Immunogenicity and Blocking Efficacy of Norovirus GII.4 Recombinant P Protein Vaccine
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Viruses, Cells, and Experimental Animals
2.2. Expression and Purification of Recombinant P Protein of NoVs
2.3. Determining the Receptor Binding Capacity of Recombinant P Protein Using Indirect ELISA
2.4. Production and Determination of Neutralizing Antibodies to NoV Recombinant P Protein
2.5. Detecting Blocking Efficacy of Neutralizing Antibody
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
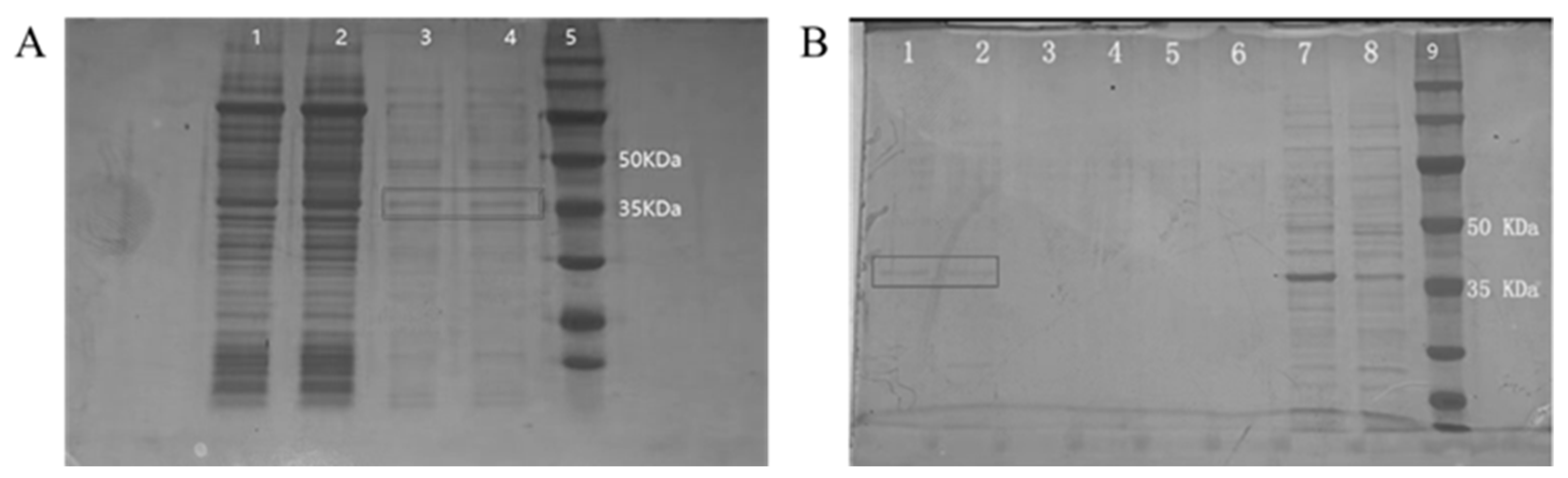
3.1. Expression and Purification of Recombinant P Protein
3.2. Binding Capacity of Recombinant P Protein to HBGAs
3.3. Neutralizing Antibody Preparation and Titer Determination
3.4. Blocking Efficacy of Neutralizing Antibody to HuNoV
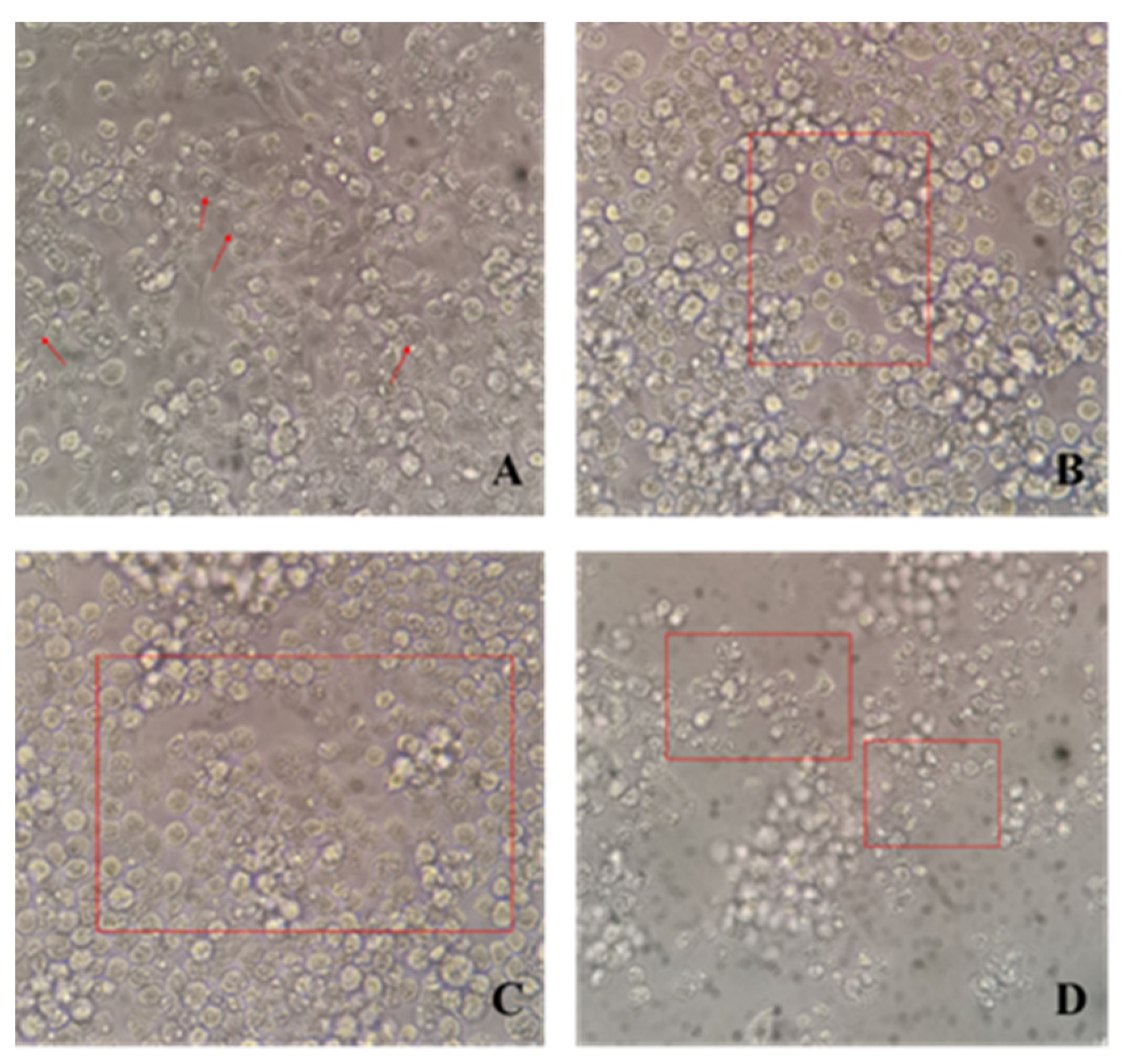
3.5. Blocking Efficacy of Neutralizing Antibody to MNV Invasion
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cao, R.-R.; Ma, X.-Z.; Li, W.-Y.; Wang, B.-N.; Yang, Y.; Wang, H.-R.; Kuang, Y.; You, J.-Z.; Zhao, Z.-Y.; Ren, M.; et al. Epidemiology of norovirus gastroenteritis in hospitalized children under five years old in western China, 2015–2019. J. Microbiol. Immunol. Infect. 2021, 54, 918–925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seitz, S.R.; Leon, J.S.; Schwab, K.J.; Lyon, G.M.; Dowd, M.; McDaniels, M.; Abdulhafid, G.; Fernandez, M.L.; Lindesmith, L.C.; Baric, R.S.; et al. Norovirus Infectivity in Humans and Persistence in Water. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2011, 77, 6884–6888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Atmar, R.L.; Ramani, S.; Estes, M.K. Human noroviruses: Recent advances in a 50-year history. Curr. Opin. Infect. Dis. 2018, 31, 422–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.; Liu, D.; Wu, Q.; Lu, Y.; Tian, P.; Wang, Z.; Wang, D. Characterization of a Histo-Blood Group Antigen-like Sub-stance in Romaine Lettuce That Contributes to Human Norovirus Attachment. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2020, 68, 1207–1212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ettayebi, K.; Tenge, V.R.; Cortes-Penfield, N.W.; Crawford, S.E.; Neill, F.H.; Zeng, X.-L.; Yu, X.; Ayyar, B.V.; Burrin, D.; Ramani, S.; et al. New Insights and Enhanced Human Norovirus Cultivation in Human Intestinal Enteroids. Msphere 2021, 6, 1120–1136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esposito, S.; Principi, N. Norovirus Vaccine: Priorities for Future Research and Development. