Vaccination Reduces Fecal Shedding and Improves Carcass Quality in Pigs with Subclinical Lawsonia intracellularis Infections
Abstract
1. Introduction
- Field trial 1 was performed to elucidate whether there was an association between the growth and fecal shedding of L. intracellularis in unvaccinated and intramuscularly vaccinated pigs in a farm with subclinical infection.
- Field trial 2 was performed to assess the impact of intradermal vaccination against L. intracellularis on clinical performance and carcass quality in a herd with subclinical infection.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Herd Selection
2.2. Field Trial 1
2.3. Field Trial 2
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Field Trial 1
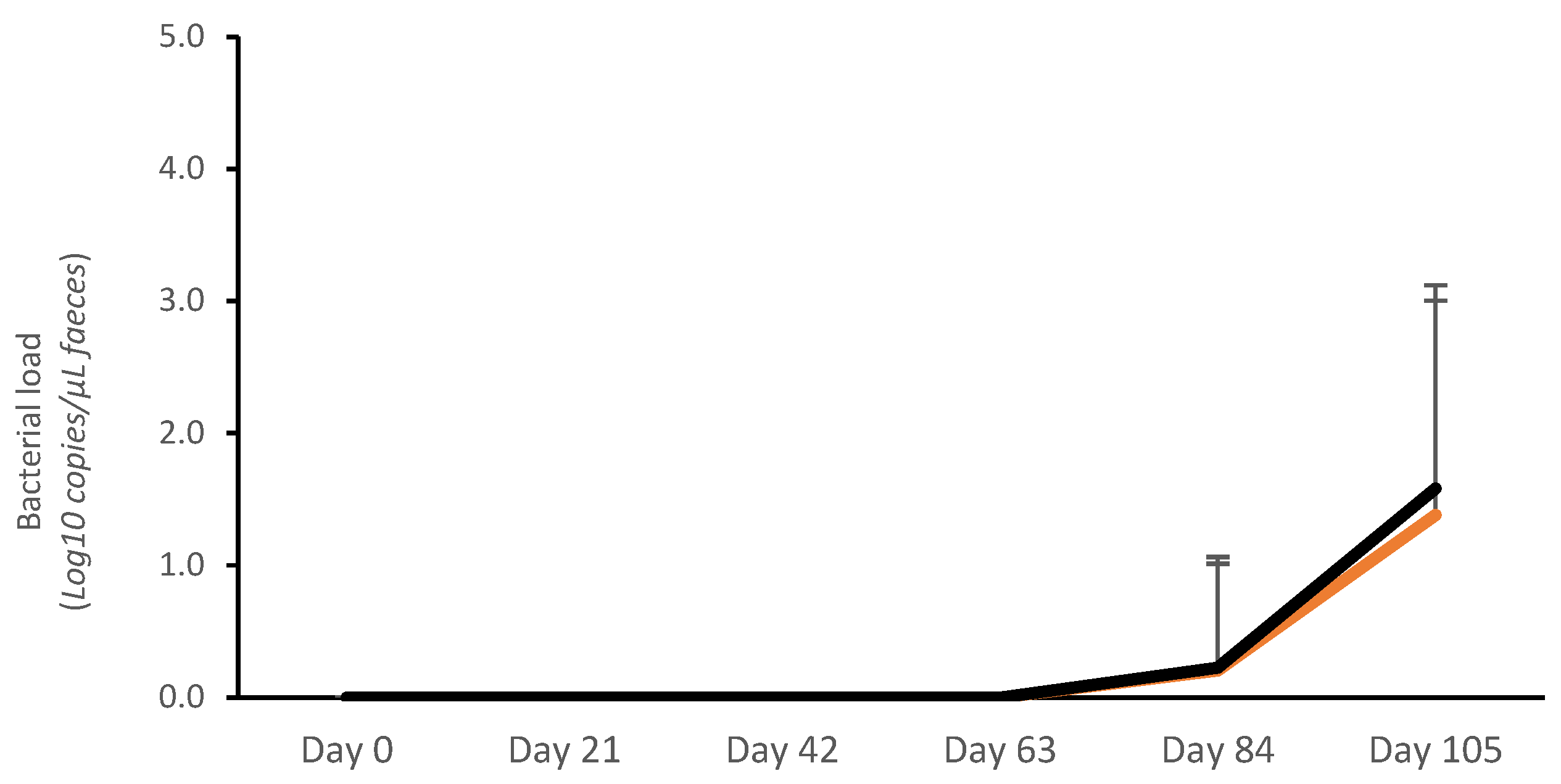
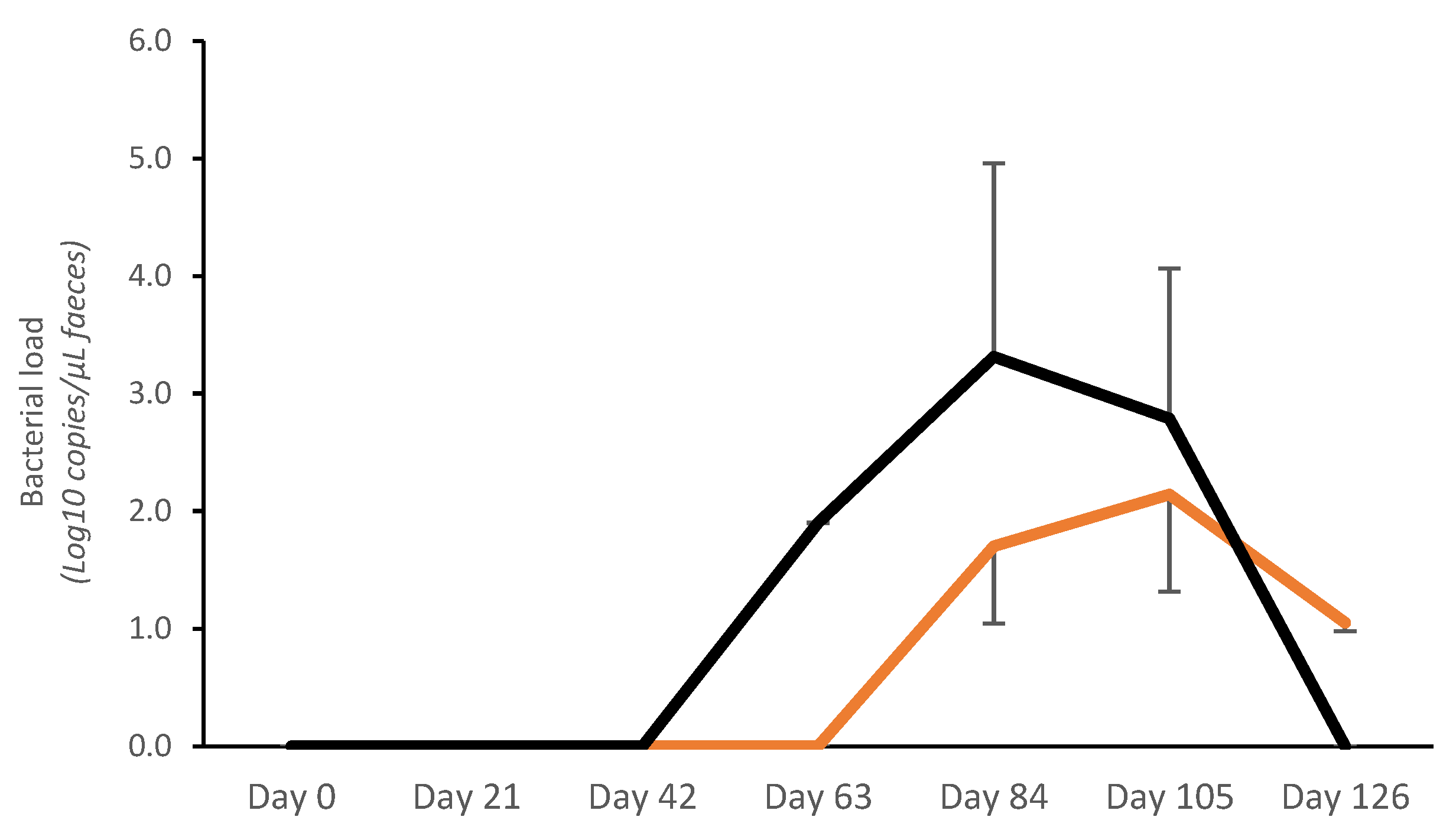
3.1.1. Fecal Bacterial Load
3.1.2. Performance
3.1.3. Association Between Fecal Load and ADG, ADI, and FCR
3.1.4. Clinical Parameters
3.2. Field Trial 2
3.2.1. Fecal Bacterial Load
3.2.2. Clinical Parameters
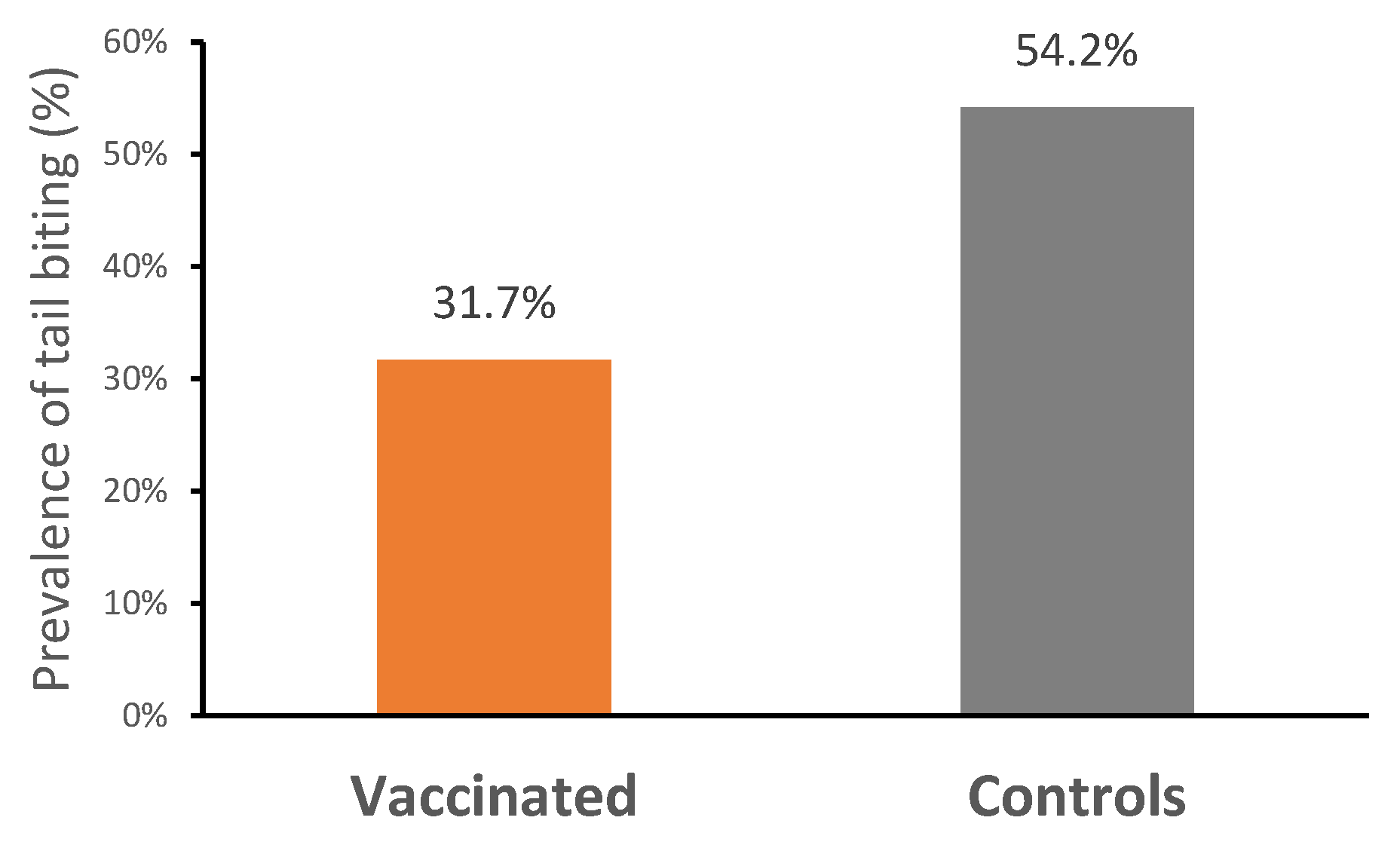
3.2.3. Carcass Quality
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| qPCR | real-time quantitative polymerase chain reaction |
| V | Vaccination group |
| C | Control group |
| AUC | Area Under the Curve |
| ADG | Average Daily Gain |
| ADI | Average Daily Feed Intake |
| FCR | Feed Conversion Ratio |
| LM% | Lean Meat percentage |
| SE | Standard Error |
| SPF | Specific Pathogen Free |
| SCFAs | Short-Chain Fatty Acids |
References
- Lawson, G.H.K.; McOrist, S.; Sabri, J.; Mackie, R.A. Intracellular Bacteria of Porcine Proliferative Enteropathy: Cultivation and Maintenance In Vitro. J. Clin. Microbiol. 1993, 31, 1136–1142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vannucci, F.A.; Gebhart, C.J.; McOrist, S. Proliferative Enteropathy. In Book Diseases of Swine, 11th ed.; Zimmerman, J.J., Karriker, L.A., Ramirez, A., Schwartz, K.J., Stevenson, G.W., Zhang, J., Eds.; John Wiley & Sons, Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 2019; pp. 898–911. [Google Scholar]
- McOrist, S.; Gebhart, C.J.; Boid, R.; Barns, S.M. Characterization of Lawsonia intracellularis gen. nov., sp.nov, the obligately intracellular bacterium of porcine proliferative enteropathy. Int. J. Syst. Bacteriol. 