Safety and Immunogenicity of sIPV in Healthy Infants Aged 2 Months Following Sequential Immunization Program Combination with bOPV: A Phase 3, Randomized, Blinded, Parallel Positive-Controlled Clinical Trial
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design and Population
2.2. Randomization and Blinding
2.3. Vaccines and Vaccinations
2.4. Safety Assessments
2.5. Immunogenicity Assessments
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
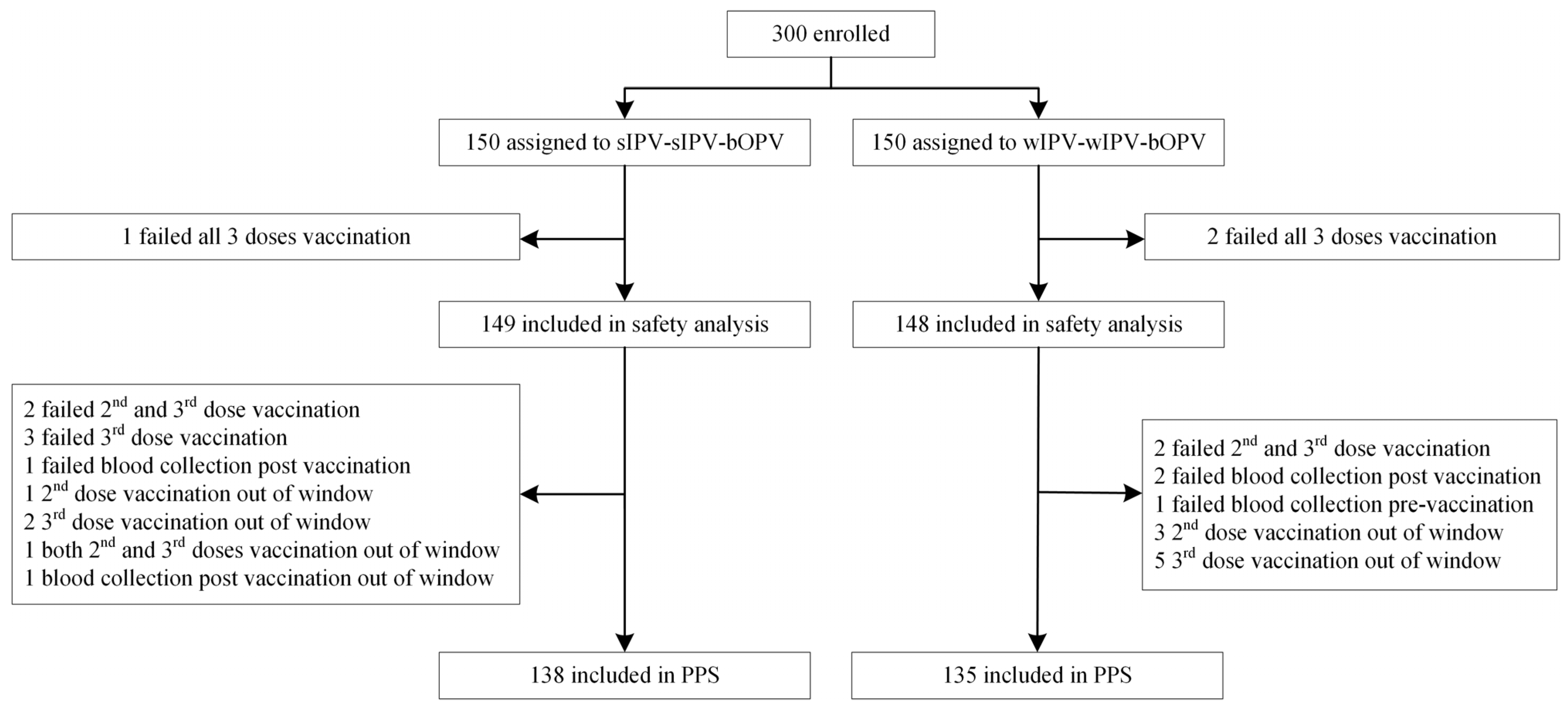
3.1. Study Population
3.2. Safety
3.3. Immunogenicity
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Concepcion, F.E.; Ruth, L.; Tom, S. Chapter 18: Poliomyelitis. In Epidemiology and Prevention of Vaccine-Preventable Diseases, A.K.A. “The Pink Book”; Centers for Disease Control and Prevention: Washington, DC, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- World Health Organization. Polio Vaccines: WHO Position Paper-June 2022; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2022.
- World Health Organization. Face Sheets. Poliomyelitis. Poliomyelitis; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2025.
