Safety and Immunogenicity of the Tetravalent Recombinant COVID-19 Protein Vaccine SCTV01E in Children and Adolescents Aged 3 to 17 Years: A Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Phase 2 Clinical Trial
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Trial Design
2.2. Study Population
2.3. Randomization and Masking
2.4. Study Interventions
2.5. Study Procedures
2.6. Safety and Immunogenicity Assessments
2.7. Study Outcomes
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
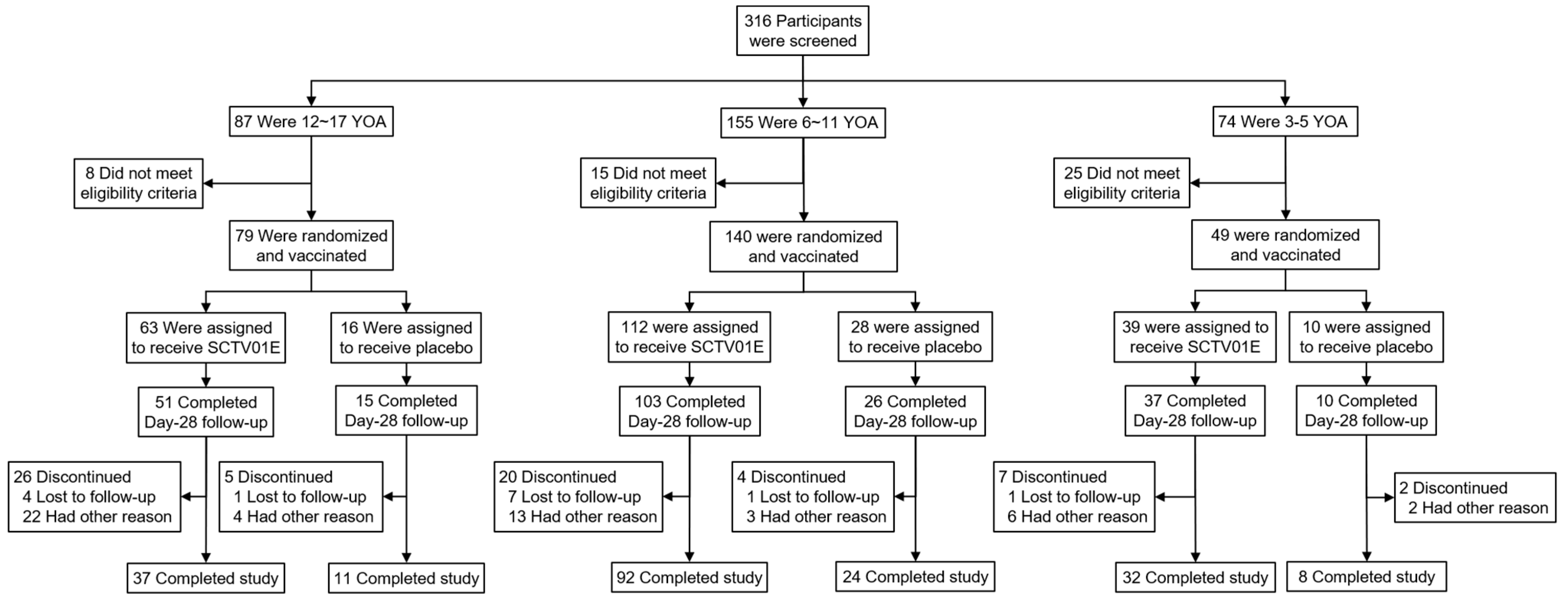
3.1. Participants, Demographics, and Baseline Characteristics
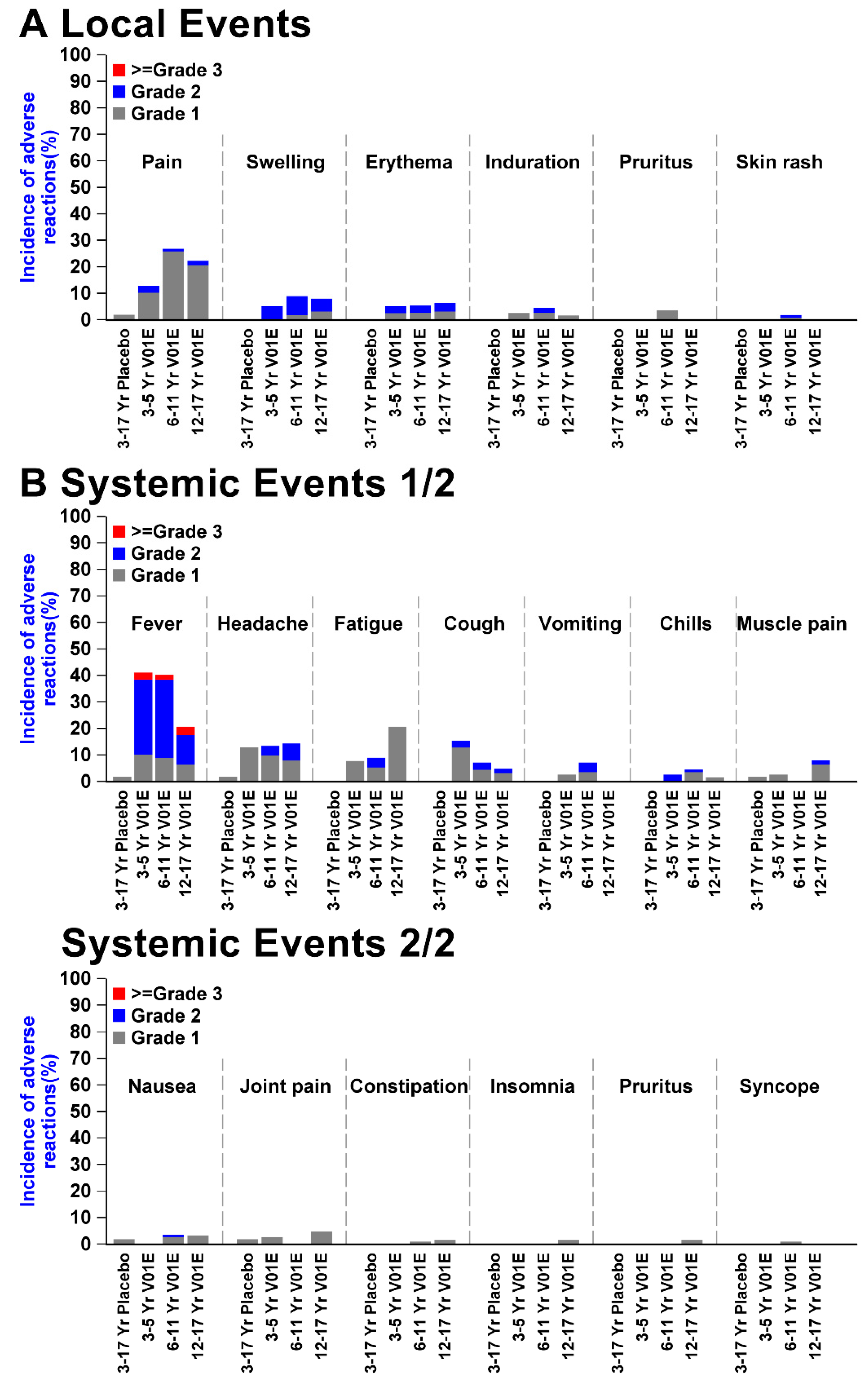
3.2. Safety Profiles
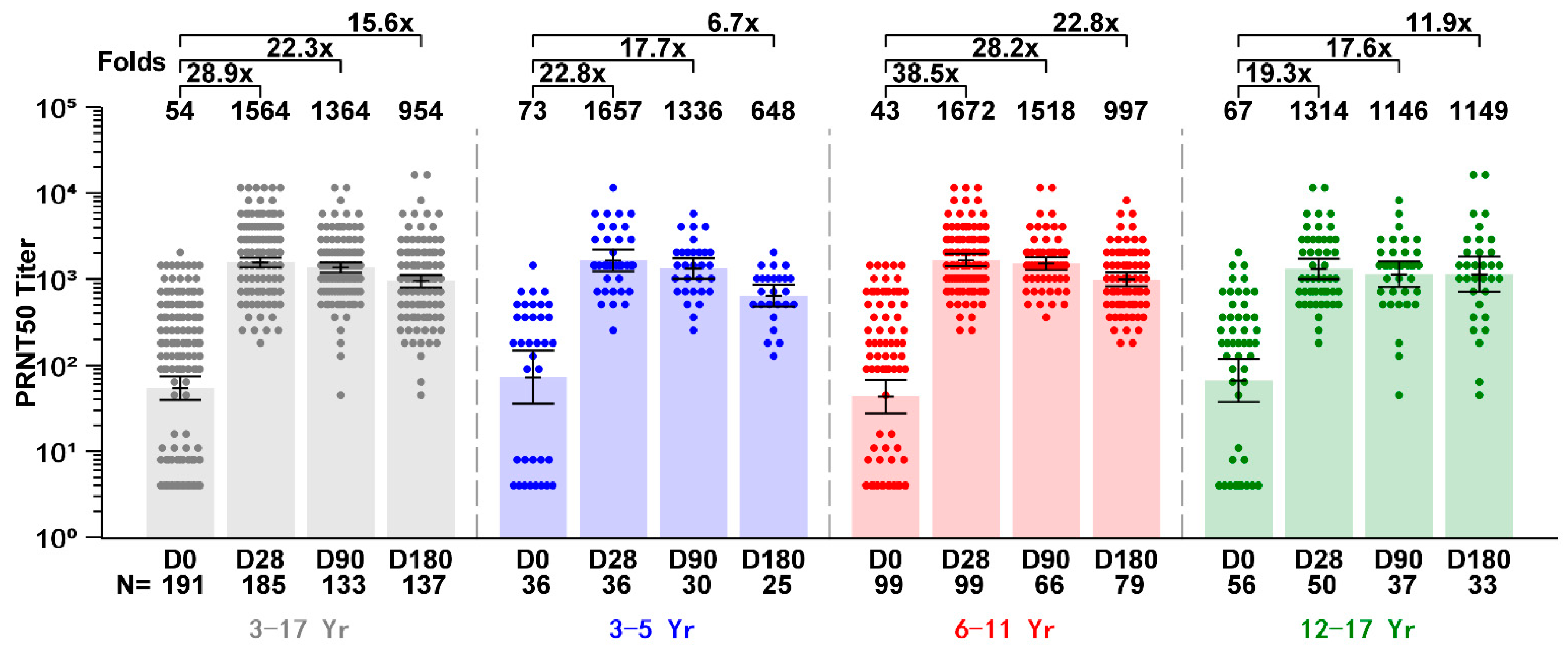
3.3. Immunogenicity Outcomes
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- WHO. Coronavirus Disease (COVID-19) Pandemic. Available online: https://www.who.int/europe/emergencies/situations/covid-19 (accessed on 3 September 2024).
- Worldometer. COVID—Coronavirus Statistics. Available online: https://www.worldometers.info/coronavirus/ (accessed on 3 September 2024).
- Sarker, R.; Roknuzzaman, A.S.M.; Nazmunnahar; Shahriar, M.; Hossain, J.; Islam, R. The WHO has declared the end of pandemic phase of COVID-19: Way to come back in the normal life. Health Sci. Rep. 2023, 6, e1544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- CDC. COVID-19 Variant Update. Available online: https://www.idsociety.org/covid-19-real-time-learning-network/diagnostics/covid-19-variant-update/ (accessed on 3 September 2024).
- Araf, Y.; Akter, F.; Tang, Y.D.; Fatemi, R.; Parvez, S.A.; Zheng, C.; Hossain, G. Omicron variant of SARS-CoV-2: Genomics, transmissibility, and responses to current COVID-19 vaccines. J. Med. Virol. 2022, 94, 1825–1832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, R.; Zhao, J.; Zhu, X.; Guan, Q.; Liu, S.; Li, M.; Gao, J.; Tan, J.; Cao, F.; Gan, B.; et al. Efficacy of the tetravalent protein COVID-19 vaccine, SCTV01E: A phase 3 double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled trial. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 6255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, G.; Zhao, K.; Han, J.; Hu, Z.; Zhang, T.; Wang, Y.; Shi, R.; Li, Y.; Song, Q.; Du, H.; et al. Safety and immunogenicity of a bivalent SARS-CoV-2 recombinant protein vaccine, SCTV01C in unvaccinated adults: A randomized, double-blinded, placebo-controlled, phase I clinical trial. J. Infect. 2023, 86, 154–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hannawi, S.; Eldin, L.S.; Abuquta, A.; Alamadi, A.; Mahmoud, S.A.; Hassan, A.; Liu, D.; Yan, L.; Xie, L. Safety and immunogenicity of a bivalent SARS-CoV-2 protein booster vaccine, SCTV01C, in adults previously vaccinated with mRNA vaccine: A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled phase 1/2 clinical trial. EBioMedicine 2023, 87, 104386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hannawi, S.; Eldin, L.S.; Abuquta, A.; Alamadi, A.; Mahmoud, S.A.; Li, J.; Chen, Y.; Xie, L. Safety and immunogenicity of a bivalent SARS-CoV-2 protein booster vaccine, SCTV01C in adults previously vaccinated with inactivated vaccine: A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled phase 1/2 clinical trial. J. Infect. 2023, 86, 154–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hannawi, S.; Eldin, L.S.; Abuquta, A.; Alamadi, A.; Mahmoud, S.A.; Hassan, A.; Xu, S.; Li, J.; Liu, D.; Baidoo, A.A.H.; et al. Safety and immunogenicity of a tetravalent and bivalent SARS-CoV-2 protein booster vaccine in men. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 4043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hannawi, S.; Yan, L.; Eldin, L.S.; Abuquta, A.; Alamadi, A.; Mahmoud, S.A.; Hassan, A.; Zhang, M.; Gao, C.; Chen, Y.; et al. Safety and immunogenicity of multivalent SARS-CoV-2 protein vaccines: A randomized phase 3 trial. EClinicalMedicine 2023, 64, 602195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, J.; Xu, Q.; Zhu, C.; Xuan, K.; Li, T.; Li, Q.; Pang, X.; Zha, Z.; Li, J.; Qiao, L.; et al. Immunogenicity of Tetravalent Protein Vaccine