Co-Administration of Molecular Adjuvants Expressing NF-Kappa B Subunit p65/RelA or Type-1 Transactivator T-bet Enhance Antigen Specific DNA Vaccine-Induced Immunity
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental
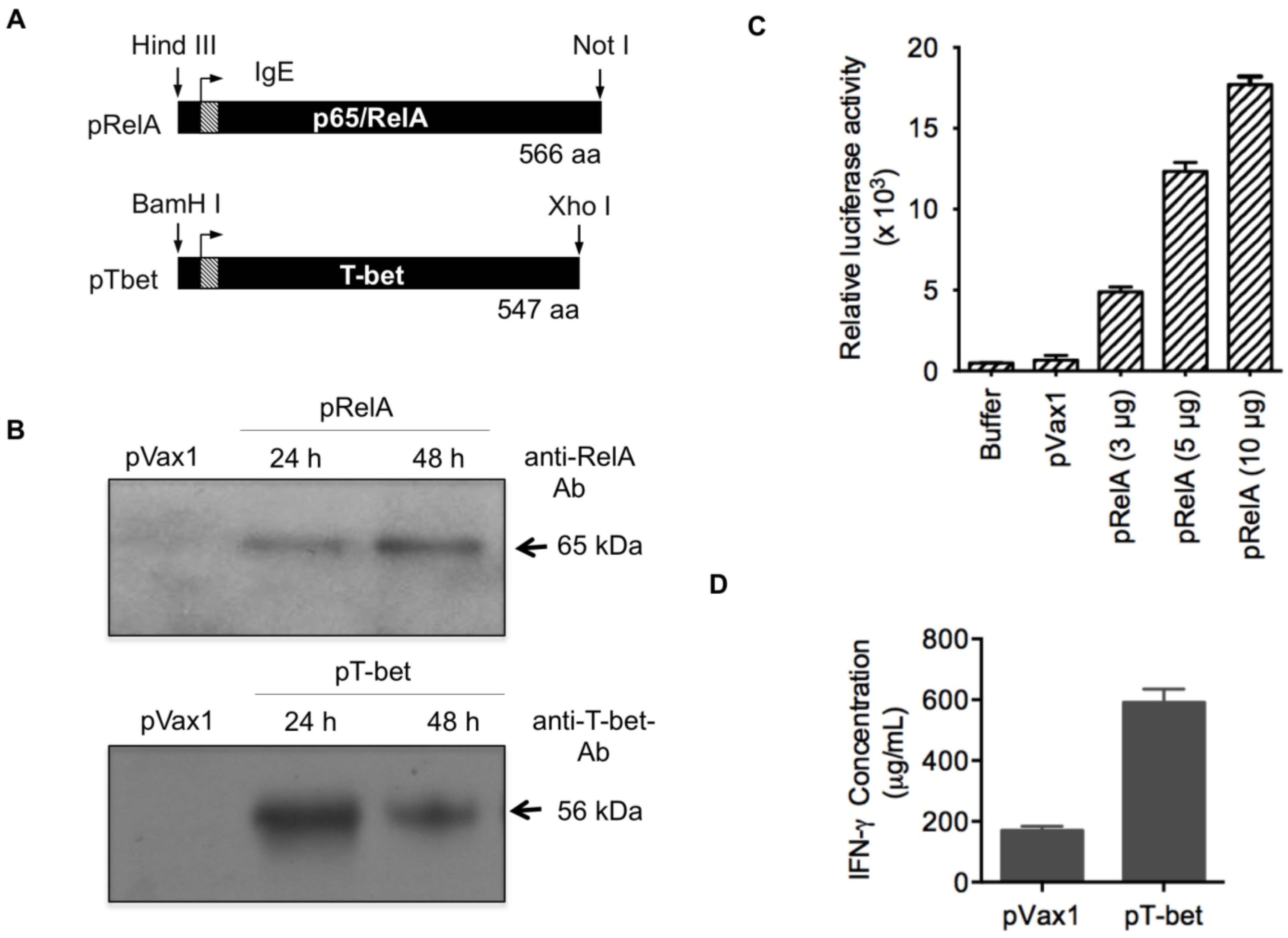
2.1. Plasmid Vaccine Constructs
2.2. Transfections and Western Blot Analysis
2.3. Confirmation of Transcription Activity of RelA/p65 and T-Bet by Luciferase Reporter Assay and IFN-Gamma Production
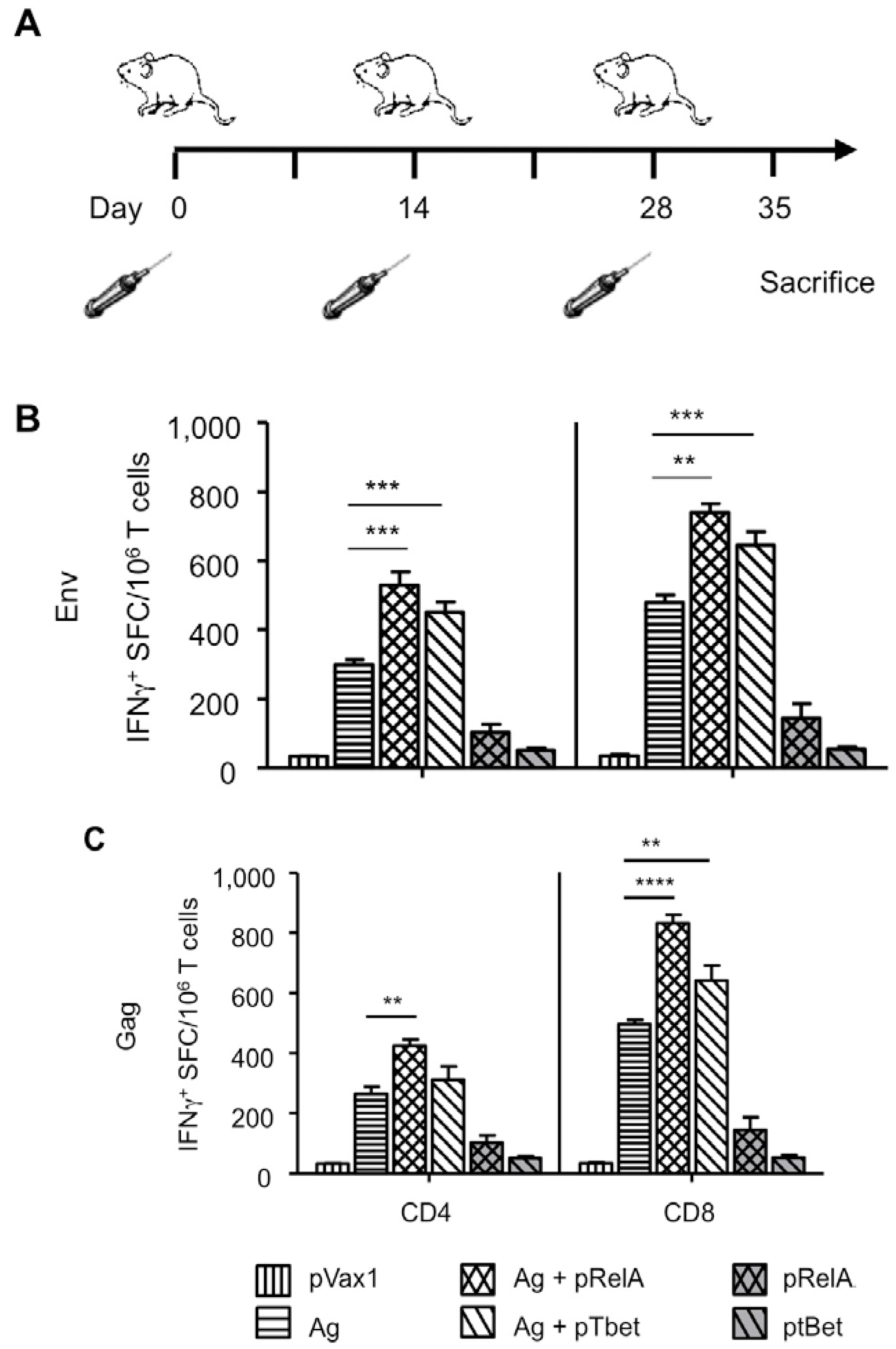
2.4. Animals and Vaccination Regimen
2.5. Splenocyte, T Cell Isolation and Cytokine Quantitation
2.6. ELISPOT Analysis
2.7. T Cell Proliferation Assay
2.8. ELISA
2.9. Flow Cytometry
2.10. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Adjuvant Construction and Expression
3.2. Enhanced Cellular Immunity

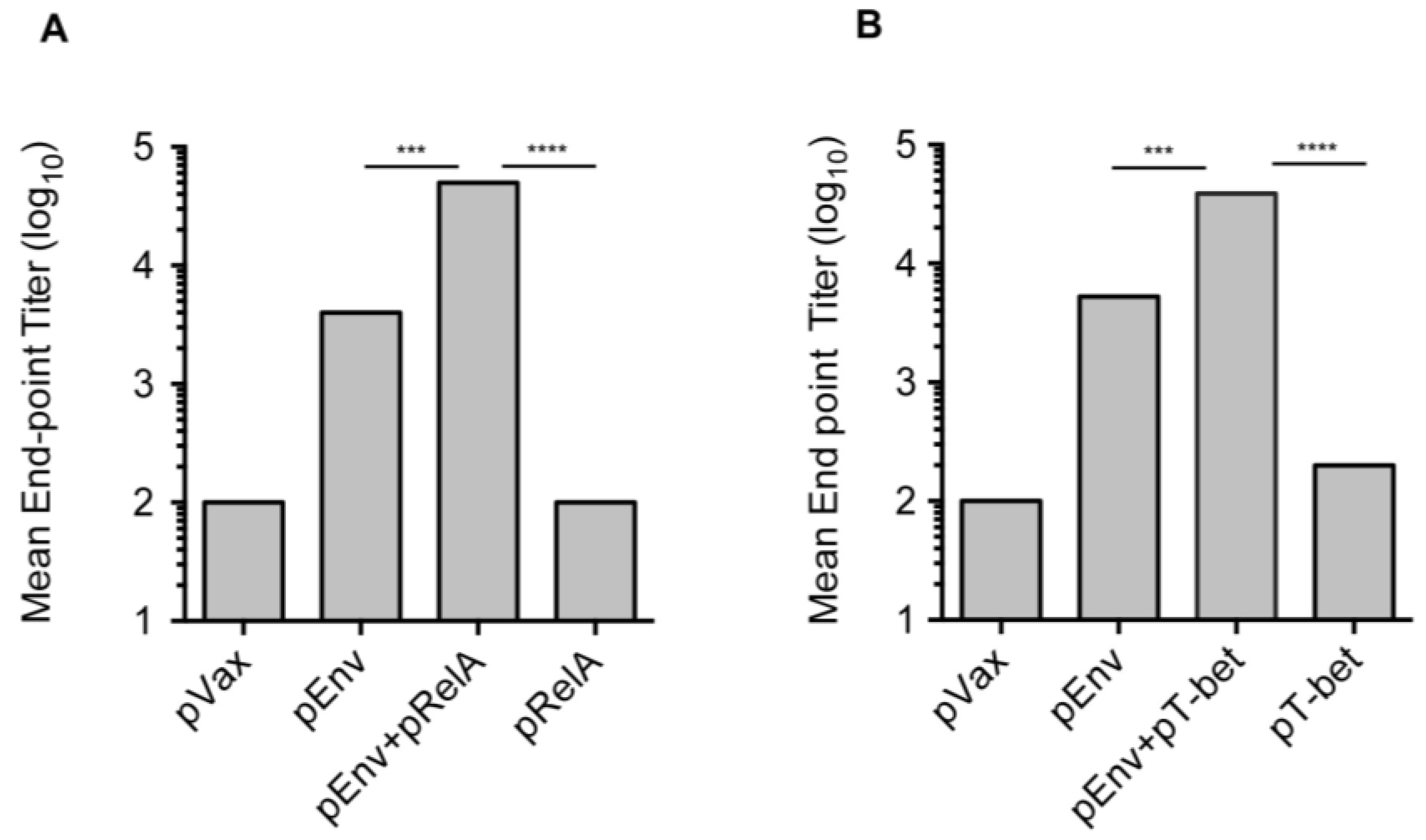
3.3. Enhanced Antibody Responses with Adjuvanted Vaccination

4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zeng, Q.; Gomez, B.P.; Viscidi, R.P.; Peng, S.; He, L.; Ma, B.; Wu, T.C.; Hung, C.F. Development of a DNA vaccine targeting merkel cell polyomavirus. Vaccine 2012, 30, 1322–1329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mascola, J.R.; Montefiori, D.C. The role of antibodies in HIV vaccines. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2010, 28, 413–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laddy, D.J.; Yan, J.; Khan, A.S.; Andersen, H.; Cohn, A.; Greenhouse, J.; Lewis, M.; Manischewitz, J.; King, L.R.; Golding, H.; et al. Electroporation of synthetic DNA antigens offers protection in nonhuman primates challenged with highly pathogenic avian influenza virus. J. Virol. 2009, 83, 4624–4630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korber, B.; Gnanakaran, S. AIDS/HIV Converging on an HIV vaccine. Science 2011, 333, 1589–1590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, T.; Georgiev, I.; Wu, X.; Yang, Z.Y.; Dai, K.; Finzi, A.; Kwon, Y.D.; Scheid, J.F.; Shi, W.; Xu, L.; et al. Structural basis for broad and potent neutralization of HIV-1 by antibody VRC01. Science 2010, 329, 811–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moir, S.; Malaspina, A.; Fauci, A.S. Prospects for an hiv vaccine: Leading B cells down the right path. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2011, 18, 1317–1321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leitner, W.W.; Baker, M.C.; Berenberg, T.L.; Lu, M.C.; Yannie, P.J.; Udey, M.C. Enhancement of DNA tumor vaccine efficacy by gene gun-mediated codelivery of threshold amounts of plasmid-encoded helper antigen. Blood 2009, 113, 37–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, J.E.; Louder, M.K.; Holman, L.A.; Gordon, I.J.; Enama, M.E.; Larkin, B.D.; Andrews, C.A.; Vogel, L.; Koup, R.A.; Roederer, M.; et