1995, 45, 820–825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pedersen, K.S.; Ståhl, M.; Guedes, R.M.C.; Angen, Ø.; Nielsen, J.P.; Jensen, T.J. Association between faecal load of Lawsonia intracellularis and pathological findings of proliferative enteropathy in pigs with diarrhoea. BMC Vet. Res. 2012, 8, 198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collins, A.M.; Barchia, I.M. The critical threshold of Lawsonia intracellularis in pig faeces that causes reduced average daily weight gains in experimentally challenged pigs. Vet. Microbiol. 2014, 168, 455–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnold, M.; Crienen, A.; Swam, H.; von Berg, S.; Jolie, R.; Nathues, H. Prevalence of Lawsonia intracellularis in pig herds in different European countries. Porc. Health Manag. 2019, 5, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vannucci, F.B.; Borges, E.L.; de Oliveira, J.S.V.; Guedes, R.M.C. Intestinal absorption and histomorphometry of Syrian hamsters (Mesocricetus auratus) experimentally infected with Lawsonia intracellularis. Vet. Microbiol. 2010, 145, 286–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winkelman, N. Subclinical ileitis: Diagnostic monitoring, R2, and economics. In Proceedings of the 49th Annual Meeting of the American Association of Swine Veterinarians AASV, San Diego, CA, USA, 3–6 March 2018; pp. 488–493. [Google Scholar]
- Karuppannan, A.K.; Opriessnig, T. Lawsonia intracellularis: Revisiting the Disease Ecology and Control of This Fastidious Pathogen in Pigs. Front. Vet. Sci. 2018, 5, 181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marsteller, T.A.; Armbruster, G.; Bane, D.P.; Gebhart, C.P.; Muller, R.; Weatherford, J.; Thacker, B. Monitoring the prevalence of Lawsonia intracellularis IgG antibodies using serial sampling in growing and breeding swine herds. J. Swine Health Prod. 2003, 11, 127–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baldasso, D.Z.; Guizzo, J.A.; Dazzi, C.C.; Paraboni Frandoloso, G.C.; Feronato, C.; von Berg, S.; Carvalho Guedes, R.M.; Wilson, H.L.; Kreutz, L.C.; Frandoloso, R. Development and validation of a flow cytometry antibody test for Lawsonia intracellularis. Front. Immunol. 2023, 14, 1145072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbosa, J.C.R.; Nicolino, R.R.; Gabardo, M.P.; Gonçalves, J.P.M.; Suarez-Duarte, M.E.; Laub, R.P.; Daniel, A.G.S.; Mariano, G.H.S.; Costa, C.M.; Correia, P.A.; et al. Subsistence swine farming: Seroprevalence and risk factors associated with Lawsonia intracellularis infection in the state of Minas Gerais Brazil in 2016. Trop. Anim. Health