SCTV01E-2 against SARS-CoV-2 EG.5 Subvaraint: A Phase 2 Trial. Vaccines 2024, 12, 175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, L.; Li, Y.; He, P.; Chen, Z.; Yang, H.; Li, F.; Zhang, S.; Wang, D.; Wang, G.; Yang, S.; et al. Safety and immunogenicity of a protein subunit COVID-19 vaccine (ZF2001) in healthy children and adolescents aged 3–17 years in China: A randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase 1 trial and an open-label, non-randomised, non-inferiority, phase 2 trial. Lancet Child Adolesc. Health 2023, 7, 269–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frenck, R.W., Jr.; Klein, N.P.; Kitchin, N.; Gurtman, A.; Absalon, J.; Lockhart, S.; Perez, J.L.; Walter, E.B.; Senders, S.; Bailey, R.; et al. Safety, Immunogenicity, and Efficacy of the BNT162b2 Covid-19 Vaccine in Adolescents. N. Engl. J. Med. 2021, 385, 239–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walter, E.B.; Talaat, K.R.; Sabharwal, C.; Gurtman, A.; Lockhart, S.; Paulsen, G.C.; Barnett, E.D.; Muñoz, F.M.; Maldonado, Y.; Pahud, B.A.; et al. Evaluation of the BNT162b2 Covid-19 Vaccine in Children 5 to 11 Years of Age. N. Engl. J. Med. 2022, 386, 35–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muñoz, F.M.; Sher, L.D.; Sabharwal, C.; Gurtman, A.; Xu, X.; Kitchin, N.; Lockhart, S.; Riesenberg, R.; Sexter, J.M.; Czajka, H.; et al. Evaluation of BNT162b2 Covid-19 Vaccine in Children Younger than 5 Years of Age. N. Engl. J. Med. 2023, 388, 621–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Creech, C.B.; Anderson, E.; Berthaud, V.; Yildirim, I.; Atz, A.M.; Baez, I.M.; Finkelstein, D.; Pickrell, P.; Kirstein, J.; Yut, C.; et al. Evaluation of mRNA-1273 Covid-19 Vaccine in Children 6 to 11 Years of Age. N. Engl. J. Med. 2022, 386, 2011–2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ali, K.; Berman, G.; Zhou, H.; Deng, W.; Faughnan, V.; Coronado-Voges, M.; Ding, B.; Dooley, J.; Girard, B.; Hillebrand, W.; et al. Evaluation of mRNA-1273 SARS-CoV-2 Vaccine in Adolescents. N. Engl. J. Med. 2021, 