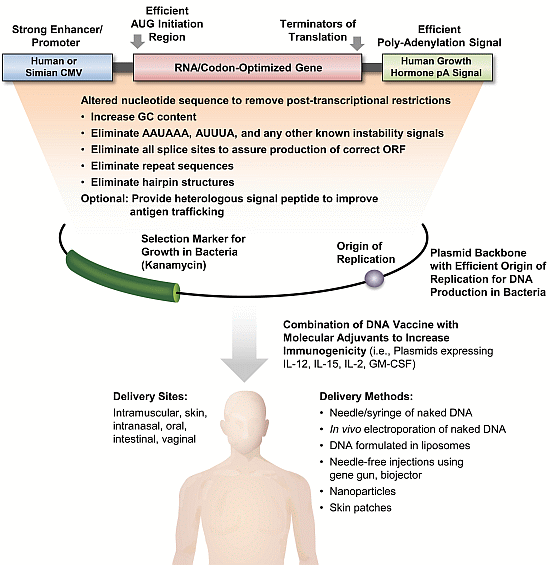
HIV DNA Vaccine: Stepwise Improvements Make a Difference
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Regulated HIV gag and env Expression
3. Method of RNA/Codon Optimization to Circumvent the Poor Expression of HIV gag/pol and env
4. Methods to Improve HIV/SIV DNA Vaccine Regimen
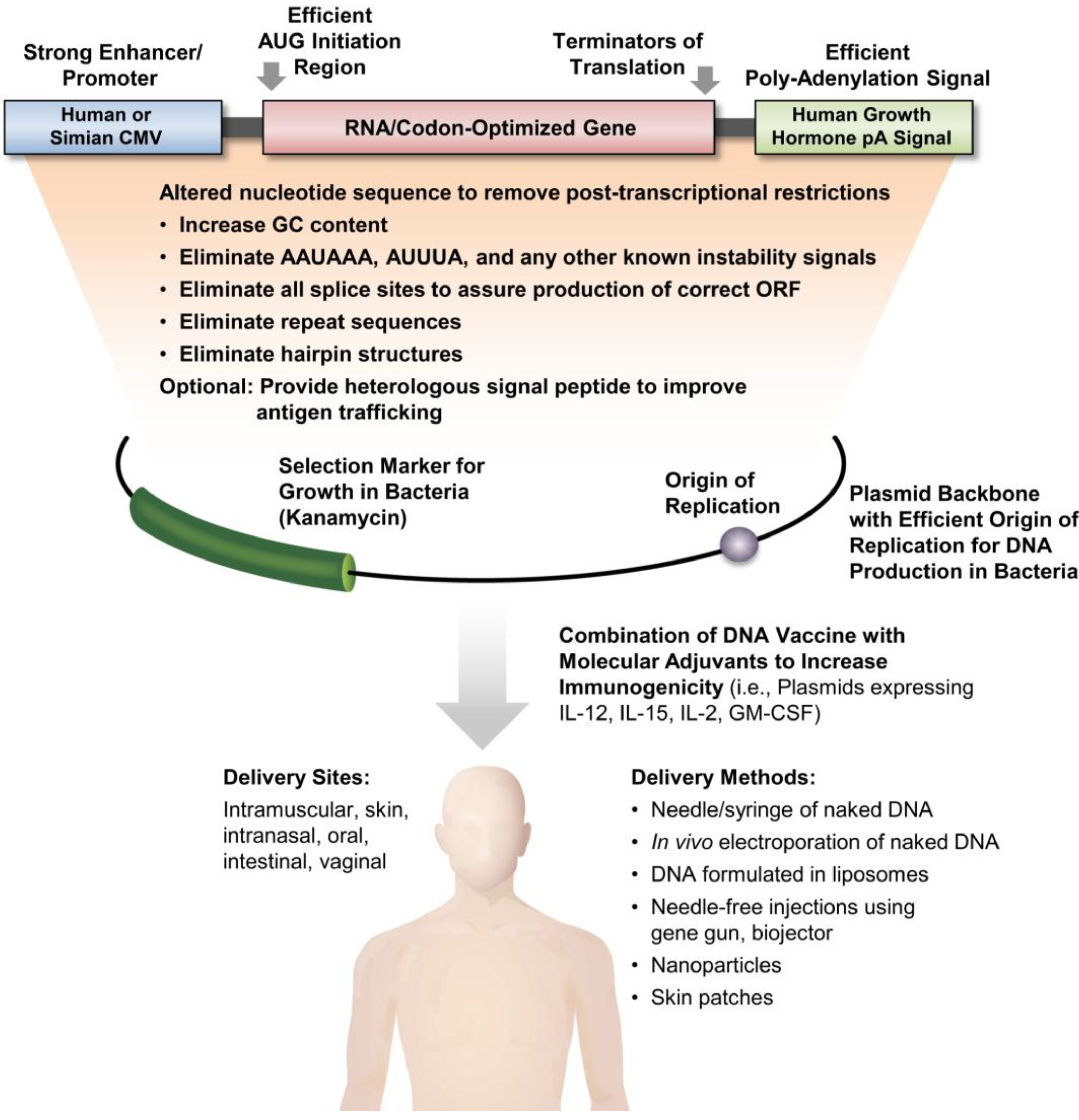
5. HIV/SIV DNA Vaccine Provide Persistent Immunity
6. HIV-1 Diversity and DNA Vaccine
7. Optimizing Both Arms of the Immune System by DNA & Protein Co-immunization Strategy
8. Efficacy of DNA Vaccine in the Macaque Model
9. Perspective and Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Berman, P.W. Development of bivalent rgp120 vaccines to prevent HIV type 1 infection. AIDS Res. Hum. Retroviruses 1998, 14, S277–S289. [Google Scholar]
- Francis, D.P.; Gregory, T.; McElrath, M.J.; Belshe, R.B.; Gorse, G.J.; Migasena, S.; Kitayaporn, D.; Pitisuttitham, P.; Matthews, T.; Schwartz, D.H.; et al. Advancing AIDSVAX to phase 3. Safety, immunogenicity, and plans for phase 3. AIDS Res. Hum. Retroviruses 1998, 14, S325–S331. [Google Scholar]
- Pitisuttithum, P.; Gilbert, P.; Gurwith, M.; Heyward, W.; Martin, M.; van Griensven, F.; Hu, D.; Tappero, J.W.; Choopanya, K. Randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled efficacy trial of a bivalent recombinant glycoprotein 120 HIV-1 vaccine among injection drug users in Bangkok, Thailand. J. Infect. Dis. 2006, 194, 1661–1671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flynn, N.M.; Forthal, D.N.; Harro, C.D.; Judson, F.N.; Mayer, K.H.; Para, M.F. Placebo-controlled phase 3 trial of a recombinant glycoprotein 120 vaccine to prevent HIV-1 infection. J. Infect. Dis. 2005, 191, 654–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McElrath, M.J.; de Rosa, S.C.; Moodie, Z.; Dubey, S.; Kierstead, L.; Janes, H.; Defawe, O.D.; Carter, D.K.; Hural, J.; Akondy, R.; et al. HIV-1 vaccine-induced immunity in the test-of-concept step study: A case-cohort analysis. Lancet 2008, 372, 1894–1905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rolland, M.; Tovanabutra, S.; deCamp, A.C.; Frahm, N.; Gilbert, P.B.; Sanders-Buell, E.; Heath, L.; Magaret, C.A.; Bose, M.; Bradfield, A.; et al. Genetic impact of vaccination on breakthrough HIV-1 sequences from the STEP trial. Nat. Med. 2011, 17, 366–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buchbinder, S.P.; Mehrotra, D.V.; Duerr, A.; Fitzgerald, D.W.; Mogg, R.; Li, D.; Gilbert, P.B.; Lama, J.R.; Marmor, M.; del Rio, C.; et al. Efficacy assessment of a cell-mediated immunity HIV-1 vaccine (the Step Study): A double-blind, randomised, placebo-controlled, test-of-concept trial. Lancet 2008, 372, 1881–1893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hammer, S.M.; Sobieszczyk, M.E.; Janes, H.; Karuna, S.T.; Mulligan, M.J.; Grove, D.; Koblin, B.A.; Buchbinder, S.P.; Keefer, M.C.; Tomaras, G.D.; et al. Efficacy trial of a DNA/rAd5 HIV-1 preventive vaccine. N. Engl. J. Med. 2013, 369, 2083–2092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rerks-Ngarm, S.; Pitisuttithum, P.; Nitayaphan, S.; Kaewkungwal, J.; Chiu, J.; Paris, R.; Premsri, N.; Namwat, C.; de Souza, M.; Adams, E.; et al. Vaccination with ALVAC and AIDSVAX to prevent HIV-1 infection in Thailand. N. Engl. J. Med. 2009, 361, 2209–2220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rolland, M.; Edlefsen, P.T.; Larsen, B.B.; Tovanabutra, S.; Sanders-Buell, E.; Hertz, T.; deCamp, A.C.; Carrico, C.; Menis, S.; Magaret, C.A.; et al. Increased HIV-1 vaccine efficacy against viruses with genetic signatures in Env V2. Nature 2012, 490, 417–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haynes, B.F.; Gilbert, P.B.; McElrath, M.J.; Zolla-Pazner, S.; Tomaras, G.D.; Alam, S.M.; Evans, D.T.; Montefiori, D.C.; Karnasuta, C.; Sutthent, R.; et al. Immune-correlates analysis of an HIV-1 vaccine efficacy trial. N. Engl. J. Med. 2012, 366, 1275–1286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gottardo, R.; Bailer, R.T.; Korber, B.T.; Gnanakaran, S.; Phillips, J.; Shen, X.; Tomaras, G.D.; Turk, E.; Imholte, G.; Eckler, L.; et al. Plasma IgG to linear epitopes in the V2 and V3 regions of HIV-1 gp120 correlate with a reduced risk of infection in the RV144 vaccine efficacy trial. PLoS One 2013, 8, e75665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zolla-Pazner, S.; deCamp, A.C.; Cardozo, T.; Karasavvas, N.; Gottardo, R.; Williams, C.; Morris, D.E.; Tomaras, G.; Rao, M.; Billings, E.; et al. Analysis of V2 antibody responses induced in vaccinees in the ALVAC/AIDSVAX HIV-1 vaccine efficacy trial. PLoS One 2013, 8, e53629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karasavvas, N.; Billings, E.; Rao, M.; Williams, C.; Zolla-Pazner, S.; Bailer, R.T.; Koup, R.A.; Madnote, S.; Arworn, D.; Shen, X.; et al. The Thai phase III HIV type 1 vaccine trial (RV144) regimen induces antibodies that target conserved regions within the V2 loop of gp120. AIDS Res. Hum. Retroviruses 2012, 28, 1444–1457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferraro, B.; Morrow, M.P.; Hutnick, N.A.; Shin, T.H.; Lucke, C.E.; Weiner, D.B. Clinical applications of DNA vaccines: Current progress. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2011, 53, 296–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salonius, K.; Simard, N.; Harland, R.; Ulmer, J.B. The road to licensure of a DNA vaccine. Curr. Opin. Investig. Drugs 2007, 8, 635–641. [Google Scholar]
- Ulmer, J.B.; Wahren, B.; Liu, M.A. DNA vaccines for HIV/AIDS. Curr. Opin. HIV AIDS 2006, 1, 309–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bunning, M.L.; Bowen, R.A.; Cropp, B.; Sullivan, K.; Davis, B.; Komar, N.; Godsey, M.; Baker, D.; Hettler, D.; Holmes, D.; et al. Experimental infection of horses with West Nile virus and their potential to infect mosquitoes and serve as amplifying hosts. Ann. NY Acad. Sci. 2001, 951, 338–339. [Google Scholar]
- Davis, B.S.; Chang, G.J.; Cropp, B.; Roehrig, J.T.; Martin, D.A.; Mitchell, C.J.; Bowen, R.; Bunning, M.L. West Nile virus recombinant DNA vaccine protects mouse and horse from virus challenge and expresses in vitro a noninfectious recombinant antigen that can be used in enzyme-linked immunosorbent assays. J. Virol. 2001, 75, 4040–4047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergman, P.J.; McKnight, J.; Novosad, A.; Charney, S.; Farrelly, J.; Craft, D.; Wulderk, M.; Jeffers, Y.; Sadelain, M.; Hohenhaus, A.E.; et al. Long-term survival of dogs with advanced malignant melanoma after DNA vaccination with xenogeneic human tyrosinase: A phase I trial. Clin. Cancer Res. 2003, 9, 1284–1290. [Google Scholar]
- Traxler, G.S.; Anderson, E.; LaPatra, S.E.; Richard, J.; Shewmaker, B.; Kurath, G. Naked DNA vaccination of Atlantic salmon Salmo salar against IHNV. Dis. Aquat. Organ. 1999, 38, 183–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corbeil, S.; Lapatra, S.E.; Anderson, E.D.; Jones, J.; Vincent, B.; Hsu, Y.L.; Kurath, G. Evaluation of the protective immunogenicity of the N, P, M, NV and G proteins of infectious hematopoietic necrosis virus in rainbow trout oncorhynchus mykiss using DNA vaccines. Dis. Aquat. Organ. 1999, 39, 29–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garver, K.A.; LaPatra, S.E.; Kurath, G. Efficacy of an infectious hematopoietic necrosis (IHN) virus DNA vaccine in Chinook Oncorhynchus tshawytscha and sockeye O. nerka salmon. Dis. Aquat. Organ. 2005, 64, 13–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, V.; Jalah, R.; Kulkarni, V.; Valentin, A.; Rosati, M.; Alicea, C.; von Gegerfelt, A.; Huang, W.; Guan, Y.; Keele, B.; et al. DNA and virus particle vaccination protects against acquisition and confers control of viremia upon heterologous SIV challenge. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 2975–2980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosati, M.; Bergamaschi, C.; Valentin, A.; Kulkarni, V.; Jalah, R.; Patel, V.; von Gegerfelt, A.S.; Montefiori, D.C.; Venzon, D.; Khan, A.S.; et al. DNA vaccination in rhesus macaques induces potent immune responses and decreases acute and chronic viremia after SIVmac251 challenge. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 15831–15836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosati, M.; von Gegerfelt, A.; Roth, P.; Alicea, C.; Valentin, A.; Robert-Guroff, M.; Venzon, D.; Montefiori, D.C.; Markham, P.; Felber, B.K.; et al. DNA vaccines expressing different forms of simian immunodeficiency virus antigens decrease viremia upon SIVmac251 challenge. J. Virol. 2005, 79, 8480–8492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cristillo, A.D.; Galmin, L.; Restrepo, S.; Hudacik, L.; Suschak, J.; Lewis, B.; Draghia-Akli, R.; Aziz, N.; Weiss, D.; Markham, P.; et al. HIV-1 Env vaccine comprised of electroporated DNA and protein co-administered with Talabostat. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2008, 370, 22–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, V.; Valentin, A.; Kulkarni, V.; Rosati, M.; Bergamaschi, C.; Jalah, R.; Alicea, C.; Minang, J.T.; Trivett, M.T.; Ohlen, C.; et al. Long-lasting humoral and cellular immune responses and mucosal dissemination after intramuscular DNA immunization. Vaccine 2010, 28, 4827–4836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jalah, R.; Kulkarni, V.; Patel, V.; Rosati, M.; Alicea, C.; Bear, J.; Yu, L.; Guan, Y.; Shen, X.; Tomaras, G.D.; et al. DNA and protein co-immunization improves the magnitude and longevity of humoral immune responses in rhesus macaques. PLoS One 2014, 9, e91550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Felber, B.K.; Zolotukhin, A.S.; Pavlakis, G.N. Posttranscriptional control of HIV-1 and other retroviruses and its practical applications. Adv. Pharmacol. 2007, 55, 161–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cochrane, A.W.; McNally, M.T.; Mouland, A.J. The retrovirus RNA trafficking granule: From birth to maturity. Retrovirology 2006, 3, e18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.Y.; Liu, X.; Boris-Lawrie, K.; Sharma, A.; Jeang, K.T. Cellular RNA helicases and HIV-1: Insights from genome-wide, proteomic, and molecular studies. Virus Res. 2013, 171, 357–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yedavalli, V.S.; Jeang, K.T. Rev-ing up post-transcriptional HIV-1 RNA expression. RNA Biol. 2011, 8, 195–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Felber, B.K.; Hadzopoulou-Cladaras, M.; Cladaras, C.; Copeland, T.; Pavlakis, G.N. rev Protein of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 affects the stability and transport of the viral mRNA. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1989, 86, 1495–1499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sodroski, J.; Goh, W.C.; Rosen, C.; Dayton, A.; Terwilliger, E.; Haseltine, W. A second post-transcriptional trans-activator gene required for HTLV-III replication. Nature 1986, 321, 412–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feinberg, M.B.; Jarrett, R.F.; Aldovini, A.; Gallo, R.C.; Wong-Staal, F. HTLV-III expression and production involve complex regulation at the levels of splicing and translation of viral RNA. Cell 1986, 46, 807–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hadzopoulou-Cladaras, M.; Felber, B.K.; Cladaras, C.; Athanassopoulos, A.; Tse, A.; Pavlakis, G.N. The rev (trs/art) protein of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 affects viral mRNA and protein expression via a cis-acting sequence in the env region. J. Virol. 1989, 63, 1265–1274. [Google Scholar]
- Malim, M.H.; Hauber, J.; Le, S.Y.; Maizel, J.V.; Cullen, B.R. The HIV-1 rev trans-activator acts through a structured target sequence to activate nuclear export of unspliced viral mRNA. Nature 1989, 338, 254–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneider, R.; Campbell, M.; Nasioulas, G.; Felber, B.K.; Pavlakis, G.N. Inactivation of the human immunodeficiency virus type 1 inhibitory elements allows Rev-independent expression of Gag and Gag/protease and particle formation. J. Virol. 1997, 71, 4892–4903. [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz, S.; Campbell, M.; Nasioulas, G.; Harrison, J.; Felber, B.K.; Pavlakis, G.N. Mutational inactivation of an inhibitory sequence in human immunodeficiency virus type 1 results in Rev-independent gag expression. J. Virol. 1992, 66, 7176–7182. [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz, S.; Felber, B.K.; Pavlakis, G.N. Distinct RNA sequences in the gag region of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 decrease RNA stability and inhibit expression in the absence of Rev protein. J. Virol. 1992, 66, 150–159. [Google Scholar]
- Nasioulas, G.; Zolotukhin, A.S.; Tabernero, C.; Solomin, L.; Cunningham, C.P.; Pavlakis, G.N.; Felber, B.K. Elements distinct from human immunodeficiency virus type 1 splice sites are responsible for the Rev dependence of env mRNA. J. Virol. 1994, 68, 2986–2993. [Google Scholar]
- Cochrane, A.W.; Jones, K.S.; Beidas, S.; Dillon, P.J.; Skalka, A.M.; Rosen, C.A. Identification and characterization of intragenic sequences which repress human immunodeficiency virus structural gene expression. J. Virol. 1991, 65, 5305–5313. [Google Scholar]
- Rosen, C.A.; Terwilliger, E.; Dayton, A.; Sodroski, J.G.; Haseltine, W.A. Intragenic cis-acting art gene-responsive sequences of the human immunodeficiency virus. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1988, 85, 2071–2075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wallace, A.; West, K.; Rothman, A.L.; Ennis, F.A.; Lu, S.; Wang, S. Post-translational intracellular trafficking determines the type of immune response elicited by DNA vaccines expressing Gag antigen of Human Immunodeficiency Virus Type 1 (HIV-1). Hum. Vaccin Immunother. 2013, 9, 2095–2102. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, S.; Farfan-Arribas, D.J.; Shen, S.; Chou, T.H.; Hirsch, A.; He, F.; Lu, S. Relative contributions of codon usage, promoter efficiency and leader sequence to the antigen expression and immunogenicity of HIV-1 Env DNA vaccine. Vaccine 2006, 24, 4531–4540. [Google Scholar]
- Kulkarni, V.; Rosati, M.; Valentin, A.; Ganneru, B.; Singh, A.K.; Yan, J.; Rolland, M.; Alicea, C.; Beach, R.K.; Zhang, G.M.; et al. HIV-1 p24gag derived conserved element DNA vaccine increases the breadth of immune response in mice. PLoS One 2013, 8, e60245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Yan, J.; Muthumani, K.; Ramanathan, M.P.; Yoon, H.; Pavlakis, G.N.; Felber, B.K.; Sidhu, M.; Boyer, J.D.; Weiner, D.B. Immunogenicity testing of a novel engineered HIV-1 envelope gp140 DNA vaccine construct. DNA Cell Biol. 2006, 25, 383–392. [Google Scholar]
- Kulkarni, V.; Jalah, R.; Ganneru, B.; Bergamaschi, C.; Alicea, C.; von Gegerfelt, A.; Patel, V.; Zhang, G.M.; Chowdhury, B.; Broderick, K.E.; et al. Comparison of immune responses generated by optimized DNA vaccination against SIV antigens in mice and macaques. Vaccine 2011, 29, 6742–6754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valentin, A.; Chikhlikar, P.; Patel, V.; Rosati, M.; Maciel, M.; Chang, K.H.; Silvera, P.; Felber, B.K.; Pavlakis, G.N.; August, J.T.; et al. Comparison of DNA vaccines producing HIV-1 Gag and LAMP/Gag chimera in rhesus macaques reveals antigen-specific T-cell responses with distinct phenotypes. Vaccine 2009, 27, 4840–4849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chikhlikar, P.; de Arruda, L.B.; Maciel, M.; Silvera, P.; Lewis, M.G.; August, J.T.; Marques, E.T. DNA encoding an HIV-1 Gag/human lysosome-associated membrane protein-1 chimera elicits a broad cellular and humoral immune response in rhesus macaques. PLoS One 2006, 1, e135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benlahrech, A.; Meiser, A.; Herath, S.; Papagatsias, T.; Athanasopoulos, T.; Li, F.; Self, S.; Bachy, V.; Hervouet, C.; Logan, K.; et al. Fragmentation of SIV-gag vaccine induces broader T cell responses. PLoS One 2012, 7, e48038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stack, J.H.; Whitney, M.; Rodems, S.M.; Pollok, B.A. A ubiquitin-based tagging system for controlled modulation of protein stability. Nat. Biotechnol. 2000, 18, 1298–1302. [Google Scholar]
