Immunogenicity and Safety of the Third Booster Dose with mRNA-1273 COVID-19 Vaccine after Receiving Two Doses of Inactivated or Viral Vector COVID-19 Vaccine
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design and Participants
2.2. Study Procedures
2.3. Immunogenicity Outcomes
2.3.1. The Receptor Binding Domain IgG (Anti-RBD IgG) and Anti-Nucleocapsid Protein (Anti-Np)
2.3.2. Surrogate Virus Neutralization Test (sVNT)
2.3.3. Interferon-Gamma (IFN-γ) Release Assay (IGRA) to Evaluate T Cell Responses
2.4. Reactogenicity
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Baseline Characteristics
3.2. Reactogenicity
3.3. Immunogenicity
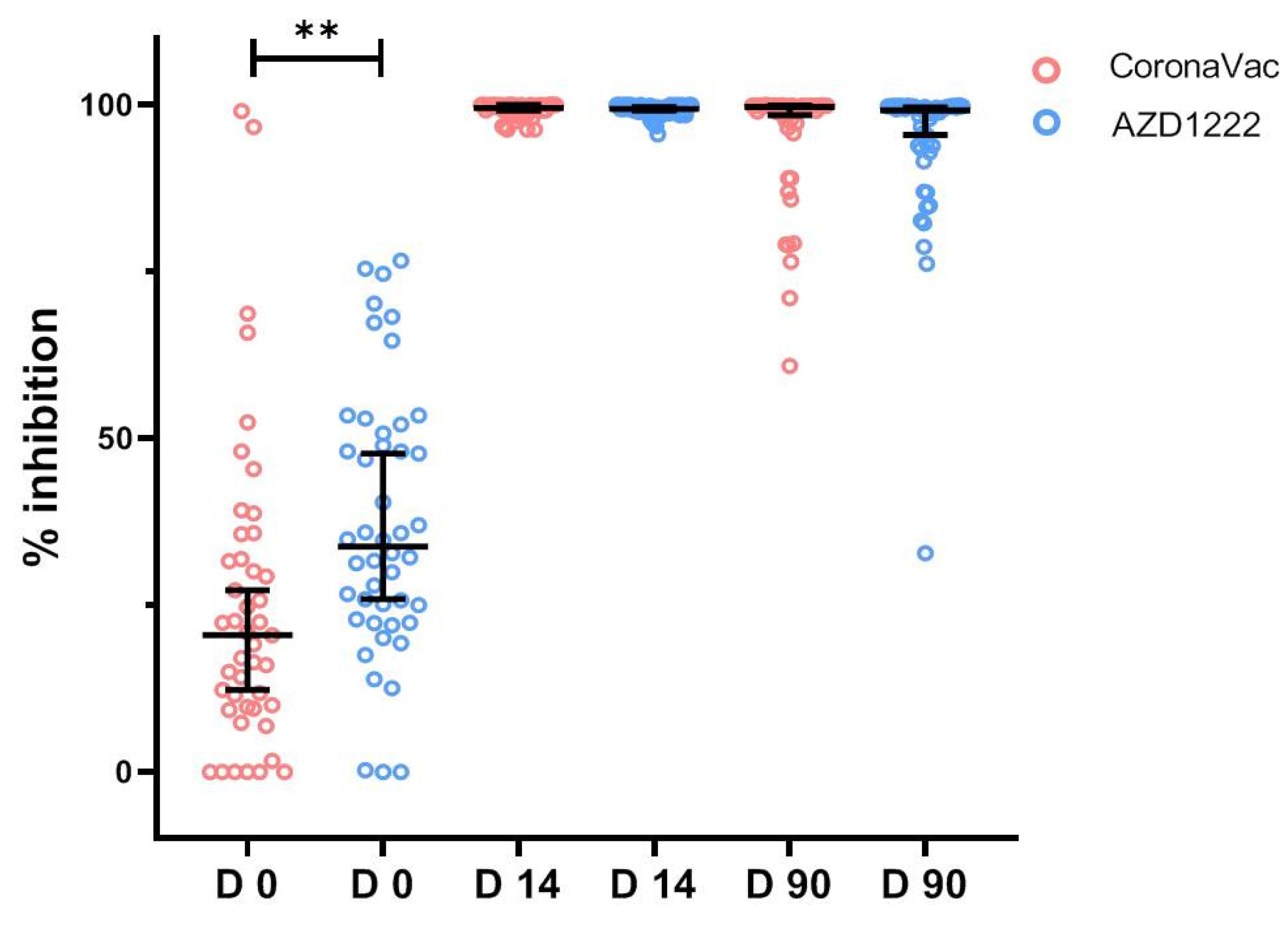
