Yeast Display Reveals Plentiful Mutations That Improve Fusion Peptide Vaccine-Elicited Antibodies Beyond 59% HIV-1 Neutralization Breadth
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Construction of DFPH-a.01 Variant Antibody Libraries
2.2. Functional Library Screening
2.3. Next-Generation Sequencing and Analysis
2.4. Antibody Expression and Purification
2.5. Virus Neutralization
2.6. Affinity Measurements by Surface Plasmon Resonance
2.7. Stability Measurements
2.8. Cryo-EM Structure Determination
2.9. Quantification and Statistical Analysis
3. Results
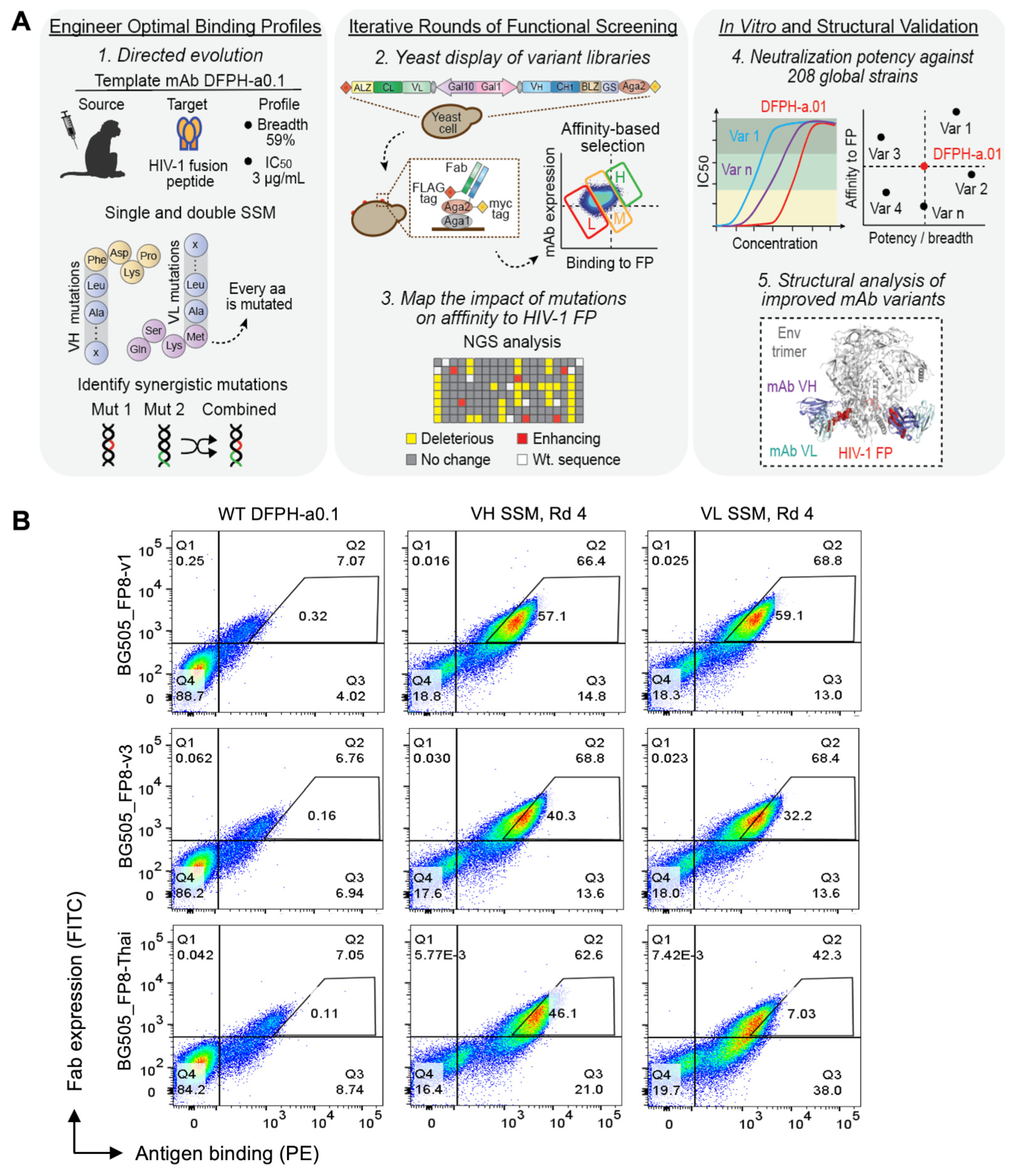
3.1. Precision Yeast Display Antibody Engineering of DFPH-a.01
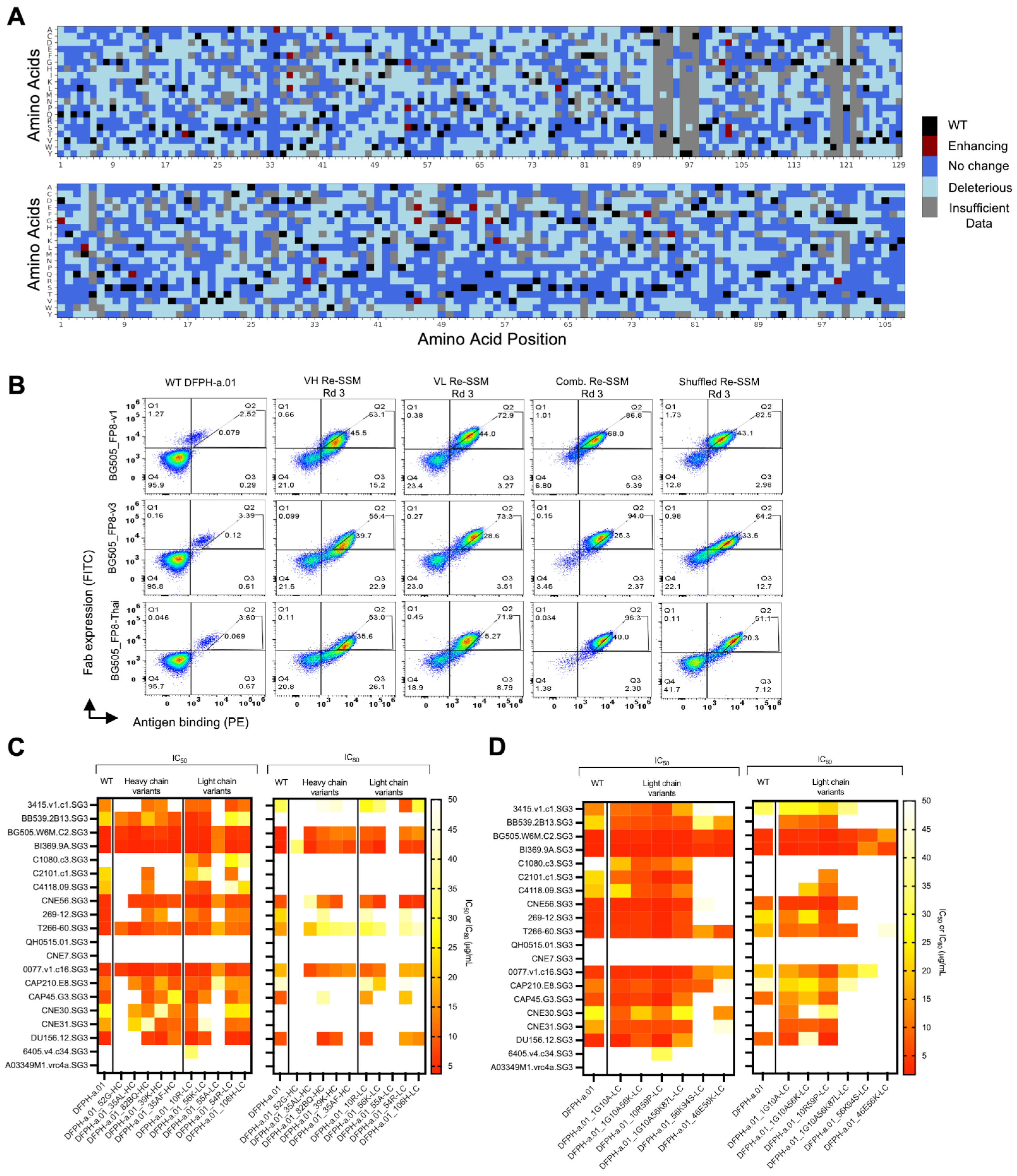
3.2. Multi-Mutation Library Generation and Screening
3.3. HIV-1 Neutralization Analysis of Mutational Variants Identified in Yeast Display
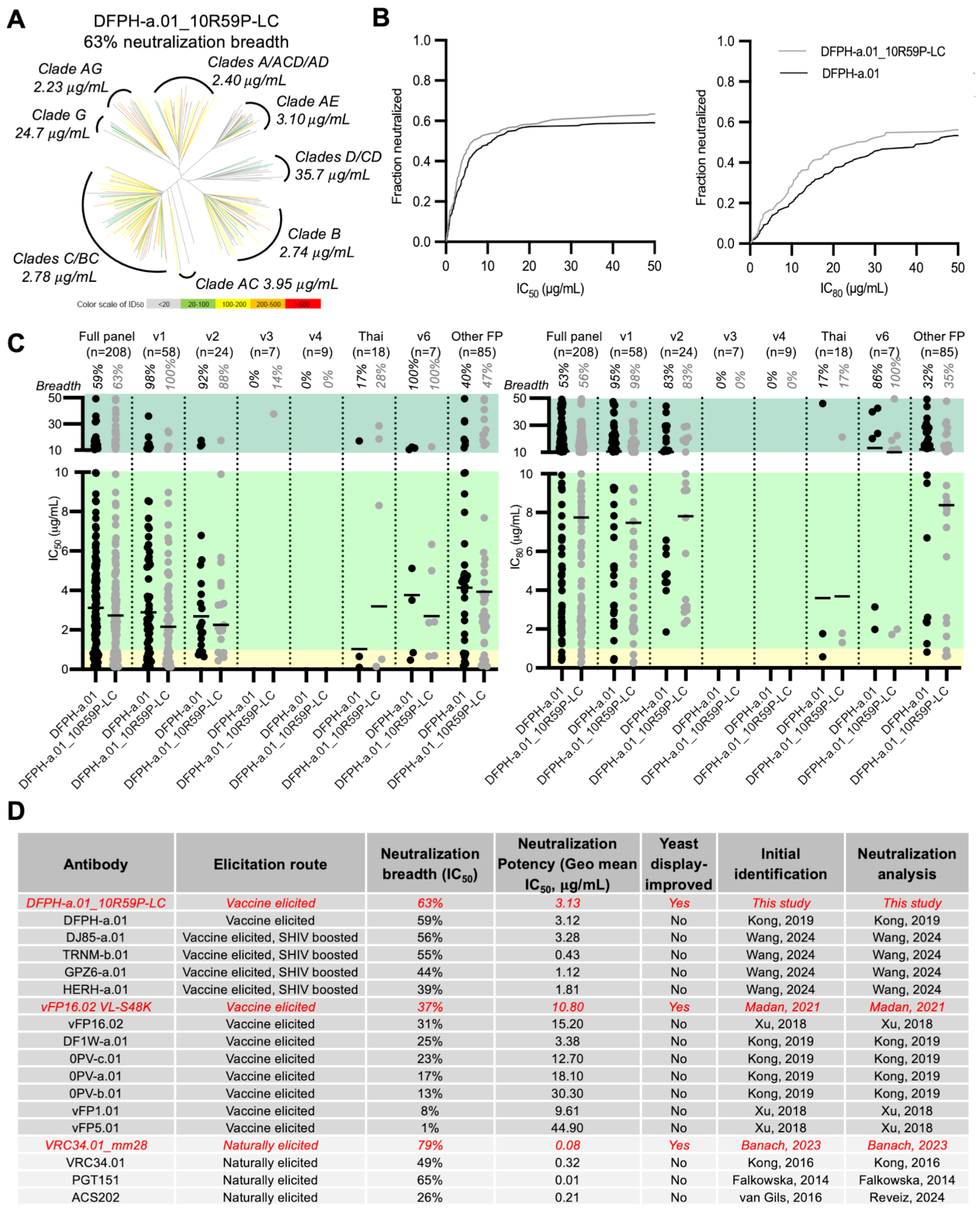
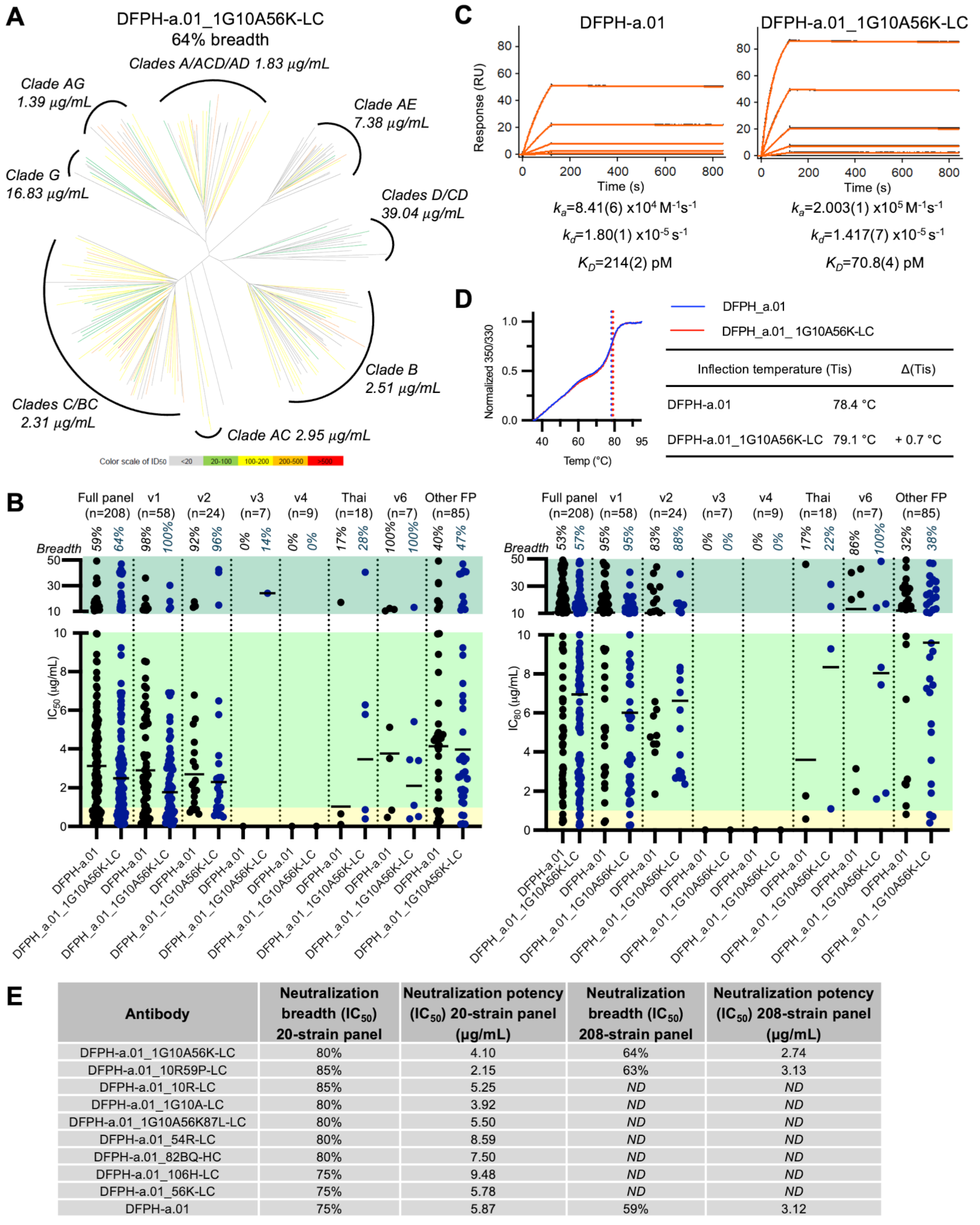
3.4. Breadth and Potency Analysis of DFPH-a.01_10R59P-LC
3.5. Surface Plasmon Resonance and Thermal Stability Analyses
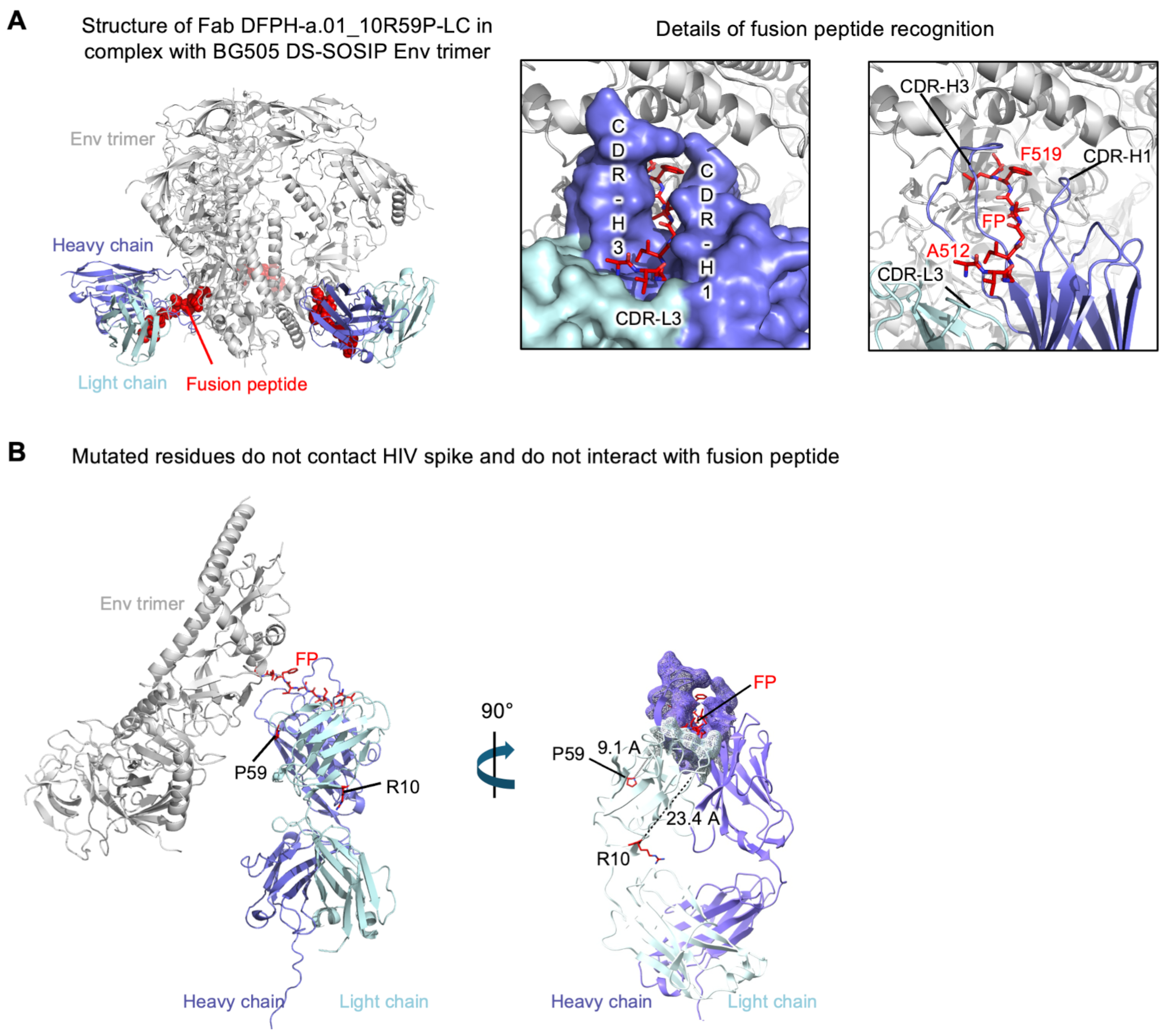
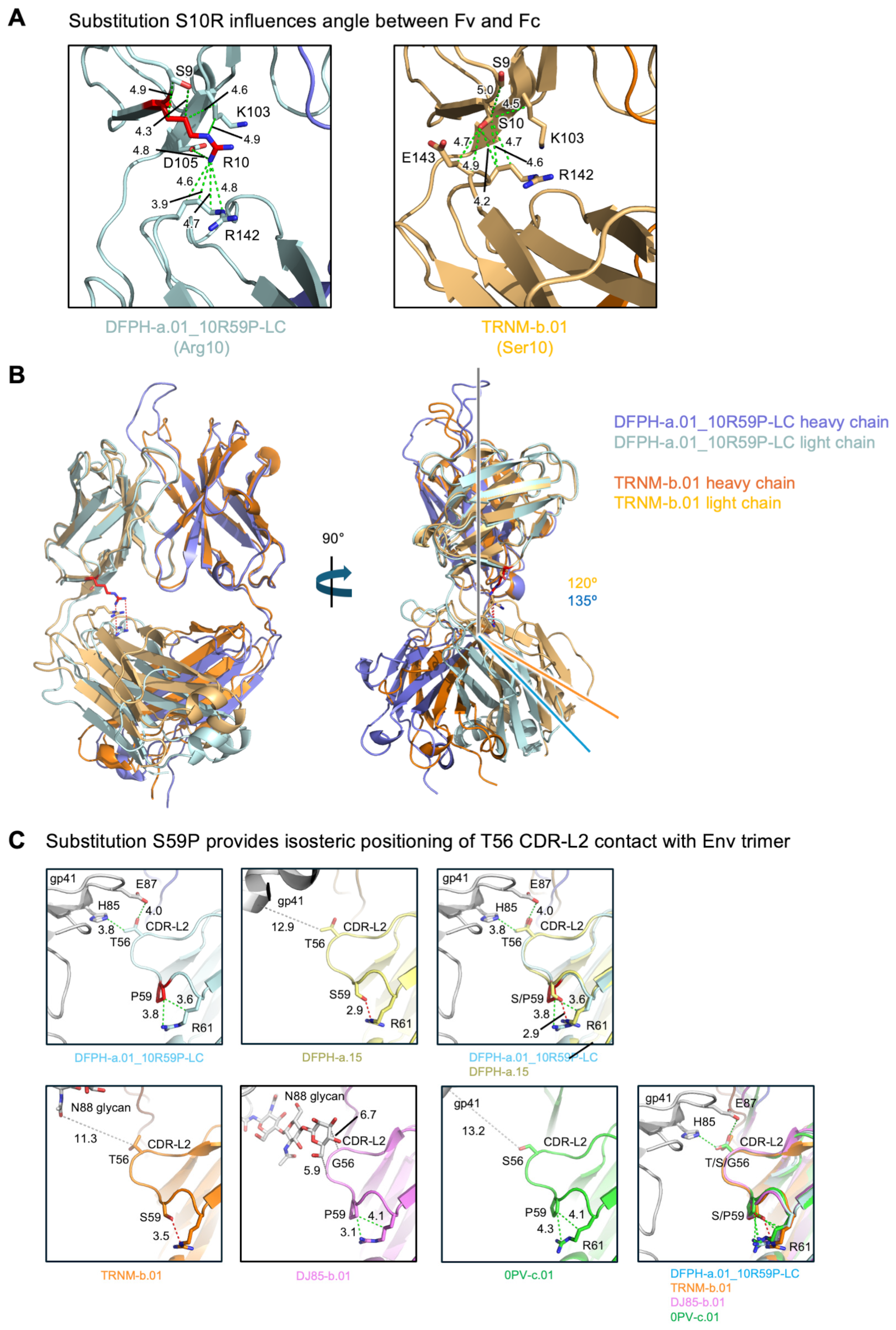
3.6. Cryo-EM Structure of Fab DFPH-a.01_10R59P-LC with BG505 DS-SOSIP Env Trimers
3.7. A Second Yeast Display-Identified Antibody, DFPH-a.01_1G10A56K-LC, with 64% Neutralization Breadth
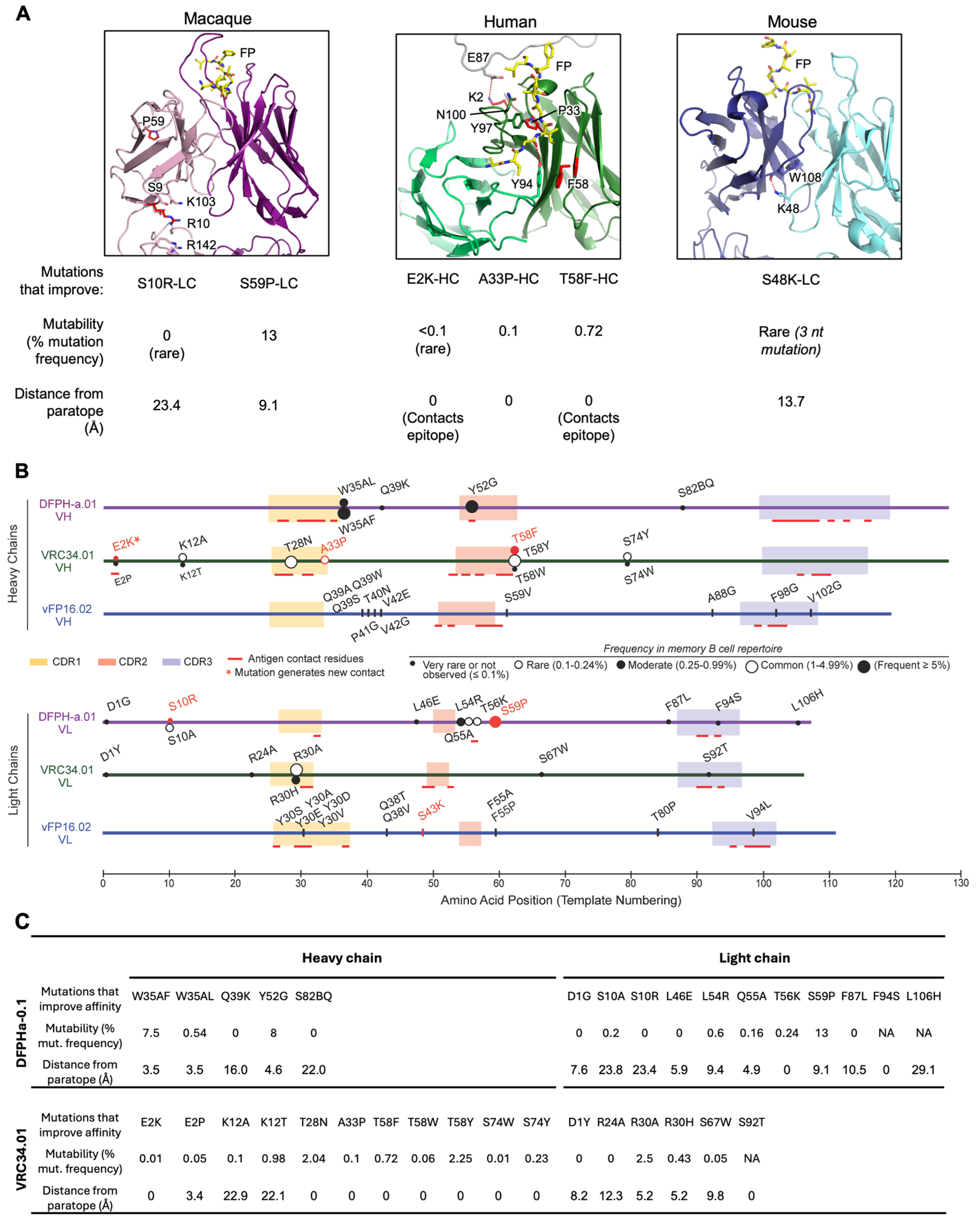
3.8. Comparative Analysis of Improving FP Broadly Neutralizing Antibody Mutations Across Macaque, Mouse, and Human Studies
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| Å | Ångström (10−10 m, used for structural resolution/length) |
| BSA | Buried Surface Area |
| °C | Degrees Celsius |
| CDR | Complementarity-Determining Region |
| Cryo-EM | Cryogenic Electron Microscopy |
| CTF | Contrast Transfer Function |
| DDM | n-Dodecyl β-D-maltoside |
| Env | Envelope Glycoprotein |
| Fab | Fragment Antigen-Binding |
| FACS | Fluorescence-Activated Cell Sorting |
| FP | Fusion Peptide |
| FR | Framework Region |
| HIV | Human Immunodeficiency Virus |
| IC50/ IC80 | Concentration of Antibody Required to Inhibit 50%/80% of Infection |
| ID50 | Inhibitory Dilution Required to Inhibit 50% of Infection |
