Epidemiology of Streptococcus pneumoniae Serotypes in Jordan Amongst Children Younger than the Age of 5: A National Cross-Sectional Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Case Definition [20,21]
2.2. Inclusion Criteria
3. Exclusion Criteria
- Children receiving routine pneumococcal vaccination as part of the private sector vaccination program or as high-risk groups. Only one case was excluded from the study due to receiving PCV-13 in a private clinic.
- Not permanently resident in the study area.
Sample Size Calculations [22,23,24]
4. Microbiology
- PCR-positive cases: For cases with radiological findings suggestive of lobar pneumonia, as described in the radiology section below, blood samples were collected on admission. PCR was used to identify Streptococcus pneumoniae and for serotyping.
- Culture-positive cases: For invasive pneumococcal disease cases (pneumonia, meningitis, septicemia, etc.) identified during the study period at study sites, a Quellung test was performed for serotyping.
5. Sample Collection and PCR Analysis
6. Culture and Identification
7. Serotyping for Culture-Positive Cases
8. Radiological Findings
9. Results
10. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Correction Statement
Appendix A
| Serotype | Primer Name | Sequence (5′-3′) | Frequency for All Participants | Frequency for Cases < 2 Year of Age, N = 754 | Mean Age | Age SD | Presence of Congenital Disease | Presence of Chronic Illness | Percentage in Pneumonia Cases |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
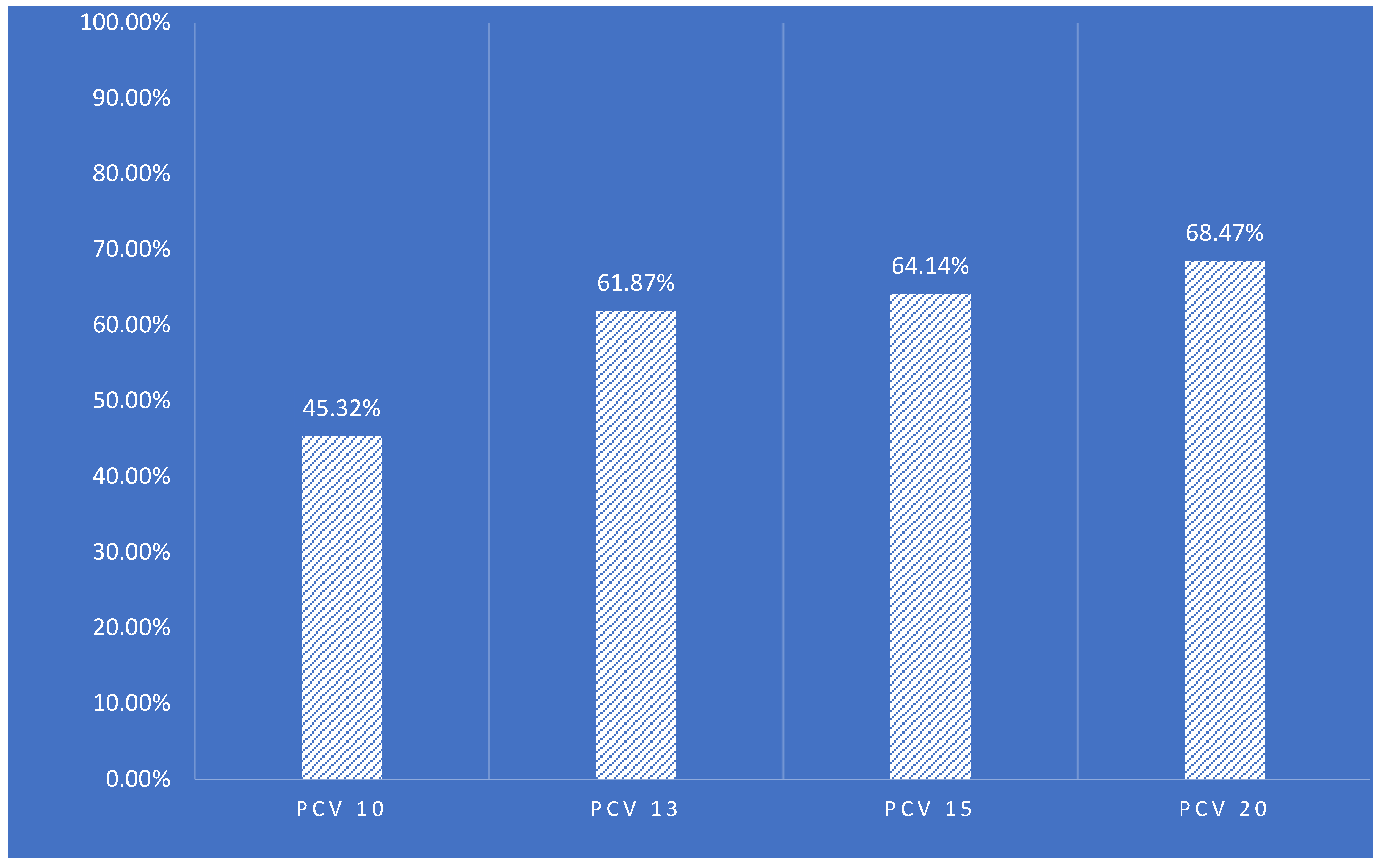
| PCV-10 | 45.32% | 45.23% | 15.5 | 16.2 | 1.77% | 7.09% | 44.63% | ||
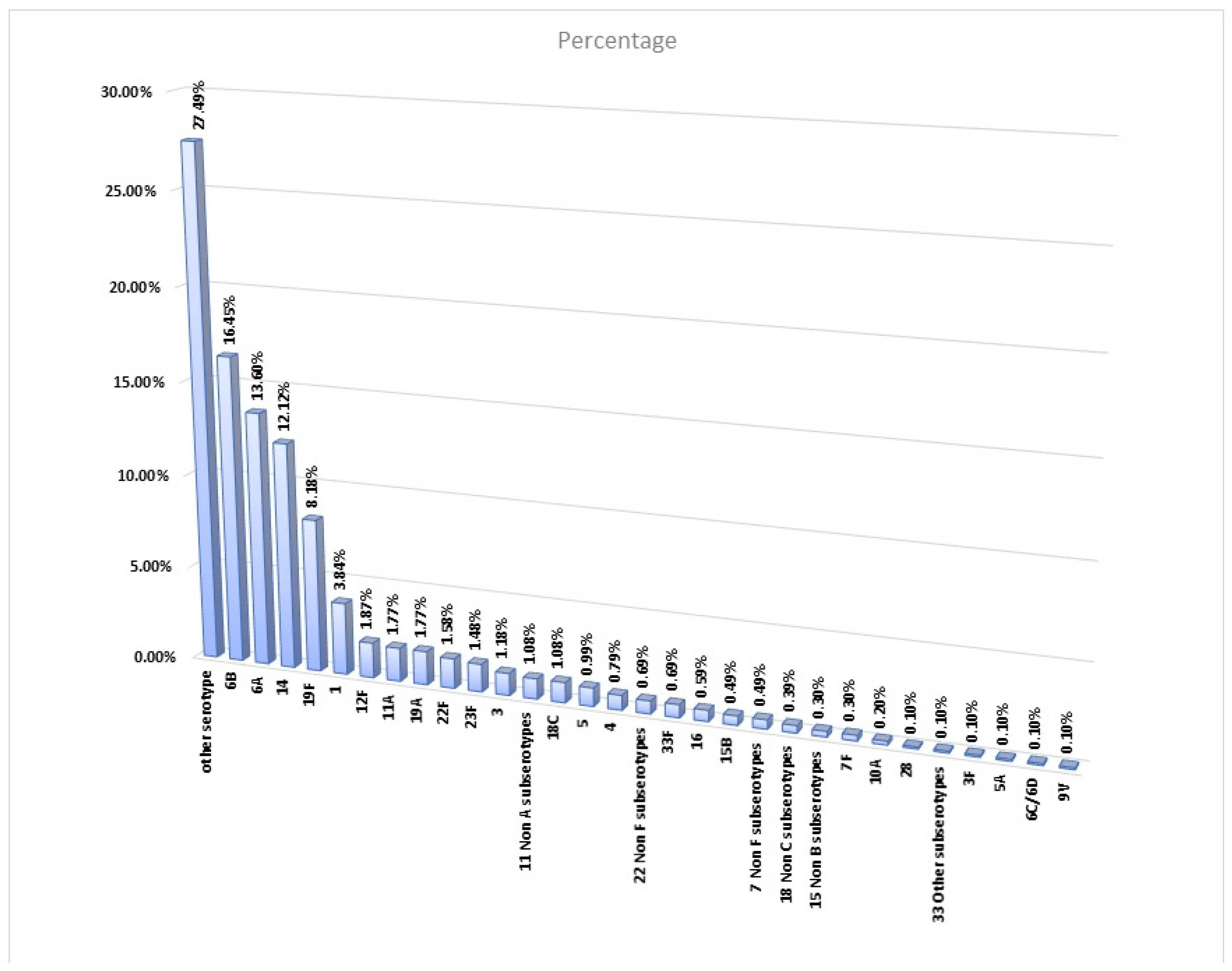
| 1 | 1-F,1-R [51] | 5′-TTTCATCCCTATGTGTGGTATAG-3′, 5′-GCTTTAGAAGGTAGAGTTAACAAC-3′ | 3.84% | 3.32% | 19.6 | 18.3 | 0.30% | 0.89% | 3.74% |
| 4 | 4-F,4-R [51] | 5′-GCTTCTGCTGTAACTGTTGTGC-3′, 5′-CACCACCATAGTAACCAAAGTTCC-3′ | 0.79% | 0.66% | 16.5 | 17.9 | 0.00% | 0.20% | 0.79% |
| 5 | 5-F,5R [51] | 5′-CATGATTTATGCCCTCTTGCAA-3′, 5′-GACAGTATAAGAAAAAGCAAGGGCTAA-3′ | 0.99% | 0.93% | 17 | 14.5 | 0.00% | 0.10% | 0.99% |
