Hepatitis A Outbreak Characteristics: A Comparison of Regions with Different Vaccination Strategies, Spain 2010–2018
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Outbreak and Case Reporting
2.2. Variables
2.3. Statistical Analysis
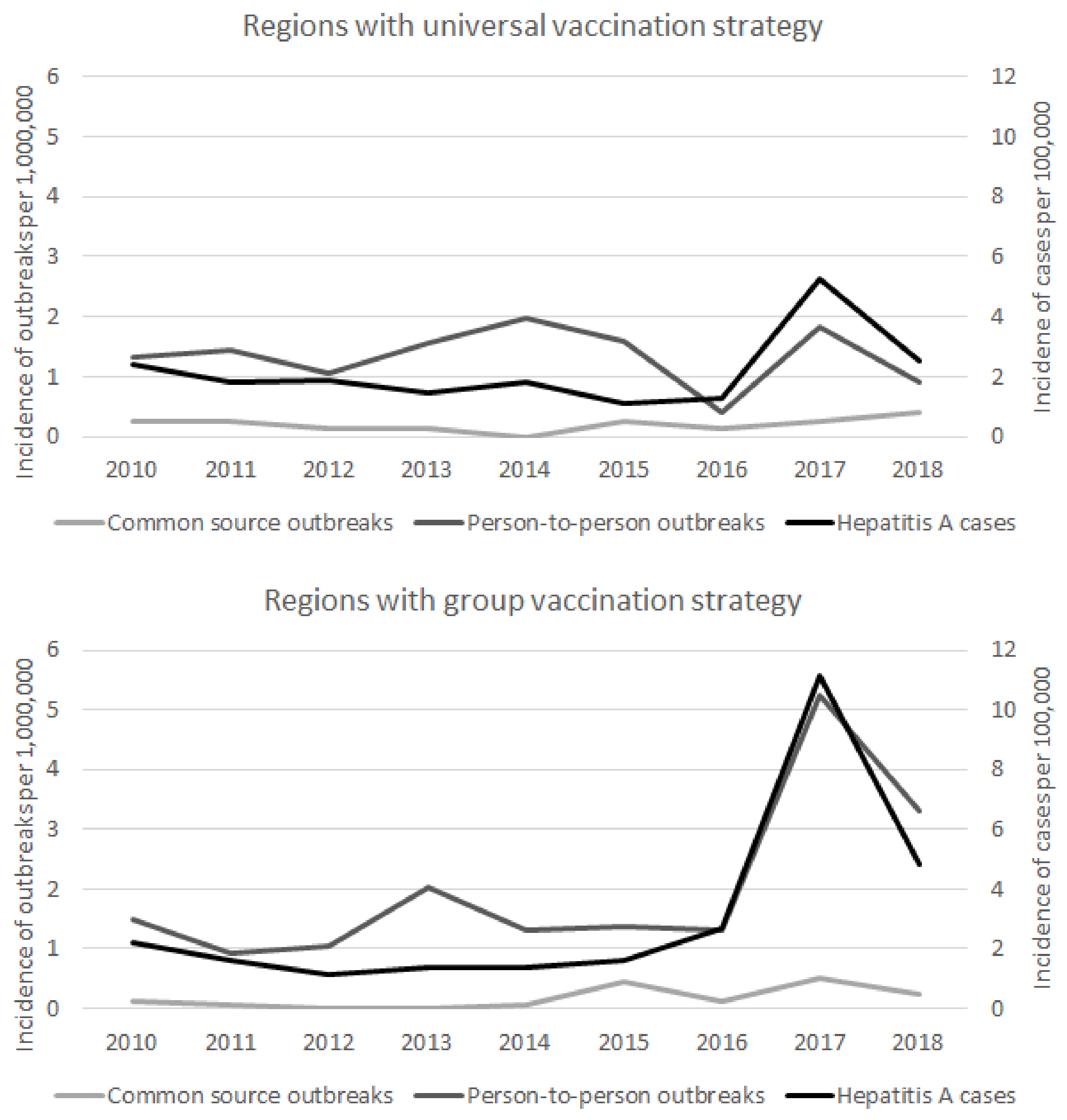
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
References
- Rosenfeld, A.B.; Racaniello, V.R. Picornaviridae: The viruses and their replication. In Fields Virology, 7th ed.; Howley, P.M., Knipe, D.M., Whelan, S., Eds.; Wolters Kluwer: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2021; Volume 1, pp. 30–85. [Google Scholar]
- James, S.L.; Abate, D.; Abate, K.H.; Abay, S.M.; Abbafati, C.; Abbasi, N.; Abbastabar, H.; Abd-Allah, F.; Abdela, J.; Abdelalim, A.; et al. Global regional, and national incidence, prevalence and years lived with disability for 354 diseases and injuries for 195 territories, 1999–2017: A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2017. Lancet 2018, 392, 1789–1858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization. Hepatitis A. Key Facts. July 2021. Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/hepatitis-a (accessed on 15 July 2021).