al. A sars DNA vaccine induces neutralizing antibody and cellular immune responses in healthy adults in a phase I clinical trial. Vaccine 2008, 26, 6338–6343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shedlock, D.J.; Aviles, J.; Talbott, K.T.; Wong, G.; Wu, S.J.; Villarreal, D.O.; Myles, D.J.; Croyle, M.A.; Yan, J.; Kobinger, G.P.; et al. Induction of broad cytotoxic T cells by protective DNA vaccination against marburg and ebola. Mol. Ther. 2013, 21, 1432–1444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shedlock, D.J.; Silvestri, G.; Weiner, D.B. Monkeying around with HIV vaccines: Using rhesus macaques to define “gatekeepers” for clinical trials. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2009, 9, 717–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shedlock, D.J.; Talbott, K.T.; Cress, C.; Ferraro, B.; Tuyishme, S.; Mallilankaraman, K.; Cisper, N.J.; Morrow, M.P.; Wu, S.J.; Kawalekar, O.U.; et al. A highly optimized DNA vaccine confers complete protective immunity against high-dose lethal lymphocytic choriomeningitis virus challenge. Vaccine 2011, 29, 6755–6762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shedlock, D.J.; Talbott, K.T.; Wu, S.J.; Wilson, C.M.; Muthumani, K.; Boyer, J.D.; Sardesai, N.Y.; Awasthi, S.; Weiner, D.B. Vaccination with synthetic constructs expressing cytomegalovirus immunogens is highly T cell immunogenic in mice. Hum. Vaccine Immunother. 