Protection Against Pneumonia Induced by Vaccination with Fimbriae Subunits from Klebsiella pneumoniae
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Bacterial Strains and Growth Conditions
2.2. Protein Production
2.3. Ethics Statements
2.4. Mouse Immunization and Challenge
2.5. Antibody Production and Isotyping
2.6. IgG Binding Assay
2.7. C3 Deposition on K. pneumoniae
2.8. Biofilm Inhibition Assay
2.9. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
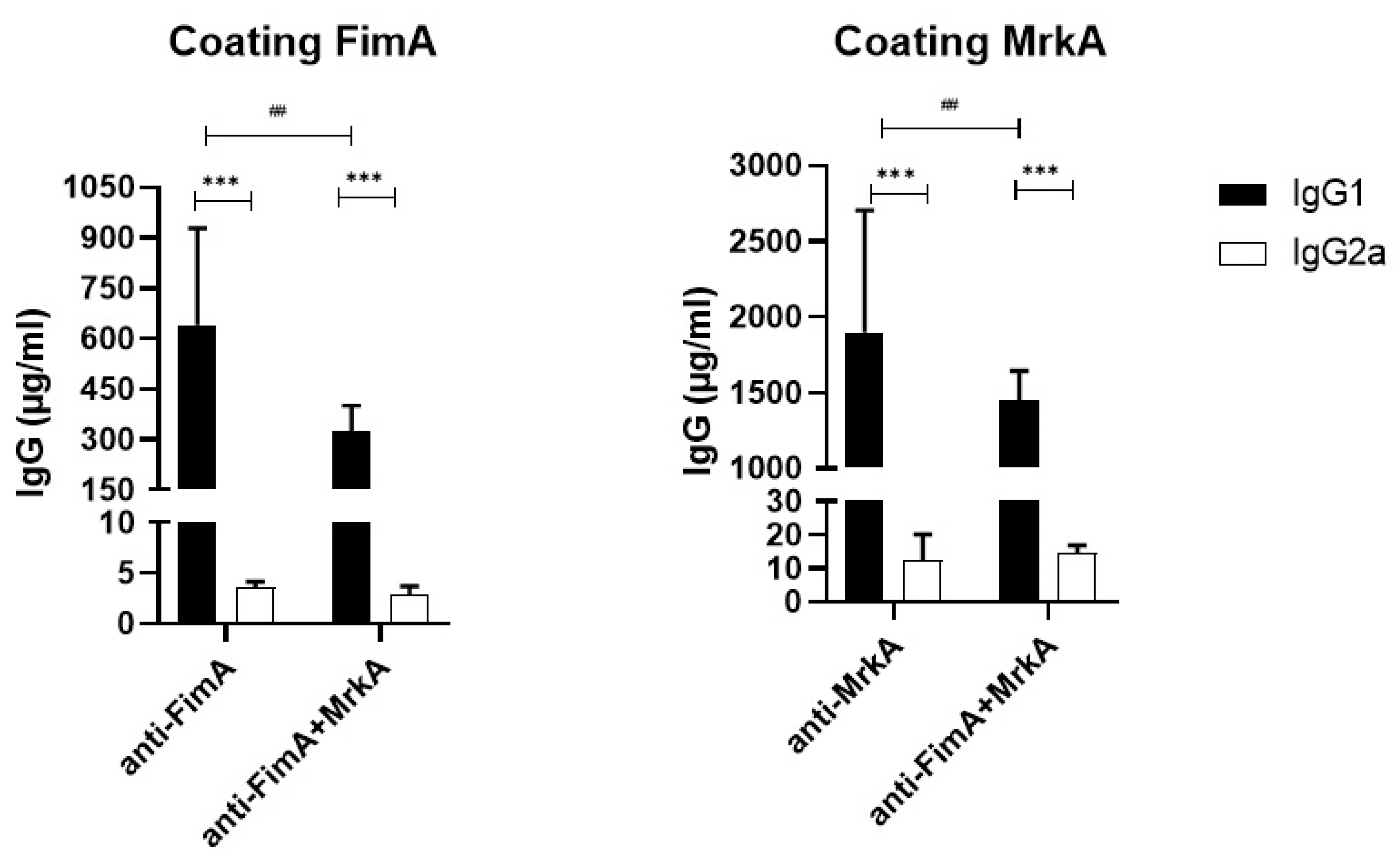
3.1. Immunization with rFimA and rMrkA Induces a Strong IgG1 Response
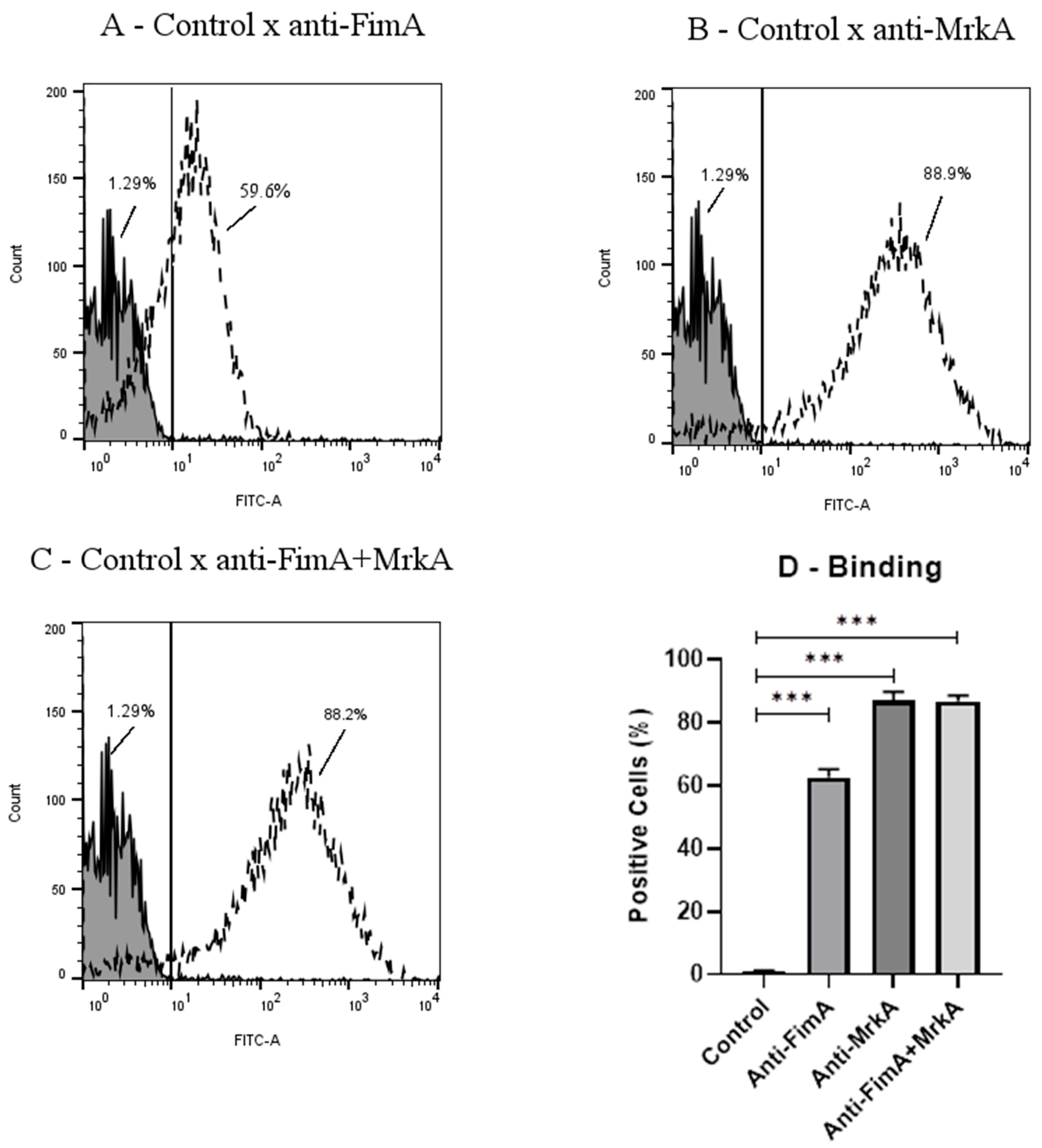
3.2. Antibody Binding onto K. pneumoniae
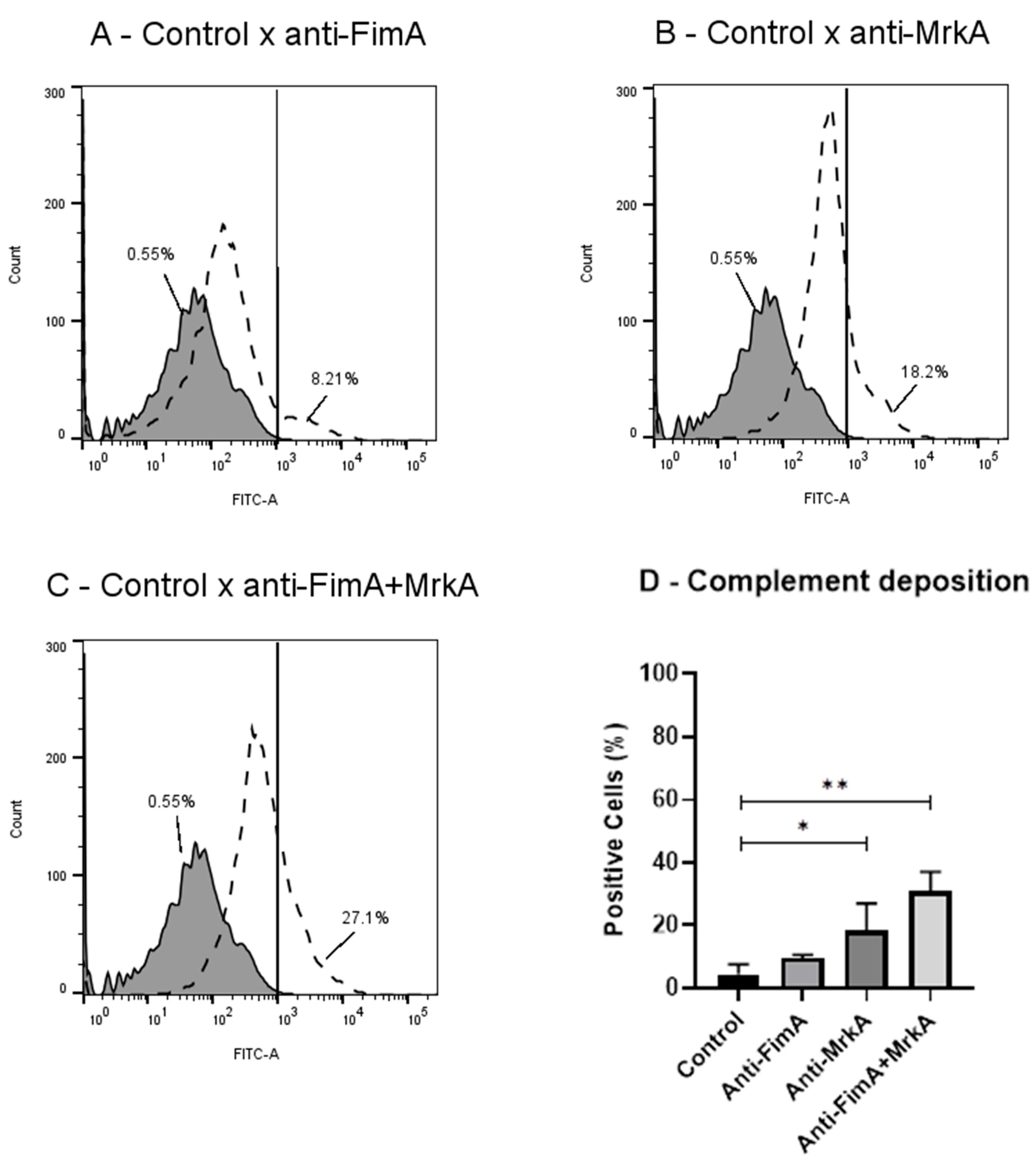
3.3. Vaccine Antibodies Induce Complement Deposition on K. pneumoniae
3.4. Biofilm Formation Is Inhibited in the Presence of Antibodies
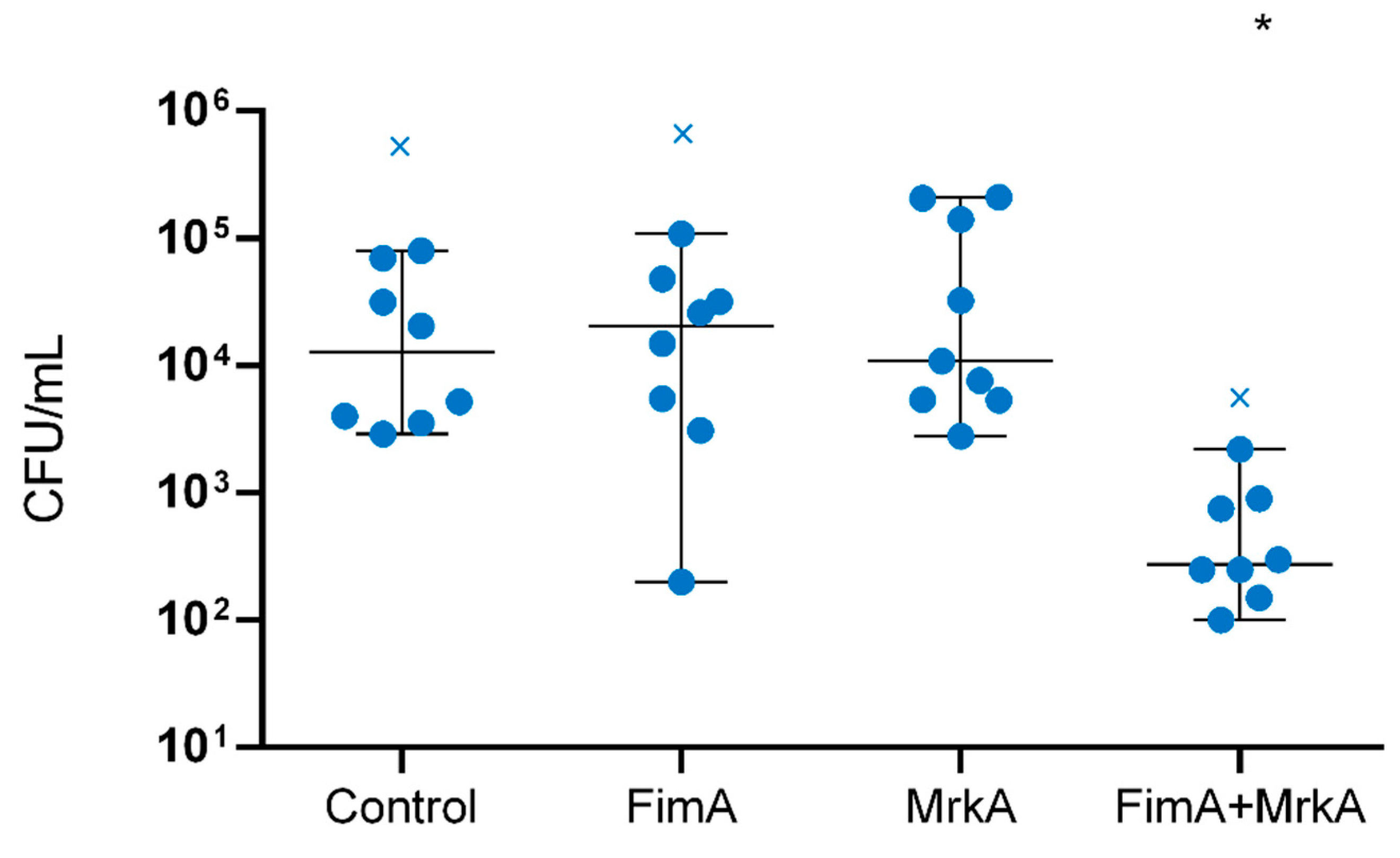
3.5. Immunization with rFimA and rMrkA Reduces Lung Colonization by K. pneumoniae
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- WHO. Bacterial Priority Pathogens List, 2024: Bacterial Pathogens of Public Health Importance to Guide Research, Development and Strategies to Prevent and Control Antimicrobial Resistance; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2024; Volume 72. [Google Scholar]
- Martin, R.M.; Bachman, M.A. Colonization, Infection, and the Accessory Genome of Klebsiella pneumoniae. Front. Cell Infect. Microbiol. 2018, 8, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, Y.H.; Arros, P.; Berrios-Pasten, C.; Wijaya, I.; Chu, W.H.W.; Chen, Y.; Cheam, G.; Mohamed Naim, A.N.; Marcoleta, A.E.; Ravikrishnan, A.; et al. Hypervirulent Klebsiella pneumoniae employs genomic island encoded toxins against bacterial competitors in the gut. ISME J. 2024, 18, wrae143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Russo, T.A.; Marr, C.M. Hypervirulent Klebsiella pneumoniae. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2019, 32, 10–1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, L.; Sun, X.; Ma, X. Systematic review and meta-analysis of mortality of patients infected with carbapenem-resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae. Ann. Clin. Microbiol. Antimicrob. 2017, 16, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magill, S.S.; Edwards, J.R.; Bamberg, W.; Beldavs, Z.G.; Dumyati, G.; Kainer, M.A.; Lynfield, R.; Maloney, M.; McAllister-Hollod, L.; Nadle, J.; et al. Multistate point-prevalence survey of health care-associated infections. N. Engl. J. Med. 2014, 370, 1198–1208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramadan, R.A.; Bedawy, A.M.; Negm, E.M.; Hassan, T.H.; Ibrahim, D.A.; ElSheikh, S.M.; Amer, R.M. Carbapenem-Resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae Among Patients with Ventilator-Associated Pneumonia: Evaluation of Antibiotic Combinations and Susceptibility to New Antibiotics. Infect. Drug Resist. 2022, 15, 3537–3548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Yao, Z.; Zhan, S.; Yang, Z.; Wei, D.; Zhang, J.; Li, J.; Kyaw, M.H. Disease burden of intensive care unit-acquired pneumonia in China: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Int. J. Infect. Dis. 2014, 29, 84–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torres, A.; Zhong, N.; Pachl, J.; Timsit, J.F.; Kollef, M.; Chen, Z.; Song, J.; Taylor, D.; Laud, P.J.; Stone, G.G.; et al. Ceftazidime-avibactam versus meropenem in nosocomial pneumonia, including ventilator-associated pneumonia (REPROVE): A randomised, double-blind, phase 3 non-inferiority trial. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2018, 18, 285–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, I.R.; Lin, S.N.; Wu, X.N.; Chou, S.H.; Wang, F.D.; Lin, Y.T. Clinical and Microbiological Characteristics of Bacteremic Pneumonia Caused by Klebsiella pneumoniae. Front. Cell Infect. Microbiol. 2022, 12, 903682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juan, C.H.; Fang, S.Y.; Chou, C.H.; Tsai, T.Y.; Lin, Y.T. Clinical characteristics of patients with pneumonia caused by Klebsiella pneumoniae in Taiwan and prevalence of antimicrobial-resistant and hypervirulent strains: A retrospective study. Antimicrob. Resist. Infect. Control 2020, 9, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicolo, S.; Mattiuz, G.; Antonelli, A.; Arena, F.; Di Pilato, V.; Giani, T.; Baccani, I.; Clemente, A.M.; Castronovo, G.; Tanturli, M.; et al. Hypervirulent Klebsiella pneumoniae Strains Modulate Human Dendritic Cell Functions and Affect T(H)1/T(H)17 Response. Microorganisms 2022, 10, 384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Q.; Yang, X.; Chan, E.W.C.; Chen, S. The hypermucoviscosity of hypervirulent K. pneumoniae confers the ability to evade neutrophil-mediated phagocytosis. Virulence 2021, 12, 2050–2059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Assoni, L.; Girardello, R.; Converso, T.R.; Darrieux, M. Current Stage in the Development of Klebsiella pneumoniae Vaccines. Infect. Dis. Ther. 2021, 10, 2157–2175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Motamed, H.; Yari, F.; Javadirad, E.; Golmohammadi, S.; Alimoradi, S.; Naleini, R.; Chegene Lorestani, R.; Nemati Zargaran, F.; Rostamian, M. Human vaccine candidates for infections caused by Klebsiella pneumoniae: A systematic review. Health Sci. Rep. 2024, 7, e70061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Ni, M. Regulation of biofilm formation in Klebsiella pneumoniae. Front. Microbiol. 