- Averhoff, F.; Khudyakov, Y.; Vellozi, C. Hepatitis A virus. In Principles and Practice of Infectious Diseases, 9th ed.; Bennett, J.E., Dolin, R., Blaser, M.J., Eds.; Elsevier: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2020; pp. 2243–2261. [Google Scholar]
- Jacobsen, K.H. Globalization and the changing epidemiology of hepatitis A virus. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Med. 2018, 8, a031716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bauer, D.; Farthofer, A.; Chromy, D.; Simbrunner, B.; Steininger, L.; Schmidbauer, C.; Binter, T.; Trauner, M.; Mandorfer, M.; Schmidt, R.; et al. Recent outbreaks of severe hepatitis A virus infections in Vienna. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2021, 40, 335–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez-Tajes, S.; Perpiñán, E.; Caballo, B.; Lens, S.; Mariño, Z.; Pérez del Pulgar, S.; Forns, X.; Koutsoudakis, G. Hepatitis A outbreak in Barcelona among men who have sex with men (MSM), January-June 2017: A hospital perspective. Liver Int. 2018, 38, 588–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- World Health Organization. WHO position paper on hepatitis A vaccines-June 2012. Wkly. Epidemiol. Rec. 2012, 28–29, 261–276. [Google Scholar]
- Ponencia del Programa y Registro de Vacunaciones. Vacunación en Grupos de Riesgo de Todas las Edades y en Determinades Situacions. Consejo Interterritorial del Sistema Nacional de Salud, Ministerio de Sanidad, Consumo y Binestar Social. 2018. Available online: https://www.mscbs.gob.es/profesionales/saludPublica/prevPromocion/vacunaciones/programasDeVacunacion/riesgo/docs/VacGruposRiesgo_todas_las_edades.pdf (accessed on 15 July 2021).
- Bruguera, M.; Salleras, L.; Vidal, J.; Vidal, J.; Navas, E.; Domínguez, A.; Batalla, J.; Taberner, J.L.; Espuñes, J. Changes in seroepidemiology of hepatitis A virus infection in Catalonia in the period 1989–1996. Implications for new vaccination strategy. Med. Clin. 1999, 112, 406–408. [Google Scholar]
- Navas, E.; Salleras, L.; Gispert, R.; Domínguez, A.; Prat, A.; Rodríguez, G.; Galí, N.; Prat, A. Efficiency of the incorporation of the hepatitis A vaccine as a combined A+B vaccine to the hepatitis B vaccination programme of preadolescents in schools. Vaccine 2005, 23, 2185–2189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ministerio de Sanidad, Servicios Sociales e Igualdad. Real Decreto 2210/1995, de 28 de diciembre, por el que se crea la Red Nacional de Vigilancia Epidemiológica. Boletín Of. Estado 1996, 21, 2153–2158. [Google Scholar]
- Mellou, K.; Chrysostomou, A.; Sideroglou, T.; Kyritsi, M.; Georgakopoulou, T.; Tsiodras, T.; Hadjichristodoulou, C. Epidemiology of hepatitis A in Greece in the last decade: Management of reported cases and outbreaks and lessons learned. Epidemiol. Infect. 2020, 148, e58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chia, V.; Clearya, S.; Bocchini, J.A. In pursuit of control and elimination: Update on hepatitis A and B epidemiology and prevention strategies. Curr. Opin. Pediatr. 