- Tobery, T.W.; Siliciano, R.F. Targeting of HIV-1 antigens for rapid intracellular degradation enhances cytotoxic T lymphocyte (CTL) recognition and the induction of de novo CTL responses in vivo after immunization. J. Exp. Med. 1997, 185, 909–920. [Google Scholar]
- Mathiesen, I. Electropermeabilization of skeletal muscle enhances gene transfer in vivo. Gene Ther. 1999, 6, 508–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heller, L.; Pottinger, C.; Jaroszeski, M.J.; Gilbert, R.; Heller, R. In vivo electroporation of plasmidsencoding GM-CSF or interleukin-2 into existing B16 melanomas combined with electrochemotherapy induces long-term antitumour immunity. Melanoma Res. 2000, 10, 577–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Widera, G.; Austin, M.; Rabussay, D.; Goldbeck, C.; Barnett, S.W.; Chen, M.; Leung, L.; Otten, G.R.; Thudium, K.; Selby, M.J.; et al. Increased DNA vaccine delivery and immunogenicity by electroporation in vivo. J. Immunol. 2000, 164, 4635–4640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selby, M.; Goldbeck, C.; Pertile, T.; Walsh, R.; Ulmer, J. Enhancement of DNA vaccine potency by electroporation in vivo. J. Biotechnol. 2000, 83, 147–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otten, G.; Schaefer, M.; Doe, B.; Liu, H.; Srivastava, I.; Megede, J.Z.; O’Hagan, D.; Donnelly, J.; Widera, G.; Rabussay, D.; et al. Enhancement of DNA vaccine potency in rhesus macaques by electroporation. Vaccine 2004, 22, 2489–2493. [Google Scholar]
- Hirao, L.A.; Wu, L.; Khan, A.S.; Hokey, D.A.; Yan, J.; Dai, A.; Betts, M.R.; Draghia-Akli, R.; Weiner, D.B. Combined effects of IL-12 and electroporation enhances the potency of DNA vaccination in macaques. Vaccine 2008, 26, 3112–3120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosati, M.; Valentin, A.; Jalah, R.; Patel, V.; von Gegerfelt, A.; Bergamaschi, C.; Alicea, C.; Weiss, D.; Treece, J.; Pal, R.; et al. Increased immune responses in rhesus macaques by DNA vaccination combined with electroporation. Vaccine 2008, 26, 5223–5229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sardesai, N.Y.; Weiner, D.B. Electroporation delivery of DNA vaccines: Prospects for success. Curr. Opin. Immunol. 2011, 23, 421–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hutnick, N.A.; Myles, D.J.; Bian, C.B.; Muthumani, K.; Weiner, D.B. Selected approaches for increasing HIV DNA vaccine immunogenicity in vivo. Curr. Opin. Virol. 2012, 1, 233–240. [Google Scholar]
- Bodles-Brakhop, A.M.; Heller, R.; Draghia-Akli, R. Electroporation for the delivery of DNA-basedvaccines and immunotherapeutics: Current clinical developments. Mol. Ther. 2009, 17, 585–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flingai, S.; Czerwonko, M.; Goodman, J.; Kudchodkar, S.B.; Muthumani, K.; Weiner, D.B. Synthetic DNA vaccines: Improved vaccine potency by electroporation and co-delivered genetic adjuvants. Front. Immunol. 2013, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hallengard, D.; Brave, A.; Isaguliants, M.; Blomberg, P.; Enger, J.; Stout, R.; King, A.; Wahren, B. A combination of intradermal jet-injection and electroporation overcomes in vivo dose restriction of DNA vaccines. Genet. Vaccines Ther. 2012, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roos, A.K.; Eriksson, F.; Timmons, J.A.; Gerhardt, J.; Nyman, U.; Gudmundsdotter, L.; Brave, A.; Wahren, B.; Pisa, P. Skin electroporation: Effects on transgene expression, DNA persistence and local tissue environment. PLoS One 2009, 4, e7226. [Google Scholar]
- Hooper, J.W.; Golden, J.W.; Ferro, A.M.; King, A.D. Smallpox DNA vaccine delivered by novel skin electroporation device protects mice against intranasal poxvirus challenge. Vaccine 2007, 25, 1814–1823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brave, A.; Gudmundsdotter, L.; Sandstrom, E.; Haller, B.K.; Hallengard, D.; Maltais, A.K.; King, A.D.; Stout, R.R.; Blomberg, P.; Hoglund, U.; et al. Biodistribution, persistence and lack of integration of a multigene HIV vaccine delivered by needle-free intradermal injection and electroporation. Vaccine 2010, 28, 8203–8209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hutnick, N.A.; Myles, D.J.; Ferraro, B.; Lucke, C.; Lin, F.; Yan, J.; Broderick, K.E.; Khan, A.S.; Sardesai, N.Y.; Weiner, D.B. Intradermal DNA vaccination enhanced by low-current electroporation improves antigen expression and induces robust cellular and humoral immune responses. Hum. Gene Ther. 2012, 23, 943–950. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, F.; Shen, X.; Kichaev, G.; Mendoza, J.M.; Yang, M.; Armendi, P.; Yan, J.; Kobinger, G.P.; Bello, A.; Khan, A.S.; et al. Optimization of electroporation-enhanced intradermal delivery of DNAvaccine using a minimally invasive surface device. Hum. Gene Ther. Methods 2012, 23, 157–168. [Google Scholar]
- Kichaev, G.; Mendoza, J.M.; Amante, D.; Smith, T.R.; McCoy, J.R.; Sardesai, N.Y.; Broderick, K.E. Electroporation mediated DNA vaccination directly to a mucosal surface results in improved immune responses. Hum. Vaccin Immunother. 2013, 9, 2041–2048. [Google Scholar]
- Heller, R.; Cruz, Y.; Heller, L.C.; Gilbert, R.A.; Jaroszeski, M.J. Electrically mediated delivery of plasmid DNA to the skin, using a multielectrode array. Hum. Gene Ther. 2010, 21, 357–362. [Google Scholar]
- Lori, F. DermaVir: A plasmid DNA-based nanomedicine therapeutic vaccine for the treatment of HIV/AIDS. Expert Rev. Vaccines 2011, 10, 1371–1384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sullivan, S.M.; Doukas, J.; Hartikka, J.; Smith, L.; Rolland, A. Vaxfectin: A versatile adjuvant for plasmid DNA- and protein-based vaccines. Expert Opin. Drug Deliv. 2010, 7, 1433–1446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulkarni, V.; Rosati, M.; Valentin, A.; Jalah, R.; Alicea, C.; Yu, L.; Guan, Y.; Shen, X.; Tomaras, G.D.; LaBranche, C.; et al. Vaccination with Vaxfectin® adjuvanted SIV DNA induces long-lasting humoral immune responses able to reduce SIVmac251 Viremia. Hum. Vaccin Immunother. 2013, 9, 2069–2080. [Google Scholar]
- Templeton, N.S.; Lasic, D.D.; Frederik, P.M.; Strey, H.H.; Roberts, D.D.; Pavlakis, G.N. Improved DNA: Liposome complexes for increased systemic delivery and gene expression. Nat. Biotechnol. 1997, 15, 647–652. [Google Scholar]
- Fuller, D.H.; Simpson, L.; Cole, K.S.; Clements, J.E.; Panicali, D.L.; Montelaro, R.C.; Murphey-Corb, M.; Haynes, J.R. Gene gun-based nucleic acid immunization alone or in combination with recombinant vaccinia vectors suppresses virus burden in rhesus macaques challenged with a heterologous SIV. Immunol. Cell Biol. 1997, 75, 389–396. [Google Scholar]
- Aguiar, J.C.; Hedstrom, R.C.; Rogers, W.O.; Charoenvit, Y.; Sacci, J.B., Jr.; Lanar, D.E.; Majam, V.F.; Stout, R.R.; Hoffman, S.L. Enhancement of the immune response in rabbits to a malaria DNA vaccine by immunization with a needle-free jet device. Vaccine 2001, 20, 275–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jackson, L.A.; Austin, G.; Chen, R.T.; Stout, R.; DeStefano, F.; Gorse, G.J.; Newman, F.K.; Yu, O.; Weniger, B.G. Safety and immunogenicity of varying dosages of trivalent inactivated influenza vaccine administered by needle-free jet injectors. Vaccine 2001, 19, 4703–4709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, J.; Fox-Leyva, L.; Christensen, C.; Fisher, D.; Schlicting, E.; Snowball, M.; Negus, S.; Mayers, J.; Koller, R.; Stout, R. Hepatitis A vaccine administration: Comparison between jet-injector and needle injection. Vaccine 2000, 18, 1939–1943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boyer, J.D.; Robinson, T.M.; Kutzler, M.A.; Parkinson, R.; Calarota, S.A.; Sidhu, M.K.; Muthumani, K.; Lewis, M.; Pavlakis, G.; Felber, B.; et al. SIV DNA vaccine co-administered with IL-12 expression plasmid enhances CD8 SIV cellular immune responses in Cynomolgus macaques. J. Med. Primatol. 2005, 34, 262–270. [Google Scholar]
