Abstract
Peste des petits ruminants (PPR) is a highly contagious viral disease that affects goats and sheep, causing severe clinical signs, high mortality, and significant economic losses in many developing countries. Pakistan is one of the endemic regions where PPR outbreaks caused by the Asian lineage IV virus have been reported frequently, affecting the livelihoods of millions of smallholder farmers who depend on these animals for food security and income generation. In this review, we provide a comprehensive overview of the current status, challenges and prospects for vaccine development against PPR in Pakistan. We discuss the epidemiology, diagnosis, and control of PPR in Pakistan, as well as the existing vaccines based on the attenuated strains and their limitations, such as low thermostability, short shelf life, and inability to differentiate between infected and vaccinated animals. We also highlight the recent advances in vaccine research and development, such as recombinant and vectored vaccines, thermostable formulations, and novel delivery methods that could overcome these limitations and enhance the immunogenicity and safety of PPR vaccines. We review the current and potential strategies for vaccine deployment, such as mass vaccination, targeted vaccination, ring vaccination, and their implications for the global eradication of PPR by 2030. We conclude by providing some recommendations for future research and development to improve vaccine efficacy, safety, and coverage in Pakistan, as well as to monitor the impact of vaccination on PPR incidence and prevalence.
1. Introduction
Peste des petits ruminants (PPR) is a highly contagious viral disease that affects goats and sheep, causing severe clinical signs, high mortality, and significant economic losses in many developing countries [1]. PPR is caused by PPR virus (PPRV), a member of the genus Morbillivirus and the family Paramyxoviridae, which is closely related to rinderpest virus (RPV), measles virus (MV), and canine distemper virus (CDV) [2,3]. PPRV has a single-stranded, negative-sense RNA genome of approximately 16 kb, encoding six structural proteins (nucleoprotein, phosphoprotein, matrix protein, fusion protein, hemagglutinin protein, and large polymerase protein) and two non-structural proteins (C and V) [4,5,6,7,8]. While Peste des petits ruminants virus (PPRV) has historically been confined to Asia and Africa, recent incursions into parts of Europe, including Bulgaria and Georgia, underscore its transboundary potential. The virus is classified into four lineages (I-IV) based on the fusion (F) gene. Among these, lineage IV is the most prevalent and is responsible for its widespread distribution across Africa, the Middle East, Asia, and its recent spread into Europe [9,10,11]. The disease is transmitted mainly through direct contact with infected animals or their secretions and excretions, such as saliva, nasal discharge, feces, and urine [12,13]. The incubation period ranges from 2 to 10 days, followed by the onset of fever, depression, anorexia, ocular and nasal discharge, erosive stomatitis, pneumonia, diarrhea, and dehydration [14,15,16]. The morbidity and mortality rates vary depending on the host species, breed, immune status, virus strain, and environmental factors, but can reach up to 90% and 80%, respectively [17].
PPR has a significant impact on the livelihoods of millions of smallholder farmers who depend on small ruminants for food security and income generation. PPR also poses a threat to wildlife conservation, as several wild ungulate species are susceptible to PPRV infection and may act as reservoirs or spillover hosts [18]. The global control and eradication of PPR is a priority for the international community, as part of the One Health initiative, which recognizes the interconnection between human, animal, and environmental health [19]. In 2015, the Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations (FAO) and the World Organization for Animal Health (OIE) launched the Global Strategy for the Control and Eradication of PPR, with the goal of eradicating PPR by 2030 [20]. The strategy is based on four stages: assessment, control, eradication, and post-eradication. The main tools for PPR control and eradication are surveillance, diagnosis, and vaccination. Vaccination is the most effective and cost-effective intervention to prevent and control PPR outbreaks. Currently, there are several live attenuated vaccines available against PPR, based on different strains of PPRV, such as Nigeria 75/1, Sungri 96, Arriah, Egypt 87, Ivory Coast 89, and Arasur 87 [21,22,23]. These vaccines are safe, immunogenic, and cross-protective against different lineages of PPRV [9]. However, they also have some limitations, such as the need for a cold chain, the inability to differentiate between infected and vaccinated animals (DIVA), the potential risk of reversion to virulence, and the interference with maternal antibodies [24]. Therefore, there is a need for the development of new generation vaccines against PPR that can overcome these limitations and enhance the global eradication efforts. In this review, we provide an overview of the current status, challenges, and prospects for vaccine development against PPR in Pakistan. We discuss the epidemiology, diagnosis, and control of PPR in Pakistan, as well as the existing vaccines and their limitations. We also highlight the recent advances in vaccine research and development, such as recombinant and vectored vaccines, thermostable formulations, and novel delivery methods. We conclude by providing some recommendations for future research and development to improve vaccine efficacy, safety, and coverage in Pakistan.
2. Epidemiology of PPR in Pakistan
Pakistan is one of the endemic regions where PPR outbreaks have been reported frequently, affecting the livelihoods of millions of smallholder farmers who depend on small ruminants for food security and income generation [1]. The first confirmed case of PPR in Pakistan was reported in 1991 in the Punjab province [25,26]. Since then, PPR has spread to all the provinces and regions of the country, with varying degrees of prevalence and distribution [27]. The prevalence and distribution of PPRV lineages in Pakistan have been investigated by several studies using serological and molecular methods. A national level serological survey conducted in 2014 revealed that the true seroprevalence of PPR in Pakistan was estimated to be 48.5% (95% CI, 46.6–50.3), and 52.9% (95% CI, 50.7–55.1) and 37.7 (95% CI, 34.4–41.0) for goats and sheep, respectively [28]. The sheep and goats exhibited a different seroprevalence pattern, with a higher prevalence in goats. The highest seroprevalence was observed in Balochistan province, followed by Khyber Pakhtunkhwa, Punjab, Sindh, and Gilgit Baltistan. The lowest seroprevalence was recorded in Azad Jammu and Kashmir [29,30,31]. Molecular characterization of PPRV isolates from Pakistan has confirmed that Lineage IV is the predominant and widespread strain, affecting all provinces and regions of the country. Phylogenetic analysis of the fusion gene further reveals that Pakistani PPRV isolates cluster into two distinct subgroups within Lineage IV, designated as IVa and IVb. The IVa subgroup shows a closer genetic relationship to isolates from China, India, and Nepal, while the IVb subgroup is more closely related to isolates from Turkey, Iran, and Iraq [32,33].
Figure 1 illustrates the provincial distribution of PPR outbreaks in Pakistan, highlighting high-risk areas based on serological and molecular data from national and regional surveys [28,29,30,31].
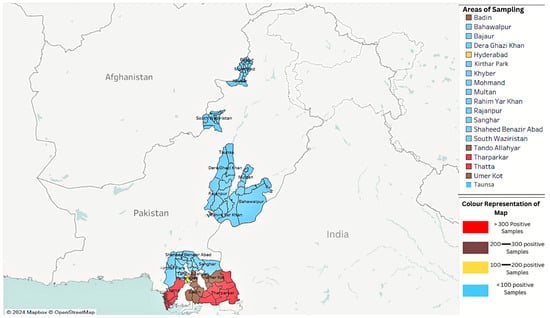
Figure 1.
Map showing the distribution of peste des petits ruminants (PPR) positive samples across different areas from 2019 to 2024.
The risk factors and transmission dynamics of PPR in Pakistan have been studied by various researchers using epidemiological models and surveys [14]. The risk factors associated with PPR infection in small ruminants included age, sex, breed, species, herd size, herd composition, vaccination status, contact with other animals, and movement patterns [31,34,35]. The transmission dynamics of PPR in Pakistan were influenced by the seasonal variations, climatic conditions, and socio-cultural practices. The disease was more prevalent in the winter and spring seasons when the animals were kept in close proximity and shared common grazing and watering sources [34]. The disease was also more prevalent in the regions where the livestock trade and movement were frequent and unregulated, such as the border areas with Afghanistan, Pakistan and Iran [36]. The socio-cultural practices, such as animal sacrifice during religious festivals, animal exchange during marriages, and animal sharing among relatives and neighbors, also facilitated the spread of PPR in Pakistan and other neighbored country [37,38].
Figure 2 summarizes the transmission dynamics of PPR in Pakistan, incorporating seasonal trends, herd management practices, livestock movement, and socio-cultural factors [34,35,36,37,38].
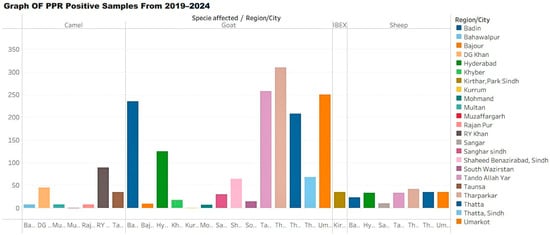
Figure 2.
Graph showing the number of peste des petits ruminants (PPR) positive samples by area from 2019 to 2024.