| 6B | 6B-F, 6B-R [52] | CGA CGT AAC AAA GAA CTA GGT GCT GAA AC, AAG TAT ATA ACC ACG CTG TAA AAC TCT GAC | 16.45% | 15.65% | 16.2 | 16.9 | 0.49% | 2.86% | 16.45% |
| 7F | 7F-F, 7F-R [53] | 5′-CCTACGGGAGGATATAAAATTATTTTTGAG-3′, 5′-CAAATACACCATATAGGCTGTTGAGACTAAC-3′ | 0.30% | 0.40% | 8.6 | 12.5 | 0.00% | 0.10% | 0.30% |
| 9V | 9V-F, 9V-R [53] | 5′-CTTCGTTAGTTAAAATTCTAAATTTTTCTAAG-3′, 5′-GTCCCAATACCAGTCCTTGCAACACAAG-3′ | 0.10% | 0.13% | 1 | 0 | 0.00% | 0.00% | 0.10% |
| 14 | 14-F, 14-R [51] | 5′-AGAGTGTATGAGGAATCC-3′, 5′-ATATATCTACTGTAGAGGGAAT-3′ | 12.12% | 12.60% | 14.5 | 16.3 | 0.59% | 1.38% | 11.72% |
| 18C | 18C-F, 18C-R [54] | 5′-CTTAATAGCTCTCATTATTCTTTTTTTAAGCC-3′, 5′-TTATCTGTAAACCATATCAGCATCTGAAAC-3′ | 1.08% | 1.19% | 12.7 | 16.1 | 0.00% | 0.10% | 1.08% |
| 19F | 19F-F, 19F-R [51] | 5′-TGAGGTTAAGATTGCTGATCG-3′, 5′-CACGAATGAGAACTCGAATAAAAG-3′ | 8.18% | 8.62% | 15.3 | 14.5 | 0.30% | 1.18% | 8.08% |
| 23F | 23F-F, 23F-R [51] | 5′-GACAGCAACGACAATAGTCATCTC-3′, 5′-TCCATCCCAACCTAACACACTTC-3′ | 1.48% | 1.72% | 9.7 | 12.6 | 0.10% | 0.30% | 1.38% |
| PCV-13 | 61.87% | 61.54% | 15.5 | 16.6 | 2.76% | 8.57% | 60.79% | ||
| 3 | 3-F, 3-R [51] | 5′-CCACTAAAGCTTTGGCAAAAGAAA-3′, 5′-CCCGAACGTAAAGCTTCTTCA-3′ | 1.18% | 0.93% | 20 | 17.5 | 0.10% | 0.10% | 1.08% |
| 6A | 6A-F, 6A-R [52] | AAT TTG TAT TTT ATT CAT GCC TAT ATC TGG, TTA GCG GAG ATA ATT TAA AAT GAT GAC TA | 13.60% | 14.06% | 14.5 | 17.6 | 0.79% | 1.28% | 13.50% |
| 19A | 19A-F, 19A-R [51] | 5′-CGCCTAGTCTAAATACCA-3′, 5′-GAGGTCAACTATAATAGTAAGAG-3′ | 1.77% | 1.33% | 18.7 | 17.9 | 0.10% | 0.10% | 1.58% |
| PCV-15 | 64.14% | 63.79% | 15.5 | 16.6 | 2.76% | 8.77% | 63.05% | ||
| 22F | 22F-F, 22F-R [51] | 5′-CTTGTCAAGTATGCTGAGGATTTG-3′, 5′-AGATTTCTCCTGGATATAATGCGAT-3′ | 1.58% | 1.59% | 15.7 | 16.6 | 0.00% | 0.20% | 1.58% |
| 33F | 33F-F, 33F-R [55] | 5′-GAAGGCAATCAATGTGATTGTGTCGCG-3′, 5′-CTTCAAAATGAAGATTATAGTACCCTTCTAC-3′ | 0.69% | 0.66% | 15.9 | 17 | 0.00% | 0.00% | 0.69% |
| PCV-20 | 68.47% | 68.44% | 15.3 | 16.6 | 2.96% | 9.36% | 67.39% | ||
| 8 | 8-F, 8-R [51] | 5′-ATTCTAATTACTACATTACTGCTTTATACTA-3′, 5′-TCTTCTTAAATCATAATGAATCGTACC-3′ | |||||||
