Safety Profile of Homologous and Heterologous Booster COVID-19 Vaccines in Physicians in Quito-Ecuador: A Cross-Sectional Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design and Ethical Conditions
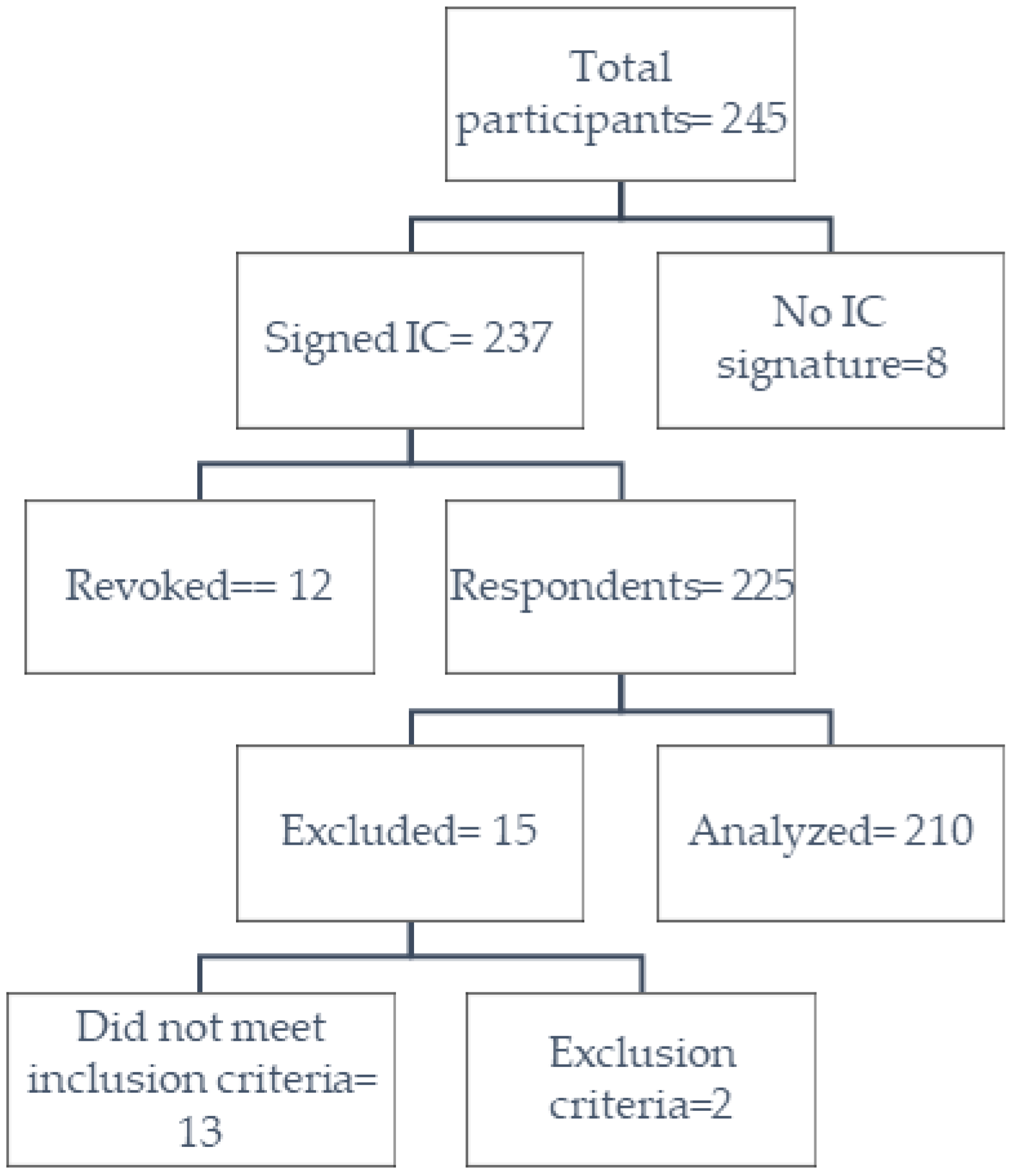
2.2. Settings, Data Source, and Participants
2.3. Measurement of Variables
2.4. Biases
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Doses Administered
3.2. Vaccine Administered
3.3. Group Vaccine
3.4. Factors Related to the Occurrence of Adverse Events
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
| Type of Regimen | First Dose | Second Dose | Booster Dose |
|---|---|---|---|
| Homologous | Oxford/AstraZeneca-Vaxzevria | Oxford/AstraZeneca-Vaxzevria | Oxford/AstraZeneca-Vaxzevria |
| Pfizer/BioNTech-Comirnaty | Pfizer/BioNTech-Comirnaty | Pfizer/BioNTech-Comirnaty | |
| Sinovac-CoronaVac | Sinovac-CoronaVac | Sinovac-CoronaVac | |
| Heterologous | Oxford/AstraZeneca-Vaxzevria | Oxford/AstraZeneca-Vaxzevria | Pfizer/BioNTech-Comirnaty |
| Pfizer/BioNTech-Comirnaty | Pfizer/BioNTech-Comirnaty | Oxford/AstraZeneca-Vaxzevria | |
| Sinovac-CoronaVac | Sinovac-CoronaVac | Pfizer/BioNTech-Comirnaty | |
| Sinovac-CoronaVac | Sinovac-CoronaVac | Oxford/AstraZeneca-Vaxzevria |
| First Dose (n = 210) | Second Dose (n = 210) | Third Dose (n = 210) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Oxford/AstraZeneca-Vaxzevria n (%) | Pfizer/BioNTech-Comirnaty n (%) | Sinovac-CoronaVac n (%) | Oxford/AstraZeneca-Vaxzevria n (%) | Pfizer/BioNTech-Comirnaty n (%) | Sinovac-CoronaVac n (%) | Oxford/AstraZeneca-Vaxzevria n (%) | Pfizer/BioNTech-Comirnaty n (%) | |