The impact of PPR on small ruminant production and livelihoods in Pakistan was estimated by several studies using economic and social indicators [38]. The direct economic losses due to PPR in Pakistan were calculated by considering the mortality, morbidity, reduced productivity, and treatment costs of the affected animals. The indirect economic losses due to PPR in Pakistan were calculated by considering the reduced market value, reduced demand, reduced trade, and reduced income of the affected farmers [1]. The social impact of PPR in Pakistan was assessed by considering the food insecurity, poverty, gender inequality, and social stigma of the affected households. The studies showed that PPR caused significant economic and social losses in Pakistan, especially for the poor and marginalized farmers who relied on small ruminants for their livelihoods [39,40]. The surveillance and reporting systems for PPR in Pakistan were evaluated by several studies using the criteria of sensitivity, specificity, timeliness, representativeness, and completeness [14,41,42,43]. The studies revealed that the surveillance and reporting systems for PPR in Pakistan were inadequate and inefficient, due to the lack of resources, infrastructure, coordination, awareness, and incentives [42,44,45]. The passive surveillance system, which relied on the reporting of clinical cases by the farmers and veterinarians, was under-reported and biased, due to the low awareness, low access, and low trust of the stakeholders. The active surveillance system, which involved the collection and testing of samples from the field, was limited and sporadic, due to the lack of funds, equipment, personnel, and protocols. The laboratory diagnosis of PPR in Pakistan was also hampered by the lack of quality, standardization, and validation of the diagnostic methods and kits. The data management and analysis of PPR in Pakistan were also poor and inconsistent, due to the lack of databases, software, and skills [39].
3. Diagnosis and Control of PPR in Pakistan
The diagnosis and control of PPR in Pakistan are crucial for the prevention and eradication of the disease, as well as for the protection of small ruminant production and livelihoods [38]. However, the diagnosis and control of PPR in Pakistan face several challenges, such as the lack of resources, infrastructure, coordination, awareness, and incentives. The diagnostic methods for PPR in Pakistan include clinical, serological, and molecular techniques [46,47,48,49]. The clinical diagnosis of PPR is based on the observation of the characteristic signs and lesions of the disease, such as fever, depression, ocular and nasal discharge, erosive stomatitis, pneumonia, diarrhea, and dehydration [28]. However, the clinical diagnosis of PPR is not reliable, as the disease can be confused with other diseases that cause similar symptoms, such as foot and mouth disease, contagious caprine pleuropneumonia, bluetongue, and sheep and goat pox [16,50,51]. The serological diagnosis of PPR is based on the detection of antibodies against PPRV in the serum of the animals, using tests such as competitive enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (cELISA), immunocapture ELISA (IcELISA), and agar gel immunodiffusion (AGID) [52]. However, the serological diagnosis of PPR has some limitations, such as the inability to differentiate between infected and vaccinated animals (DIVA), the interference with maternal antibodies, and the cross-reactivity with other morbilliviruses [34,53,54]. The molecular diagnosis of PPR is based on the detection of PPRV nucleic acid in the samples of the animals, using techniques such as reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR), real-time RT-PCR, and loop-mediated isothermal amplification (LAMP) [55]. Recent advancements have expanded molecular diagnostics to include qPCR-based multiplex panels capable of simultaneously detecting PPRV and co-infecting respiratory pathogens, as demonstrated by [56]. Additionally, biomarker- and cytokine-based approaches have emerged as novel supportive diagnostic tools for early-stage PPR detection, as reported by [57]. These modern molecular and immunological tools enhance detection sensitivity, specificity, and early differentiation of infection stages, allowing for genotyping and phylogenetic analysis of circulating PPRV strains. control measures for PPR in Pakistan include biosecurity, quarantine, culling, and vaccination. The biosecurity measures for PPR involve the prevention of contact between infected and susceptible animals, as well as the disinfection of the premises, equipment, and vehicles that may be contaminated with PPRV [38]. The quarantine measures for PPR involve the isolation and observation of the animals that may have been exposed to PPRV, as well as the restriction of their movement and trade [48]. The culling measures for PPR involve the slaughter and disposal of the animals that are confirmed or suspected to be infected with PPRV, as well as the compensation of the owners for their losses. The vaccination measures for PPR involve the administration of vaccines that can induce protective immunity against PPRV in the animals, as well as the monitoring of their efficacy and safety [29]. The national and regional strategies and policies for PPR in Pakistan are aligned with the Global Strategy for the Control and Eradication of PPR, launched by the Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations (FAO) and the World Organization for Animal Health (OIE) in 2015, with the goal of eradicating PPR by 2030 [20].
The national strategy for PPR in Pakistan is based on four stages: assessment, control, eradication, and post-eradication [14,41,42]. The assessment stage evaluates epidemiological trends, diagnostic capacity, vaccine availability, and socio-economic impacts, while the control stage emphasizes targeted vaccination, biosecurity enforcement, and outbreak investigation in endemic and high-risk zones such as the border areas of Khyber Pakhtunkhwa and Baluchistan. Currently, Pakistan is implementing the Government of Pakistan, Ministry of National Food Security & Research, National Peste des Petits Ruminants (PPR) Eradication Programme; Phase-I, Risk-Based PPR Control in Sheep and Goats of Pakistan (2021–2025). This national program focuses on risk-based vaccination, community awareness, and strengthened passive surveillance. To date, it has vaccinated over 70 million small ruminants, achieving a significant reduction in outbreak frequency in targeted districts. The eradication phase will focus on verifying disease-free zones, while the post-eradication phase emphasizes sustained surveillance and prevention of viral re-entry from neighboring endemic countries [58].
The regional strategy for PPR in Pakistan involves the coordination and collaboration with the neighboring countries and regions, such as Afghanistan, Iran, India, and China, where PPR is also endemic or epidemic, to harmonize the surveillance, diagnosis, and control of PPR across the borders [36,59].
4. Pakistan’s National PPR Control Program
Pakistan’s strategic efforts to combat Peste des Petits Ruminants (PPR) are framed within its national livestock policies and its commitment to the WOAH/FAO Global Eradication Strategy. According to recent assessments, Pakistan is currently positioned in Stage 2 (Risk Reduction) of the Progressive Control Pathway (PCP) for PPR [60]. In this stage, the national objective is to reduce infection pressure in targeted populations and geographic areas through the implementation of risk-based, controlled vaccination programs, rather than achieving nationwide freedom from the disease. The foundation of this control program is the delineation of risk zones, which enables the efficient allocation of limited resources. Pakistani authorities classify areas as high-risk based on multiple criteria, including a history of recurrent outbreaks, proximity to borders with endemic countries such as Afghanistan and Iran, and the density of small ruminant populations along trade and migration routes [38,61]. This risk mapping approach ensures that interventions are focused where they are most needed, particularly in the border regions of Khyber Pakhtunkhwa and Balochistan, which serve as key livestock movement corridors. Within these defined high-risk zones, the primary control measure involves targeted vaccination campaigns. The strategy includes the prophylactic use of the live-attenuated Nigeria 75/1 vaccine, often produced domestically at the Veterinary Research Institute (VRI) Lahore, to build herd immunity and reduce virus circulation [62,63]. This vaccination strategy is complemented by passive and active surveillance systems designed to ensure early outbreak detection. When a PPR outbreak is confirmed, immediate response measures are triggered, including quarantine enforcement, restriction of animal movement, and ring vaccination around the epicenter to contain viral spread. Despite the clear policy framework and national coordination, implementation challenges persist. These include logistical difficulties in vaccinating nomadic and transhumant herders, limited cold chain infrastructure in remote districts, inadequate funding for sustained vaccination coverage, and ongoing virus incursions across porous borders. Bridging these operational gaps is vital for Pakistan to transition from Stage 2 (Risk Reduction) to Stage 3 (Control), demonstrating tangible progress toward the national and global goal of PPR eradication. The Government of Pakistan, through the Ministry of National Food Security and Research (MNFSR), is leading these efforts under the National PPR Eradication Programme: Phase I (2021–2025), which is focused on risk-based control, surveillance enhancement, and regional coordination with neighboring countries. Successful transition to the next PCP stage will depend on sustained vaccination coverage, active sero-monitoring, and strengthened cross-border collaboration, aligning national actions with the global PPR eradication goal by 2030.