385, 2241–2251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anderson, E.J.; Creech, C.B.; Berthaud, V.; Piramzadian, A.; Johnson, K.A.; Zervos, M.; Garner, F.; Griffin, C.; Palanpurwala, K.; Turner, M.; et al. Evaluation of mRNA-1273 Vaccine in Children 6 Months to 5 Years of Age. N. Engl. J. Med. 2022, 387, 1673–1687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anez, G.; Dunkle, L.M.; Gay, C.L.; Kotloff, K.L.; Adelglass, J.M.; Essink, B.; Campbell, J.D.; Cloney-Clark, S.; Zhu, M.; Plested, J.S.; et al. Safety, Immunogenicity and Efficacy of NVX-CoV2373 in Adolescents in PREVENT-19: A Randomized, Phase 3 Trial. medRxiv 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khoury, D.S.; Cromer, D.; Reynaldi, A.; Schlub, T.E.; Wheatley, A.K.; Juno, J.A.; Subbarao, K.; Kent, S.J.; Triccas, J.A.; Davenport, M.P. Neutralizing antibody levels are highly predictive of immune protection from symptomatic SARS-CoV-2 infection. Nat. Med. 2021, 27, 1205–1211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| 3–17 YOA, n (%) | ≥18 YOA (Phase 3 MRCT), n (%) | |
|---|---|---|
| Sample size | 214 (100) | 188 (100) |
| Age at vaccination (years) | ||
| Mean (SD) | 9.1 (3.50) | 52.4 (15.13) |
| Median (range) | 8.0 (3–17) | 53.5 (18–82) |
| Sex—n (%) | ||
| Male | 116 (54.2) | 127 (67.6) |
| Female | 98 (45.8) | 61 (32.4) |
| History of COVID-19 vaccination | ||
| Two-dose vaccination | 214 (100.0) | 10 (5.3) |
| Boosted vaccination | 0 | 178 (94.7) |
| Types of last received COVID-19 vaccine | ||
| Inactivated vaccine | 214 (100.0) | 121 (64.4) |
| Non-inactivated vaccine | 0 | 67 (35.6) |
| Vaccination intervals | ||
| 6–12 months | 6 (2.8) | 79 (42.0) |
| 12–24 months | 208 (97.2) | 109 (58.0) |
| BMI (kg/m2) | ||
| Mean (SD) | 17.1 (3.13) | 24.0 (3.24) |
| Median (range) | 16.2 (12.8–28.3) | 23.5 (18.3–37.2) |
| Age Group | No. of Participants | Geometric Mean 50% Neutralizing Titer (95% CI) | Geometric Mean Ratio (95% CI), 3–17 Years vs. ≥18 Years | Difference Between the Percentage Achieved Seroresponse (95% CI), 3–17 Years vs. ≥ 18 Years |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 3–17 years | 95 | 1290 (1077, 1545) | 8.78 (6.05, 12.74) | 6.34 (0.93, 11.22) |