| 10A | 10A-F, 10A-R [51] | 5′-TAGTGTCGGCAGACAAATTAT-3′, 5′-CACGCTCATACACTTTATTTGA-3′ | 0.20% | 0.13% | 34.5 | 29 | 0.00% | 0.00% | 0.20% |
| 11A | 11A-F, 11A-R [55] | 5′-GGACATGTTCAGGTGATTTCCCAATATAGTG-3′, 5′-GATTATGAGTGTAATTTATTCCAACTTCTCCC-3′ | 1.77% | 1.86% | 12.9 | 15.9 | 0.00% | 0.30% | 1.77% |
| 12F | 12F-F, 12F-R [55] | 5′-GCAACAAACGGCGTGAAAGTAGTTG-3′, 5′-CAAGATGAATATCACTACCAATAACAAAAC-3′ | 1.87% | 1.99% | 11.9 | 15.9 | 0.00% | 0.10% | 1.87% |
| 15B | 15B-F, 15B-R [54] | 5′-ATTAGTACAGCTGCTGGAATATCTCTTC-3′, 5′-GATCTAGTGAACGTACTATTCCAAAC-3′ | 0.49% | 0.66% | 4.4 | 6.2 | 0.20% | 0.20% | 0.49% |
| Total other serotypes | 31.53% | 31.56% | 14.3 | 15.2 | 1.28% | 3.25% | 31.43% | ||
| 11 Non-A subserotypes | Quellung test for culture-positive cases | 1.08% | 1.06% | 15.6 | 16.6 | 0.10% | 0.20% | 1.08% | |
| 15 Non-B subserotypes | Quellung test for culture-positive cases | 0.30% | 0.13% | 20 | 9.5 | 0.00% | 0.10% | 0.30% | |
| 16 | Quellung test for culture-positive cases | 0.59% | 0.53% | 20.7 | 15.3 | 0.10% | 0.20% | 0.59% | |
| 18 Non-C subserotypes | Quellung test for culture-positive cases | 0.39% | 0.40% | 14.8 | 17.3 | 0.00% | 0.00% | 0.39% | |
| 22 Non-F subserotypes | Quellung test for culture-positive cases | 0.69% | 0.53% | 21.4 | 13.3 | 0.00% | 0.10% | 0.69% | |
| 28 | Quellung test for culture-positive cases | 0.10% | 0.13% | 6 | 0 | 0.00% | 0.10% | 0.00% | |
| 33 Other subserotypes | Quellung test for culture-positive cases | 0.10% | 0.13% | 20 | 0 | 0.00% | 0.10% | 0.10% | |
| 3F | Quellung test for culture-positive cases | 0.10% | 0.13% | 5 | 0 | 0.00% | 0.00% | 0.10% | |
| 5A | Quellung test for culture-positive cases | 0.10% | 0.00% | 26 | 0 | 0.00% | 0.00% | 0.10% | |
| 6C/6D | Quellung test for culture-positive cases | 0.10% | 0.13% | 7 | 0 | 0.00% | 0.00% | 0.10% | |
| 7 Non-F subserotypes | Quellung test for culture-positive cases | 0.49% | 0.40% | 22 | 20.7 | 0.00% | 0.00% | 0.49% | |
| other serotype | Not identified through above primers for PCR-positive cases | 27.49% | 27.98% | 13.8 | 15.3 | 1.08% | 2.46% | 27.49% |
References