2023, 14, 1238482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paczosa, M.K.; Mecsas, J. Klebsiella pneumoniae: Going on the Offense with a Strong Defense. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 2016, 80, 629–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Struve, C.; Bojer, M.; Krogfelt, K.A. Characterization of Klebsiella pneumoniae type 1 fimbriae by detection of phase variation during colonization and infection and impact on virulence. Infect. Immun. 2008, 76, 4055–4065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pacheco, T.; Gomes, A.E.I.; Siqueira, N.M.G.; Assoni, L.; Darrieux, M.; Venter, H.; Ferraz, L.F.C. SdiA, a Quorum-Sensing Regulator, Suppresses Fimbriae Expression, Biofilm Formation, and Quorum-Sensing Signaling Molecules Production in Klebsiella pneumoniae. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 597735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramos, C.R.; Abreu, P.A.; Nascimento, A.L.; Ho, P.L. A high-copy T7 Escherichia coli expression vector for the production of recombinant proteins with a minimal N-terminal His-tagged fusion peptide. Braz. J. Med. Biol. Res. 2004, 37, 1103–1109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Tobias, R.; McClure, S.; Styba, G.; Shi, Q.; Jackowski, G. Removal of endotoxin from recombinant protein preparations. Clin. Biochem. 1997, 30, 455–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, B.R.; Kim, S.J.; Lee, J.M.; Kang, S.H.; Han, H.J.; Jang, Y.S.; Seo, G.Y.; Kim, P.H. Alum Directly Modulates Murine B Lymphocytes to Produce IgG1 Isotype. Immune Netw. 2013, 13, 10–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Motley, M.P.; Diago-Navarro, E.; Banerjee, K.; Inzerillo, S.; Fries, B.C. The Role of IgG Subclass in Antibody-Mediated Protection against Carbapenem-Resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae. mBio 2020, 