| KD | Equilibrium Dissociation Constant |
| ka | Association Rate Constant |
| kd | Dissociation Rate Constant |
| LD | Linear Dichroism |
| mg/mL | Milligrams per Milliliter (Concentration Unit) |
| µg/mL | Micrograms per Milliliter (Concentration Unit) |
| µL | Microliter (10−6 L) |
| µM | Micromolar (10−6 Molar Concentration) |
| nM | Nanomolar (10−9 Molar Concentration) |
| NGS | Next-Generation Sequencing |
| PDB | Protein Data Bank |
| RU | Response Units (Surface Plasmon Resonance Readout) |
| SHIV | Simian–Human Immunodeficiency Virus |
| SHM | Somatic Hypermutation |
| SPR | Surface Plasmon Resonance |
| SSM | Site-Saturation Mutagenesis |
| VH | Variable Heavy Chain |
| VL | Variable Light Chain |
References
- Willis, J.R.; Berndsen, Z.T.; Ma, K.M.; Steichen, J.M.; Schiffner, T.; Landais, E.; Liguori, A.; Kalyuzhniy, O.; Allen, J.D.; Baboo, S.; et al. Human immunoglobulin repertoire analysis guides design of vaccine priming immunogens targeting HIV V2-apex broadly neutralizing antibody precursors. Immunity 2022, 55, 2149–2167.e9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haynes, B.F.; Wiehe, K.; Borrow, P.; Saunders, K.O.; Korber, B.; Wagh, K.; McMichael, A.J.; Kelsoe, G.; Hahn, B.H.; Alt, F.; et al. Strategies for HIV-1 vaccines that induce broadly neutralizing antibodies. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2023, 23, 142–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burton, D.R.; Hangartner, L. Broadly Neutralizing Antibodies to HIV and Their Role in Vaccine Design. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2016, 34, 635–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medina-Ramirez, M.; Garces, F.; Escolano, A.; Skog, P.; de Taeye, S.W.; Del Moral-Sanchez, I.; McGuire, A.T.; Yasmeen, A.; Behrens, A.J.; Ozorowski, G.; et al. Design and crystal structure of a native-like HIV-1 envelope trimer that engages multiple broadly neutralizing antibody precursors in vivo. J. Exp. Med. 2017, 214, 2573–2590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schleich, F.A.; Bale, S.; Guenaga, J.; Ozorowski, G.; Adori, M.; Lin, X.; Castro Dopico, X.; Wilson, R.; Chernyshev, M.; Cotgreave, A.T.; et