Evaluation of the Effect of the Mycoplasma hyopneumoniae Live Vaccine (Strain 168) in Ningxiang Pigs
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. M. hyopneumoniae Vaccine and Experimental Animals
2.2. Animal Experiment
2.3. Sample Collection and Testing
2.4. Production Performance and Clinical Observations
2.5. Lung Lobe Lesion Index Statistics and Lung Scoring at Slaughter
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Medication Usage Results During the Weaning Stage
3.2. Weaning Weight and Mortality Rate of Suckling Piglets in Each Group
3.3. Average Daily Weight Gain and Mortality Rate During the Nursery Phase for Each Group
3.4. Lung Lesion Scores and Average Pneumonia Reduction Rate at Slaughter
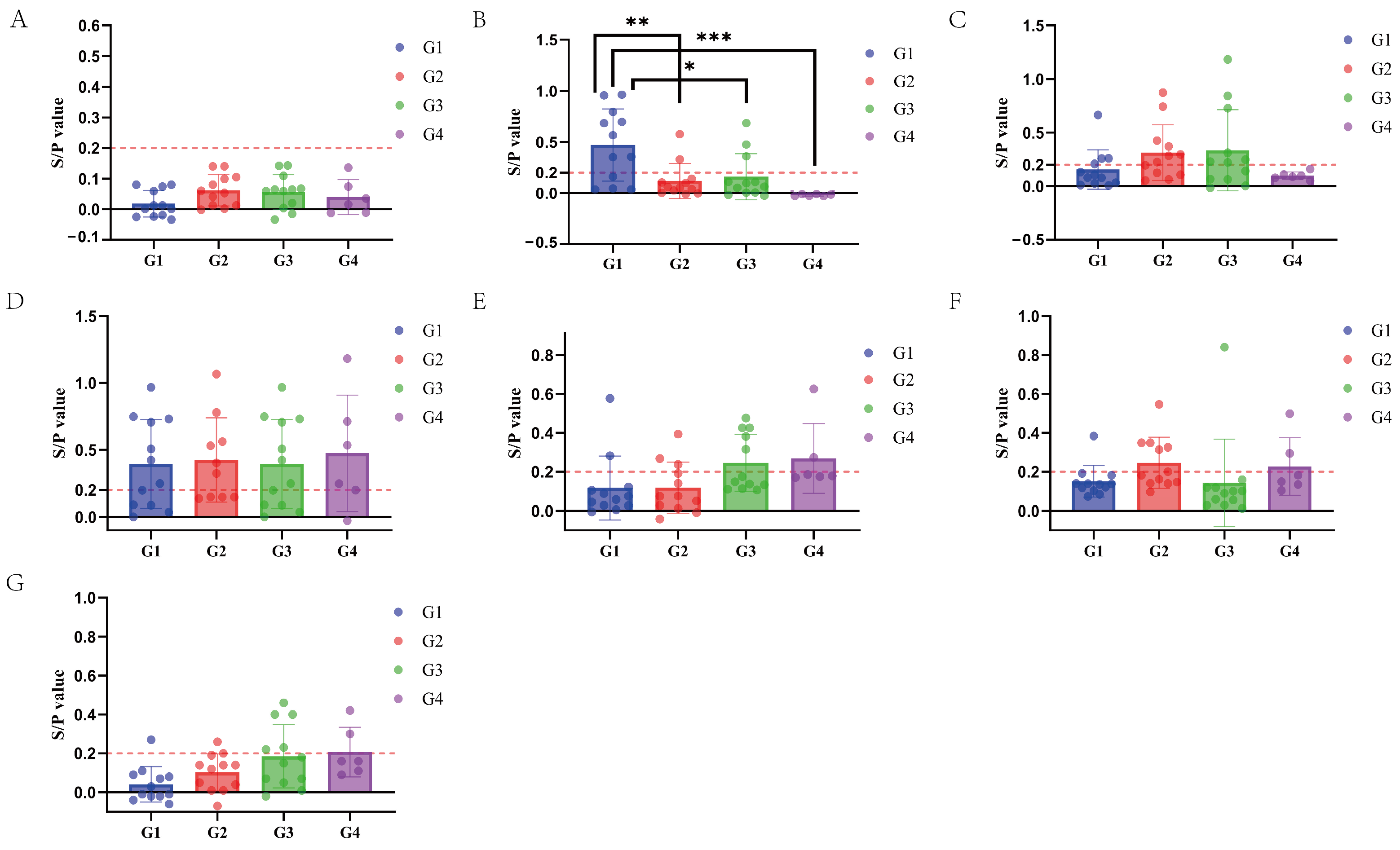
3.5. Results of the M. hyopneumoniae-Specific SIgA Antibody Detection in Nasal Swabs
3.6. Results of the M. hyopneumoniae-Specific IgG Antibody Detection in Serum
3.7. Results of the M. hyopneumoniae DNA Detection in Nasal Swabs
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sipos, W.; Sipos, S. Clinical Efficacy of Two Novel, Differentially Administered (IM, ID) Vaccines against Mycoplasma hyopneumoniae and PCV2 in Swine under Field Conditions. Animals 2022, 12, 3467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maes, D.; Segales, J.; Meyns, T.; Sibila, M.; Haesebrouck, F. Control of Mycoplasma hyopneumoniae infection in pigs. Vet. Microbiol. 2008, 126, 297–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chae, C.; Choi, K.; Jeong, J.; Seo, H.W.; Kang, I.; Park, C. Comparison of 2 commercial single-dose Mycoplasma hyopneumoniae vaccines and porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus (PRRSV) vaccines on pigs dually infected with M. hyopneumoniae and PRRSV. Can. J. Vet. Res. 2016, 80, 112–123. [Google Scholar]
- Cho, H.; Ahn, Y.; Oh, T.; Suh, J.; Chae, C. Non-Inferiority Field Study Comparing the Administrations by Conventional Needle-Syringe and Needle-Free Injectors of a Trivalent Vaccine Containing Porcine Circovirus Types 2a/2b and Mycoplasma hyopneumoniae. Vaccines 2022, 10, 358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maes, D.; Sibila, M.; Kuhnert, P.; Segalés, J.; Haesebrouck, F.; Pieters, M. Update on Mycoplasma hyopneumoniae infections in pigs: Knowledge gaps for improved disease control. Transbound. Emerg. Dis. 2018, 65, 110–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Fang, L.; Liu, W.; Song, T.; Zhao, F.; Zhang, R.; Wang, D.; Xiao, S. Quantitative proteomic analyses of a pathogenic strain and its highly passaged attenuated strain of Mycoplasma hyopneumoniae. Biomed Res. Int. 2019, 2019, 4165735. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, R.; Xing, X.; Feng, Z.; Hua, L.; Xiong, Q.; Ali Ishag, H.Z.; Shao, G. The research of immune protective efficacy of Mycoplasma hyoneumoniae vaccine ‘168 strain’ by intranasal route. J. Agric. Univ. Hebei 2016, 39, 93–97. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, R.S.; Feng, Z.X.; Ishag, H.Z.A.; Hua, L.Z.; Shao, G.Q. Protective efficacy of the attenuated Mycoplasma hyopneumoniaevaccine strain 168 in piglets administered by intranasal route. In Proceedings of the 21st Congress of the International Organization for Mycoplasmology, Brisbane, Australia, 3–7 July 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Maes, D.; Boyen, F.; Devriendt, B.; Kuhnert, P.; Haesebrouck, F. Perspectives for improvement of Mycoplasma hyopneumoniae vaccines in pigs. Vet. Res. 2021, 52, 67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y.; Hu, W.; Wei, Y.; Feng, Z.; Yang, Q. The immune mechanism of Mycoplasma hyopneumoniae 168 vaccine strain through dendritic cells. BMC Vet. Res. 2017, 13, 285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, Y.; Gan, Y.; Hua, L.-Z.; Nathues, H.; Yang, H.; Wei, Y.-N.; Wu, M.; Shao, G.-Q.; Feng, Z.-X. Application of a sIgA-ELISA method for differentiation of Mycoplasma hyopneumoniae infected from vaccinated pigs. Vet. Microbiol. 2018, 223, 86–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bustin, S.A.; Benes, V.; Garson, J.A.; Hellemans, J.; Huggett, J.; Kubista, M.; Mueller, R.; Nolan, T.; Pfaffl, M.W.; Shipley, G.L. The MIQE Guidelines: M inimum I nformation for Publication of Q uantitative Real-Time PCR E xperiments. Clin. Chem. 2009, 55, 611–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Madec, F.; Kobish, M. A survey of pulmonary lesions in bacon pigs.(Observations made at the slaughterhouse). Anim. Res. 1982, 31, 341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goodwin, R.F. Field trials with a formalinized vaccine against enzootic pneumonia of pigs. Br. Vet. J. 1973, 129, 465–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barile, M.F.; Chandler, D.K.F.; Yoshida, H.; Grabowski, M.W.; Ahmed, O.A. Hamster challenge potency assay for evaluation of Mycoplasma pneumoniae vaccines. Isr. J. Med. Sci. 1981, 17, 682–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tukey, J.W. Comparing Individual Means in the Analysis of Variance. Biometrics 1949, 5, 99–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holst, S.; Yeske, P.; Pieters, M. Elimination of Mycoplasma hyopneumoniae from breed-to-wean farms: A review of current protocols with emphasis on herd closure and medication. J. Swine Health Prod. 2015, 23, 321–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vranckx, K.; Maes, D.; Marchioro, S.B.; Villarreal, I.; Chiers, K.; Pasmans, F.; Haesebrouck, F. Vaccination reduces macrophage infiltration in bronchus-associated lymphoid tissue in pigs infected with a highly virulent Mycoplasma hyopneumoniae strain. BMC Vet. Res. 2012, 8, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Oliveira, N.R.; Jorge, S.; Gomes, C.K.; Rizzi, C.; Pacce, V.D.; Collares, T.F.; Monte, L.G.; Dellagostin, O.A.N. A novel chimeric protein composed of recombinant Mycoplasma hyopneumoniae antigens as a vaccine candidate evaluated in mice. Vet. Microbiol. 