2018, 30, 689–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fahrni, O.; Posfay Barbe, K.M.; Wagner, N. Immunization against hepatitis A in migrant children. Three vaccination strategies, a retrospective study. Pediatr. Infect. Dis. J. 2020, 39, 164–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gassowski, M.; Michaelis, K.; Wenzel, J.J.; Faber, M.; Figoni, J.; Mouna, L.; Friesema, I.H.; Vennema, H.; Avellon, A.; Varela, C.; et al. Two concurrent outbreaks of hepatitis A highlight the risk of infection for non-immune travellers to Morocco, January to June 2018. Eurosurveillance 2018, 23, 1800329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, E.L.; Sinn, D.H.; Lee, H.W.; Kim, J.H. Current status and strategies for the control of viral hepatitis A in Korea. Clin. Mol. Hepatol. 2017, 23, 196–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batdorf, S.J.; Hofmeister, M.G.; Surtees, T.C.; Thomasson, E.D.; McBeeb, S.M.; Pauly, N.J. Estimated Medicaid costs associated with hepatitis A during an outbreak—West Virginia, 2018–2019. Morb. Mortal. Wkly. Rep. MMWR 2021, 70, 269–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghildayal, N. Cost-effectiveness of hepatitis A vaccination in a developed and developing country. Int. J. Health Care Qual. Assur. 2019, 32, 1175–1199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papaevangelou, V.; Alexopoulou, Z.; Hadjichristodoulou, C.; Kourlamba, G.; Katsioulis, A.; Theodoridou, K.; Spoulou, V.; Theodoridou, M. Time trends in pediatric hospitalizations for hepatitis A in Greece (1999–2013): Assessment of the impact of universal infant immunization in 2008. Hum. Vaccines Immunother. 2016, 12, 1852–1856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Plunkett, J.; Mandal, S.; Balogun, K.; Beebeejaun, K.; Ngui, L.L.; Ramsay, M.; Edelstein, M. Hepatitis A outbreak among men who have sex with men (MSM) in England, 2016–2018: The contribution of past and current vaccination policy and practice. Vaccine X 2019, 1, 100014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Connor, L.; McGovern, E.; O’Meara, M.; Dean, J.; Ward, M.; O’Connor, M. Extensive hepatitis A outbreak in an urban childcare facility in Ireland, associated with considerable adult morbidity. Epidemiol. Infect. 2018, 146, 705–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hofmeister, M.G.; Xing, J.; Foster, M.A.; Augustine, R.J.; Burkholder, C.; Collins, J.; McBee, S.; Thomasson, E.D.; Thoroughman, D.; Weng, M.K.; et al. Hepatitis A person-to-person outbreaks: Epidemiology, morbidity burden, and factors associated with hospitalization—Multiple States, 2016–2019. J. Infect. Dis. 2021, 223, 426–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torner, N.; Broner, S.; Martínez, A.; Godoy, P.; Batalla, J.; Domínguez, A. Hepatitis A outbreaks: The effect of a mass vaccination programme. J. Viral Hepat. 2011, 18, e1–e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guzzetta, G.; Minosse, C.; Pisapia, R.; Giombini, E.; Mammone, A.; Vairo, F.; Garbuglia, A.R.; Scognamiglio, P.; Capobianchi, M.R.; Merler, S.; et al. Household transmission and disease transmissibility of a large HAV outbreak in Lazio, Italy, 2016–2017. Epidemics 2019, 29, 100351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mello, V.M.; Lago, B.V.; Sousa, P.S.F.; Mello, F.C.A.; Souza, C.B.; Pinto, L.C.M.; Ginuino, C.F.; Fernandes, C.A.S.; Aguiar, S.F.; Villar, L.M.; et