| N | 32 (100.0) | 135 (100.0) | 43 (100.0) | 32 (100.0) | 135 (100.0) | 43 (100.0) | 182 (100.0) | 28 (100.0) |
| Adverse Events | 25 (78.1) | 84 (62.2) | 17 (39.5) | 17 (53.1) | 76 (56.3) | 17 (39.5) | 142 (78.0) | 16 (57.1) |
| Pain | 18 (56.3) | 74 (54.8) | 15 (34.9) | 11 (34.4) | 64 (47.4) | 16 (37.2) | 100 (54.9) | 14 (50.0) |
| Edema | 2 (6.3) | 7 (5.2) | 2 (4.7) | 0 (0.0) | 3 (2.2) | 2 (4.7) | 21 (11.5) | 3 (10.7) |
| Erythema | 2 (6.3) | 11 (8.1) | 1 (2.3) | 0 (0.0) | 3 (2.2) | 3 (7.0) | 14 (7.7) | 2 (7.1) |
| Pruritus | 1 (3.1) | 9 (6.7) | 1 (2.3) | 3 (9.4) | 6 (4.4) | 2 (4.7) | 14 (7.7) | 3 (10.7) |
| Thermal elevation | 9 (28.1) | 19 (14.1) | 2 (4.7) | 1 (3.1) | 16 (11.9) | 2 (4.7) | 81 (44.5) | 6 (21.4) |
| Diarrhea | 2 (6.3) | 2 (1.5) | 0 (0.0) | 0 (0.0) | 2 (1.5) | 0 (0.0) | 12 (6.6) | 2 (7.1) |
| Nausea | 2 (6.3) | 2 (1.5) | 0 (0.0) | 1 (3.1) | 5 (3.7) | 0 (0.0) | 15 (8.2) | 0 (0.0) |
| Vomiting | 1 (3.1) | 0 (0.0) | 0 (0.0) | 0 (0.0) | 1 (0.7) | 0 (0.0) | 2 (1.1) | 0 (0.0) |
| Myalgia | 14 (43.8) | 29 (21.5) | 2 (4.7) | 7 (21.9) | 26 (19.3) | 3 (7.0) | 90 (49.5) | 7 (25.0) |
| Arthralgia | 12 (37.5) | 17 (12.6) | 0 (0.0) | 5 (15.6) | 11 (8.1) | 1 (2.3) | 61 (33.5) | 4 (14.3) |
| Headache | 12 (37.5) | 24 (17.8) | 7 (16.3) | 5 (15.6) | 22 (16.3) | 3 (7.0) | 77 (42.3) | 7 (25.0) |
| Other types of adverse events | 5 (15.6) | 16 (11.9) | 0 (0.0) | 2 (6.3) | 5 (3.7) | 0 (0.0) | 20 (11.0) | 3 (10.7) |
References
- WHO. WHO Coronavirus (COVID-19) Dashboard|WHO Coronavirus (COVID-19) Dashboard with Vaccination Data. Available online: https://covid19.who.int/ (accessed on 20 April 2022).