- Van der Poll, T.; Opal, S.M. Pathogenesis, Treatment, and Prevention of Pneumococcal Pneumonia. Lancet 2009, 374, 1543–1556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, B.G.; Gouws, E.; Boschi-Pinto, C.; Bryce, J.; Dye, C. Estimates of World-Wide Distribution of Child Deaths from Acute Respiratory Infections. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2002, 2, 25–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marrie, T.J. Pneumococcal Pneumonia: Epidemiology and Clinical Features. Semin. Respir. Infect. 1999, 14, 227–236. [Google Scholar]
- Thadchanamoorthy, V.; Dayasiri, K. Review on Pneumococcal Infection in Children. Cureus 2021, 13, e14913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pineda Solas, V.; Pérez Benito, A.; Domingo Puiggros, M.; Larramona Carrera, H.; Segura Porta, F.; Fontanals Aymerich, D. Neumonía Neumocócica Bacteriémica. An. Esp. Pediatr. 2002, 57, 408–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, J.S. Community-Acquired Pneumonia. Clin. Med. J. R. Coll. Phys. Lond. 2012, 12, 538–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ostroff, S.M.; Harrison, L.H.; Khallaf, N.; Assaad, M.T.; Guirguis, N.I.; Harrington, S.; El-Alamy, M. Resistance Patterns of Streptococcus Pneumoniae and Haemophilus Influenzae Isolates Recovered in Egypt from Children with Pneumonia. Clin. Infect. Dis. 1996, 23, 1069–1074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gruber, M.F.; Pratt, D.; Haase, M. Licensing of Pneumococcal Conjugate Vaccines for Children and Adults: Regulatory Perspective from the European Medicines Agency and the U.S. Food and Drug Administration. In Pneumococcal Vaccines; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2014; pp. 183–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Committee for Medicinal Products for Human Use. European Public Assessment Report for Synflorix Pneumococcal Polysaccharide Conjugate Vaccine (Adsorbed) Pneumococcal Infection, Immunization, I. 2014. Available online: https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/medicines/human/EPAR/synflorix (accessed on 1 June 2023).
