Baseline Anti-SARS-CoV-2 IgG and Protection from Symptomatic Infection: Post Hoc Analysis of the SCTV01E Phase 3 Randomized Trial
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design and Participants
2.2. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Proportion of Participants with Different Baseline IgG Levels with the Enrollment Date
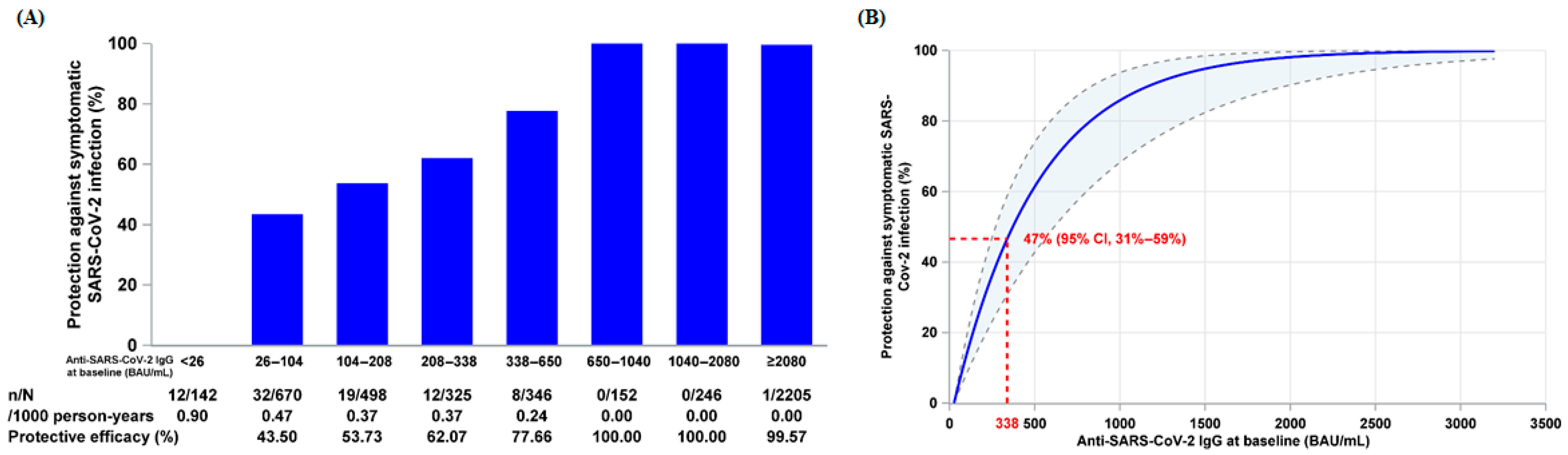
3.2. Relationship Between Baseline Anti-SARS-CoV-2 IgG and Relative Protection Against Symptomatic SARS-CoV-2 Infection
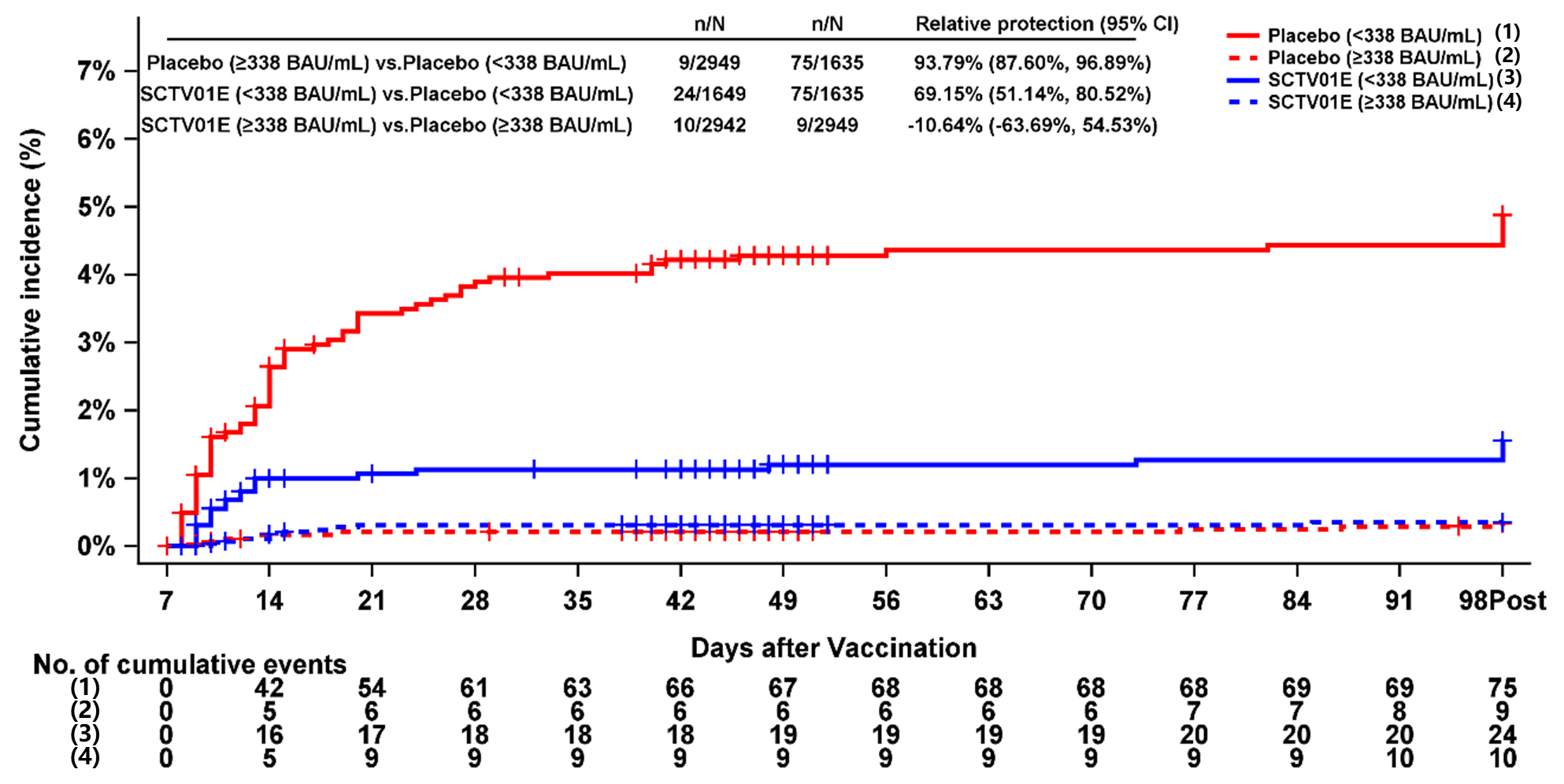
3.3. Stratified Analysis of Relative Protection Against Symptomatic SARS-CoV-2 Infection by Baseline IgG Levels
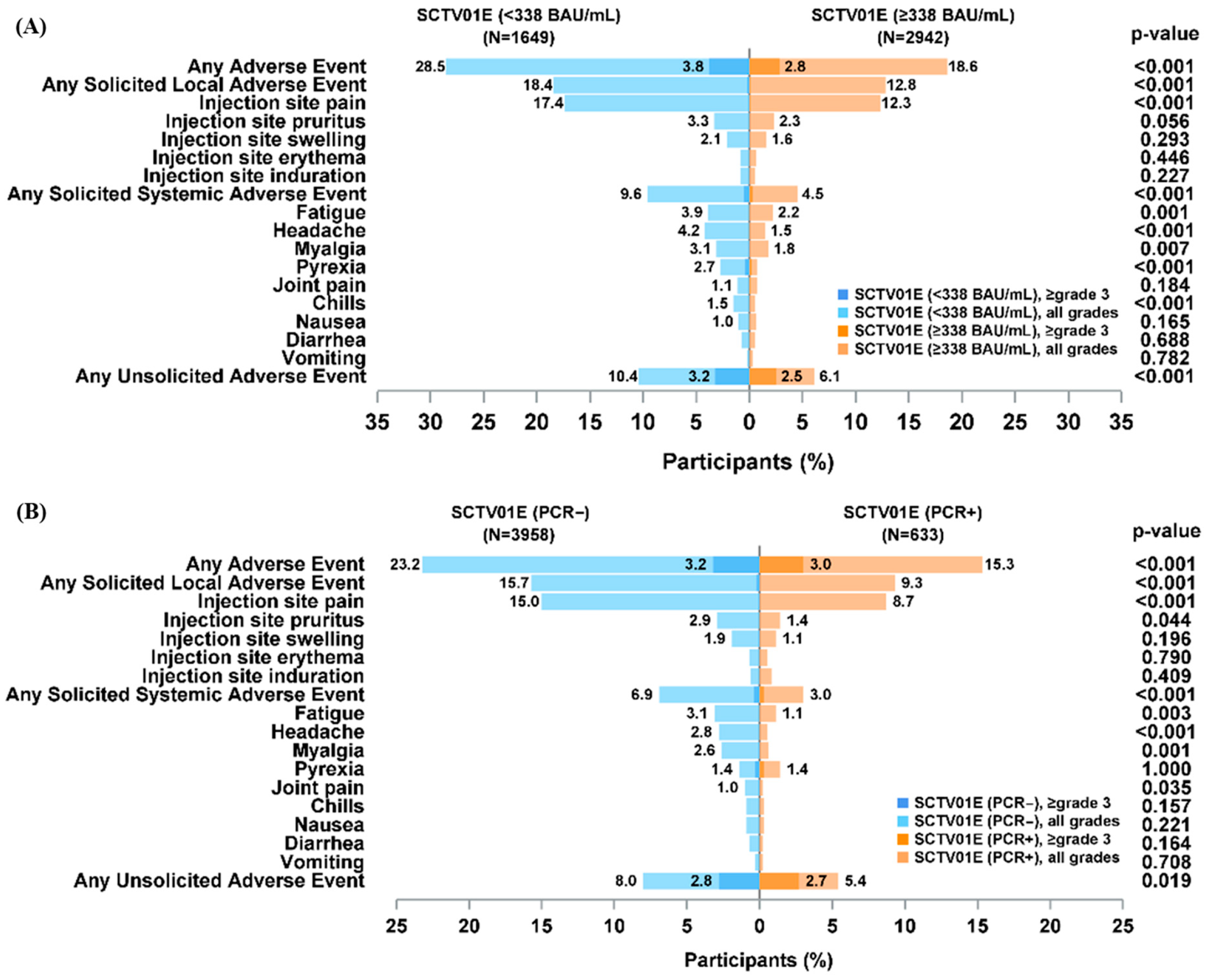
3.4. Safety
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- WHO COVID-19 Dashboard. Available online: https://data.who.int/dashboards/covid19/deaths?n=c (accessed on 30 December 2024).
- Calabrò, G.E.; Pappalardo, C.; D’ambrosio, F.; Vece, M.; Lupi, C.; Lontano, A.; Di Russo, M.; Ricciardi, R.; de Waure, C. The Impact of Vaccination on COVID-19 Burden of Disease in the Adult and Elderly Population: A Systematic Review of Italian Evidence. Vaccines 2023, 11, 1011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Polack, F.P.; Thomas, S.J.; Kitchin, N.; Absalon, J.; Gurtman, A.; Lockhart, S.; Perez, J.L.; Pérez Marc, G.; Moreira, E.D.; Zerbini, C.; et al. Safety and Efficacy of the BNT162b2 mRNA COVID-19 Vaccine. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 383, 2603–2615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al Kaabi, N.; Zhang, Y.; Xia, S.; Yang, Y.; Al Qahtani, M.M.; Abdulrazzaq, N.; Al Nusair, M.; Hassany, M.; Jawad, J.S.; Abdalla, J. Effect of 2 Inactivated SARS-CoV-2 Vaccines on Symptomatic COVID-19 Infection in Adults: A Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA 2021, 326, 35–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baden, L.R.; El Sahly, H.M.; Essink, B.; Kotloff, K.; Frey, S.; Novak, R.; Diemert, D.; Spector, S.A.; Rouphael, N.; Creech, C.B.; et al. Efficacy and Safety of the mRNA-1273 SARS-CoV-2 Vaccine. N. Engl. J. Med. 2021, 384, 403–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Denning, D.W.; Kilcoyne, A.; Ucer, C. Non-infectious status indicated by detectable IgG antibody to SARS-CoV-2. Br. Dent. J. 2020, 229, 521–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Löfström, E.; Eringfält, A.; Kötz, A.; Wickbom, F.; Tham, J.; Lingman, M.; Nygren, J.M.; Undén, J. Dynamics of IgG-avidity and antibody levels after COVID-19. J. Clin. Virol. 2021, 144, 104986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, L.; Tang, R.; Wu, S.; Guo, X.; Huang, H.; Hou, L.; Chen, X.; Zhu, T.; Gou, J.; Zhong, J.; et al. Antibody persistence and safety after heterologous boosting with orally aerosolised Ad5-nCoV in individuals primed with two-dose CoronaVac previously: 12-month analyses of a randomized controlled trial. Emerg. Microbes Infect. 