11, 10–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lopatto, E.D.B.; Pinkner, J.S.; Sanick, D.A.; Potter, R.F.; Liu, L.X.; Bazán Villicaña, J.; Tamadonfar, K.O.; Ye, Y.; Zimmerman, M.I.; Gualberto, N.C.; et al. Conformational ensembles in Klebsiella pneumoniae FimH impact uropathogenesis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2024, 121, e2409655121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reisner, A.; Maierl, M.; Jorger, M.; Krause, R.; Berger, D.; Haid, A.; Tesic, D.; Zechner, E.L. Type 1 fimbriae contribute to catheter-associated urinary tract infections caused by Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol 2014, 196, 931–939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lavender, H.; Jagnow, J.J.; Clegg, S. Klebsiella pneumoniae type 3 fimbria-mediated immunity to infection in the murine model of respiratory disease. Int. J. Med. Microbiol. 2005, 295, 153–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Chang, C.S.; Pennini, M.; Pelletier, M.; Rajan, S.; Zha, J.; Chen, Y.; Cvitkovic, R.; Sadowska, A.; Heidbrink Thompson, J.; et al. Target-Agnostic Identification of Functional Monoclonal Antibodies Against Klebsiella pneumoniae Multimeric MrkA Fimbrial Subunit. J. Infect. Dis. 2016, 213, 1800–1808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Chen, Y.; Cvitkovic, R.; Pennini, M.E.; Chang, C.S.; Pelletier, M.; Bonnell, J.; Koksal, A.C.; Wu, H.; Dall'Acqua, W.F.; et al. Anti-MrkA Monoclonal Antibodies Reveal Distinct Structural and Antigenic Features of MrkA. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0170529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berry, S.K.; Rust, S.; Irving, L.; Bartholdson Scott, J.; Weinert, L.A.; Dougan, G.; Christie, G.; Warrener, P.; Minter, R.; Grant, A.J. Characterization of mAbs against Klebsiella pneumoniae type 3 fimbriae isolated in a target-independent phage display campaign. Microbiol. Spectr. 