3.3.1. SARS-CoV-2 Neutralizing Antibody by Surrogate Virus Neutralization Test
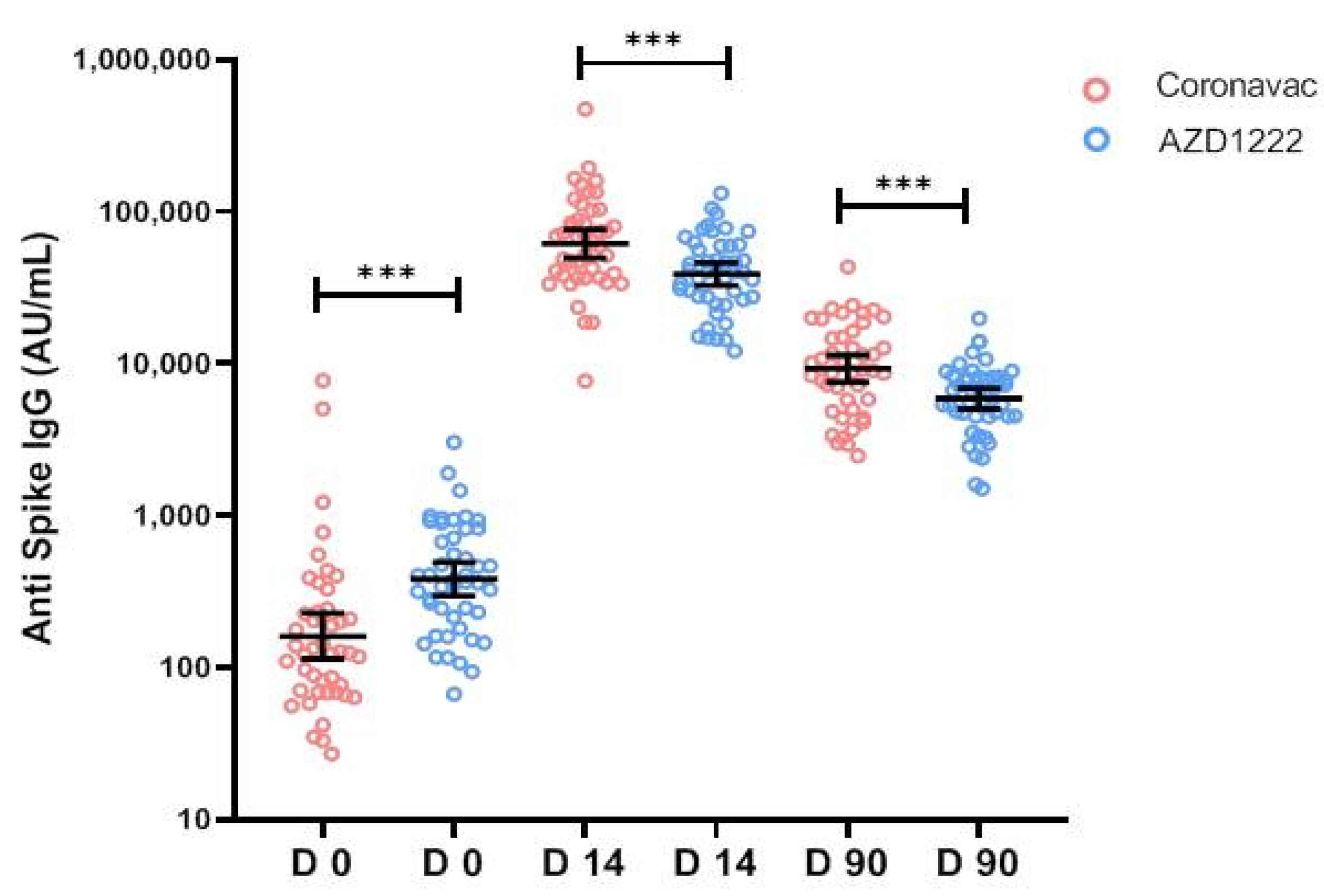
3.3.2. Quantitative IgG against Receptor-Binding Domain
3.4. Cell-Mediated Immune Response by IGRA Assay
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhu, N.; Zhang, D.; Wang, W.; Li, X.; Yang, B.; Song, J.; Zhao, X.; Huang, B.; Shi, W.; Lu, R.; et al. A Novel Coronavirus from Patients with Pneumonia in China. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 382, 727–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- World Health Organization. Novel Coronavirus—Thailand (ex-China). Available online: https://www.who.int/emergencies/disease-outbreak-news/item/2020-DON234 (accessed on 24 March 2022).
