Chronic Diseases and Influenza Vaccines
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Global and China’s Current Chronic Disease Burden
3. Influenza Virus Infection and Immune Dysfunction in Chronic Diseases
3.1. Immune Dysregulation Induced by Chronic Diseases
3.2. Direct Immunopathological Injury and Hypersensitive Reactions Induced by Influenza
3.2.1. Cytokine Storm
3.2.2. Immunosuppression
3.2.3. Secondary Infection
3.3. Influenza Infection Exacerbates Chronic Diseases: Pathological Mechanisms
4. Epidemiology
5. Application of Influenza Vaccines
6. Efficacy of Influenza Vaccines in Patients with Chronic Diseases
7. Influenza Vaccination Safety and Efficacy in Immunocompromised Populations
8. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Piovani, D.; Nikolopoulos, G.K.; Bonovas, S. Non-Communicable Diseases: The Invisible Epidemic. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 5939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ngaruiya, C.; Bernstein, R.; Leff, R.; Wallace, L.; Agrawal, P.; Selvam, A.; Hersey, D.; Hayward, A. Systematic review on chronic non-communicable disease in disaster settings. BMC Public Health 2022, 22, 1234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, H.; Wang, M.; Qin, C.; Shi, Y.; Mandizadza, O.O.; Ni, H.; Ji, C. Trends in the burden of chronic diseases attributable to diet-related risk factors from 1990 to 2021 and the global projections through 2030: A population-based study. Front. Nutr. 2025, 12, 1570321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, M.; Zhang, J.; Liang, D.; Qiu, J.; Fu, Y.; Zeng, Z.; Han, J.; Zheng, J.; Lin, L. Global and regional trends and projections of chronic pain from 1990 to 2035: Analyses based on global burden of diseases study 2019. Br. J. Pain. 2024, 19, 20494637241310697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitchell, E.; Walker, R. Global ageing: Successes, challenges and opportunities. Br. J. Hosp. Med. 2020, 81, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fong, J.H. Disability incidence and functional decline among older adults with major chronic diseases. BMC Geriatr. 2019, 19, 323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, L.; Cai, M.; Liu, Q.; Ying, X.; Wu, S. Trends and regional variations in chronic diseases and their risk factors in China: An observational study based on National Health Service Surveys. Int. J. Equity Health 2023, 22, 120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandes, J.B.; Teixeira, F.; Godinho, C. Personalized Care and Treatment Compliance in Chronic Conditions. J. Pers. Med. 2022, 12, 737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jayathilaka, R.; Joachim, S.; Mallikarachchi, V.; Perera, N.; Ranawaka, D. Do chronic illnesses and poverty go hand in hand? PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0241232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holman, H.R. The Relation of the Chronic Disease Epidemic to the Health Care Crisis. ACR Open Rheumatol. 2020, 2, 167–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tu, W.J.; Zhang, X.; Wang, H.Q.; Fan, Y.Y.; Cao, J.L.; Ren, Y.L.; Bu, S.; Bian, H.T.; Yue, W.; Li, J.L.; et al. Establishing integrated chronic non-communicable disease management clinics to address China’s looming health burden. Mil. Med. Res. 2025, 12, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peteranderl, C.; Herold, S.; Schmoldt, C. Human Influenza Virus Infections. Semin. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2016, 37, 487–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pleschka, S. Overview of influenza viruses. Curr. Top. Microbiol. Immunol. 2013, 370, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harrington, W.N.; Kackos, C.M.; Webby, R.J. The evolution and future of influenza pandemic preparedness. Exp. Mol. Med. 2021, 53, 737–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pascual Hernandez, A.; Pachon, J. The first influenza pandemic of the 21st century. The REIPI/SEIMC experience. Enferm. Infecc. Microbiol. Clin. 2012, 30 (Suppl. S4), 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scalera, N.M.; Mossad, S.B. The first pandemic of the 21st century: A review of the 2009 pandemic variant influenza A (H1N1) virus. Postgrad. Med. 2009, 121, 43–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saunders-Hastings, P.R.; Krewski, D. Reviewing the History of Pandemic Influenza: Understanding Patterns of Emergence and Transmission. Pathogens 2016, 5, 66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Monto, A.S.; Fukuda, K. Lessons From Influenza Pandemics of the Last 100 Years. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2020, 70, 951–957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, B.; Asha, K.; Khanna, M.; Ronsard, L.; Meseko, C.A.; Sanicas, M. The emerging influenza virus threat: Status and new prospects for its therapy and control. Arch. Virol. 2018, 163, 831–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shao, W.; Li, X.; Goraya, M.U.; Wang, S.; Chen, J.L. Evolution of Influenza A Virus by Mutation and Re-Assortment. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 1650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrova, V.N.; Russell, C.A. The evolution of seasonal influenza viruses. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2018, 16, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keilich, S.R.; Bartley, J.M.; Haynes, L. Diminished immune responses with aging predispose older adults to common and uncommon influenza complications. Cell Immunol. 2019, 345, 103992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Macias, A.E.; McElhaney, J.E.; Chaves, S.S.; Nealon, J.; Nunes, M.C.; Samson, S.I.; Seet, B.T.; Weinke, T.; Yu, H. The disease burden of influenza beyond respiratory illness. Vaccine 2021, 39 (Suppl. S1), A6–A14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalil, A.C.; Thomas, P.G. Influenza virus-related critical illness: Pathophysiology and epidemiology. Crit. Care 2019, 23, 258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boutayeb, A. The double burden of communicable and non-communicable diseases in developing countries. Trans. R. Soc. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2006, 100, 191–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boutayeb, A.; Boutayeb, S. The burden of non communicable diseases in developing countries. Int. J. Equity Health 2005, 4, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Z.Y.; Hua, Y.T.; Huang, W.T.; Wu, J.S.; Ou, H.T. Reduced risks of influenza-associated hospitalization and complications following vaccination among over 2 million older individuals: A nationwide study using target trial emulation framework. BMC Med. 2025, 23, 157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, J.; Cong, S.; Wang, N.; Bao, H.; Wang, B.; Feng, Y.; Lv, X.; Zhang, Y.; Zha, Z.; Yu, L.; et al. Influenza vaccination rate and its association with chronic diseases in China: Results of a national cross-sectional study. Vaccine 2020, 38, 2503–2511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calabro, G.E.; D’Ambrosio, F.; Fallani, E.; Ricciardi, W. Influenza Vaccination Assessment according to a Value-Based Health Care Approach. Vaccines 2022, 10, 1675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chockalingam, A.; Campbell, N.R.; Fodor, J.G. Worldwide epidemic of hypertension. Can. J. Cardiol. 2006, 22, 553–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luk, A.O. Changing landscape of diabetes in Asia—What are the unmet needs? J. Diabetes Investig. 2024, 15, 402–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joynt Maddox, K.E.; Elkind, M.S.V.; Aparicio, H.J.; Commodore-Mensah, Y.; de Ferranti, S.D.; Dowd, W.N.; Hernandez, A.F.; Khavjou, O.; Michos, E.D.; Palaniappan, L.; et al. Forecasting the Burden of Cardiovascular Disease and Stroke in the United States Through 2050-Prevalence of Risk Factors and Disease: A Presidential Advisory From the American Heart Association. Circulation 2024, 150, e65–e88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kazi, D.S.; Elkind, M.S.V.; Deutsch, A.; Dowd, W.N.; Heidenreich, P.; Khavjou, O.; Mark, D.; Mussolino, M.E.; Ovbiagele, B.; Patel, S.S.; et al. Forecasting the Economic Burden of Cardiovascular Disease and Stroke in the United States Through 2050: A Presidential Advisory From the American Heart Association. Circulation 2024, 150, e89–e101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nedkoff, L.; Briffa, T.; Zemedikun, D.; Herrington, S.; Wright, F.L. Global Trends in Atherosclerotic Cardiovascular Disease. Clin. Ther. 2023, 45, 1087–1091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsao, C.W.; Aday, A.W.; Almarzooq, Z.I.; Anderson, C.A.M.; Arora, P.; Avery, C.L.; Baker-Smith, C.M.; Beaton, A.Z.; Boehme, A.K.; Buxton, A.E.; et al. Heart Disease and Stroke Statistics-2023 Update: A Report From the American Heart Association. Circulation 2023, 147, e93–e621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yahya, T.; Jilani, M.H.; Khan, S.U.; Mszar, R.; Hassan, S.Z.; Blaha, M.J.; Blankstein, R.; Virani, S.S.; Johansen, M.C.; Vahidy, F.; et al. Stroke in young adults: Current trends, opportunities for prevention and pathways forward. Am. J. Prev. Cardiol. 2020, 3, 100085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bizuayehu, H.M.; Ahmed, K.Y.; Kibret, G.D.; Dadi, A.F.; Belachew, S.A.; Bagade, T.; Tegegne, T.K.; Venchiarutti, R.L.; Kibret, K.T.; Hailegebireal, A.H.; et al. Global Disparities of Cancer and Its Projected Burden in 2050. JAMA Netw. Open 2024, 7, e2443198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soerjomataram, I.; Bray, F. Planning for tomorrow: Global cancer incidence and the role of prevention 2020–2070. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2021, 18, 663–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.Y.; Gao, T.Y.; Fang, W.; Xian-Yu, C.Y.; Deng, N.J.; Zhang, C.; Niu, Y.M. Global, regional and national burden of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease over a 30-year period: Estimates from the 1990 to 2019 Global Burden of Disease Study. Respirology 2023, 28, 29–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boers, E.; Barrett, M.; Su, J.G.; Benjafield, A.V.; Sinha, S.; Kaye, L.; Zar, H.J.; Vuong, V.; Tellez, D.; Gondalia, R.; et al. Global Burden of Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease Through 2050. JAMA Netw. Open 2023, 6, e2346598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pirillo, A.; Norata, G.D. The burden of hypercholesterolemia and ischemic heart disease in an ageing world. Pharmacol. Res. 2023, 193, 106814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salari, N.; Darvishi, N.; Bartina, Y.; Larti, M.; Kiaei, A.; Hemmati, M.; Shohaimi, S.; Mohammadi, M. Global prevalence of osteoporosis among the world older adults: A comprehensive systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Orthop. Surg. Res. 2021, 16, 669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salari, N.; Ghasemi, H.; Mohammadi, L.; Behzadi, M.H.; Rabieenia, E.; Shohaimi, S.; Mohammadi, M. The global prevalence of osteoporosis in the world: A comprehensive systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Orthop. Surg. Res. 2021, 16, 609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, P.L.; Cui, A.Y.; Hsu, C.J.; Peng, R.; Jiang, N.; Xu, X.H.; Ma, Y.G.; Liu, D.; Lu, H.D. Global, regional prevalence, and risk factors of osteoporosis according to the World Health Organization diagnostic criteria: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Osteoporos. Int. 2022, 33, 2137–2153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kovesdy, C.P. Epidemiology of chronic kidney disease: An update 2022. Kidney Int. Suppl. (2011) 2022, 12, 7–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, L.; Guo, S.; Liu, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Liu, Y.; Zheng, X.; Yu, X.; Shuai, P. Global, regional, and national burden of chronic kidney disease and its underlying etiologies from 1990 to 2021: A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2021. BMC Public Health 2025, 25, 636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shilian, H.; Jing, W.; Cui, C.; Xinchun, W. Analysis of epidemiological trends in chronic diseases of Chinese residents. Aging Med. 2020, 3, 226–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, W.; Chan, J.C.; Wong, T.Y.; Fisher, E.B. Diabetes in China: Epidemiology, pathophysiology and multi-omics. Nat. Metab. 2025, 7, 16–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Center For Cardiovascular Diseases The Writing Committee Of The Report On Cardiovascular Health And Diseases In China. Report on Cardiovascular Health and Diseases in China 2023: An Updated Summary. Biomed. Environ. Sci. 2024, 37, 949–992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, B.; Zheng, R.; Zeng, H.; Wang, S.; Sun, K.; Chen, R.; Li, L.; Wei, W.; He, J. Cancer incidence and mortality in China, 2022. J. Natl. Cancer Cent. 2024, 4, 47–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, K.; Zhang, B.; Lei, S.; Zheng, R.; Liang, X.; Li, L.; Feng, X.; Zhang, S.; Zeng, H.; Yao, Y.; et al. Incidence, mortality, and disability-adjusted life years of female breast cancer in China, 2022. Chin Med. J. 2024, 137, 2429–2436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fang, L.; Gao, P.; Bao, H.; Tang, X.; Wang, B.; Feng, Y.; Cong, S.; Juan, J.; Fan, J.; Lu, K.; et al. Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease in China: A nationwide prevalence study. Lancet Respir. Med. 2018, 6, 421–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Liu, M.; Liu, F.; Chen, S.; Huang, K.; Cao, J.; Shen, C.; Liu, X.; Yu, L.; Zhao, Y.; et al. Age and Genetic Risk Score and Rates of Blood Lipid Changes in China. JAMA Netw. Open 2023, 6, e235565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Y.; Gao, L.; Xie, X.; Tan, S.C. Epidemiology of dyslipidemia in Chinese adults: Meta-analysis of prevalence, awareness, treatment, and control. Popul. Health Metr. 2014, 12, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Shu, B.; Tang, D.Z.; Li, C.G.; Xie, X.W.; Jiang, L.J.; Jiang, X.B.; Chen, B.L.; Lin, X.C.; Wei, X.; et al. The prevalence of osteoporosis in China, a community based cohort study of osteoporosis. Front. Public Health 2023, 11, 1084005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Yu, W.; Yin, X.; Cui, L.; Tang, S.; Jiang, N.; Cui, L.; Zhao, N.; Lin, Q.; Chen, L.; et al. Prevalence of Osteoporosis and Fracture in China: The China Osteoporosis Prevalence Study. JAMA Netw. Open 2021, 4, e2121106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagatini, M.D.; Cardoso, A.M.; Dos Santos, A.A.; Carvalho, F.B. Immune System and Chronic Diseases. J. Immunol. Res. 2017, 2017, 4284327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagatini, M.D.; Cardoso, A.M.; Reschke, C.R.; Carvalho, F.B. Immune System and Chronic Diseases 2018. J. Immunol. Res. 2018, 2018, 8653572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noack, M.; Miossec, P. Th17 and regulatory T cell balance in autoimmune and inflammatory diseases. Autoimmun. Rev. 2014, 13, 668–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, M.; Zhou, Y.; Yao, Z.; Tang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Liao, J.; Cai, X.; Liu, L. T cell dysregulation in rheumatoid arthritis: Recent advances and natural product interventions. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2025, 153, 114499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouyang, W.; Kolls, J.K.; Zheng, Y. The biological functions of T helper 17 cell effector cytokines in inflammation. Immunity 2008, 28, 454–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talaat, R.M.; Mohamed, S.F.; Bassyouni, I.H.; Raouf, A.A. Th1/Th2/Th17/Treg cytokine imbalance in systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) patients: Correlation with disease activity. Cytokine 2015, 72, 146–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Orange, J.S.; Ballas, Z.K. Natural killer cells in human health and disease. Clin. Immunol. 