- Chong, S.Y.; Egan, M.A.; Kutzler, M.A.; Megati, S.; Masood, A.; Roopchard, V.; Garcia-Hand, D.; Montefiori, D.C.; Quiroz, J.; Rosati, M.; et al. Comparative ability of plasmid IL-12 and IL-15 to enhance cellular and humoral immune responses elicited by a SIVgag plasmid DNA vaccine and alter disease progression following SHIV(89.6P) challenge in rhesus macaques. Vaccine 2007, 25, 4967–4982. [Google Scholar]
- Schadeck, E.B.; Sidhu, M.; Egan, M.A.; Chong, S.Y.; Piacente, P.; Masood, A.; Garcia-Hand, D.; Cappello, S.; Roopchand, V.; Megati, S.; et al. A dose sparing effect by plasmid encoded IL-12 adjuvant on a SIVgag-plasmid DNA vaccine in rhesus macaques. Vaccine 2006, 24, 4677–4687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robinson, T.M.; Sidhu, M.K.; Pavlakis, G.N.; Felber, B.K.; Silvera, P.; Lewis, M.G.; Eldridge, J.; Weiner, D.B.; Boyer, J.D. Macaques co-immunized with SIVgag/pol-HIVenv and IL-12 plasmid have increased cellular responses. J. Med. Primatol. 2007, 36, 276–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halwani, R.; Boyer, J.D.; Yassine-Diab, B.; Haddad, E.K.; Robinson, T.M.; Kumar, S.; Parkinson, R.; Wu, L.; Sidhu, M.K.; Phillipson-Weiner, R.; et al. Therapeutic vaccination with simian immunodeficiency virus (SIV)-DNA+IL-12 or IL-15 induces distinct CD8 memory subsets in SIV-infected macaques. J. Immunol. 2008, 180, 7969–7979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manrique, M.; Micewicz, E.; Kozlowski, P.A.; Wang, S.W.; Aurora, D.; Wilson, R.L.; Ghebremichael, M.; Mazzara, G.; Montefiori, D.; Carville, A.; et al. DNA-MVA vaccine protectionafter X4 SHIV challenge in macaques correlates with day-of-challenge antiviral CD4+ cell-mediated immunity levels and postchallenge preservation of CD4+ T cell memory. AIDS Res. Hum. Retrovir. 2008, 24, 505–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jalah, R.; Patel, V.; Kulkarni, V.; Rosati, M.; Alicea, C.; Ganneru, B.; von Gegerfelt, A.; Huang, W.; Guan, Y.; Broderick, K.E.; et al. IL-12 DNA as molecular vaccine adjuvant increases the cytotoxic T cell responses and breadth of humoral immune responses in SIV DNA vaccinated macaques. Hum. Vaccin Immunother. 2012, 8, 1620–1629. [Google Scholar]
- Manrique, M.; Kozlowski, P.A.; Wang, S.W.; Wilson, R.L.; Micewicz, E.; Montefiori, D.C.; Mansfield, K.G.; Carville, A.; Aldovini, A. Nasal DNA-MVA SIV vaccination provides more significant protection from progression to AIDS than a similar intramuscular vaccination. Mucosal Immunol. 2009, 2, 536–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valentin, A.; von Gegerfelt, A.; Rosati, M.; Miteloudis, G.; Alicea, C.; Bergamaschi, C.; Jalah, R.; Patel, V.; Khan, A.S.; Draghia-Akli, R.; et al. Repeated DNA therapeutic vaccination of chronically SIV-infected macaques provides additional virological benefit. Vaccine 2010, 28, 1962–1974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calarota, S.A.; Dai, A.; Trocio, J.N.; Weiner, D.B.; Lori, F.; Lisziewicz, J. IL-15 as memory T-cell adjuvant for topical HIV-1 DermaVir vaccine. Vaccine 2008, 26, 5188–5195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manrique, M.; Kozlowski, P.A.; Cobo-Molinos, A.; Wang, S.W.; Wilson, R.L.; Mdel, P.M.-V.; Montefiori, D.C.; Carville, A.; Aldovini, A. Resistance to infection, early and persistent suppression of simian immunodeficiency virus SIVmac251 viremia, and significant reduction of tissue viral burden after mucosal vaccination in female rhesus macaques. J. Virol., 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Manrique, M.; Kozlowski, P.A.; Cobo-Molinos, A.; Wang, S.W.; Wilson, R.L.; Montefiori, D.C.; Carville, A.; Aldovini, A. Immunogenicity of a vaccine regimen composed of simian immunodeficiency virus DNA, rMVA, and viral particles administered to female rhesus macaques via four different mucosal routes. J. Virol. 2013, 87, 4738–4750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manrique, M.; Kozlowski, P.A.; Cobo-Molinos, A.; Wang, S.W.; Wilson, R.L.; Montefiori, D.C.; Mansfield, K.G.; Carville, A.; Aldovini, A. Long-term control of simian immunodeficiency virus mac251 viremia to undetectable levels in half of infected female rhesus macaques nasally vaccinated with simian immunodeficiency virus DNA/recombinant modified vaccinia virus Ankara. J. Immunol. 2011, 186, 3581–3593. [Google Scholar]
- Lai, L.; Kwa, S.; Kozlowski, P.A.; Montefiori, D.C.; Ferrari, G.; Johnson, W.E.; Hirsch, V.; Villinger, F.; Chennareddi, L.; Earl, P.L.; et al. Prevention of infection by a granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor co-expressing DNA/modified vaccinia ankara simian immunodeficiency virus vaccine. J. Infect. Dis. 2011, 204, 164–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, L.; Vodros, D.; Kozlowski, P.A.; Montefiori, D.C.; Wilson, R.L.; Akerstrom, V.L.; Chennareddi, L.; Yu, T.; Kannanganat, S.; Ofielu, L.; et al. GM-CSF DNA: An adjuvant for higher avidity IgG, rectal IgA, and increased protection against the acute phase of a SHIV-89.6P challenge by a DNA/MVA immunodeficiency virus vaccine. Virology 2007, 369, 153–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Neill, E.; Bostik, V.; Montefiori, D.C.; Kraiselburd, E.; Villinger, F. IL-12/GM-CSF coadministration in an SIV DNA prime/protein boost protocol enhances Gag-specific T cells but not virus-specific neutralizing antibodies in rhesus macaques. AIDS Res. Hum. Retrovir. 2003, 19, 883–890. [Google Scholar]
- Hellerstein, M.; Xu, Y.; Marino, T.; Lu, S.; Yi, H.; Wright, E.R.; Robinson, H.L. Co-expression of HIV-1 virus-like particles and granulocyte-macrophage colony stimulating factor by GEO-D03 DNA vaccine. Hum. Vaccin. Immunother. 2012, 8, 1654–1658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belisle, S.E.; Yin, J.; Shedlock, D.J.; Dai, A.; Yan, J.; Hirao, L.; Kutzler, M.A.; Lewis, M.G.; Andersen, H.; Lank, S.M.; et al. Long-term programming of antigen-specific immunityfrom gene expression signatures in the PBMC of rhesus macaques immunized with an SIV DNA vaccine. PLoS One 2011, 6, e19681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ihata, A.; Watabe, S.; Sasaki, S.; Shirai, A.; Fukushima, J.; Hamajima, K.; Inoue, J.; Okuda, K. Immunomodulatory effect of a plasmid expressing CD40 ligand on DNA vaccination against human immunodeficiency virus type-1. Immunology 1999, 98, 436–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Yu, Q.; Stone, G.W.; Yue, F.Y.; Ngai, N.; Jones, R.B.; Kornbluth, R.S.; Ostrowski, M.A. CD40L expressed from the canarypox vector, ALVAC, can boost immunogenicity of HIV-1 canarypox vaccine in mice and enhance the in vitro expansion of viral specific CD8+ T cell memory responses from HIV-1-infected and HIV-1-uninfected individuals. Vaccine 2008, 26, 4062–4072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franco, D.; Liu, W.; Gardiner, D.F.; Hahn, B.H.; Ho, D.D. CD40L-containing virus-like particle as a candidate HIV-1 vaccine targeting dendritic cells. J. Acquir. Immune Defic. Syndr. 2011, 56, 393–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.W.; Bertley, F.M.; Kozlowski, P.A.; Herrmann, L.; Manson, K.; Mazzara, G.; Piatak, M.; Johnson, R.P.; Carville, A.; Mansfield, K.; et al. An SHIV DNA/MVA rectal vaccination in macaques provides systemic and mucosal virus-specific responses and protection against AIDS. AIDS Res. Hum. Retroviruses 2004, 20, 846–859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winstone, N.; Wilson, A.J.; Morrow, G.; Boggiano, C.; Chiuchiolo, M.J.; Lopez, M.; Kemelman, M.; Ginsberg, A.A.; Mullen, K.; Coleman, J.W.; et al. Enhanced control of pathogenic SIVmac239 replication in macaques immunized with a plasmid IL12 and a DNA prime, viral vector boost vaccine regimen. J. Virol. 2011, 85, 9578–9587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalams, S.A.; Parker, S.; Jin, X.; Elizaga, M.; Metch, B.; Wang, M.; Hural, J.; Lubeck, M.; Eldridge, J.; Cardinali, M.; et al. Safety and immunogenicity of an HIV-1 gag DNA vaccine with or without IL-12 and/or IL-15 plasmid cytokine adjuvant in healthy, HIV-1 uninfected adults. PLoS One 2012, 7, e29231. [Google Scholar]
