A Modified Variant of Fasciola hepatica FhSAP-2 (mFhSAP-2) as a Recombinant Vaccine Candidate Induces High-Avidity IgG2c Antibodies and Enhances T Cell Activation in C57BL/6 Mice
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
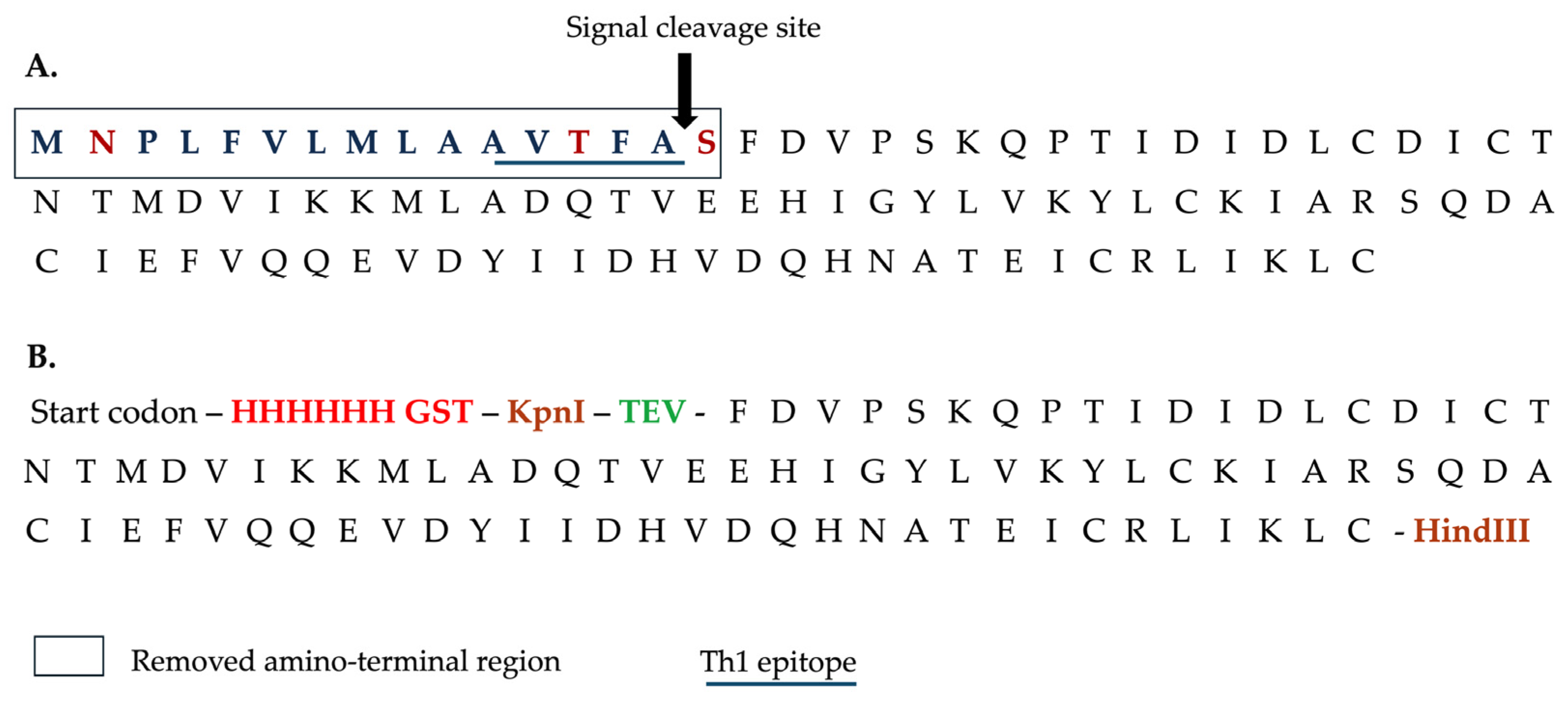
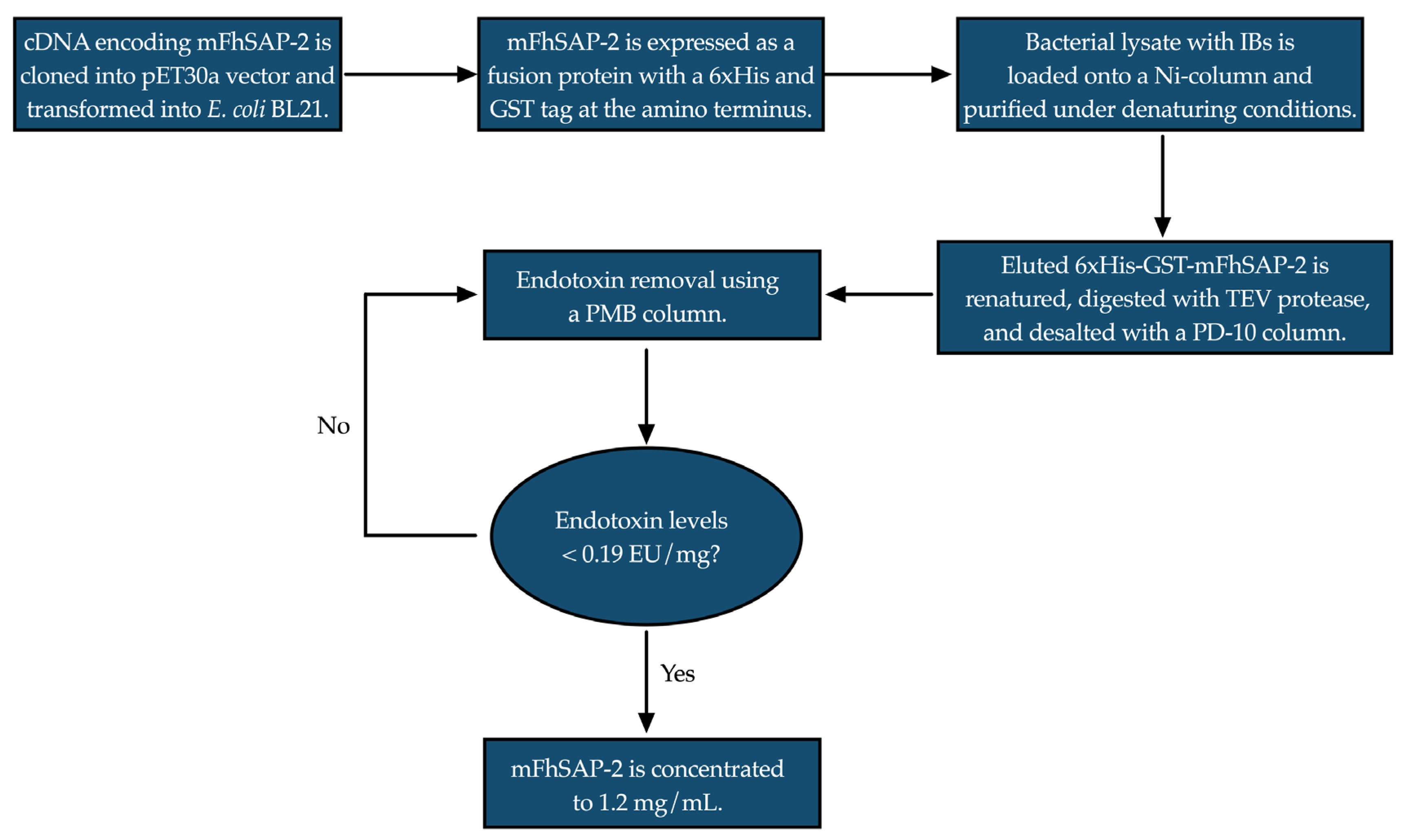
2.1. Recombinant Protein Production and Purification
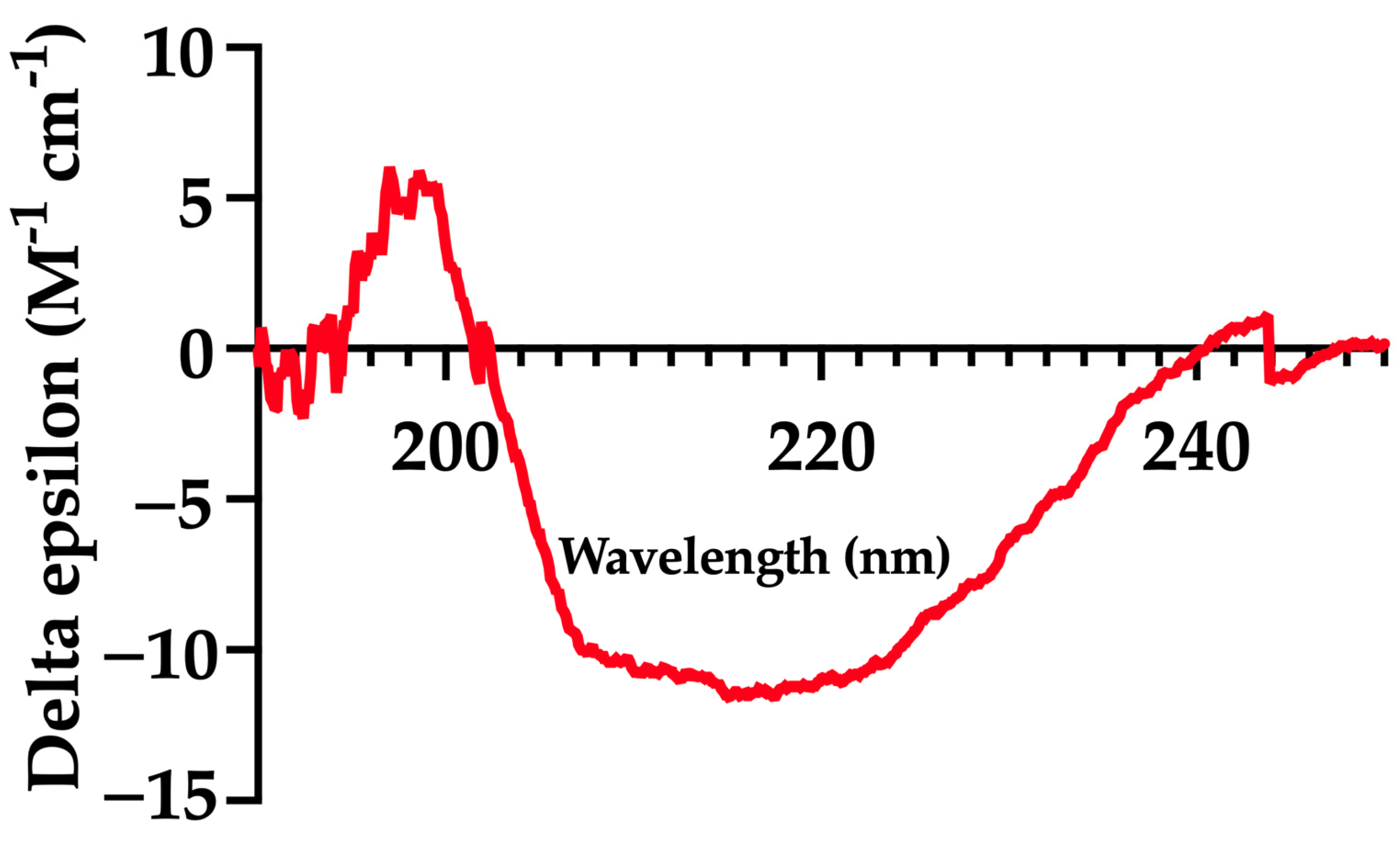
2.2. Circular Dichroism (CD)
2.3. Animals
2.4. Cell Culture, mFhSAP-2 Treatment, and Measurement of TNFα Levels by ELISA
2.5. Cell Viability Assay
2.6. Sera from Fasciola hepatica-Infected Animals
2.7. Immunization of C57BL/6 Mice with mFhSAP-2
2.8. Enzyme-Linked Immunoassay (ELISA) for Determining Total Antibody Levels of IgG and IgG Isotypes
2.9. Avidity of Anti-mFhSAP-2 IgG2a and IgG2c Antibodies
2.10. Splenocyte Proliferation
2.11. Flow Cytometry
2.12. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. mFhSAP-2 Was Successfully Expressed in E. coli with High Purity and Yield
3.2. mFhSAP-2 Exhibits a Secondary Structure Similar to That Predicted for the Full-Length Protein
3.3. mFhSAP-2 Induces TNFα Production in RAW264.7 Cells Without Affecting Cell Viability
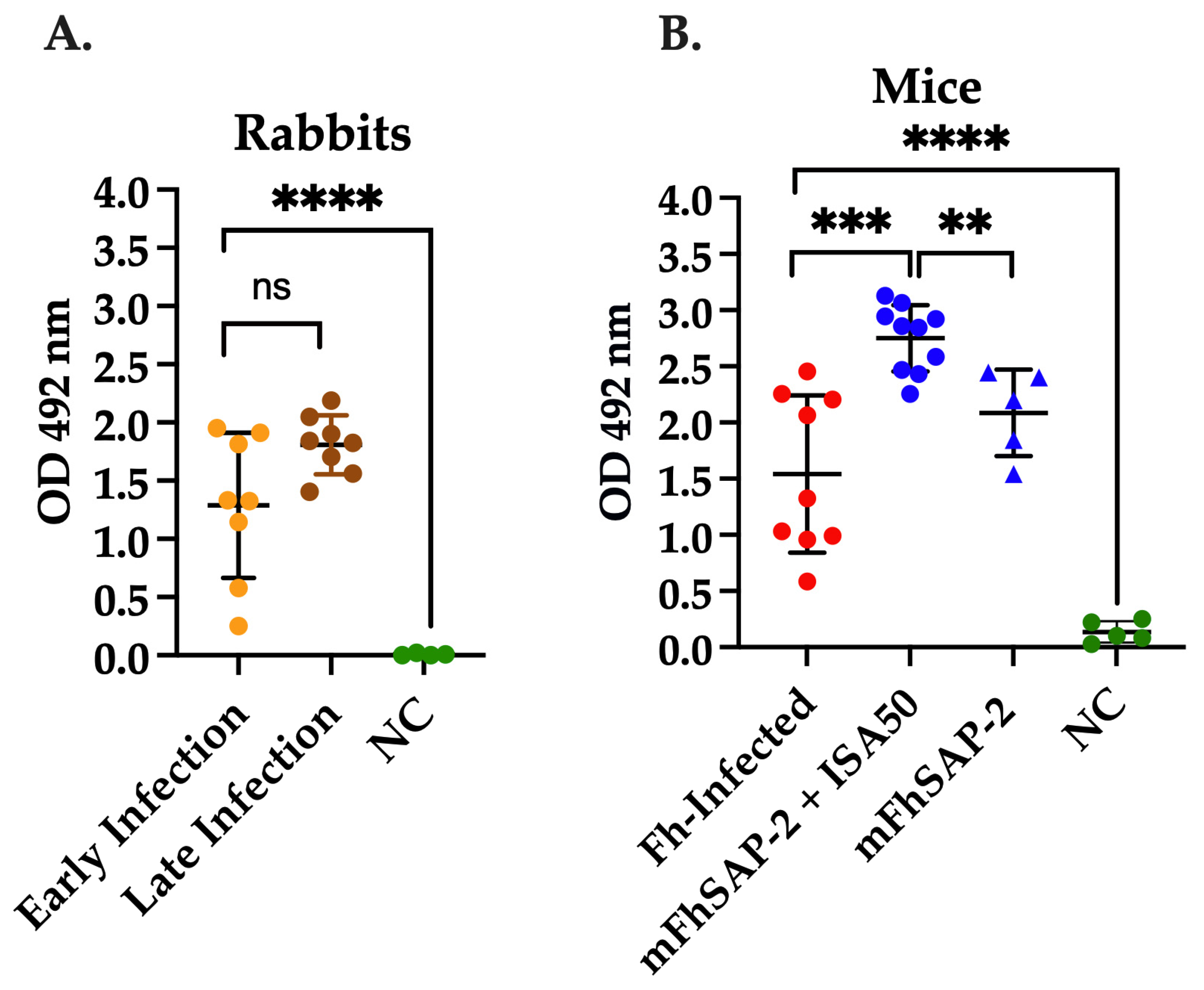
3.4. mFhSAP-2 Induces Strong Anti-mFhSAP-2 IgG Response in F. hepatica-Infected and Immunized Animals
3.5. mFhSAP-2 Induces a Predominant Th1 Antibody Response in Immunized Mice and a Predominant Th2 Antibody Response in Infected Animals
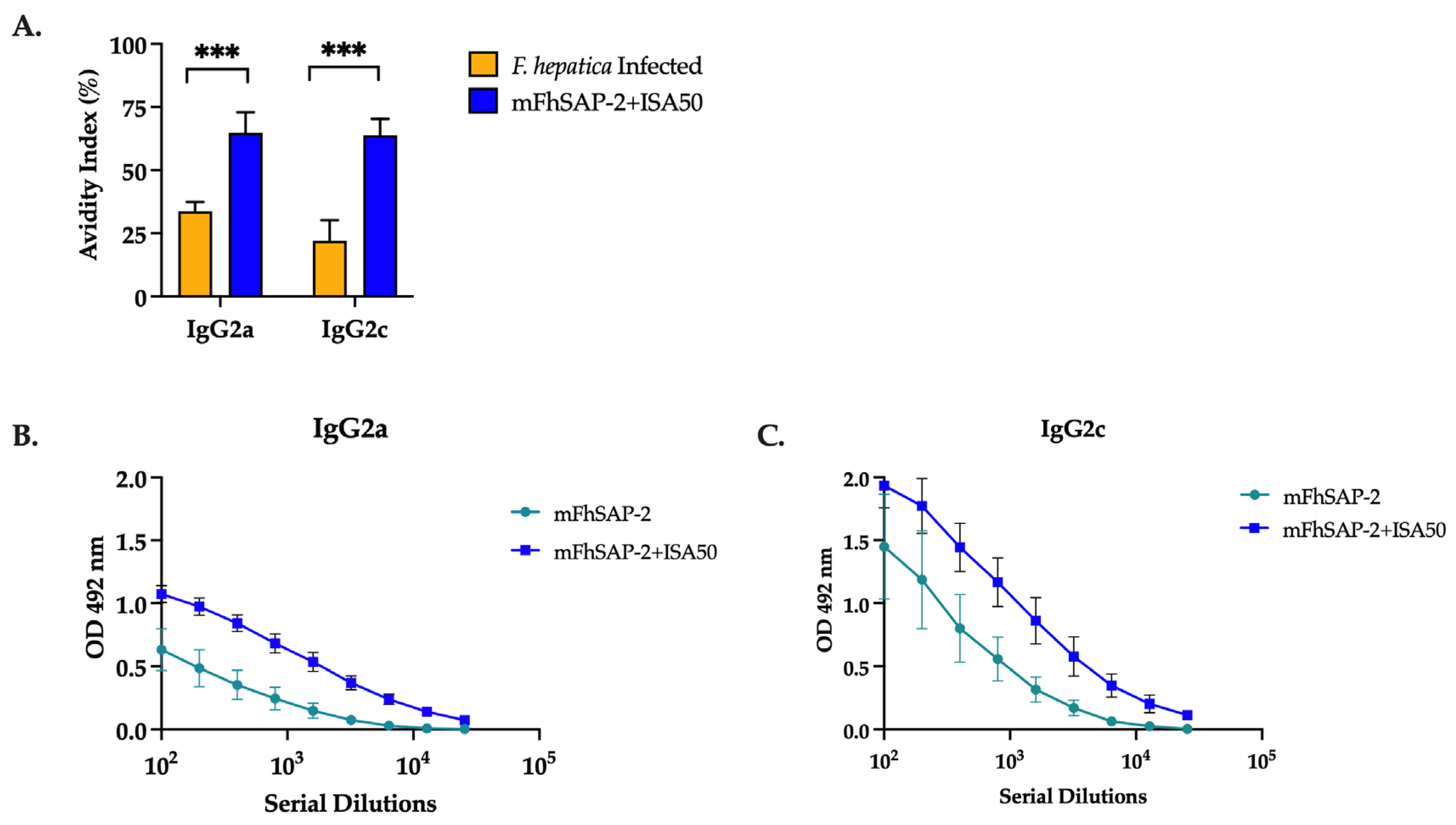
3.6. mFhSAP-2 Induces High-Avidity IgG2a and IgG2c Antibodies with a Predominance of IgG2c over IgG2a in Immunized C57BL/6 Mice
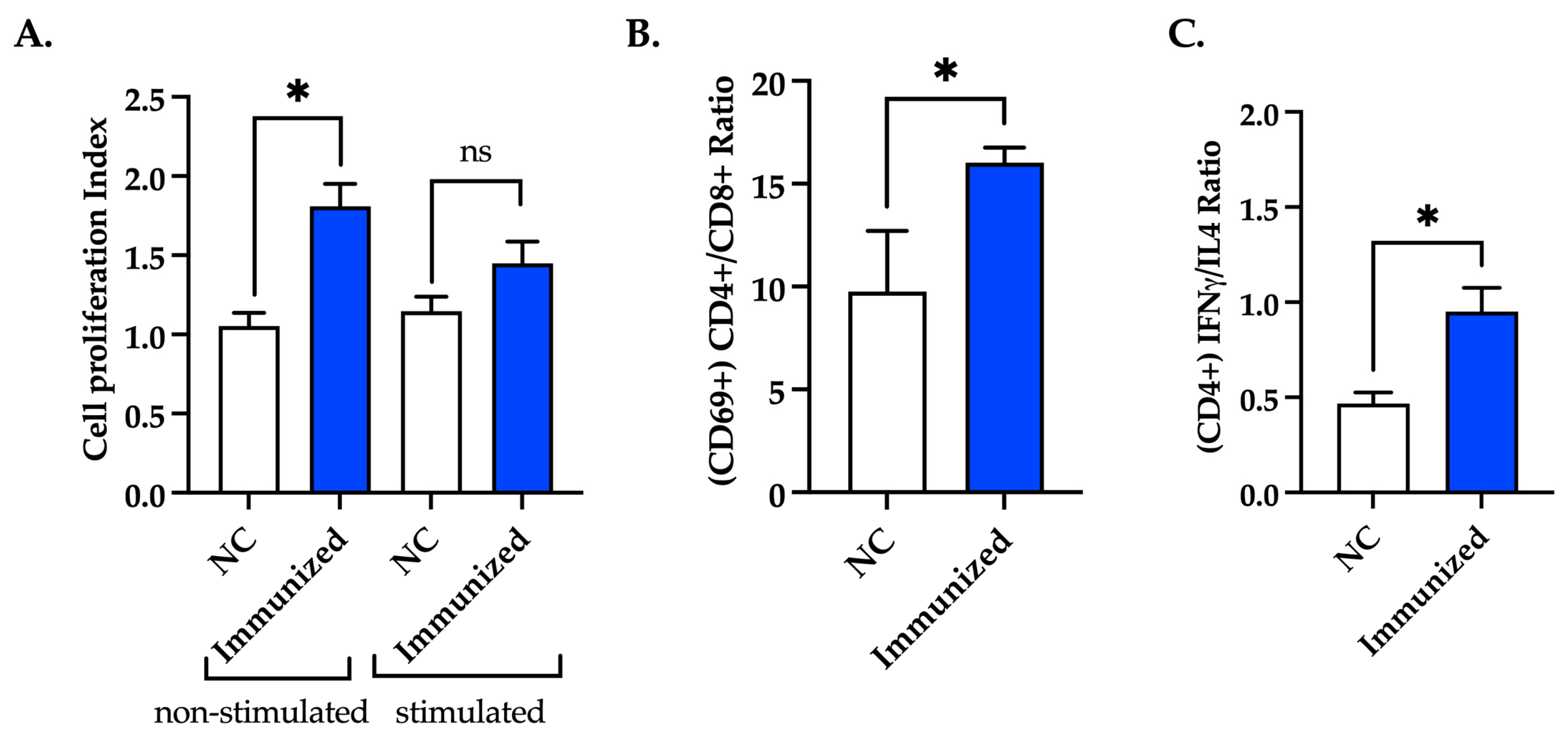
3.7. Immunization with mFhSAP-2 Induces Splenocyte Proliferation and Predominance of CD4+ T Cells over CD8+ T Cells with Higher IFNγ than IL-4 Production
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions and Study Limitations
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mas-Coma, S.; Valero, M.A.; Bargues, M.D. Chapter 2. Fasciola, lymnaeids and human fascioliasis, with a global overview on disease transmission, epidemiology, evolutionary genetics, molecular epidemiology and control. Adv. Parasitol. 2009, 69, 41–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Molina-Hernandez, V.; Mulcahy, G.; Perez, J.; Martinez-Moreno, A.; Donnelly, S.; O’Neill, S.M.; Dalton, J.P.; Cwiklinski, K. Fasciola hepatica vaccine: We may not be there yet but we’re on the right road. Vet. Parasitol. 2015, 208, 101–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Gonzalez, L.C.; Esteban, J.G.; Bargues, M.D.; Valero, M.A.; Ortiz, P.; Naquira, C.; Mas-Coma, S. Hyperendemic human fascioliasis in Andean valleys: An altitudinal transect analysis in children of Cajamarca province, Peru. Acta Trop. 2011, 120, 119–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vazquez, A.A.; de Vargas, M.; Alba, A.; Sanchez, J.; Alda, P.; Sabourin, E.; Vittecoq, M. Reviewing Fasciola hepatica transmission in the West Indies and novel perceptions from experimental infections of sympatric vs. allopatric snail/fluke combinations. Vet. Parasitol. 