- Ministerio de Salud Pública. Situación Epidemiológica Nacional COVID-19, Ecuador. 2022. Available online: https://www.salud.gob.ec/wp-content/uploads/2022/01/10.1.2022-epi.pdf (accessed on 28 July 2022).
- COE Provincial de Pichincha. Situación Cantonal por COVID-19. Distrito Metropolitano de Quito. 2021. Available online: https://coe-pichincha.senescyt.gob.ec/situacion-cantones-pichincha/ (accessed on 28 July 2022).
- Valeria Heredia. 8 000 Vacunas Contra el Covid-19 Llegaron a Ecuador este 20 de enero. El Comercio. 2021. Available online: https://www.elcomercio.com/tendencias/sociedad/vacunas-covid19-llegaron-ecuador-quito.html (accessed on 2 February 2023).
- Ministrio de Salud Pública. Plan Nacional de Vacunación Contra la COVID-19. Plan 9/100. 2021. Available online: https://www.salud.gob.ec/wp-content/uploads/2022/04/Plan-Nacional-de-Vacunacion-plan-9-100.pdf (accessed on 3 February 2023).
- Ministerio de Salud Pública. Inicia Fase 2 del Plan de Vacunación 9/100 en Ecuador. 2021. Available online: https://www.salud.gob.ec/inicia-fase-2-del-plan-de-vacunacion-9-100-en-ecuador/ (accessed on 3 February 2023).
- PRIMICIAS. Ecuador Alcanza la Meta de Vacunar a Nueve Millones de Personas en 100 Días. 2021. Available online: https://www.primicias.ec/noticias/sociedad/ecuador-nueve-millones-vacunas-covid/ (accessed on 3 February 2023).
- Ministerio de Salud Pública. Mañana Inicia Vacunación de Refuerzo a Personas Mayores de 18 años Que Cumplieron Seis Meses de Aplicada la Segunda Dosis—Ministerio de Salud Pública. 2021. Available online: https://www.salud.gob.ec/mspmanana-inicia-vacunacion-de-refuerzo-a-personas-mayores-de-18-anos-que-cumplieron-seis-meses-de-aplicada-la-segunda-dosis/ (accessed on 3 February 2023).
- WHO. The World Health Report. 2006: Working Together for Health; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2006.
- Bandyopadhyay, S.; Baticulon, R.E.; Kadhum, M.; Alser, M.; Ojuka, D.K.; Badereddin, Y.; Kamath, A.; Parepalli, S.A.; Brown, G.; Iharchane, S.; et al. Infection and mortality of healthcare workers worldwide from COVID-19: A systematic review. BMJ Glob. Health 2020, 5, 3097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- La Federación Médica Reporta Decesos de Profesionales de la Salud por Ómicron. Ecuavisa. 2022. Available online: https://www.ecuavisa.com/noticias/ecuador/la-federacion-medica-reporta-decesos-de-profesionales-de-la-salud-por-omicron-DJ1281757 (accessed on 28 July 2022).
- WHO. Access and Allocation: How Will There Be Fair and Equitable Allocation of Limited Supplies? 2021. Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/feature-stories/detail/access-and-allocation-how-will-there-be-fair-and-equitable-allocation-of-limited-supplies (accessed on 26 July 2022).
