Predictors of Tetanus Vaccine Uptake among Pregnant Women in Khartoum State, Sudan: A Hospital-Based Cross-Sectional Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design
2.2. Population and Sampling
2.2.1. Population
2.2.2. Sampling and Sample Size
- n = sample size
- z = (1 − α) is the z-score corresponding to a 95% confidence interval and was computed as 1.96.
- p = 0.288 which is the probability/percentage of women who received at least two doses of the TT vaccine during their last pregnancy in Khartoum State based on the 2014 MICS report.
- q = (1 − p) = 0.712
- d = desired margin of error of 0.05.
2.3. Data Collection
2.4. Statistical Analysis
2.5. Ethical Consideration
3. Results
3.1. Characteristics of the Study Participants
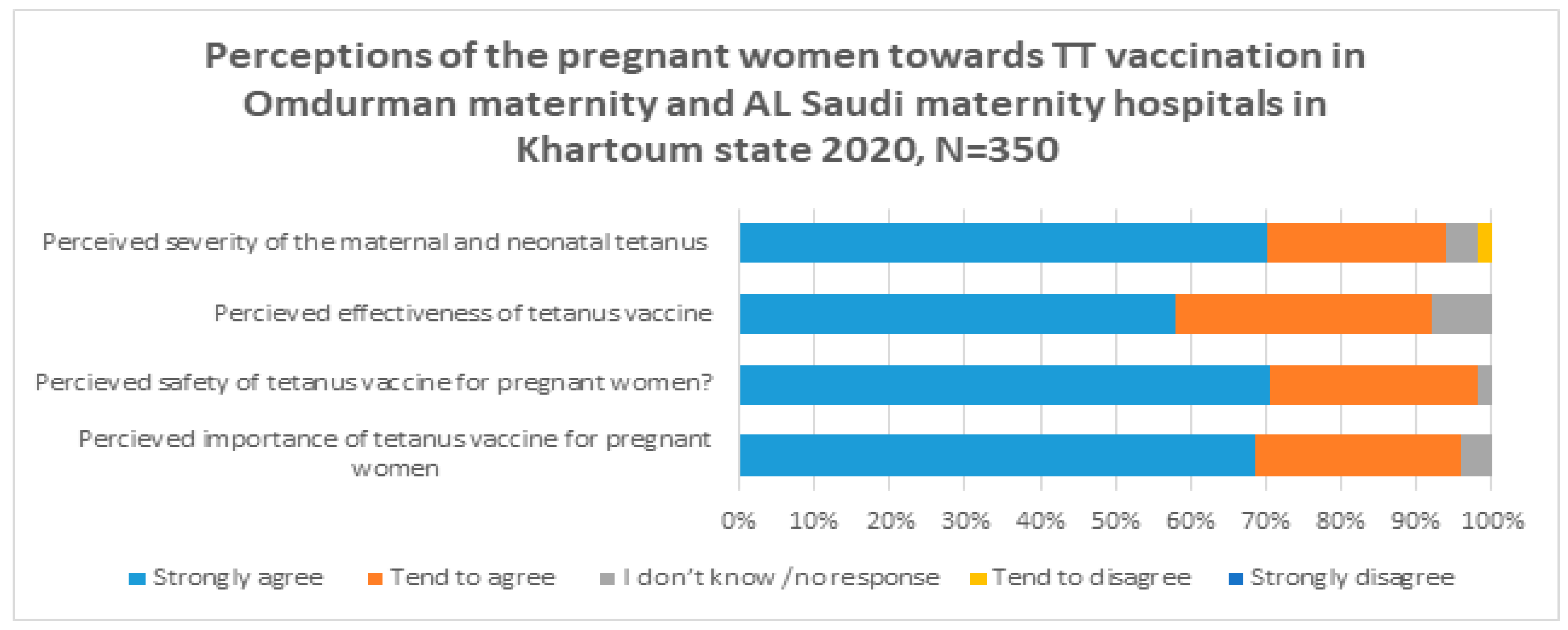
3.2. Perception of the Pregnant Women in Sudan towards the TT Vaccine
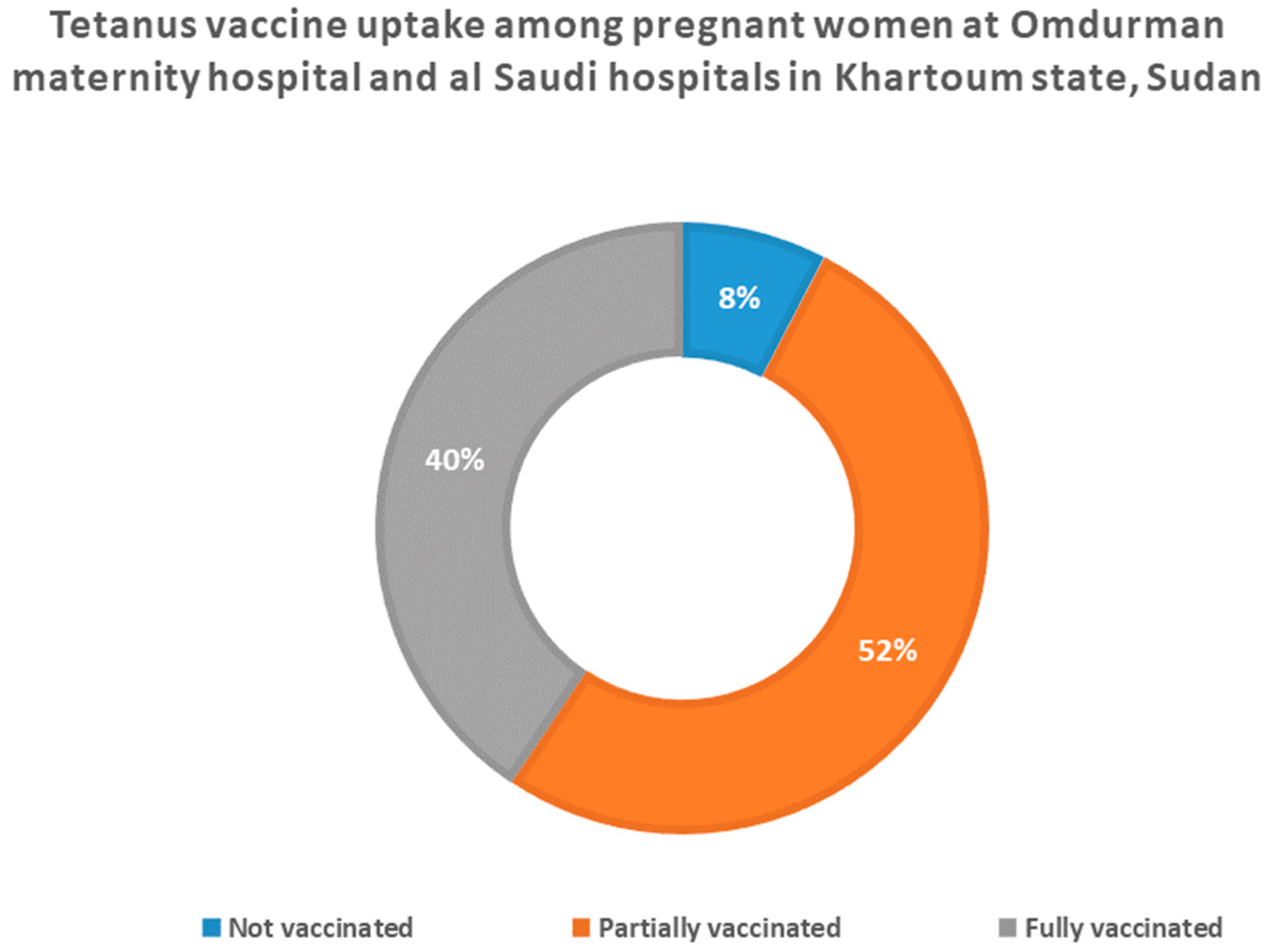
3.3. Tetanus Vaccine Uptake
3.4. Factors Associated with Tetanus Vaccine Uptake among Pregnant Women in Sudan
3.5. Predictors of Tetanus Vaccine Uptake among Pregnant Women in Sudan
4. Discussion
Limitation
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Li, J.; Liu, Z.; Yu, C.; Tan, K.; Gui, S.; Zhang, S.; Shen, Y. Global epidemiology and burden of tetanus from 1990 to 2019: A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2019. Int. J. Infect. Dis. 2023, 132, 118–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dhir, S.K.; Dewan, P.; Gupta, P. Maternal and Neonatal Tetanus Elimination: Where are We Now? Res. Rep. Trop. Med. 2021, 12, 247–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- World Health Organization. Tetanus vaccines: WHO position paper, February 2017—Recommendations. Vaccine 2018, 36, 3573–3575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roper, M.; Vandelaer, J.; Gasse, F. Maternal and neonatal tetanus. Lancet 2007, 370, 1947–1959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- WHO. Maternal and Neonatal Tetanus Elimination (MNTE). 2019. Available online: https://www.who.int/immunization/diseases/MNTE_initiative/en/ (accessed on 18 June 2019).