2019, 275, 108955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fairweather, I.; Brennan, G.P.; Hanna, R.E.B.; Robinson, M.W.; Skuce, P.J. Drug resistance in liver flukes. Int. J. Parasitol. Drugs Drug Resist. 2020, 12, 39–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Kelley, J.M.; Elliott, T.P.; Beddoe, T.; Anderson, G.; Skuce, P.; Spithill, T.W. Current Threat of Triclabendazole Resistance in Fasciola hepatica. Trends Parasitol. 2016, 32, 458–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buffoni, L.; Martinez-Moreno, F.J.; Zafra, R.; Mendes, R.E.; Perez-Ecija, A.; Sekiya, M.; Mulcahy, G.; Perez, J.; Martinez-Moreno, A. Humoral immune response in goats immunised with cathepsin L1, peroxiredoxin and Sm14 antigen and experimentally challenged with Fasciola hepatica. Vet. Parasitol. 2012, 185, 315–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Casanueva, P.; Hillyer, G.V.; Ramajo, V.; Oleaga, A.; Espinoza, E.Y.; Muro, A. Immunoprophylaxis against Fasciola hepatica in rabbits using a recombinant Fh15 fatty acid-binding protein. J. Parasitol. 2001, 87, 697–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martinez-Fernandez, A.R.; Nogal-Ruiz, J.J.; Lopez-Aban, J.; Ramajo, V.; Oleaga, A.; Manga-Gonzalez, Y.; Hillyer, G.V.; Muro, A. Vaccination of mice and sheep with Fh12 FABP from Fasciola hepatica using the new adjuvant/immunomodulator system ADAD. Vet. Parasitol. 2004, 126, 287–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramajo, V.; Oleaga, A.; Casanueva, P.; Hillyer, G.V.; Muro, A. Vaccination of sheep against Fasciola hepatica with homologous fatty acid binding proteins. Vet. Parasitol. 2001, 97, 35–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buffoni, L.; Zafra, R.; Perez-Ecija, A.; Martinez-Moreno, F.J.; Martinez-Galisteo, E.; Moreno, T.; Perez, J.; Martinez-Moreno, A. Immune response of goats immunised with glutathione S-transferase and experimentally challenged with Fasciola hepatica. Parasitol. Int. 2010, 59, 147–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sexton, J.L.; Milner, A.R.; Panaccio, M.; Waddington, J.; Wijffels, G.; Chandler, D.; Thompson, C.; Wilson, L.; Spithill, T.W.; Mitchell, G.F.; et al. Glutathione S-transferase. Novel vaccine against Fasciola hepatica infection in sheep. J. Immunol. 1990, 145, 3905–3910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zerna, G.; Cameron, T.C.; Toet, H.; Spithill, T.W.; Beddoe, T. Bovine Natural Antibody Relationships to Specific Antibodies and Fasciola hepatica Burdens after Experimental Infection and Vaccination with Glutathione S-Transferase. Vet. Sci. 2022, 9, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Golden, O.; Flynn, R.J.; Read, C.; Sekiya, M.; Donnelly, S.M.; Stack, C.; Dalton, J.P.; Mulcahy, G. Protection of cattle against a natural infection of Fasciola hepatica by vaccination with recombinant cathepsin L1 (rFhCL1). Vaccine 2010, 28, 5551–5557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piacenza, L.; Acosta, D.; Basmadjian, I.; Dalton, J.P.; Carmona, C. Vaccination with cathepsin L proteinases and with leucine aminopeptidase induces high levels of protection against fascioliasis in sheep. Infect. Immun. 