- Wang, P.; Nair, M.S.; Liu, L.; Iketani, S.; Luo, Y.; Guo, Y.; Wang, M.; Yu, J.; Zhang, B.; Kwong, P.D.; et al. Antibody resistance of SARS-CoV-2 variants B.1.351 and B.1.1.7. Nature 2021, 593, 130–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wall, E.C.; Wu, M.; Harvey, R.; Kelly, G.; Warchal, S.; Sawyer, C.; Daniels, R.; Hobson, P.; Hatipoglu, E.; Ngai, Y.; et al. Neutralising antibody activity against SARS-CoV-2 VOCs B.1.617.2 and B.1.351 by BNT162b2 vaccination. Lancet 2021, 397, 2331–2333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khoury, D.S.; Cromer, D.; Reynaldi, A.; Schlub, T.E.; Wheatley, A.K.; Juno, J.A.; Subbarao, K.; Kent, S.J.; Triccas, J.A.; Davenport, M.P. Neutralizing antibody levels are highly predictive of immune protection from symptomatic SARS-CoV-2 infection. Nat. Med. 2021, 27, 1205–1211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ministerio de Salud Pública. Vacunómetro COVID-19. 2022. Available online: https://app.powerbi.com/view?r=eyJrIjoiYTkzNTFkMmUtZmUzNi00NDcwLTg0MDEtNjFkNzhhZTg5ZWYyIiwidCI6IjcwNjIyMGRiLTliMjktNGU5MS1hODI1LTI1NmIwNmQyNjlmMyJ9&pageName=ReportSection (accessed on 26 July 2022).
- CDC. Selected Adverse Events Reported after COVID-19 Vaccination|CDC. Vaccines. 2022. Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/coronavirus/2019-ncov/vaccines/safety/adverse-events.html (accessed on 21 April 2022).
- Nohl, A.; Brune, B.; Weichert, V.; Standl, F.; Stang, A.; Dudda, M. COVID-19: Vaccination Side Effects and Sick Leave in Frontline Healthcare-Workers-A Web-Based Survey in Germany. 2022. Available online: https://www.mdpi.com/2076-393X/10/3/411 (accessed on 21 April 2022).
- Kitro, A.; Sirikul, W.; Thongkum, W.; Soponpong, S.; Yasamut, U.; Kiratipaisarl, W.; Kosai, A.; Kasinrerk, W.; Tayapiwatana, C.; Srithanaviboonchai, K. Dynamic of Anti-Spike Receptor Binding Domain (RBD) Levels and Short-Term Adverse Events Following a Heterologous Booster Dose of BNT162b2 after Two Doses of CoronaVac in Thai Health Care Workers. Available online: https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0264410X22004388?via%3Dihub (accessed on 21 April 2022).
- Hillus, D.; Schwarz, T.; Tober-Lau, P.; Vanshylla, K.; Hastor, H.; Thibeault, C.; Jentzsch, S.; Helbig, E.T.; Lippert, L.J.; Tscheak, P.; et al. Safety, reactogenicity, and immunogenicity of homologous and heterologous prime-boost immunisation with ChAdOx1 nCoV-19 and BNT162b2: A prospective cohort study. Lancet Respir. Med. 2021, 9, 1255–1265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akbulut, S.; Gokce, A.; Boz, G.; Saritas, H.; Unsal, S.; Ozer, A.; Akbulut, M.S.; Colak, C. Evaluation of Vaccine Hesitancy and Anxiety Levels among Hospital Cleaning Staff and Caregivers during COVID-19 Pandemic. Vaccines 2022, 10, 1426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- von Elm, E.; Altman, D.G.; Egger, M.; Pocock, S.J.; Gøtzsche, P.C.; Vandenbroucke, J.P. The Strengthening the Reporting of Observational Studies in Epidemiology (STROBE) statement: Guidelines for reporting observational studies. J. Clin. Epidemiol. 2008, 61, 344–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Helsinki Statement. WMA Declaration of Helsinki—Ethical Principles for Medical Research Involving Human Subjects. 64th WMA General Assembly. Fortaleza, Brazil. 2013. Available online: https://www.wma.net/policies-post/wma-declaration-of-helsinki-ethical-principles-for-medical-research-involving-human-subjects/ (accessed on 15 December 2022).