2023, 12, 2155251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, X.-M.; Xu, Q.-Y.; Jia, Z.-J.; Wu, M.-J.; Liu, Y.-Y.; Lin, L.-R.; Liu, L.-L.; Yang, T.-C. A Third Dose of an Inactivated Vaccine Dramatically Increased the Levels and Decay Times of Anti-SARS-CoV-2 Antibodies, but Disappointingly Declined Again: A Prospective, Longitudinal, Cohort Study at 18 Serial Time Points over 368 Days. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 876037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lumley, S.F.; O’Donnell, D.; Stoesser, N.E.; Matthews, P.C.; Howarth, A.; Hatch, S.B.; Marsden, B.D.; Cox, S.; James, T.; Warren, F.; et al. Antibody Status and Incidence of SARS-CoV-2 Infection in Health Care Workers. N. Engl. J. Med. 2021, 384, 533–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goldblatt, D.; Fiore-Gartland, A.; Johnson, M.; Hunt, A.; Bengt, C.; Zavadska, D.; Snipe, H.D.; Brown, J.S.; Workman, L.; Zar, H.J.; et al. Towards a population-based threshold of protection for COVID-19 vaccines. Vaccine 2022, 40, 306–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- China CDC. Available online: https://www.chinacdc.cn/jksj/xgbdyq/202411/t20241112_302571.html (accessed on 25 January 2023).