2006, 118, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whiteside, T.L.; Herberman, R.B. Role of human natural killer cells in health and disease. Clin. Diagn. Lab. Immunol. 1994, 1, 125–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, L.; Van Kaer, L. Natural killer T cells in health and disease. Front. Biosci. (Schol. Ed.) 2011, 3, 236–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, Y.; Le, Y.; Xiong, J.; Pei, Y.; Sun, Y. NK Cells in the Pathogenesis of Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 666045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fathollahi, A.; Samimi, L.N.; Akhlaghi, M.; Jamshidi, A.; Mahmoudi, M.; Farhadi, E. The role of NK cells in rheumatoid arthritis. Inflamm. Res. 2021, 70, 1063–1073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thangjam, N.; Dey, B.; Khonglah, Y.; Tiewsoh, I.; Ksoo, R. Natural Killer Cell Count in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus Patients: A Flow Cytometry-Based Study. Cureus 2023, 15, e46885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villasenor-Altamirano, A.B.; Jain, D.; Jeong, Y.; Menon, J.A.; Kamiya, M.; Haider, H.; Manandhar, R.; Sheikh, M.D.A.; Athar, H.; Merriam, L.T.; et al. Activation of CD8(+) T Cells in Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease Lung. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2023, 208, 1177–1195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kemeny, D.M.; Vyas, B.; Vukmanovic-Stejic, M.; Thomas, M.J.; Noble, A.; Loh, L.C.; O’Connor, B.J. CD8(+) T cell subsets and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 1999, 160, S33–S37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lourenco, J.D.; Ito, J.T.; Martins, M.A.; Tiberio, I.; Lopes, F. Th17/Treg Imbalance in Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease: Clinical and Experimental Evidence. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 804919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, H.Y.; Wang, L.; Das, J.K.; Kumar, A.; Ballard, D.J.; Ren, Y.; Xiong, X.; de Figueiredo, P.; Yang, J.M.; Song, J. Control of CD4(+) T cells to restrain inflammatory diseases via eukaryotic elongation factor 2 kinase. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2023, 8, 415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lai, Y.; Zhong, Z.; Li, R.; Liang, T.; He, X.; Liu, Y.; Yu, H.; Zhang, C.; Xiao, Y.; Liu, L.; et al. Unveiling the crucial role of CD8(+) T cell and endothelial cell interaction in rheumatoid arthritis through the integrated analysis of spatial transcriptomics and bulk/single-cell RNA-seq. J. Transl. Autoimmun. 2025, 10, 100285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, P.M.; Tsokos, G.C. The role of CD8(+) T-cell systemic lupus erythematosus pathogenesis: An update. Curr. Opin. Rheumatol. 2021, 33, 586–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Azizi, G.; Jadidi-Niaragh, F.; Mirshafiey, A. Th17 Cells in Immunopathogenesis and treatment of rheumatoid arthritis. Int. J. Rheum. Dis. 2013, 16, 243–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, S.R.; van der Burgh, A.C.; Peeters, R.P.; van Hagen, P.M.; Dalm, V.; Chaker, L. Determinants of Serum Immunoglobulin Levels: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 664526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Megha, K.B.; Mohanan, P.V. Role of immunoglobulin and antibodies in disease management. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2021, 169, 28–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schussler, E.; Beasley, M.B.; Maglione, P.J. Lung Disease in Primary Antibody Deficiencies. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. Pract. 2016, 4, 1039–1052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furst, D.E. Serum immunoglobulins and risk of infection: How low can you go? Semin. Arthritis Rheum. 2009, 39, 18–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Li, P.; Wu, D.; Xu, D.; Hou, Y.; Wang, Q.; Li, M.; Li, Y.; Zeng, X.; Zhang, F.; et al. Serum IgG subclasses in autoimmune diseases. Medicine 2015, 94, e387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, D.; Jiang, W. Infectious diseases, autoantibodies, and autoimmunity. J. Autoimmun. 2023, 137, 102962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaftel, S.S.; Kyrkanides, S.; Olschowka, J.A.; Miller, J.N.; Johnson, R.E.; O’Banion, M.K. Sustained hippocampal IL-1 beta overexpression mediates chronic neuroinflammation and ameliorates Alzheimer plaque pathology. J. Clin. Investig. 2007, 117, 1595–1604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velikova, T.V.; Kabakchieva, P.P.; Assyov, Y.S.; Georgiev Tcapital, A.C. Targeting Inflammatory Cytokines to Improve Type 2 Diabetes Control. Biomed. Res. Int. 2021, 2021, 7297419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tylutka, A.; Walas, L.; Zembron-Lacny, A. Level of IL-6, TNF, and IL-1beta and age-related diseases: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Front. Immunol. 2024, 15, 1330386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pirola, L.; Ferraz, J.C. Role of pro- and anti-inflammatory phenomena in the physiopathology of type 2 diabetes and obesity. World J. Biol. Chem. 2017, 8, 120–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.J.; Han, X.W.; Jiang, Y.H.; Wang, Y.L.; He, X.L.; Liu, D.H.; Huang, J.; Liu, H.H.; Ye, T.C.; Li, S.J.; et al. Impact of inflammation and anti-inflammatory modalities on diabetic cardiomyopathy healing: From fundamental research to therapy. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2023, 123, 110747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lorenzo-Vizcaya, A.; Isenberg, D.A. The use of anti-TNF-alpha therapies for patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Where are we now? Expert. Opin. Biol. Ther. 2021, 21, 639–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, L.J.; Yang, X.; Yu, X.Q. Anti-TNF-alpha therapies in systemic lupus erythematosus. J. Biomed. Biotechnol. 2010, 2010, 465898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogata, A.; Kato, Y.; Higa, S.; Yoshizaki, K. IL-6 inhibitor for the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis: A comprehensive review. Mod. Rheumatol. 2019, 29, 258–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, Y.; Martin Mola, E. IL-6 targeting compared to TNF targeting in rheumatoid arthritis: Studies of olokizumab, sarilumab and sirukumab. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2014, 73, 1595–1597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steiner, G.; Toes, R.E.M. Autoantibodies in rheumatoid arthritis-rheumatoid factor, anticitrullinated protein antibodies and beyond. Curr. Opin. Rheumatol. 2024, 36, 217–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molina, J.M.; Medina, P.G.; Gomez, R.A.; Herrera, J.R.; Martinez, N.L.; Hernandez, B.; Garcia, Y. Autoantibodies against beta cells to predict early insulin requirements in pediatric patients with clinically diagnosed type 2 diabetes. World J. Diabetes 2024, 15, 1717–1725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pihoker, C.; Gilliam, L.K.; Hampe, C.S.; Lernmark, A. Autoantibodies in diabetes. Diabetes 2005, 54 (Suppl. S2), S52–S61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pugliese, A. Autoreactive T cells in type 1 diabetes. J. Clin. Investig. 2017, 127, 2881–2891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Scott, N.A.; Fynch, S.; Elkerbout, L.; Wong, W.W.; Mason, K.D.; Strasser, A.; Huang, D.C.; Kay, T.W.; Thomas, H.E. Autoreactive T cells induce necrosis and not BCL-2-regulated or death receptor-mediated apoptosis or RIPK3-dependent necroptosis of transplanted islets in a mouse model of type 1 diabetes. Diabetologia 2015, 58, 140–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, M.J.; Simmons, K.M.; Cambier, J.C. B cells in type 1 diabetes mellitus and diabetic kidney disease. Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 2017, 13, 712–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neppelenbroek, S.; Blomberg, N.J.; Kampstra, A.S.B.; van der Hem, J.G.K.; Huizinga, T.W.J.; Toes, R.E.M.; Scherer, H.U. Autoreactive B cells remain active despite clinical disease control in rheumatoid arthritis. J. Autoimmun. 2024, 149, 103320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, Y.; Li, J.; Wu, Y. Evolving understanding of autoimmune mechanisms and new therapeutic strategies of autoimmune disorders. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2024, 9, 263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Wang, F.S.; Gershwin, M.E. Human autoimmune diseases: A comprehensive update. J. Intern. Med. 2015, 278, 369–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farrugia, M.; Baron, B. The Role of Toll-Like Receptors in Autoimmune Diseases through Failure of the Self-Recognition Mechanism. Int. J. Inflam. 2017, 2017, 8391230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freigeh, G.E.; Michniacki, T.F. NF-kappaB and Related Autoimmune and Autoinflammatory Diseases. Rheum. Dis. Clin. N. Am. 2023, 49, 805–823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnabei, L.; Laplantine, E.; Mbongo, W.; Rieux-Laucat, F.; Weil, R. NF-kappaB: At the Borders of Autoimmunity and Inflammation. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 716469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarapultsev, A.; Gusev, E.; Komelkova, M.; Utepova, I.; Luo, S.; Hu, D. JAK-STAT signaling in inflammation and stress-related diseases: Implications for therapeutic interventions. Mol. Biomed. 2023, 4, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takeuchi, O.; Akira, S. Pattern recognition receptors and inflammation. Cell 2010, 140, 805–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, V.; Barrett, J.E. Toll-Like Receptors (TLRs) in Health and Disease: An Overview. Handb. Exp. Pharmacol. 2022, 276, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, K.; Huang, H.; Zhan, Q.; Ding, H.; Li, Y. Toll-like receptors in health and disease. MedComm (2020) 2024, 5, e549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kawai, T.; Akira, S. Signaling to NF-kappaB by Toll-like receptors. Trends Mol. Med. 2007, 13, 460–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ntoufa, S.; Vilia, M.G.; Stamatopoulos, K.; Ghia, P.; Muzio, M. Toll-like receptors signaling: A complex network for NF-kappaB activation in B-cell lymphoid malignancies. Semin. Cancer Biol. 2016, 39, 15–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makarov, S.S. NF-kappaB as a therapeutic target in chronic inflammation: Recent advances. Mol. Med. Today 2000, 6, 441–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawrence, T. The nuclear factor NF-kappaB pathway in inflammation. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2009, 1, a001651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.; Lin, L.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, H.; Hu, H. Targeting NF-kappaB pathway for the therapy of diseases: Mechanism and clinical study. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2020, 5, 209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yap, D.Y.H.; Chan, T.M. B Cell Abnormalities in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus and Lupus Nephritis-Role in Pathogenesis and Effect of Immunosuppressive Treatments. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 6231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Vega, W.C.; Vernon, S.D.; McGowan, P.O. DNA methylation modifications associated with chronic fatigue syndrome. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e104757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Helliwell, A.M.; Sweetman, E.C.; Stockwell, P.A.; Edgar, C.D.; Chatterjee, A.; Tate, W.P. Changes in DNA methylation profiles of myalgic encephalomyelitis/chronic fatigue syndrome patients reflect systemic dysfunctions. Clin. Epigenetics 2020, 12, 167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Su, J.; Li, S.; Chen, F.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, X.; Yuan, Z.; Ren, S.; et al. Structural Modifications and Prospects of Histone Deacetylase (HDAC) Inhibitors in Cancer. Curr. Med. Chem. 2025, 32, 8530–8555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Zhang, M.; Wang, Y. The roles of histone modifications in tumorigenesis and associated inhibitors in cancer therapy. J. Natl. Cancer Cent. 2022, 2, 277–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, G.; Wang, Z.; Song, P.; Zhan, X. DNA and histone modifications as potent diagnostic and therapeutic targets to advance non-small cell lung cancer management from the perspective of 3P medicine. EPMA J. 2022, 13, 649–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berglund, A.; Putney, R.M.; Hamaidi, I.; Kim, S. Epigenetic dysregulation of immune-related pathways in cancer: Bioinformatics tools and visualization. Exp. Mol. Med. 2021, 53, 761–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Booven, D.J.; Gamer, J.; Joseph, A.; Perez, M.; Zarnowski, O.; Pandya, M.; Collado, F.; Klimas, N.; Oltra, E.; Nathanson, L. Stress-Induced Transcriptomic Changes in Females with Myalgic Encephalomyelitis/Chronic Fatigue Syndrome Reveal Disrupted Immune Signatures. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 2698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henrot, P.; Prevel, R.; Berger, P.; Dupin, I. Chemokines in COPD: From Implication to Therapeutic Use. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 2785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, Q.; Xie, Y.; He, Y.; Yu, Y.; Fang, G.; Yu, W.; Wu, J.; Li, J.; Zhao, L.; Deng, X.; et al. Lung microbiome and cytokine profiles in different disease states of COPD: A cohort study. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 5715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nielepkowicz-Gozdzinska, A.; Fendler, W.; Robak, E.; Kulczycka-Siennicka, L.; Gorski, P.; Pietras, T.; Brzezianska, E.; Pietrusinska, M.; Antczak, A. The Role of CXC Chemokines in Pulmonary Fibrosis of Systemic Lupus Erythematosus Patients. Arch. Immunol. Ther. Exp. 2015, 63, 465–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Strieter, R.M.; Gomperts, B.N.; Keane, M.P. The role of CXC chemokines in pulmonary fibrosis. J. Clin. Investig. 2007, 117, 549–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Knudsen, L.; Ruppert, C.; Ochs, M. Tissue remodelling in pulmonary fibrosis. Cell Tissue Res. 2017, 367, 607–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeffery, P.K. Remodeling in asthma and chronic obstructive lung disease. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2001, 164, S28–S38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grzela, K.; Litwiniuk, M.; Zagorska, W.; Grzela, T. Airway Remodeling in Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease and Asthma: The Role of Matrix Metalloproteinase-9. Arch. Immunol. Ther. Exp. 2016, 64, 47–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greer, J.M.; McCombe, P.A. The role of epigenetic mechanisms and processes in autoimmune disorders. Biologics 2012, 6, 307–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazzone, R.; Zwergel, C.; Artico, M.; Taurone, S.; Ralli, M.; Greco, A.; Mai, A. The emerging role of epigenetics in human autoimmune disorders. Clin. Epigenetics 2019, 11, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; He, Z.; Du, J.; Chen, Z.; Creemers, J.W.M.; Wang, B.; Li, F.; Wang, Y. Epigenetic modulations of immune cells: From normal development to tumor progression. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2023, 19, 5120–5144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shanmugam, M.K.; Sethi, G. Role of epigenetics in inflammation-associated diseases. Subcell. Biochem. 2013, 61, 627–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, W.; Qiao, X.; Fang, Y.; Guo, R.; Bai, P.; Liu, S.; Li, T.; Jiang, Y.; Wei, S.; Na, Z.; et al. Epigenetics-targeted drugs: Current paradigms and future challenges. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2024, 9, 332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heerboth, S.; Lapinska, K.; Snyder, N.; Leary, M.; Rollinson, S.; Sarkar, S. Use of epigenetic drugs in disease: An overview. Genet. Epigenet 2014, 6, 9–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdel-Magid, A.F. Potential of Histone Deacetylase 6 Inhibitors as a Treatment of Neurodegenerative Diseases. ACS Med. Chem. Lett. 2025, 16, 210–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hedayat, F.; Faghfuri, E. Harnessing histone deacetylase inhibitors for enhanced cancer immunotherapy. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2025, 997, 177620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hosseini, M.S.; Sanaat, Z.; Akbarzadeh, M.A.; Vaez-Gharamaleki, Y.; Akbarzadeh, M. Histone deacetylase inhibitors for leukemia treatment: Current status and future directions. Eur. J. Med. Res. 2024, 29, 514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Theodoropoulou, M.A.; Mantzourani, C.; Kokotos, G. Histone Deacetylase (HDAC) Inhibitors as a Novel Therapeutic Option Against Fibrotic and Inflammatory Diseases. Biomolecules 2024, 14, 1605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mata, R.; Yao, Y.; Cao, W.; Ding, J.; Zhou, T.; Zhai, Z.; Gao, C. The Dynamic Inflammatory Tissue Microenvironment: Signality and Disease Therapy by Biomaterials. Research 2021, 2021, 4189516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, B.; Liu, C.; Luo, M.; Chen, J.; Tian, S.; Zhan, T.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, H.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, J.; et al. Spatiotemporal dynamic changes of meningeal microenvironment influence meningeal lymphatic function following subarachnoid hemorrhage: From inflammatory response to tissue remodeling. J. Neuroinflammation 2025, 22, 131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landskron, G.; De la Fuente, M.; Thuwajit, P.; Thuwajit, C.; Hermoso, M.A. Chronic inflammation and cytokines in the tumor microenvironment. J. Immunol. Res. 2014, 2014, 149185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, L.; Xia, J.W.; Gong, Y.; Chen, Z.; Yang, H.H.; Zhang, J.; He, J.; Chen, X.D. Effect of lianhuaqingwen capsules on airway inflammation in patients with acute exacerbation of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Evid. Based Complement. Alternat Med. 2014, 2014, 637969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hurst, J.R.; Perera, W.R.; Wilkinson, T.M.; Donaldson, G.C.; Wedzicha, J.A. Systemic and upper and lower airway inflammation at exacerbation of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2006, 173, 71–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perng, D.W.; Chen, P.K. The Relationship between Airway Inflammation and Exacerbation in Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease. Tuberc. Respir. Dis. 2017, 80, 325–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, Y.; Miao, T.W.; Xiao, W.; Mao, B.; Du, L.Y.; Wang, Y.; Fu, J.J. Andrographolide Attenuates NLRP3 Inflammasome Activation and Airway Inflammation in Exacerbation of Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease. Drug Des. Devel. Ther. 2024, 18, 1755–1770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Strzelec, M.; Detka, J.; Mieszczak, P.; Sobocinska, M.K.; Majka, M. Immunomodulation-a general review of the current state-of-the-art and new therapeutic strategies for targeting the immune system. Front. Immunol. 2023, 14, 1127704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moudgil, K.D.; Venkatesha, S.H. The Anti-Inflammatory and Immunomodulatory Activities of Natural Products to Control Autoimmune Inflammation. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 24, 95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baer, A.; Colon-Moran, W.; Bhattarai, N. Characterization of the effects of immunomodulatory drug fingolimod (FTY720) on human T cell receptor signaling pathways. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 10910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bedoui, Y.; Giry, C.; Jaffar-Bandjee, M.C.; Selambarom, J.; Guiraud, P.; Gasque, P. Immunomodulatory drug methotrexate used to treat patients with chronic inflammatory rheumatisms post-chikungunya does not impair the synovial antiviral and bone repair responses. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2018, 12, e0006634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kristiansen, P.S.; Nielsen, L.N. Immunomodulatory and immunosuppressive drug protocols in the treatment of canine primary immune thrombocytopenia, a scoping review. Acta Vet. Scand. 2021, 63, 54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Julkunen, I.; Sareneva, T.; Pirhonen, J.; Ronni, T.; Melen, K.; Matikainen, S. Molecular pathogenesis of influenza A virus infection and virus-induced regulation of cytokine gene expression. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2001, 12, 171–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marquez-Bandala, A.H.; Gutierrez-Xicotencatl, L.; Esquivel-Guadarrama, F. Pathogenesis Induced by Influenza Virus Infection: Role of the Early Events of the Infection and the Innate Immune Response. Viruses 2025, 17, 694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ladman, B.S.; Rosenberger, S.C.; Rosenberger, J.K.; Pope, C.R.; Gelb, J., Jr. Virulence of low pathogenicity H7N2 avian influenza viruses from the Delmarva peninsula for broiler and leghorn chickens and turkeys. Avian Dis. 2008, 52, 623–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Y. Pathogenicity and virulence of influenza. Virulence 2023, 14, 2223057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neumann, G. H5N1 influenza virulence, pathogenicity and transmissibility: What do we know? Future Virol. 2015, 10, 971–980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhu, J.; Li, Y.; Bradley, K.C.; Cao, J.; Chen, H.; Jin, M.; Zhou, H. Glycosylation on hemagglutinin affects the virulence and pathogenicity of pandemic H1N1/2009 influenza A virus in mice. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e61397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, D.; Wu, M. Pattern recognition receptors in health and diseases. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2021, 6, 291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suresh, R.; Mosser, D.M. Pattern recognition receptors in innate immunity, host defense, and immunopathology. Adv. Physiol. Educ. 2013, 37, 284–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mogensen, T.H. Pathogen recognition and inflammatory signaling in innate immune defenses. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2009, 22, 240–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iwasaki, A.; Medzhitov, R. Control of adaptive immunity by the innate immune system. Nat. Immunol. 2015, 16, 343–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herold, K.; Mrowka, R. Inflammation—Dysregulated inflammatory response and strategies for treatment. Acta Physiol. 2019, 226, e13284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Lin, J.; Zhao, Y.; Ma, X.; Yi, H. Toll-like receptor 3 (TLR3) regulation mechanisms and roles in antiviral innate immune responses. J. Zhejiang Univ. Sci. B 2021, 22, 609–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xagorari, A.; Chlichlia, K. Toll-like receptors and viruses: Induction of innate antiviral immune responses. Open Microbiol. J. 2008, 2, 49–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kell, A.M.; Gale, M., Jr. RIG-I in RNA virus recognition. Virology 2015, 479–480, 110–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schlee, M.; Roth, A.; Hornung, V.; Hagmann, C.A.; Wimmenauer, V.; Barchet, W.; Coch, C.; Janke, M.; Mihailovic, A.; Wardle, G.; et al. Recognition of 5’ triphosphate by RIG-I helicase requires short blunt double-stranded RNA as contained in panhandle of negative-strand virus. Immunity 2009, 31, 25–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kelley, N.; Jeltema, D.; Duan, Y.; He, Y. The NLRP3 Inflammasome: An Overview of Mechanisms of Activation and Regulation. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 3328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramachandran, R.; Manan, A.; Kim, J.; Choi, S. NLRP3 inflammasome: A key player in the pathogenesis of life-style disorders. Exp. Mol. Med. 2024, 56, 1488–1500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Xu, Z.; Cao, Y. Host-Virus Interaction: How Host Cells Defend against Influenza A Virus Infection. Viruses 2020, 12, 376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Liu, S.; Goraya, M.U.; Maarouf, M.; Huang, S.; Chen, J.L. Host Immune Response to Influenza A Virus Infection. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, Y.; Zuo, X.; Zhang, S.; Ouyang, Z.; Jiang, S.; Wang, F.; Wang, G. The Mechanism behind Influenza Virus Cytokine Storm. Viruses 2021, 13, 1362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Zhou, Y.H.; Yang, Z.Q. The cytokine storm of severe influenza and development of immunomodulatory therapy. Cell Mol. Immunol. 2016, 13, 3–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chauhan, R.P.; Gordon, M.L. An overview of influenza A virus genes, protein functions, and replication cycle highlighting important updates. Virus Genes 2022, 58, 255–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, J.S.; Howard, W.A.; Nunez, A.; Moncorge, O.; Lycett, S.; Banks, J.; Barclay, W.S. The effect of the PB2 mutation 627K on highly pathogenic H5N1 avian influenza virus is dependent on the virus lineage. J. Virol. 2013, 87, 9983–9996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Dong, Y.; Bian, Y.; Xu, N.; Wu, Y.; Yang, F.; Du, Y.; Qin, T.; Chen, S.; Peng, D.; et al. The influenza virus PB2 protein evades antiviral innate immunity by inhibiting JAK1/STAT signalling. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 6288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graef, K.M.; Vreede, F.T.; Lau, Y.F.; McCall, A.W.; Carr, S.M.; Subbarao, K.; Fodor, E. The PB2 subunit of the influenza virus RNA polymerase affects virulence by interacting with the mitochondrial antiviral signaling protein and inhibiting expression of beta interferon. J. Virol. 2010, 84, 8433–8445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, J.C.; Fodor, E. The PB2 Subunit of the Influenza A Virus RNA Polymerase Is Imported into the Mitochondrial Matrix. J. Virol. 2016, 90, 8729–8738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Zhu, Y.; Ren, C.; Yang, S.; Tian, S.; Chen, H.; Jin, M.; Zhou, H. Influenza A virus protein PB1-F2 impairs innate immunity by inducing mitophagy. Autophagy 2021, 17, 496–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheung, P.H.; Lee, T.T.; Chan, C.P.; Jin, D.Y. Influenza A virus PB1-F2 protein: An ambivalent innate immune modulator and virulence factor. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2020, 107, 763–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reis, A.L.; McCauley, J.W. The influenza virus protein PB1-F2 interacts with IKKbeta and modulates NF-kappaB signalling. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e63852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Ma, C.; Liu, X. PA-X: A key regulator of influenza A virus pathogenicity and host immune responses. Med. Microbiol. Immunol. 2018, 207, 255–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bavagnoli, L.; Cucuzza, S.; Campanini, G.; Rovida, F.; Paolucci, S.; Baldanti, F.; Maga, G. The novel influenza A virus protein PA-X and its naturally deleted variant show different enzymatic properties in comparison to the viral endonuclease PA. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015, 43, 9405–9417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Hu, Z.; Zhang, X.; Chen, M.; Wang, Z.; Xu, G.; Bi, Y.; Tong, Q.; Wang, M.; Sun, H.; et al. An R195K Mutation in the PA-X Protein Increases the Virulence and Transmission of Influenza A Virus in Mammalian Hosts. J. Virol. 2020, 94, 1220–1229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; van Kuppeveld, F.J.; de Haan, C.A.; de Vries, E. Gradual adaptation of animal influenza A viruses to human-type sialic acid receptors. Curr. Opin. Virol. 2023, 60, 101314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, A.J.; Paulson, J.C. Adaptation of influenza viruses to human airway receptors. J. Biol. Chem. 2021, 296, 100017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mair, C.M.; Ludwig, K.; Herrmann, A.; Sieben, C. Receptor binding and pH stability—How influenza A virus hemagglutinin affects host-specific virus infection. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2014, 1838, 1153–1168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shelton, H.; Roberts, K.L.; Molesti, E.; Temperton, N.; Barclay, W.S. Mutations in haemagglutinin that affect receptor binding and pH stability increase replication of a PR8 influenza virus with H5 HA in the upper respiratory tract of ferrets and may contribute to transmissibility. J. Gen. Virol. 2013, 94, 1220–1229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suguitan, A.L., Jr.; Matsuoka, Y.; Lau, Y.F.; Santos, C.P.; Vogel, L.; Cheng, L.I.; Orandle, M.; Subbarao, K. The multibasic cleavage site of the hemagglutinin of highly pathogenic A/Vietnam/1203/2004 (H5N1) avian influenza virus acts as a virulence factor in a host-specific manner in mammals. J. Virol. 2012, 86, 2706–2714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamamoto, Y.; Tamiya, S.; Shibuya, M.; Nakase, I.; Yoshioka, Y. Peptides with the multibasic cleavage site of the hemagglutinin from highly pathogenic influenza viruses act as cell-penetrating via binding to heparan sulfate and neuropilins. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2019, 512, 453–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, C.U.; Jeong, Y.J.; Lee, P.; Lee, M.S.; Park, J.H.; Kim, Y.S.; Kim, D.J. Extracellular nucleoprotein exacerbates influenza virus pathogenesis by activating Toll-like receptor 4 and the NLRP3 inflammasome. Cell Mol. Immunol. 2022, 19, 715–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Y.; Zeng, Y.; Zhang, X.; Xu, S.; Wang, Z.; Du, Y.; Zhang, B.; Lei, C.Q.; Zhu, Q. The Nucleoprotein of H7N9 Influenza Virus Positively Regulates TRAF3-Mediated Innate Signaling and Attenuates Viral Virulence in Mice. J. Virol. 2020, 94, e01640-20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, Z.; Zhang, X.; Gu, Y.; Liu, Y.; Lan, L.M.; Liu, Y.; Li, Y.; Yang, G.; Wan, P.; Chen, X. Regulation and functions of the NLRP3 inflammasome in RNA virus infection. Front. Cell Infect. Microbiol. 2023, 13, 1309128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, B.; Wurtzer, S.; Rameix-Welti, M.A.; Dwyer, D.; van der Werf, S.; Naffakh, N.; Clavel, F.; Labrosse, B. Enhancement of the influenza A hemagglutinin (HA)-mediated cell-cell fusion and virus entry by the viral neuraminidase (NA). PLoS ONE 2009, 4, e8495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, J.C.C.; Karunarathna, H.; Wong, H.H.; Peiris, J.S.M.; Nicholls, J.M. Neuraminidase activity and specificity of influenza A virus are influenced by haemagglutinin-receptor binding. Emerg. Microbes Infect. 2019, 8, 327–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaymard, A.; Le Briand, N.; Frobert, E.; Lina, B.; Escuret, V. Functional balance between neuraminidase and haemagglutinin in influenza viruses. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2016, 22, 975–983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, T.; Zhu, J.; Ma, R.; Yin, Y.; Chen, S.; Peng, D.; Liu, X. Compatibility between haemagglutinin and neuraminidase drives the recent emergence of novel clade 2.3.4.4 H5Nx avian influenza viruses in China. Transbound. Emerg. Dis. 2018, 65, 1757–1769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yen, H.L.; Peiris, J.S. The role of balanced haemagglutinin-neuraminidase activity in the genesis of transmissible neuraminidase inhibitor-resistant variants in seasonal and novel pandemic influenza A H1N1 viruses. Hong Kong Med. J. 2016, 22 (Suppl. S7), 6–9. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Jiang, H.; Zhang, Z. Immune response in influenza virus infection and modulation of immune injury by viral neuraminidase. Virol. J. 2023, 20, 193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, N.; Li, X.; Jiang, H.; Dai, Y.; Xu, G.; Zhang, Z. Influenza Virus Neuraminidase Engages CD83 and Promotes Pulmonary Injury. J. Virol. 