- Food and Drug Administration. Toxicity Grading Scale for Healthy Adult and Adolescent Volunteers Enrolled in Preventive Vaccine Clinical Trials|FDA. Center for Biologics Evaluation and Research, Editor. 2007; pp. 1–10. Available online: https://www.fda.gov/regulatory-information/search-fda-guidance-documents/toxicity-grading-scale-healthy-adult-and-adolescent-volunteers-enrolled-preventive-vaccine-clinical (accessed on 19 April 2022).
- Organización Panamericana de la Salud. Introducción de la Vacuna Contra la COVID-19: Orientaciones Para Determinar los Grupos Prioritarios y Elaborar la Micro-planificación. 2021. Report No.: 1. Available online: https://www.campusvirtualsp.org/es (accessed on 27 December 2022).
- Naito, T.; Tsuchida, N.; Kusunoki, S.; Kaneko, Y.; Tobita, M.; Hori, S.; Ito, S. Reactogenicity and immunogenicity of BNT162b2 or mRNA-1273 COVID-19 booster vaccinations after two doses of BNT162b2 among healthcare workers in Japan: A prospective observational study. Expert Rev. Vaccines 2022, 21, 1319–1329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, P.-Y.; Wu, B.-J.; Su, M.-C.; Lin, Y.-H.; Chiang, S.-C.; Wu, J.-C.; Chen, T.-J.; Chen, Y.-C. Risk Factors and Incidence Rates of Self-Reported Short-Term Adverse Events of COVID-19 Vaccine Booster Dose. Vaccines 2022, 10, 1115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Warkentin, L.; Zeschick, N.; Kühlein, T.; Steininger, P.; Überla, K.; Kaiser, I.; Gall, C.; Sebastião, M.; Hueber, S. Reactogenicity after Heterologous and homologous COVID-19 Prime-Boost Vaccination Regimens: Descriptive Interim Results of a Comparative Observational Cohort Study. 2021. Available online: https://bmcinfectdis.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/s12879-022-07443-x (accessed on 5 February 2023).
- Bonelli, M.; Mrak, D.; Tobudic, S.; Sieghart, D.; Koblischke, M.; Mandl, P.; Kornek, B.; Simader, E.; Radner, H.; Perkmann, T.; et al. Additional heterologous versus homologous booster vaccination in immunosuppressed patients without SARS-CoV-2 antibody seroconversion after primary mRNA vaccination: A randomised controlled trial. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2022, 81, 687–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nachtigall, I.; Bonsignore, M.; Hohenstein, S.; Bollmann, A.; Günther, R.; Kodde, C.; Englisch, M.; Ahmad-Nejad, P.; Schröder, A.; Glenz, C.; et al. Effect of gender, age and vaccine on reactogenicity and incapacity to work after COVID-19 vaccination: A survey among health care workers. BMC Infect. Dis. 2022, 22, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cohen, G.; Jungsomsri, P.; Sangwongwanich, J.; Tawinprai, K.; Siripongboonsitti, T.; Porntharukchareon, T.; Wittayasak, K.; Thonwirak, N.; Soonklang, K.; Sornsamdang, G.; et al. Immunogenicity and reactogenicity after heterologous prime-boost vaccination with CoronaVac and ChAdox1 nCov-19 (AZD1222) vaccines. Hum. Vaccines Immunother. 2022, 18, 2052525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alqahtani, S.; Jokhdar, H.; Al-Tawfiq, J.A.; Al-Otaibi, S.; Assiri, A.; Almudarra, S.; Alabdulkareem, K.; Haji, A. Adverse events following administration of COVID-19 vaccines in Saudi Arabia. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 19551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Montano, D. Frequency and Associations of Adverse Reactions of COVID-19 Vaccines Reported to Pharmacovigilance Systems in the European Union and the United States. Front. Public Health 2022, 9, 2237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kouhpayeh, H.; Ansari, H. Adverse events following COVID-19 vaccination: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2022, 109, 108906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Villalpando, J.M.G.; Tapia, S.D.J.R.; Flores, G.D.C.B.; Castillo, J.L.B.; Rojop, I.E.J.; Junco, F.I.L.; Hernández, V.O.; Gomez, S.Q.; Quiñones, J.A.R.; Priego, C.G.G. Prevalence and Risk Factors of Adverse Effects and Allergic Reactions after COVID-19 Vaccines in a Mexican Population: An Analytical Cross-Sectional Study. 2022. Available online: https://www.mdpi.com/2076-393X/10/12/2012 (accessed on 5 February 2023).