al. Hepatitis A strain linked to the European outbreaks during gay events between 2016 and 2017, identified in a Brazilian homosexual couple in 2017. Viruses 2019, 11, 281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Werber, D.; Michaelis, K.; Hausner, M.; Sissolak, D.; Wenzel, J.; Bitzegeio, J.; Belting, A.; Sagebiel, D.; Faber, M. Ongoing outbreaks of hepatitis A among men who have sex with men (MSM), Berlin, November 2016 to January 2017—Linked to other German cities and European countries. Eurosurveillance 2017, 22, 30457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ndumbi, P.; Freidl, G.S.; Williams, C.J.; Mårdh, O.; Varela, C.; Avellón, A.; Friesema, I.; Vennema, H.; Beebeejaun, K.; Ngui, S.L.; et al. Hepatitis A outbreak disproportionately affecting men who have sex with men (MSM) in the European Union ad European Economic Area, June 2016 to May 2017. Eurosurveillance 2018, 23, 1700641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hernández Bustabad, A.; Morales Arráez, D.; González, A.; de Vera, A.; Díaz-Flores, F.; Fernández, L.M.; Gómez-Sirvent, J.L.; Avellón, A.; Hernández-Guerra, M. Sexual behaviour and poor hygiene are related to recent hepatitis A virus community outbreaks. Rev. Esp. Enferm. Dig. 2020, 112, 448–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lorenzo Ortega, R.; O’Donnell Cortés, B.; Ortiz González Serna, R.; Gallardo García, V.; López Hernández, B. Changes in Hepatitis A epidemiological pattern in Andalucía: 2007–2017. Rev. Esp. Salud Pública 2018, 92, e1–e7. [Google Scholar]
- Fortea, J.I.; Fernández González, M.; Samaniego Vega, L.; Puente, Á.; Cuadrado, A.; Cabezas, J.; Llerena, S.; Sáez López, A.; Crespo, J.; Fábrega, E. Epidemiology and clinical course of hepatitis A in Cantabria before and after the epidemic outbreak of June 2016. Rev. Clin. Esp. 2020, 220, 400–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nelson, N.P.; Weng, M.K.; Hofmeister, M.G.; Moore, K.L.; Doshani, M.; Kamili, S.; Koneru, A.; Haber, P.; Hagan, L.; Romero, J.R.; et al. Prevention of Hepatitis A Virus Infection in the United States: Recommendations of the Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices, 2020. MMWR Recomm. Rep. 2020, 69, 1–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tortajada, C.; Garcia de Olalla, P.; Diez, E.; Pinto, R.M.; Bosch, A.; Perez, U.; Sanz, M.; Caylà, J.A. Hepatitis A among men who have sex with men in Barcelona, 1989–2010: Insufficient control and need for new approaches. BMC Infect. Dis. 2012, 12, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brower, A.F.; Zelner, J.L.; Eisenberg, M.C.; Kimmins, L.; Ladisky, M.; Collins, J.; Eisenberg, J.N.S. The impact of vaccination efforts on the spatiotemporal patterns of the hepatitis A outbreak in Michigan, 2016–2018. Epidemiology 2020, 31, 628–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wooten, D.A. Forgotten but not gone: Learning from the hepatitis A outbreak and public health response in San Diego. Top. Antivir. Med. 2019, 26, 117–121. [Google Scholar]