2021, 95, e01753-20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beale, R.; Wise, H.; Stuart, A.; Ravenhill, B.J.; Digard, P.; Randow, F. A LC3-interacting motif in the influenza A virus M2 protein is required to subvert autophagy and maintain virion stability. Cell Host Microbe 2014, 15, 239–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Wang, L.; An, Y.; Chen, Z. The applications of live attenuated influenza a virus with modified NS1 gene. Mol. Ther. Nucleic Acids 2025, 36, 102471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klemm, C.; Boergeling, Y.; Ludwig, S.; Ehrhardt, C. Immunomodulatory Nonstructural Proteins of Influenza A Viruses. Trends Microbiol. 2018, 26, 624–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haynes, L. Aging of the Immune System: Research Challenges to Enhance the Health Span of Older Adults. Front. Aging 2020, 1, 602108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samy, R.P.; Lim, L.H. DAMPs and influenza virus infection in ageing. Ageing Res. Rev. 2015, 24, 83–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quiros-Roldan, E.; Sottini, A.; Natali, P.G.; Imberti, L. The Impact of Immune System Aging on Infectious Diseases. Microorganisms 2024, 12, 775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morgan, R.; Klein, S.L. The intersection of sex and gender in the treatment of influenza. Curr. Opin. Virol. 2019, 35, 35–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ogasawara, K. Pandemic influenza and gender imbalance: Mortality selection before births. Soc. Sci. Med. 2022, 311, 115299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shaikh, S.R.; MacIver, N.J.; Beck, M.A. Obesity Dysregulates the Immune Response to Influenza Infection and Vaccination Through Metabolic and Inflammatory Mechanisms. Annu. Rev. Nutr. 2022, 42, 67–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Green, W.D.; Beck, M.A. Obesity Impairs the Adaptive Immune Response to Influenza Virus. Ann. Am. Thorac. Soc. 2017, 14, S406–S409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, W.; Wang, S.; Guan, C.; Liu, S.; Zhang, H. Type III interferon, age and IFNL gene single nucleotide polymorphisms determine the characteristics of H1N1 influenza infection. Front. Immunol. 2025, 16, 1592841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nogales, A.; DeDiego, M.L. Host Single Nucleotide Polymorphisms Modulating Influenza A Virus Disease in Humans. Pathogens 2019, 8, 168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, Y.; Hsu, A.C.; Pang, Z.; Pan, H.; Zuo, X.; Wang, G.; Zheng, J.; Wang, F. Role of the Innate Cytokine Storm Induced by the Influenza A Virus. Viral Immunol. 2019, 32, 244–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hufford, M.M.; Kim, T.S.; Sun, J.; Braciale, T.J. The effector T cell response to influenza infection. Curr. Top. Microbiol. Immunol. 2015, 386, 423–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Madan, R.; Karp, C.L.; Braciale, T.J. Effector T cells control lung inflammation during acute influenza virus infection by producing IL-10. Nat. Med. 2009, 15, 277–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Summerfield, A.; McCullough, K.C. Dendritic Cells in Innate and Adaptive Immune Responses against Influenza Virus. Viruses 2009, 1, 1022–1034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varghese, P.M.; Kishore, U.; Rajkumari, R. Innate and adaptive immune responses against Influenza A Virus: Immune evasion and vaccination strategies. Immunobiology 2022, 227, 152279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cho, J.; Miyake, Y.; Honda, A.; Kushiro, K.; Takai, M. Analysis of the Changes in Expression Levels of Sialic Acid on Influenza-Virus-Infected Cells Using Lectin-Tagged Polymeric Nanoparticles. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7, 1147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kongsomros, S.; Thanunchai, M.; Manopwisedjaroen, S.; Na-Ek, P.; Wang, S.F.; Taechalertpaisarn, T.; Thitithanyanont, A. Trogocytosis with monocytes associated with increased alpha2,3 sialic acid expression on B cells during H5N1 influenza virus infection. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0239488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bohannon, C.D.; Ende, Z.; Cao, W.; Mboko, W.P.; Ranjan, P.; Kumar, A.; Mishina, M.; Amoah, S.; Gangappa, S.; Mittal, S.K.; et al. Influenza Virus Infects and Depletes Activated Adaptive Immune Responders. Adv. Sci. 2021, 8, e2100693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frank, K.; Paust, S. Dynamic Natural Killer Cell and T Cell Responses to Influenza Infection. Front. Cell Infect. Microbiol. 2020, 10, 425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jureka, A.S.; Kleinpeter, A.B.; Tipper, J.L.; Harrod, K.S.; Petit, C.M. The influenza NS1 protein modulates RIG-I activation via a strain-specific direct interaction with the second CARD of RIG-I. J. Biol. Chem. 2020, 295, 1153–1164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Xie, Y.; Munoz-Moreno, R.; Wang, J.; Zhang, L.; Esparza, M.; Garcia-Sastre, A.; Fontoura, B.M.A.; Ren, Y. Structural basis for influenza virus NS1 protein block of mRNA nuclear export. Nat. Microbiol. 2019, 4, 1671–1679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nacken, W.; Mayr, J.; Schreiber, A.; Ludwig, S. Influenza A virus NS1 suppresses nuclear speckles promoted gene expression by inhibition of transcription. Npj Viruses 2025, 3, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drappier, M.; Michiels, T. Inhibition of the OAS/RNase L pathway by viruses. Curr. Opin. Virol. 2015, 15, 19–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Min, J.Y.; Krug, R.M. The primary function of RNA binding by the influenza A virus NS1 protein in infected cells: Inhibiting the 2’-5’ oligo (A) synthetase/RNase L pathway. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 7100–7105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jia, D.; Rahbar, R.; Chan, R.W.; Lee, S.M.; Chan, M.C.; Wang, B.X.; Baker, D.P.; Sun, B.; Peiris, J.S.; Nicholls, J.M.; et al. Influenza virus non-structural protein 1 (NS1) disrupts interferon signaling. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e13927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsiang, T.Y.; Zhou, L.; Krug, R.M. Roles of the phosphorylation of specific serines and threonines in the NS1 protein of human influenza A viruses. J. Virol. 2012, 86, 10370–10376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, A.; Pal, S.; Chacon, J.; Meraz, K.; Gonzalez, J.; Prieto, K.; Rosas-Acosta, G. SUMOylation affects the interferon blocking activity of the influenza A nonstructural protein NS1 without affecting its stability or cellular localization. J. Virol. 2013, 87, 5602–5620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Smith, A.M.; McCullers, J.A. Secondary bacterial infections in influenza virus infection pathogenesis. Curr. Top. Microbiol. Immunol. 2014, 385, 327–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Short, K.R.; Kasper, J.; van der Aa, S.; Andeweg, A.C.; Zaaraoui-Boutahar, F.; Goeijenbier, M.; Richard, M.; Herold, S.; Becker, C.; Scott, D.P.; et al. Influenza virus damages the alveolar barrier by disrupting epithelial cell tight junctions. Eur. Respir. J. 2016, 47, 954–966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onufer, A.P.; Mell, J.C.; Cort, L.; Rao, A.; Mdluli, N.V.; Carey, A.J. Influenza virus-induced type I interferons disrupt alveolar epithelial repair and tight junction integrity in the developing lung. Mucosal Immunol. 2025, 18, 607–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rowe, H.M.; Meliopoulos, V.A.; Iverson, A.; Bomme, P.; Schultz-Cherry, S.; Rosch, J.W. Direct interactions with influenza promote bacterial adherence during respiratory infections. Nat. Microbiol. 2019, 4, 1328–1336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campigotto, A.; Simor, A.E.; McGeer, A.; Kiss, A.; Mubareka, S. Nasal colonization with Streptococcus pneumoniae and Staphylococcus aureus among hospitalized patients with laboratory-confirmed influenza. Diagn. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2018, 92, 133–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kahan, S.M.; Wherry, E.J.; Zajac, A.J. T cell exhaustion during persistent viral infections. Virology 2015, 479–480, 180–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, L.; Zhou, T.J.; Zhou, L.L.; Luo, J.; Qin, Z.; You, J.Z.; Jian, J.; Zhao, Z.Y.; Zhou, Y.S.; Ye, Y.C.; et al. Influenza a virus and Streptococcus pneumonia coinfection potentially promotes bacterial colonization and enhances B lymphocyte depression and reduction. J. Biol. Regul. Homeost. Agents 2019, 33, 1437–1449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, K.M.; Chen, Y.J.; Shen, C.W.; Ou, S.K.; Chen, C.Y. The Influence of Influenza Virus Infections in Patients with Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease. Int. J. Chron. Obstruct Pulmon Dis. 2022, 17, 2253–2261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mallia, P.; Johnston, S.L. Influenza infection and COPD. Int. J. Chron. Obstruct Pulmon Dis. 2007, 2, 55–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Plusa, T. Influence of influenza virus infection on asthma and COPD. Pol. Merkur. Lekarski 2003, 14, 569–571. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Mitchell, A.B.; Mourad, B.; Buddle, L.; Peters, M.J.; Oliver, B.G.G.; Morgan, L.C. Viruses in bronchiectasis: A pilot study to explore the presence of community acquired respiratory viruses in stable patients and during acute exacerbations. BMC Pulm. Med. 2018, 18, 84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, Y.E.; Sung, H.; Oh, Y.M. Respiratory Viruses in Acute Exacerbations of Bronchiectasis. J. Korean Med. Sci. 2021, 36, e217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koul, P.A.; Mir, H.; Akram, S.; Potdar, V.; Chadha, M.S. Respiratory viruses in acute exacerbations of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Lung India 2017, 34, 29–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.J.; Thomas, P.G. New fronts emerge in the influenza cytokine storm. Semin. Immunopathol. 2017, 39, 541–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryabkova, V.A.; Churilov, L.P.; Shoenfeld, Y. Influenza infection, SARS, MERS and COVID-19: Cytokine storm—The common denominator and the lessons to be learned. Clin. Immunol. 2021, 223, 108652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crouse, J.; Kalinke, U.; Oxenius, A. Regulation of antiviral T cell responses by type I interferons. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2015, 15, 231–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prabhu, N.; Ho, A.W.; Wong, K.H.; Hutchinson, P.E.; Chua, Y.L.; Kandasamy, M.; Lee, D.C.; Sivasankar, B.; Kemeny, D.M. Gamma interferon regulates contraction of the influenza virus-specific CD8 T cell response and limits the size of the memory population. J. Virol. 2013, 87, 12510–12522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Merz, M.P.; Seal, S.V.; Grova, N.; Meriaux, S.; Guebels, P.; Kanli, G.; Mommaerts, E.; Nicot, N.; Kaoma, T.; Keunen, O.; et al. Early-life influenza A (H1N1) infection independently programs brain connectivity, HPA AXIS and tissue-specific gene expression profiles. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 5898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bailey, M.; Engler, H.; Hunzeker, J.; Sheridan, J.F. The hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis and viral infection. Viral Immunol. 2003, 16, 141–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silverman, M.N.; Pearce, B.D.; Biron, C.A.; Miller, A.H. Immune modulation of the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal (HPA) axis during viral infection. Viral Immunol. 2005, 18, 41–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohno, M.; Sekiya, T.; Nomura, N.; Daito, T.J.; Shingai, M.; Kida, H. Influenza virus infection affects insulin signaling, fatty acid-metabolizing enzyme expressions, and the tricarboxylic acid cycle in mice. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 10879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, S.; Ouhtit, A.; Al Khatib, H.A.; Eid, A.H.; Mathew, S.; Nasrallah, G.K.; Emara, M.M.; Al Maslamani, M.A.; Yassine, H.M. Burden and disease pathogenesis of influenza and other respiratory viruses in diabetic patients. J. Infect. Public Health 2022, 15, 412–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raber, J.; Rhea, E.M.; Banks, W.A. The Effects of Viruses on Insulin Sensitivity and Blood-Brain Barrier Function. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 2377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Modin, D.; Claggett, B.; Johansen, N.D.; Solomon, S.D.; Trebbien, R.; Grove Krause, T.; Staehr Jensen, J.U.; Porsborg Andersen, M.; Gislason, G.; Biering-Sorensen, T. Excess Mortality and Hospitalizations Associated With Seasonal Influenza in Patients With Heart Failure. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2024, 84, 2460–2467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sin, P.; Siddiqui, M.; Wozniak, R.; Bare, I.; Minion, J.; Sanche, S.; Udell, J.; Lavoie, A.; Dehghani, P. Heart Failure after Laboratory Confirmed Influenza Infection (FLU-HF). Glob. Heart 2022, 17, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vardeny, O.; Solomon, S.D. Influenza and Heart Failure: A Catchy Comorbid Combination. JACC Heart Fail. 2019, 7, 118–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watanabe, T. Renal complications of seasonal and pandemic influenza A virus infections. Eur. J. Pediatr. 2013, 172, 15–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin-Loeches, I.; Papiol, E.; Rodriguez, A.; Diaz, E.; Zaragoza, R.; Granada, R.M.; Socias, L.; Bonastre, J.; Valverdu, M.; Pozo, J.C.; et al. Acute kidney injury in critical ill patients affected by influenza A (H1N1) virus infection. Crit. Care 2011, 15, R66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adams, D.H.; Hubscher, S.G. Systemic viral infections and collateral damage in the liver. Am. J. Pathol. 2006, 168, 1057–1059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schutte, A.; Ciesek, S.; Wedemeyer, H.; Lange, C.M. Influenza virus infection as precipitating event of acute-on-chronic liver failure. J. Hepatol. 2019, 70, 797–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nonaka, K.; Matsuda, Y.; Kakizaki, M.; Takakuma, S.; Hamamatsu, A.; Sakashita, Y.; Matsubara, T.; Murayama, S.; Ishiwata, T.; Yamanaka, N.; et al. Acute Liver Failure Associated with Influenza A Virus Infection: An Autopsy Case Report. Jpn. J. Infect. Dis. 2019, 72, 347–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levi, M.; Keller, T.T.; van Gorp, E.; ten Cate, H. Infection and inflammation and the coagulation system. Cardiovasc. Res. 2003, 60, 26–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Zheng, Q.; Yang, L.; Wu, L. Comparison of inflammatory markers, coagulation indicators and outcomes between influenza and COVID-19 infection amongst children: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Heliyon 2024, 10, e30391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Tang, H. Aberrant coagulation causes a hyper-inflammatory response in severe influenza pneumonia. Cell Mol. Immunol. 2016, 13, 432–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, X.; Liu, M.; Wang, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Kong, L.; Zhou, L. Thrombosis in Critically Ill Influenza Patients: Incidence and Risk Factors. Clin. Appl. Thromb. Hemost. 2024, 30, 10760296241278615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Pu, F.; Yang, X.; Feng, X.; Zhang, J.; Duan, K.; Nian, X.; Ma, Z.; Ma, X.X.; Yang, X.M. Immunosuppressants exert antiviral effects against influenza A(H1N1)pdm09 virus via inhibition of nucleic acid synthesis, mRNA splicing, and protein stability. Virulence 2024, 15, 2301242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kunisaki, K.M.; Janoff, E.N. Influenza in immunosuppressed populations: A review of infection frequency, morbidity, mortality, and vaccine responses. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2009, 9, 493–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greffe, S.; Guerrisi, C.; Souty, C.; Vilcu, A.M.; Hayem, G.; Costantino, F.; Padovano, I.; Bourgault, I.; Trad, S.; Ponsoye, M.; et al. Influenza-like illness in individuals treated with immunosuppressants, biologics, and/or systemic corticosteroids for autoimmune or chronic inflammatory disease: A crowdsourced cohort study, France, 2017–2018. Influenza Other Respir. Viruses 2023, 17, e13148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dimopoulos, G.; Lerikou, M.; Tsiodras, S.; Chranioti, A.; Perros, E.; Anagnostopoulou, U.; Armaganidis, A.; Karakitsos, P. Viral epidemiology of acute exacerbations of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Pulm. Pharmacol. Ther. 2012, 25, 12–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zwaans, W.A.; Mallia, P.; van Winden, M.E.; Rohde, G.G. The relevance of respiratory viral infections in the exacerbations of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease-a systematic review. J. Clin. Virol. 2014, 61, 181–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wedzicha, J.A. Role of viruses in exacerbations of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Proc. Am. Thorac. Soc. 2004, 1, 115–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Chen, D.; Gu, X.; Su, X.; Song, Y.; Shi, Y. Prevalence and risk of viral infection in patients with acute exacerbation of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: A meta-analysis. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2014, 41, 4743–4751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gopal, R.; Marinelli, M.A.; Alcorn, J.F. Immune Mechanisms in Cardiovascular Diseases Associated With Viral Infection. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 570681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skaarup, K.G.; Modin, D.; Nielsen, L.; Jensen, J.U.S.; Biering-Sorensen, T. Influenza and cardiovascular disease pathophysiology: Strings attached. Eur. Heart J. Suppl. 2023, 25, A5–A11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Estabragh, Z.R.; Mamas, M.A. The cardiovascular manifestations of influenza: A systematic review. Int. J. Cardiol. 2013, 167, 2397–2403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mamas, M.A.; Fraser, D.; Neyses, L. Cardiovascular manifestations associated with influenza virus infection. Int. J. Cardiol. 2008, 130, 304–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, T.H.O.; Koutsakos, M.; van de Sandt, C.E.; Crawford, J.C.; Loh, L.; Sant, S.; Grzelak, L.; Allen, E.K.; Brahm, T.; Clemens, E.B.; et al. Immune cellular networks underlying recovery from influenza virus infection in acute hospitalized patients. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 2691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Louie, A.Y.; Kim, J.S.; Drnevich, J.; Dibaeinia, P.; Koito, H.; Sinha, S.; McKim, D.B.; Soto-Diaz, K.; Nowak, R.A.; Das, A.; et al. Influenza A virus infection disrupts oligodendrocyte homeostasis and alters the myelin lipidome in the adult mouse. J. Neuroinflammation 2023, 20, 190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dusedau, H.P.; Steffen, J.; Figueiredo, C.A.; Boehme, J.D.; Schultz, K.; Erck, C.; Korte, M.; Faber-Zuschratter, H.; Smalla, K.H.; Dieterich, D.; et al. Influenza A Virus (H1N1) Infection Induces Microglial Activation and Temporal Dysbalance in Glutamatergic Synaptic Transmission. mBio 2021, 12, e0177621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rommel, M.G.E.; Walz, L.; Fotopoulou, F.; Kohlscheen, S.; Schenk, F.; Miskey, C.; Botezatu, L.; Krebs, Y.; Voelker, I.M.; Wittwer, K.; et al. Influenza A virus infection instructs hematopoiesis to megakaryocyte-lineage output. Cell Rep. 2022, 41, 111447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filgueiras-Rama, D.; Vasilijevic, J.; Jalife, J.; Noujaim, S.F.; Alfonso, J.M.; Nicolas-Avila, J.A.; Gutierrez, C.; Zamarreno, N.; Hidalgo, A.; Bernabe, A.; et al. Human influenza A virus causes myocardial and cardiac-specific conduction system infections associated with early inflammation and premature death. Cardiovasc. Res. 2021, 117, 876–889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kenney, A.D.; Aron, S.L.; Gilbert, C.; Kumar, N.; Chen, P.; Eddy, A.; Zhang, L.; Zani, A.; Vargas-Maldonado, N.; Speaks, S.; et al. Influenza virus replication in cardiomyocytes drives heart dysfunction and fibrosis. Sci. Adv. 2022, 8, eabm5371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, C.T.; Fong, L.Y.; Tan, J.J.; Abdullah, M.N.H. Endothelial barrier disruptive effect of IFN-Y and TNF-alpha: Synergism of pro-inflammatory cytokines. Cytokine 2025, 190, 156922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altyar, A.E.; Bhardwaj, S.; Ghaboura, N.; Kaushik, P.; Alenezi, S.K.; Mantargi, M.J.S.; Afzal, M. Role of IL-2, IL-6, and TNF-alpha as Potential Biomarkers in Ischemic Heart Disease: A Comparative Study of Patients with CAD and Non-CAD. Med. Sci. 2025, 13, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Dhalla, N.S. The Role of Pro-Inflammatory Cytokines in the Pathogenesis of Cardiovascular Disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 1082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blomqvist, A.; Engblom, D. Neural Mechanisms of Inflammation-Induced Fever. Neuroscientist 2018, 24, 381–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pongratz, G.; Straub, R.H. The sympathetic nervous response in inflammation. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2014, 16, 504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bahadoran, A.; Bezavada, L.; Smallwood, H.S. Fueling influenza and the immune response: Implications for metabolic reprogramming during influenza infection and immunometabolism. Immunol. Rev. 2020, 295, 140–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayari, A.; Rosa-Calatrava, M.; Lancel, S.; Barthelemy, J.; Pizzorno, A.; Mayeuf-Louchart, A.; Baron, M.; Hot, D.; Deruyter, L.; Soulard, D.; et al. Influenza infection rewires energy metabolism and induces browning features in adipose cells and tissues. Commun. Biol. 2020, 3, 237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smallwood, H.S.; Duan, S.; Morfouace, M.; Rezinciuc, S.; Shulkin, B.L.; Shelat, A.; Zink, E.E.; Milasta, S.; Bajracharya, R.; Oluwaseum, A.J.; et al. Targeting Metabolic Reprogramming by Influenza Infection for Therapeutic Intervention. Cell Rep. 2017, 19, 1640–1653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezinciuc, S.; Bezavada, L.; Bahadoran, A.; Duan, S.; Wang, R.; Lopez-Ferrer, D.; Finkelstein, D.; McGargill, M.A.; Green, D.R.; Pasa-Tolic, L.; et al. Dynamic metabolic reprogramming in dendritic cells: An early response to influenza infection that is essential for effector function. PLoS Pathog. 2020, 16, e1008957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, S.; Dai, M.Y.; Huang, Y.; Ren, X.C.; Jiang, M.L.; Qiao, J.P.; Zhang, W.Y.; Xu, Y.H.; Shen, J.L.; Zhang, R.Q.; et al. Influenza a virus triggers acute exacerbation of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease by increasing proinflammatory cytokines secretion via NLRP3 inflammasome activation. J. Inflamm. 2022, 19, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Q.; Liu, Y.; Lu, A.; Ni, K.; Xiang, Z.; Wen, K.; Tu, W. Influenza virus infection exacerbates experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis disease by promoting type I T cells infiltration into central nervous system. J. Autoimmun. 2017, 77, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stegemann-Koniszewski, S.; Behrens, S.; Boehme, J.D.; Hochnadel, I.; Riese, P.; Guzman, C.A.; Kroger, A.; Schreiber, J.; Gunzer, M.; Bruder, D. Respiratory Influenza A Virus Infection Triggers Local and Systemic Natural Killer Cell Activation via Toll-Like Receptor 7. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pizzolla, A.; Smith, J.M.; Brooks, A.G.; Reading, P.C. Pattern recognition receptor immunomodulation of innate immunity as a strategy to limit the impact of influenza virus. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2017, 101, 851–861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Vincenzo, F.; Del Gaudio, A.; Petito, V.; Lopetuso, L.R.; Scaldaferri, F. Gut microbiota, intestinal permeability, and systemic inflammation: A narrative review. Intern. Emerg. Med. 2024, 19, 275–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martel, J.; Chang, S.H.; Ko, Y.F.; Hwang, T.L.; Young, J.D.; Ojcius, D.M. Gut barrier disruption and chronic disease. Trends Endocrinol. Metab. 2022, 33, 247–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Froes, F.; Timoteo, A.; Almeida, B.; Raposo, J.F.; Oliveira, J.; Carrageta, M.; Duque, S.; Morais, A. Influenza vaccination in older adults and patients with chronic disorders: A position paper from the Portuguese Society of Pulmonology, the Portuguese Society of Cardiology, the Portuguese Society of Diabetology, the Portuguese Society of Infectious Diseases and Clinical Microbiology, the Portuguese Society of Geriatrics and Gerontology, and the Study Group of Geriatrics of the Portuguese Society of Internal Medicine. Pulmonology 2024, 30, 422–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Antonelli Incalzi, R.; Consoli, A.; Lopalco, P.; Maggi, S.; Sesti, G.; Veronese, N.; Volpe, M. Influenza vaccination for elderly, vulnerable and high-risk subjects: A narrative review and expert opinion. Intern. Emerg. Med. 2024, 19, 619–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mettelman, R.C.; Thomas, P.G. Human Susceptibility to Influenza Infection and Severe Disease. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Med. 2021, 11, a038711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosero, C.I.; Gravenstein, S.; Saade, E.A. Influenza and Aging: Clinical Manifestations, Complications, and Treatment Approaches in Older Adults. Drugs Aging 2025, 42, 39–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.C.; Liu, Y.; Lu, K.T.; Wei, C.; Su, K.; Hsu, W.T.; Chen, S.C. Comparison of influenza hospitalization outcomes among adults, older adults, and octogenarians: A US national population-based study. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2021, 27, 435–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, R.; Liu, X.; Yang, P.; Du, X.; He, L.; Chen, T.; Li, X.; Xie, G.; Wu, S.; Su, J.; et al. Influenza-associated cardiovascular mortality in older adults in Beijing, China: A population-based time-series study. BMJ Open 2020, 10, e042487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, T.Y.; Huang, K.Y.; Huang, T.T.; Huang, Y.S.; Ho, H.C.; Chou, P.; Lin, C.H.; Wei, C.K.; Lian, W.C.; Chen, T.C.; et al. The impact of influenza vaccinations on the adverse effects and hospitalization rate in the elderly: A national based study in an Asian country. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e50337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paget, J.; Staadegaard, L.; Wang, X.; Li, Y.; van Pomeren, T.; van Summeren, J.; Duckers, M.; Chaves, S.S.; Johnson, E.K.; Mahe, C.; et al. Global and national influenza-associated hospitalisation rates: Estimates for 40 countries and administrative regions. J. Glob. Health 2023, 13, 04003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allard, R.; Leclerc, P.; Tremblay, C.; Tannenbaum, T.N. Diabetes and the severity of pandemic influenza A (H1N1) infection. Diabetes Care 2010, 33, 1491–1493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marshall, R.J.; Armart, P.; Hulme, K.D.; Chew, K.Y.; Brown, A.C.; Hansbro, P.M.; Bloxham, C.J.; Flint, M.; Ronacher, K.; Bielefeldt-Ohmann, H.; et al. Glycemic Variability in Diabetes Increases the Severity of Influenza. mBio 2020, 11, e02841-19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miron, V.D.; Sandulescu, O.; Streinu-Cercel, A.; Florea, D.; Paraschiv, S.; Banica, L.; Vlaicu, O.; Otelea, D.; Bilasco, A.; Pitigoi, D.; et al. Age, comorbidity burden and late presentation are significant predictors of hospitalization length and acute respiratory failure in patients with influenza. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 15563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Collaborators, G.B.D.I. Mortality, morbidity, and hospitalisations due to influenza lower respiratory tract infections, 2017: An analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2017. Lancet Respir. Med. 2019, 7, 69–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, J.L.; Yang, W.; Ito, K.; Matte, T.D.; Shaman, J.; Kinney, P.L. Seasonal Influenza Infections and Cardiovascular Disease Mortality. JAMA Cardiol. 2016, 1, 274–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yedlapati, S.H.; Khan, S.U.; Talluri, S.; Lone, A.N.; Khan, M.Z.; Khan, M.S.; Navar, A.M.; Gulati, M.; Johnson, H.; Baum, S.; et al. Effects of Influenza Vaccine on Mortality and Cardiovascular Outcomes in Patients With Cardiovascular Disease: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2021, 10, e019636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Han, X.; Li, Y.; Zhang, C.; Xing, X. The severity and risk factors for mortality in immunocompromised adult patients hospitalized with influenza-related pneumonia. Ann. Clin. Microbiol. Antimicrob. 2021, 20, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kodde, C.; Bonsignore, M.; Schondube, D.; Bauer, T.; Hohenstein, S.; Bollmann, A.; Meier-Hellmann, A.; Kuhlen, R.; Nachtigall, I. Mortality in cancer patients with SARS-CoV-2 or seasonal influenza: An observational cohort study from a German-wide hospital network. Infection 2023, 51, 119–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Modin, D.; Claggett, B.; Jorgensen, M.E.; Kober, L.; Benfield, T.; Schou, M.; Jensen, J.S.; Solomon, S.D.; Trebbien, R.; Fralick, M.; et al. Flu Vaccine and Mortality in Hypertension: A Nationwide Cohort Study. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2022, 11, e021715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bacurau, A.G.M.; Francisco, P. Reasons for non-vaccination against influenza among older adults with hypertension in Brazil: A cross-sectional study. Sao Paulo Med. J. 2020, 138, 322–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jong, H.C.; Zheng, J.Q.; Zheng, C.M.; Lin, C.H.; Chiu, C.C.; Hsu, M.H.; Fang, Y.A.; Hao, W.R.; Chen, C.C.; Yang, T.Y.; et al. Effect of Annual Influenza Vaccination on the Risk of Lung Cancer Among Patients With Hypertension: A Population-Based Cohort Study in Taiwan. Int. J. Public Health 2023, 68, 1605370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Zhang, M.; Chen, H.; Wu, F.; Xian, J.; Zheng, L.; Liang, M.; Cao, H.; Zhou, X.; Gu, Z.; et al. Influenza Vaccination Coverage among Older Adults with Hypertension in Shenzhen, China: A Cross-Sectional Survey during the COVID-19 Pandemic. Vaccines 2021, 9, 105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malacara-Villasenor, A.; Ilaraza-Lomeli, H.; Tapia-Conyer, R.; Sarti, E. Influenza and morbidity and mortality risk in patients in Mexico with systemic arterial hypertension alone or with comorbidities: A retrospective, observational, cross-sectional study from 2014 to 2020. BMJ Open 2021, 11, e057225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Godoy, P.; Castilla, J.; Mayoral, J.M.; Delgado-Rodriguez, M.; Martin, V.; Astray, J.; Soldevila, N.; Gonzalez-Candelas, F.; Castro, A.; Baricot, M.; et al. Smoking may increase the risk of hospitalization due to influenza. Eur. J. Public. Health 2016, 26, 882–887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Godoy, P.; Castilla, J.; Soldevila, N.; Mayoral, J.M.; Toledo, D.; Martin, V.; Astray, J.; Egurrola, M.; Morales-Suarez-Varela, M.; Dominguez, A.; et al. Smoking may increase the risk of influenza hospitalization and reduce influenza vaccine effectiveness in the elderly. Eur. J. Public Health 2018, 28, 150–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, L.; Ran, J.; Mak, Y.W.; Suen, L.K.; Lee, P.H.; Peiris, J.S.M.; Yang, L. Smoking and Influenza-associated Morbidity and Mortality: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. Epidemiology 2019, 30, 405–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hilton, D.D. Cigarette smoking and influenza. Br. Med. J. 1970, 1, 566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Lawrence, H.; Hunter, A.; Murray, R.; Lim, W.S.; McKeever, T. Cigarette smoking and the occurrence of influenza—Systematic review. J. Infect. 