5. PPR Vaccination Strategies and Progress in Pakistan
In Pakistan, vaccination against Peste des Petits Ruminants (PPR) serves as the cornerstone of disease prevention and control under the National PPR Eradication Programme (Phase I, 2021–2025), which is fully funded and implemented by the Government of Pakistan through the Ministry of National Food Security and Research (MNFSR). The program is coordinated by the Animal Husbandry Commissioner’s Office, with technical guidance and strategic alignment provided by the Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO) and the World Organisation for Animal Health (WOAH, formerly OIE).The country primarily employs a live-attenuated vaccine derived from the Nigeria 75/1 strain, locally produced and quality-assured by the Veterinary Research Institute (VRI), Lahore, under the supervision of the Animal Husbandry Commissioner’s Office [64]. In addition, the Sindh Poultry Vaccine Centre (SPVC), Tandojam, contributes to local vaccine production and regional distribution within Sindh province. These vaccines are used in localized mass vaccination campaigns, particularly targeting high-risk districts in Sindh, Punjab, Balochistan, and Khyber Pakhtunkhwa, where seropositivity and outbreak recurrence remain consistently high [40,65,66]. Despite the availability of effective vaccines, national immunization coverage remains suboptimal, averaging only 35–45% of the estimated 120 million small-ruminant population [62]. Coverage gaps arise due to cold-chain fragility, limited logistical infrastructure, funding constraints, and low farmer compliance and awareness, particularly in semi-arid and tribal regions where pastoral mobility complicates systematic vaccination [67,68]. These weaknesses lead to uneven herd immunity and periodic re-emergence of PPR outbreaks, even with ongoing campaigns. To address vaccine thermolability, national research efforts have prioritized thermostabilization and formulation improvements. Locally tested thermostable preparations of the Nigeria 75/1 vaccine have shown full protective efficacy after exposure to 37 °C for up to 14 days under Sindh’s semi-arid conditions [68]. Furthermore, recent research [69] demonstrated that lentinan, a β-glucan-based natural adjuvant, significantly enhanced PPR vaccine immunogenicity by increasing both antibody titers and cytokine-mediated immune responses [69]. These findings support the integration of novel adjuvant systems into national vaccine formulations to enhance immune durability, memory response, and field efficacy under challenging environmental conditions. Parallel efforts at the National Veterinary Laboratory (NVL), Islamabad, are focused on molecular characterization and phylogenetic mapping of circulating lineage IV strains of the PPR virus to ensure homologous antigenic matching and continuous genomic surveillance for emerging mutations [65,66]. Collectively, these developments underscore Pakistan’s advancing technical capacity and institutional commitment toward achieving the FAO–WOAH Global Eradication Goal for PPR by 2030 [60]. Nevertheless, large-scale field validation, post-vaccination seromonitoring, and farmer-focused awareness programs remain vital to sustaining vaccine-driven herd immunity and preventing resurgence in endemic clusters.
6. Comparative Aspects of PPR Vaccination in Sheep and Goats
A one-size-fits-all vaccination approach for small ruminants is suboptimal due to marked interspecies differences. Firstly, goats are profoundly more susceptible to PPR, suffering mortality rates that can surpass 80% in naïve herds, compared to 10–40% in sheep [61]. Secondly, their immune responses diverge: sheep mount a consistently robust and long-lasting antibody response to vaccines like Nigeria 75/1, while goats often show variable and sometimes weaker neutralizing antibody titers, with evidence pointing to a greater reliance on cell-mediated immunity and potentially shorter duration of protection [11]. These biological disparities translate directly to field practice. The heightened susceptibility of goats mandates their prioritization during outbreak containment [70]. Furthermore, their quicker waning immunity suggests they may need more frequent booster vaccinations and should be the primary focus of post-vaccination seromonitoring campaigns
7. Recent Advances in Vaccine Research and Development
The global endeavor to develop next-generation PPR vaccines is largely driven by the inherent limitations of existing Live Attenuated Vaccines (LAVs), including their stringent cold-chain requirements, the inability to differentiate infected from vaccinated animals (DIVA), and potential safety concerns in immunocompromised or pregnant animals [64]. For a country like Pakistan, where high ambient temperatures and an unreliable cold chain are pervasive issues, these limitations are not merely theoretical but represent critical operational failures [68]. Consequently, the pursuit of thermostable, recombinant, and DIVA-compatible vaccines has become a paramount national research priority.
The direction of this research is critically guided by precise local epidemiological data. Nationwide phylogenetic studies have consistently shown that the PPR virus strains circulating in Pakistan are not random but belong almost exclusively (>98%) to lineage IV, with further subdivisions into genetically distinct sub-clusters IVa and IVb that show phylogenetic links to viruses from China and the Middle East, respectively [11]. This finding is crucial because it underscores the necessity for antigenic matching to ensure that vaccines deployed in Pakistan elicit the strongest possible immune response against the viruses actually present in the field.
In response, Pakistan’s national research capacity is being actively mobilized. Leading institutions, including the University of Veterinary and Animal Sciences (UVAS) in Lahore and the National Veterinary Laboratories (NVL) in Islamabad, are at the forefront of developing second-generation vaccines tailored to the local context [60,71]. Their work leverages cutting-edge platforms. Recombinant and vectored vaccines, which use benign viruses as carriers for PPRV genes, are a major focus as they inherently allow for DIVA strategies. Promisingly, preliminary challenge studies for a UVAS-developed recombinant candidate vaccine demonstrated a 100% protection rate in goats exposed [65,72]. Furthermore, global and local experimental data confirm that recombinant vaccines expressing the Hemagglutinin (H) or Fusion (F) proteins from lineage IV viruses can induce neutralizing antibody titers that are 4 to 8 times higher than those generated by the conventional Nigeria 75/1 (lineage II) vaccine [73].
The most advanced technological approach being explored is reverse genetics, a technique that allows for the precise engineering of the entire PPRV genome. This platform enables scientists to create tailored vaccine strains for instance, by building upon the proven Nigeria 75/1 backbone but inserting key immunogenic genes from the local lineage IV viruses thereby designing vaccines that are both safe and optimally effective against the circulating Pakistani strains.
Pakistan is transitioning from being a mere consumer of global vaccine technology to an active participant in its innovation. The collaboration between its leading academic and diagnostic institutions is yielding promising, locally relevant vaccine candidates. The critical next steps involve channeling investment and effort into large-scale field efficacy trials, rigorous safety profiling, and navigating the regulatory pathways to integrate these advanced vaccine prototypes into the NPCEP, ultimately accelerating the country’s progress towards eradication. A summary of recent global and regional advancements in PPR vaccine research, including Pakistan’s contributions, is presented in Table 1.

Table 1.
Summary of Recent Advancements and Key Characteristics of Peste des Petits Ruminants (PPR) Vaccine Candidates and Platforms across Different Regions.
8. Prospects and Challenges for the Commercial Production of PPR Vaccines
The transition of a promising vaccine candidate from the laboratory to a commercially available product is a complex and costly process. Although the pipeline of next-generation PPR vaccines including recombinant, vectored, and DIVA compatible candidates is robust, their path to market is non-trivial [79]. Significant hurdles in scale-up and cost-effectiveness remain. Producing vaccines under stringent Good Manufacturing Practice (GMP) conditions requires substantial investment in infrastructure and quality control, which can be prohibitive for manufacturers targeting affordable products for developing economies [80]. This challenge is underscored by a dynamic intellectual property landscape, with numerous patents protecting various platforms, from improved live-attenuated strains to novel recombinant technologies, which must be navigated. For countries like Pakistan, this global challenge presents a specific opportunity. The well-established local production of the Nigeria 75/1 vaccine at institutions such as the Veterinary Research Institute (VRI) in Lahore provides a critical foundational platform. This existing capacity could be strategically leveraged for technology transfer agreements to produce advanced thermostable formulations, thereby reducing reliance on international suppliers and ensuring a stable, cost-effective vaccine supply for national and regional eradication campaigns [81]. Ultimately, fostering strong public–private partnerships is essential to de-risk investment for pharmaceutical companies, manage intellectual property, and ensure these advanced vaccines reach the farmers who need them most.
9. Thermostable Formulations
Thermostable PPR vaccines represent a major breakthrough in the control and eradication of Peste des Petits Ruminants, especially in developing countries such as Pakistan, where climatic extremes and logistical barriers frequently undermine the cold-chain integrity required for conventional vaccines. These vaccines are developed by incorporating stabilizing agents such as trehalose and gelatin, which enhance thermal stability, extend shelf-life, and minimize dependence on refrigeration during transportation and storage [82,83]. This advancement is of particular significance for Pakistan, where rugged geography, high ambient temperatures, and weak infrastructure often restrict access to remote pastoral areas. By simplifying field vaccination and improving outreach, thermostable formulations offer a practical and sustainable solution for protecting small ruminant populations in isolated or nomadic settings [84,85,86]. Several experimental formulations employing various stabilizers have shown promising results under laboratory and field conditions [87,88]. Among these, the thermostable live-attenuated Nigeria 75/1 vaccine is a landmark innovation, as it meets FAO/WOAH performance standards by retaining potency for more than three days at 45 °C [89,90]. Field trials conducted under Pakistan’s semi-arid conditions confirmed its high safety, immunogenicity, and efficacy, reinforcing its potential as a core component of the National PPR Control Programme, particularly for hard-to-reach districts in Balochistan and Khyber Pakhtunkhwa [83]. Comparable advancements have also been achieved in neighboring India, where the Sungri 96 thermostable vaccine demonstrated similar success, further validating the regional feasibility and reliability of thermostable vaccine technology [19,91]. Moreover, alternative stabilizers such as mannitol, sorbitol, and polymer-based matrices have been explored, each showing favorable results in enhancing vaccine durability and field stability [92]. The strategic incorporation of thermostable vaccine technology into Pakistan’s national immunization framework is therefore crucial for overcoming logistical bottlenecks, ensuring consistent vaccine performance, and achieving equitable and sustained PPR control across all ecological zones of the country.