- Duggan, S.T. Pneumococcal Polysaccharide Conjugate Vaccine (13-Valent, Adsorbed) Prevenar 13®. Drugs 2010, 70, 1973–1986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balsells, E.; Guillot, L.; Nair, H.; Kyaw, M.H. Serotype Distribution of Streptococcus Pneumoniae Causing Invasive Disease in Children in the Post-PCV Era: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0177113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shibl, A.M.; Memish, Z.A.; Al-Kattan, K.M. Antibiotic Resistance and Serotype Distribution of Invasive Pneumococcal Diseases before and after Introduction of Pneumococcal Conjugate Vaccine in the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia (KSA). Vaccine 2012, 30, G32–G36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ceyhan, M.; Ozsurekci, Y.; Gürler, N.; Öksüz, L.; Aydemir, S.; Ozkan, S.; Yuksekkaya, S.; Keser Emiroglu, M.; Gültekin, M.; Yaman, A.; et al. Serotype Distribution of Streptococcus Pneumoniae in Children with Invasive Diseases in Turkey: 2008–2014. Hum. Vaccines Immunother. 2016, 12, 308–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McFetridge, R.; ter Meulen, A.S.; Folkerth, S.D.; Hoekstra, J.A.; Dallas, M.; Hoover, P.A.; Marchese, R.D.; Zacholski, D.M.; Watson, W.J.; Stek, J.E.; et al. Safety, Tolerability, and Immunogenicity of 15-Valent Pneumococcal Conjugate Vaccine in Healthy Adults. Vaccine 2015, 33, 2793–2799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skinner, J.M.; Indrawati, L.; Cannon, J.; Blue, J.; Winters, M.; MacNair, J.; Pujar, N.; Manger, W.; Zhang, Y.; Antonello, J.; et al. Pre-Clinical Evaluation of a 15-Valent Pneumococcal Conjugate Vaccine (PCV15-CRM197) in an Infant-Rhesus Monkey Immunogenicity Model. Vaccine 2011, 29, 8870–8876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grant, L.R.; Slack, M.P.E.; Theilacker, C.; Vojicic, J.; Dion, S.; Reinert, R.-R.; Jodar, L.; Gessner, B.D. Distribution of Serotypes Causing Invasive Pneumococcal Disease in Children from High-Income Countries and the Impact of Pediatric Pneumococcal Vaccination. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2023, 76, e1062–e1070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Two New Pneumococcal Vaccines—Prevnar 20 and Vaxneuvance. JAMA 2021, 326, 2521–2522. [CrossRef]
- Fitz-Patrick, D.; Young, M.; Scott, D.A.; Scully, I.L.; Baugher, G.; Peng, Y.; Jansen, K.U.; Gruber, W.; Watson, W. A Randomized Phase 1 Study of the Safety and Immunogenicity of 2 Novel Pneumococcal Conjugate Vaccines in Healthy Japanese Adults in the United States. Hum. Vaccines Immunother. 2021, 17, 2249–2256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Lahham, A. Prevalence of Pneumococcal Carriage among Jordanian Infants in the First 6 Months of Age, 2008–2016. Vaccines 2021, 9, 1283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russell, F.; Sanderson, C.; Temple, B.; Mulholland, K. Global Review of the Distribution of Pneumococcal Disease by Age and Region; WHO Pneumococcal Epidemiology Report 31102011 v3 (2011); WHO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Active Bacterial Core Surveillance (ABCs) Report Emerging Infections Program Network Streptococcus Pneumoniae, 2010 (ORIG); Centers for Disease Control and Prevention: Atlanta, GA, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Elashoff, J.D.; Lemeshow, S. Sample Size Determination in Epidemiologic Studies. In Handbook of Epidemiology; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2007; pp. 559–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lachenbruch, P.A.; Lwanga, S.K.; Lemeshow, S. Sample Size Determination in Health Studies: A Practical Manual. J. Am. Stat. Assoc. 1991, 86, 1149–1150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasiulevičius, V.; Sapoka, V.; Filipavičiūtė, R. Sample Size Calculation in Epidemiological Studies. Gerontologija 2006, 7, 225–231. [Google Scholar]