2012, 8, 1668–1681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mallilankaraman, K.; Shedlock, D.J.; Bao, H.; Kawalekar, O.U.; Fagone, P.; Ramanathan, A.A.; Ferraro, B.; Stabenow, J.; Vijayachari, P.; Sundaram, S.G.; et al. A DNA vaccine against chikungunya virus is protective in mice and induces neutralizing antibodies in mice and nonhuman primates. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2011, 5, e928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muthumani, K.; Lankaraman, K.M.; Laddy, D.J.; Sundaram, S.G.; Chung, C.W.; Sako, E.; Wu, L.; Khan, A.; Sardesai, N.; Kim, J.J.; et al. Immunogenicity of novel consensus-based DNA vaccines against chikungunya virus. Vaccine 2008, 26, 5128–5134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagarazzi, M.L.; Yan, J.; Morrow, M.P.; Shen, X.; Parker, R.L.; Lee, J.C.; Giffear, M.; Pankhong, P.; Khan, A.S.; Broderick, K.E.; et al. Immunotherapy against HPV16/18 generates potent th1 and cytotoxic cellular immune responses. Sci. Transl. Med. 2012, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kublin, J. Welcome to the HVTNEWS. Available online: http://www.hvtn.org/science/hvtnews/HVTNews-SpecialEdition-Sept2011-web.pdf (accessed on 1 November 2013).