10. Novel Delivery Methods
The novel delivery methods for PPR vaccines are based on the administration of vaccines through alternative routes or devices, which can bypass the conventional needle-based injection. The advantages of novel delivery methods include the reduction in pain, fear, and anxiety, the improvement of compliance and acceptability, and the enhancement of immunogenicity and protection [93]. For Pakistan, where mass vaccination campaigns are logistically complex and farmer compliance can be variable, such methods could significantly increase participation rates and campaign efficiency. Several novel delivery methods for PPR vaccines are being developed, including oral, intranasal, aerosol, and needle-free approaches [94,95]. This approach would be particularly advantageous for reaching nomadic or free-grazing herds in Pakistan’s extensive rangeland systems. However, oral delivery of PPR vaccines faces some challenges, such as the degradation of the vaccines by the gastric acid and enzymes, the low absorption of the vaccines by the intestinal epithelium, and the induction of immunological tolerance or anergy [96,97]. Oral delivery enables vaccine ingestion to induce systemic and mucosal immunity, though it faces challenges like gastric degradation and potential immune tolerance. Similarly, intranasal administration through the nasal cavity can stimulate both systemic and mucosal immune responses, but encounters obstacles such as mucociliary clearance, low nasal epithelium permeability, and possible immunological tolerance [95]. Aerosol delivery of PPR vaccines involves the inhalation of vaccines by the animals, which can induce both systemic and mucosal immune responses, as well as pulmonary tolerance [22,98,99,100]. This method could enable rapid mass vaccination in the dense livestock markets and communal holding areas common in Pakistan. However, aerosol delivery of PPR vaccines also faces some challenges, such as the deposition of the vaccines in the upper airways, the clearance of the vaccines by the alveolar macrophages, and the induction of immunological tolerance or anergy [101]. Needle-free delivery of PPR vaccines administers vaccines through the skin or mucosa using devices like jet injectors, microneedles, or electroporation, inducing systemic and mucosal immune responses by targeting antigen-presenting cells and lymphoid tissues [102,103,104]. The use of needle-free devices could improve safety and speed during large-scale vaccination drives in Pakistan, reducing the need for highly trained personnel and addressing needle-phobia among handlers. However, needle-free delivery of PPR vaccines also faces some challenges, such as the pain, bleeding, and infection associated with some devices, the variability of the skin or mucosa thickness and permeability, and the optimization of the vaccine dose and formulation. A concerted effort to pilot and evaluate the most suitable novel delivery methods within Pakistan’s specific infrastructure is a vital next step for enhancing the national PPR control program.
11. Intellectual Property Landscape
The global PPR vaccine patent landscape reflects key technological advances, spanning from conventional live-attenuated vaccines to next-generation thermostable, DIVA-compatible, and DNA-based platforms [105,106]. This progression underscores a committed international effort to develop practical solutions for PPR eradication [107].
12. Current and Potential Strategies for Vaccine Deployment
The vaccine deployment for PPR involves the planning, implementation, and evaluation of the vaccination activities, which aim to achieve the optimal coverage and impact of the vaccines in the target populations [52]. The vaccine deployment for PPR depends on several factors, such as the availability, accessibility, affordability, acceptability, and quality of the vaccines, as well as the logistics, infrastructure, coordination, communication, and monitoring of the vaccination programs [23]. In Pakistan, these factors are profoundly influenced by the country’s diverse husbandry systems, from intensive farms in Punjab to the vast nomadic and transhumant herds in Balochistan and Khyber Pakhtunkhwa, necessitating a flexible and multi-pronged deployment strategy. The current strategies for vaccine deployment for PPR include mass vaccination, targeted vaccination, and ring vaccination. Mass vaccination involves the vaccination of all susceptible animals in a defined area or region, regardless of their exposure or infection status [108]. Mass vaccination is suitable for the areas where PPR is endemic or epidemic, and where the resources and infrastructure are sufficient to reach a high coverage (>80%) of the target population. Mass vaccination can rapidly reduce the disease incidence and transmission and create herd immunity [109]. This approach may be most feasible in Pakistan’s central agricultural districts with higher veterinary service density. However, mass vaccination also has some drawbacks, such as the high cost, the waste of vaccines, the interference with surveillance and eradication, and the potential adverse effects. Targeted vaccination involves the vaccination of specific subgroups of animals that are at higher risk of exposure or infection, such as young animals, pregnant animals, or animals in certain locations or seasons [110]. Targeted vaccination is suitable for the areas where PPR is sporadic or emerging, and where the resources and infrastructure are limited to achieve a high coverage of the whole population [111]. Targeted vaccination can efficiently protect the most vulnerable animals and reduce the disease morbidity and mortality. For Pakistan, targeting key entry points like border regions with Afghanistan and Iran, or major livestock markets, could be a highly strategic use of resources. However, targeted vaccination also has some limitations, such as the difficulty of identifying and reaching the target subgroups, the low impact on disease transmission and elimination, and the potential selection of resistant strains. Ring vaccination involves the vaccination of the animals that are in contact or proximity with the confirmed or suspected cases of PPR, as well as the animals in the surrounding areas or regions [112]. Ring vaccination is suitable for the areas where PPR is rare or absent, and where the surveillance and diagnosis are rapid and accurate to detect and contain the disease outbreaks. The effectiveness of ring vaccination in Pakistan is currently hampered by delays in disease reporting and diagnostic confirmation, highlighting a critical area for system strengthening. Ring vaccination can effectively prevent the spread of the disease and eliminate the residual infection. However, ring vaccination also has some challenges, such as the complexity of tracing and vaccinating the contacts, the delay of the vaccination response, and the dependence on the cooperation and compliance of the stakeholders. The potential strategies for vaccine deployment for PPR include novel approaches that can improve the efficiency, effectiveness, and sustainability of the vaccination programs [113]. For example, the use of thermostable formulations can eliminate or reduce the need for cold chain and facilitate the vaccine delivery and administration in remote and rural areas. As previously discussed, the adoption of thermostable vaccines is a paramount strategy for Pakistan to overcome its specific logistical constraints. The use of novel delivery methods can reduce the pain, fear, and anxiety associated with needle-based injection, and improve the compliance and acceptability of the vaccination [114]. Piloting novel delivery methods like oral or needle-free systems could be transformative for increasing farmer participation in Pakistan’s diverse cultural and farming contexts. The use of recombinant and vectored vaccines can enable the differentiation between infected and vaccinated animals (DIVA) and enhance the surveillance and monitoring of the vaccination impact. Implementing a DIVA strategy in the long term would be invaluable for Pakistan to accurately assess progress toward eradication. The use of simulation models and decision support tools can optimize the vaccination strategies and policies, based on the epidemiological, economic, and social parameters. Developing such models with Pakistan-specific data on livestock mobility, population density, and resource allocation is an essential research priority to guide the national eradication campaign.
Table 2 provides a consolidated summary of major serological and molecular studies reporting PPR prevalence, sample sizes, and lineage distributions across Pakistani provinces. The table is introduced here to allow direct comparison of prevalence between goats and sheep and among various regions, contextualizing the epidemiological overview provided in this subsection.

Table 2.
Diagnostic results of peste des petits ruminants (PPR) from 2019 to 2024, indicating region/city, species affected, number of samples tested, positive cases, diagnostic methods, and references.