1999, 67, 1954–1961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Acosta, D.; Cancela, M.; Piacenza, L.; Roche, L.; Carmona, C.; Tort, J.F. Fasciola hepatica leucine aminopeptidase, a promising candidate for vaccination against ruminant fasciolosis. Mol. Biochem. Parasitol. 2008, 158, 52–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maggioli, G.; Acosta, D.; Silveira, F.; Rossi, S.; Giacaman, S.; Basika, T.; Gayo, V.; Rosadilla, D.; Roche, L.; Tort, J.; et al. The recombinant gut-associated M17 leucine aminopeptidase in combination with different adjuvants confers a high level of protection against Fasciola hepatica infection in sheep. Vaccine 2011, 29, 9057–9063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cwiklinski, K.; Drysdale, O.; Lopez Corrales, J.; Corripio-Miyar, Y.; De Marco Verissimo, C.; Jewhurst, H.; Smith, D.; Lalor, R.; McNeilly, T.N.; Dalton, J.P. Targeting Secreted Protease/Anti-Protease Balance as a Vaccine Strategy against the Helminth Fasciola hepatica. Vaccines 2022, 10, 155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Silvane, L.; Celias, D.P.; Romagnoli, P.A.; Maletto, B.A.; Sanchez Vallecillo, M.F.; Chiapello, L.S.; Palma, S.D.; Allemandi, D.A.; Sanabria, R.E.F.; Pruzzo, C.I.; et al. A Vaccine Based on Kunitz-Type Molecule Confers Protection Against Fasciola hepatica Challenge by Inducing IFN-gamma and Antibody Immune Responses Through IL-17A Production. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 2087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Cwiklinski, K.; McEvoy, A.; Lopez Corrales, J.; Jewhurst, H.; Calvani, N.E.D.; De Marco Verissimo, C.; Dorey, A.L.; Keane, O.M.; Dalton, J.P.; Lalor, R. Fasciola hepatica antioxidant and protease-inhibitor cocktail recombinant vaccines administered five times elicit potent and sustained immune responses in sheep but do not confer protection. Vet. Parasitol. 2023, 323, 110049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maggioli, G.; Silveira, F.; Martin-Alonso, J.M.; Salinas, G.; Carmona, C.; Parra, F. A recombinant thioredoxin-glutathione reductase from Fasciola hepatica induces a protective response in rabbits. Exp. Parasitol. 2011, 129, 323–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zafra, R.; Perez-Ecija, R.A.; Buffoni, L.; Moreno, P.; Bautista, M.J.; Martinez-Moreno, A.; Mulcahy, G.; Dalton, J.P.; Perez, J. Early and late peritoneal and hepatic changes in goats immunized with recombinant cathepsin L1 and infected with Fasciola hepatica. J. Comp. Pathol. 2013, 148, 373–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adams, P.N.; Aldridge, A.; Vukman, K.V.; Donnelly, S.; O’Neill, S.M. Fasciola hepatica tegumental antigens indirectly induce an M2 macrophage-like phenotype in vivo. Parasite Immunol. 2014, 36, 531–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vukman, K.V.; Adams, P.N.; Dowling, D.; Metz, M.; Maurer, M.; O’Neill, S.M. The effects of Fasciola hepatica tegumental antigens on mast cell function. Int. J. Parasitol. 2013, 43, 531–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Donnelly, S.; O’Neill, S.M.; Sekiya, M.; Mulcahy, G.; Dalton, J.P. Thioredoxin peroxidase secreted by Fasciola hepatica induces the alternative activation of macrophages. Infect. Immun. 