al. Vaccination of nonhuman primates elicits a broadly neutralizing antibody lineage targeting a quaternary epitope on the HIV-1 Env trimer. Immunity 2025, 58, 1598–1613.e8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dubrovskaya, V.; Tran, K.; Ozorowski, G.; Guenaga, J.; Wilson, R.; Bale, S.; Cottrell, C.A.; Turner, H.L.; Seabright, G.; O’Dell, S.; et al. Vaccination with Glycan-Modified HIV NFL Envelope Trimer-Liposomes Elicits Broadly Neutralizing Antibodies to Multiple Sites of Vulnerability. Immunity 2019, 51, 915–929.e7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, K.; Acharya, P.; Kong, R.; Cheng, C.; Chuang, G.Y.; Liu, K.; Louder, M.K.; O’Dell, S.; Rawi, R.; Sastry, M.; et al. Epitope-based vaccine design yields fusion peptide-directed antibodies that neutralize diverse strains of HIV-1. Nat. Med. 2018, 24, 857–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kong, R.; Duan, H.; Sheng, Z.; Xu, K.; Acharya, P.; Chen, X.; Cheng, C.; Dingens, A.S.; Gorman, J.; Sastry, M.; et al. Antibody Lineages with Vaccine-Induced Antigen-Binding Hotspots Develop Broad HIV Neutralization. Cell 2019, 178, 567–584.e19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pegu, A.; Lovelace, S.E.; DeMouth, M.E.; Cully, M.D.; Morris, D.J.; Li, Y.; Wang, K.; Schmidt, S.D.; Choe, M.; Liu, C.; et al. Antibodies targeting the fusion peptide on the HIV envelope provide protection to rhesus macaques against mucosal SHIV challenge. Sci. Transl. Med. 2024, 16, eadh9039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, R.; Xu, K.; Zhou, T.; Acharya, P.; Lemmin, T.; Liu, K.; Ozorowski, G.; Soto, C.; Taft, J.D.; Bailer, R.T.; et al. Fusion peptide of HIV-1 as a site of vulnerability to neutralizing antibody. Science 2016, 352, 828–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banach, B.B.; Pletnev, S.; Olia, A.S.; Xu, K.; Zhang, B.; Rawi, R.; Bylund, T.; Doria-Rose, N.A.; Nguyen, T.D.; Fahad, A.S.; et al. Antibody-directed evolution reveals a mechanism for enhanced neutralization at the HIV-1 fusion peptide site. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 7593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banach, B.B.; Tripathi, P.; Da Silva Pereira, L.; Gorman, J.; Nguyen, T.D.; Dillon, M.; Fahad, A.S.; Kiyuka, P.K.; Madan, B.; Wolfe, J.R.; et al. Highly protective antimalarial antibodies via precision library generation and yeast display screening. J. Exp. Med. 2022, 219, e20220323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madan, B.; Zhang, B.; Xu, K.; Chao, C.W.; O’Dell, S.; Wolfe, J.R.; Chuang, G.Y.; Fahad, A.S.; Geng, H.; Kong, R.; et al. Mutational fitness landscapes reveal genetic and structural improvement pathways for a vaccine-elicited HIV-1 broadly neutralizing antibody. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2021, 118, e2011653118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, T.; Zhu, J.; Wu, X.; Moquin, S.; Zhang, B.; Acharya, P.; Georgiev, I.S.; Altae-Tran, H.R.; Chuang, G.Y.; Joyce, M.G.; et al. Multidonor analysis reveals structural elements, genetic determinants, and maturation pathway for HIV-1 neutralization by VRC01-class antibodies. Immunity 2013, 39, 245–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwong, P.D.; Mascola, J.R. Human antibodies that neutralize HIV-1: Identification, structures, and B cell ontogenies. Immunity 2012, 37, 412–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwong, P.D.; Mascola, J.R. HIV-1 Vaccines Based on Antibody Identification, B Cell Ontogeny, and Epitope Structure. Immunity 2018, 48, 855–871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Cheng, C.; Dal Santo, J.L.; Shen, C.H.; Bylund, T.; Henry, A.R.; Howe, C.A.; Hwang, J.; Morano, N.C.; Morris, D.J.; et al. Potent and broad HIV-1 neutralization in fusion peptide-primed SHIV-infected macaques. Cell 2024, 187, 7214–7231.e23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wrenbeck, E.E.; Klesmith, J.R.; Stapleton, J.A.; Adeniran, A.; Tyo, K.E.; Whitehead, T.A. Plasmid-based one-pot saturation mutagenesis. Nat. Method 2016, 13, 928–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyer, A.J.; Ellefson, J.W.; Ellington, A.D. Library generation by gene shuffling. Curr. Protoc. Mol. Biol. 2014, 105, 15.12.1–15.12.7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whitehead, T.A.; Chevalier, A.; Song, Y.; Dreyfus, C.; Fleishman, S.J.; De Mattos, C.; Myers, C.A.; Kamisetty, H.; Blair, P.; Wilson, I.A.; et al. Optimization of affinity, specificity and function of designed influenza inhibitors using deep sequencing. Nat. Biotechnol. 