13. Conclusions and Future Perspectives
The global eradication of Peste des Petits Ruminants (PPR) by 2030 is an ambitious goal that demands a decisive shift from conventional control to a strategic, technology-driven eradication campaign. The foundation of this effort lies in the widespread adoption of next-generation vaccines, specifically thermostable formulations that bypass cold-chain limitations and DIVA-compatible (Differentiating Infected from Vaccinated Animals) systems that are essential for accurate surveillance and proving freedom from disease. For Pakistan, this global initiative presents a critical opportunity to translate its existing infrastructure into regional leadership. By leveraging its domestic vaccine production capabilities at the Veterinary Research Institute (VRI) and aligning its national control program with international standards, Pakistan can serve as a model for effective PPR management. Prioritizing the integration of advanced vaccines into its national strategy, bolstered by robust surveillance and data-driven deployment, will be crucial for progress. Ultimately, success hinges on a unified approach that seamlessly connects scientific innovation with on-the-ground implementation. This requires sustained political commitment, increased investment in local research, and strengthened cross-border collaboration. By championing this integrated strategy, Pakistan can not only secure the livelihoods of its millions of small ruminant farmers but also cement its legacy as a key contributor to one of the most significant veterinary public health achievements of our time.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, A.K. and resources, A.U.R., M.A., M.T.J., A.A.K. and M.S.; writing—original draft preparation, A.K., A.U.R., M.A., M.T.J., A.A.K. and M.L.; Manuscript writing—review and editing, A.K. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
The open access publication fees for this article were supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China for International Young Scientists (No. 42150410383) and the SUMC Scientific Research Initiation Grant (SRIG) (No. 009-510858073).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Only the literature mentioned was studied in the current article, and no experiments on animals were carried out.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Data are contained within the article.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Abubakar, M.; Irfan, M.; Manzoor, S. Peste des petits ruminants in Pakistan; past, present and future perspectives. J. Anim. Sci. Technol. 2015, 57, 32. Available online: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/26528398/ (accessed on 19 October 2025). [CrossRef]
- Gibbs, E.P.J.; Taylor, W.P.; Lawman, M.J.P.; Bryant, J. Classification of Peste des Petits Ruminants Virus as the Fourth Member of the Genus Morbillivirus. Intervirology 1979, 11, 268–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vinayagamurthy, B.; Gurrappa Naidu, G.; Roy, P. Peste des Petits Ruminants Virus. In Emerging and Transboundary Animal Viruses; Malik, Y.S., Ed.; Springer: Singapore, 2020; pp. 315–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diallo, A.; Barrett, T.; Lefevre, P.C.; Taylor, W.P. Comparison of Proteins Induced in Cells Infected with Rinderpest and Peste des Petits Ruminants Viruses. J. Gen. Virol. 1987, 68, 2033–2038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seth, S.; Shaila, M.S. The Fusion Protein of Peste des Petits Ruminants Virus Mediates Biological Fusion in the Absence of Hemagglutinin–Neuraminidase Protein. Virology 2001, 289, 86–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sweetman, D.A.; Miskin, J.; Baron, M.D. Rinderpest Virus C and V Proteins Interact with the Major (L) Component of the Viral Polymerase. Virology 2001, 281, 193–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nishie, T.; Nagata, K.; Takeuchi, K. The C Protein of Wild-Type Measles Virus Has the Ability to Shuttle Between the Nucleus and the Cytoplasm. Microbes Infect. 2007, 9, 344–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baron, M.D.; Samal, S.K. Rinderpest and Peste des Petits Ruminants. In The Biology of Paramyxoviruses; Samal, S.K., Ed.; Caister Academic Press: Norfolk, UK, 2011; pp. 293–339. Available online: https://www.caister.com/paramyxo (accessed on 19 October 2025).
- Byadovskaya, O.; Shalina, K.; Prutnikov, P.; Shumilova, I.; Tenitilov, N.; Konstantinov, A.; Sprygin, A. The Live Attenuated Vaccine Strain “ARRIAH” Completely Protects Goats from a Virulent Lineage IV Field Strain of Peste des Petits Ruminants Virus. Vaccines 2024, 12, 110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Padhi, A.; Ma, L. Genetic and Epidemiological Insights into the Emergence of Peste des Petits Ruminants Virus (PPRV) across Asia and Africa. Sci. Rep. 2014, 4, 7040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munir, M.; Zohari, S.; Berg, M. Molecular Biology and Pathogenesis of Peste des Petits Ruminants Virus; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2012; Available online: https://link.springer.com/book/10.1007/978-3-642-31451-3 (accessed on 19 October 2025).
- Kutumbetov, L.; Myrzakhmetova, B.; Tussipova, A.; Zhapparova, G.; Bissenbayeva, K.; Tlenchiyeva, T.; Nurabayev, S.; Kerimbayev, A.; Orynbayev, M.; Makhashov, E.; et al. Susceptibility and Transmission Dynamics of Peste des Petits Ruminants Virus in Domestic and Wild Ruminants: Experimental Insights from Kazakhstan. Viruses 2025, 17, 1231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chauhan, H.C.; Chandel, B.S.; Kher, H.N.; Dadawala, A.I.; Agrawal, S.M. Peste des Petits Ruminants Virus Infection in Animals. Vet. World 2009, 2, 150–151. Available online: https://www.cabidigitallibrary.org/doi/pdf/10.5555/20093107654 (accessed on 19 October 2025).
- Abubakar, M.; Khan, H.A.; Arshed, M.J.; Hussain, M.; Ali, Q. Peste des Petits Ruminants (PPR): Disease Appraisal with Global and Pakistan Perspective. Small Rumin. Res. 2011, 96, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aklilu, F.; Ashenafi, H.; Kassa, T.; Chaka, H.; Sibhatu, D.; Shegu, D.; Aliy Mohammed, A.; Belaineh, R.; Kidane, M.; Asgedom, H.; et al. Comparative Pathogenesis of Ethiopia/Habru/2014 Lineage-IV Peste des Petits Ruminants Virus in Goats and Cattle. BMC Vet. Res. 2024, 20, 473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munir, M.; Zohari, S.; Berg, M. Pathophysiology and Clinical Assessment of Peste des Petits Ruminants. In Molecular Biology and Pathogenesis of Peste des Petits Ruminants Virus; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2013; pp. 33–48. Available online: https://link.springer.com/chapter/10.1007/978-3-642-31451-3_3 (accessed on 19 October 2025).
- Abu-Elzein, E.M.E.; Hassanien, M.M.; Al-Afaleq, A.I.; Abd-Elhadi, M.A.; Housawi, F.M.I. Isolation of Peste des Petits Ruminants from Goats in Saudi Arabia. Vet. Rec. 1990, 127, 309–310. [Google Scholar]
- Fine, A.E.; Pruvot, M.; Benfield, C.T.; Caron, A.; Cattoli, G.; Chardonnet, P.; Njeumi, F. Eradication of Peste des Petits Ruminants Virus and the Wildlife–Livestock Interface. Front. Vet. Sci. 2020, 7, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imanbayeva, D.; Pérez Aguirreburualde, M.S.; Knauer, W.; Tegzhanov, A.; Yustyniuk, V.; Arzt, J.; Parida, S. A Scoping Review on Progression Towards Freedom from Peste des Petits Ruminants (PPR) and the Role of the PPR Monitoring and Assessment Tool (PMAT). Viruses 2025, 17, 563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- FAO; OIE. Global Strategy for the Control and Eradication of PPR; FAO/OIE: Rome, Italy, 2015; Available online: https://www.fao.org/publications/card/en/c/0a5b5e2b-bd1b-53a8-8ff5-7bfa3eaf55f0/ (accessed on 19 October 2025).
- Fawzi, E.M.; Menaze, A.M.; Essa, M.I.; Mahmoud, M.M. Assessment of the Duration of Maternal Antibodies Specific to Live Attenuated Peste des Petits Ruminants Virus Vaccine in Lambs and Kids. Zagazig Vet. J. 2017, 45, 181–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahapatra, M.; Selvaraj, M.; Parida, S. Comparison of Immunogenicity and Protective Efficacy of PPR Live Attenuated Vaccines (Nigeria 75/1 and Sungri 96) Administered by Intranasal and Subcutaneous Routes. Vaccines 2020, 8, 168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rojas, J.M.; Sevilla, N.; Martín, V. A New Look at Vaccine Strategies against PPRV Focused on Adenoviral Candidates. Front. Vet. Sci. 2021, 8, 729879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eloiflin, R.; Boyer, M.; Kwiatek, O.; Guendouz, S.; Loire, E.; Servan de Almeida, R.; Libeau, G.; Bataille, A. Evolution of Attenuation and Risk of Reversal in Peste des Petits Ruminants Vaccine Strain Nigeria 75/1. Viruses 2019, 11, 724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Athar, M.; Muhammad, G.; Azim, F.; Shakoor, A. An Outbreak of Peste des Petits Ruminants-Like Disease among Goats in Punjab (Pakistan). Pak. Vet. J. 1995, 15, 140–141. [Google Scholar]
- Pervez, K.; Ashfaq, M.; Khan, M.S.; Hussain, M.; Azim, E. A rinderpest like disease in goats in Punjab, Pakistan. Pak. J. Livest. Res. 1993, 1, 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Rahman, H.; Ali, A.; Abro, S.; Abubakar, M. An investigation on the prevalence of peste des petits ruminants in the camels of Sindh, Pakistan. Trop. Anim. Health Prod. 2020, 52, 1863–1867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abubakar, M.; Zahur, A.B.; Afzal, M.; Ali, Q.; Gonzales, J. Peste des petits ruminants (PPR) in Pakistan: Analysis of a national level serological data. Small Rumin. Res. 2017, 155, 57–65. Available online: https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S0921448817302304 (accessed on 19 October 2025). [CrossRef]
- Zahur, A.B.; Ullah, A.; Hussain, M.; Irshad, H.; Hameed, A.; Jahangir, M.; Farooq, M.S. Sero-epidemiology of peste des petits ruminants (PPR) in Pakistan. Prev. Vet. Med. 2011, 102, 87–92. Available online: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/21788090/ (accessed on 19 October 2025). [CrossRef]
- Rasheed, M.; Akhtar, T.; Mukhtar, N.; Shahid, M.F.; Imran, M.; Yaqub, S. Sero-prevalence of peste des petits ruminant (PPR) virus in sheep and goat population of Gilgit Baltistan Province of Pakistan. Punjab Univ. J. Zool. 2020, 35, 123–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munibullah, M.; Li, Y.; Munib, K.; Zhang, Z. Regional epidemiology and associated risk factors of peste des petits ruminants in Asia—A review. Slov. Vet. Res. 2022, 59, 75–87. Available online: https://www.cabidigitallibrary.org/doi/full/10.5555/20220351725 (accessed on 19 October 2025).