- WHO. WHO Coronavirus (COVID-19) Dashboard. Available online: https://covid19.who.int/ (accessed on 17 April 2022).
- WHO. COVID-19 Weekly Epidemiological Update Edition 68; WHO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2021; Available online: https://www.who.int/publications/m/item/weekly-epidemiological-update-on-covid-19---30-november-2021 (accessed on 7 December 2021).
- World Health Organization. Draft Landscape of COVID-19 Candidate Vaccines. Available online: https://www.who.int/publications/m/item/draft-landscape-of-covid-19-candidate-vaccines (accessed on 20 October 2020).
- Jara, A.; Undurraga, E.A.; Gonzalez, C.; Paredes, F.; Fontecilla, T.; Jara, G.; Pizarro, A.; Acevedo, J.; Leo, K.; Leon, F.; et al. Effectiveness of an Inactivated SARS-CoV-2 Vaccine in Chile. N. Engl. J. Med. 2021, 385, 875–884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Voysey, M.; Clemens, S.A.C.; Madhi, S.A.; Weckx, L.Y.; Folegatti, P.M.; Aley, P.K.; Angus, B.; Baillie, V.; Barnabas, S.; Bhorat, Q.; et al. Safety and efficacy of the AZD1222nCoV-19 vaccine (AZD1222) against SARS-CoV-2: An interim analysis of four randomised controlled trials in Brazil, South Africa, and the UK. Lancet 2021, 397, 99–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- WHO. Background Document on the Inactivated Vaccine Sinovac-CoronaVac against COVID-19. 2021. Available online: https://www.who.int/publications/i/item/WHO-2019-nCoV-vaccines-SAGE_recommendation-Sinovac-CoronaVac-background-2021.1 (accessed on 31 July 2021).
- Jantarabenjakul, W.; Chantasrisawad, N.; Puthanakit, T.; Wacharapluesadee, S.; Hirankarn, N.; Ruenjaiman, V.; Paitoonpong, L.; Suwanpimolkul, G.; Torvorapanit, P.; Pradit, R.; et al. Short-term immune response after inactivated SARS-CoV-2 (CoronaVac(R), Sinovac) and AZD1222nCoV-19 (Vaxzevria(R), Oxford-AstraZeneca) vaccinations in health care workers. Asian Pac. J. Allergy Immunol. 2021, 40, 269–277. [Google Scholar]
- Vacharathit, V.; Aiewsakun, P.; Manopwisedjaroen, S.; Srisaowakarn, C.; Laopanupong, T.; Ludowyke, N.; Phuphuakrat, A.; Setthaudom, C.; Ekronarongchai, S.; Srichatrapimuk, S.; et al. CoronaVac induces lower neutralising activity against variants of concern than natural infection. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2021, 21, 1352–1354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WHO. Interim Statement on COVID-19 Vaccine Booster Doses 2021 [Updated 10 August 2021]. Available online: https://www.who.int/news/item/10-08-2021-interim-statement-on-covid-19-vaccine-booster-doses (accessed on 29 August 2021).