2019, 79, 401–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, C.M.; Yang, L.; Chan, K.P.; Chan, W.M.; Song, L.; Lai, H.K.; Thach, T.Q.; Ho, L.M.; Chan, K.H.; Lam, T.H.; et al. Cigarette smoking as a risk factor for influenza-associated mortality: Evidence from an elderly cohort. Influenza Other Respir. Viruses 2013, 7, 531–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Willis, G.A.; Preen, D.B.; Richmond, P.C.; Jacoby, P.; Effler, P.V.; Smith, D.W.; Robins, C.; Borland, M.L.; Levy, A.; Keil, A.D.; et al. The impact of influenza infection on young children, their family and the health care system. Influenza Other Respir. Viruses 2019, 13, 18–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.; Chen, W.; Zeng, M.; Shen, G.; Sun, C.; Liu, G.; Gong, H.; Wang, C.; Ge, M.; Xu, J.; et al. Clinical features and risk factors for severe influenza in children: A study from multiple hospitals in Shanghai. Pediatr. Neonatol. 2021, 62, 428–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, S.J.; Li, H.; Liu, M.; Liu, Y.M.; Zhou, F.; Liu, B.; Qu, J.X.; Cao, B. Mortality prediction to hospitalized patients with influenza pneumonia: PO(2) /FiO(2) combined lymphocyte count is the answer. Clin. Respir. J. 2017, 11, 352–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hollingsworth, R.; El Guerche-Seblain, C.; Tsai, T.; Vasiliev, Y.; Lee, S.; Bright, H.; Barbosa, P. Assessment of the benefits of seasonal influenza vaccination: Elements of a framework to interpret estimates of vaccine effectiveness and support robust decision-making and communication. Influenza Other Respir. Viruses 2021, 15, 164–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grohskopf, L.A.; Ferdinands, J.M.; Blanton, L.H.; Broder, K.R.; Loehr, J. Prevention and Control of Seasonal Influenza with Vaccines: Recommendations of the Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices—United States, 2024–2025 Influenza Season. MMWR Recomm. Rep. 2024, 73, 1–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brydak, L.B.; Wozniak Kosek, A.; Nitsch-Osuch, A. Influenza vaccines and vaccinations in Poland—Past, present and future. Med. Sci. Monit. 2012, 18, RA166–RA171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davenport, F.M. Inactivated influenza virus vaccines. Past, present, and future. Am. Rev. Respir. Dis. 1961, 83 Pt 2, 146–156. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, Y.H.; Hong, K.J.; Kim, H.; Nam, J.H. Influenza vaccines: Past, present, and future. Rev. Med. Virol. 2022, 32, e2243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talbot, H.K.; Nian, H.; Zhu, Y.; Chen, Q.; Williams, J.V.; Griffin, M.R. Clinical effectiveness of split-virion versus subunit trivalent influenza vaccines in older adults. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2015, 60, 1170–1175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, A.P.Y.; Cohen, C.A.; Leung, N.H.L.; Fang, V.J.; Gangappa, S.; Sambhara, S.; Levine, M.Z.; Iuliano, A.D.; Perera, R.; Ip, D.K.M.; et al. Immunogenicity of standard, high-dose, MF59-adjuvanted, and recombinant-HA seasonal influenza vaccination in older adults. NPJ Vaccines 2021, 6, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isakova-Sivak, I.; Rudenko, L. Next-generation influenza vaccines based on mRNA technology. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2025, 25, 2–3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernstein, D.I.; Yan, L.; Treanor, J.; Mendelman, P.M.; Belshe, R.; Cold-Adapted, T.I.V.S.G. Effect of yearly vaccinations with live, attenuated, cold-adapted, trivalent, intranasal influenza vaccines on antibody responses in children. Pediatr. Infect. Dis. J. 2003, 22, 28–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karron, R.A.; Talaat, K.; Luke, C.; Callahan, K.; Thumar, B.; Dilorenzo, S.; McAuliffe, J.; Schappell, E.; Suguitan, A.; Mills, K.; et al. Evaluation of two live attenuated cold-adapted H5N1 influenza virus vaccines in healthy adults. Vaccine 2009, 27, 4953–4960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kendal, A.P. Cold-adapted live attenuated influenza vaccines developed in Russia: Can they contribute to meeting the needs for influenza control in other countries? Eur. J. Epidemiol. 1997, 13, 591–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subbarao, K. Live Attenuated Cold-Adapted Influenza Vaccines. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Med. 2021, 11, a038653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hegde, N.R. Cell culture-based influenza vaccines: A necessary and indispensable investment for the future. Hum. Vaccin. Immunother. 2015, 11, 1223–1234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bechini, A.; Ninci, A.; Del Riccio, M.; Biondi, I.; Bianchi, J.; Bonanni, P.; Mannucci, E.; Monami, M. Impact of Influenza Vaccination on All-Cause Mortality and Hospitalization for Pneumonia in Adults and the Elderly with Diabetes: A Meta-Analysis of Observational Studies. Vaccines 2020, 8, 263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bekkat-Berkani, R.; Wilkinson, T.; Buchy, P.; Dos Santos, G.; Stefanidis, D.; Devaster, J.M.; Meyer, N. Seasonal influenza vaccination in patients with COPD: A systematic literature review. BMC Pulm. Med. 2017, 17, 79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Domnich, A.; de Waure, C. Comparative effectiveness of adjuvanted versus high-dose seasonal influenza vaccines for older adults: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Int. J. Infect. Dis. 2022, 122, 855–863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Esposito, S.; Principi, N. Different influenza vaccine formulations and adjuvants for childhood influenza vaccination. Vaccine 2011, 29, 7535–7541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liprandi, A.S.; Liprandi, M.I.S.; Zaidel, E.J.; Aisenberg, G.M.; Baranchuk, A.; Barbosa, E.C.D.; Sanchez, G.B.; Alexander, B.; Zanetti, F.T.L.; Santi, R.L.; et al. Influenza Vaccination for the Prevention of Cardiovascular Disease in the Americas: Consensus document of the Inter-American Society of Cardiology and the Word Heart Federation. Glob. Heart 2021, 16, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carro, A. The impact of influenza vaccination on cardiovascular diseases. Eur. Heart J. Suppl. 2023, 25, A25–A30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loeb, M.; Dokainish, H.; Dans, A.; Palileo-Villanueva, L.M.; Roy, A.; Karaye, K.; Zhu, J.; Liang, Y.; Goma, F.; Damasceno, A.; et al. Randomized controlled trial of influenza vaccine in patients with heart failure to reduce adverse vascular events (IVVE): Rationale and design. Am. Heart J. 2019, 212, 36–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loeb, M.; Roy, A.; Dokainish, H.; Dans, A.; Palileo-Villanueva, L.M.; Karaye, K.; Zhu, J.; Liang, Y.; Goma, F.; Damasceno, A.; et al. Influenza vaccine to reduce adverse vascular events in patients with heart failure: A multinational randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Lancet Glob. Health 2022, 10, e1835–e1844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gershon, A.S.; Chung, H.; Porter, J.; Campitelli, M.A.; Buchan, S.A.; Schwartz, K.L.; Crowcroft, N.S.; Campigotto, A.; Gubbay, J.B.; Karnauchow, T.; et al. Influenza Vaccine Effectiveness in Preventing Hospitalizations in Older Patients With Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease. J. Infect. Dis. 2020, 221, 42–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kopsaftis, Z.; Wood-Baker, R.; Poole, P. Influenza vaccine for chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD). Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2018, 6, CD002733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Ma, Y.; An, Z.; Yue, C.; Wang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Yuan, X.; Zhang, S.; Shao, M.; Li, C.; et al. Immunogenicity of trivalent seasonal influenza vaccine in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Hum. Vaccin. Immunother. 2021, 17, 3131–3136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lupatkin, H. Influenza Vaccine in the Elderly and Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease. Curr. Infect. Dis. Rep. 2005, 7, 200–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neuzil, K.M.; O’Connor, T.Z.; Gorse, G.J.; Nichol, K.L. Recognizing influenza in older patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease who have received influenza vaccine. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2003, 36, 169–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poole, P.J.; Chacko, E.; Wood-Baker, R.W.; Cates, C.J. Influenza vaccine for patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2006, 25, CD002733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tippett, A.; Ess, G.; Hussaini, L.; Reese, O.; Salazar, L.; Kelly, M.; Taylor, M.; Ciric, C.; Keane, A.; Cheng, A.; et al. Influenza Vaccine Effectiveness Pre-pandemic Among Adults Hospitalized With Congestive Heart Failure or Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease and Older Adults. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2024, 78, 1065–1072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young-Xu, Y.; Smith, J.; Nealon, J.; Mahmud, S.M.; Van Aalst, R.; Thommes, E.W.; Neupane, N.; Lee, J.K.H.; Chit, A. Influenza vaccine in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease among elderly male veterans. PLoS ONE 2022, 17, e0262072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koesnoe, S.; Hasibuan, A.S.; Suastika, K.; Kartasasmita, C.; Aman, A.M.; Kshanti, I.A.; Wisnu, W.; Djauzi, S.; Rengganis, I.; Widhani, A.; et al. Consensus Guidelines for Influenza Vaccination in Patients with Diabetes. Acta Med. Indones. 2024, 56, 126–133. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Verket, M.; Jacobsen, M.; Schutt, K.; Marx, N.; Muller-Wieland, D. Influenza vaccination in patients affected by diabetes. Eur. Heart J. Suppl. 2023, 25, A36–A41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seo, Y.B.; Baek, J.H.; Lee, J.; Song, J.Y.; Lee, J.S.; Cheong, H.J.; Kim, W.J. Long-Term Immunogenicity and Safety of a Conventional Influenza Vaccine in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes. Clin. Vaccine Immunol. 2015, 22, 1160–1165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Skaarup, K.G.; Lassen, M.C.H.; Modin, D.; Johansen, N.D.; Loiacono, M.M.; Harris, R.C.; Lee, J.K.H.; Dufournet, M.; Vardeny, O.; Peikert, A.; et al. The relative vaccine effectiveness of high-dose vs standard-dose influenza vaccines in preventing hospitalization and mortality: A meta-analysis of evidence from randomized trials. J. Infect. 2024, 89, 106187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jagielska, A.M.; Brydak, L.B.; Nitsch-Osuch, A.S. Immunogenicity of Split Inactivated Quadrivalent Influenza Vaccine in Adults with Obesity in the 2017/2018 Season. Med. Sci. Monit. 2021, 27, e929572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karlsson, E.A.; Hertz, T.; Johnson, C.; Mehle, A.; Krammer, F.; Schultz-Cherry, S. Obesity Outweighs Protection Conferred by Adjuvanted Influenza Vaccination. mBio 2016, 7, e01144-16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harris, J.A.; Moniz, M.H.; Iott, B.; Power, R.; Griggs, J.J. Obesity and the receipt of influenza and pneumococcal vaccination: A systematic review and meta-analysis. BMC Obes. 2016, 3, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartholdy, K.V.; Johansen, N.D.; Janstrup, K.H.; Modin, D.; Nealon, J.; Samson, S.; Loiacono, M.M.; Harris, R.; Schade Larsen, C.; Reimer Jensen, A.M.; et al. High-Dose vs Standard-Dose Influenza Vaccine in Chronic Kidney Disease: A Secondary Analysis of DANFLU-1. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2024, 84, 1144–1148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Layton, J.B.; McGrath, L.J.; Sahrmann, J.M.; Ma, Y.; Dharnidharka, V.R.; O’Neil, C.; Weber, D.J.; Butler, A.M. Comparative safety of high-dose versus standard-dose influenza vaccination in patients with end-stage renal disease. Vaccine 2020, 38, 5178–5186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shrestha, A.B.; Mohammed, Y.A.; Umar, T.P.; Shrestha, S.; Mehta, A.; Jaiswal, V. Exploring the possible therapeutic role of influenza vaccine in chronic kidney disease patients. Ann. Med. Surg. 2023, 85, 642–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, B.M.; Yap, D.Y.H.; Yip, T.P.S.; Hung, I.F.N.; Tang, S.C.W.; Chan, T.M. Vaccination in patients with chronic kidney disease-Review of current recommendations and recent advances. Nephrology 2021, 26, 5–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gianella, S.; Anderson, C.; Chaillon, A.; Wells, A.; Porrachia, M.; Caballero, G.; Meneses, M.; Lonergan, J.; Woodworth, B.; Gaitan, N.C.; et al. Impact of influenza and pneumococcal vaccines on HIV persistence and immune dynamics during suppressive antiretroviral therapy. AIDS 2024, 38, 1131–1140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Sun, H.; Atiquzzaman, M.; Sou, J.; Anis, A.H.; Cooper, C. Influenza vaccination for HIV-positive people: Systematic review and network meta-analysis. Vaccine 2018, 36, 4077–4086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ceravolo, A.; Orsi, A.; Parodi, V.; Ansaldi, F. Influenza vaccination in HIV-positive subjects: Latest evidence and future perspective. J. Prev. Med. Hyg. 2013, 54, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kroon, F.P.; van Dissel, J.T.; de Jong, J.C.; Zwinderman, K.; van Furth, R. Antibody response after influenza vaccination in HIV-infected individuals: A consecutive 3-year study. Vaccine 2000, 18, 3040–3049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Remschmidt, C.; Wichmann, O.; Harder, T. Influenza vaccination in HIV-infected individuals: Systematic review and assessment of quality of evidence related to vaccine efficacy, effectiveness and safety. Vaccine 2014, 32, 5585–5592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hirzel, C.; Kumar, D. Influenza vaccine strategies for solid organ transplant recipients. Curr. Opin. Infect. Dis. 2018, 31, 309–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, D.; Blumberg, E.A.; Danziger-Isakov, L.; Kotton, C.N.; Halasa, N.B.; Ison, M.G.; Avery, R.K.; Green, M.; Allen, U.D.; Edwards, K.M.; et al. Influenza vaccination in the organ transplant recipient: Review and summary recommendations. Am. J. Transplant. 2011, 11, 2020–2030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cordero, E.; Manuel, O. Influenza vaccination in solid-organ transplant recipients. Curr. Opin. Organ. Transplant. 2012, 17, 601–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vermeiren, P.; Aubert, V.; Sugamele, R.; Aubert, J.D.; Venetz, J.P.; Meylan, P.; Pascual, M.; Manuel, O. Influenza vaccination and humoral alloimmunity in solid organ transplant recipients. Transpl. Int. 2014, 27, 903–908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harmala, S.; Parisinos, C.; Shallcross, L.; O’Brien, A.; Hayward, A. Effectiveness of pneumococcal and influenza vaccines to prevent serious health complications in adults with chronic liver disease: A protocol for a systematic review. BMJ Open 2018, 8, e018223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harmala, S.; Parisinos, C.A.; Shallcross, L.; O’Brien, A.; Hayward, A. Effectiveness of influenza vaccines in adults with chronic liver disease: A systematic review and meta-analysis. BMJ Open 2019, 9, e031070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, P.H.; Nowalk, M.P.; Zimmerman, R.K.; Olson, S.M.; Talbot, H.K.; Zhu, Y.; Gaglani, M.; Murthy, K.; Monto, A.S.; Martin, E.T.; et al. Vaccine effectiveness against influenza-associated hospitalizations in adults with liver disease, 2015–2020: US Hospitalized Adult Influenza Vaccine Effectiveness Network (HAIVEN). Hum. Vaccin. Immunother. 2025, 21, 2457205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaeta, G.B.; Pariani, E.; Amendola, A.; Brancaccio, G.; Cuomo, G.; Stornaiuolo, G.; Zappa, A.; Zanetti, A. Influenza vaccination in patients with cirrhosis and in liver transplant recipients. Vaccine 2009, 27, 3373–3375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall, V.G.; Smibert, O.C.; Sullivan, S.G.; Lim, C.; Barr, I.G.; Peck, H.; Fuge-Larsen, P.; Demajo, J.; Klimevski, E.; Tennakoon, S.; et al. Influenza Vaccination Strategies in Patients with Hematologic Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2025, 392, 306–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halasa, N.B.; Savani, B.N.; Asokan, I.; Kassim, A.; Simons, R.; Summers, C.; Bourgeois, J.; Clifton, C.; Vaughan, L.A.; Lucid, C.; et al. Randomized Double-Blind Study of the Safety and Immunogenicity of Standard-Dose Trivalent Inactivated Influenza Vaccine versus High-Dose Trivalent Inactivated Influenza Vaccine in Adult Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation Patients. Biol. Blood Marrow Transplant. 2016, 22, 528–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abu-Shakra, M.; Press, J.; Buskila, D.; Sukenik, S. Influenza vaccination of patients with systemic lupus erythematosus: Safety and immunogenecity issues. Autoimmun. Rev. 2007, 6, 543–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abu-Shakra, M.; Zalmanson, S.; Neumann, L.; Flusser, D.; Sukenik, S.; Buskila, D. Influenza virus vaccination of patients with systemic lupus erythematosus: Effects on disease activity. J. Rheumatol. 2000, 27, 1681–1685. [Google Scholar]
