Booster Vaccination with BNT162b2 Improves Cellular and Humoral Immune Response in the Pediatric Population Immunized with CoronaVac
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design and Population
2.2. Serum and PBMCs Preparation
2.3. Antibody Detection
2.4. Generation of rVSV-SARS2-S-BA.1
2.5. rVSV-SARS2-S Microneutralization Assays
2.6. Detection of T lymphocytes Activated against SARS-CoV-2 by Flow Cytometry
2.7. Statistical Analysis
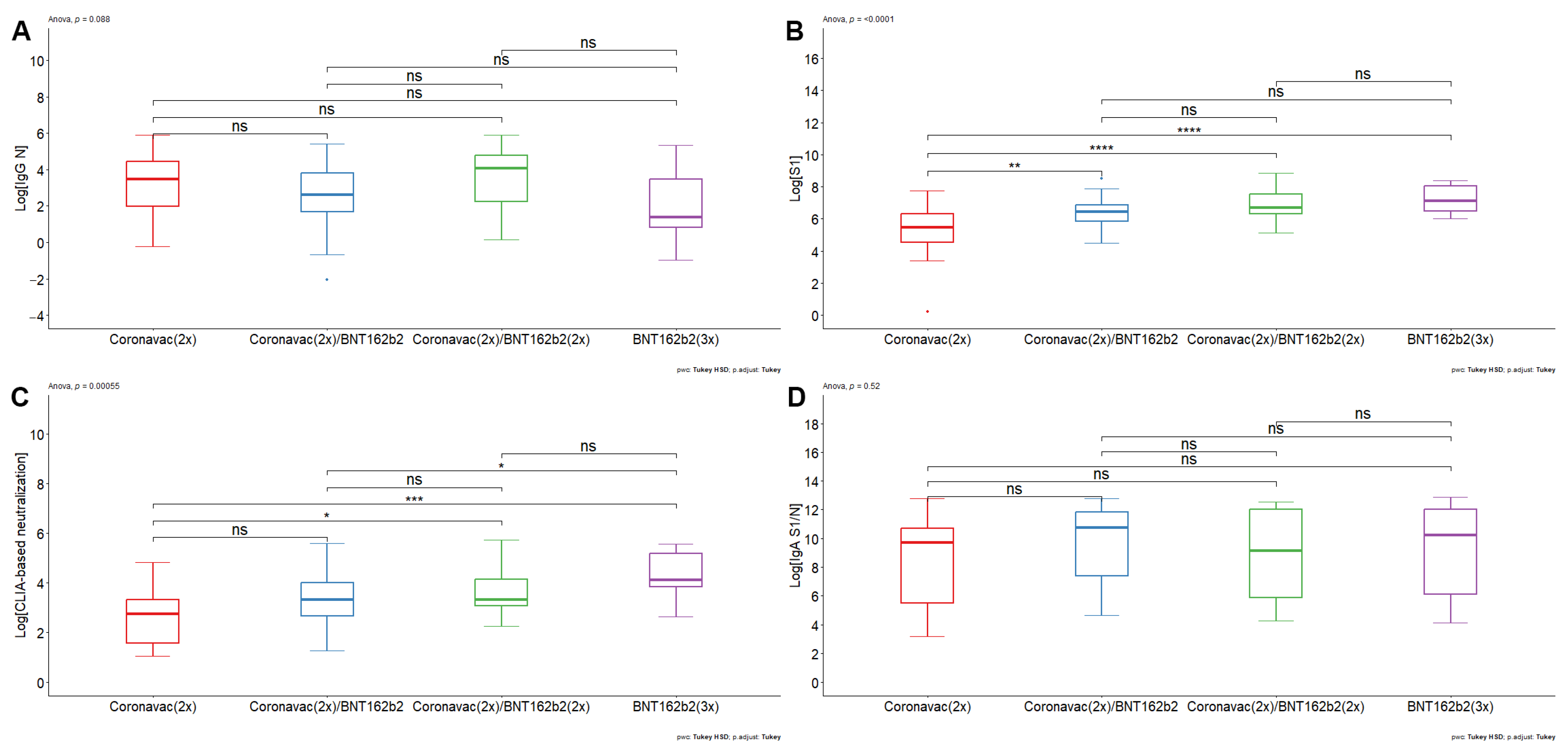
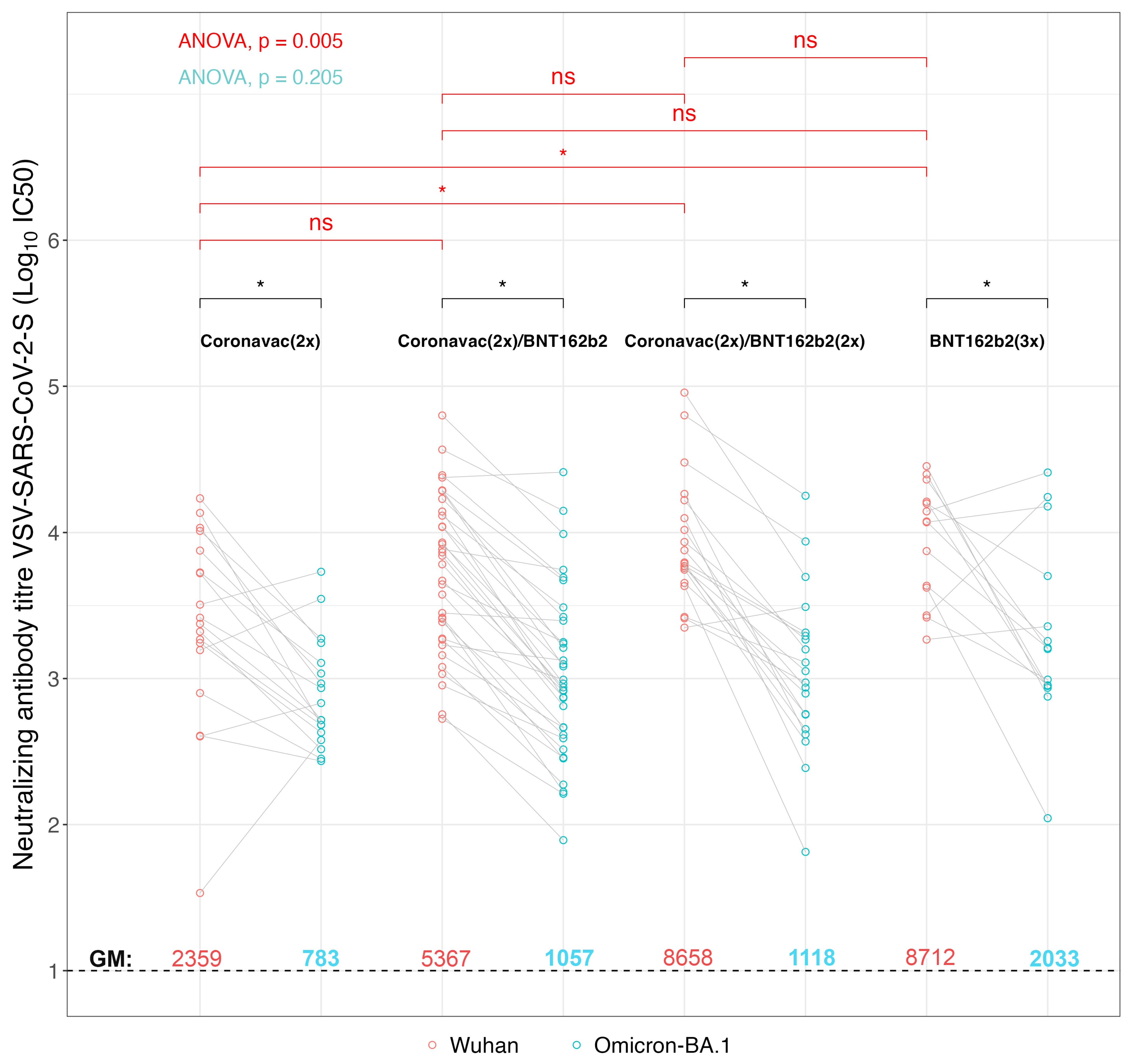
3. Results
- The double booster with BNT162b2 generated an increase in humoral immunity against SARS-CoV-2
- Antibodies induced by CoronaVac- and BNT162b2-based vaccine schemes decrease their neutralizing efficacy against Omicron BA.1.
- Vaccination schemes based on BNT162b2 improve cellular immune responses against Omicron BA.1. in pediatric population.
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- COVID-19 Epidemiological Update—22 December 2023. Available online: https://www.who.int/publications/m/item/covid-19-epidemiological-update---22-december-2023 (accessed on 1 February 2024).
- Cifras Oficiales-Gob.cl. Available online: https://www.gob.cl/pasoapaso/cifrasoficiales/ (accessed on 1 February 2024).
