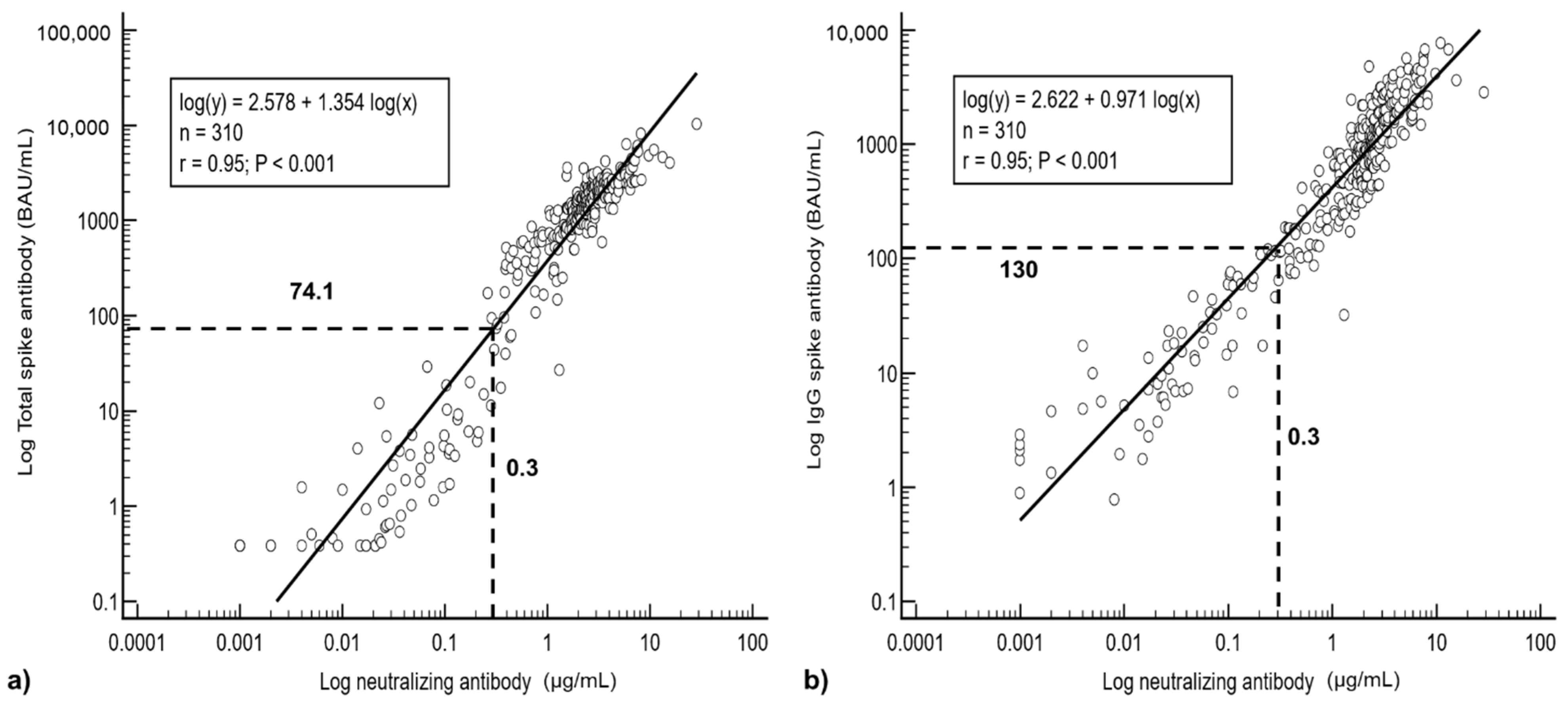
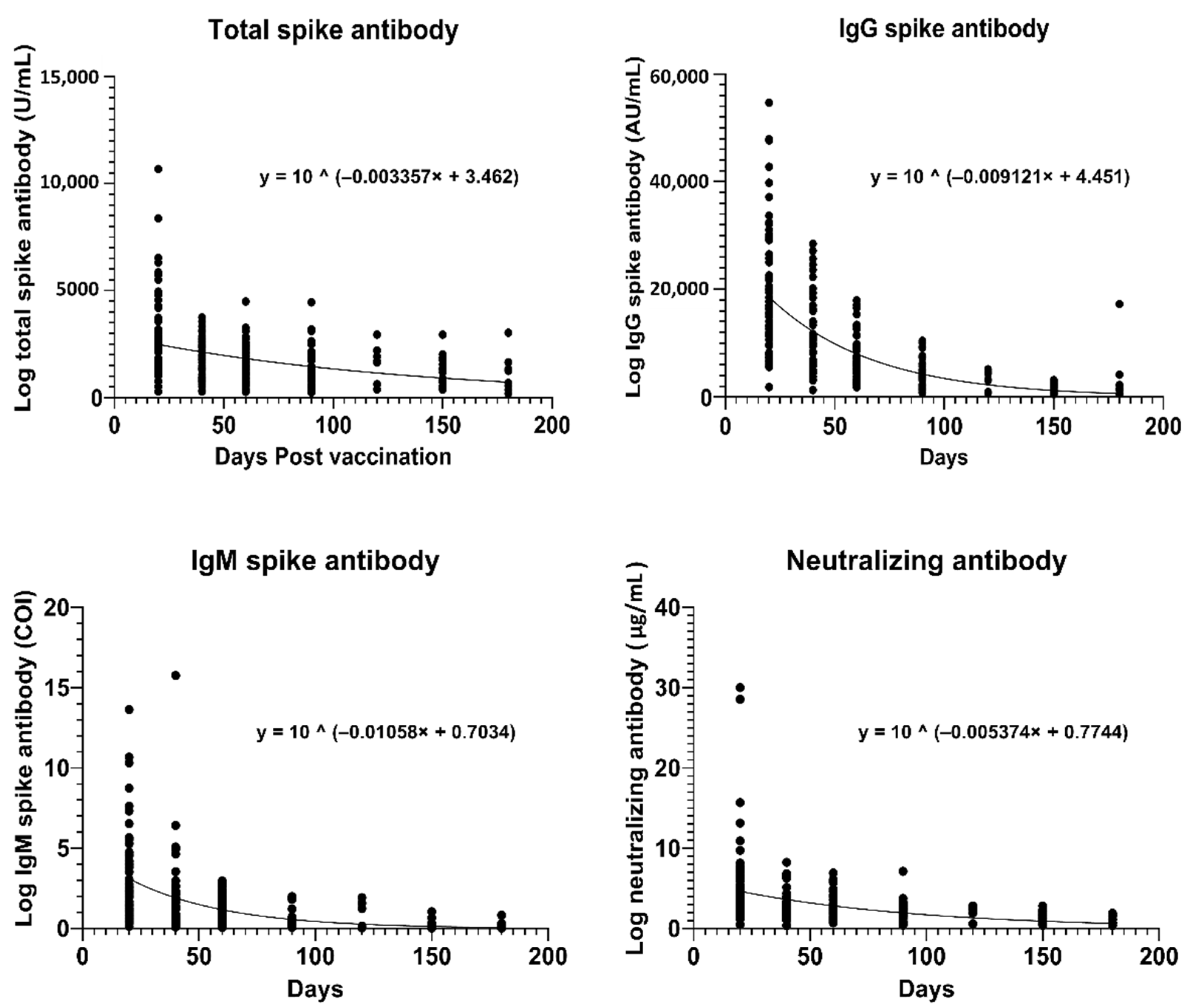
3. Results
3.1. COVID-Naïve Status of All Subjects
3.2. S-Ab and N-Ab Responses
3.3. Regression Analysis
3.4. Estimation of Antibody Half-Lives
3.5. Age and Gender Group Analysis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| SARS-CoV-2 | Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus type 2 |
| COVID-19 | Coronavirus disease 2019 |
| Nuc-Ab | Nucleocapsid antibody |
| S-Ab | Spike antibody |
| N-Ab | Neutralizing antibody |
| ELISA | Enzyme-linked immunoassay |
| CLIA | Chemiluminescent immunoassay |
| HCWs | Healthcare workers |
| T-Ab | Total spike antibody |
| ECLIA | Electro-chemiluminescent immunoassay |
| COI | Cut-off index |
| CI | Confidence interval |
References
- Favresse, J.; Elsen, M.; Eucher, C.; Laffineur, K.; Eeckhoudt, S.V.; Nicolas, J.B.; Gillot, C.; Dogne, J.M.; Douxfils, J. Long-term kinetics of anti-SARS-CoV-2 antibodies in a cohort of 197 hospitalized and non-hospitalized COVID-19 patients. Clin. Chem. Lab. Med. 2020, 59, e179–e183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Favresse, J.; Eucher, C.; Elsen, M.; Gillot, C.; Eeckhoudt, S.V.; Dogne, J.M.; Douxfils, J. Persistence of Anti-SARS-CoV-2 Antibodies Depends on the Analytical Kit: A Report for Up to 10 Months after Infection. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lau, C.S.; Phua, S.K.; Liang, Y.L.; Oh, M.L.H.; Aw, T.C. BNT162b2 mRNA COVID-19 Vaccine Elicited Antibody Responses in COVID-19-naïve Subjects. J. Exp. Pathol. 2021, 2, 117–127. [Google Scholar]
- Favresse, J.; Bayart, J.L.; Mullier, F.; Elsen, M.; Eucher, C.; Eeckhoudt, S.V.; Roy, T.; Wieers, G.; Laurent, C.; Dogne, J.M.; et al. Antibody titers decline 3-month post-vaccination with BNT162b2. Emerg. Microbes. Infect. 2021, 10, 1495–1498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grenache, D.G.; Ye, C.; Bradfute, S.B. Correlation of SARS-CoV-2 Neutralizing Antibodies to an Automated Chemiluminescent Serological Immunoassay. J. Appl. Lab. Med. 2021, 6, 491–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piccoli, L.; Park, Y.J.; Tortorici, M.A.; Czudnochowski, N.; Walls, A.C.; Beltramello, M.; Silacci-Fregni, C.; Pinto, D.; Rosen, L.E.; Bowen, J.E.; et al. Mapping Neutralizing and Immunodominant Sites on the SARS-CoV-2 Spike Receptor-Binding Domain by Structure-Guided High-Resolution Serology. Cell 2020, 183, 1024–1042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suhandynata, R.T.; Hoffman, M.A.; Huang, D.; Tran, J.T.; Kelner, M.J.; Reed, S.L.; McLawhon, R.W.; Voss, J.E.; Nemazee, D.; Fitzgerald, R.L. Commercial Serology Assays Predict Neutralization