2012, 30, 543–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; DeKosky, B.J.; Timm, M.R.; Lee, J.; Normandin, E.; Misasi, J.; Kong, R.; McDaniel, J.R.; Delidakis, G.; Leigh, K.E.; et al. Functional interrogation and mining of natively paired human V(H):V(L) antibody repertoires. Nat. Biotechnol. 2018, 36, 152–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McDaniel, J.R.; DeKosky, B.J.; Tanno, H.; Ellington, A.D.; Georgiou, G. Ultra-high-throughput sequencing of the immune receptor repertoire from millions of lymphocytes. Nat. Protoc. 2016, 11, 429–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Edgar, R.C. Search and clustering orders of magnitude faster than BLAST. Bioinformatics 2010, 26, 2460–2461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fahad, A.S.; Gutierrez-Gonzalez, M.F.; Madan, B.; DeKosky, B.J. Clonal Variant Analysis of Antibody Engineering Libraries. Cold Spring Harb. Protoc. 2025, 2025, pdb prot108626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chuang, G.Y.; Zhou, J.; Acharya, P.; Rawi, R.; Shen, C.H.; Sheng, Z.; Zhang, B.; Zhou, T.; Bailer, R.T.; Dandey, V.P.; et al. Structural Survey of Broadly Neutralizing Antibodies Targeting the HIV-1 Env Trimer Delineates Epitope Categories and Characteristics of Recognition. Structure 2019, 27, 196–206.e6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mastronarde, D.N. Automated electron microscope tomography using robust prediction of specimen movements. J. Struct. Biol. 2005, 152, 36–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Punjani, A.; Rubinstein, J.L.; Fleet, D.J.; Brubaker, M.A. cryoSPARC: Algorithms for rapid unsupervised cryo-EM structure determination. Nat. Method 2017, 14, 290–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirdita, M.; Schutze, K.; Moriwaki, Y.; Heo, L.; Ovchinnikov, S.; Steinegger, M. ColabFold: Making protein folding accessible to all. Nat. Method 2022, 19, 