- Wu, Z.; McGoogan, J.M. Characteristics of and Important Lessons from the Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) Outbreak in China: Summary of a Report of 72,314 Cases from the Chinese Center for Disease Control and Prevention. JAMA 2020, 323, 1239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, A.K.; Gillies, C.L.; Singh, R.; Singh, A.; Chudasama, Y.; Coles, B.; Seidu, S.; Zaccardi, F.; Davies, M.J.; Khunti, K. Prevalence of co-morbidities and their association with mortality in patients with COVID-19: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2020, 22, 1915–1924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheung, E.W.; Zachariah, P.; Gorelik, M.; Boneparth, A.; Kernie, S.G.; Orange, J.S.; Milner, J.D. Multisystem Inflammatory Syndrome Related to COVID-19 in Previously Healthy Children and Adolescents in New York City. JAMA 2020, 324, 294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feldstein, L.R.; Rose, E.B.; Horwitz, S.M.; Collins, J.P.; Newhams, M.M.; Son, M.B.F.; Newburger, J.W.; Kleinman, L.C.; Heidemann, S.M.; Martin, A.A.; et al. Multisystem Inflammatory Syndrome in U.S. Children and Adolescents. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 383, 334–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Whittaker, E.; Bamford, A.; Kenny, J.; Kaforou, M.; Jones, C.E.; Shah, P.; Ramnarayan, P.; Fraisse, A.; Miller, O.; Davies, P.; et al. Clinical Characteristics of 58 Children with a Pediatric Inflammatory Multisystem Syndrome Temporally Associated with SARS-CoV-2. JAMA 2020, 324, 259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mannar, D.; Saville, J.W.; Sun, Z.; Zhu, X.; Marti, M.M.; Srivastava, S.S.; Berezuk, A.M.; Zhou, S.; Tuttle, K.S.; Sobolewski, M.D.; et al. SARS-CoV-2 variants of concern: Spike protein mutational analysis and epitope for broad neutralization. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 4696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, F. Structure, Function, and Evolution of Coronavirus Spike Proteins. Annu. Rev. Virol. 2016, 3, 237–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wrapp, D.; Wang, N.; Corbett, K.S.; Goldsmith, J.A.; Hsieh, C.-L.; Abiona, O.; Graham, B.S.; McLellan, J.S. Cryo-EM structure of the 2019-nCoV spike in the prefusion conformation. Science 2020, 367, 1260–1263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soh, W.T. The N-terminal domain of spike glycoprotein mediates SARS-CoV-2 infection by associating with L-SIGN and DC-SIGN. BioRxiv 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, M.; Song, L. Novel antibody epitopes dominate the antigenicity of spike glycoprotein in SARS-CoV-2 compared to SARS-CoV. Cell. Mol. Immunol. 2020, 17, 536–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polack, F.P.; Thomas, S.J.; Kitchin, N.; Absalon, J.; Gurtman, A.; Lockhart, S.; Perez, J.L.; Pérez Marc, G.; Moreira, E.D.; Zerbini, C.; et al. Safety and Efficacy of the BNT162b2 mRNA COVID-19 Vaccine. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 383, 2603–2615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Montgomerie, I.; Bird, T.W.; Palmer, O.R.; Mason, N.C.; Pankhurst, T.E.; Lawley, B.; Hernández, L.C.; Harfoot, R.; Authier-Hall, A.; Anderson, D.E.; et al. Incorporation of SARS-CoV-2 spike NTD to RBD protein vaccine improves immunity against viral variants. iScience 2023, 26, 106256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dowell, A.C.; Butler, M.S.; Jinks, E.; Tut, G.; Lancaster, T.; Sylla, P.; Begum, J.; Bruton, R.; Pearce, H.; Verma, K.; et al. Children develop robust and sustained cross-reactive spike-specific immune responses to SARS-CoV-2 infection. Nat. Immunol. 2022, 23, 40–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karron, R.A.; Garcia Quesada, M.; Schappell, E.A.; Schmidt, S.D.; Deloria Knoll, M.; Hetrich, M.K.; Veguilla, V.; Doria-Rose, N.; Dawood, F.S. Binding and neutralizing antibody responses to SARS-CoV-2 in very young children exceed those in adults. JCI Insight 2022, 7, e157963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Renk, H.; Dulovic, A.; Seidel, A.; Becker, M.; Fabricius, D.; Zernickel, M.; Junker, D.; Groß, R.; Müller, J.; Hilger, A.; et al. Robust and durable serological response following pediatric SARS-CoV-2 infection. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nickbakhsh, S.; Ho, A.; Marques, D.F.P.; McMenamin, J.; Gunson, R.N.; Murcia, P.R. Epidemiology of Seasonal Coronaviruses: Establishing the Context for the Emergence of Coronavirus Disease 2019. J. Infect. Dis. 2020, 222, 17–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gaunt, E.R.; Hardie, A.; Claas, E.C.J.; Simmonds, P.; Templeton, K.E. Epidemiology and Clinical Presentations of the Four Human Coronaviruses 229E, HKU1, NL63, and OC43 Detected over 3 Years Using a Novel Multiplex Real-Time PCR Method. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2010, 48, 2940–2947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, E.; Du, H.; Gardner, L. An interactive web-based dashboard to track COVID-19 in real time. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2020, 20, 533–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bates, T.A.; McBride, S.K.; Leier, H.C.; Guzman, G.; Lyski, Z.L.; Schoen, D.; Winders, B.; Lee, J.-Y.; Lee, D.X.; Messer, W.B.; et al. Vaccination before or after SARS-CoV-2 infection leads to robust humoral response and antibodies that effectively neutralize variants. Sci. Immunol. 2022, 7, eabn8014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cerqueira-Silva, T.; Andrews, J.R.; Boaventura, V.S.; Ranzani, O.T.; De Araújo Oliveira, V.; Paixão, E.S.; Júnior, J.B.; Machado, T.M.; Hitchings, M.D.T.; Dorion, M.; et al. Effectiveness of CoronaVac, ChAdOx1 nCoV-19, BNT162b2, and Ad26.COV2.S among individuals with previous SARS-CoV-2 infection in Brazil: A test-negative, case-control study. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2022, 22, 791–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiolet, T.; Kherabi, Y.; MacDonald, C.-J.; Ghosn, J.; Peiffer-Smadja, N. Comparing COVID-19 vaccines for their characteristics, efficacy and effectiveness against SARS-CoV-2 and variants of concern: A narrative review. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2022, 28, 202–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, Q.; Bao, L.; Mao, H.; Wang, L.; Xu, K.; Yang, M.; Li, Y.; Zhu, L.; Wang, N.; Lv, Z.; et al. Development of an inactivated vaccine candidate for SARS-CoV-2. Science 2020, 369, 77–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levin, E.G.; Lustig, Y.; Cohen, C.; Fluss, R.; Indenbaum, V.; Amit, S.; Doolman, R.; Asraf, K.; Mendelson, E.; Ziv, A.; et al. Waning Immune Humoral Response to BNT162b2 COVID-19 Vaccine over 6 Months. N. Engl. J. Med. 2021, 385, e84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goldberg, Y.; Mandel, M.; Bar-On, Y.M.; Bodenheimer, O.; Freedman, L.; Ash, N.; Alroy-Preis, S.; Huppert, A.; Milo, R. Protection and waning of natural and hybrid COVID-19 immunity. medRxiv 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nanduri, S.; Pilishvili, T.; Derado, G.; Soe, M.M.; Dollard, P.; Wu, H.; Li, Q.; Bagchi, S.; Dubendris, H.; Link-Gelles, R.; et al. Effectiveness of Pfizer-BioNTech and Moderna Vaccines in Preventing SARS-CoV-2 Infection among Nursing Home Residents Before and during Widespread Circulation of the SARS-CoV-2 B.1.617.2 (Delta) Variant—National Healthcare Safety Network, March 1–August 1, 2021. MMWR Morb. Mortal. Wkly. Rep. 2021, 70, 1163–1166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gruell, H.; Vanshylla, K.; Tober-Lau, P.; Hillus, D.; Schommers, P.; Lehmann, C.; Kurth, F.; Sander, L.E.; Klein, F. mRNA booster immunization elicits potent neutralizing serum activity against the SARS-CoV-2 Omicron variant. Nat. Med. 2022, 28, 477–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control (An Agency of the European Union). SARS-CoV-2 Variants of Concern as of 2 February 2024; European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control: Solna, Sweden, 2024.