Activity against SARS-CoV-2. Clin. Chem. 2021, 67, 404–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doria-Rose, N.; Suthar, M.S.; Makowski, M.; O’Connell, S.; McDermott, A.B.; Flach, B.; Ledgerwood, J.E.; Mascola, J.R.; Graham, B.S.; Lin, B.C.; et al. Antibody Persistence through 6 Months after the Second Dose of mRNA-1273 Vaccine for COVID-19. N. Engl. J. Med. 2021, 384, 2259–2261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lau, C.S.; Hoo, S.P.; Liang, Y.L.; Phua, S.K.; Aw, T.C. Performance of an automated chemiluminescent immunoassay for SARS-COV-2 IgM and head-to-head comparison of Abbott and Roche COVID-19 antibody assays. Pract. Lab. Med. 2021, 25, e00230. [Google Scholar]
- Lau, C.S.; Hoo, S.P.; Yew, S.F.; Ong, S.K.; Lum, L.T.; Heng, P.Y.; Tan, J.G.; Wong, M.S.; Aw, T.C. Evaluation of an Electrochemiluminescent SARS-CoV-2 Antibody Assay. J. Appl. Lab. Med. 2020, 5, 1313–1323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lau, C.S.; Oh, H.M.L.; Hoo, S.P.; Liang, Y.L.; Phua, S.K.; Aw, T.C. Performance of an automated chemiluminescence SARS-CoV-2 IG-G assay. Clin. Chim. Acta 2020, 510, 760–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- SydPath Half-Life Calculator. Available online: http://www.sydpath.stvincents.com.au/other/HalfLifeCalculator.htm (accessed on 28 September 2021).