- Gallone, M.F.; Desiante, F.; Gallone, M.S.; Barbuti, G.; Tafuri, S.; Germinario, C. Serosurveillance of hepatitis A in a region which adopted the universal mass vaccination. Medicine 2017, 96, e5884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gozlan, Y.; Bar-Or, I.; Rakovsky, A.; Savion, M.; Amitai, Z.; Sheffer, R.; Ceder, N.; Anis, E.; Grotto, I.; Mendelson, E.; et al. Ongoing hepatitis A among men who have sex with men (MSM) linked to outbreaks in Europe in Tel Aviv area, Israel, December 2016–June 2017. Eurosurveillance 2017, 22, 30575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Global disease elimination and eradication as public health strategies. Morb. Mortal. Wkly. Rep. MMWR 1999, 48, 1–211. [Google Scholar]
- Wong, C.K.H.; Liao, Q.; Guo, V.Y.W.; Xin, Y.; Lam, C.L.K. Cost-effectiveness analysis of vaccinations and decision makings on vaccination programmes in Hong Kong: A systematic review. Vaccine 2017, 35, 3153–3161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hankin-Wei, A.; Rein, D.B.; Hernandez-Romieu, A.; Kennedy, M.J.; Bulkow, L.; Rosenberg, E.; Trigg, M.; Nelson, N.P. Cost-effectiveness analysis of catch-up hepatitis A vaccination among unvaccinated/partially-vaccinated children. Vaccine 2016, 34, 4243–4249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramsay, L.C.; Anyiwe, K.; Li, M.; Macdonald, L.; Coyte, P.C.; Sander, B. Economic evaluation of a publicly funded hepatitis A travel vaccination program in Ontario, Canada. Vaccine 2019, 37, 1467–1475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arteaga-Rodríguez, A.; Carrasco-Garrido, P.; López de Andrés, A.; Gil de Miguel, A.; Santos, J.; Jiménez-García, R. Changes in the epidemiology of hepatitis A in Spain (2005–2008): Trends of acute hepatitis A hospitalizations, comorbidities, and costs associated with hospitalization. Eur. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2010, 22, 1284–1289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, K.Y.; Fang, C.T. Public health responses to person-to-person hepatitis A outbreaks. J. Infect. Dis. 2021, 223, 359–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharp, A.; Coles, S.; Pegorie, M.; Harwood, C.; Ngui, S.L.; Welfare, W.; Mandal, S.; Balogun, K.; Gent, M. Vaccination strategies for control of community outbreaks of hepatitis A: A comparison of two outbreaks in England. Vaccine 2019, 37, 1521–1527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stuurman, A.L.; Maranob, C.; Bungea, E.M.; De Moerloozeb, L.; Shouval, D. Impact of universal mass vaccination with monovalent inactivated hepatitis A vaccines—A systematic review. Hum. Vaccines Immunother. 2017, 13, 724–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, S.; Barker, L.; Ly, K.N.; Kilmer, G.; Foster, M.A.; Drobeniuc, J.; Jiles, R.B. Susceptibility to hepatitis A virus infection in the United States, 2007–2016. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2020, 71, e571–e579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L. Hepatitis A vaccination. Hum. Vaccines Immunother. 2020, 16, 1565–1573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Regions with Universal Vaccination Strategy n = 120 n (CIR) | Regions with Risk-Group Vaccination Strategy n = 330 n (CIR) | Rate Ratio (95% CI) | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Outbreak incidence | 16.04 | 20.75 | 0.77 (0.62–0.95) | 0.01 |
| Transmission mode | ||||