| n (%) | ||
|---|---|---|
| General | 210 (100.0) | |
| Sex | Female | 138 (65.7) |
| Male | 72 (34.3) | |
| Age (Years) | Under 30 years of age | 88 (41.9) |
| 30 to 39 years old | 70 (33.3) | |
| 40 to 49 years old | 25 (11.9) | |
| 50 to 59 years old | 15 (7.1) | |
| Over 60 years old | 12 (5.7) | |
| Vaccine | Total | 630 (100.0) |
| Pfizer/BioNTech-Comirnaty | 298 (47.3) | |
| Oxford/AstraZeneca-Vaxzevria | 246 (39.0) | |
| Sinovac-CoronaVac | 86 (13.7) | |
| Total n (%) | First Dose n (%) | Second Dose n (%) | Third Dose n (%) | p-Value (*) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| General | 630 (100.0) | 210 (33.3) | 210 (33.3) | 210 (33.4) | |
| Adverse Events | 394 (62.5) | 126 (60.0) | 110 (52.4) | 158 (75.2) | <0.001 |
| Pain | 312 (49.5) | 107 (51.0) | 91 (43.3) | 114 (54.3) | 0.071 |
| Myalgia | 178 (28.3) | 45 (21.4) | 36 (17.1) | 97 (46.2) | <0.001 |
| Headache | 157 (24.9) | 43 (20.5) | 30 (14.3) | 84 (40.0) | <0.001 |
| Thermal elevation | 136 (21.6) | 30 (14.3) | 19 (9.0) | 87 (41.4) | <0.001 |
| Arthralgia | 111 (17.6) | 29 (13.8) | 17 (8.1) | 65 (31.0) | <0.001 |
| Edema | 40 (6.3) | 11 (5.2) | 5 (2.4) | 24 (11.4) | 0.001 |
| Pruritus | 39 (6.2) | 11 (5.2) | 11 (5.2) | 17 (8.1) | 0.374 |
| Erythema | 36 (5.7) | 14 (6.7) | 6 (2.9) | 16 (7.6) | 0.084 |
| Other types of adverse events | 100 (15.9) | 30 (3.6) | 16 (7.3) | 54 (25.8) | 0.008 |
| Use of medication | 305 (48.4) | 93 (44.3) | 78 (37.1) | 134 (63.8) | <0.001 |
| 1 drug | 243 (79.7) | 84 (90.3) | 68 (87.2) | 91 (67.9) | - |
| 2 drugs | 54 (17.7) | 6 (6.5) | 8 (10.3) | 40 (29.9) | - |
| 3 or more drugs | 8 (2.6) | 3 (3.2) | 2 (2.6) | 3 (2.2) | - |
| Daily Activities | 394 (100.0) | 126 (100.0) | 110 (100.0) | 158 (100.0) | - |
| Do not interfere with your daily activities and no treatment is administered | 158 (40.1) | 64 (50.8) | 56 (50.9) | 38 (24.1) | - |
| Interferes with daily activities and/or required pharmacological treatment. | 176 (44.7) | 55 (43.7) | 46 (41.8) | 75 (47.5) | - |
| Impedes the performance of daily activities and required treatment | 57 (14.5) | 7 (5.6) | 8 (7.3) | 42 (26.6) | - |
| Was hospitalized | 3 (0.8) | 0 (0.0) | 0 (0.0) | 86 (1.9) | - |
| Oxford/AstraZeneca-Vaxzevria n (%) | Pfizer/BioNTech-Comirnaty n (%) | Sinovac-CoronaVac n (%) | p-Value (*) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| General | 246 (100.0) | 298 (100.0) | 86 (100.0) | |
| Adverse Events | 184 (74.8) | 176 (59.1) | 34 (39.5) | <0.001 |
| Pain | 129 (52.4) | 152 (51.0) | 31 (36.0) | 0.025 |
| Myalgia | 111 (45.1) | 62 (20.8) | 5 (5.8) | <0.001 |
| Headache | 94 (38.2) | 53 (17.8) | 10 (11.6) | <0.001 |
| Thermal elevation | 91 (37.0) | 41 (13.8) | 4 (4.7) | <0.001 |