- Holvast, A.; Huckriede, A.; Wilschut, J.; Horst, G.; De Vries, J.J.; Benne, C.A.; Kallenberg, C.G.; Bijl, M. Safety and efficacy of influenza vaccination in systemic lupus erythematosus patients with quiescent disease. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2006, 65, 913–918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holvast, B.; Huckriede, A.; Kallenberg, C.G.; Bijl, M. Influenza vaccination in systemic lupus erythematosus: Safe and protective? Autoimmun. Rev. 2007, 6, 300–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mercado, U.; Acosta, H.; Avendano, L. Influenza vaccination of patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Rev. Investig. Clin. 2004, 56, 16–20. [Google Scholar]
- Martinez-Baz, I.; Casado, I.; Navascues, A.; Portillo, M.E.; Guevara, M.; Ezpeleta, C.; Castilla, J. Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease and influenza vaccination effect in preventing outpatient and inpatient influenza cases. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 4862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bao, W.; Li, Y.; Wang, T.; Li, X.; He, J.; Wang, Y.; Wen, F.; Chen, J. Effects of influenza vaccination on clinical outcomes of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Ageing Res. Rev. 2021, 68, 101337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Remschmidt, C.; Wichmann, O.; Harder, T. Vaccines for the prevention of seasonal influenza in patients with diabetes: Systematic review and meta-analysis. BMC Med. 2015, 13, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dicembrini, I.; Silverii, G.A.; Clerico, A.; Fornengo, R.; Gabutti, G.; Sordi, V.; Tafuri, S.; Peruzzi, O.; Mannucci, E. Influenza: Diabetes as a risk factor for severe related-outcomes and the effectiveness of vaccination in diabetic population. A meta-analysis of observational studies. Nutr. Metab. Cardiovasc. Dis. 2023, 33, 1099–1110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silverii, G.A.; Gabutti, G.; Tafuri, S.; Sarti, F.; Pratesi, A.; Clerico, A.; Fornengo, R.; Greco, C.; Irace, C.; Sordi, V.; et al. Diabetes as a risk factor for pneumococcal disease and severe related outcomes and efficacy/effectiveness of vaccination in diabetic population. Results from meta-analysis of observational studies. Acta Diabetol. 2024, 61, 1029–1039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goeijenbier, M.; van Sloten, T.T.; Slobbe, L.; Mathieu, C.; van Genderen, P.; Beyer, W.E.P.; Osterhaus, A. Benefits of flu vaccination for persons with diabetes mellitus: A review. Vaccine 2017, 35, 5095–5101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bersanelli, M.; Verzoni, E.; Cortellini, A.; Giusti, R.; Calvetti, L.; Ermacora, P.; Di Napoli, M.; Catino, A.; Guadalupi, V.; Guaitoli, G.; et al. Impact of influenza vaccination on survival of patients with advanced cancer receiving immune checkpoint inhibitors (INVIDIa-2): Final results of the multicentre, prospective, observational study. EClinicalMedicine 2023, 61, 102044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bitterman, R.; Eliakim-Raz, N.; Vinograd, I.; Zalmanovici Trestioreanu, A.; Leibovici, L.; Paul, M. Influenza vaccines in immunosuppressed adults with cancer. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2018, 2, CD008983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eliakim-Raz, N.; Vinograd, I.; Zalmanovici Trestioreanu, A.; Leibovici, L.; Paul, M. Influenza vaccines in immunosuppressed adults with cancer. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2013, 2013, CD008983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lisy, K. Influenza vaccines in immunosuppressed adults with cancer. Clin. J. Oncol. Nurs. 2014, 18, 367–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- L’Huillier, A.G.; Ferreira, V.H.; Hirzel, C.; Nellimarla, S.; Ku, T.; Natori, Y.; Humar, A.; Kumar, D. T-cell responses following Natural Influenza Infection or Vaccination in Solid Organ Transplant Recipients. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 10104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manuel, O.; Lopez-Medrano, F.; Keiser, L.; Welte, T.; Carratala, J.; Cordero, E.; Hirsch, H.H. Influenza and other respiratory virus infections in solid organ transplant recipients. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2014, 20 (Suppl. S7), 102–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mombelli, M.; Kampouri, E.; Manuel, O. Influenza in solid organ transplant recipients: Epidemiology, management, and outcomes. Expert. Rev. Anti Infect. Ther. 2020, 18, 103–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cordero, E.; Bulnes-Ramos, A.; Aguilar-Guisado, M.; Gonzalez Escribano, F.; Olivas, I.; Torre-Cisneros, J.; Gavalda, J.; Aydillo, T.; Moreno, A.; Montejo, M.; et al. Effect of Influenza Vaccination Inducing Antibody Mediated Rejection in Solid Organ Transplant Recipients. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 1917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harboe, Z.B.; Modin, D.; Gustafsson, F.; Perch, M.; Gislason, G.; Sorensen, S.S.; Rasmussen, A.; Biering-Sorensen, T.; Nielsen, S.D. Effect of influenza vaccination in solid organ transplant recipients: A nationwide population-based cohort study. Am. J. Transplant. 2022, 22, 2409–2417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, S.Y.; Singleton, J.A.; McCauley, M.M.; Orenstein, W.A.; Hughes, J.M.; Mawle, A.C.; Modlin, J.F. Influenza vaccine for healthy working adults. JAMA 2001, 285, 291–292. [Google Scholar]
- Granwehr, B. Inactivated influenza vaccine prevented influenza in healthy adults. ACP J. Club 2007, 146, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grotto, I.; Mandel, Y.; Green, M.S.; Varsano, N.; Gdalevich, M.; Ashkenazi, I.; Shemer, J. Influenza vaccine efficacy in young, healthy adults. Clin. Infect. Dis. 1998, 26, 913–917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendelman, P.M.; Cordova, J.; Cho, I. Safety, efficacy and effectiveness of the influenza virus vaccine, trivalent, types A and B, live, cold-adapted (CAIV-T) in healthy children and healthy adults. Vaccine 2001, 19, 2221–2226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Treanor, J.; Keitel, W.; Belshe, R.; Campbell, J.; Schiff, G.; Zangwill, K.; Wolff, M.; Klimov, A.; Levandowski, R.; Lambert, L. Evaluation of a single dose of half strength inactivated influenza vaccine in healthy adults. Vaccine 2002, 20, 1099–1105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abu Aid, O.; Rohana, H.; Azrad, M.; Peretz, A. Evaluation of vaccine perceptions in Israel’s Elderly: A Comparative study of COVID-19 and influenza vaccination attitudes. Vaccine X 2024, 20, 100569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alvarez, F.P.; Chevalier, P.; Borms, M.; Bricout, H.; Marques, C.; Soininen, A.; Sainio, T.; Petit, C.; de Courville, C. Cost-effectiveness of influenza vaccination with a high dose quadrivalent vaccine of the elderly population in Belgium, Finland, and Portugal. J. Med. Econ. 2023, 26, 710–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Billings, W.Z.; Ge, Y.; Knight, J.H.; Hemme, H.; Hammerton, S.M.; Skarlupka, A.L.; Cao, W.; Shen, Y.; Bahl, J.; Thomas, P.G.; et al. High dose inactivated influenza vaccine inconsistently improves heterologous antibody responses in an elderly human cohort. J. Infect. Dis. 2025, 231, 1536–1543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marbaix, S.; Dauby, N.; Mould-Quevedo, J. Cost-effectiveness of the adjuvanted quadrivalent influenza vaccine in the elderly Belgian population. Expert. Rev. Vaccines 2023, 22, 608–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, T.; Tang, L.; Li, P.; Li, B.; Ye, L.; Zhou, J. Effectiveness of inactivated influenza vaccine against laboratory-confirmed influenza among Chinese elderly: A test-negative design. BMC Geriatr. 2024, 24, 404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, L.; Li, G.; Zhang, Y.; Zhao, X.; Wang, K.; Jia, C.; Zhang, W.; Tan, J.; Chen, X.; Li, Q.; et al. The Safety and Immunogenicity of a Quadrivalent Influenza Subunit Vaccine in Healthy Children Aged 6-35 Months: A Randomized, Blinded and Positive-Controlled Phase III Clinical Trial. Vaccines 2025, 13, 467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.E.; Park, S.B.; Kim, H.Y.; Baik, S.H.; Jung, K.; Kim, J.; Park, J.Y. Safety and Influenza Infections in Children Aged 6–35 Months Receiving Cell Culture-Derived Inactivated Quadrivalent Influenza Vaccine During the 2023–2024 Influenza Season in South Korea. Vaccines 2025, 13, 501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.L.; Kwan, M.Y.W.; Murphy, C.; Chan, E.L.Y.; Wong, J.S.C.; Sullivan, S.G.; Peiris, M.; Cowling, B.J. Influenza vaccine effectiveness against influenza-associated hospitalizations in children, Hong Kong, November 2023 to June 2024. Vaccine X 2024, 20, 100570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shinjoh, M.; Yaginuma, M.; Yamaguchi, Y.; Tamura, K.; Furuichi, M.; Tsumura, Y.; Itaki, R.; Iqbal, A.; Maeda, N.; Narabayashi, A.; et al. Effectiveness of inactivated influenza vaccine in children during the 2023/24 season: The first season after relaxation of intensive COVID-19 measures. Vaccine 2024, 42, 126241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, X.; Zhou, Y.; Deng, P.; Xu, N.; Liu, X.; Guo, Y.; Fang, A.; Liu, P.; Yan, Y.; Yang, L.; et al. Effectiveness and safety of a novel intranasal influenza vaccine in Chinese children: A phase IV multi-Center, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled clinical trial. Vaccine 2025, 59, 127268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Wang, Y.; Chen, D.; Xu, W.; Duan, P.; Ji, W.; Liu, W.; Huang, W.; Wu, B.; Chai, W.; et al. Safety and immunogenicity of full-dose quadrivalent influenza vaccine in children 6-35 months of age in China: A randomized, double-blind, clinical trial. Hum. Vaccin. Immunother. 2024, 20, 2425149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christensen, J.; Johansen, N.D.; Modin, D.; Janstrup, K.H.; Nealon, J.; Samson, S.; Loiacono, M.; Harris, R.; Larsen, C.S.; Jensen, A.M.R.; et al. Relative Effectiveness of High-Dose Versus Standard-Dose Quadrivalent Influenza Vaccine in Older Adults With Cardiovascular Disease: A Prespecified Analysis of the DANFLU-1 Randomized Clinical Trial. Circ. Cardiovasc. Qual. Outcomes 2025, 18, e011496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cooper, F.; Eisenman, B.; Hennekens, C.H.; Drowos, J. High- or Standard-Dose Influenza Vaccine for Middle-Aged Adults with Cardiovascular Disease: What’s a Doctor to Do. Cardiology 2016, 133, 195–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diaz-Arocutipa, C.; Saucedo-Chinchay, J.; Mamas, M.A.; Vicent, L. Influenza vaccine improves cardiovascular outcomes in patients with coronary artery disease: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Travel. Med. Infect. Dis. 2022, 47, 102311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peikert, A.; Claggett, B.L.; Udell, J.A.; Joseph, J.; Hegde, S.M.; Kim, K.; Mao, L.; Wang, T.; Havighurst, T.C.; Farkouh, M.E.; et al. Influenza Vaccine Immune Response in Patients With High-Risk Cardiovascular Disease: A Secondary Analysis of the INVESTED Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA Cardiol. 2024, 9, 574–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, A.; Yadav, S. Influenza vaccine in cardiovascular disease: Current evidence and practice in India. Indian. Heart J. 2024, 76, 365–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vardeny, O. Influenza vaccine in cardiovascular disease: Time to move the needle. Eur. Heart J. 2022, 43, 4389–4391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vardeny, O.; Kim, K.; Udell, J.A.; Joseph, J.; Desai, A.S.; Farkouh, M.E.; Hegde, S.M.; Hernandez, A.F.; McGeer, A.; Talbot, H.K.; et al. Effect of High-Dose Trivalent vs Standard-Dose Quadrivalent Influenza Vaccine on Mortality or Cardiopulmonary Hospitalization in Patients With High-risk Cardiovascular Disease: A Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA 2021, 325, 39–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, G.P.; Irving, L.B.; Jarnicki, A.; Kedzierska, K.; Koutsakos, M.; Kent, S.; Hurt, A.C.; Wheatley, A.K.; Nguyen, T.H.O.; Snape, N.; et al. Prime-boost, double-dose influenza vaccine immunity in COPD: A pilot observational study. ERJ Open Res. 2023, 9, 00641-2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chuaychoo, B.; Kositanont, U.; Rittayamai, N.; Niyomthong, P.; Songserm, T.; Maranetra, K.N.; Rattanasaengloet, K.; Nana, A. The immunogenicity of the intradermal injection of seasonal trivalent influenza vaccine containing influenza A(H1N1)pdm09 in COPD patients soon after a pandemic. Hum. Vaccin. Immunother. 2016, 12, 1728–1737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Roux, A.; Marx, A.; Burkhardt, O.; Schweiger, B.; Borkowski, A.; Banzhoff, A.; Pletz, M.W.; Lode, H. Impact of corticosteroids on the immune response to a MF59-adjuvanted influenza vaccine in elderly COPD-patients. Vaccine 2006, 24, 1537–1542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Snape, N.; Anderson, G.P.; Irving, L.B.; Jarnicki, A.G.; Hurt, A.C.; Collins, T.; Xi, Y.; Upham, J.W. Vaccine strain affects seroconversion after influenza vaccination in COPD patients and healthy older people. NPJ Vaccines 2022, 7, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Z.; Yang, T. Effectiveness of inactivated influenza vaccine against laboratory-confirmed influenza in elderly Chinese patients with diabetes: A test-negative design case-control study. Hum. Vaccin. Immunother. 2025, 21, 2458814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lassen, M.C.H.; Johansen, N.D.; Modin, D.; Nealon, J.; Samson, S.; Dufournet, M.; Loiacono, M.M.; Larsen, C.S.; Jensen, A.M.R.; Landler, N.E.; et al. Effects of high-dose versus standard-dose quadrivalent influenza vaccine among patients with diabetes: A post-hoc analysis of the DANFLU-1 trial. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2024, 26, 1821–1829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vamos, E.P.; Pape, U.J.; Curcin, V.; Harris, M.J.; Valabhji, J.; Majeed, A.; Millett, C. Effectiveness of the influenza vaccine in preventing admission to hospital and death in people with type 2 diabetes. CMAJ 2016, 188, E342–E351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, R.W.K.; Leung, W.M. Influenza vaccine uptake and associated factors in adult patients with type 2 diabetes in a general outpatient clinic in Hong Kong. Aust. J. Gen. Pract. 