- Kutzler, M.A.; Weiner, D.B. DNA vaccines: Ready for prime time? Nat. Rev. Genet. 2008, 9, 776–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalams, S.A.; Parker, S.D.; Elizaga, M.; Metch, B.; Edupuganti, S.; Hural, J.; de Rosa, S.; Carter, D.K.; Rybczyk, K.; Frank, I.; et al. Safety and comparative immunogenicity of an HIV-1 DNA vaccine in combination with plasmid interleukin 12 and impact of intramuscular electroporation for delivery. J. Infect. Dis. 2013, 208, 818–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kee, S.T.; Gehl, J.; Lee, E.W. Clinical Aspects of Electroporation, 1st ed.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2011; p. 268. [Google Scholar]
- Laddy, D.J.; Yan, J.; Kutzler, M.; Kobasa, D.; Kobinger, G.P.; Khan, A.S.; Greenhouse, J.; Sardesai, N.Y.; Draghia-Akli, R.; Weiner, D.B. Heterosubtypic protection against pathogenic human and avian influenza viruses via in vivo electroporation of synthetic consensus DNA antigens. PLoS One 2008, 3, e2517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, J.; Yoon, H.; Kumar, S.; Ramanathan, M.P.; Corbitt, N.; Kutzler, M.; Dai, A.; Boyer, J.D.; Weiner, D.B. Enhanced cellular immune responses elicited by an engineered HIV-1 subtype B consensus-based envelope DNA vaccine. Mol. Ther. 2007, 15, 411–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henke, A.; Chiang, C.S.; Zell, R.; Stelzner, A. Co-expression of interleukin-2 to increase the efficacy of DNA vaccine-mediated protection in coxsackievirus B3-infected mice. Antivir. Res. 2004, 64, 131–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takahashi, S.; Yotnda, P.; Rousseau, R.F.; Mei, Z.; Smith, S.; Rill, D.; Younes, A.; Brenner, M.K. Transgenic expression of CD40L and interleukin-2 induces an autologous antitumor immune response in patients with non-hodgkin’s lymphoma. Cancer Gene Ther. 2001, 8, 378–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santra, S.; Barouch, D.H.; Sharpe, A.H.; Letvin, N.L. B7 co-stimulatory requirements differ for induction of immune responses by DNA, protein and recombinant pox virus vaccination. Eur. J. Immunol. 2000, 30, 2650–2659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beignon, A.S.; McKenna, K.; Skoberne, M.; Manches, O.; DaSilva, I.; Kavanagh, D.G.; Larsson, M.; Gorelick, R.J.; Lifson, J.D.; Bhardwaj, N. Endocytosis of HIV-1 activates plasmacytoid dendritic cells via toll-like receptor-viral rna interactions. J. Clin. Invest. 2005, 115, 3265–3275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palma, C.; Vendetti, S.; Cassone, A. Role of 4-1bb receptor in the control played by CD8+ T cells on IFN-gamma production by mycobacterium tuberculosis antigen-specific CD4+ T cells. PLoS One 2010, 5, e11019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Auten, M.W.; Huang, W.; Dai, G.; Ramsay, A.J. Cd40 ligand enhances immunogenicity of vector-based vaccines in immunocompetent and CD4+ T cell deficient individuals. Vaccine 2012, 30, 2768–2777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sin, J.I. Myd88 signal is required for more efficient induction of Ag-specific adaptive immune responses and antitumor resistance in a human papillomavirus E7 DNA vaccine model. Vaccine 2011, 29, 4125–4131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belisle, S.E.; Yin, J.; Shedlock, D.J.; Dai, A.; Yan, J.; Hirao, L.; Kutzler, M.A.; Lewis, M.G.; Andersen, H.; Lank, S.M.; et al. Long-term programming of antigen-specific immunity from gene expression signatures in the PBMC of rhesus macaques immunized with an SIV DNA vaccine. PLoS One 2011, 6, e19681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirao, L.A.; Wu, L.; Khan, A.S.; Satishchandran, A.; Draghia-Akli, R.; Weiner, D.B. Intradermal/subcutaneous immunization by electroporation improves plasmid vaccine delivery and potency in pigs and rhesus macaques. Vaccine 2008, 26, 440–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fagone, P.; Shedlock, D.J.; Bao, H.; Kawalekar, O.U.; Yan, J.; Gupta, D.; Morrow, M.P.; Patel, A.; Kobinger, G.P.; Muthumani, K.; et