- Kalams, S.A.; Parker, S.D.; Elizaga, M.; Metch, B.; Edupuganti, S.; Hural, J.; de Rosa, S.; Carter, D.K.; Rybczyk, K.; Frank, I.; et al. Safety and comparative immunogenicity of an HIV-1 DNA vaccine in combination with plasmid interleukin 12 and impact of intramuscular electroporation for delivery. J. Infect. Dis. 2013, 208, 818–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tavel, J.A.; Martin, J.E.; Kelly, G.G.; Enama, M.E.; Shen, J.M.; Gomez, P.L.; Andrews, C.A.; Koup, R.A.; Bailer, R.T.; Stein, J.A.; et al. Safety and immunogenicity of a Gag-Pol candidate HIV-1 DNA vaccine administered by a needle-free device in HIV-1-seronegative subjects. J. Acquir. Immune Defic. Syndr. 2007, 44, 601–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Troilo, P.J.; Wang, X.; Griffiths, T.G.; Pacchione, S.J.; Barnum, A.B.; Harper, L.B.; Pauley, C.J.; Niu, Z.; Denisova, L.; et al. Detection of integration of plasmid DNA into host genomic DNA following intramuscular injection and electroporation. Gene Ther. 2004, 11, 711–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graham, B.S.; Koup, R.A.; Roederer, M.; Bailer, R.T.; Enama, M.E.; Moodie, Z.; Martin, J.E.; McCluskey, M.M.; Chakrabarti, B.K.; Lamoreaux, L.; et al. Phase 1 safety and immunogenicity evaluation of a multiclade HIV-1 DNA candidate vaccine. J. Infect. Dis. 2006, 194, 1650–1660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mwau, M.; Cebere, I.; Sutton, J.; Chikoti, P.; Winstone, N.; Wee, E.G.; Beattie, T.; Chen, Y.H.; Dorrell, L.; McShane, H.; et al. A human immunodeficiency virus 1 (HIV-1) clade A vaccine in clinical trials: Stimulation of HIV-specific T-cell responses by DNA and recombinant modified vaccinia virus Ankara (MVA) vaccines in humans. J. Gen. Virol. 2004, 85, 911–919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bansal, A.; Jackson, B.; West, K.; Wang, S.; Lu, S.; Kennedy, J.S.; Goepfert, P.A. MultifunctionalT-cell characteristics induced by a polyvalent DNA prime/protein boost human immunodeficiency virus type 1 vaccine regimen given to healthy adults are dependent on the route and dose of administration. J. Virol. 2008, 82, 6458–6469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaoko, W.; Nakwagala, F.N.; Anzala, O.; Manyonyi, G.O.; Birungi, J.; Nanvubya, A.; Bashir, F.; Bhatt, K.; Ogutu, H.; Wakasiaka, S.; et al. Safety and immunogenicity of recombinant low-dosage HIV-1 A vaccine candidates vectored by plasmid pTHr DNA or modified vaccinia virus Ankara (MVA) in humans in East Africa. Vaccine 2008, 26, 2788–2795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, C.C.; Newman, M.J.; Livingston, B.D.; MaWhinney, S.; Forster, J.E.; Scott, J.; Schooley, R.T.; Benson, C.A. Clinical phase 1 testing of the safety and immunogenicity of an epitope-based DNA vaccine in human immunodeficiency virus type 1-infected subjects receiving highly active antiretroviral therapy. Clin. Vaccine Immunol. 2008, 15, 986–994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Kennedy, J.S.; West, K.; Montefiori, D.C.; Coley, S.; Lawrence, J.; Shen, S.; Green, S.; Rothman, A.L.; Ennis, F.A.; et al. Cross-subtype antibody and cellular immune responses induced by a polyvalent DNA prime-protein boost HIV-1 vaccine in healthy human volunteers. Vaccine 2008, 26, 1098–1110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorse, G.J.; Baden, L.R.; Wecker, M.; Newman, M.J.; Ferrari, G.; Weinhold, K.J.; Livingston, B.D.; Villafana, T.L.; Li, H.; Noonan, E.; et al. Safety and immunogenicity of cytotoxic T-lymphocyte poly-epitope, DNA plasmid (EP HIV-1090) vaccine in healthy, human immunodeficiency virus type 1 (HIV-1)-uninfected adults. Vaccine 2008, 26, 215–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eller, M.A.; Eller, L.A.; Opollo, M.S.; Ouma, B.J.; Oballah, P.O.; Galley, L.; Karnasuta, C.; Kim, S.R.; Robb, M.L.; Michael, N.L.; et al. Induction of HIV-specific functional immune responses by a multiclade HIV-1 DNA vaccine candidate in healthy Ugandans. Vaccine 2007, 25, 7737–7742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Catanzaro, A.T.; Roederer, M.; Koup, R.A.; Bailer, R.T.; Enama, M.E.; Nason, M.C.; Martin, J.E.; Rucker, S.; Andrews, C.A.; Gomez, P.L.; et al. Phase I clinical evaluation of a six-plasmid multiclade HIV-1 DNA candidate vaccine. Vaccine 2007, 25, 4085–4092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kutzler, M.A.; Weiner, D.B. DNA vaccines: Ready for prime time? Nat. Rev. Genet. 2008, 9, 776–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasan, S.; Hurley, A.; Schlesinger, S.J.; Hannaman, D.; Gardiner, D.F.; Dugin, D.P.; Boente-Carrera, M.; Vittorino, R.; Caskey, M.; Andersen, J.; et al. In vivo electroporation enhances the immunogenicity of an HIV-1 DNA vaccine candidate in healthy volunteers. PLoS One 2011, 6, e19252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cristillo, A.D.; Weiss, D.; Hudacik, L.; Restrepo, S.; Galmin, L.; Suschak, J.; Draghia-Akli, R.; Markham, P.; Pal, R. Persistent antibody and T cell responses induced by HIV-1 DNA vaccine delivered by electroporation. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2008, 366, 29–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulkarni, V.; Rosati, M.; Bear, J.; Pilkington, G.R.; Jalah, R.; Bergamaschi, C.; Singh, A.K.; Alicea, C.; Chowdhury, B.; Zhang, G.-M.; et al. Comparison of intradermal and intramuscular delivery of SIV env DNA by in vivo electroporation in macaques. Hum. Vaccin Immunother. 2013, 9, 2081–2094. [Google Scholar]
- Kulkarni, V.; Rosati, M.; Jalah, R.; Ganneru, B.; Alicea, C.; Yu, L.; Guan, Y.; LaBranche, C.; Montefiori, D.C.; King, A.D.; et al. DNA vaccination by intradermal electroporation induces long-lasting immune responses in Rhesus macaques. J. Med. Primatol. in press.
- Lichterfeld, M.; Yu, X.G.; le Gall, S.; Altfeld, M. Immunodominance of HIV-1-specific CD8+ T-cell responses in acute HIV-1 infection: At the crossroads of viral and host genetics. Trends Immunol. 2005, 26, 166–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friedrich, T.C.; Valentine, L.E.; Yant, L.J.; Rakasz, E.G.; Piaskowski, S.M.; Furlott, J.R.; Weisgrau, K.L.; Burwitz, B.; May, G.E.; Leon, E.J.; et al. Subdominant CD8+ T-cell responses are involved in durable control of AIDS virus replication. J. Virol. 2007, 81, 3465–3476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; McNevin, J.; Rolland, M.; Zhao, H.; Deng, W.; Maenza, J.; Stevens, C.E.; Collier, A.C.; McElrath, M.J.; Mullins, J.I. Conserved HIV-1 epitopes continuously elicit subdominant cytotoxic T-lymphocyte responses. J. Infect. Dis. 2009, 200, 1825–1833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Ewald, B.A.; Lynch, D.M.; Nanda, A.; Sumida, S.M.; Barouch, D.H. Modulation of DNA vaccine-elicited CD8+ T-lymphocyte epitope immunodominance hierarchies. J. Virol. 2006, 80, 11991–11997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frahm, N.; Kiepiela, P.; Adams, S.; Linde, C.H.; Hewitt, H.S.; Sango, K.; Feeney, M.E.; Addo, M.M.; Lichterfeld, M.; Lahaie, M.P.; et al. Control of human immunodeficiency virus replication by cytotoxic T lymphocytes targeting subdominant epitopes. Nat. Immunol. 2006, 7, 173–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bockl, K.; Wild, J.; Bredl, S.; Kindsmuller, K.; Kostler, J.; Wagner, R. Altering an artificial gagpolnef polyprotein and mode of env co-administration affects the immunogenicity of a clade C HIV DNA vaccine. PLoS One 2012, 7, e34723. [Google Scholar]