- Ridpath, A.D.; Scobie, H.M.; Shibeshi, M.E.; Yakubu, A.; Zulu, F.; Raza, A.A.; Masresha, B.; Tohme, R. Progress towards achieving and maintaining maternal and neonatal tetanus elimination in the African region. Pan Afr. Med. J. 2017, 27 (Suppl. 3), 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Milstien, J.; Griffin, P.D.; Lee, J.-W. Damage to immunisation programmes from misinformation on contraceptive vaccines. Reprod. Health Matters 1995, 3, 24–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larson, H.J. Maternal immunization: The new ”normal” (or it should be). Vaccine 2015, 33, 6374–6375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sudan: WHO and UNICEF Estimate of Immunization Coverage: 2019 Revision. Available online: www.sho.gov.sd (accessed on 15 February 2022).
- FMOH. Simple Spatial Survey Method (S3M II) for Sudan—2018. 2018. Available online: http://sho.gov.sd (accessed on 20 May 2022).
- Central Bureau of Statistics (CBS); UNICEF Sudan. Multiple Indicator Cluster Survey 2014 Sudan; Final Report; CBS and UNICEF Sudan: Khartoum, Sudan, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Daniel, W.W.; Cross, C.L. Biostatistics: A Foundation for Analysis in the Health Sciences; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2018; Available online: https://www.wiley.com/en-sd/Biostatistics%3A+A+Foundation+for+Analysis+in+the+Health+Sciences%2C+11th+Edition-p-9781119496571 (accessed on 22 May 2022).
- Gallup. Wellcome Global Monitor—First Wave Findings. 19 June 2019. Available online: https://wellcome.ac.uk/sites/default/files/wellcome-global-monitor-2018.pdf (accessed on 22 May 2022).
- Gebremedhin, T.S.; Welay, F.T.; Mengesha, M.B.; Assefa, N.E.; Werid, W.M. Tetanus Toxoid Vaccination Uptake and Associated Factors among Mothers Who Gave Birth in the Last 12 Months in Errer District, Somali Regional State, Eastern Ethiopia. BioMed Res. Int. 2020, 2020, 4023031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mamoro, M.D.; Hanfore, L.K. Tetanus Toxoid Immunization Status and Associated Factors among Mothers in Damboya Woreda, Kembata Tembaro Zone, SNNP, Ethiopia. J. Nutr. Metab. 2018, 2018, 2839579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nigussie, J.; Girma, B.; Molla, A.; Mareg, M. Tetanus Toxoid Vaccination Coverage and Associated Factors among Childbearing Women in Ethiopia: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. BioMed Res. Int. 2021, 2021, 5529315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yusuf, N.; Raza, A.A.; Chang-Blanc, D.; Ahmed, B.; Hailegebriel, T.; Luce, R.R.; Tanifum, P.; Masresha, B.; Faton, M.; Omer, M.D.; et al. Progress and barriers towards maternal and neonatal tetanus elimination in the remaining 12 countries. Lancet Glob. Health 2021, 9, e1610–e1617, Erratum in Lancet Glob. Health 2022, 10, e185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teshale, A.B.; Tesema, G.A. Determinants of births protected against neonatal tetanus in Ethiopia: A multilevel analysis using EDHS 2016 data. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0243071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Glatman-Freedman, A.; Nichols, K. The effect of social determinants on immunization programs. Hum. Vaccines Immunother. 2012, 8, 293–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Participants’ Profile | TT Immunization Status | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fewer than the Recommended Doses (≤2 Doses) N (%) = 186 (59.4%) | Recommended Doses (≥3 Doses) N (%) = 127 (40.6%) | Total N (%) | p-Value | ||