- Zahur, A.B.; Ullah, A.; Irshad, H.; Latif, A.; Ullah, R.W.; Afzal, M.; Mahboob, K. Isolation and characterization of lineage-IV peste des petits ruminants (PPR) virus strains from Pakistan. Int. J. Innov. Appl. Stud. 2014, 8, 185–194. [Google Scholar]
- Anees, M.; Shabbir, M.Z.; Muhammad, K.; Nazir, J.; Shabbir, M.A.B.; Wensman, J.J.; Munir, M. Genetic analysis of peste des petits ruminants virus from Pakistan. BMC Vet. Res. 2013, 9, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kihu, S.M. Risk Factors and Socioeconomic Effects Associated with Spread of Peste des Petits Ruminants (PPR) in Turkana County, Kenya. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Nairobi, Nairobi, Kenya, 2014. Available online: https://erepository.uonbi.ac.ke/handle/11295/75255 (accessed on 19 October 2025).
- Salih, H.A.M. Risk Assessment and Management for Peste des Petites Ruminants (PPR) in Sudan. Ph.D. Thesis, Sudan University of Science and Technology, Khartoum, Sudan, 2015. Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/380162663 (accessed on 19 October 2025).
- Azizi, N.A. Peste des petits ruminants in Afghanistan. In Proceedings of the FAO/OIE Regional Conference on PPR Control, Damascus, Syria, 22–24 November 2010; Available online: https://openknowledge.fao.org/handle/1834/5589 (accessed on 19 October 2025).
- Rondeau, A. Assessment of the Risk of Spread of Peste des Petits Ruminants in South Africa Through Use of Spatial Multi-Criteria Decision Analysis. Master’s Thesis, University of Pretoria, Pretoria, South Africa, 2017. Available online: https://repository.up.ac.za/handle/2263/65607 (accessed on 19 October 2025).
- Munibullah, M.; Li, Y.; Munib, K.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, Z. Prevalence and Associated Risk Factors of Peste des Petits Ruminants in Selected Districts of the Northern Border Region of Pakistan. BMC Vet. Res. 2024, 20, 225. Available online: https://bmcvetres.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/s12917-024-04033-8 (accessed on 19 October 2025). [CrossRef]
- Khan, H.A.; Siddique, M.; Abubakar, M.; Arshad, M.J.; Hussain, M. Prevalence and distribution of peste des petits ruminants virus infection in small ruminants. Small Rumin. Res. 2008, 79, 152–157. Available online: www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S0921448808001624 (accessed on 19 October 2025). [CrossRef]
- Abbas, F.; Ullah, A.; Awan, M.A.; Tariq, M.M.; Ali, M.; Khan, F.A.; Bajwa, M.A.; Ahmad, Z.; Rashid, N.; Wadood, A. Production of tissue culture based peste des petits ruminants (PPR) vaccine at CASVAB, Quetta, Pakistan. Pak. J. Life Soc. Sci. 2012, 10, 80–83. [Google Scholar]
- Ali, S.N.; Khan, S.A.; Vandiar, M.; Ullah, R.W.; Kazmi, S.U. One year study to estimate prevalence of peste des petits ruminants (PPR) in Sindh province of Pakistan. FUUAST J. Biol. 2019, 9, 147–155. [Google Scholar]
- Hussain, M.; Afzal, M.; Ali, Q.; Taylor, W.; Mariner, J.; Roeder, P. The epidemiology of peste des petits ruminants in Pakistan and possible control policies. Rev. Sci. Tech. 2008, 27, 869–878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nadeem, M.; Rizwan, M.; Ahmad, T.; Kashif, M.; Zameer, A.; Durrani, M.A.; Waheed, S.F. Participatory surveillance of infectious and non-infectious diseases of livestock in Pakistan. Punjab Univ. J. Zool. 2022, 37, 143–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, F.M. Participatory appraisal and scanning surveillance based contagious diseases risk profile of district Rahim Yar Khan (Pakistan). Pak. Vet. J. 2010, 30, 198–202. [Google Scholar]
- Mehmood, A.; Ali, Q.; Gadahi, J.A.; Malik, S.A.; Shah, S.I. Detection of peste des petits ruminants (PPR) virus antibodies in sheep and goat populations of the North West Frontier Province (NWFP) of Pakistan by competitive ELISA (cELISA). Vet. World 2009, 2, 151–154. [Google Scholar]
- Jalees, M.M.; Hussain, I.; Arshad, M.; Mohammad, G.; Khan, Q.M. Seroprevalence and molecular detection of peste des petits ruminants virus (PPRV) in different breeds of sheep and goat of Punjab (Pakistan) and its status in gravid animals. Pak. J. Life Soc. Sci. 2016, 14, 12–17. [Google Scholar]
- Ahamed, S.; Nazir, K.N.H.; Yousuf, M.A.; Islam, M.M.; Arafat, M.Y.; Islam, M.A.; Mahmud, M.M.; Islam, M.R. Seromonitoring of peste des petits ruminants in goats and molecular characterization of PPR virus from field cases. J. Adv. Vet. Anim. Res. 2019, 6, 416–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kabir, A.; Mirani, A.H.; Kashif, J.; Manzoor, S.; Iqbal, A.; Khan, I.U.; Abubakar, M. Serological detection and confirmation of PPR among sheep and goat kept under different production systems. Pak. J. Zool. 2020, 52, 1137–1143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baloch, S.; Yousaf, A.; Shaheen, S.; Shaheen, S.; Sarki, I.; Babar, A.; Sakhawat, A.; Arshad, M.; Khalil-Ur-Rehman, M.; Musakhail, S.; et al. Study on the prevalence of peste des petits virus antibodies in caprine and ovine through the contrast of serological assessments in Sindh, Pakistan. Am. J. Biosci. Bioeng. 2021, 9, 131–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, A. Pakistan on way to containing goat disease. Dawn. 2017. Available online: https://www.dawn.com/news/1368256 (accessed on 19 October 2025).
- Diallo, A.; Bataille, A.; Lancelot, R.; Libeau, G. Peste des petits ruminants. In Transboundary Animal Diseases in Sahelian Africa and Connected Regions; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2019; pp. 233–266. Available online: https://link.springer.com/chapter/10.1007/978-3-030-25385-1_12 (accessed on 19 October 2025).
- Eltahir, Y.M.; Aburizq, W.; Bensalah, O.K.; Mohamed, M.S.; Al Shamisi, A.; AbdElkader, A.I.; Al-Majali, A. Modeling for smart vaccination against peste des petits ruminants (PPR) in the Emirate of Abu Dhabi, United Arab Emirates. Animals 2023, 13, 3248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Libeau, G. Current Advances in Serological Diagnosis of Peste des Petits Ruminants Virus. In Peste des Petits Ruminants Virus; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2014; pp. 133–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vinayagamurthy, B. Peste des Petits Ruminants. In Emerging and Re-Emerging Infectious Diseases of Livestock; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2017; pp. 55–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahsan, A.; Usman, M.; Ullah, I.; Zahur, A.B.; Malik, A.R. Molecular diagnostic assays for the detection of peste des petits ruminants virus: A concise review. Vet. Sci. Res. Rev. 2017, 3, 53–57. Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/324467524_Molecular_Diagnostic_Assays_for_the_Detection_of_Peste_des_Petits_Ruminants_Virus_A_Concise_Review (accessed on 19 October 2025). [CrossRef]
- Doğan, M.; Öz, M.E.; Akbaba, S. One-Run qPCR Assays for Identification of Domestic Ruminant Abortion: Verification and Application Process. Pak. Vet. J. 2025, 45, 553–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dik, I.; Gulersoy, E.; Simsek, A. Importance of Biomarkers and Cytokines in the Prognosis of Canine Parvovirus Infection. Pak. Vet. J. 2024, 44, 875–881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Legnardi, M.; Raizman, E.; Beltran-Alcrudo, D.; Cinardi, G.; Robinson, T.; Falzon, L.C.; Benfield, C.T. Peste des Petits Ruminants in Central and Eastern Asia/West Eurasia: Epidemiological Situation and Status of Control and Eradication Activities after the First Phase of the PPR Global Eradication Programme (2017–2021). Animals 2022, 12, 2030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weka, R.; Luka, P.D.; Chabiri, L.A.; Lazarus, D.D. Strategic Control of Peste des Petits Ruminants. In Peste des Petits Ruminants Virus; Munir, M., Abubakar, M., Eds.; Springer Nature: Cham, Switzerland, 2025; pp. 29–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations (FAO). Final evaluation of “Progressive Control of Peste des Petits Ruminants in Pakistan” (GCP/PAK/127/USA); FAO: Rome, Italy, 2017; Available online: https://www.fao.org/publications/card/en/c/CA6042EN (accessed on 19 October 2025).