| Common source | 14 (1.87) | 25 (1.57) | 1.19 (0.60–2.28) | 0.60 |
| Person-to-person | 92 (12.30) | 290 (18.24) | 0.67 (0.53–0.85) | 0.001 |
| Setting | ||||
| Family/household | 93 (12.43) | 266 (16.74) | 0.74 (0.58–0.94) | 0.01 |
| School | 7 (0.94) | 23 (1.45) | 0.65 (0.26–1.46) | 0.31 |
| Restaurant/facility canteen | 0 (0) | 8 (0.50) | 0.12 (0.01–2.16) | 0.19 |
| Leisure facility/summer camp | 1 (0.13) | 2 (0.13) | 1.06 (0.04–13.97) | 0.96 |
| Community/other/various | 6 (0.80) | 26 (1.64) | 0.49 (0.18–1.14) | 0.10 |
| Other closed facilities | 0 (0) | 3 (0.19) | 0.30 (0.02–5.87) | 0.63 |
| Imported outbreak | 52 (6.95) | 68 (4.28) | 1.62 (1.13–2.33) | 0.01 |
| Regions with Universal Vaccination Strategy n = 120 | Regions with Risk-Group Vaccination Strategy n = 330 | Crude Odds Ratio (95% CI) | p-Value | Adjusted Odds Ratio (95% CI) | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Transmission mode | ||||||
| Common source | 14 (13.2%) | 25 (7.9%) | 1.76 (0.88–3.54) | 0.11 | 1.54 (0.64–3.68) | 0.34 |
| Person-to-person | 92 (86.8%) | 290 (92.1%) | Ref. | Ref. | ||
| Setting | ||||||
| Family/household | 93 (86.9%) | 266 (81.1%) | Ref. | Ref. | ||
| School | 7 (6.5%) | 23 (7.0%) | 0.87 (0.36–2.10) | 0.76 | 1.67 (0.54–5.18) | 0.37 |
| Restaurant/facility canteen | 0 (0%) | 8 (2.4%) | - | - | ||
| Leisure facility/summer camp | 1 (0.9%) | 2 (0.6%) | 1.43 (0.13–15.96) | 0.77 | 2.03 (0.15–27.44) | 0.59 |
| Community/other/various | 6 (5.6%) | 26 (7.9%) | 0.66 (0.26–1.65) | 0.37 | 0.73 (0.23–2.31) | 0.59 |
| Other closed facilities | 0 (0%) | 3 (0.9%) | - | - | ||
| Imported outbreak | ||||||
| Yes | 52 (65.0%) | 68 (28.7%) | 4.62 (2.69–7.91) | <0.001 | 3.88 (2.13–7.09) | <0.001 |
| No | 28 (35.0%) | 169 (71.3%) | Ref. | |||
| No. of exposed people *, median (range) | 5 (2–422) | 5 (2–35240) | 0.24 | 0.77 | ||
| No. of affected people, median (range) | 2 (2–218) | 2 (2–88) | 0.52 | 0.22 | ||
| No. of hospitalized cases †, median (range) | 0 (0–5) | 1 (0–47) | <0.001 | 0.07 | ||
| IG recommended to exposed people | ||||||
| Yes | 21 (31.3%) | 16 (32.7%) | 0.94 (0.43–2.07) | 0.88 | 2.16 (0.67–6.97) | 0.20 |
| No | 46 (68.7%) | 33 (67.3%) | Ref. | Ref. | ||
| Vaccine recommended to exposed people | ||||||
| Yes | 81 (92.0%) | 230 (95.0%) | 0.60 (0.23–1.59) | 0.31 | 0.44 (0.11–1.71) | 0.23 |
| No | 7 (8.0%) | 12 (5.0%) | Ref. | Ref. | ||
| No. of exposed people administered IG ‡, median (range) | 0 (0–68) | 0 (0–80) | 0.79 | 0.76 | ||
| No. of exposed people administered vaccine §, median (range) | 3 (0–482) | 3 (0–672) | 0.36 | 0.11 |
| Regions with Universal Vaccination Strategy n = 120 | Regions with Risk-Group Vaccination Strategy n = 330 | Crude Odds Ratio (95% CI) | p-Value | Adjusted Odds Ratio (95% CI) | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| COMMON SOURCE OUTBREAKS | ||||||
| Setting | ||||||
| Family/household | 12 (92.3%) | 20 (87.0%) | - | - | ||
| Restaurant/facility canteen | 0 (0%) | 3 (13.0%) | - | - | ||
| Community/other/various | 1 (7.7%) | 0 (0%) | - | - | ||
| Imported outbreak | 7 (53.8%) | 10 (47.6%) | 1.28 (0.32–5.13) | 0.72 | 1.67 (0.33–8.47) | 0.53 |
| No. of exposed people, median (range) | 5 (2–38) | 5 (2–400) | 0.92 | 0.82 | ||