- Direct and Indirect Effects of Routine Vaccination of Children with 7-Valent Pneumococcal Conjugate Vaccine on Incidence of Invasive Pneumococcal Disease—United States, 1998–2003. JAMA J. Am. Med. Assoc. 2005, 294, 2022–2026. [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Robinson, K.A.; Baughman, W.; Rothrock, G.; Barrett, N.L.; Pass, M.; Lexau, C.; Damaske, B.; Stefonek, K.; Barnes, B.; Patterson, J.; et al. Epidemiology of Invasive Streptococcus Pneumoniae Infections in the United States, 1995–1998 Opportunities for Prevention in the Conjugate Vaccine Era. JAMA 2001, 285, 1729–1735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z. Martin Bland (2015): An Introduction to Medical Statistics. Stat. Pap. 2017, 58, 953–954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Driscoll, A.J.; Karron, R.A.; Morpeth, S.C.; Bhat, N.; Levine, O.S.; Baggett, H.C.; Brooks, W.A.; Feikin, D.R.; Hammitt, L.L.; Howie, S.R.C.; et al. Standardization of Laboratory Methods for the PERCH Study. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2017, 64, S245–S252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carvalho, M.D.G.S.; Tondella, M.L.; McCaustland, K.; Weidlich, L.; McGee, L.; Mayer, L.W.; Steigerwalt, A.; Whaley, M.; Facklam, R.R.; Fields, B.; et al. Evaluation and Improvement of Real-Time PCR Assays Targeting LytA, Ply, and PsaA Genes for Detection of Pneumococcal DNA. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2007, 45, 2460–2466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leach, R. Critical Care Medicine at a Glance; Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2014; ISBN 13: 978-1118302767. [Google Scholar]
- Satzke, C.; Turner, P.; Virolainen-Julkunen, A.; Adrian, P.V.; Antonio, M.; Hare, K.M.; Henao-Restrepo, A.M.; Leach, A.J.; Klugman, K.P.; Porter, B.D.; et al. Standard Method for Detecting Upper Respiratory Carriage of Streptococcus Pneumoniae: Updated Recommendations from the World Health Organization Pneumococcal Carriage Working Group. Vaccine 2013, 32, 165–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Austrian, R. The Quellung Reaction, a Neglected Microbiologic Technique. Mt. Sinai J. Med. 1976, 43, 699–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Habib, M.; Porter, B.D.; Satzke, C. Capsular Serotyping of Streptococcus Pneumoniae Using the Quellung Reaction. J. Vis. Exp. 2014, 84, e51208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaltoft, M.S.; Skov Sørensen, U.B.; Slotved, H.C.; Konradsen, H.B. An Easy Method for Detection of Nasopharyngeal Carriage of Multiple Streptococcus Pneumoniae Serotypes. J. Microbiol. Methods 2008, 75, 540–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ben Shimol, S.; Dagan, R.; Givon-Lavi, N.; Tal, A.; Aviram, M.; Bar-Ziv, J.; Zodicov, V.; Greenberg, D. Evaluation of the World Health Organization Criteria for Chest Radiographs for Pneumonia Diagnosis in Children. Eur. J. Pediatr. 2012, 171, 369–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, V.; Abbas, A.K.; Aster, J.C. Robbins Basic Pathology E-Book; Elsevier Health Sciences: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Mihai Danciu, M.-S.M. Atlas of Pathology. 2004–2012, 2nd ed. 2004. Available online: http://www.pathologyatlas.ro (accessed on 20 March 2023).