- Zafar, S.; Sarfraz, M.S.; Ali, S.; Saeed, L.; Mahmood, M.S.; Khan, A.U.; Anwar, M.N. Recapitulation of peste des petits ruminants (PPR) prevalence in small ruminant populations of Pakistan from 2004 to 2023: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Vet. Sci. 2024, 11, 280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, H.A.; Siddique, M.; Arshad, M.; Abubakar, M.; Akhtar, M.; Arshad, M.J.; Ashraf, M. Post-vaccination antibodies profile against peste des petits ruminants (PPR) virus in sheep and goats of Punjab, Pakistan. Trop. Anim. Health Prod. 2009, 41, 427–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zahur, A.B.; Irshad, H.; Ullah, A.; Afzal, M.; Latif, A.; Wasee Ullah, R.; Farooq, U.; Samo, M.H.; Jahangir, M.; Ferrari, G.; et al. Peste des petits ruminants vaccine (Nigerian strain 75/1) confers protection for at least 3 years in sheep and goats. J. Biosci. Med. 2014, 2, 27–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zahid, F.; Latif, A. Unlocking the Potential Role of Live Attenuated Vaccines and Current Therapeutics for Effective Peste des Petits Ruminants (PPR) Control Globally. In Foundations of Holistic Healing: Complementary and Alternative Medicine; García-Rubio, V.G., Alvi, M.A., Saeed, Z., Ahmad, M., Eds.; Unique Scientific Publishers: Faisalabad, Pakistan, 2025; pp. 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamal, T.; Khan, S.U.H.; Hassan, F.; Zahoor, A.B.; Ullah, A.; Andrabi, S.M.H.; Razak, S. Molecular characterization of Lineage-IV peste des petits ruminants virus and the development of in-house indirect enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (IELISA) for its rapid detection. Biol. Proced. Online 2024, 26, 22. Available online: https://biologicalproceduresonline.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/s12575-024-00249-y (accessed on 19 October 2025). [CrossRef]
- Abubakar, M.; Qureshi, M.; Zahur, A.B.; Naeem, K.; Khan, M.A.; Qureshi, S. Field and molecular epidemiology of peste des petits ruminants in Pakistan. Pak. J. Zool. 2018, 50, 559–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taheri Hosseinkhani, N. Global food security amid geopolitical tensions and climate risk: Trade governance and adaptive strategies. SSRN 2025, 5448314, preprint. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rashid, A.; Hussain, A.; Asim, M. Evaluation of peste des petits ruminants cell culture vaccine in sheep and goats in Pakistan. Vet. Ital. 2010, 46, 315–318. Available online: https://www.cabidigitallibrary.org/doi/pdf/10.5555/20103355917 (accessed on 19 October 2025).
- Dik, I.; Orbay, H.F.; Ozgur, F.B.; Dik, B. The effect of the combination of peste des petits ruminants (PPR) vaccine with different doses of Lentinan on cytokines and antibody levels of sheep. Pak. Vet. J. 2023, 43, 683–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Njeumi, F.; Bailey, D.; Soula, J.J.; Diop, B.; Tekola, B.G. Eradicating the scourge of peste des petits ruminants from the world. Viruses 2020, 12, 313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Latif, M.Z.; Muhammad, K.; Hussain, R.; Siddique, F.; Altaf, I.; Anees, M.; Imran, M.; Hameed, M.; Farooq, M. Effect of stabilizers on infectivity titer of freeze dried peste des petits ruminants virus vaccine. Pak. Vet. J. 2018, 38, 169. Available online: https://pvj.com.pk/pdf-files/38_2/169-173.pdf (accessed on 19 October 2025). [CrossRef]
- Yaser, T.; Bkear, N.; Badr, Y.; Ibrahim, E.E.S.; Khodeir, M.H. Investigation of the effect of mutual vaccination with peste des petits ruminants and polyvalent foot and mouth disease vaccines on the immune response of sheep. Open Vet. J. 2023, 13, 1669. Available online: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/38292706/ (accessed on 19 October 2025). [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muniraju, M.B. Establishment of reverse genetics system for PPR virus to develop recombinant vaccines. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Warwick, Coventry, UK, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Diallo, A.; Taylor, W.P.; Lefèvre, P.C.; Provost, A. Peste des petits ruminants (PPR): A threat to small ruminant production in Africa, the Middle East and Asia. Vet. Res. 2007, 38, 375–380. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, N.; Maherchandani, S.; Kashyap, S.K.; Singh, S.V.; Sharma, S.; Chaubey, K.K.; Ly, H. Peste des petits ruminants virus infection of small ruminants: A comprehensive review. Viruses 2014, 6, 2287–2327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munir, M.; Saeed, A.; Abubakar, M.; Kanwal, S.; Berg, M. Molecular characterization of peste des petits ruminants viruses from outbreaks caused by unrestricted movements of small ruminants in Pakistan. Transbound. Emerg. Dis. 2015, 62, 108–114. Available online: https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1111/tbed.12089 (accessed on 19 October 2025). [CrossRef]
- Banyard, A.C.; Parida, S.; Batten, C.; Oura, C.; Kwiatek, O.; Libeau, G. Global distribution of peste des petits ruminants virus and prospects for improved diagnosis and control. J. Gen. Virol. 2010, 91, 2885–2897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, X.-X.; Wang, H.; Liu, Y.; Meng, D.-M.; Fan, Z.-C. Development of Vaccines for Prevention of Peste-des-Petits-Ruminants Virus Infection. Microb. Pathog. 2020, 142, 104045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, F.; Wu, X.; Liu, W.; Li, L.; Wang, Z. Current Perspectives on Conventional and Novel Vaccines against Peste des Petits Ruminants. Vet. Res. Commun. 2014, 38, 307–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kardjadj, M.; Luka, P.D. Factors Affecting PPRV in African Countries and Their Countermeasures. Br. J. Virol. 2016, 3, 63–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, M.P.; Singh, R.K.; Malik, Y.S. Emerging and transboundary animal viral diseases: Perspectives and preparedness. In Emerging and Transboundary Animal Viruses; Malik, Y.S., Singh, R.K., Yadav, M.P., Eds.; Springer: Singapore, 2020; pp. 1–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riyesh, T.; Balamurugan, V.; Sen, A.; Bhanuprakash, V.; Venkatesan, G.; Yadav, V.; Singh, R.K. Evaluation of Efficacy of Stabilizers on the Thermostability of Live Attenuated Thermo-Adapted Peste des Petits Ruminants Vaccines. Virol. Sin. 2011, 26, 324–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mariner, J.C.; Gachanja, J.; Tindih, S.H.; Toye, P. A thermostable presentation of the live, attenuated peste des petits ruminants vaccine in use in Africa and Asia. Vaccine 2017, 35, 3773–3779. Available online: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/28566253/ (accessed on 19 October 2025). [CrossRef]
- Bora, M.; Yousuf, R.W.; Dhar, P.; Singh, R.P. An overview of process intensification and thermo-stabilization for upscaling of peste des petits ruminants vaccines in view of global control and eradication. VirusDisease 2018, 29, 285–296. Available online: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/30159362/ (accessed on 19 October 2025). [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bora, M.; Patel, C.L.; Rajak, K.K.; Verma, M.R.; Yousuf, R.W.; Singh, R.P. Development of a process for upscaling and production of thermotolerant peste-des-petits ruminants vaccine. VirusDisease 2020, 31, 357–368. Available online: https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s13337-020-00608-9 (accessed on 19 October 2025). [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fanelli, A.; Mantegazza, L.; Hendrickx, S.; Capua, I. Thermostable vaccines in veterinary medicine: State of the art and opportunities to be seized. Vaccines 2022, 10, 245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sen, A.; Balamurugan, V.; Rajak, K.K.; Chakravarti, S.; Bhanuprakash, V.; Singh, R.K. Role of heavy water in biological sciences with an emphasis on thermostabilization of vaccines. Expert Rev. Vaccines 2009, 8, 1587–1602. Available online: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/19863251/ (accessed on 19 October 2025). [CrossRef]
- Shawky, Y.A.; Hussein, A.; Salman, O.G.; Eid, A.A. Comparative protective efficiency of different stabilizers for live Newcastle Disease Virus vaccine production. J. Adv. Vet. Res. 2022, 12, 658–664. [Google Scholar]