Prod. 2023, 55, 314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McOrist, S. Prevalence and impact of proliferative enteropathy = ileitis, in East Asia. In Proceedings of the 2nd Asian Pig Veterinary Society. Congress. APVS, Shangri-La, Pasig City, Philippines, 19–21 September 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Yeh, J.Y.; Lee, J.H.; Yeh, H.R.; Kim, A.; Lee, J.Y.; Hwang, J.M.; Kang, B.K.; Kim, J.M.; Choi, I.S.; Lee, J.B. Antimicrobial susceptibility testing of two Lawsonia intracellularis isolates associated with proliferative hemorrhagic enteropathy and porcine intestinal adenomatosis in South Korea. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2011, 55, 4451–4453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Z.; Ling, Y.; Tian, D.; Pan, Q.; Heegaard, P.M.H.; He, C. Seroprevalence of Lawsonia intracellularis antibodies in intensive pig farms in China. BMC Vet. Res. 2014, 10, 100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, T.C.; Maghfira, C.R.; Young, N.; Samatiwat, K.; Kaewpaluk, C.; Laothanakit, A.; Mungprasittichai, P.; Thanawongnuwech, R.; Panyasing, Y. Seroprevalence of Lawsonia intracellularis Antibodies among Large-scale Swine Farming Systems in Thailand. Thai. J. Vet. Med. 2024, 53, 481–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Wu, W.; Zhao, L.; Zhu, Z.; Yao, X.; Fan, J.; Chen, H.; Song, W.; Huang, X.; Hua, L.; et al. Fecal PCR survey and genome analysis of Lawsonia intracellularis in China. Front. Vet. Sci. 2024, 11, 1324768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steven McOrist. Defining the full costs of endemic porcine proliferative enteropathy. Vet. J. 2005, 170, 8–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paradis, M.A.; Gebhart, C.J.; Toole, D.; Vessie, G.; Winkelman, N.L.; Bauer, A.A.; Wilson, J.B.; McClure, C.A. Subclinical ileitis: Diagnostic and performance parameters in a multi-dose mucosal homogenate challenge model. J. Swine Health Prod. 2012, 20, 137–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pedersen, K.S.; Skrubel, R.; Stege, H.; Angen, Ø.; Ståhl, M.; Hjulsager, C.; Larsen, L.E.; Nielsen, J.P. Association between average daily gain, faecal dry matter content and concentration of Lawsonia intracellularis in faeces. Acta Vet. Scand. 