679–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jumper, J.; Evans, R.; Pritzel, A.; Green, T.; Figurnov, M.; Ronneberger, O.; Tunyasuvunakool, K.; Bates, R.; Zidek, A.; Potapenko, A.; et al. Highly accurate protein structure prediction with AlphaFold. Nature 2021, 596, 583–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pettersen, E.F.; Goddard, T.D.; Huang, C.C.; Couch, G.S.; Greenblatt, D.M.; Meng, E.C.; Ferrin, T.E. UCSF Chimera--a visualization system for exploratory research and analysis. J. Comput. Chem. 2004, 25, 1605–1612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emsley, P.; Cowtan, K. Coot: Model-building tools for molecular graphics. Acta Crystallogr. D Biol. Crystallogr. 2004, 60, 2126–2132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emsley, P.; Lohkamp, B.; Scott, W.G.; Cowtan, K. Features and development of Coot. Acta Crystallogr. D Biol. Crystallogr. 2010, 66, 486–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liebschner, D.; Afonine, P.V.; Baker, M.L.; Bunkóczi, G.; Chen, V.B.; Croll, T.I.; Hintze, B.; Hung, L.W.; Jain, S.; McCoy, A.J.; et al. Macromolecular structure determination using X-rays, neutrons and electrons: Recent developments in Phenix. Acta Crystallogr. D Struct. Biol. 2019, 75, 861–877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, I.W.; Murray, L.W.; Richardson, J.S.; Richardson, D.C. MOLPROBITY: Structure validation and all-atom contact analysis for nucleic acids and their complexes. Nucleic Acids Res 2004, 32, W615–W619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, V.B.; Arendall, W.B., 3rd; Headd, J.J.; Keedy, D.A.; Immormino, R.M.; Kapral, G.J.; Murray, L.W.; Richardson, J.S.; Richardson, D.C. MolProbity: All-atom structure validation for macromolecular crystallography. Acta Crystallogr. D Biol. Crystallogr. 2010, 66, 12–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krissinel, E.; Henrick, K. Inference of macromolecular assemblies from crystalline state. J. Mol. Biol. 2007, 372, 774–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pettersen, E.F.; Goddard, T.D.; Huang, C.C.; Meng, E.C.; Couch, G.S.; Croll, T.I.; Morris, J.H.; Ferrin, T.E. UCSF