- Iversen, A.K.; Stewart-Jones, G.; Learn, G.H.; Christie, N.; Sylvester-Hviid, C.; Armitage, A.E.; Kaul, R.; Beattie, T.; Lee, J.K.; Li, Y.; et al. Conflicting selective forces affect T cell receptor contacts in an immunodominant human immunodeficiency virus epitope. Nat. Immunol. 2006, 7, 179–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneidewind, A.; Brumme, Z.L.; Brumme, C.J.; Power, K.A.; Reyor, L.L.; O’Sullivan, K.; Gladden, A.; Hempel, U.; Kuntzen, T.; Wang, Y.E.; et al. Transmission and long-term stability of compensated CD8 escape mutations. J. Virol. 2009, 83, 3993–3997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altfeld, M.; Kalife, E.T.; Qi, Y.; Streeck, H.; Lichterfeld, M.; Johnston, M.N.; Burgett, N.; Swartz, M.E.; Yang, A.; Alter, G.; et al. HLA alleles associated with delayed progression to AIDS contribute strongly to the initial CD8+ T cell response against HIV-1. PLoS Med. 2006, 3, e403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friedrich, D.; Jalbert, E.; Dinges, W.L.; Sidney, J.; Sette, A.; Huang, Y.; McElrath, M.J.; Horton, H. Vaccine-induced HIV-specific CD8+ T cells utilize preferential HLA alleles and target-specific regions of HIV-1. J. Acquir. Immune Defic. Syndr. 2011, 58, 248–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maurer, K.; Harrer, E.G.; Goldwich, A.; Eismann, K.; Bergmann, S.; Schmitt-Haendle, M.; Spriewald, B.; Mueller, S.M.; Harrer, T. Role of cytotoxic T-lymphocyte-mediated immune selection in a dominant human leukocyte antigen-B8-restricted cytotoxic T-lymphocyte epitope in Nef. J. Acquir. Immune Defic. Syndr. 2008, 48, 133–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Finnefrock, A.C.; Dubey, S.A.; Korber, B.T.; Szinger, J.; Cole, S.; McElrath, M.J.; Shiver, J.W.; Casimiro, D.R.; Corey, L.; et al. Mapping HIV-1 vaccine induced T-cell responses: Bias towards less-conserved regions and potential impact on vaccine efficacy in the step study. PLoS One 2011, 6, e20479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nickle, D.C.; Rolland, M.; Jensen, M.A.; Pond, S.L.; Deng, W.; Seligman, M.; Heckerman, D.; Mullins, J.I.; Jojic, N. Coping with viral diversity in HIV vaccine design. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2007, 3, e75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nickle, D.C.; Jojic, N.; Heckerman, D.; Jojic, V.; Kirovski, D.; Rolland, M.; Pond, S.K.; Mullins, J.I. Comparison of immunogen designs that optimize peptide coverage: Reply to Fischer et al. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2008, 4, e25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barouch, D.H.; O’Brien, K.L.; Simmons, N.L.; King, S.L.; Abbink, P.; Maxfield, L.F.; Sun, Y.H.; la Porte, A.; Riggs, A.M.; Lynch, D.M.; et al. Mosaic HIV-1 vaccines expand the breadth and depth of cellular immune responses in rhesus monkeys. Nat. Med. 2010, 16, 319–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santra, S.; Liao, H.X.; Zhang, R.; Muldoon, M.; Watson, S.; Fischer, W.; Theiler, J.; Szinger, J.; Balachandran, H.; Buzby, A.; et al. Mosaic vaccines elicit CD8+ T lymphocyte responses that confer enhanced immune coverage of diverse HIV strains in monkeys. Nat. Med. 2010, 16, 324–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fischer, W.; Perkins, S.; Theiler, J.; Bhattacharya, T.; Yusim, K.; Funkhouser, R.; Kuiken, C.; Haynes, B.; Letvin, N.L.; Walker, B.D.; et al. Polyvalent vaccines for optimal coverage of potential T-cell epitopes in global HIV-1 variants. Nat. Med. 2007, 13, 100–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fischer, W.; Liao, H.X.; Haynes, B.F.; Letvin, N.L.; Korber, B. Coping with viral diversity in HIV vaccine design: A response to Nickle et al. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2008, 4, e15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doria-Rose, N.A.; Learn, G.H.; Rodrigo, A.G.; Nickle, D.C.; Li, F.; Mahalanabis, M.; Hensel, M.T.; McLaughlin, S.; Edmonson, P.F.; Montefiori, D.; et al. Human immunodeficiency virus type 1 subtype B ancestral envelope protein is functional and elicits neutralizing antibodies in rabbits similar to those elicited by a circulating subtype B envelope. J. Virol. 2005, 79, 11214–11224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mullins, J.I.; Nickle, D.C.; Heath, L.; Rodrigo, A.G.; Learn, G.H. Immunogen sequence: The fourth tier of AIDS vaccine design. Expert Rev. Vaccines 2004, 3, S151–S159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nickle, D.C.; Jensen, M.A.; Gottlieb, G.S.; Shriner, D.; Learn, G.H.; Rodrigo, A.G.; Mullins, J.I. Consensus and ancestral state HIV vaccines. Science 2003, 299, 1515–1518. [Google Scholar]
- Dahirel, V.; Shekhar, K.; Pereyra, F.; Miura, T.; Artyomov, M.; Talsania, S.; Allen, T.M.; Altfeld, M.; Carrington, M.; Irvine, D.J.; et al. Coordinate linkage of HIV evolution reveals regions of immunological vulnerability. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 11530–11535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Letourneau, S.; Im, E.J.; Mashishi, T.; Brereton, C.; Bridgeman, A.; Yang, H.; Dorrell, L.; Dong, T.; Korber, B.; McMichael, A.J.; et al. Design and pre-clinical evaluation of a universal HIV-1 vaccine. PLoS One 2007, 2, e984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosario, M.; Bridgeman, A.; Quakkelaar, E.D.; Quigley, M.F.; Hill, B.J.; Knudsen, M.L.; Ammendola, V.; Ljungberg, K.; Borthwick, N.; Im, E.J.; et al. Long peptides induce polyfunctional T cells against conserved regions of HIV-1 with superior breadth to single-gene vaccines in macaques. Eur. J. Immunol. 2010, 40, 1973–1984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Groot, A.S.; Rivera, D.S.; McMurry, J.A.; Buus, S.; Martin, W. Identification of immunogenic HLA-B7 “Achilles’ heel” epitopes within highly conserved regions of HIV. Vaccine 2008, 26, 3059–3071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, C.C.; McKinney, D.; Anders, M.; MaWhinney, S.; Forster, J.; Crimi, C.; Southwood, S.; Sette, A.; Chesnut, R.; Newman, M.J.; et al. Development of a DNA vaccine designed to induce cytotoxic T lymphocyte responses to multiple conserved epitopes in HIV-1. J. Immunol. 2003, 171, 5611–5623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaufman, D.R.; Li, F.; Cruz, A.N.; Self, S.G.; Barouch, D.H. Focus and breadth of cellular immune responses elicited by a heterologous insert prime-boost vaccine regimen in rhesus monkeys. Vaccine 2012, 30, 506–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosa, D.S.; Ribeiro, S.P.; Cunha-Neto, E. CD4+ T cell epitope discovery and rational vaccine design. Arch. Immunol. Ther. Exp. 2010, 58, 121–130. [Google Scholar]
- Ribeiro, S.P.; Rosa, D.S.; Fonseca, S.G.; Mairena, E.C.; Postol, E.; Oliveira, S.C.; Guilherme, L.; Kalil, J.; Cunha-Neto, E. A vaccine encoding conserved promiscuous HIV CD4 epitopes induces broad T cell responses in mice transgenic to multiple common HLA class II molecules. PLoS One 2010, 5, e11072. [Google Scholar]
- Almeida, R.R.; Rosa, D.S.; Ribeiro, S.P.; Santana, V.C.; Kallas, E.G.; Sidney, J.; Sette, A.; Kalil, J.; Cunha-Neto, E. Broad and cross-clade CD4+ T-cell responses elicited by a DNA vaccine encoding highly conserved and promiscuous HIV-1 M-group consensus peptides. PLoS One 2012, 7, e45267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kulkarni, V.; Valentin, A.; Rosati, M.; Alicea, C.; Singh, A.K.; Jalah, R.; Broderick, K.E.; Sardesai, N.Y.; le Gall, S.; Mothe, B.; et al. Altered immunodominance hierarchy and increased T-cell breadth upon HIV-1 conserved element DNA vaccination in macaques. PLoS One 2014, 9, e86254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanke, T. Conserved immunogens in prime-boost strategies for the next-generation HIV-1 vaccines. Expert Opin. Biol. Ther. 2014, 14, 601–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mothe, B.; Llano, A.; Ibarrondo, J.; Zamarreno, J.; Schiaulini, M.; Miranda, C.; Ruiz-Riol, M.; Berger, C.T.; Herrero, M.J.; Palou, E.; et al. CTL responses of high functional avidity and broad variant cross-reactivity are associated with HIV control. PLoS One 2012, 7, e29717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rolland, M.; Nickle, D.C.; Mullins, J.I. HIV-1 group M conserved elements vaccine. PLoS Pathog. 2007, 3, e157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulkarni, V.; Valentin, A.; Rosati, M.; Rolland, M.; Mullins, J.I.; Pavlakis, G.N.; Felber, B.K.; Vaccine Branch, Center for Cancer Research, National Cancer Institute at Frederick, Frederick, MD, USA. Unpublished work. 2014.