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 1383–1392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Fu, M.; Hu, Q. Advances in Human Norovirus Vaccine Research. Vaccines 2021, 9, 732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, B.J.; Jang, Y.; Bin Kwon, S.; Yu, J.E.; Lim, J.; Roh, Y.H.; Seong, B.L. RNA-assisted self-assembly of monomeric antigens into virus-like particles as a recombinant vaccine platform. Biomaterials 2021, 269, 120650–120661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sherwood, J.; Mendelman, P.M.; Lloyd, E.; Liu, M.; Boslego, J.; Borkowski, A.; Jackson, A.; Faix, D.; US Navy Study Team. Efficacy of an intramuscular bivalent norovirus GI.1/GII.4 virus-like particle vaccine candidate in healthy US adults. Vaccine 2020, 38, 6442–6449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Q.; Ni, P.; Liu, D.; Yin, Y.; Li, Q.; Zhang, J.; Wu, Q.; Tian, P.; Shi, X.; Wang, D. A Bacterial Surface Display System Expressing Cleavable Capsid Proteins of Human Norovirus: A Novel System to Discover Candidate Receptors. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 2405–2414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Liu, Z.; Chen, J.; Zou, S.; Jin, Y.; Zhang, R.; Sheng, Y.; Liao, N.; Hu, B.; Cheng, D. Effect of Direct Viral-Bacterial Interac-tions on the Removal of Norovirus from Lettuce. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 731379–731389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, P.; Yang, D.; Shan, L.; Li, Q.; Liu, D.; Wang, D. Estimation of Human Norovirus Infectivity from Environmental Water Samples by In Situ Capture RT-qPCR Method. Food Environ. Virol. 2018, 10, 29–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Razafimahefa, R.M.; Ludwig-Begall, L.F.; Le Guyader, F.S.; Farnir, F.; Mauroy, A.; Thiry, E. Optimisation of a PMAxx-RT-qPCR Assay and the Preceding Extraction Method to Selectively Detect Infectious Murine Norovirus Particles in Mussels. Food Environ. Virol. 2021, 13, 93–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suschak, J.J.; Bixler, S.L.; Badger, C.V.; Spik, K.W.; Kwilas, S.A.; Rossi, F.D.; Twenhafel, N.; Adams, M.L.; Shoemaker, C.J.; Spiegel, E.; et al. A DNA vaccine targeting VEE virus delivered by needle-free jet-injection protects macaques against aerosol challenge. NPJ Vaccines 2022, 7, 46–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Li, X.; Zhang, H.; Hao, G.; Shang, X.; Wang, H.; Chen, H.; Qian, P. Evaluation of Immunoreactivity and Protection Efficacy of Seneca Valley Virus Inactivated Vaccine in Finishing Pigs Based on Screening of Inactivated Agents and Adjuvants. Vaccines 2022, 10, 631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saikia, K.; Saharia, N.; Singh, C.S.; Borah, P.P.; Namsa, N.D. Association of histo-blood group antigens and predisposition to gastrointestinal diseases. J. Med. Virol. 2022, 94, 5149–5162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, B.; Wang, Y.; Wang, X.; Jia, L.; Tian, Y.; Yan, H.; Li, W.; Shen, L.; Wang, Q.; Gao, Z. Excess acute diarrhoea cases attributed to norovirus variants in Beijing, China between 2011 and 2018. J. Med. Virol. 