2023, 52, 643–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, W.J.; Lee, D.K.; Lee, S.Y.; Sohn, S.H.; Park, H.L.; Park, Y.W.; Kim, H.; Nam, J.H. Diet-induced obesity reduces the production of influenza vaccine-induced antibodies via impaired macrophage function. Acta Virol. 2016, 60, 298–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clarke, M.; Mathew, S.M.; Giles, L.C.; Pena, A.S.; Barr, I.G.; Richmond, P.C.; Marshall, H.S. A Prospective Study Investigating the Impact of Obesity on the Immune Response to the Quadrivalent Influenza Vaccine in Children and Adolescents. Vaccines 2022, 10, 699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaposy, C. The influence of the stigma of obesity on H1N1 influenza vaccine sequencing in Canada in 2009. Vaccine 2011, 29, 9607–9610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.C.; Hao, W.R.; Hong, H.J.; Lin, K.J.; Chiu, C.C.; Yang, T.Y.; Fang, Y.A.; Jian, W.; Chen, M.Y.; Hsu, M.H.; et al. Protective Effects of Influenza Vaccine against Colorectal Cancer in Populations with Chronic Kidney Disease: A Nationwide Population-Based Cohort Study. Cancers 2023, 15, 2398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hao, W.R.; Yang, T.L.; Lai, Y.H.; Lin, K.J.; Fang, Y.A.; Chen, M.Y.; Hsu, M.H.; Chiu, C.C.; Yang, T.Y.; Chen, C.C.; et al. The Association between Influenza Vaccine and Risk of Chronic Kidney Disease/Dialysis in Patients with Hypertension. Vaccines 2023, 11, 1098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heryaman, H.; Juli, C.; Nazir, A.; Syamsunarno, M.; Yahaya, B.H.; Turbawaty, D.K.; Sari, R.M.; Permana, H.; Supriyadi, R.; Atik, N. Immunogenicity, Safety, and Efficacy of Influenza Vaccine in T2DM and T2DM with Chronic Kidney Disease. Vaccines 2024, 12, 227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bickel, M.; Wieters, I.; Khaykin, P.; Nisius, G.; Haberl, A.; Stephan, C.; Von Hentig, N.; Herrmann, E.; Doerr, H.W.; Brodt, H.R.; et al. Low rate of seroconversion after vaccination with a split virion, adjuvanted pandemic H1N1 influenza vaccine in HIV-1-infected patients. AIDS 2010, 24, F31–F35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cordero, E.; Roca-Oporto, C.; Bulnes-Ramos, A.; Aydillo, T.; Gavalda, J.; Moreno, A.; Torre-Cisneros, J.; Montejo, J.M.; Fortun, J.; Munoz, P.; et al. Two Doses of Inactivated Influenza Vaccine Improve Immune Response in Solid Organ Transplant Recipients: Results of TRANSGRIPE 1-2, a Randomized Controlled Clinical Trial. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2017, 64, 829–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bianchi, F.P.; Losito, F.; Labarile, N.; Shahini, E.; Cozzolongo, R. Prevention of influenza complications in patients with liver disease: A retrospective cohort study. Front. Public Health 2023, 11, 1288126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cherif, H.; Hoglund, M.; Pauksens, K. Adjuvanted influenza a (H1N1) 2009 vaccine in patients with hematological diseases: Good safety and immunogenicity even in chemotherapy-treated patients. Eur. J. Haematol. 2013, 90, 413–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whitaker, J.A.; Parikh, S.A.; Shanafelt, T.D.; Kay, N.E.; Kennedy, R.B.; Grill, D.E.; Goergen, K.M.; Call, T.G.; Kendarian, S.S.; Ding, W.; et al. The humoral immune response to high-dose influenza vaccine in persons with monoclonal B-cell lymphocytosis (MBL) and chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL). Vaccine 2021, 39, 1122–1130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiesik-Szewczyk, E.; Romanowska, M.; Mielnik, P.; Chwalinska-Sadowska, H.; Brydak, L.B.; Olesinska, M.; Zabek, J. Anti-influenza vaccination in systemic lupus erythematosus patients: An analysis of specific humoral response and vaccination safety. Clin. Rheumatol. 2010, 29, 605–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crowe, S.R.; Merrill, J.T.; Vista, E.S.; Dedeke, A.B.; Thompson, D.M.; Stewart, S.; Guthridge, J.M.; Niewold, T.B.; Franek, B.S.; Air, G.M.; et al. Influenza vaccination responses in human systemic lupus erythematosus: Impact of clinical and demographic features. Arthritis Rheum. 2011, 63, 2396–2406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puges, M.; Biscay, P.; Barnetche, T.; Truchetet, M.E.; Richez, C.; Seneschal, J.; Gensous, N.; Lazaro, E.; Duffau, P. Immunogenicity and impact on disease activity of influenza and pneumococcal vaccines in systemic lupus erythematosus: A systematic literature review and meta-analysis. Rheumatology 2016, 55, 1664–1672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, C.C.; Chang, Y.S.; Chen, W.S.; Chen, Y.H.; Chen, J.H. Effects of annual influenza vaccination on morbidity and mortality in patients with Systemic Lupus Erythematosus: A Nationwide Cohort Study. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 37817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liao, Z.; Tang, H.; Xu, X.; Liang, Y.; Xiong, Y.; Ni, J. Immunogenicity and Safety of Influenza Vaccination in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus Patients Compared with Healthy Controls: A Meta-Analysis. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0147856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sim, J.J.L.; Lim, C.C. Influenza Vaccination in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus: Efficacy, Effectiveness, Safety, Utilization, and Barriers. Am. J. Med. 2022, 135, 286–296.e9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bayle, A.; Khettab, M.; Lucibello, F.; Chamseddine, A.N.; Goldschmidt, V.; Perret, A.; Ropert, S.; Scotte, F.; Loulergue, P.; Mir, O. Immunogenicity and safety of influenza vaccination in cancer patients receiving checkpoint inhibitors targeting PD-1 or PD-L1. Ann. Oncol. 2020, 31, 959–961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keam, B.; Kang, C.K.; Jun, K.I.; Moon, S.M.; Suh, K.J.; Lee, D.W.; Ock, C.Y.; Kim, M.; Choi, Y.; Lim, Y.; et al. Immunogenicity of Influenza Vaccination in Patients with Cancer Receiving Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2020, 71, 422–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waqar, S.N.; Boehmer, L.; Morgensztern, D.; Wang-Gillam, A.; Sorscher, S.; Lawrence, S.; Gao, F.; Guebert, K.; Williams, K.; Govindan, R. Immunogenicity of Influenza Vaccination in Patients With Cancer. Am. J. Clin. Oncol. 2018, 41, 248–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

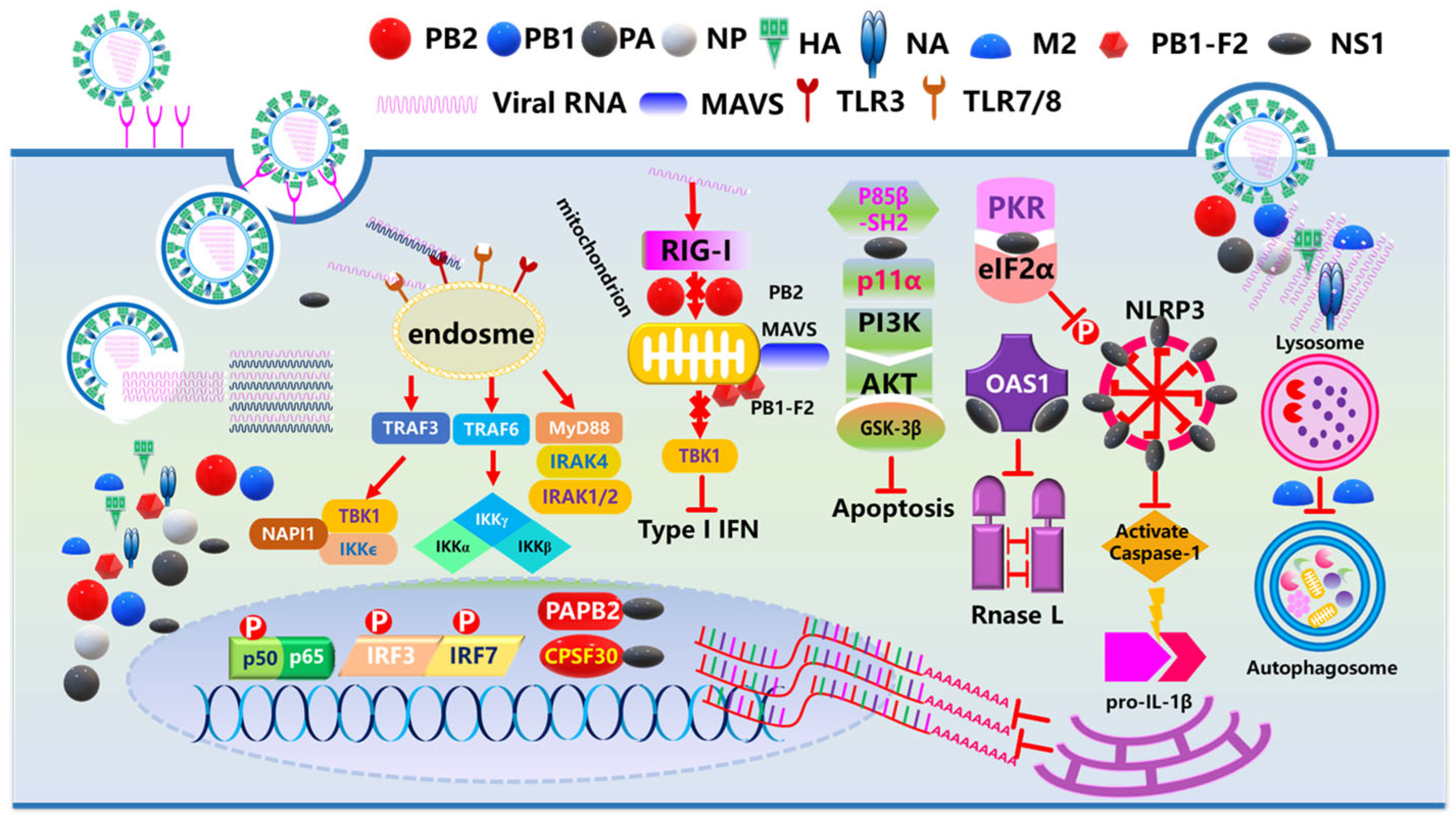
| Abnormality Type | Key Features | Associated Diseases | Molecular Mechanisms | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cellular Immunity Dysfunction | Th17/Treg imbalance; NK cell dysfunction; Reduced CD8+ T-cell cytotoxicity | COPD; Rheumatoid arthritis; SLE | Th17 cells secrete proinflammatory cytokines (IL-17/IL-22); Treg dysfunction leads to loss of immune tolerance; CD8+ T cells exhibit mitochondrial dysfunction | [59,60,61,62,63,64,65,66,67,68,69,70,71,72,73,74,75] |
| Humoral Immunity Dysfunction | Decreased IgG/IgA/IgM levels; Impaired antibody response | Chronic infections; Autoimmune diseases | Abnormal B cell activation; Reduced antibody production; Impaired pathogen clearance | [76,77,78,79,80,81] |
| Cytokine Dysregulation | Persistent overexpression of IL-6; IL-1β; and TNF-α; Proinflammatory/anti-inflammatory imbalance | Cardiovascular diseases; Diabetes; SLE | NF-κB pathway activation → excessive cytokine release → tissue damage and chronic inflammation | [82,83,84,85,86,87,88,89,90] |
| Autoimmune Reactions | Elevated autoantibodies (e.g., anti-nuclear antibodies); Activation of autoreactive T/B cells | Rheumatoid arthritis; Type 1 diabetes | Breakdown of immune tolerance; Attack on self-antigens | [91,92,93,94,95,96,97,98,99] |
| Signaling Pathway Abnormalities | Overactivation of TLR/NF-κB pathways; Dysregulation of JAK-STAT pathways | Autoimmune diseases; Chronic inflammation | TLR recognizes pathogens → NF-κB → proinflammatory cytokine release- JAK-STAT mediates abnormal cytokine signaling | [100,101,102,103,104,105,106,107,108,109,110,111,112] |
| Epigenetic Mechanisms | Abnormal DNA methylation/histone modification; Dysregulated immune-related gene expression | Chronic fatigue syndrome; Cancer | HDAC activity changes; gene silencing or activation | [113,114,115,116,117,118,119] |
| Microenvironmental Influences | Disrupted cytokine/chemokine microenvironment; Tissue fibrosis or remodeling | COPD; Pulmonary fibrosis | Inflammatory mediators (e.g., TGF-β) promote abnormal tissue repair, organ dysfunction | [120,121,122,123,124,125,126] |
| Mechanism Category | Pathological Mechanism | Associated Chronic Diseases | Clinical Symptoms and Hazards | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Inflammatory Response and Cytokine Storm | Influenza virus activates the immune system, releasing proinflammatory cytokines (IL-6, TNF-α) that trigger systemic inflammatory response syndrome (SIRS). | Cardiovascular diseases; COPD/asthma; autoimmune diseases | Cardiovascular: Plaque rupture and myocardial fibrosis; COPD/asthma: Airway spasm and increased mucus production; Autoimmune diseases: Activation of autoimmune responses. | [168,169,209,239,240] |
| Immune System Dysfunction and Secondary Infections | Viral suppression of interferon signaling leads to T-cell exhaustion and secondary bacterial infections (e.g., Streptococcus pneumoniae). | Diabetes; chronic kidney/liver diseases | Diabetes: Increased risk of severe pneumonia; Kidney/liver diseases: Increased sepsis risk and accelerated organ failure. | [241,242] |
| Metabolic and Homeostatic Dysregulation | Infection activates the HPA axis, leading to insulin resistance and increased catabolism. | Diabetes; heart failure | Diabetes: Stress-induced hyperglycemia and diabetic ketoacidosis; Heart failure: Sympathetic activation → increased cardiac workload. | [243,244,245,246,247,248,249,250,251] |
| Organ Compensatory Insufficiency | Patients with chronic disease have reduced organ reserve capacity, with infection-induced metabolic demands exceeding compensatory ability. | Chronic kidney disease; chronic liver disease | Kidney disease: Dehydration/sepsis and acute kidney injury (AKI); Liver disease: Hepatocyte necrosis and hepatic encephalopathy/coagulopathy | [252,253,254,255,256] |
| Coagulation Abnormalities | The virus activates endothelial cells and platelets, inducing a hypercoagulable state (tissue factor release). | Cardiovascular diseases; malignant tumors | Cardiovascular: Increased risk of deep vein thrombosis (DVT) and pulmonary embolism (PE); Tumors: Superimposed thrombotic risk | [257,258,259,260] |
| Drug Interactions | Immunosuppressants (e.g., glucocorticoids) inhibit antiviral immunity; β-blockers mask infection symptoms. | Patients using immunosuppressants/ cardiovascular drugs | Prolonged viral replication time; Delayed infection diagnosis. | [261,262,263] |
| Health Indicator | Disease Category | Statistical Value | Risk Comparison (vs. Healthy Population) | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hospitalization Rate | Chronic Respiratory Diseases | 3–5× higher risk | Accounts for 21.4% of total hospitalizations | [299] |
| Cardiovascular Diseases | 2.8x higher rate | Contributes to 18.6% of hospitalization causes | [23,300] | |
| Severity Rate | Diabetes | 40% higher severity conversion rate | Accounts for 63% of influenza severe cases | [301,302] |
| Elderly Chronic Patients (≥65 years) | 12.7% severity rate | Contributes to 71% of ICU cases | [296,303] | |
| Mortality Rate | Overall Chronic Patients | 82% of influenza deaths | February 2025 mortality rate: 0.01% | [304] |
| Cardiovascular and Cerebrovascular Diseases | 278.6 per 100,000 | 1.8x higher death risk | [305,306] | |
| Cancer Patients | 320 per 100,000 | 3.2x higher mortality | [307,308] | |
| Special Risk Factors | Hypertension (Awareness Rate: 45.72%) | Significantly increases complication risk | / | [309,310,311,312,313] |
| Chronic Patients with Smoking History | 55% higher severity rate | / | [314,315,316,317,318,319] |
| Population Group | Hospitalization Rate Reduction (vs. Unvaccinated in the Same Group) | Mortality Rate Reduction (vs. Unvaccinated in the Same Group) | Vaccine Types | Mechanism of Vaccine Protection | References | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Elderly (≥65 years) | 43–52% | 38–56% | High-dose/adjuvanted vaccines | Enhanced immunogenicity in immunosenescent populations | [338] | |
| Children (6 months-5 years) | 40–70% | 65–75% | Standard pediatric formulations | Immature immune system priming | [339] | |
| Patients with Chronic Disease | Cardiovascular Disease | 30–56% | 18–34% | Standard formulations | Reduction in cardiovascular stress during infection | [340,341,342,343] |
| COPD Patients | 32–52% | 50–70% | Standard formulations | Alleviation of respiratory impairment during infection | [344,345,346,347,348,349,350,351] | |
| Diabetes (Type 1/2) | 23–58% | 16–46% | Standard formulations | Glycemic stabilization during infection | [352,353,354,355] | |
| Obesity | 20–40% | 10–25% | Standard formulations | Mitigation of metabolic stress during infection | [205,356,357,358] | |
| Chronic Kidney Disease | 11–30% | 15–30% | Standard formulations | Mitigation of renal burden and dialysis dependence | [359,360,361,362] | |
| HIV/AIDS | 20–40% | 10–25% | High-dose vaccines | Immune reconstitution effects | [363,364,365,366,367] | |
| Post-Organ Transplant | 20–40% | 10–40% | Standard formulations | Immunosuppression modulation | [368,369,370,371] | |
| Chronic Liver Disease | 27–50% | 10–20% | Standard formulations | Hepatic protective effects | [372,373,374,375] | |
| Hematologic Diseases | 20–40% | 10–25% | Standard formulations | Reduction in infection-induced disease exacerbations | [376,377] | |
| Systemic Lupus Erythematosus | 18–52% | 40–59% | Standard formulations | Autoimmune modulation effects | [378,379,380,381,382] | |
| Population Group | H1N1 Seroconversion Rate | H3N2 Seroconversion Rate | B-Type Influenza Seroconversion Rate | Vaccine Type | References | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Healthy Adults | 40–60% | 30–50% | 35–55% | Standard inactivated vaccine | [398,399,400,401,402] | |
| Elderly (≥65 years) | 40–50% | 30–40% | 25–35% | High-dose/adjuvanted vaccine | [403,404,405,406,407] | |
| Children (6 months-5 years) | 40–70% | 65–75% | 50–70% | Pediatric formulation | [408,409,410,411,412,413] | |
| Patients with Chronic Disease | Cardiovascular Disease | 30–50% | 20–40% | 25–45% | Standard vaccine | [414,415,416,417,418,419,420] |
| COPD | 35–55% | 25–45% | 30–50% | Standard vaccine | [345,421,422,423,424] | |
| Diabetes (Type 1/2) | 24–58% | 18–42% | 20–40% | High-dose vaccine | [354,425,426,427,428] | |
| Obesity | 30–50% | 20–40% | 25–45% | Standard vaccine | [356,429,430,431] | |
| Chronic Kidney Disease | 50–60% | 40–50% | 30–40% | Standard vaccine | [359,361,432,433,434] | |
| HIV/AIDS | 40–60% | 30–50% | 30–50% | High-dose vaccine | [435] | |
| Post-Organ Transplant | 40–60% | 30–50% | 20–40% | Standard vaccine | [436] | |
| Chronic Liver Disease | 35–55% | 25–45% | 30–50% | Standard vaccine | [372,373,437] | |
| Hematologic Diseases | 30–50% | 20–40% | 25–45% | Standard vaccine | [438,439] | |
| Systemic Lupus Erythematosus | 35–55% | 25–45% | 30–50% | Standard vaccine | [382,440,441,442,443,444,445] | |
| Malignant Tumors | 30–50% | 20–40% | 10–30% | Standard/high-dose vaccine | [446,447,448] | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lian, R.; Zhang, H.; An, Y.; Chen, Z. Chronic Diseases and Influenza Vaccines. Vaccines 2025, 13, 936. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines13090936
Lian R, Zhang H, An Y, Chen Z. Chronic Diseases and Influenza Vaccines. Vaccines. 2025; 13(9):936. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines13090936
Chicago/Turabian StyleLian, Rui, Hongbo Zhang, Youcai An, and Ze Chen. 2025. "Chronic Diseases and Influenza Vaccines" Vaccines 13, no. 9: 936. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines13090936
APA StyleLian, R., Zhang, H., An, Y., & Chen, Z. (2025). Chronic Diseases and Influenza Vaccines. Vaccines, 13(9), 936. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines13090936