2017, 201, 146–153. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, W.; Jiang, P.; Song, T.; Yang, K.; Yuan, F.; Gao, T.; Liu, Z.; Li, C.; Guo, R.; Xiao, S. A Recombinant Chimera Vaccine Composed of LTB and Mycoplasma hyopneumoniae Antigens P97R1, mhp390 and P46 Elicits Cellular Immunologic Response in Mice. Vaccines 2023, 11, 1291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Z.-X.; Wei, Y.-N.; Li, G.-L.; Lu, X.-M.; Wan, X.-F.; Pharr, G.T.; Wang, Z.-W.; Kong, M.; Gan, Y.; Bai, F.-F. Development and validation of an attenuated Mycoplasma hyopneumoniae aerosol vaccine. Vet. Microbiol. 2013, 167, 417–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Z.-x.; Shao, G.-q.; Liu, M.-j.; Wu, X.-s.; Zhou, Y.-q.; Yuan, G. Immune responses to the attenuated Mycoplasma hyopneumoniae 168 strain vaccine by intrapulmonic immunization in piglets. Agric. Sci. China 2010, 9, 423–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, Y.; Shu, J.; Chen, J.; Wu, Y.; He, Y. A concise review of vaccines against Mycoplasma hyopneumoniae. Res. Vet. Sci. 2019, 123, 144–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maes, D.; Deluyker, H.; Verdonck, M.; Castryck, F.; Miry, C.; Lein, A.; Vrijens, B.; de Kruif, A. The effect of vaccination against Mycoplasma hyopneumoniae in pig herds with a continuous production system. J. Vet. Med. Ser. B 1998, 45, 495–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maes, D.; Deluyker, H.; Verdonck, M.; Castryck, F.; Miry, C.; Vrijens, B.; Verbeke, W.; Viaene, J.; Kruif, A.D. Effect of vaccination against Mycoplasma hyopneumoniae in pig herds with an all-in/all-out production system. Vaccine. 1999, 17, 1024–1034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villarreal, I.; Meyns, T.; Dewulf, J.; Vranckx, K.; Calus, D.; Pasmans, F.; Haesebrouck, F.; Maes, D. The effect of vaccination on the transmission of Mycoplasma hyopneumoniae in pigs under field conditions. Vet. J. 2011, 188, 48–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Morante, B.; Segalés, J.; Fraile, L.; de Rozas, A.P.; Maiti, H.; Coll, T.; Sibila, M. Assessment of Mycoplasma hyopneumoniae-induced pneumonia using different lung lesion scoring systems: A comparative review. J. Comp. Pathol. 