2012, 54, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johansen, M.; Nielsen, M.; Dahl, J.; Svensmark, B.; Bækbo, P.; Kristensen, C.S.; Hjulsager, C.K.; Jensen, T.K.; Ståhl, M.; Larsen, L.E.; et al. Investigation of the association of growth rate in grower-finishing pigs with the quantification of Lawsonia intracellularis and porcine circovirus type 2. Prev. Vet. Med. 2013, 108, 63–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nathues, H.; Holthaus, K.; grosse Beilage, E. Quantification of Lawsonia intracellularis in porcine faeces by real-time PCR. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2009, 107, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ståhl, M.; Kokotovic, B.; Hjulsager, C.K.; Breum, S.Ø.; Angen, Ø. The use of quantitative PCR for identification and quantification of Brachyspira pilosicoli, Lawsonia intracellularis and Escherichia coli fimbrial types F4 and F18 in pig feces. Vet. Microbiol. 2011, 151, 307–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johansen, M.; Nielsen, M.; Dahl, J.; Svensmark, B.; Bækbo, P.; Ståhl, M.; Hjulsager, C.K.; Angen, Ø. Effects of Lawsonia intracellularis on Average Daily Gain in finisher pigs. In Proceedings of the 22nd International Pig Veterinary Society Congress IPVS, Jeju, Republic of South Korea, 10–13 June 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Pedersen, K.S.; Stege, H.; Jensen, T.K.; Guedes, R.; Stahl, M.; Nielsen, J.P.; Hjulsager, C.; Larsen, L.E.; Angen, Ø. Diagnostic performance of fecal real-time polymerase chain reaction for detection of Lawsonia intracellularis-associated proliferative enteropathy in nursery pigs. J. Vet. Diagn. Investig. 2013, 25, 336–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacobs, A.A.C.; Harks, F.; Hazenberg, L.; Hoeijmakers, M.J.H.; Nell, T.; Pel, S.; Segers, R.P.A.M. Efficacy of a novel inactivated Lawsonia intracellularis vaccine in pigs against experimental infection and under field conditions. Vaccine 2019, 37, 2149–2157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jacobs, A.A.C.; Harks, F.; Pauwels, R.; Cao, Q.; Holtslag, H.; Pel, S.; Segers, R.P.A.M. Efficacy of a novel intradermal Lawsonia intracellularis vaccine in pigs against experimental infection and under field conditions. Porcine Health Manag. 