2005, 73, 166–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Donnelly, S.; Stack, C.M.; O’Neill, S.M.; Sayed, A.A.; Williams, D.L.; Dalton, J.P. Helminth 2-Cys peroxiredoxin drives Th2 responses through a mechanism involving alternatively activated macrophages. FASEB J. 2008, 22, 4022–4032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pacheco, I.L.; Abril, N.; Zafra, R.; Molina-Hernandez, V.; Morales-Prieto, N.; Bautista, M.J.; Ruiz-Campillo, M.T.; Perez-Caballero, R.; Martinez-Moreno, A.; Perez, J. Fasciola hepatica induces Foxp3 T cell, proinflammatory and regulatory cytokine overexpression in liver from infected sheep during early stages of infection. Vet. Res. 2018, 49, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Pleasance, J.; Wiedosari, E.; Raadsma, H.W.; Meeusen, E.; Piedrafita, D. Resistance to liver fluke infection in the natural sheep host is correlated with a type-1 cytokine response. Parasite Immunol. 2011, 33, 495–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Espino, A.M.; Hillyer, G.V. Molecular cloning of a member of the Fasciola hepatica saposin-like protein family. J. Parasitol. 2003, 89, 545–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caban-Hernandez, K.; Espino, A.M. Differential expression and localization of saposin-like protein 2 of Fasciola hepatica. Acta Trop. 2013, 128, 591–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Espino, A.M.; Torres, D.; Morales, A.; Delgado, B.; Quetel, J.; Osuna, A. Fasciola hepatica: Identification of CD4+ T-helper epitopes from the 11.5 kDa saposin-like protein SAP-2 using synthetic peptides. Exp. Parasitol. 2007, 117, 65–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Torres, D.; Espino, A.M. Mapping of B-cell epitopes on a novel 11.5-kilodalton Fasciola hepatica-Schistosoma mansoni cross-reactive antigen belonging to a member of the, F. hepatica saposin-like protein family. Infect. Immun. 2006, 74, 4932–4938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Espino, A.M.; Rivera, F. Quantitation of cytokine mRNA by real-time RT-PCR during a vaccination trial in a rabbit model of fascioliasis. Vet. Parasitol. 2010, 169, 82–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Rivera, F.; Espino, A.M. Adjuvant-enhanced antibody and cellular responses to inclusion bodies expressing FhSAP2 correlates with protection of mice to Fasciola hepatica. Exp. Parasitol. 2016, 160, 31–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Beckham, S.A.; Law, R.H.; Smooker, P.M.; Quinsey, N.S.; Caffrey, C.R.; McKerrow, J.H.; Pike, R.N.; Spithill, T.W. Production and processing of a recombinant Fasciola hepatica cathepsin B-like enzyme (FhcatB1) reveals potential processing mechanisms in the parasite. Biol. Chem. 2006, 387, 1053–1061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spithill, T.W.; Toet, H.; Rathinasamy, V.; Zerna, G.; Swan, J.; Cameron, T.; Smooker, P.M.; Piedrafita, D.M.; Dempster, R.; Beddoe, T. Vaccines for Fasciola (liver fluke): New thinking for an old problem. In Fasciolosis, 2nd ed.; CAB International: Wallingford, UK, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Espino, A.M.; Morales, A.; Delgado, B.; Rivera, F.M.; Figueroa, O.; Suarez, E. Partial immunity to Fasciola hepatica in mice after vaccination with FhSAP2 delivered as recombinant protein or DNA construct. Ethn. Dis. 2010, 20, S17–S23. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Nazeri, S.; Zakeri, S.; Mehrizi, A.A.; Sardari, S.; Djadid, N.D. Measuring of IgG2c isotype instead of IgG2a in immunized C57BL/6 mice with Plasmodium vivax TRAP as a subunit vaccine candidate in order to correct interpretation of Th1 versus Th2 immune response. Exp. Parasitol. 2020, 216, 107944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vacca, F.; Le Gros, G. Tissue-specific immunity in helminth infections. Mucosal Immunol. 2022, 15, 1212–1223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Dalton, J.P.; Robinson, M.W.; Mulcahy, G.; O’Neill, S.M.; Donnelly, S. Immunomodulatory molecules of Fasciola hepatica: Candidates for both vaccine and immunotherapeutic development. Vet. Parasitol. 2013, 195, 272–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McNeilly, T.N.; Nisbet, A.J. Immune modulation by helminth parasites of ruminants: Implications for vaccine development and host immune competence. Parasite 2014, 21, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Pleasance, J.; Raadsma, H.W.; Estuningsih, S.E.; Widjajanti, S.; Meeusen, E.; Piedrafita, D. Innate and adaptive resistance of Indonesian Thin Tail sheep to liver fluke: A comparative analysis of Fasciola gigantica and Fasciola hepatica infection. Vet. Parasitol. 2011, 178, 264–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ortega-Vargas, S.; Espitia, C.; Sahagun-Ruiz, A.; Parada, C.; Balderas-Loaeza, A.; Villa-Mancera, A. Moderate protection is induced by a chimeric protein composed of leucine aminopeptidase and cathepsin L1 against Fasciola hepatica challenge in sheep. Vaccine 2019, 37, 3234–3240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wesolowska, A.; Basalaj, K.; Norbury, L.J.; Sielicka, A.; Wedrychowicz, H.; Zawistowska-Deniziak, A. Vaccination against Fasciola hepatica using cathepsin L3 and B3 proteases delivered alone or in combination. Vet. Parasitol. 2018, 250, 15–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Espino, A.M.; Hillyer, G.V. A novel Fasciola hepatica saposinlike recombinant protein with immunoprophylactic potential. J. Parasitol. 2004, 90, 876–879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ranganathan, S.; Nakai, K.; Schonbach, C. Chapter: Immunoinformatics Databases. In Encyclopedia of Bioinformatics and Computational Biology; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2019; ISBN 978-0-12-811432-2. [Google Scholar]
- Park, P.H.; McMullen, M.R.; Huang, H.; Thakur, V.; Nagy, L.E. Short-term treatment of RAW264.7 macrophages with adiponectin increases tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-alpha) expression via ERK1/2 activation and Egr-1 expression: Role of TNF-alpha in adiponectin-stimulated interleukin-10 production. J. Biol. Chem. 2007, 282, 21695–21703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Zhu, W.; Yu, J.; Nie, Y.; Shi, X.; Liu, Y.; Li, F.; Zhang, X.L. Disequilibrium of M1 and M2 macrophages correlates with the development of experimental inflammatory bowel diseases. Immunol. Investig. 