| No. of affected people, median (range) | 2 (2–38) | 2 (2–31) | 0.59 | 0.49 | ||
| No. of hospitalized cases, median (range) | 0 (0–5) | 1 (0–16) | 0.38 | 0.65 | ||
| PERSON-TO-PERSON TRANSMISSION OUTBREAKS | ||||||
| Setting | ||||||
| Family/household | 71 (86.6%) | 233 (80.3%) | Ref. | Ref. | ||
| School | 6 (7.3%) | 22 (7.6%) | 0.90 (0.35–2.29) | 0.82 | 1.69 (0.65–6.59) | 0.22 |
| Restaurant/facility canteen | 0 (0%) | 5 (1.7%) | - | - | ||
| Leisure facility/summer camp | 1 (1.2%) | 2 (0.7%) | 1.64 (0.15–18.36) | 0.69 | 2.39 (0.18–32.34) | 0.51 |
| Community/other/various | 4 (4.9%) | 25 (8.6%) | 0.53 (0.18–1.56) | 0.25 | 0.44 (0.10–2.04) | 0.29 |
| Other closed facilities | 0 (0%) | 3 (1.0%) | - | - | ||
| Imported outbreak | 36 (62.1%) | 54 (26.2%) | 4.61 (2.49–8.52) | <0.001 | 4.38 (2.29–8.35) | <0.001 |
| No. of exposed people, median (range) | 5 (2–422) | 5 (2–473) | 0.44 | 0.46 | ||
| No. of affected people, median (range) | 2 (2–218) | 2 (2–88) | 0.58 | 0.71 | ||
| No. of hospitalized people, median (range) | 0 (0–3) | 1 (0–47) | <0.001 | 0.03 | ||
| Regions with Universal Vaccination Strategy n = 120 | Regions with Risk-Group Vaccination Strategy n = 330 | Crude Odds Ratio (95% CI) | p-Value | Adjusted Odds Ratio (95% CI) | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age | ||||||
| 0–14 years | 68 (58.6%) | 86 (47.5%) | Ref. | Ref. | ||
| 15–44 years | 36 (31.0%) | 78 (43.1%) | 0.58 (0.35–0.97) | 0.04 | 0.54 (0.32–0.92) | 0.02 |
| ≥45 years | 12 (10.3%) | 17 (9.4%) | 0.89 (0.40–2.00) | 0.78 | 0.83 (0.36–1.89) | 0.65 |
| Sex | ||||||
| Male | 77 (67.5%) | 138 (72.3%) | Ref. | Ref. | ||
| Female | 37 (32.5%) | 53 (27.7%) | 1.25 (0.76–2.07) | 0.38 | 1.13 (0.66–1.95) | 0.65 |
| Born in Spain | ||||||
| Yes | 36 (65.5%) | 51 (67.1%) | 0.93 (0.45–1.93) | 0.84 | 1.10 (0.48–2.54) | 0.81 |
| No | 19 (34.5%) | 25 (32.9%) | Ref. | Ref. | ||
| Occupation | ||||||
| Food handler | 4 (5.1%) | 6 (6.7%) | Ref. | Ref. | ||
| Healthcare worker | 0 (0%) | 2 (2.2%) | - | - | ||
| Nursery/school/high school worker | 3 (3.8%) | 5 (5.6%) | 0.90 (0.13–6.08) | 0.91 | 1.02 (0.14–7.56) | 0.99 |
| School/Student | 70 (88.6%) | 77 (85.6%) | 1.36 (0.37–5.03) | 0.64 | 1.34 (0.34–5.24) | 0.68 |
| Other * | 2 (2.5%) | 0 (0%) | - | - | ||
| Hepatitis A vaccinated | ||||||
| Yes | 0 (0%) | 1 (0.9%) | - | - | ||
| No | 84 (100%) | 132 (99.2%) | Ref. | Ref. | ||
| Men who have sex with men † | ||||||
| Yes | 5 (23.8%) | 27 (67.5%) | 0.15 (0.04–0.50) | 0.002 | 0.23 (0.07–0.82) | 0.02 |
| No | 16 (76.2%) | 13 (32.5%) | Ref. | Ref. | ||
| Drug user ‡ | ||||||
| Yes | 1 (3.0%) | 0 (0%) | - | - | ||
| No | 32 (97.0%) | 12 (100%) | Ref. | Ref. |
| Regions with Universal Vaccination Strategy n = 120 | Regions with Risk-Group Vaccination Strategy n = 330 | Crude Odds Ratio (95% CI) | p-Value | Adjusted Odds Ratio (95% CI) | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| COMMON SOURCE | ||||||
| Age | ||||||
| 0–14 years | 7 (53.8%) | 10 (58.8%) | Ref. | Ref. | ||
| 15–44 years | 4 (30.8%) | 6 (35.3%) | 0.95 (0.19–4.68) | 0.95 | 0.96 (0.19–4.80) | 0.96 |
| ≥45 years | 2 (15.4%) | 1 (5.9%) | 2.86 (0.21–37.99) | 0.43 | 2.86 (0.21–38.04) | 0.43 |
| Sex | ||||||
| Male | 9 (69.2%) | 12 (70.6%) | Ref. | Ref. | ||