ChimeraX: Structure visualization for researchers, educators, and developers. Protein Sci. 2021, 30, 70–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- FlowJo. FlowJo™ Software for Mac; Becton, Dickinson and Company: Ashland, OR, USA, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Falkowska, E.; Le, K.M.; Ramos, A.; Doores, K.J.; Lee, J.H.; Blattner, C.; Ramirez, A.; Derking, R.; van Gils, M.J.; Liang, C.H.; et al. Broadly neutralizing HIV antibodies define a glycan-dependent epitope on the prefusion conformation of gp41 on cleaved envelope trimers. Immunity 2014, 40, 657–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Gils, M.J.; van den Kerkhof, T.L.; Ozorowski, G.; Cottrell, C.A.; Sok, D.; Pauthner, M.; Pallesen, J.; de Val, N.; Yasmeen, A.; de Taeye, S.W.; et al. An HIV-1 antibody from an elite neutralizer implicates the fusion peptide as a site of vulnerability. Nat. Microbiol. 2016, 2, 16199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reveiz, M.; Xu, K.; Lee, M.; Wang, S.; Olia, A.S.; Harris, D.R.; Liu, K.; Liu, T.; Schaub, A.J.; Stephens, T.; et al. Vaccine-elicited and naturally elicited antibodies differ in their recognition of the HIV-1 fusion peptide. Front. Immunol. 2024, 15, 1484029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henderson, R.; Zhou, Y.; Stalls, V.; Wiehe, K.; Saunders, K.O.; Wagh, K.; Anasti, K.; Barr, M.; Parks, R.; Alam, S.M.; et al. Structural basis for breadth development in the HIV-1 V3-glycan targeting DH270 antibody clonal lineage. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 2782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steichen, J.M.; Kulp, D.W.; Tokatlian, T.; Escolano, A.; Dosenovic, P.; Stanfield, R.L.; McCoy, L.E.; Ozorowski, G.; Hu, X.; Kalyuzhniy, O.; et al. HIV Vaccine Design to Target Germline Precursors of Glycan-Dependent Broadly Neutralizing Antibodies. Immunity 2016, 45, 483–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Swanson, O.M.; Zhang, Q.E.; Van Itallie, E.; Tian, M.; Brown, A.R.; Harris, C.; Kapingidza, A.B.; Rhodes, B.; Smith, L.M.; Venkatayogi, S.; et al. An engineered immunogen activates diverse HIV broadly neutralizing