2016, 154, 125–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez, F.; Rosales, R.S.; Ramírez, A.S.; Poveda, J.B. Vaccination upregulates Th1 cytokines in the lung of pigs experimentally infected with mycoplasma hyopneumoniae. Animals 2023, 13, 520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merialdi, G.; Dottori, M.; Bonilauri, P.; Luppi, A.; Gozio, S.; Pozzi, P.; Spaggiari, B.; Martelli, P. Survey of pleuritis and pulmonary lesions in pigs at abattoir with a focus on the extent of the condition and herd risk factors. Vet. J. 2012, 193, 234–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paz-Sánchez, Y.; Herráez, P.; Quesada-Canales, Ó.; Poveda, C.G.; Díaz-Delgado, J.; Quintana-Montesdeoca, M.d.P.; Plamenova Stefanova, E.; Andrada, M. Assessment of lung Disease in finishing pigs at slaughter: Pulmonary lesions and implications on productivity parameters. Animals 2021, 11, 3604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sibila, M.; Nofrarias, M.; Lopez-Soria, S.; Segales, J.; Riera, P.; Llopart, D.; Calsamiglia, M. Exploratory field study on Mycoplasma hyopneumoniae infection in suckling pigs. Vet. Microbiol. 2007, 121, 352–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyns, T.; Dewulf, J.; De Kruif, A.; Calus, D.; Haesebrouck, F.; Maes, D. Comparison of transmission of Mycoplasma hyopneumoniae in vaccinated and non-vaccinated populations. Vaccine 2006, 24, 7081–7086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woof, J.M.; Kerr, M.A. The function of immunoglobulin A in immunity. J. Pathol. 2006, 208, 270–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Renegar, K.B.; Small, P.A.; Boykins, L.G.; Wright, P.F. Role of IgA versus IgG in the Control of Influenza Viral Infection in the Murine Respiratory Tract. J. Immunol. 2004, 173, 1978–1986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thacker, E.L.; Thacker, B.J.; Boettcher, T.B.; Jayappa, H. Comparison of antibody production, lymphocyte stimulation, and protection induced by four commercial Mycoplasma hyopneumoniae bacterins. J. Swine Health Prod. 1998, 6, 107–112. [Google Scholar]
- Thacker, E.L.; Halbur, P.G.; Ross, R.F.; Thanawongnuwech, R.; Thacker, B.J. Mycoplasma hyopneumoniae potentiation of porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus-induced pneumonia. J. Clin. Microbiol. 1999, 37, 620–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goodwin, R.; Hodgson, R.G.; Whittlestone, P.; Woodhams, R.L. Some experiments relating to artificial immunity in enzootic pneumonia of pigs. Epidemiol. Infect. 1969, 67, 465–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Djordjevic, S.; Eamens, G.; Romalis, L.; Nicholls, P.; Taylor, V.; Chin, J. Serum and mucosal antibody responses and protection in pigs vaccinated against Mycoplasma hyopneumoniae with vaccines containing a denatured membrane antigen pool and adjuvant. Aust. Vet. J. 1997, 75, 504–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andreasen, M.; Mousing, J.; Thomsen, L.K. No overall relationship between average daily weight gain and the serological response to Mycoplasma hyopneumoniae and Actinobacillus pleuropneumoniae in eight