- Rachlin, A.; Patel, J.C.; Burns, C.C.; Jorba, J.; Tallis, G.; O’lEary, A.; Wassilak, S.G.; Vertefeuille, J.F. Progress Toward Polio Eradication—Worldwide, January 2020–April 2022. Morb. Mortal. Wkly. Rep. 2022, 71, 650–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, P.; Bird, C.; Holland, D.; Joshi, S.B.; Volkin, D.B. Current and next-generation formulation strategies for inactivated polio vaccines to lower costs, increase coverage, and facilitate polio eradication. Hum. Vaccines Immunother. 2022, 18, 2154100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- China Medical Products Administration. Guidelines for Grading Standards of Adverse Events in Clinical Trials of Preventive Vaccines; China Medical Products Administration: Beijing, China, 2019. (In Chinese)
- Hu, Y.; Wang, J.; Zeng, G.; Chu, K.; Jiang, D.; Zhu, F.; Ying, Z.; Chen, L.; Li, C.; Zhu, F.; et al. Immunogenicity and Safety of a Sabin Strain-Based Inactivated Polio Vaccine: A Phase 3 Clinical Trial. J. Infect. Dis. 2019, 220, 1551–1557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- World Health Organization. WHO Expanded Program on Immunization, Manual for the Virologic Investigation of Poliomyelitis; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 1990.
- Plotkin, S.A.; Orenstein, W.A.; Offit, P.A. Poliovirus and Its Vaccines. In Vaccines, 6th ed.; Elsevier: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2018; Volume 3, pp. 687–721. [Google Scholar]
- Gamage, D.; Palihawadana, P.; Mach, O.; Weldon, W.C.; Oberste, S.M.; Sutter, R.W. Achieving high seroprevalence against polioviruses in Sri Lanka-results from a serological survey, 2014. J. Epidemiol. Glob. Health 2015, 5 (Suppl. 1), S67–S71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Böttiger, M. Polio immunity to killed vaccine: An 18-year follow-up. Vaccine 1990, 8, 443–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dowdle, W.R.; De Gourville, E.; Kew, O.M.; Pallansch, M.A.; Wood, D.J. Polio eradication: The OPV paradox. Rev. Med. Virol. 2003, 13, 277–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Platt, L.R.; Estívariz, C.F.; Sutter, R.W. Vaccine-associated paralytic poliomyelitis: A review of the epidemiology and estimation of the global burden. J. Infect. Dis. 2014, 210 (Suppl. 1), S380–S389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bakker, W.A.; Thomassen, Y.E.; Oever, A.G.V.; Westdijk, J.; van Oijen, M.G.; Sundermann, L.C.; Veld, P.V.; Sleeman, E.; van Nimwegen, F.W.; Hamidi, A.; et al. Inactivated polio vaccine development for technology transfer using attenuated Sabin poliovirus strains to shift from Salk-IPV to Sabin-IPV. Vaccine 2011, 29, 7188–7196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, S.; Ying, Z.; Liu, Y.; Li, Y.; Yu, Y.; Huang, M.; Huang, Z.; Ou, Z.; Liao, Y.; Zhang, Y.; et al. A phase 3 randomized, open-label study evaluating the immunogenicity and safety of concomitant and staggered administration of a live, pentavalent rotavirus vaccine and an inactivated poliomyelitis vaccine in healthy infants in China. Hum. Vaccines Immunother. 2024, 20, 2324538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, S.; Chen, H.; Zhang, Z.; Chang, S.; Xiao, Y.; Luo, L.; Zhang, Z.; Sun, L.; Chen, X.; Yang, Y.; et al. Immunogenicity and safety of different sequential schedules of Sabin strain-based inactivated poliovirus vaccination: A randomized, controlled, open-label, phase IV clinical trial in China. Vaccine 2020, 38, 6274–6279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| sIPV-sIPV-bOPV (n = 138) | wIPV-wIPV-bOPV (n = 135) | p Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age, mean ± SD (months) | 2.25 ± 0.23 | 2.30 ± 0.25 | 0.13 |
| sex, n (%) | |||
| Male: n (%) | 65 (47) | 66 (49) | 0.77 |
| Female: n (%) | 73 (53) | 69 (51) | |
| axillary temperature at enrolment, mean ± SD (°C) | 36.84 ± 0.16 | 36.83 ± 0.16 | 0.88 |
| BMI, mean ± SD (kg/m2) | 16.08 ± 1.52 | 15.88 ± 1.47 | 0.27 |
| Type 1 | |||
| Pre-immune GMT (95% CI) | 2.62 ± 1.87 (2.35~2.92) | 2.70 ± 1.94 (2.41~3.03) | 0.70 |