- Bates, T.A.; Leier, H.C.; Lyski, Z.L.; McBride, S.K.; Coulter, F.J.; Weinstein, J.B.; Goodman, J.R.; Lu, Z.; Siegel, S.A.R.; Sullivan, P.; et al. Neutralization of SARS-CoV-2 variants by convalescent and BNT162b2 vaccinated serum. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 5135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, R.E.; Zhang, X.; Case, J.B.; Winkler, E.S.; Liu, Y.; VanBlargan, L.A.; Liu, J.; Errico, J.M.; Xie, X.; Suryadevara, N.; et al. Resistance of SARS-CoV-2 variants to neutralization by monoclonal and serum-derived polyclonal antibodies. Nat. Med. 2021, 27, 717–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopez Bernal, J.; Andrews, N.; Gower, C.; Gallagher, E.; Simmons, R.; Thelwall, S.; Stowe, J.; Tessier, E.; Groves, N.; Dabrera, G.; et al. Effectiveness of Covid-19 Vaccines against the B.1.617.2 (Delta) Variant. N. Engl. J. Med. 2021, 385, 585–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarke, A.; Coelho, C.H.; Zhang, Z.; Dan, J.M.; Yu, E.D.; Methot, N.; Bloom, N.I.; Goodwin, B.; Phillips, E.; Mallal, S.; et al. SARS-CoV-2 vaccination induces immunological T cell memory able to cross-recognize variants from Alpha to Omicron. Cell 2022, 185, S0092867422000733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Beltran, W.F.; St. Denis, K.J.; Hoelzemer, A.; Lam, E.C.; Nitido, A.D.; Sheehan, M.L.; Berrios, C.; Ofoman, O.; Chang, C.C.; Hauser, B.M.; et al. mRNA-based COVID-19 vaccine boosters induce neutralizing immunity against SARS-CoV-2 Omicron variant. Cell 2022, 185, 457–466.e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, L.; Mok, B.W.Y.; Chen, L.L.; Chan, J.M.C.; Tsang, O.T.Y.; Lam, B.H.S.; Chuang, V.W.M.; Chu, A.W.H.; Chan, W.M.; Ip, J.D.; et al. Neutralization of Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2 Omicron Variant by Sera from BNT162b2 or CoronaVac Vaccine Recipients. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2022, 75, e822–e826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Liang, H.; Ding, X.; Cao, Y.; Yang, D.; Duan, Y. Effectiveness of COVID-19 vaccine in children and adolescents with the Omicron variant: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Infect. 2023, 86, e64–e66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leung, D.; Rosa Duque, J.S.; Yip, K.M.; So, H.K.; Wong, W.H.S.; Lau, Y.L. Effectiveness of BNT162b2 and CoronaVac in children and adolescents against SARS-CoV-2 infection during Omicron BA.2 wave in Hong Kong. Commun. Med. 2023, 3, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soto, J.A.; Melo-González, F.; Gutierrez-Vera, C.; Schultz, B.M.; Berríos-Rojas, R.V.; Rivera-Pérez, D.; Piña-Iturbe, A.; Hoppe-Elsholz, G.; Duarte, L.F.; Vázquez, Y.; et al. Inactivated Vaccine-Induced SARS-CoV-2 Variant-Specific Immunity in Children. mBio 2022, 13, e0131122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sacco, C.; Del Manso, M.; Mateo-Urdiales, A.; Rota, M.C.; Petrone, D.; Riccardo, F.; Bella, A.; Siddu, A.; Battilomo, S.; Proietti, V.; et al. Effectiveness of BNT162b2 vaccine against SARS-CoV-2 infection and severe COVID-19 in children aged 5–11 years in Italy: A retrospective analysis of January–April, 2022. Lancet 2022, 400, 97–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosa Duque, J.S.; Wang, X.; Leung, D.; Cheng, S.M.S.; Cohen, C.A.; Mu, X.; Hachim, A.; Zhang, Y.; Chan, S.M.; Chaothai, S.; et al. Immunogenicity and reactogenicity of SARS-CoV-2 vaccines BNT162b2 and CoronaVac in healthy adolescents. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 3700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, B.; Song, Y.; Li, C.; Yang, W.; Ma, Q.; Jiang, Z.; Li, M.; Lian, X.; Jiao, W.; Wang, L.; et al. Safety, tolerability, and immunogenicity of an inactivated SARS-CoV-2 vaccine (CoronaVac) in healthy children and adolescents: A double-blind, randomised, controlled, phase 1/2 clinical trial. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2021, 21, 1645–1653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosa Duque, J.S.; Leung, D.; Yip, K.M.; Lee, D.H.L.; So, H.; Wong, W.H.S.; Lau, Y.L. COVID-19 vaccines versus pediatric hospitalization. Cell Rep. Med. 2023, 4, 100936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.-L.; Chua, G.T.; Lu, L.; Chan, B.P.-C.; Wong, J.S.-C.; Chow, C.C.-K.; Yu, T.-C.; Leung, A.S.-Y.; Lam, S.-Y.; Wong, T.-W.; et al. Omicron variant susceptibility to neutralizing antibodies induced in children by natural SARS-CoV-2 infection or COVID-19 vaccine. Emerg. Microbes Infect. 2022, 11, 543–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, V.K.C.; Cheng, F.W.T.; Chui, C.S.L.; Lai, F.T.T.; Wong, C.K.H.; Li, X.; Wan, E.Y.F.; Wong, J.S.C.; Chan, E.W.Y.; Wong, I.C.K.; et al. Effectiveness of BNT162b2 and CoronaVac vaccines in preventing SARS-CoV-2 Omicron infections, hospitalizations, and severe complications in the pediatric population in Hong Kong: A case-control study. Emerg. Microbes Infect. 2023, 12, 2185455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wan, E.Y.F.; Mok, A.H.Y.; Yan, V.K.C.; Ying Chan, C.I.; Wang, B.; Lai, F.T.T.; Chui, C.S.L.; Li, X.; Wong, C.K.H.; Lau, C.S.; et al. Effectiveness of BNT162b2 and CoronaVac vaccinations against SARS-CoV-2 omicron infection in people aged 60 years or above: A case-control study. J. Travel Med. 2022, 29, taac119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- División de Prevención y Control de Enfermedades Departamento de Inmunizaciones Subsecretaría de Salud Pública. Dosis de Refuerzo en la Campaña de Vacunación Contra SARS-CoV-2 en Chile en Fase 3: Niños, Niñas y Adolescentes (NNA) [Internet]. 2022. Available online: https://www.minsal.cl/wp-content/uploads/2022/01/Dosis-de-Refuerzo-en-la-Campan%CC%83a-de-Vacunacio%CC%81n-contra-SARS-CoV-2-Fase-3-Nin%CC%83os-Nin%CC%83as-y-Adolescentes-NNA-2.pdf (accessed on 1 February 2024).
- Informe Epidemiológico N°46 Vigilancia Genómica de SARS-CoV-2 (COVID-19) [Internet]. MINSAL: Santiago, Chile. 2022. Available online: https://www.minsal.cl/wp-content/uploads/2023/01/Informe_Epidemiologico_-N%C2%B0-46_Vigilancia-Geno%CC%81mica_de-SARS-CoV-2.pdf (accessed on 1 February 2024).
- Diaz-Dinamarca, D.; Diaz, P.; Barra, G.; Puentes, R.; Arata, L.; Grossolli, J.; Rivero, B.; Ardiles, L.; Santelices, J.; Vasquez-Saes, V.; et al. Humoral immunity against SARS-CoV-2 evoked by heterologous vaccination groups using the CoronaVac (Sinovac) and BNT162b2 (Pfizer/BioNTech) vaccines in Chile. Front. Public Health 2023, 11, 1229045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dieterle, M.E.; Haslwanter, D.; Bortz, R.H.; Wirchnianski, A.S.; Lasso, G.; Vergnolle, O.; Abbasi, S.A.; Fels, J.M.; Laudermilch, E.; Florez, C.; et al. A Replication-Competent Vesicular Stomatitis Virus for Studies of SARS-CoV-2 Spike-Mediated Cell Entry and Its Inhibition. Cell Host Microbe 2020, 28, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muena, N.A.; García-Salum, T.; Pardo-Roa, C.; Avendaño, M.J.; Serrano, E.F.; Levican, J.; Almonacid, L.I.; Valenzuela, G.; Poblete, E.; Strohmeier, S.; et al. Induction of SARS-CoV-2 neutralizing antibodies by CoronaVac and BNT162b2 vaccines in naïve and previously infected individuals. eBioMedicine 2022, 78, 103972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aguilera, X.; Hormazábal, J.; Vial, C.; Cortes, L.J.; González, C.; Rubilar, P.; Apablaza, M.; Ramírez-Santana, M.; Icaza, G.; Nuñez-Franz, L.; et al. SARS-CoV-2 Neutralizing Antibodies in Chile after a Vaccination Campaign with Five Different Schemes. Vaccines 2022, 10, 1051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rice, P.; Longden, I.; Bleasby, A. EMBOSS: The European Molecular Biology Open Software Suite. Trends Genet. TIG 2000, 16, 276–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hertanto, D.M.; Sutanto, H.; Lusida, M.I.; Kuntaman, K.; Santoso, D. The genomic and clinical features of the COVID-19 Omicron variant: A narrative review. F1000Research 2022, 11, 353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grifoni, A.; Weiskopf, D.; Ramirez, S.I.; Mateus, J.; Dan, J.M.; Moderbacher, C.R.; Rawlings, S.A.; Sutherland, A.; Premkumar, L.; Jadi, R.S.; et