| ≥18 years | 188 | 123 (98, 155) | — | — |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhu, F.; Huang, T.; Jin, P.; Zhang, L.; Jin, Z.; Zhang, W.; Yuan, D.; Wang, Z.; Deng, Y.; Li, J.; et al. Safety and Immunogenicity of the Tetravalent Recombinant COVID-19 Protein Vaccine SCTV01E in Children and Adolescents Aged 3 to 17 Years: A Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Phase 2 Clinical Trial. Vaccines 2025, 13, 43. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines13010043
Zhu F, Huang T, Jin P, Zhang L, Jin Z, Zhang W, Yuan D, Wang Z, Deng Y, Li J, et al. Safety and Immunogenicity of the Tetravalent Recombinant COVID-19 Protein Vaccine SCTV01E in Children and Adolescents Aged 3 to 17 Years: A Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Phase 2 Clinical Trial. Vaccines. 2025; 13(1):43. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines13010043
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhu, Fengcai, Ting Huang, Pengfei Jin, Linglin Zhang, Zhongqiang Jin, Wenli Zhang, Dongya Yuan, Zhong Wang, Yusong Deng, Jiaxin Li, and et al. 2025. "Safety and Immunogenicity of the Tetravalent Recombinant COVID-19 Protein Vaccine SCTV01E in Children and Adolescents Aged 3 to 17 Years: A Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Phase 2 Clinical Trial" Vaccines 13, no. 1: 43. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines13010043
APA StyleZhu, F., Huang, T., Jin, P., Zhang, L., Jin, Z., Zhang, W., Yuan, D., Wang, Z., Deng, Y., Li, J., Shen, X., Fu, Y., Li, J., Yang, X., Li, J., & Xie, L. (2025). Safety and Immunogenicity of the Tetravalent Recombinant COVID-19 Protein Vaccine SCTV01E in Children and Adolescents Aged 3 to 17 Years: A Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Phase 2 Clinical Trial. Vaccines, 13(1), 43. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines13010043