- Kopycinski, J.; Cheeseman, H.; Ashraf, A.; Gill, D.; Hayes, P.; Hannaman, D.; Gilmour, J.; Cox, J.H.; Vasan, S. A DNA-based candidate HIV vaccine delivered via in vivo electroporation induces CD4 responses toward the α4β7-binding V2 loop of HIV gp120 in healthy volunteers. Clin. Vaccine Immunol. 2012, 19, 1557–1559. [Google Scholar]
- Kennedy, J.S.; Co, M.; Green, S.; Longtine, K.; Longtine, J.; O’Neill, M.A.; Adams, J.P.; Rothman, A.L.; Yu, Q.; Johnson-Leva, R.; et al. The safety and tolerability of an HIV-1 DNA prime-protein boost vaccine (DP6–001) in healthy adult volunteers. Vaccine 2008, 26, 4420–4424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goepfert, P.A.; Elizaga, M.L.; Sato, A.; Qin, L.; Cardinali, M.; Hay, C.M.; Hural, J.; DeRosa, S.C.; DeFawe, O.D.; Tomaras, G.D.; et al. Phase 1 safety and immunogenicity testing of DNA and recombinant modified vaccinia Ankara vaccines expressing HIV-1 virus-like particles. J. Infect. Dis. 2011, 203, 610–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayes, P.; Gilmour, J.; von Lieven, A.; Gill, D.; Clark, L.; Kopycinski, J.; Cheeseman, H.; Chung, A.; Alter, G.; Dally, L.; et al. Safety and immunogenicity of DNA prime and modified vaccinia ankara virus-HIV subtype C vaccine boost in healthy adults. Clin. Vaccine Immunol. 2013, 20, 397–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gudmundsdotter, L.; Nilsson, C.; Brave, A.; Hejdeman, B.; Earl, P.; Moss, B.; Robb, M.; Cox, J.; Michael, N.; Marovich, M.; et al. Recombinant Modified Vaccinia Ankara (MVA) effectively boosts DNA-primed HIV-specific immune responses in humans despite pre-existing vaccinia immunity. Vaccine 2009, 27, 4468–4474. [Google Scholar]
- Sandstrom, E.; Nilsson, C.; Hejdeman, B.; Brave, A.; Bratt, G.; Robb, M.; Cox, J.; Vancott, T.; Marovich, M.; Stout, R.; et al. Broad immunogenicity of a multigene, multiclade HIV-1 DNA vaccine boosted with heterologous HIV-1 recombinant modified vaccinia virus Ankara. J. Infect. Dis. 2008, 198, 1482–1490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakari, M.; Aboud, S.; Nilsson, C.; Francis, J.; Buma, D.; Moshiro, C.; Aris, E.A.; Lyamuya, E.F.; Janabi, M.; Godoy-Ramirez, K.; et al. Broad and potent immune responses to a low dose intradermal HIV-1 DNA boosted with HIV-1 recombinant MVA among healthy adults in Tanzania. Vaccine 2011, 29, 8417–8428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borthwick, N.; Ahmed, T.; Ondondo, B.; Hayes, P.; Rose, A.; Ebrahimsa, U.; Hayton, E.J.; Black, A.; Bridgeman, A.; Rosario, M.; et al. Vaccine-elicited human T cells recognizing conserved protein regions Inhibit HIV-1. Mol. Ther. 2014, 22, 464–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Valentin, A.; Kulkarni, V.; Rosati, M.; Beach, R.K.; Alicea, C.; Bear, J.; Hannaman, D.; Reed, S.G.; Felber, B.K.; et al. HIV/SIV DNA vaccine combined with protein in a co-immunization protocol elicits highest humoral responses to envelope in mice and macaques. Vaccine 2013, 31, 3747–3755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaworski, J.P.; Krebs, S.J.; Trovato, M.; Kovarik, D.N.; Brower, Z.; Sutton, W.F.; Waagmeester, G.; Sartorius, R.; D’Apice, L.; Caivano, A.; et al. Co-immunization with multimeric scaffolds and DNA rapidly induces potent autologous HIV-1 neutralizing antibodies and CD8+ T cells. PLoS One 2012, 7, e31464. [Google Scholar]
- Vargas-Inchaustegui, D.A.; Tuero, I.; Mohanram, V.; Musich, T.; Pegu, P.; Valentin, A.; Sui, Y.; Rosati, M.; Bear, J.; Kulkarni, V.; et al. Humoral immunity induced by mucosal and/or systemic SIV-specific vaccine platforms suggest novel combinatorial approaches for enhancing responses. Clin. Immunol. submitted for publication. 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Boyer, J.D.; Robinson, T.M.; Kutzler, M.A.; Vansant, G.; Hokey, D.A.; Kumar, S.; Parkinson, R.; Wu, L.; Sidhu, M.K.; Pavlakis, G.N.; et al. Protection against simian/human immunodeficiency virus (SHIV) 89.6P in macaques after coimmunization with SHIV antigen and IL-15 plasmid. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 18648–18653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muthumani, K.; Bagarazzi, M.; Conway, D.; Hwang, D.S.; Manson, K.; Ciccarelli, R.; Israel, Z.; Montefiori, D.C.; Ugen, K.; Miller, N.; et al. A Gag-Pol/Env-Rev SIV239 DNA vaccine improves CD4 counts, and reduce viral loads after pathogenic intrarectal SIV(mac)251 challenge in rhesus macaques. Vaccine 2003, 21, 629–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boyer, J.D.; Maciag, P.C.; Parkinson, R.; Wu, L.; Lewis, M.G.; Weiner, D.B.; Paterson, Y. Rhesus macaques with high levels of vaccine induced IFN-gamma producing cells better control viral set-point following challenge with SIV239. Vaccine 2006, 24, 4498–4502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haigwood, N.L.; Pierce, C.C.; Robertson, M.N.; Watson, A.J.; Montefiori, D.C.; Rabin, M.; Lynch, J.B.; Kuller, L.; Thompson, J.; Morton, W.R.; et al. Protection from pathogenic SIV challenge using multigenic DNA vaccines. Immunol. Lett. 1999, 66, 183–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, J.; Dai, A.; Lecureux, J.; Arango, T.; Kutzler, M.A.; Yan, J.; Lewis, M.G.; Khan, A.; Sardesai, N.Y.; Montefiore, D.; et al. High antibody and cellular responses induced to HIV-1 clade C envelope following DNA vaccines delivered by electroporation. Vaccine 2011, 29, 6763–6770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Von Gegerfelt, A.S.; Alicea, C.; Valentin, A.; Morrow, M.; van Rompay, K.K.; Ayash-Rashkovsky, M.; Markham, P.; Else, J.G.; Marthas, M.L.; Pavlakis, G.N.; et al. Long lasting control and lack of pathogenicity of the attenuated Rev-independent SIV in rhesus macaques. AIDS Res. Hum. Retroviruses 2006, 22, 516–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pal, R.; Wang, S.; Kalyanaraman, V.S.; Nair, B.C.; Whitney, S.; Keen, T.; Hocker, L.; Hudacik, L.; Rose, N.; Cristillo, A.; et al. Polyvalent DNA prime and envelope protein boost HIV-1 vaccine elicits humoral and cellular responses and controls plasma viremia in rhesus macaques following rectal challenge with an R5 SHIV isolate. J. Med. Primatol. 2005, 34, 226–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pal, R.; Kalyanaraman, V.S.; Nair, B.C.; Whitney, S.; Keen, T.; Hocker, L.; Hudacik, L.; Rose, N.; Mboudjeka, I.; Shen, S.; et al. Immunization of rhesus macaques with a polyvalent DNA prime/protein boost human immunodeficiency virus type 1 vaccine elicits protective antibody response against simian human immunodeficiency virus of R5 phenotype. Virology 2006, 348, 341–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasmussen, R.A.; Hofmann-Lehman, R.; Montefiori, D.C.; Li, P.L.; Liska, V.; Vlasak, J.; Baba, T.W.; Schmitz, J.E.; Kuroda, M.J.; Robinson, H.L.; et al. DNA prime/protein boost vaccine strategy in neonatal macaques against simian human immunodeficiency virus. J. Med. Primatol. 2002, 31, 40–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koopman, G.; Mortier, D.; Hofman, S.; Mathy, N.; Koutsoukos, M.; Ertl, P.; Overend, P.; van Wely, C.; Thomsen, L.L.; Wahren, B.; et al. Immune-response profiles induced by human immunodeficiency virus type 1 vaccine DNA, protein or mixed-modality immunization: Increased protection from pathogenic simian-human immunodeficiency virus viraemia with protein/DNA combination. J. Gen. Virol. 2008, 89, 540–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hel, Z.; Nacsa, J.; Tryniszewska, E.; Tsai, W.P.; Parks, R.W.; Montefiori, D.C.; Felber, B.K.; Tartaglia, J.; Pavlakis, G.N.; Franchini, G. Containment of simian immunodeficiency virus infection in vaccinated macaques: Correlation with the magnitude of virus-specific pre- and postchallenge CD4+ and CD8+ T cell responses. J. Immunol. 2002, 169, 4778–4787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hel, Z.; Tsai, W.P.; Thornton, A.; Nacsa, J.; Giuliani, L.; Tryniszewska, E.; Poudyal, M.; Venzon, D.; Wang, X.; Altman, J.; et al. Potentiation of simian immunodeficiency virus (SIV)-specific CD4+ and CD8+ T cell responses by a DNA-SIV and NYVAC-SIV prime/boost regimen. J. Immunol. 2001, 167, 7180–7191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hel, Z.; Tsai, W.P.; Tryniszewska, E.; Nacsa, J.; Markham, P.D.; Lewis, M.G.; Pavlakis, G.N.; Felber, B.K.; Tartaglia, J.; Franchini, G. Improved vaccine protection from simian AIDS by the addition of nonstructural simian immunodeficiency virus genes. J. Immunol. 2006, 176, 85–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hutnick, N.A.; Myles, D.J.; Hirao, L.; Scott, V.L.; Ferraro, B.; Khan, A.S.; Lewis, M.G.; Miller, C.J.; Bett, A.J.; Casimiro, D.; et al. An optimized SIV DNA vaccine can serve as a boost for Ad5 and provide partial protection from a high-dose SIVmac251 challenge. Vaccine 2012, 30, 3202–3208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, N.A.; Keele, B.F.; Reed, J.S.; Piaskowski, S.M.; MacNair, C.E.; Bett, A.J.; Liang, X.; Wang, F.; Thoryk, E.; Heidecker, G.J.; et al. Vaccine-induced cellular responses control simian immunodeficiency virus replication after heterologous challenge. J. Virol. 2009, 83, 6508–6521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casimiro, D.R.; Wang, F.; Schleif, W.A.; Liang, X.; Zhang, Z.Q.; Tobery, T.W.; Davies, M.E.; McDermott, A.B.; O’Connor, D.H.; Fridman, A.; et al. Attenuation of simian immunodeficiency virus SIVmac239 infection by prophylactic immunization with dna and recombinant adenoviral vaccine vectors expressing Gag. J. Virol. 2005, 79, 15547–15555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, N.A.; Reed, J.; Napoe, G.S.; Piaskowski, S.; Szymanski, A.; Furlott, J.; Gonzalez, E.J.; Yant, L.J.; Maness, N.J.; May, G.E.; et al. Vaccine-induced cellular immune responses reduce plasma viral concentrations after repeated low-dose challenge with pathogenic simian immunodeficiency virus SIVmac239. J. Virol. 2006, 80, 5875–5885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suh, Y.S.; Park, K.S.; Sauermann, U.; Franz, M.; Norley, S.; Wilfingseder, D.; Stoiber, H.; Fagrouch, Z.; Heeney, J.; Hunsmann, G.; et al. Reduction of viral loads by multigenic DNA priming and adenovirus boosting in the SIVmac-macaque model. Vaccine 2006, 24, 1811–1820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Ewald, B.A.; Lynch, D.M.; Denholtz, M.; Abbink, P.; Lemckert, A.A.; Carville, A.; Mansfield, K.G.; Havenga, M.J.; Goudsmit, J.; et al. Magnitude and phenotype of cellular immune responses elicited by recombinant adenovirus vectors and heterologous prime-boost regimens in rhesus monkeys. J. Virol. 2008, 82, 4844–4852. [Google Scholar]