2024, 12, e0040024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Han, W.Y.; Li, Z.J.; Lei, L.C. Klebsiella pneumoniae MrkD adhesin-mediated immunity to respiratory infection and mapping the antigenic epitope by phage display library. Microb. Pathog. 2009, 46, 144–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Li, Z.J.; Han, W.Y.; Lei, L.C.; Sun, C.J.; Feng, X.; Du, C.T.; Du, T.F.; Gu, J.M. Identification and characterization of Th cell epitopes in MrkD adhesin of Klebsiella pneumoniae. Microb. Pathog. 2010, 49, 8–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Gou, Q.; Yuan, Y.; Zhang, X.; Zhao, Z.; Liao, J.; Zeng, X.; Jing, H.; Jiang, S.; Zhang, W.; et al. Vaccination with a trivalent Klebsiella pneumoniae vaccine confers protection in a murine model of pneumonia. Vaccine 2024, 42, 126217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, Y.S.; Moon, J.H.; Kim, T.G.; Lee, J.Y. Potent In Vitro and In Vivo Activity of Plantibody Specific for Porphyromonas gingivalis FimA. Clin. Vaccine Immunol. 2016, 23, 346–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koh, E.M.; Kim, J.; Kim, T.G.; Moon, J.H.; Oh, J.H.; Lee, J.Y.; Jang, Y.S. Cloning and characterization of heavy and light chain genes encoding the FimA-specific monoclonal antibodies that inhibit Porphyromonas gingivalis adhesion. Microbiol. Immunol. 2011, 55, 199–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koh, E.M.; Kim, J.; Lee, J.Y.; Kim, T.G. Production of Monoclonal Antibodies Specific to FimA of Porphyromonas gingivalis and Their Inhibitory Activity on Bacterial Binding. Immune Netw. 2009, 9, 203–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramezanalizadeh, F.; Owlia, P.; Rasooli, I. Type I pili, CsuA/B and FimA