chronically infected Danish swine herds. Prev. Vet. Med. 2001, 49, 19–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baccaro, M.R.; Hirose, F.; Umehara, O.; Gon?Alves, L.C.B.; Doto, D.S.; PaixãO, R.; Shinya, L.T.; Moreno, A.M. Comparative efficacy of two single-dose bacterins in the control of Mycoplasma hyopneumoniae in swine raised under commercial conditions in Brazil. Vet. J. 2006, 172, 526–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Groups | No. of Pigs | Age (Days) | Dosage | Vaccination Times | Immune Pathway |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Group 1 | 98 | 7, 21 | One (2.0 mL) | 2 | Intramuscular injection |
| Group 2 | 98 | 7, 21 | One (2.0 mL) | 2 | Intramuscular injection (7 day) Intramuscular injection (21 day) |
| Group 3 | 96 | 7 | One (2.0 mL) | 1 | Intrapulmonary injection |
| Group 4 | 21 | - | - | - | - |
| Primer and Probe | Primer Sequence (5′–3′) | Product Length/bp |
|---|---|---|
| Mhp183-F | CAAAGCGAGTATGAAGAACAAGAAA | 128 |
| Mhp183-R | GTCATCATTGGGTGGCTAAGT | 128 |
| Mhp183-P | ROX-TCCAGGAAGTCAAGGTAACTAGTGACCA-BHQ | 128 |
| Index/Groups | Group 1 | Group 2 | Group 3 | Group 4 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Medication Usage | Florfenicol injection Lincomycin injection Sulfamonomethoxine injection Penicillin sodium Ceftiofur sodium Aminopyrine injection | Florfenicol injection Lincomycin injection Penicillin sodium Ceftiofur sodium Aminopyrine injection | Florfenicol injection Lincomycin injection | Florfenicol injection Lincomycin injection Penicillin sodium |
| Index/Group | Group 1 | Group 2 | Group 3 | Group 4 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Average weaning weight (kg/pig) | 5.76 ± 0.51 a | 5.61 ± 0.48 b | 6.63 ± 0.48 c | 6.50 ± 0.65 a |
| Mortality rate | 3.1% | 1% | 0 | 0 |
| Index/Groups | Group 1 | Group 2 | Group 3 | Group 4 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Average daily weight gain (kg/d) | 0.33 ± 0.05 a | 0.30 ± 0.05 b | 0.35 ± 0.05 b | 0.34 ± 0.06 b |
| Mortality rate | 4.2% | 2.1% | 0 | 0 |
| Related Indicators | Group 1 | Group 2 | Group 3 | Group 4 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Consolidated lungs proportion (%) | 100% (10/10) | 90% (9/10) | 70% (7/10) | 100% (10/10) |
| Consolidated lungs average score | 12.90 ± 4.28 a | 6.78 ± 4.32 b | 4.43 ± 2.44 b | 14.40 ± 3.53 a |
| Pneumonia lesion reduction rate (%) | 10.41% | 57.64% | 69.44% | / |
| Groups | Days | Positive Rate (%) | Correlation Value | p Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Group 1 | 0 | 0 | −0.198 | 0.662 |
| 14 | 66.7 | |||
| 28 | 33.3 | |||
| 56 | 58.3 | |||
| 84 | 16.7 | |||
| 112 | 8.3 | |||
| 140 | 8.3 | |||
| Group 2 | 0 | 0 | 0.179 | 0.713 |
| 14 | 16.7 | |||
| 28 | 58.3 | |||
| 56 | 60.0 | |||
| 84 | 25.0 | |||
| 112 | 41.7 | |||
| 140 | 8.3 | |||