2014, 43, 638–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carter, D.; Reed, S.G. Role of adjuvants in modeling the immune response. Curr. Opin. HIV AIDS 2010, 5, 409–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Coffman, R.L.; Sher, A.; Seder, R.A. Vaccine adjuvants: Putting innate immunity to work. Immunity 2010, 33, 492–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Facciola, A.; Visalli, G.; Lagana, A.; Di Pietro, A. An Overview of Vaccine Adjuvants: Current Evidence and Future Perspectives. Vaccines 2022, 10, 819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Cetre, C.; Pierrot, C.; Cocude, C.; Lafitte, S.; Capron, A.; Capron, M.; Khalife, J. Profiles of Th1 and Th2 cytokines after primary and secondary infection by Schistosoma mansoni in the semipermissive rat host. Infect. Immun. 1999, 67, 2713–2719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Firacative, C.; Gressler, A.E.; Schubert, K.; Schulze, B.; Muller, U.; Brombacher, F.; von Bergen, M.; Alber, G. Identification of T helper (Th)1-and Th2-associated antigens of Cryptococcus neoformans in a murine model of pulmonary infection. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 2681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Zhang, Z.; Goldschmidt, T.; Salter, H. Possible allelic structure of IgG2a and IgG2c in mice. Mol. Immunol. 2012, 50, 169–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schulte, S.; Sukhova, G.K.; Libby, P. Genetically programmed biases in Th1 and Th2 immune responses modulate atherogenesis. Am. J. Pathol. 2008, 172, 1500–1508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Fiorino, F.; Rondini, S.; Micoli, F.; Lanzilao, L.; Alfini, R.; Mancini, F.; MacLennan, C.A.; Medaglini, D. Immunogenicity of a Bivalent Adjuvanted Glycoconjugate Vaccine against Salmonella typhimurium and Salmonella enteritidis. Front. Immunol. 2017, 8, 168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Lucca, L.E.; Desbois, S.; Ramadan, A.; Ben-Nun, A.; Eisenstein, M.; Carrie, N.; Guery, J.C.; Sette, A.; Nguyen, P.; Geiger, T.L.; et al. Bispecificity for myelin and neuronal self-antigens is a common feature of CD4 T cells in C57BL/6 mice. J. Immunol. 2014, 193, 3267–3277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dummer, L.A.; Araujo, I.L.; Finger, P.F.; dos Santos, A.G.; dos Santos, A.G., Jr.; Conceicao, F.R.; Fischer, G.; van Drunen Littel-van den Hurk, S.; Leite, F.P. Immune responses of mice against recombinant bovine herpesvirus 5 glycoprotein, D. Vaccine 2014, 32, 2413–2419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jones, G.L.; Spencer, L.; Lord, R.; Mollard, R.; Pye, D.; Saul, A. Peptide vaccines derived from a malarial surface antigen: Effects of dose and adjuvants on immunogenicity. Immunol. Lett. 1990, 24, 253–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sahar, E.A.; Can, H.; Iz, S.G.; Doskaya, A.D.; Kalantari-Dehaghi, M.; Deveci, R.; Guruz, A.Y.; Doskaya, M. Development of a hexavalent recombinant protein vaccine adjuvanted with Montanide ISA 50 V and determination of its protective efficacy against acute toxoplasmosis. BMC Infect. Dis. 2020, 20, 493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Shokri, M.; Roohvand, F.; Alimohammadian, M.H.; Ebrahimirad, M.; Ajdary, S. Comparing Montanide ISA 720 and 50-V2 adjuvants formulated with LmSTI1 protein of Leishmania major indicated the potential cytokine patterns for induction of protective immune responses in BALB/c mice. Mol. Immunol. 