2023, 95, 28627–28633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calderwood, L.E.; Wikswo, M.E.; Mattison, C.P.; Kambhampati, A.K.; Balachandran, N.; Vinjé, J.; Barclay, L.; Hall, A.J.; Parashar, U.; Mirza, S.A. Norovirus Outbreaks in Long-term Care Facilities in the United States, 2009–2018: A Decade of Surveillance. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2022, 74, 113–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, M. Norovirus Vaccines: Current Clinical Development and Challenges. Pathogens 2021, 10, 1641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.; Wang, S.; von Seidlein, L.; Wang, X. The epidemiology of norovirus gastroenteritis in China: Disease burden and distribution of genotypes. Front. Med. 2020, 14, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ballard, S.-B.; Requena, D.; Mayta, H.; Sanchez, G.J.; Oyola-Lozada, M.G.; Aliaga, F.D.C.; Cabrera, L.; Mondonedo, M.D.V.; Taquiri, C.; Tilley, C.D.H.; et al. Enteropathogen Changes After Rotavirus Vaccine Scale-up. Pediatrics 2022, 149, e2020049884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eigner, U.; Verstraeten, T.; Weil, J. Decrease in norovirus infections in Germany following COVID-19 containment measures. J. Infect. 2021, 82, 276–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kraay, A.N.M.; Han, P.; Kambhampati, A.K.; Wikswo, M.E.; Mirza, S.A.; Lopman, B.A. Impact of Nonpharmaceutical Inter-ventions for Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2 on Norovirus Outbreaks: An Analysis of Outbreaks Reported By 9 US States. J. Infect. Dis. 2021, 224, 9–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, F.; Jiang, B.; Guo, X.; Hou, L.; Tian, Y.; Zhang, J.; Li, Q.; Jia, L.; Yang, P.; Wang, Q.; et al. Norovirus outbreaks in China, 2000–2018: A systematic review. Rev. Med. Virol. 2022, 32, 2382–2393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nordgren, J.; Svensson, L. Genetic Susceptibility to Human Norovirus Infection: An Update. Viruses 2019, 11, 226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, M.; Jiang, X. Norovirus P particle: A subviral nanoparticle for vaccine development against norovirus, rotavirus and influenza virus. Nanomedicine 2012, 7, 889–897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavicchio, L.; Laconi, A.; Piccirillo, A.; Beato, M.S. Swine Norovirus: Past, Present, and Future. Viruses 2022, 14, 537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shanker, S.; Choi, J.-M.; Sankaran, B.; Atmar, R.L.; Estes, M.K.; Prasad, B.V.V. Structural Analysis of Histo-Blood Group Antigen Binding Specificity in a Norovirus GII.4 Epidemic Variant: Implications for Epochal Evolution. J. Virol. 