al. Targets of T Cell Responses to SARS-CoV-2 Coronavirus in Humans with COVID-19 Disease and Unexposed Individuals. Cell 2020, 181, 1489–1501.e15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez-Then, E.; Lucas, C.; Monteiro, V.S.; Miric, M.; Brache, V.; Cochon, L.; Vogels, C.B.F.; Malik, A.A.; De la Cruz, E.; Jorge, A.; et al. Neutralizing antibodies against the SARS-CoV-2 Delta and Omicron variants following heterologous CoronaVac plus BNT162b2 booster vaccination. Nat. Med. 2022, 28, 481–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zeng, G.; Pan, H.; Li, C.; Hu, Y.; Chu, K.; Han, W.; Chen, Z.; Tang, R.; Yin, W.; et al. Safety, tolerability, and immunogenicity of an inactivated SARS-CoV-2 vaccine in healthy adults aged 18–59 years: A randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase 1/2 clinical trial. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2021, 21, 181–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Z.; Hu, Y.; Xu, M.; Chen, Z.; Yang, W.; Jiang, Z.; Li, M.; Jin, H.; Cui, G.; Chen, P.; et al. Safety, tolerability, and immunogenicity of an inactivated SARS-CoV-2 vaccine (CoronaVac) in healthy adults aged 60 years and older: A randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase 1/2 clinical trial. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2021, 21, 803–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weiskopf, D.; Schmitz, K.S.; Raadsen, M.P.; Grifoni, A.; Okba, N.M.A.; Endeman, H.; van den Akker, J.P.C.; Molenkamp, R.; Koopmans, M.P.G.; van Gorp, E.C.M.; et al. Phenotype and kinetics of SARS-CoV-2–specific T cells in COVID-19 patients with acute respiratory distress syndrome. Sci. Immunol. 2020, 5, eabd2071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grifoni, A.; Sidney, J.; Zhang, Y.; Scheuermann, R.H.; Peters, B.; Sette, A. A Sequence Homology and Bioinformatic Approach Can Predict Candidate Targets for Immune Responses to SARS-CoV-2. Cell Host Microbe 2020, 27, 671–680.e2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, B.; Su, X.; Yu, G.; Yang, S.; Wang, F.; Huang, T.; Zhou, L.; Hui, Z.; Liao, Y.; Qiu, Y.; et al. An automated chemiluminescent immunoassay (CLIA) detects SARS-CoV-2 neutralizing antibody levels in COVID-19 patients and vaccinees. Int. J. Infect. Dis. 2022, 115, 116–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moga, E.; Lynton-Pons, E.; Domingo, P. The Robustness of Cellular Immunity Determines the Fate of SARS-CoV-2 Infection. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 904686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Nicols, A.; Turtle, L.; Richter, A.; Duncan, C.J.; Dunachie, S.J.; Klenerman, P.; Payne, R.P. T cell immune memory after covid-19 and vaccination. BMJ Med. 2023, 2, e000468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dan, J.M.; Lindestam Arlehamn, C.S.; Weiskopf, D.; Da Silva Antunes, R.; Havenar-Daughton, C.; Reiss, S.M.; Brigger, M.; Bothwell, M.; Sette, A.; Crotty, S. A Cytokine-Independent Approach to Identify Antigen-Specific Human Germinal Center T Follicular Helper Cells and Rare Antigen-Specific CD4+ T Cells in Blood. J. Immunol. 2016, 197, 983–993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Edara, V.-V.; Pinsky, B.A.; Suthar, M.S.; Lai, L.; Davis-Gardner, M.E.; Floyd, K.; Flowers, M.W.; Wrammert, J.; Hussaini, L.; Ciric, C.R.; et al. Infection and Vaccine-Induced Neutralizing-Antibody Responses to the SARS-CoV-2 B.1.617 Variants. N. Engl. J. Med. 2021, 385, 664–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jara, A.; Undurraga, E.A.; Zubizarreta, J.R.; González, C.; Acevedo, J.; Pizarro, A.; Vergara, V.; Soto-Marchant, M.; Gilabert, R.; Flores, J.C.; et al. Effectiveness of CoronaVac in children 3–5 years of age during the SARS-CoV-2 Omicron outbreak in Chile. Nat. Med. 2022, 28, 1377–1380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puthanakit, T.; Nantanee, R.; Jaru-Ampornpan, P.; Chantasrisawad, N.; Sophonphan, J.; Meepuksom, T.; Jupimai, T.; Sodsai, P.; Anugulruengkitt, S.; Hirankarn, N.; et al. Heterologous Prime-boost of SARS-CoV-2 inactivated vaccine and mRNA BNT162b2 among Healthy Thai Adolescents. Vaccine X 2022, 12, 100211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mok, C.K.P.; Cohen, C.A.; Cheng, S.M.S.; Chen, C.; Kwok, K.