2020, 6, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Horsington, J.; Witvliet, M.; Jacobs, A.A.C.; Segers, R.P.A.M. Efficacy of Simultaneous Intradermal Vaccination of Swine against Porcine Circovirus 2, Porcine Reproductive and Respiratory Syndrome Virus, Mycoplasma hyopneumoniae and Lawsonia intracellularis. Animals 2021, 11, 2225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Musse, S.L.; Nielsen, G.B.; Stege, H.; Weber, N.R.; Houe, H. Productivity parameters, antimicrobial consumption, and prevalence of enteric pathogens before and after intramuscular vaccination against Lawsonia intracellularis in naturally infected Danish weaner and finisher pig herds. Prev. Vet. Med. 2023, 217, 105973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Musse, S.L.; Nielsen, G.B.; Stege, H.; Weber, N.R.; Houe, H. Effect of intramuscular vaccination against Lawsonia intracellularis on production parameters, diarrhea occurrence, antimicrobial treatment, bacterial shedding, and lean meat percentage in two Danish naturally infected finisher pig herds. Prev. Vet. Med. 2023, 212, 105837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Del Pozo Sacristan, R.; Lunt, J.; Berkshire, D.; Swam, H. Reduction on Lawsonia intracellularis faecal shedding in pigs chronically infected after intramuscular vaccination against Lawsonia intracellularis. In Proceedings of the 13th European Symposium of Porcine Health Management ESPHM, Budapest, Hungary, 11–13 May 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Lindecrona, R.H.; Jensen, T.K.; Andersen, P.H.; Moller, K. Application of 5’ nuclease assay for detection of Lawsonia intracellularis in fecal samples from pigs. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2002, 40, 984–987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Musse, S.L.; Nielsen, G.B.; Stege, H.; Weber, N.R.; Houe, H. Difference in Lawsonia intracellularis between batches and days post entry must be considered when performing diagnostics of ileitis in finisher herds. In Proceedings of the 13th European Symposium of Porcine Health Management ESPHM, Budapest, Hungary, 11–13 May 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Pedersen, K.S.; Holyoake, P.; Stege, H.; Nielsen, J.P. Diagnostic performance of different fecal Lawsonia intracellularis-specific polymerase chain reaction assays as diagnostic tests for proliferative enteropathy in pigs: A review. J. Vet. Diagn. Investig. 2010, 22, 487–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brandt, D.; Kaim, U.; Baumgartner, W.; Wendt, M. Evaluation of Lawsonia intracellularis infection in a group of pigs in a subclinically affected herd from weaning to slaughter. Vet. Microbiol. 