2011, 85, 8635–8645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, M.; Jiang, X. Norovirus Capsid Protein-Derived Nanoparticles and Polymers as Versatile Platforms for Antigen Presenta-tion and Vaccine Development. Pharmaceutics 2019, 11, 472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Devant, J.M.; Hansman, G.S. Structural heterogeneity of a human norovirus vaccine candidate. Virology 2021, 553, 23–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campillay-Véliz, C.P.; Carvajal, J.J.; Avellaneda, A.M.; Escobar, D.; Covián, C.; Kalergis, A.M.; Lay, M.K. Human Norovirus Proteins: Implications in the Replicative Cycle, Pathogenesis, and the Host Immune Response. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 961–975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cortes-Penfield, N.W.; Ramani, S.; Estes, M.K.; Atmar, R.L. Prospects and Challenges in the Development of a Norovirus Vac-cine. Clin. Ther. 2017, 39, 1537–1549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, M.; Fang, P.; Chachiyo, T.; Xia, M.; Huang, P.; Fang, Z.; Jiang, W.; Jiang, X. Noroviral P particle: Structure, function and applications in virus-host interaction. Virology 2008, 382, 115–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heggelund, J.E.; Varrot, A.; Imberty, A.; Krengel, U. Histo-blood group antigens as mediators of infections. Curr. Opin. Struct. Biol. 2017, 44, 190–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Le Pendu, J. Histo-blood group antigen and human milk oligosaccharides: Genetic polymorphism and risk of infectious dis-eases. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2004, 554, 135–143. [Google Scholar]
- Jin, M.; Zhou, Y.-K.; Xie, H.-P.; Fu, J.-G.; He, Y.-Q.; Zhang, S.; Jing, H.-B.; Kong, X.-Y.; Sun, X.-M.; Li, H.-Y.; et al. Characterization of the new GII.17 norovirus variant that emerged recently as the predominant strain in China. J. Gen. Virol. 2016, 97, 2620–2632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansman, G.S.; Biertümpfel, C.; Georgiev, I.; McLellan, J.S.; Chen, L.; Zhou, T.; Katayama, K.; Kwong, P.D. Crystal Structures of GII.10 and GII.12 Norovirus Protruding Domains in Complex with Histo-Blood Group Antigens Reveal Details for a Potential Site of Vulnerability. J. Virol. 2011, 85, 6687–6701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frenck, R.; Bernstein, D.I.; Xia, M.; Huang, P.; Zhong, W.; Parker, S.; Dickey, M.; McNeal, M.; Jiang, X. Predicting Susceptibility to Norovirus GII.4 by Use of a Challenge Model Involving Humans. J. Infect. Dis. 2012, 206, 1386–1393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atmar, R.L.; Bernstein, D.I.; Harro, C.D.; Al-Ibrahim, M.S.; Chen, W.H.; Ferreira, J.; Estes, M.K.; Graham, D.Y.; Opekun, A.R.; Richardson, C.; et al. Norovirus Vaccine against Experimental Human Norwalk Virus Illness. N. Engl. J. Med. 