2016, 76, 108–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Azizi, H.; Mirzaeei, H.; Bagheri, A.; Bazi, A.; Khamesipour, A.; Yaghoobi, H.; Mirzapour, A.; Khatami, M.; Elikaee, S. A Survey on the Adjuvant Role of Naloxone Alone or Combined with Alum in Vaccination Against Fasciolosis in BALB/c Mice. Acta Parasitol. 2019, 64, 236–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Changklungmoa, N.; Kueakhai, P.; Riengrojpitak, S.; Chaithirayanon, K.; Chaichanasak, P.; Preyavichyapugdee, N.; Chantree, P.; Sansri, V.; Itagaki, T.; Sobhon, P. Immunization with recombinant leucine aminopeptidase showed protection against Fasciola gigantica in mice. Parasitol. Res. 2013, 112, 3653–3659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kueakhai, P.; Changklungmoa, N.; Riengrojpitak, S.; Chaichanasak, P.; Meemon, K.; Chaithirayanon, K.; Chantree, P.; Sansri, V.; Itagaki, T.; Sobhon, P. Vaccine potential of recombinant saposin-like protein 2 against Fasciolosis gigantica in mice. Vaccine 2013, 31, 5518–5523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Changklungmoa, N.; Cheukamud, W.; Jaikua, W.; Meemon, K.; Sobhon, P.; Kueakhai, P. Combination Vaccines of Fasciola gigantica Saposin-like Protein-2 and Leucine Aminopeptidase. Trop. Med. Infect. Dis. 2023, 8, 334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Oostindie, S.C.; Lazar, G.A.; Schuurman, J.; Parren, P. Avidity in antibody effector functions and biotherapeutic drug design. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2022, 21, 715–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Ugurlar, D.; Howes, S.C.; de Kreuk, B.J.; Koning, R.I.; de Jong, R.N.; Beurskens, F.J.; Schuurman, J.; Koster, A.J.; Sharp, T.H.; Parren, P.; et al. Structures of C1-IgG1 provide insights into how danger pattern recognition activates complement. Science 2018, 359, 794–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mulcahy, G.; O’Connor, F.; McGonigle, S.; Dowd, A.; Clery, D.G.; Andrews, S.J.; Dalton, J.P. Correlation of specific antibody titre and avidity with protection in cattle immunized against Fasciola hepatica. Vaccine 1998, 16, 932–939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flores-Velazquez, L.M.; Ruiz-Campillo, M.T.; Herrera-Torres, G.; Martinez-Moreno, A.; Martinez-Moreno, F.J.; Zafra, R. Fasciolosis: Pathogenesis, host-parasite interactions, and implication in vaccine development. Front. Vet. Sci. 2023, 10, 1270064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Escamilla, A.; Perez-Caballero, R.; Zafra, R.; Bautista, M.J.; Pacheco, I.L.; Ruiz, M.T.; Martinez-Cruz, M.S.; Martinez-Moreno, A.; Molina-Hernandez, V.; Perez, J. Apoptosis of peritoneal leucocytes during early stages of Fasciola hepatica infections in sheep. Vet. Parasitol. 