| Arthralgia | 78 (31.7) | 32 (10.7) | 1 (1.2) | <0.001 |
| Edema | 23 (9.30) | 13 (4.4) | 4 (4.7) | 0.047 |
| Pruritus | 18 (7.3) | 18 (6.0) | 3 (3.5) | 0.443 |
| Erythema | 16 (6.5) | 16 (5.4) | 4 (4.7) | 0.767 |
| Other types of adverse events | 62 (22.3) | 38 (12.7) | 0 (0.0) | 0.006 |
| Use of medication | 155 (63.0) | 126 (42.3) | 24 (27.9) | <0.001 |
| 1 drug | 111 (71.6) | 110 (87.3) | 22 (91.7) | - |
| 2 drugs | 40 (25.8) | 12 (9.5) | 2 (8.3) | - |
| 3 or more drugs | 4 (2.6) | 4 (3.2) | 0 (0.0) | - |
| Daily Activities | 184 (100.0) | 176 (100.0) | 34 (100.0) | - |
| Do not interfere with your daily activities and no treatment is administered | 54 (77.0) | 79 (44.9) | 25 (73.5) | - |
| Interferes with daily activities and/or required pharmacological treatment. | 88 (79.0) | 79 (44.9) | 9 (26.5) | - |
| Impedes the performance of daily activities and required treatment | 39 (18.0) | 18 (10.2) | 0 (0.0) | - |
| Was hospitalized | 3 (1.6) | 0 (0.0) | 0 (0.0) | - |
| Heterologous n (%) | Homologous n (%) | p-Value (*) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| General | 171 (100.0) | 39 (100.0) | |
| Adverse Events | 137 (80.1) | 21 (53.8) | <0.001 |
| Pain | 97 (56.7) | 17 (43.6) | 0.156 |
| Myalgia | 89 (52.0) | 8 (20.5) | <0.001 |
| Thermal elevation | 80 (46.8) | 7 (17.9) | 0.001 |
| Headache | 78 (45.6) | 6 (15.4) | <0.001 |
| Arthralgia | 61 (35.7) | 4 (10.3) | 0.002 |
| Edema | 23 (13.5) | 1 (2.6) | 0.055 |
| Pruritus | 15 (8.80) | 2 (5.1) | 0.745 |
| Erythema | 14 (8.20) | 2 (5.1) | 0.742 |
| Other types of adverse events | 51 (29.9) | 3 (7.7) | <0.001 |
| Use of medication | 120 (70.2) | 14 (35.9) | <0.001 |
| 1 drug | 82 (68.3) | 9 (64.3) | - |
| 2 drugs | 35 (29.2) | 5 (35.7) | - |
| 3 or more drugs | 3 (2.5) | 0 (0.0) | - |
| Daily Activities | 137 (100.0) | 21 (100.0) | - |
| Do not interfere with your daily activities and no treatment is administered | 28 (20.4) | 10 (47.6) | - |
| Interferes with daily activities and/or required pharmacological treatment. | 68 (49.6) | 7 (33.3) | - |
| Impedes the performance of daily activities and required treatment | 38 (27.7) | 4 (19.0) | - |
| Was hospitalized | 3 (2.2) | 0 (0.0) | - |
| Total (n/%) | Adverse Event No (n/%) | Adverse Event Yes (n/%) | p Value (*) | OR (CI 95%) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Overall | 630 (100.0) | 236 (37.5) | 394 (62.5) | - | - | |
| Sex | ||||||
| Female | 414 (65.7) | 136 (57.6) | 278 (70.6) | 0.001 | 1.76 (1.25–2.46) | |
| Male (+) | 216 (34.3) | 100 (42.4) | 116 (29.4) | |||
| Age | ||||||
| Over or equal 32 years old | 522 (82.9) | 193 (81.8) | 329 (83.5) | 0.579 | 1.12 (0.73–1.72) | |