al. Molecular adjuvant HMGB1 enhances anti-influenza immunity during DNA vaccination. Gene Ther. 2011, 18, 1070–1077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muthumani, G.; Laddy, D.J.; Sundaram, S.G.; Fagone, P.; Shedlock, D.J.; Kannan, S.; Wu, L.; Chung, C.W.; Lankaraman, K.M.; Burns, J.; et al. Co-immunization with an optimized plasmid-encoded immune stimulatory interleukin, high-mobility group box 1 protein, results in enhanced interferon-gamma secretion by antigen-specific cd8 t cells. Immunology 2009, 128, e612–e620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kutzler, M.A.; Kraynyak, K.A.; Nagle, S.J.; Parkinson, R.M.; Zharikova, D.; Chattergoon, M.; Maguire, H.; Muthumani, K.; Ugen, K.; Weiner, D.B. Plasmids encoding the mucosal chemokines ccl27 and ccl28 are effective adjuvants in eliciting antigen-specific immunity in vivo. Gene Ther. 2010, 17, 72–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boyer, J.D.; Robinson, T.M.; Kutzler, M.A.; Parkinson, R.; Calarota, S.A.; Sidhu, M.K.; Muthumani, K.; Lewis, M.; Pavlakis, G.; Felber, B.; et al. SIV DNA vaccine co-administered with IL-12 expression plasmid enhances CD8 SIV cellular immune responses in cynomolgus macaques. J. Med. Primatol. 2005, 34, 262–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirao, L.A.; Wu, L.; Khan, A.S.; Hokey, D.A.; Yan, J.; Dai, A.; Betts, M.R.; Draghia-Akli, R.; Weiner, D.B. Combined effects of IL-12 and electroporation enhances the potency of DNA vaccination in macaques. Vaccine 2008, 26, 3112–3120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boyer, J.D.; Robinson, T.M.; Kutzler, M.A.; Vansant, G.; Hokey, D.A.; Kumar, S.; Parkinson, R.; Wu, L.; Sidhu, M.K.; Pavlakis, G.N.; et al. Protection against simian/human immunodeficiency virus (SHIV) 89.6 P in macaques after coimmunization with shiv antigen and IL-15 plasmid. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 18648–18653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pietila, T.E.; Veckman, V.; Lehtonen, A.; Lin, R.; Hiscott, J.; Julkunen, I. Multiple NF-κb and IFN regulatory factor family transcription factors regulate CCL19 gene expression in human monocyte-derived dendritic cells. J. Immunol. 2007, 178, 253–261. [Google Scholar]
- Gocke, A.R.; Hussain, R.Z.; Yang, Y.; Peng, H.; Weiner, J.; Ben, L.H.; Drew, P.D.; Stuve, O.; Lovett-Racke, A.E.; Racke, M.K. Transcriptional modulation of the immune response by peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-{alpha} agonists in autoimmune disease. J. Immunol. 2009, 182, 4479–4487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilmore, T.D.; Herscovitch, M. Inhibitors of NF-kappab signaling: 785 and counting. Oncogene 2006, 25, 6887–6899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, S.M.; Tran, A.C.; Grilli, M.; Lenardo, M.J. Nf-κ B subunit regulation in nontransformed CD4+ T lymphocytes. Science 1992, 256, 1452–1456. [Google Scholar]
- Doi, T.S.; Takahashi, T.; Taguchi, O.; Azuma, T.; Obata, Y. Nf-κb rela-deficient lymphocytes: Normal development of T cells and B cells, impaired production of IGA and IGG1 and reduced proliferative responses. J. Exp. Med. 1997, 185, 953–961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouwmeester, T.; Bauch, A.; Ruffner, H.; Angrand, P.O.; Bergamini, G.; Croughton, K.; Cruciat, C.; Eberhard, D.; Gagneur, J.; Ghidelli, S.; et al. A physical and functional map of the human TNF-α/NF-κb signal transduction pathway. Nat. Cell Biol. 2004, 6, 97–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DiDonato, J.A. IKK alpha on center stage. Sci. STKE 2001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DiDonato, J.A.; Hayakawa, M.; Rothwarf, D.M.; Zandi, E.; Karin, M. A cytokine-responsive ikappab kinase that activates the transcription factor nf-kappab. Nature 1997, 388, 548–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DiDonato, J.A.; Mercurio, F.; Karin, M. Nf-κb and the link between inflammation and cancer. Immunol. Rev. 2012, 246, 379–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vallabhapurapu, S.; Karin, M. Regulation and function of NF-κb transcription factors in the immune system. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2009, 27, 693–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, D.; Wu, J.; Zhang, R.; Chen, L. T-bet acts as a powerful adjuvant in AG85B DNA-based vaccination against tuberculosis. Mol. Med. Rep. 2012, 6, 139–144. [Google Scholar]