antibody precursors and promotes acquisition of improbable mutations. Sci. Transl. Med. 2025, 17, eadr2218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gristick, H.B.; Hartweger, H.; Nishimura, Y.; Gavor, E.; Nagashima, K.; Koranda, N.S.; Gnanapragasam, P.N.P.; Kakutani, L.M.; Segovia, L.N.; Donau, O.K.; et al. Design and characterization of HIV-1 vaccine candidates to elicit antibodies targeting multiple epitopes. J. Exp. Med. 2025, 222, e20250693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
França, C.T.; Pletnev, S.; Madan, B.; Katsamba, P.S.; McKee, K.; Morano, N.C.; Zhang, B.; Bahna, F.; Bylund, T.; Lin, B.C.; et al. Yeast Display Reveals Plentiful Mutations That Improve Fusion Peptide Vaccine-Elicited Antibodies Beyond 59% HIV-1 Neutralization Breadth. Vaccines 2025, 13, 1098. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines13111098
França CT, Pletnev S, Madan B, Katsamba PS, McKee K, Morano NC, Zhang B, Bahna F, Bylund T, Lin BC, et al. Yeast Display Reveals Plentiful Mutations That Improve Fusion Peptide Vaccine-Elicited Antibodies Beyond 59% HIV-1 Neutralization Breadth. Vaccines. 2025; 13(11):1098. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines13111098
Chicago/Turabian StyleFrança, Camila T., Sergei Pletnev, Bharat Madan, Phinikoula S. Katsamba, Krisha McKee, Nicholas C. Morano, Baoshan Zhang, Fabiana Bahna, Tatsiana Bylund, Bob C. Lin, and et al. 2025. "Yeast Display Reveals Plentiful Mutations That Improve Fusion Peptide Vaccine-Elicited Antibodies Beyond 59% HIV-1 Neutralization Breadth" Vaccines 13, no. 11: 1098. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines13111098
APA StyleFrança, C. T., Pletnev, S., Madan, B., Katsamba, P. S., McKee, K., Morano, N. C., Zhang, B., Bahna, F., Bylund, T., Lin, B. C., Louder, M. K., Mannepalli, S., Nimrania, R., O’Dell, S., Doria-Rose, N. A., Kwong, P. D., Shapiro, L., Sheng, Z., Zhou, T., & DeKosky, B. J. (2025). Yeast Display Reveals Plentiful Mutations That Improve Fusion Peptide Vaccine-Elicited Antibodies Beyond 59% HIV-1 Neutralization Breadth. Vaccines, 13(11), 1098. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines13111098