induce a protective immune response against Acinetobacter baumannii. Vaccine 2020, 38, 5436–5446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Hu, Y.H.; Chi, H.; Sun, L. The major fimbrial subunit protein of Edwardsiella tarda: Vaccine potential, adjuvant effect, and involvement in host infection. Fish. Shellfish. Immunol. 2013, 35, 858–865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karan, S.; Garg, L.C.; Choudhury, D.; Dixit, A. Recombinant FimH, a fimbrial tip adhesin of Vibrio parahaemolyticus, elicits mixed T helper cell response and confers protection against Vibrio parahaemolyticus challenge in murine model. Mol. Immunol. 2021, 135, 373–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.F.; Chen, J.L.; Li, W.Y.; Fan, M.W.; Li, Y.H. FimH as a mucosal adjuvant enhances persistent antibody response and protective efficacy of the anti-caries vaccine. Arch. Oral. Biol. 2019, 101, 122–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, X.; Yue, Y.; Xiong, S. Incorporation of a bi-functional protein FimH enhances the immunoprotection of chitosan-pVP1 vaccine against coxsackievirus B3-induced myocarditis. Antiviral Res. 2017, 140, 121–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mestas, J.; Hughes, C.C. Of mice and not men: Differences between mouse and human immunology. J. Immunol. 2004, 172, 2731–2738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Assoni, L.; Couto, A.J.M.; Vieira, B.; Milani, B.; Lima, A.S.; Converso, T.R.; Darrieux, M. Animal models of Klebsiella pneumoniae mucosal infections. Front. Microbiol. 2024, 15, 1367422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

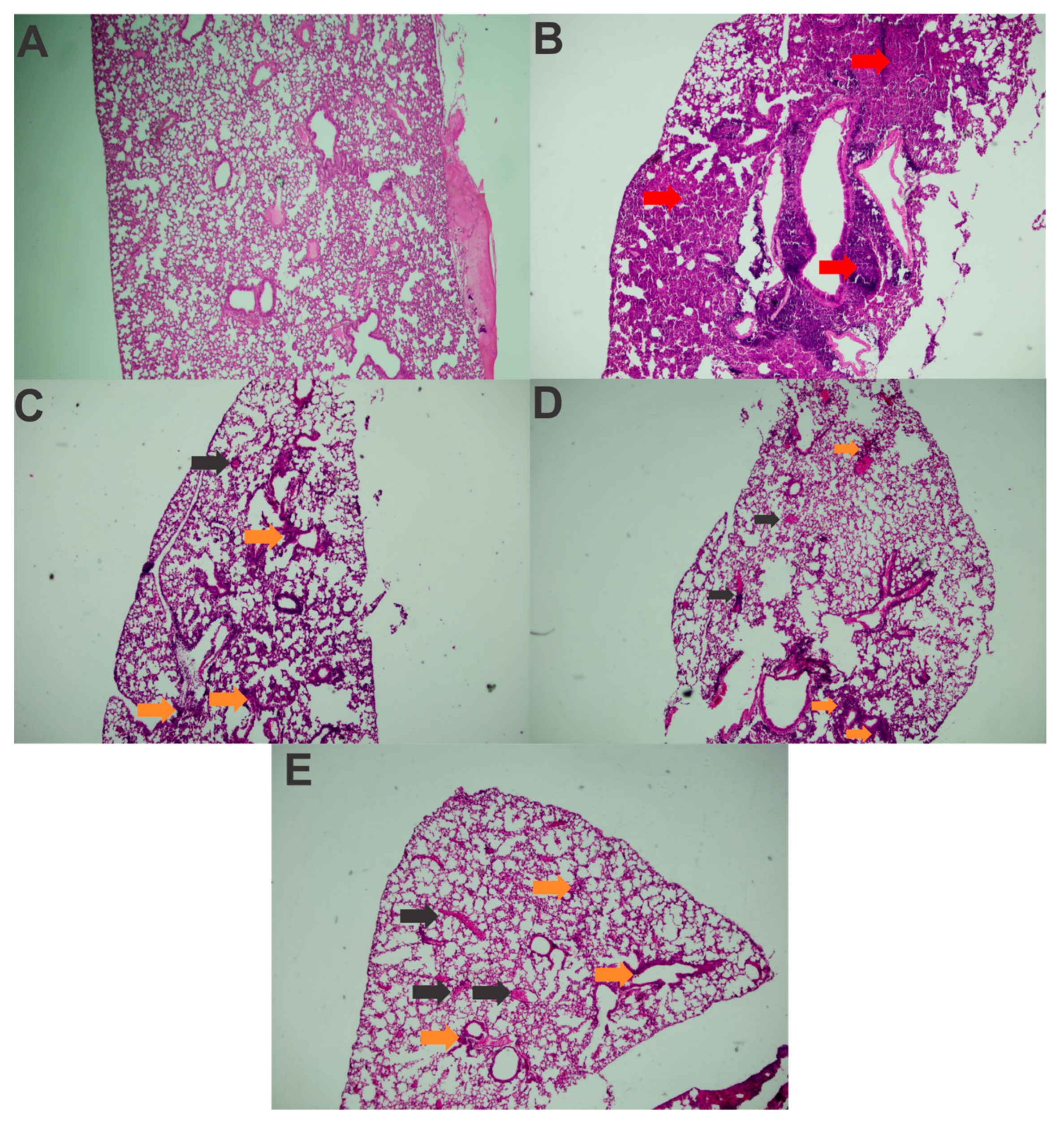
| Healthy Control | Challenged Control | FimA | MrkA | FimA + MrkA | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Polymorphonuclear Inflammatory Infiltrate | - | +++ | ++ | ++ | ++ |