| Pre-immune susceptible subjects: n (%) | 131 (95) | 128 (95) | 0.97 |
| Type 2 | |||
| Pre-immune GMT (95% CI) | 2.59 ± 1.93 (2.31~2.89) | 2.44 ± 1.97 (2.17~2.74) | 0.48 |
| Pre-immune susceptible subjects: n (%) | 134 (97) | 133 (99) | 0.68 |
| Type 3 | |||
| Pre-immune GMT (95% CI) | 3.20 ± 1.73 (2.91~3.51) | 3.34 ± 1.65 (3.06~3.63) | 0.50 |
| Pre-immune susceptible subjects: n (%) | 138 (100) | 135 (100) | / |
| sIPV-sIPV-bOPV (n = 149) | wIPV-wIPV-bOPV (n = 148) | p Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Total AEs | 65 (44%) | 57 (39%) | 0.37 |
| Grade 1 | 48 (32%) | 44 (30%) | 0.64 |
| Grade 2 | 29 (19%) | 29 (20%) | 0.98 |
| Grade 3 | 7 (5%) | 3 (2%) | 0.34 |
| Solicited local AEs | 8 (5%) | 11 (7%) | 0.47 |
| Grade 1 | 5 (3%) | 9 (6%) | 0.27 |
| Grade 2 | 2 (1%) | 2 (1%) | 1.00 |
| Grade 3 | 1 (0.67%) | 0 (0.00%) | 1.00 |
| Solicited systemic AEs | 62 (42%) | 53 (36%) | 0.30 |
| Grade 1 | 32 (21%) | 24 (16%) | 0.25 |
| Grade 2 | 24 (16%) | 26 (18%) | 0.74 |
| Grade 3 | 6 (4%) | 3 (2%) | 0.50 |
| sIPV-sIPV-bOPV | wIPV-wIPV-bOPV | p Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| First injection, n/NSS1 | 35/149 (23%) | 33/148 (22%) | 0.81 |
| Second injection, n/NSS2 | 22/147 (15%) | 24/146 (16%) | 0.73 |
| Third injection, n/NSS3 | 19/144 (13%) | 24/146 (16%) | 0.44 |
| sIPV-sIPV-bOPV | wIPV-wIPV-bOPV | p Value | Difference% (95% CI) | Non-Inferiority * Yes/No | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Type 1 | |||||
| Seropositive (%) (95% CI) | 100 (97.22~100.00) | 100 (97.16~100.00) | / | ||
| Seroconversion (%) (95% CI) | 100 (97.22~100.00) | 100 (97.16~100.00) | / | 0.00 (−2.85~2.91) | Yes |
| GMT (95% CI) | 8622.64 ± 2.08 (7594.47~9790.01) | 2687.65 ± 1.97 (2386.47~3026.83) | <0.0001 | ||
| Type 2 | |||||
| Seropositive (%) (95% CI) | 99 (95.91~99.98) | 95 (90.44~98.33) | 0.07 | ||
| Seroconversion (%) (95% CI) | 99 (95.91~99.98) | 95 (90.44~98.33) | 0.07 | 3.77 (−0.05~7.58) | Yes |
| GMT (95% CI) | 207.73 ± 3.05 (171.67~251.37) | 54.06 ± 2.93 (44.96~65.00) | <0.0001 | ||
| Type 3 | |||||
| Seropositive (%) (95% CI) | 100 (97.36~100.00) | 100 (97.30~100.00) | / | ||
| Seroconversion (%) (95% CI) | 100 (97.36~100.00) | 100 (97.30~100.00) | / | 0.00 (−2.71~2.77) | Yes |
| GMT (95% CI) | 2121.74 ± 2.59 (1807.25~2490.95) | 1699.12 ± 2.26 (1479.26~1951.65) | 0.04 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, Y.; Liu, X.; Zhang, L.; Chang, X.; Xiong, P.; Guan, Y.; Li, Y.; Zhang, W.; Xuan, L.; Li, Y.; et al. Safety and Immunogenicity of sIPV in Healthy Infants Aged 2 Months Following Sequential Immunization Program Combination with bOPV: A Phase 3, Randomized, Blinded, Parallel Positive-Controlled Clinical Trial. Vaccines 2025, 13, 1094. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines13111094
Liu Y, Liu X, Zhang L, Chang X, Xiong P, Guan Y, Li Y, Zhang W, Xuan L, Li Y, et al. Safety and Immunogenicity of sIPV in Healthy Infants Aged 2 Months Following Sequential Immunization Program Combination with bOPV: A Phase 3, Randomized, Blinded, Parallel Positive-Controlled Clinical Trial. Vaccines. 2025; 13(11):1094. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines13111094
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Yafei, Xiaodong Liu, Li Zhang, Xianyun Chang, Ping Xiong, Yanxin Guan, Yixin Li, Weiling Zhang, Lili Xuan, Yan Li, and et al. 2025. "Safety and Immunogenicity of sIPV in Healthy Infants Aged 2 Months Following Sequential Immunization Program Combination with bOPV: A Phase 3, Randomized, Blinded, Parallel Positive-Controlled Clinical Trial" Vaccines 13, no. 11: 1094. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines13111094
APA StyleLiu, Y., Liu, X., Zhang, L., Chang, X., Xiong, P., Guan, Y., Li, Y., Zhang, W., Xuan, L., Li, Y., Ying, Z., & Xu, Q. (2025). Safety and Immunogenicity of sIPV in Healthy Infants Aged 2 Months Following Sequential Immunization Program Combination with bOPV: A Phase 3, Randomized, Blinded, Parallel Positive-Controlled Clinical Trial. Vaccines, 13(11), 1094. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines13111094