- Bai, Y.; Peng, Z.; Wei, F.; Jin, Z.; Wang, J.; Xu, X.; Zhang, X.; Xu, J.; Ren, Z.; Lu, B.; et al. Study on the COVID-19 epidemic in mainland China between November 2022 and January 2023, with prediction of its tendency. J. Biosaf. Biosecurity 2023, 5, 39–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, R.; Zhao, J.; Zhu, X.; Guan, Q.; Liu, S.; Li, M.; Gao, J.; Tan, J.; Cao, F.; Gan, B.; et al. Efficacy of the tetravalent protein COVID-19 vaccine, SCTV01E: A phase 3 double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled trial. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 6255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Weng, Z.; Zheng, Y.; Zheng, M.; Chen, W.; He, H.; Ye, X.; Zheng, Y.; Xie, J.; Zheng, K.; et al. Epidemiological and clinical features of SARS-CoV-2 Omicron variant infection in Quanzhou, Fujian province: A retrospective study. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 22152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hannawi, S.; Abuquta, A.; Eldin, L.S.; Hassan, A.; Alamadi, A.; Gao, C.; Baidoo, A.A.H.; Yang, X.; Su, H.; Zhang, J.; et al. Immunogenicity and Safety of Omicron-Containing Multivalent COVID-19 Vaccines in Unvaccinated and Previously Vaccinated Adults. Vaccines 2024, 12, 1109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hannawi, S.; Eldin, L.S.; Abuquta, A.; Alamadi, A.; Mahmoud, S.A.; Li, J.; Chen, Y.; Xie, L. Safety and immunogenicity of a bivalent SARS-CoV-2 protein booster vaccine, SCTV01C in adults previously vaccinated with inactivated vaccine: A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled phase 1/2 clinical trial. J. Infect. 2023, 86, 154–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hannawi, S.; Yan, L.; Eldin, L.S.; Abuquta, A.; Alamadi, A.; Mahmoud, S.A.; Hassan, A.; Zhang, M.; Gao, C.; Chen, Y.; et al. Safety and immunogenicity of multivalent SARS-CoV-2 protein vaccines: A randomized phase 3 trial. EClinicalMedicine 2023, 64, 102195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, G.; Zhao, K.; Zhao, X.; Cui, Y.; He, P.; Zhang, T.; Wang, Y.; Shi, R.; Li, Y.; Wang, Q.; et al. Sustained immunogenicity of bivalent protein COVID-19 vaccine SCTV01C against antigen matched and mismatched variants. Expert Rev. Vaccines 2025, 24, 128–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yan, L.; Yi, J.; Liu, D.; Li, J.; Baidoo, A.A.H.; Xie, L. Baseline Anti-SARS-CoV-2 IgG and Protection from Symptomatic Infection: Post Hoc Analysis of the SCTV01E Phase 3 Randomized Trial. Vaccines 2025, 13, 984. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines13090984
Yan L, Yi J, Liu D, Li J, Baidoo AAH, Xie L. Baseline Anti-SARS-CoV-2 IgG and Protection from Symptomatic Infection: Post Hoc Analysis of the SCTV01E Phase 3 Randomized Trial. Vaccines. 2025; 13(9):984. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines13090984
Chicago/Turabian StyleYan, Lixin, Jiang Yi, Dongfang Liu, Jian Li, Adam Abdul Hakeem Baidoo, and Liangzhi Xie. 2025. "Baseline Anti-SARS-CoV-2 IgG and Protection from Symptomatic Infection: Post Hoc Analysis of the SCTV01E Phase 3 Randomized Trial" Vaccines 13, no. 9: 984. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines13090984
APA StyleYan, L., Yi, J., Liu, D., Li, J., Baidoo, A. A. H., & Xie, L. (2025). Baseline Anti-SARS-CoV-2 IgG and Protection from Symptomatic Infection: Post Hoc Analysis of the SCTV01E Phase 3 Randomized Trial. Vaccines, 13(9), 984. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines13090984