| Mononuclear Inflammatory Infiltrate | - | ++ | ++ | + | ++ |
| Alveolar Structure Loss | - | ++ | + | + | ++ |
| Congestion | - | +++ | ++ | ++ | ++ |
| Edema | - | + | + | + | + |
| Pulmonary hemorrhage | - | +++ | ++ | ++ | ++ |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Assoni, L.; Ciaparin, I.; Trentini, M.M.; Baboghlian, J.; Rodrigo, G.; Ferreira, B.V.; Pereira, J.A.; Martinez, C.; Ferraz, L.; Girardello, R.; et al. Protection Against Pneumonia Induced by Vaccination with Fimbriae Subunits from Klebsiella pneumoniae. Vaccines 2025, 13, 303. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines13030303
Assoni L, Ciaparin I, Trentini MM, Baboghlian J, Rodrigo G, Ferreira BV, Pereira JA, Martinez C, Ferraz L, Girardello R, et al. Protection Against Pneumonia Induced by Vaccination with Fimbriae Subunits from Klebsiella pneumoniae. Vaccines. 2025; 13(3):303. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines13030303
Chicago/Turabian StyleAssoni, Lucas, Isabelle Ciaparin, Monalisa Martins Trentini, Juliana Baboghlian, Gabriel Rodrigo, Brenda Vieira Ferreira, José Aires Pereira, Carlos Martinez, Lucio Ferraz, Raquel Girardello, and et al. 2025. "Protection Against Pneumonia Induced by Vaccination with Fimbriae Subunits from Klebsiella pneumoniae" Vaccines 13, no. 3: 303. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines13030303
APA StyleAssoni, L., Ciaparin, I., Trentini, M. M., Baboghlian, J., Rodrigo, G., Ferreira, B. V., Pereira, J. A., Martinez, C., Ferraz, L., Girardello, R., Carvalho, L. M., Hakansson, A. P., Converso, T. R., & Darrieux, M. (2025). Protection Against Pneumonia Induced by Vaccination with Fimbriae Subunits from Klebsiella pneumoniae. Vaccines, 13(3), 303. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines13030303