- Mattapallil, J.J.; Douek, D.C.; Buckler-White, A.; Montefiori, D.; Letvin, N.L.; Nabel, G.J.; Roederer, M. Vaccination preserves CD4 memory T cells during acute simian immunodeficiency virus challenge. J. Exp. Med. 2006, 203, 1533–1541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mattapallil, J.J.; Hill, B.; Douek, D.C.; Roederer, M. Systemic vaccination prevents the total destruction of mucosal CD4 T cells during acute SIV challenge. J. Med. Primatol. 2006, 35, 217–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Letvin, N.L.; Huang, Y.; Chakrabarti, B.K.; Xu, L.; Seaman, M.S.; Beaudry, K.; Korioth-Schmitz, B.; Yu, F.; Rohne, D.; Martin, K.L.; et al. Heterologous envelope immunogens contribute to AIDS vaccine protection in rhesus monkeys. J. Virol. 2004, 78, 7490–7497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seaman, M.S.; Santra, S.; Newberg, M.H.; Philippon, V.; Manson, K.; Xu, L.; Gelman, R.S.; Panicali, D.; Mascola, J.R.; Nabel, G.J.; et al. Vaccine-elicited memory cytotoxic T lymphocytes contribute to Mamu-A*01-associated control of simian/human immunodeficiency virus 89.6P replication in rhesus monkeys. J. Virol. 2005, 79, 4580–4588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Schmitz, J.E.; Buzby, A.P.; Barker, B.R.; Rao, S.S.; Xu, L.; Yang, Z.Y.; Mascola, J.R.; Nabel, G.J.; Letvin, N.L. Virus-specific cellular immune correlates of survival in vaccinated monkeys after simian immunodeficiency virus challenge. J. Virol. 2006, 80, 10950–10956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamamoto, T.; Johnson, M.J.; Price, D.A.; Wolinsky, D.I.; Almeida, J.R.; Petrovas, C.; Nason, M.; Yeh, W.W.; Shen, L.; Roederer, M.; et al. Virus inhibition activity of effector memory CD8+ T cells determines simian immunodeficiency virus load in vaccinated monkeys after vaccine breakthrough infection. J. Virol. 2012, 86, 5877–5884. [Google Scholar]
- Letvin, N.L.; Rao, S.S.; Montefiori, D.C.; Seaman, M.S.; Sun, Y.; Lim, S.Y.; Yeh, W.W.; Asmal, M.; Gelman, R.S.; Shen, L.; et al. Immune and genetic correlates of vaccine protection against mucosal infection by SIV in monkeys. Sci. Transl. Med. 2011, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koup, R.A.; Roederer, M.; Lamoreaux, L.; Fischer, J.; Novik, L.; Nason, M.C.; Larkin, B.D.; Enama, M.E.; Ledgerwood, J.E.; Bailer, R.T.; et al. Priming immunization with DNA augments immunogenicity of recombinant adenoviral vectors for both HIV-1 specific antibody and T-cell responses. PLoS One 2010, 5, e9015. [Google Scholar]
- Kaur, A.; Sanford, H.B.; Garry, D.; Lang, S.; Klumpp, S.A.; Watanabe, D.; Bronson, R.T.; Lifson, J.D.; Rosati, M.; Pavlakis, G.N.; et al. Ability of herpes simplex virus vectors to boost immune responses to DNA vectors and to protect against challenge by simian immunodeficiency virus. Virology 2007, 357, 199–214. [Google Scholar]
- Earl, P.L.; Wyatt, L.S.; Montefiori, D.C.; Bilska, M.; Woodward, R.; Markham, P.D.; Malley, J.D.; Vogel, T.U.; Allen, T.M.; Watkins, D.I.; et al. Comparison of vaccine strategies using recombinant env-gag-pol MVA with or without an oligomeric Env protein boost in the SHIV rhesus macaque model. Virology 2002, 294, 270–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amara, R.R.; Patel, K.; Niedziela, G.; Nigam, P.; Sharma, S.; Staprans, S.I.; Montefiori, D.C.; Chenareddi, L.; Herndon, J.G.; Robinson, H.L.; et al. A combination DNA and attenuated simian immunodeficiency virus vaccine strategy provides enhanced protection from simian/human immunodeficiency virus-induced disease. J. Virol. 2005, 79, 15356–15367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robinson, H.L.; Montefiori, D.C.; Villinger, F.; Robinson, J.E.; Sharma, S.; Wyatt, L.S.; Earl, P.L.; McClure, H.M.; Moss, B.; Amara, R.R. Studies on GM-CSF DNA as an adjuvant for neutralizing Ab elicited by a DNA/MVA immunodeficiency virus vaccine. Virology 2006, 352, 285–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Lai, L.; Amara, R.R.; Montefiori, D.C.; Villinger, F.; Chennareddi, L.; Wyatt, L.S.; Moss, B.; Robinson, H.L. Preclinical studies of human immunodeficiency virus/AIDS vaccines: Inverse correlation between avidity of anti-Env antibodies and peak postchallenge viremia. J. Virol. 2009, 83, 4102–4111. [Google Scholar]
- Barouch, D.H.; Liu, J.; Li, H.; Maxfield, L.F.; Abbink, P.; Lynch, D.M.; Iampietro, M.J.; SanMiguel, A.; Seaman, M.S.; Ferrari, G.; et al. Vaccine protection against acquisition of neutralization-resistant SIV challenges in rhesus monkeys. Nature 2012, 482, 89–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaccari, M.; Boasso, A.; Ma, Z.M.; Cecchinato, V.; Venzon, D.; Doster, M.N.; Tsai, W.P.; Shearer, G.M.; Fuchs, D.; Felber, B.K.; et al. CD4+ T-cell loss and delayed expression of modulators of immune responses at mucosal sites of vaccinated macaques following SIV(mac251) infection. Mucosal Immunol. 2008, 1, 497–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaccari, M.; Mattapallil, J.; Song, K.; Tsai, W.P.; Hryniewicz, A.; Venzon, D.; Zanetti, M.; Reimann, K.A.; Roederer, M.; Franchini, G. Reduced protection from simian immunodeficiency virus SIVmac251 infection afforded by memory CD8+ T cells induced by vaccination during CD4+ T-cell deficiency. J. Virol. 2008, 82, 9629–9638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cox, J.H.; Ferrari, M.G.; Earl, P.; Lane, J.R.; Jagodzinski, L.L.; Polonis, V.R.; Kuta, E.G.; Boyer, J.D.; Ratto-Kim, S.; Eller, L.A.; et al. Inclusion of a CRF01_AE HIV envelope protein boost with a DNA/MVA prime-boost vaccine: Impact on humoral and cellular immunogenicity and viral load reduction after SHIV-E challenge. Vaccine 2012, 30, 1830–1840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Virnik, K.; Hockenbury, M.; Ni, Y.; Beren, J.; Pavlakis, G.N.; Felber, B.K.; Berkower, I. Live attenuated rubella vectors expressing SIV and HIV vaccine antigens replicate and elicit durable immune responses in rhesus macaques. Retrovirology. 2013, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Von Gegerfelt, A.S.; Rosati, M.; Alicea, C.; Valentin, A.; Roth, P.; Bear, J.; Franchini, G.; Albert, P.S.; Bischofberger, N.; Boyer, J.D.; et al. Long-lasting decrease in viremia in macaques chronically infected with simian immunodeficiency virus SIVmac251 after therapeutic DNA immunization. J. Virol. 2007, 81, 1972–1979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palma, P.; Romiti, M.L.; Montesano, C.; Santilli, V.; Mora, N.; Aquilani, A.; Dispinseri, S.; Tchidjou, H.K.; Montano, M.; Eriksson, L.E.; et al. Therapeutic DNA vaccination of vertically HIV-infected children: Report of the first pediatric randomised trial (PEDVAC). PLoS One 2013, 8, e79957. [Google Scholar]
- Rodriguez, B.; Asmuth, D.M.; Matining, R.M.; Spritzler, J.; Jacobson, J.M.; Mailliard, R.B.; Li, X.D.; Martinez, A.I.; Tenorio, A.R.; Lori, F.; et al. Safety, tolerability, and immunogenicity of repeated doses of dermavir, a candidate therapeutic HIV vaccine, in HIV-infected patients receiving combination antiretroviral therapy: Results of the ACTG 5176 trial. J. Acquir. Immune Defic. Syndr. 2013, 64, 351–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casazza, J.P.; Bowman, K.A.; Adzaku, S.; Smith, E.C.; Enama, M.E.; Bailer, R.T.; Price, D.A.; Gostick, E.; Gordon, I.J.; Ambrozak, D.R.; et al. Therapeutic vaccination expands and improves the function of the HIV-specific memory T-cell repertoire. J. Infect. Dis. 2013, 207, 1829–1840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lisziewicz, J.; Bakare, N.; Calarota, S.A.; Banhegyi, D.; Szlavik, J.; Ujhelyi, E.; Toke, E.R.; Molnar, L.; Lisziewicz, Z.; Autran, B.; et al. Single DermaVir immunization: Dose-dependent expansion of precursor/memory T cells against all HIV antigens in HIV-1 infected individuals. PLoS One 2012, 7, e35416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carcelain, G.; Autran, B. Immune interventions in HIV infection. Immunol. Rev. 2013, 254, 355–371. [Google Scholar]
- Gudmundsdotter, L.; Sjodin, A.; Bostrom, A.C.; Hejdeman, B.; Theve-Palm, R.; Alaeus, A.; Lidman, K.; Wahren, B. Therapeutic immunization for HIV. Springer Semin. Immunopathol. 2006, 28, 221–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2014 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Felber, B.K.; Valentin, A.; Rosati, M.; Bergamaschi, C.; Pavlakis, G.N. HIV DNA Vaccine: Stepwise Improvements Make a Difference. Vaccines 2014, 2, 354-379. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines2020354
Felber BK, Valentin A, Rosati M, Bergamaschi C, Pavlakis GN. HIV DNA Vaccine: Stepwise Improvements Make a Difference. Vaccines. 2014; 2(2):354-379. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines2020354
Chicago/Turabian StyleFelber, Barbara K., Antonio Valentin, Margherita Rosati, Cristina Bergamaschi, and George N. Pavlakis. 2014. "HIV DNA Vaccine: Stepwise Improvements Make a Difference" Vaccines 2, no. 2: 354-379. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines2020354
APA StyleFelber, B. K., Valentin, A., Rosati, M., Bergamaschi, C., & Pavlakis, G. N. (2014). HIV DNA Vaccine: Stepwise Improvements Make a Difference. Vaccines, 2(2), 354-379. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines2020354