| Female | 4 (30.8%) | 5 (29.4%) | 1.07 (0.22–5.14) | 0.94 | 0.98 (0.20–4.94) | 0.98 |
| Born in Spain | 7 (87.5%) | 8 (53.3%) | 6.12 (0.60–62.82) | 0.13 | 6.27 (0.47–82.57) | 0.16 |
| Occupation | ||||||
| Food handler | 1 (11.1%) | 0 (0%) | Ref. | Ref. | ||
| School/Student | 7 (11.1%) | 3 (100%) | - | - | ||
| Others * | 1 (77.8%) | 0 (0%) | - | - | ||
| Hepatitis A vaccinated | 0 (0%) | 0 (0%) | - | - | ||
| Men who have sex with men† | 2 (100%) | 0 (0%) | - | - | ||
| Drug user ‡ | 0 (0%) | 0 (0%) | - | - | ||
| PERSON-TO-PERSON TRANSMISSION OUTBREAKS | ||||||
| Age | ||||||
| 0–14 years | 52 (56.5%) | 74 (46.5%) | Ref. | Ref. | ||
| 15–44 years | 31 (33.7%) | 69 (43.4%) | 0.64 (0.37–1.11) | 0.11 | 0.57 (0.32–1.01) | 0.05 |
| ≥45 years | 9 (9.8%) | 16 (10.1%) | 0.80 (0.33–1.95) | 0.62 | 0.73 (0.29–1.82) | 0.50 |
| Sex | ||||||
| Male | 61 (67.0%) | 124 (72.5%) | Ref. | Ref. | ||
| Female | 30 (33.0%) | 47 (27.5%) | 1.30 (0.75–2.25) | 0.35 | 1.18 (0.65–2.13) | 0.59 |
| Born in Spain | 26 (63.4%) | 43 (71.7%) | 0.68 (0.29–1.60) | 0.38 | 0.75 (0.30–1.90) | 0.54 |
| Occupation | ||||||
| Food handler | 2 (3.4%) | 6 (7.1%) | Ref. | Ref. | ||
| Healthcare worker | 0 (0%) | 2 (2.4%) | - | - | ||
| Nursery/school/high school worker | 3 (5.1%) | 5 (5.9%) | 1.80 (0.21–15.41) | 0.59 | 2.08 (0.22–19.59) | 0.52 |
| School/Student | 53 (89.8%) | 72 (84.7%) | 2.21 (0.43–11.37) | 0.34 | 2.27 (0.42–12.31) | 0.34 |
| Other § | 1 (1.7%) | 0 (0%) | - | - | ||
| Hepatitis A vaccinated | 0 (0%) | 1 (0.9%) | - | - | ||
| Men who have sex with men† | 3 (16.7%) | 27 (71.1%) | 0.08 (0.02–0.34) | 0.001 | 0.13 (0.03–0.55) | 0.006 |
| Drug user ‡ | 1 (3.7%) | 0 (0%) | - | - | ||
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Domínguez, A.; Varela, C.; Soldevila, N.; Izquierdo, C.; Guerrero, M.; Peñuelas, M.; Martínez, A.; Godoy, P.; Borràs, E.; Rius, C.; et al. Hepatitis A Outbreak Characteristics: A Comparison of Regions with Different Vaccination Strategies, Spain 2010–2018. Vaccines 2021, 9, 1214. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines9111214
Domínguez A, Varela C, Soldevila N, Izquierdo C, Guerrero M, Peñuelas M, Martínez A, Godoy P, Borràs E, Rius C, et al. Hepatitis A Outbreak Characteristics: A Comparison of Regions with Different Vaccination Strategies, Spain 2010–2018. Vaccines. 2021; 9(11):1214. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines9111214
Chicago/Turabian StyleDomínguez, Angela, Carmen Varela, Núria Soldevila, Conchita Izquierdo, María Guerrero, Marina Peñuelas, Ana Martínez, Pere Godoy, Eva Borràs, Cristina Rius, and et al. 2021. "Hepatitis A Outbreak Characteristics: A Comparison of Regions with Different Vaccination Strategies, Spain 2010–2018" Vaccines 9, no. 11: 1214. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines9111214
APA StyleDomínguez, A., Varela, C., Soldevila, N., Izquierdo, C., Guerrero, M., Peñuelas, M., Martínez, A., Godoy, P., Borràs, E., Rius, C., Torner, N., Avellón, A. M., Castilla, J., & PREVICET Working Group on Viral Hepatitis. (2021). Hepatitis A Outbreak Characteristics: A Comparison of Regions with Different Vaccination Strategies, Spain 2010–2018. Vaccines, 9(11), 1214. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines9111214