-O.; Yiu, K.; Chan, T.-O.; Bull, M.; Ling, K.C.; Dai, Z.; et al. Comparison of the immunogenicity of BNT162b2 and CoronaVac COVID-19 vaccines in Hong Kong. Respirol. Carlton Vic. 2022, 27, 301–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jara, A.; Undurraga, E.A.; González, C.; Paredes, F.; Fontecilla, T.; Jara, G.; Pizarro, A.; Acevedo, J.; Leo, K.; Leon, F.; et al. Effectiveness of an Inactivated SARS-CoV-2 Vaccine in Chile. N. Engl. J. Med. 2021, 385, 875–884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Melo-González, F.; Soto, J.A.; González, L.A.; Fernández, J.; Duarte, L.F.; Schultz, B.M.; Gálvez, N.M.S.; Pacheco, G.A.; Ríos, M.; Vázquez, Y.; et al. Recognition of Variants of Concern by Antibodies and T Cells Induced by a SARS-CoV-2 Inactivated Vaccine. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 747830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fong, C.H.-Y.; Zhang, X.; Chen, L.-L.; Poon, R.W.-S.; Chan, B.P.-C.; Zhao, Y.; Wong, C.K.-H.; Chan, K.-H.; Yuen, K.-Y.; Hung, I.F.-N.; et al. Effect of vaccine booster, vaccine type, and hybrid immunity on humoral and cellular immunity against SARS-CoV-2 ancestral strain and Omicron variant sublineages BA.2 and BA.5 among older adults with comorbidities: A cross sectional study. eBioMedicine 2023, 88, 104446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuloğlu, Z.E.; El, R.; Guney-Esken, G.; Tok, Y.; Talay, Z.G.; Barlas, T.; Kuskucu, M.A.; Albayrak, Ö.; Doğan, Ö.; Yavuz, S.Ş.; et al. Effect of BTN162b2 and CoronaVac boosters on humoral and cellular immunity of individuals previously fully vaccinated with CoronaVac against SARS-CoV-2: A longitudinal study. Allergy 2022, 77, 2459–2467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Zhao, X.; Zhou, H.; Zhu, H.; Jiang, S.; Wang, P. Broadly neutralizing antibodies to SARS-CoV-2 and other human coronaviruses. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2023, 23, 189–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Díaz-Dinamarca, D.A.; Cárdenas-Cáceres, S.; Muena, N.A.; Díaz, P.; Barra, G.; Puentes, R.; Escobar, D.F.; Díaz-Samirin, M.; Santis-Alay, N.T.; Canales, C.; et al. Booster Vaccination with BNT162b2 Improves Cellular and Humoral Immune Response in the Pediatric Population Immunized with CoronaVac. Vaccines 2024, 12, 919. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines12080919
Díaz-Dinamarca DA, Cárdenas-Cáceres S, Muena NA, Díaz P, Barra G, Puentes R, Escobar DF, Díaz-Samirin M, Santis-Alay NT, Canales C, et al. Booster Vaccination with BNT162b2 Improves Cellular and Humoral Immune Response in the Pediatric Population Immunized with CoronaVac. Vaccines. 2024; 12(8):919. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines12080919
Chicago/Turabian StyleDíaz-Dinamarca, Diego A., Simone Cárdenas-Cáceres, Nicolás A. Muena, Pablo Díaz, Gisselle Barra, Rodrigo Puentes, Daniel F. Escobar, Michal Díaz-Samirin, Natalia T. Santis-Alay, Cecilia Canales, and et al. 2024. "Booster Vaccination with BNT162b2 Improves Cellular and Humoral Immune Response in the Pediatric Population Immunized with CoronaVac" Vaccines 12, no. 8: 919. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines12080919
APA StyleDíaz-Dinamarca, D. A., Cárdenas-Cáceres, S., Muena, N. A., Díaz, P., Barra, G., Puentes, R., Escobar, D. F., Díaz-Samirin, M., Santis-Alay, N. T., Canales, C., Díaz, J., García-Escorza, H. E., Grifoni, A., Sette, A., Tischler, N. D., & Vasquez, A. E. (2024). Booster Vaccination with BNT162b2 Improves Cellular and Humoral Immune Response in the Pediatric Population Immunized with CoronaVac. Vaccines, 12(8), 919. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines12080919