| Hospital | Omdurman Maternity Hospital | 92 (53.2%) | 81 (46.8%) | 173 (55.2%) | 0.012 * |
| Al Saudi Hospital | 94 (67.1%) | 46 (32.9%) | 140 (44.7%) | ||
| Mother’s Education | Not educated | 4 (66.7%) | 2 (33.3%) | 6 (1.9%) | 0.001 * a |
| Primary | 68 (72.3%) | 26 (27.7%) | 94 (30%) | ||
| Secondary | 49 (69.0%) | 22 (31.0%) | 71 (22.68%) | ||
| University | 65 (45.8%) | 77 (54.2%) | 142 (45.36%) | ||
| Family income | High | 9 (69.2%) | 4 (30.8%) | 13 (4.15%) | 0.134 |
| Medium | 164 (57.7%) | 120 (42.3%) | 284 (90.7%) | ||
| Low | 13 (81.3%) | 3 (18.8%) | 16 (5.11%) | ||
| Number of children | 1–2 children | 86 (64.2%) | 48 (35.8%) | 134 (42.8%) | 0.001* a |
| 3–4 children | 63 (72.4%) | 24 (27.6%) | 87 (27.79%) | ||
| 5 children and more | 37 (40.2%) | 55 (59.8%) | 92 (29.39%) | ||
| Mother’s employment | Not employed | 155 (58.3%) | 111 (41.7%) | 266 (85.0%) | 0.322 |
| Employed | 31 (66.0%) | 16 (34.0%) | 47 (15.0%) | ||
| Predictors | OR (95% C.I. of OR) | aOR (95% C.I. of aOR) |
|---|---|---|
| Hospital | ||
| Omdurman Maternity Hospital | ||
| Al Saudi Hospital | 0.56 (0.350–0.882) * | 0.49 (0.29–0.82) * |
| Mother’s Education | ||
| Not educated ® | ||
| Primary | 0.77 (0.13–4.43) | 0.5 (0.07–3.51) |
| Secondary | 0.89 (0.15–5.27) | 0.62 (0.09–4.72) |
| University | 2.37 (0.42–13.35) | 2.05 (0.30–13.99) |
| Number of Children | ||
| Have not had children yet ® | ||
| 1–2 children | 2.9 (1.522–5.520) * | 3.31 (1.67–6.56) * |
| 3–4 children | 4.77 (2.34–9.75) * | 5.05 (2.37–10.79) * |
| 5 children and more | 5.11 (2.26–11.54) * | 10.54 (4.30–25.86) * |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ibrahim, Z.A.; Sabahelzain, M.M.; Elhadi, Y.A.M.; Malande, O.O.; Babiker, S. Predictors of Tetanus Vaccine Uptake among Pregnant Women in Khartoum State, Sudan: A Hospital-Based Cross-Sectional Study. Vaccines 2023, 11, 1268. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines11071268
Ibrahim ZA, Sabahelzain MM, Elhadi YAM, Malande OO, Babiker S. Predictors of Tetanus Vaccine Uptake among Pregnant Women in Khartoum State, Sudan: A Hospital-Based Cross-Sectional Study. Vaccines. 2023; 11(7):1268. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines11071268
Chicago/Turabian StyleIbrahim, Zienab A., Majdi M. Sabahelzain, Yasir Ahmed Mohammed Elhadi, Ombeva Oliver Malande, and Suad Babiker. 2023. "Predictors of Tetanus Vaccine Uptake among Pregnant Women in Khartoum State, Sudan: A Hospital-Based Cross-Sectional Study" Vaccines 11, no. 7: 1268. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines11071268
APA StyleIbrahim, Z. A., Sabahelzain, M. M., Elhadi, Y. A. M., Malande, O. O., & Babiker, S. (2023). Predictors of Tetanus Vaccine Uptake among Pregnant Women in Khartoum State, Sudan: A Hospital-Based Cross-Sectional Study. Vaccines, 11(7), 1268. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines11071268