2011, 365, 2178–2187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reeck, A.; Kavanagh, O.; Estes, M.K.; Opekun, A.R.; Gilger, M.A.; Graham, D.Y.; Atmar, R.L. Serological Correlate of Protection against Norovirus-Induced Gastroenteritis. J. Infect. Dis. 2010, 202, 1212–1218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costantini, V.P.; Cooper, E.M.; Hardaker, H.L.; Lee, L.E.; DeBess, E.E.; Cieslak, P.R.; Hall, A.J.; Vinjé, J. Humoral and Mucosal Immune Responses to Human Norovirus in the Elderly. J. Infect. Dis. 2020, 221, 1864–1874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Labayo, H.K.M.; Pajuelo, M.J.; Tohma, K.; Ford-Siltz, L.A.; Gilman, R.H.; Cabrera, L.; Mayta, H.; Sanchez, G.J.; Cornejo, A.T.; Bern, C.; et al. Norovirus-specific immunoglobulin A in breast milk for protection against norovirus-associated diarrhea among infants. EClinicalMedicine 2020, 27, 100561–100571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lindesmith, L.; Moe, C.; Marionneau, S.; Ruvoen, N.; Jiang, X.; Lindblad, L.; Stewart, P.; LePendu, J.; Baric, R. Human suscepti-bility and resistance to Norwalk virus infection. Nat. Med. 2003, 9, 548–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramani, S.; Estes, M.K.; Atmar, R.L. Correlates of Protection against Norovirus Infection and Disease-Where Are We Now, Where Do We Go? PLoS Pathog. 2016, 12, 1005334–1005340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Primer | Sequence (5′-3′) |
|---|---|
| HuNoV-F | CAAGAGTCAATGTTTAGGTGGATGAG |
| HuNoV-R | TCGACGCCATCTTCATTCACA |
| HuNoV-P | FAM-AGATTGCGATCGCCCTCCCA-TAMRAR |
| MNV-F | CCGCCATGGTCCTGGAGAATG |
| MNV-R | GCACAACGGCACTACCAATCTTG |
| MNV-P | RoX-CGTCGTCGCCTCGGTCCTTGTCAA-BHQ2 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yu, Z.; Shao, Q.; Xu, Z.; Chen, C.; Li, M.; Jiang, Y.; Cheng, D. Immunogenicity and Blocking Efficacy of Norovirus GII.4 Recombinant P Protein Vaccine. Vaccines 2023, 11, 1053. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines11061053
Yu Z, Shao Q, Xu Z, Chen C, Li M, Jiang Y, Cheng D. Immunogenicity and Blocking Efficacy of Norovirus GII.4 Recombinant P Protein Vaccine. Vaccines. 2023; 11(6):1053. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines11061053
Chicago/Turabian StyleYu, Zhendi, Qingyi Shao, Zhangkai Xu, Chenghao Chen, Mingfan Li, Yi Jiang, and Dongqing Cheng. 2023. "Immunogenicity and Blocking Efficacy of Norovirus GII.4 Recombinant P Protein Vaccine" Vaccines 11, no. 6: 1053. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines11061053
APA StyleYu, Z., Shao, Q., Xu, Z., Chen, C., Li, M., Jiang, Y., & Cheng, D. (2023). Immunogenicity and Blocking Efficacy of Norovirus GII.4 Recombinant P Protein Vaccine. Vaccines, 11(6), 1053. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines11061053