2017, 238, 49–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Magombedze, G.; Eda, S.; Ganusov, V.V. Competition for antigen between Th1 and Th2 responses determines the timing of the immune response switch during Mycobaterium avium subspecies paratuberulosis infection in ruminants. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2014, 10, e1003414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Pacheco, I.L.; Abril, N.; Morales-Prieto, N.; Bautista, M.J.; Zafra, R.; Escamilla, A.; Ruiz, M.T.; Martinez-Moreno, A.; Perez, J. Th1/Th2 balance in the liver and hepatic lymph nodes of vaccinated and unvaccinated sheep during acute stages of infection with Fasciola hepatica. Vet. Parasitol. 2017, 238, 61–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Panda, S.K.; Kumar, S.; Tupperwar, N.C.; Vaidya, T.; George, A.; Rath, S.; Bal, V.; Ravindran, B. Chitohexaose activates macrophages by alternate pathway through TLR4 and blocks endotoxemia. PLoS Pathog. 2012, 8, e1002717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]


| Method | α-Helix (%) | β-Sheet (%) | Extended or Random Coil (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Circular dichroism (25 °C) | 66.00 | - | 34.00 |
| SOPMA Server * | 67.33 | 3.96 | 18.71 |
| Avidity Index (% ± SEM) | ||
|---|---|---|
| Group | IgG2a | IgG2c |
| 1-F. hepatica-infected | 42.55% 1.46 | 21.45% 15.84 |
| 2-mFhSAP-2+ISA50-immunized | 72.73% 23.01 | 66.16 19.18 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ramos-Nieves, R.; Armina-Rodriguez, A.; Figueroa-Gispert, M.D.M.; Figueroa-Quiñones, G.; Ocasio-Malavé, C.; Espino, A.M. A Modified Variant of Fasciola hepatica FhSAP-2 (mFhSAP-2) as a Recombinant Vaccine Candidate Induces High-Avidity IgG2c Antibodies and Enhances T Cell Activation in C57BL/6 Mice. Vaccines 2025, 13, 545. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines13050545
Ramos-Nieves R, Armina-Rodriguez A, Figueroa-Gispert MDM, Figueroa-Quiñones G, Ocasio-Malavé C, Espino AM. A Modified Variant of Fasciola hepatica FhSAP-2 (mFhSAP-2) as a Recombinant Vaccine Candidate Induces High-Avidity IgG2c Antibodies and Enhances T Cell Activation in C57BL/6 Mice. Vaccines. 2025; 13(5):545. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines13050545
Chicago/Turabian StyleRamos-Nieves, Riseilly, Albersy Armina-Rodriguez, Maria Del Mar Figueroa-Gispert, Ghalib Figueroa-Quiñones, Carlimar Ocasio-Malavé, and Ana M. Espino. 2025. "A Modified Variant of Fasciola hepatica FhSAP-2 (mFhSAP-2) as a Recombinant Vaccine Candidate Induces High-Avidity IgG2c Antibodies and Enhances T Cell Activation in C57BL/6 Mice" Vaccines 13, no. 5: 545. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines13050545
APA StyleRamos-Nieves, R., Armina-Rodriguez, A., Figueroa-Gispert, M. D. M., Figueroa-Quiñones, G., Ocasio-Malavé, C., & Espino, A. M. (2025). A Modified Variant of Fasciola hepatica FhSAP-2 (mFhSAP-2) as a Recombinant Vaccine Candidate Induces High-Avidity IgG2c Antibodies and Enhances T Cell Activation in C57BL/6 Mice. Vaccines, 13(5), 545. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines13050545