- Mbata, G.; Chukwuka, C.; Onyedum, C.; Onwubere, B.; Aguwa, E. The Role of Complications of Community Acquired Pneumonia on the Outcome of the Illness: A Prospective Observational Study in a Tertiary Institution in Eastern Nigeria. Ann. Med. Health Sci. Res. 2013, 3, 365–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cunha, B.A. Severe Community-Acquired Pneumonia. Crit. Care Clin. 1998, 14, 105–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asadollahi, K.; Hastings, I.M.; Beeching, N.J.; Gill, G.V.; Asadollahi, P. Leukocytosis as an Alarming Sign for Mortality in Patients Hospitalized in General Wards. Iran J. Med. Sci. 2011, 36, 45–49. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Feldman, C.; Anderson, R. Recent Advances in the Epidemiology and Prevention of Streptococcus Pneumoniae Infections. F1000Res 2020, 9, 338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Troeger, C.; Blacker, B.F.; Khalil, I.A.; Rao, P.C.; Cao, S.; Zimsen, S.R.; Albertson, S.B.; Stanaway, J.D.; Deshpande, A.; Abebe, Z.; et al. Estimates of the Global, Regional, and National Morbidity, Mortality, and Aetiologies of Diarrhoea in 195 Countries: A Systematic Analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2016. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2018, 18, 1211–1228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geno, K.A.; Gilbert, G.L.; Song, J.Y.; Skovsted, I.C.; Klugman, K.P.; Jones, C.; Konradsen, H.B.; Nahm, M.H. Pneumococcal Capsules and Their Types: Past, Present, and Future. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2015, 28, 871–899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pilishvili, T.; Gierke, R.; Farley, M.M.; Schaffner, W.; Thomas, A.; Reingold, A.; Harrison, L.; Holtzman, C.; Burzlaff, K.; Petit, S.; et al. 1470. Epidemiology of Invasive Pneumococcal Disease (IPD) Following 18 Years of Pneumococcal Conjugate Vaccine (PCV) Use in the United States. Open Forum Infect. Dis. 2020, 7, S736–S737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masaadeh, H.A.; Hayajneh, W.A.; Al Azzam, I.A.; Ahed, J. Alkhatib Prevalence of Streptococcus Pneumoniae Serotypes (Nasopharyngeal Colonization) in Children in North Jordan: Genotypic and Phenotypic Characteristics. Res. J. Biol. Sci. 2016, 11, 23–33. [Google Scholar]
- Hausdorff, W.P.; Bryant, J.; Paradiso, P.R.; Siber, G.R. Which Pneumococcal Serogroups Cause the Most Invasive Disease: Implications for Conjugate Vaccine Formulation and Use, Part I. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2000, 30, 100–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Hoek, A.J.; Andrews, N.; Waight, P.A.; George, R.; Miller, E. Effect of Serotype on Focus and Mortality of Invasive Pneumococcal Disease: Coverage of Different Vaccines and Insight into Non-Vaccine Serotypes. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e39150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Htar, M.T.T.; Christopoulou, D.; Schmitt, H.J. Pneumococcal Serotype Evolution in Western Europe. BMC Infect. Dis. 2015, 15, 419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lagousi, T.; Papadatou, I.; Strempas, P.; Chatzikalil, E.; Spoulou, V. Pneumococcal Immunization Strategies for High-Risk Pediatric Populations Worldwide: One Size Does Not Fit All. Vaccines 2021, 9, 1390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jauregui, B.; Garcia, A.G.F.; Bess Janusz, C.; Blau, J.; Munier, A.; Atherly, D.; Mvundura, M.; Hajjeh, R.; Lopman, B.; Clark, A.D.; et al. Evidence-Based Decision-Making for Vaccine Introductions: Overview of the ProVac International Working Group’s Experience. Vaccine 2015, 33, A28–A33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Velusamy, S.; Tran, T.; Mongkolrattanothai, T.; Walker, H.; McGee, L.; Beall, B. Expanded Sequential Quadriplex Real-Time Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR) for Identifying Pneumococcal Serotypes, Penicillin Susceptibility, and Resistance Markers. Diagn. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2020, 97, 115037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shormin, M.; Afroz, S.; Shamsuzzaman, S.M.; Sultana, N. Detection of Pneumococcal Carriage among under Five Healthy Children with Multiple Co-Colonizing Serotypes with Impact of Pneumococcal Conjugate Vaccine. Microbes Infect. Dis. 2020, 2, 49–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coskun-Ari, F.F.; Guldemir, D.; Durmaz, R. One-Step Multiplex PCR Assay for Detecting Streptococcus Pneumoniae Serogroups/Types Covered by 13-Valent Pneumococcal Conjugate Vaccine (PCV13). PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e50406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Esteghamati, A.; Nazari-Alam, A.; Badamchi, A.; Faramarzi, M.; Alipoor, M.; Moghaddam, A.B.; Tavakoli, A.; Rahbar, M.; Aghmiyuni, Z.F.; Sayyafar, S. Determination of Streptococcus Pneumonia Serotypes Isolated from Clinical Specimens: A Step Toward the Production of a Native Vaccine in Iran. Arch. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2021, 16, 112897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pai, R.; Gertz, R.E.; Beall, B. Sequential Multiplex PCR Approach for Determining Capsular Serotypes of Streptococcus Pneumoniae Isolates. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2006, 44, 124–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Pneumococcal Vaccine | Covered Serotypes |
|---|---|
| PCV-7 [8] | 4, 6B, 9V, 14, 18C, 19F, and 23F |
| PCV-10 [9] | PCV-7 plus 1, 5, and 7F |
| PCV-13 [10] | PCV-10 plus 3, 6A, and 19A |
| PCV-15 [14] | PCV-13 plus 22F and 33F |
| PCV-20 [17] | PCV-15 plus 8, 10A, 11A, 12F, and 15 |
| Variable | Category | N (%) |
|---|---|---|
| Sex | Male | 584 (57.5%) |
| Female | 431 (42.5%) | |
| Birth history | Full term | 937 (92.3%) |
| Preterm | 78 (7.7%) | |
| Mode of delivery | Normal VD | 683 (67.3%) |
| Caesarean section | 332 (32.2%) | |
| Congenital conditions | Yes | 78 (7.7%) |
| Congenital heart disease | Yes | 43 (4.2%) |
| Chronic illness | Yes | 128 (12.6%) |
| Asthma | Yes | 25 (2.5%) |
| Family members’ smoking place | Inside home | 438 (43.2%) |
| Only outside home | 42 (4.1%) | |
| Not smoker | 535 (52.7%) | |
| Patient received antibiotics within a week of admission | Yes | 213 (21.0%) |
| Previous hospitalization | Yes | 220 (21.7%) |
| Patient receives regular medications | Yes | 59 (5.8%) |
| Fever | Yes | 715 (70.4%) |
| Blood culture | Positive | 23 (2.2%) |
| Negative | 987 (97.3%) | |
| Not performed | 5 (0.5%) | |
| Complications during admission | Yes | 117 (11.5%) |
| Required ICU admission | Not admitted | 774 (76.2%) |
| Admitted and intubated | 95 (9.4%) | |
| Admitted and not intubated | 146 (14.4%) | |
| WBC (leukocytosis) | Negative | 255 (25.1%) |
| Positive | 760 (74.9%) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Abu-Helalah, M.; Al-Mnayyis, A.; Alzoubi, H.; Al-Abdallah, R.; Jdaitawi, H.; Nafi, O.; Abu-Sal, K.; Altawalbeh, A.; Khlaifat, A.; Al-Zayadneh, E.; et al. Epidemiology of Streptococcus pneumoniae Serotypes in Jordan Amongst Children Younger than the Age of 5: A National Cross-Sectional Study. Vaccines 2023, 11, 1396. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines11091396
Abu-Helalah M, Al-Mnayyis A, Alzoubi H, Al-Abdallah R, Jdaitawi H, Nafi O, Abu-Sal K, Altawalbeh A, Khlaifat A, Al-Zayadneh E, et al. Epidemiology of Streptococcus pneumoniae Serotypes in Jordan Amongst Children Younger than the Age of 5: A National Cross-Sectional Study. Vaccines. 2023; 11(9):1396. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines11091396
Chicago/Turabian StyleAbu-Helalah, Munir, Asma’a Al-Mnayyis, Hamed Alzoubi, Ruba Al-Abdallah, Hussein Jdaitawi, Omar Nafi, Kamel Abu-Sal, Alaa Altawalbeh, Alia Khlaifat, Enas Al-Zayadneh, and et al. 2023. "Epidemiology of Streptococcus pneumoniae Serotypes in Jordan Amongst Children Younger than the Age of 5: A National Cross-Sectional Study" Vaccines 11, no. 9: 1396. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines11091396
APA StyleAbu-Helalah, M., Al-Mnayyis, A., Alzoubi, H., Al-Abdallah, R., Jdaitawi, H., Nafi, O., Abu-Sal, K., Altawalbeh, A., Khlaifat, A., Al-Zayadneh, E., Almaaitah, I., Borghol, I., Batarseh, F., Okkeh, O., Dalal, A., Alhendi, A., Almaaitah, M., Al-Lahham, A., Gazo, M., ... Elnasser, Z. (2023). Epidemiology of Streptococcus pneumoniae Serotypes in Jordan Amongst Children Younger than the Age of 5: A National Cross-Sectional Study. Vaccines, 11(9), 1396. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines11091396