2010, 146, 361–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Del Pozo Sacristan, R.; Lunt, J.; Berkshire, D.; Swam, H. Intramuscular vaccination against Lawsonia intracellularis as a tool to reduce antimicrobial consumption—A case report. In Proceedings of the 26th International Pig Veterinary Society Congress IPVS, Rio De Janeiro, Brazil, 21–24 June 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Marcos Cienfuegos, M.; Jimenez, M.; Menjon, R.; Llorente, C.; Perez, M.L.; Bollo, J.; Romero, A.; Santos, L.; Serrano, D.; Tejedor, T. Control of ileitis in growers and finisher pigs after Lawsonia intracellularis parenteral vaccination. In Proceedings of the 14th European Symposium of Porcine Health Management ESPHM, Thessaloniki, Greece, 31 May–2 June 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Henry, M.; Jansen, H.; Amezcua, M.D.R.; O’Sullivan, T.L.; Niel, L.; Shoveller, A.K.; Friendship, R.M. Tail-Biting in Pigs: A Scoping Review. Animals 2021, 11, 2002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rabhi, N.; Thibodeau, A.; Côté, J.C.; Devillers, N.; Laplante, B.; Fravalo, P.; Larivière-Gauthier, G.; Thériault, W.P.; Faucitano, L.; Beauchamp, G.; et al. Association Between Tail-Biting and Intestinal Microbiota Composition in Pigs. Front. Vet. Sci. 2020, 7, 563762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verbeek, E.; Keeling, L.; Landberg, R.; Lindberg, J.E.; Dicksved, J. The gut microbiota and microbial metabolites are associated with tail biting in pigs. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 20547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Konig, E.; Heponiemi, P.; Kivinen, S.; Rakkolainen, J.; Beasley, S.; Hukkinen, V.; Norring, M.; Sali, V.; Salminen, S.; Heinonen, M.; et al. Relation of Faecal lactobacilli to manipulative behaviour in pigs. In Proceedings of the 55th Congress of the International Society for Applied Ethology (ISAE), Ohird, North Macedonia, 4–8 September 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Valros, A. Managing tail biting in pigs: Preventing risk factors or docking tails? In Book Advances in Pig Welfare, 2nd ed.; Camerlink, I., Baxter, E.M., Eds.; Woodhead Publishing: Sawston, UK, 2024; pp. 261–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobek-Kjeldager, C.; Schönherz, A.A.; Canibe, N.; Pedersen, L.J. Diet and microbiota-gut-brain axis in relation to tail biting in pigs: A review. Appl. Anim. Behav. Sci. 2022, 246, 105514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molbak, L.; Johnsen, K.; Boye, M.; Jensen, T.K.; Johansen, M.; Moller, K.; Leser, T.D. The microbiota of pigs influenced by diet texture and severity of Lawsonia intracellularis infection. Vet. Microbiol. 