- Martins, G.A.; Hutchins, A.S.; Reiner, S.L. Transcriptional activators of helper T cell fate are required for establishment but not maintenance of signature cytokine expression. J. Immunol. 2005, 175, 5981–5985. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, J.S.; Kim, J.J.; Hwang, D.; Choo, A.Y.; Dang, K.; Maguire, H.; Kudchodkar, S.; Ramanathan, M.P.; Weiner, D.B. Induction of potent Th1-type immune responses from a novel DNA vaccine for west nile virus new york isolate (WNV-NY1999). J. Infect. Dis. 2001, 184, 809–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Egan, M.A.; Megati, S.; Roopchand, V.; Garcia-Hand, D.; Luckay, A.; Chong, S.Y.; Rosati, M.; Sackitey, S.; Weiner, D.B.; Felber, B.K.; et al. Rational design of a plasmid DNA vaccine capable of eliciting cell-mediated immune responses to multiple hiv antigens in mice. Vaccine 2006, 24, 4510–4523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muthumani, K.; Zhang, D.; Dayes, N.S.; Hwang, D.S.; Calarota, S.A.; Choo, A.Y.; Boyer, J.D.; Weiner, D.B. Novel engineered HIV-1 east african clade-a gp160 plasmid construct induces strong humoral and cell-mediated immune responses in vivo. Virology 2003, 314, 134–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muthumani, K.; Choo, A.Y.; Zong, W.X.; Madesh, M.; Hwang, D.S.; Premkumar, A.; Thieu, K.P.; Emmanuel, J.; Kumar, S.; Thompson, C.B.; et al. The HIV-1 vpr and glucocorticoid receptor complex is a gain-of-function interaction that prevents the nuclear localization of PARP-1. Nat. Cell Biol. 2006, 8, 170–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muthumani, K.; Shedlock, D.J.; Choo, D.K.; Fagone, P.; Kawalekar, O.U.; Goodman, J.; Bian, C.B.; Ramanathan, A.A.; Atman, P.; Tebas, P.; et al. HIV-mediated phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/serine-threonine kinase activation in APCS leads to programmed death-1 ligand upregulation and suppression of HIV-specific CD8 T cells. J. Immunol. 2011, 187, 2932–2943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muthumani, K.; Choo, A.Y.; Shedlock, D.J.; Laddy, D.J.; Sundaram, S.G.; Hirao, L.; Wu, L.; Thieu, K.P.; Chung, C.W.; Lankaraman, K.M.; et al. Human immunodeficiency virus type 1 Nef induces programmed death 1 expression through a p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase-dependent mechanism. J. Virol. 2008, 82, 11536–11544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muthumani, K. Transient transfection and luciferase assay. Protoc. Exchange 2006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szabo, S.J.; Kim, S.T.; Costa, G.L.; Zhang, X.; Fathman, C.G.; Glimcher, L.H. A novel transcription factor, T-bet, directs Th1 lineage commitment. Cell 2000, 100, 655–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shedlock, D.J.; Shen, H. Requirement for CD4 T cell help in generating functional CD8 T cell memory. Science 2003, 300, 337–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirao, L.A.; Wu, L.; Satishchandran, A.; Khan, A.S.; Draghia-Akli, R.; Finnefrock, A.C.; Bett, A.J.; Betts, M.R.; Casimiro, D.R.; Sardesai, N.Y.; et al. Comparative analysis of immune responses induced by vaccination with SIV antigens by recombinant AD5 vector or plasmid DNA in rhesus macaques. Mol. Ther. 2010, 18, 1568–1576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GraphPad Prism5 Software. GraphPad Software, Inc.: La Jolla, CA, USA, 2013.