- Worrall, E.E.; Litamoi, J.K.; Seck, B.M.; Ayelet, G. Xerovac: An ultra-rapid method for the dehydration and preservation of live attenuated rinderpest and peste des petits ruminants vaccines. Vaccine 2000, 19, 834–839. Available online: https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S0264410X00002292 (accessed on 19 October 2025). [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baba, S.S.; El-Yuguda, A.D.; Egwu, G.O.; Ribadu, A.Y.; Ambali, A.G.; Abubakar, M.D.; Zoyem, N. Development and evaluation of the efficacy of heat tolerant Peste des petits ruminants (PPR) vaccine in Nigeria. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Adaptive Science & Technology (ICAST), Ottawa, ON, Canada, 3–5 October 2007; pp. 138–141. [Google Scholar]
- Sarkar, J.; Sreenivasa, B.P.; Singh, R.P.; Dhar, P. Comparative efficacy of various chemical stabilizers on the thermostability of a live-attenuated peste des petits ruminants (PPR) vaccine. Vaccine 2003, 21, 4728–4735. Available online: https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S0264410X03005127 (accessed on 19 October 2025). [CrossRef]
- Smith, L.C.; Nelson, P. Formulation design considerations and good practice for live attenuated vaccine development. In Practical Aspects of Vaccine Development; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2022; pp. 27–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasannejad-Asl, B.; Pooresmaeil, F.; Takamoli, S.; Dabiri, M.; Bolhassani, A. Cell penetrating peptide: A potent delivery system in vaccine development. Front. Pharmacol. 2022, 13, 4834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, L.; Kate, P.; Torchilin, V.P. Matrix Metalloprotease 2-Responsive Multifunctional Liposomal Nanocarrier for Enhanced Tumor Targeting. ACS Nano 2012, 6, 3491–3498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mangla, B.; Javed, S.; Sultan, M.H.; Ahsan, W.; Aggarwal, G.; Kohli, K. Nanocarriers-assisted needle-free vaccine delivery through oral and intranasal transmucosal routes: A novel therapeutic conduit. Front. Pharmacol. 2022, 12, 757761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dam, K.M. Immunoinformatics approach for multi-epitope vaccine design against structural proteins and ORF1a polyprotein of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus-2 (SARS-CoV-2). Trop. Dis. Travel Med. Vaccines 2021, 7, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almofti, Y.A.; Abd-Elrahman, K.A.; Eltilib, E.E. Vaccinomic approach for novel multi-epitopes vaccine against severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus-2 (SARS-CoV-2). BMC Immunol. 2021, 22, 22. Available online: https://bmcimmunol.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/s12865-021-00412-0 (accessed on 19 October 2025). [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calderon-Nieva, D.; Goonewardene, K.B.; Gomis, S.; Foldvari, M. Veterinary vaccine nanotechnology: Pulmonary and nasal delivery in livestock animals. Drug Deliv. Transl. Res. 2017, 7, 558–570. Available online: https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s13346-017-0400-9 (accessed on 19 October 2025). [CrossRef]
- Jia, Y.; Krishnan, L.; Omri, A. Nasal and Pulmonary Vaccine Delivery Using Particulate Carriers. Expert Opin. Drug Deliv. 2015, 12, 993–1008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ezeasor, C.K.; Shoyinka, S.V.; E MIKPE, B.O.; Udeani, I.J.; Nwankpa, N.; Bodjo, C.S.; Sabri, M.Y. The influence of intranasal peste des petits ruminants vaccine application methods on the induction of immune responses in goats: Clinicopathological and immunohistochemical findings. Thai J. Vet. Med. 2021, 51, 637–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, N.; Barua, S.; Riyesh, T.; Tripathi, B.N. Advances in peste des petits ruminants vaccines. Vet. Microbiol. 2017, 206, 91–101. Available online: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/28161212/ (accessed on 19 October 2025). [CrossRef]
- Gerdts, V. Adjuvants for veterinary vaccines–types and modes of action. Berl. Munch Tierarztl. Wochenschr. 2015, 128, 456–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Wang, Y.; Sun, Y.; Cui, H.; Zhu, S.J.; Qiu, H.J. Mucosal vaccines: Strategies and challenges. Immunol. Lett. 2020, 217, 116–125. Available online: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/31669546/ (accessed on 19 October 2025). [CrossRef]
- Salahuddin, M.; Habib, M.; Unger, H. Development of a mucosal vaccine formulation against peste des petits ruminants virus for small ruminants. Sustain. Anim. Prod. Health 2021, 6, 1–12. [Google Scholar]
- Martín, V.; Rodríguez-Martín, D.; Sevilla, N.; Rojas, J.M. Advances in vaccination against PPRV. In Peste des Petits Ruminants Virus; Springer Nature: Cham, Switzerland, 2025; pp. 207–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niedbalski, W. Progress in Vaccines against Peste des Petits Ruminants Virus. Med. Weter. 2023, 79, 31–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chukwudi, I.C.; Weka, R.; Inusa, D.; Luka, P.D. Challenges and Opportunities in the Eradication Campaign of PPR. Peste Des Petits Rumin. Virus 2025, 1, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plotkin, S.A. (Ed.) Mass Vaccination: Global Aspects—Progress and Obstacles; Springer Science & Business Media: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2006; Available online: https://link.springer.com/book/10.1007/3-540-36583-4 (accessed on 19 October 2025).
- Tago, D.; Sall, B.; Lancelot, R.; Pradel, J. VacciCost—A Tool to Estimate the Resource Requirements for Implementing Livestock Vaccination Campaigns. Application to Peste des Petits Ruminants (PPR) Vaccination in Senegal. Prev. Vet. Med. 2017, 144, 13–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zepp, F. Principles of Vaccination. In Vaccine Design: Methods and Protocols, 1st ed.; Thomas, S., Ed.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2016; Volume 1403, pp. 57–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Njeumi, F.; Parida, S.; Benfield, C.T. Progress towards eradication of peste des petits ruminants through vaccination. Viruses 2021, 13, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chazya, R.; Muma, J.B.; Mwacalimba, K.K.; Karimuribo, E.; Mkandawire, E.; Simuunza, M. A Qualitative Assessment of the Risk of Introducing Peste des Petits Ruminants into Northern Zambia from Tanzania. Vet. Med. Int. 2014, 202618, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ElArbi, A.S.; Kane, Y.; Metras, R.; Hammami, P.; Ciss, M.; Beye, A.; Lancelot, R.; Diallo, A.; Apolloni, A. PPR Control in a Sahelian Setting: What Vaccination Strategy for Mauritania? Front. Vet. Sci. 2019, 6, 242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rind, A.L.; Abro, S.H.; Kaleri, R.R.; Solangi, G.M.; Mangi, R.A.; Memon, M.A.; Bhuptani, D.K.; Noor, S.; Lanjar, Z.; Mangrio, Z.H.; et al. Prevalence of the Peste des Petits Ruminants in Goat and Sheep in District Sanghar, Sindh, Pakistan. J. Innov. Sci. 2023, 9, 192–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Unar, S.; Kalhoro, D.; Abro, S.; Nizamani, A.; Channo Abdullah, K.; Kaka, A.; Bakhsh, M.; Parhiyar, A.; Kalhoro, M.; Channo, A.Q.; et al. Seroprevalence and Risk Factors Assessment of Peste des Petits Ruminants in Goats in District Shaheed Benazirabad, Pakistan. Int. J. Agric. Biol. 2024, 31, 111–115. Available online: https://api.fspublishers.org/viewPaper/62384_05%20doi%2015.2121%20IJAB-23-0309%20%285%29%20111-115.pdf?utm_source=chatgpt.com (accessed on 19 October 2025).
- Mal, R.; Kalhoro, H.; Baloch, H.; Kalhoro, M.; Kolachi, H.; Janyaro, H.; Panhwar, M.; Ahmed, F.; Ali, A.; Mangi, M.; et al. Sero-Prevalence of Peste des Petits Ruminants Among Goats of Different Zones of District Thatta, Sindh. BioSight 2024, 5, 76–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kabir, A. 5th Peste des Petits Ruminants Global Research and Expertise Network (PPR-GREN) Meeting, Montpellier, France, 7–9 December 2022; FAO: Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations: Rome, Italy, 2022; Available online: https://www.fao.org/ppr/news-and-events/events/detail/en/c/1609779/ (accessed on 19 October 2025).
- Shabbir, M.; Sohail, T.; Ul-Rahman, A.; Abbas, T.; Ali, Q.; Rehman Zu Khan, I.; Yaqub, T.; Muhammad, J.; Ahmed, S.; Imran, M.; et al. Sentinel Surveillance of Selected Veterinary and Public Health Pathogens in Camel Population Originating from Southern Punjab Province, Pakistan. Acta Trop. 2020, 205, 105435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Afsheen, R. PPR Disease Claims Lives of 35 Wild Goats at Kirthar National Park. The Truth International. 2023. Available online: https://thetruthinternational.com/national/ppr-disease-claims-lives-of-35-wild-goats-at-kirthar-national-park/ (accessed on 1 January 2024).
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).