- World Medical Association. World Medical Association Declaration of Helsinki: Ethical principles for medical research involving human subjects. JAMA 2013, 310, 2191–2194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Levin, E.G.; Lusting, Y.; Cohen, C.; Fluss, R.; Indenbaum, V.; Amit, S.; Doolman, R.; Asraf, K.; Mendelson, E.; Ziv, A.; et al. Waning Immune Humoral Response to BNT162b2 COVID-19 Vaccine over 6 Months. N. Engl. J. Med. 2021, NEJMoa2114583, Online ahead of print. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bayart, J.L.; Douxfils, J.; Gillot, C.; David, C.; Mullier, F.; Elsen, M.; Eucher, C.; Eeckhoudt, S.V.; Roy, T.; Gerin, V.; et al. Waning of IgG, Total and Neutralizing Antibodies 6 Months Post-Vaccination with BNT162b2 in Healthcare Workers. Vaccines 2021, 9, 1092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khoury, D.S.; Cromer, D.; Reynaldi, A.; Schlub, T.E.; Wheatley, A.K.; Juno, J.A.; Subbarao, K.; Kent, S.J.; Triccas, J.A.; Davenport, M.P. Neutralizing antibody levels are highly predictive of immune protection from symptomatic SARS-CoV-2 infection. Nat. Med. 2021, 27, 1205–1211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Favresse, J.; Gillot, C.; Chiaro, L.D.; Eucher, C.; Elsen, M.; Eeckhoudt, S.V.; David, C.; Morimont, L.; Dogne, J.M.; Douxfils, J. Neutralizing Antibodies in COVID-19 Patients and Vaccine Recipients after Two Doses of BNT162b2. Viruses 2021, 13, 1364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roltgen, K.; Nielsen, S.C.A.; Arunachalam, P.S.; Yang, F.; Hoh, R.A.; Wirz, O.F.; Lee, A.S.; Gao, F.; Mallajosyula, V.; Li, C.; et al. mRNA vaccination compared to infection elicits an IgG-predominant response with greater SARS-CoV-2 specificity and similar decrease in variant spike recognition. medRxiv 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, Q.X.; Liu, B.Z.; Deng, H.J.; Wu, G.C.; Deng, K.; Chen, Y.K.; Liao, P.; Qiu, J.F.; Lin, Y.; Cai, X.F.; et al. Antibody responses to SARS-CoV-2 in patients with COVID-19. Nat. Med. 2020, 26, 845–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, J.; Stoesser, N.; Matthews, P.C.; Ayoubkhani, D.; Studley, R.; Bell, I.; Bell, J.I.; Newton, J.N.; Farrar, J.; Diamond, I.; et al. Antibody responses to SARS-CoV-2 vaccines in 45,965 adults from the general population of the United Kingdom. Nat. Microbiol. 2021, 6, 1140–1149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demonbreun, A.R.; Sancilio, A.; Velez, M.P.; Ryan, D.T.; Saber, R.; Vaµght, L.A.; Reiser, N.L.; Hsieh, R.R.; D’Aquila, R.T.; Mustanski, B.; et al. Comparison of IgG and neutralizing antibody responses after one or two doses of COVID-19 mRNA vaccine in previously infected and uninfected individuals. EClinicalMedicine. 2021, 38, 101018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steensels, D.; Pierlet, N.; Penders, J.; Mesotten, D.; Heylen, L. Comparison of SARS-CoV-2 Antibody Response Following Vaccination With BNT162b2 and mRNA-1273. JAMA 2021, 326, 1533–1535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, M.G.; Stenehjem, E.; Grannis, S.; Ball, S.W.; Naleway, A.L.; Ong, T.C.; DeSilva, M.B.; Natarajan, K.; Bozio, C.H.; Lewis, N.; et al. Effectiveness of COVID-19 Vaccines in Ambulatory and Inpatient Care Settings. N. Engl. J. Med. 2021, 385, 1355–1371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jalkanen, P.; Kolehmainen, P.; Hakkinen, H.K.; Huttunen, M.; Tahtinen, P.A.; Lundberg, R.; Maljanen, S.; Reinholm, A.; Tauriainen, S.; Pakkanen, S.H.; et al. COVID-19 mRNA vaccine induced antibody responses against three SARS-CoV-2 variants. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 3991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tretyn, A.; Szczepanek, J.; Skorupa, M.; Jarkiewicz-Tretyn, J.; Sandomierz, D.; Dejewska, J.; Ciechanowska, K.; Jarkiewicz-Tretyn, A.; Koper, W.; Palgan, K. Differences in the Concentration of Anti-SARS-CoV-2 IgG Antibodies Post-COVID-19 Recovery or Post-Vaccination. Cells 2021, 10, 1952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elslande, J.V.; Gruwier, L.; Godderis, L.; Vermeersch, P. Estimated half-life of SARS-CoV-2 anti-spike antibodies more than double the half-life of anti-nucleocapsid antibodies in healthcare workers. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2021, ciab219, Online ahead of print. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaebler, C.; Wang, Z.; Lorenzi, J.C.C.; Muecksch, F.; Finkin, S.; Tokuyama, M.; Tokuyama, M.; Cho, A.; Jankovic, M.; Schaefer-Babajew, D.; et al. Evolution of antibody immunity to SARS-CoV-2. Nature 2021, 591, 639–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wheatley, A.K.; Juno, J.A.; Wang, J.J.; Selva, K.J.; Reynaldi, A.; Tan, H.X.; Lee, W.S.; Wragg, K.M.; Kelly, H.G.; Esterbauer, R.; et al. Evolution of immune responses to SARS-CoV-2 in mild-moderate COVID-19. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 1162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dan, J.M.; Mateus, J.; Kato, Y.; Hastie, K.M.; Yu, E.D.; Faliti, C.E.; Grifoni, A.; Ramirez, S.I.; Haupt, S.; Frazier, A.; et al. Immunological memory to SARS-CoV-2 assessed for up to 8 months after infection. Science 2021, 371, eabf4063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goel, R.R.; Apostolidis, S.A.; Painter, M.M.; Mathew, D.; Pattekar, A.; Kuthuru, O.; Gouma, S.; Hicks, P.; Meng, W.; Rosenfeld, A.M.; et al. Distinct antibody and memory B cell responses in SARS-CoV-2 naïve and recovered individuals following mRNA vaccination. Sci. Immunol. 2021, 6, eabi6950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muller, L.; Andree, M.; Moskorz, W.; Drexler, I.; Walotka, L.; Grothmann, R.; Ptok, J.; Hillebrandt, J.; Ritchie, A.; Rabl, D.; et al. Age-dependent immune response to the Biontech/Pfizer BNT162b2 COVID-19 vaccination. Clin. Infect. Dis 2021, ciab381, Online ahead of print. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Days Post-Vaccination | 20 | 40 | 60 | 90 | 120 | 150 | 180 | Half-Life | Days to N-Ab Cut-Off * |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total (U/mL) | 2482 | 2127 | 1822 | 1445 | 1146 | 909 | 721 | 90 days | 470 |
| IgG (AU/mL) | 18,560 | 12,194 | 8012 | 4267 | 2272 | 1210 | 644 | 33 days | 163 |
| N-Ab (µg/mL) | 4.64 | 3.63 | 2.83 | 1.95 | 1.35 | 0.93 | 0.64 | 56 days | 241 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lau, C.-S.; Phua, S.K.; Liang, Y.-L.; Oh, H.M.-L.; Aw, T.-C. Robust SARS-CoV-2 Antibody Responses in Asian COVID-Naïve Subjects 180 Days after Two Doses of BNT162b2 mRNA COVID-19 Vaccine. Vaccines 2021, 9, 1241. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines9111241
Lau C-S, Phua SK, Liang Y-L, Oh HM-L, Aw T-C. Robust SARS-CoV-2 Antibody Responses in Asian COVID-Naïve Subjects 180 Days after Two Doses of BNT162b2 mRNA COVID-19 Vaccine. Vaccines. 2021; 9(11):1241. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines9111241
Chicago/Turabian StyleLau, Chin-Shern, Soon Kieng Phua, Ya-Li Liang, Helen May-Lin Oh, and Tar-Choon Aw. 2021. "Robust SARS-CoV-2 Antibody Responses in Asian COVID-Naïve Subjects 180 Days after Two Doses of BNT162b2 mRNA COVID-19 Vaccine" Vaccines 9, no. 11: 1241. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines9111241
APA StyleLau, C.-S., Phua, S. K., Liang, Y.-L., Oh, H. M.-L., & Aw, T.-C. (2021). Robust SARS-CoV-2 Antibody Responses in Asian COVID-Naïve Subjects 180 Days after Two Doses of BNT162b2 mRNA COVID-19 Vaccine. Vaccines, 9(11), 1241. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines9111241