2008, 128, 96–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borewicz, K.A.; Kim, H.B.; Singer, R.S.; Gebhart, C.J.; Sreevatsan, S.; Johnson, T.; Isaacson, R.E. Changes in the porcine intestinal microbiome in response to infection with Salmonella enterica and Lawsonia intracellularis. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0139106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hankel, J.; Sander, S.; Muthukumarasamy, U.; Strowig, T.; Kamphues, J.; Jung, K.; Visscher, C. Microbiota of vaccinated and non-vaccinated clinically inconspicuous and conspicuous piglets under natural Lawsonia intracellularis infection. Front. Vet. Sci. 2022, 9, 1004506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marcos Cienfuegos, M.; Jimenez, M.; Menjon, R.; Llorente, C.; Perez, M.L.; Bollo, J.; Romero, A.; Santos, L.; Serrano, D.; Tejedor, T. Carcass performance at slaughterhouse after parenteral ileitis vaccination. In Proceedings of the 14th European Symposium of Porcine Health Management ESPHM, Thessaloniki, Greece, 31 May–2 June 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Kamoei, M.; Massaferro, L.; Luiz, H.; Figueiredo MPereira, S.; Marques, B. Immunization against ileitis in swine: A farm to slaughterhouse performance study. In Proceedings of the 13th European Symposium of Porcine Health Management ESPHM, Budapest, Hungary, 11–13 May 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Pluske, J.R.; Hampson, D.J.; Williams, I.H. Factors influencing the structure and function of the small intestine in the weaned pig: A review. Livest. Prod. Sci. 1996, 46, 215–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pluske, J.R.; Turpin, D.L.; Kim, J.C. Gastrointestinal tract (gut) health in the young pig. Anim. Nutr. 2018, 4, 187–196. [Google Scholar]
- Han, Q.; Huang, X.; Yan, F.; Yin, J.; Xiao, Y. The Role of Gut Microbiota in the Skeletal Muscle Development and Fat Deposition in Pigs. Antibiotics 2022, 11, 793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boyen, F.; Haesebrouck, F.; Vanparys, A.; Volf, J.; Mahu, M.; Van Immerseel, F.; Rychlik, I.; Dewulf, J.; Ducatelle, R.; Pasmans, F. Coated fatty acids alter virulence properties of Salmonella Typhimurium and decrease intestinal colonization of pigs. Vet. Microbiol. 