- Zloza, A.; Kohlhapp, F.J.; Lyons, G.E.; Schenkel, J.M.; Moore, T.V.; Lacek, A.T.; O’Sullivan, J.A.; Varanasi, V.; Williams, J.W.; Jagoda, M.C.; et al. Nkg2d signaling on CD8+ T cells represses T-bet and rescues CD4-unhelped CD8+ T cell memory recall but not effector responses. Nat. Med. 2012, 18, 422–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, M.Y.; Kim, H.S.; Hong, H.J.; Youn, B.S.; Kim, T.S. Adiponectin induces dendritic cell activation via PLCGamma/JNK/NF-κb pathways, leading to Th1 and Th17 polarization. J. Immunol. 2012, 188, 2592–2601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tas, S.W.; de Jong, E.C.; Hajji, N.; May, M.J.; Ghosh, S.; Vervoordeldonk, M.J.; Tak, P.P. Selective inhibition of NF-κb in dendritic cells by the nemo-binding domain peptide blocks maturation and prevents T cell proliferation and polarization. Eur. J. Immunol. 2005, 35, 1164–1174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouaaz, F.; Arron, J.; Zheng, Y.; Choi, Y.; Beg, A.A. Dendritic cell development and survival require distinct NF-κb subunits. Immunity 2002, 16, 257–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.C.; Rosenbloom, C.L.; Anderson, D.C.; Manning, A.M. Selective inhibition of E-selectin, vascular cell adhesion molecule-1, and intercellular adhesion molecule-1 expression by inhibitors of I kappa B-alpha phosphorylation. J. Immunol. 1995, 155, 3538–3545. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, N.S.; McHeyzer-Williams, L.J.; Okitsu, S.L.; Burris, T.P.; Reiner, S.L.; McHeyzer-Williams, M.G. Divergent transcriptional programming of class-specific B cell memory by T-bet and roralpha. Nat. Immunol. 2012, 13, 604–611. [Google Scholar]
- Perkins, N.D. The diverse and complex roles of NF-κb subunits in cancer. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2012, 12, 121–132. [Google Scholar]
- Imanifooladi, A.A.; Yazdani, S.; Nourani, M.R. The role of nuclear factor-kappab in inflammatory lung disease. Inflamm. Allergy Drug Targets 2000, 9, 197–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2014 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Shedlock, D.J.; Tingey, C.; Mahadevan, L.; Hutnick, N.; Reuschel, E.L.; Kudchodkar, S.; Flingai, S.; Yan, J.; Kim, J.J.; Ugen, K.E.; et al. Co-Administration of Molecular Adjuvants Expressing NF-Kappa B Subunit p65/RelA or Type-1 Transactivator T-bet Enhance Antigen Specific DNA Vaccine-Induced Immunity. Vaccines 2014, 2, 196-215. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines2020196
Shedlock DJ, Tingey C, Mahadevan L, Hutnick N, Reuschel EL, Kudchodkar S, Flingai S, Yan J, Kim JJ, Ugen KE, et al. Co-Administration of Molecular Adjuvants Expressing NF-Kappa B Subunit p65/RelA or Type-1 Transactivator T-bet Enhance Antigen Specific DNA Vaccine-Induced Immunity. Vaccines. 2014; 2(2):196-215. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines2020196
Chicago/Turabian StyleShedlock, Devon J., Colleen Tingey, Lavanya Mahadevan, Natalie Hutnick, Emma L. Reuschel, Sagar Kudchodkar, Seleeke Flingai, Jenny Yan, Joseph J. Kim, Kenneth E. Ugen, and et al. 2014. "Co-Administration of Molecular Adjuvants Expressing NF-Kappa B Subunit p65/RelA or Type-1 Transactivator T-bet Enhance Antigen Specific DNA Vaccine-Induced Immunity" Vaccines 2, no. 2: 196-215. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines2020196
APA StyleShedlock, D. J., Tingey, C., Mahadevan, L., Hutnick, N., Reuschel, E. L., Kudchodkar, S., Flingai, S., Yan, J., Kim, J. J., Ugen, K. E., Weiner, D. B., & Muthumani, K. (2014). Co-Administration of Molecular Adjuvants Expressing NF-Kappa B Subunit p65/RelA or Type-1 Transactivator T-bet Enhance Antigen Specific DNA Vaccine-Induced Immunity. Vaccines, 2(2), 196-215. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines2020196