| Group 3 | 0 | 00.0 | 0.236 | 0.662 |
| 14 | 25.0 | |||
| 28 | 58.3 | |||
| 56 | 58.3 | |||
| 84 | 41.7 | |||
| 112 | 8.3 | |||
| 140 | 41.7 | |||
| Group 4 | 0 | 0 | 0.694 | 0.110 |
| 14 | 0 | |||
| 28 | 0 | |||
| 56 | 66.7 | |||
| 84 | 33.3 | |||
| 112 | 33.3 | |||
| 140 | 33.3 |
| Groups | Days | Positive Rate (%) | Correlation Value | p Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Group 1 | 0 | 0.00 | 0.991 | 0.003 ** |
| 14 | 16.7 | |||
| 28 | 25.0 | |||
| 56 | 58.3 | |||
| 84 | 91.7 | |||
| 112 | 91.7 | |||
| 140 | 100.0 | |||
| Group 2 | 0 | 8.3 | 0.901 | 0.012 * |
| 14 | 41.7 | |||
| 28 | 8.3 | |||
| 56 | 58.3 | |||
| 84 | 83.3 | |||
| 112 | 66.7 | |||
| 140 | 100.0 | |||
| Group 3 | 0 | 0.00 | 0.808 | 0.048 * |
| 14 | 0.00 | |||
| 28 | 0.00 | |||
| 56 | 16.7 | |||
| 84 | 0.00 | |||
| 112 | 58.3 | |||
| 140 | 91.7 | |||
| Group 4 | 0 | 0.0 | 0.946 | 0.007 ** |
| 14 | 0.0 | |||
| 28 | 16.7 | |||
| 56 | 16.7 | |||
| 84 | 66.7 | |||
| 112 | 100.0 | |||
| 140 | 83.3 |
| Groups | Days | Positive Rate (%) | Correlation Value | p Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Group 1 | 0 | 0.0 | 0.316 | 0.556 |
| 14 | 0.0 | |||
| 28 | 8.33 | |||
| 56 | 0.0 | |||
| 84 | 0.0 | |||
| 112 | 0.0 | |||
| 140 | 8.33 | |||
| Group 2 | 0 | 0.0 | 0.316 | 0.556 |
| 14 | 0.0 | |||
| 28 | 8.33 | |||
| 56 | 0.0 | |||
| 84 | 0.0 | |||
| 112 | 0.0 | |||
| 140 | 8.33 | |||
| Group 3 | 0 | 0.0 | 0.478 | 0.302 |
| 14 | 25.0 | |||
| 28 | 0.0 | |||
| 56 | 0.0 | |||
| 84 | 0.0 | |||
| 112 | 66.67 | |||
| 140 | 25.0 | |||
| Group 4 | 0 | 0.0 | −0.112 | 0.783 |
| 14 | 50.0 | |||
| 28 | 33.33 | |||
| 56 | 16.67 | |||
| 84 | 0.0 | |||
| 112 | 50.00 | |||
| 140 | 0.0 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Qin, Z.; Zhao, P.; Chen, L.; Han, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Zhao, J. Evaluation of the Effect of the Mycoplasma hyopneumoniae Live Vaccine (Strain 168) in Ningxiang Pigs. Vaccines 2024, 12, 1332. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines12121332
Qin Z, Zhao P, Chen L, Han Z, Zhang Y, Zhao J. Evaluation of the Effect of the Mycoplasma hyopneumoniae Live Vaccine (Strain 168) in Ningxiang Pigs. Vaccines. 2024; 12(12):1332. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines12121332
Chicago/Turabian StyleQin, Zhanguo, Pengfei Zhao, Lunyong Chen, Zhen Han, Yuankui Zhang, and Junlong Zhao. 2024. "Evaluation of the Effect of the Mycoplasma hyopneumoniae Live Vaccine (Strain 168) in Ningxiang Pigs" Vaccines 12, no. 12: 1332. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines12121332
APA StyleQin, Z., Zhao, P., Chen, L., Han, Z., Zhang, Y., & Zhao, J. (2024). Evaluation of the Effect of the Mycoplasma hyopneumoniae Live Vaccine (Strain 168) in Ningxiang Pigs. Vaccines, 12(12), 1332. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines12121332