| Under to 32 years of age (+) | 108 (17.1) | 43 (18.2) | 65 (16.5) | |||
| Doses administered (+) | ||||||
| First Dose | Yes | 210 (33.3) | 84 (35.6) | 126 (32.0) | 0.353 | 0.85 (0.60–1.19) |
| No (+) | 420 (66.7) | 152 (64.4) | 268 (68.0) | |||
| Second Dose | Yes | 210 (33.3) | 100 (42.4) | 110 (27.9) | <0.001 | 0.52 (0.37–0.74) |
| No (+) | 420 (66.7) | 136 (57.6) | 284 (72.1) | |||
| Third Dose | Yes | 210 (33.3) | 52 (22.0) | 158 (40.1) | <0.001 | 2.36 (1.64–3.42) |
| No (+) | 420 (66.7) | 184 (78.0) | 236 (59.9) | |||
| Vaccine | ||||||
| Pfizer/BioNTech-Comirnaty | Yes | 298 (47.3) | 122 (51.7) | 176 (44.7) | 0.087 | 0.75 (0.55–1.04) |
| No (+) | 332 (52.7) | 114 (48.3) | 218 (55.3) | |||
| Oxford/AstraZeneca-Vaxzevria | Yes | 246 (39.0) | 62 (26.3) | 184 (46.7) | <0.001 | 2.45 (1.73–3.49) |
| No (+) | 384 (61.0) | 174 (73.7) | 210 (53.3) | |||
| Sinovac-CoronaVac | Yes | 86 (13.7) | 52 (22.0) | 34 (8.6) | <0.001 | 0.33 (0.20–0.53) |
| No (+) | 544 (86.3) | 184 (78.0) | 360 (91.4) | |||
| Group Vaccine | ||||||
| Heterologous | 171 (81.4) | 51 (29.8) | 120 (70.2) | <0.001 | 4.20 (2.02–8.73) | |
| Homologous (+) | 39 (18.6) | 25 (64.1) | 14 (35.9) | |||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Flores-Lastra, N.; Rivadeneira-Dueñas, J.; Fuenmayor-González, L.; Guayasamín-Tipanta, G.; Jácome-García, M.; Otzen, T.; Manterola, C. Safety Profile of Homologous and Heterologous Booster COVID-19 Vaccines in Physicians in Quito-Ecuador: A Cross-Sectional Study. Vaccines 2023, 11, 676. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines11030676
Flores-Lastra N, Rivadeneira-Dueñas J, Fuenmayor-González L, Guayasamín-Tipanta G, Jácome-García M, Otzen T, Manterola C. Safety Profile of Homologous and Heterologous Booster COVID-19 Vaccines in Physicians in Quito-Ecuador: A Cross-Sectional Study. Vaccines. 2023; 11(3):676. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines11030676
Chicago/Turabian StyleFlores-Lastra, Nancy, Josue Rivadeneira-Dueñas, Luis Fuenmayor-González, Glenda Guayasamín-Tipanta, Michelle Jácome-García, Tamara Otzen, and Carlos Manterola. 2023. "Safety Profile of Homologous and Heterologous Booster COVID-19 Vaccines in Physicians in Quito-Ecuador: A Cross-Sectional Study" Vaccines 11, no. 3: 676. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines11030676
APA StyleFlores-Lastra, N., Rivadeneira-Dueñas, J., Fuenmayor-González, L., Guayasamín-Tipanta, G., Jácome-García, M., Otzen, T., & Manterola, C. (2023). Safety Profile of Homologous and Heterologous Booster COVID-19 Vaccines in Physicians in Quito-Ecuador: A Cross-Sectional Study. Vaccines, 11(3), 676. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines11030676