2008, 132, 319–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Riet, M.M.J.; Vartiainen, S.; Jurgens, G.; Seppala, A.; Rikkola, K.; Vermaut, S.; Peeters, I. Inhibitory effect of SCFA and MCFA on contaminants of liquid pig feed and intestinal bacteria. In Proceedings of the European Federation of Animal Science Congress, Ghent, Belgium, 26–30 August 2019. [Google Scholar]
| Control Pigs | Vaccinated Pigs | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PCC | p-Value | PCC | p-Value | |
| ADG | R2 = −0.193 | p < 0.05 | R2 = 3.831 × 10−4 | p > 0.05 |
| ADI | R2 = −0.111 | p < 0.1 | R2 = 0.008 | p > 0.05 |
| FCR | R2 = 0.136 | p < 0.05 | R2 = 0.018 | p > 0.05 |
| Control Pigs | Vaccinated Pigs | |
|---|---|---|
| Mortality % | 1.7 | 0 |
| Individual treatment incidences % | 15.8 | 17.5 |
| Tail biting % | 16.7 | 15.8 |
| Controls | Vaccinated | Difference | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Mortality % | 0.8 | 0 | NA |
| Individual treatment incidences % | 32.5 | 35.8 | NA |
| Tail biting % | 54.2 A | 31.7 B | −22.5 |
| Carcass weight (kg) | 113.7 | 115.6 | NA |
| Back fat (mm) | 10.9 | 10.5 | −0.4 |
| Lean Meat % | 62.1 A | 62.7 B | +0.6 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Del Pozo Sacristán, R.; Swam, H.; von Berg, S.; Taylor, A.E. Vaccination Reduces Fecal Shedding and Improves Carcass Quality in Pigs with Subclinical Lawsonia intracellularis Infections. Vaccines 2025, 13, 728. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines13070728
Del Pozo Sacristán R, Swam H, von Berg S, Taylor AE. Vaccination Reduces Fecal Shedding and Improves Carcass Quality in Pigs with Subclinical Lawsonia intracellularis Infections. Vaccines. 2025; 13(7):728. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines13070728
Chicago/Turabian StyleDel Pozo Sacristán, Rubén, Hanny Swam, Stephan von Berg, and Amy Elizabeth Taylor. 2025. "Vaccination Reduces Fecal Shedding and Improves Carcass Quality in Pigs with Subclinical Lawsonia intracellularis Infections" Vaccines 13, no. 7: 728. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines13070728
APA StyleDel Pozo Sacristán, R., Swam, H., von Berg, S., & Taylor, A. E. (2025). Vaccination Reduces Fecal Shedding and Improves Carcass Quality in Pigs with Subclinical Lawsonia intracellularis Infections. Vaccines, 13(7), 728. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines13070728