- Barros-Martins, J.; Hammerschmidt, S.I.; Cossmann, A.; Odak, I.; Stankov, M.V.; Morillas Ramos, G.; Dopfer-Jablonka, A.; Heidemann, A.; Ritter, C.; Friedrichsen, M.; et al. Immune responses against SARS-CoV-2 variants after heterologous and homologous AZD1222nCoV-19/BNT162b2 vaccination. Nat. Med. 2021, 27, 1525–1529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munro, A.P.S.; Janani, L.; Cornelius, V.; Aley, P.K.; Babbage, G.; Baxter, D.; Bula, M.; Cathie, K.; Chatterjee, K.; Dodd, K.; et al. Safety and immunogenicity of seven covid-19 vaccines as a third dose (booster) following two doses of AZD1222ncov-19 or bnt162b2 in the uk (cov-boost): A blinded, multicentre, randomised, controlled, phase 2 trial. Lancet 2021, 398, 2258–2276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, S.M.S.; Mok, C.K.P.; Leung, Y.W.Y.; Ng, S.S.; Chan, K.C.K.; Ko, F.W.; Chen, C.; Yiu, K.; Lam, B.H.S.; Lau, E.H.Y.; et al. Neutralizing antibodies against the sars-cov-2 omicron variant following homologous and heterologous coronavac or bnt162b2 vaccination. Nat. Med. 2022, 28, 486–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa Clemens, S.A.; Weckx, L.; Clemens, R.; Almeida Mendes, A.V.; Ramos Souza, A.; Silveira, M.B.V.; da Guarda, S.N.F.; de Nobrega, M.M.; de Moraes Pinto, M.I.; Gonzalez, I.G.S.; et al. Heterologous versus homologous COVID-19 booster vaccination in previous recipients of two doses of coronavac covid-19 vaccine in brazil (rhh-001): A phase 4, non-inferiority, single blind, randomise study. Lancet 2022, 399, 521–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perez-Then, E.; Lucas, C.; Monteiro, V.S.; Miric, M.; Brache, V.; Cochon, L.; Vogels, C.B.F.; Malik, A.A.; De la Cruz, E.; Jorge, A.; et al. Neutralizing antibodies against the sars-cov-2 delta and omicron variants following heterologous coronavac plus bnt162b2 booster vaccination. Nat. Med. 2022, 28, 481–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Shaw, R.H.; Stuart, A.S.V.; Greenland, M.; Aley, P.K.; Andrews, N.J.; Cameron, C.; Charlton, S.; Clutterbuck, E.; Collins, A.; et al. Safety and immunogenicity of heterologous versus homologous prime-boost schedules with an adenoviral vectored and mRNA COVID-19 vaccine (Com-COV): A single-blind, randomised, non-inferiority trial. Lancet 2021, 398, 856–869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiu, N.-C.; Chi, H.; Tu, Y.-K.; Huang, Y.-N.; Tai, Y.-L.; Weng, S.-L.; Chang, L.; Huang, D.T.-N.; Huang, F.-Y.; Lin, C.-Y.; et al. To mix or not to mix? A rapid systematic review of heterologous prime-boost COVID-19 vaccination. Expert Rev. Vaccines 2021, 20, 1211–1220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baden, L.R.; El Sahly, H.M.; Essink, B.; Kotloff, K.; Frey, S.; Novak, R.; Diemert, D.; Spector, S.A.; Rouphael, N.; Creech, C.B.; et al. Efficacy and Safety of the mRNA-1273 SARS-CoV-2 Vaccine. N. Engl. J. Med. 2021, 384, 403–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, C.W.; Chia, W.N.; Qin, X.; Liu, P.; Chen, M.I.; Tiu, C.; Hu, Z.; Chen, V.C.-W.; Young, B.; Sia, W.R.; et al. A SARS-CoV-2 surrogate virus neutralization test based on antibody-mediated blockage of ACE2-spike protein-protein interaction. Nat. Biotechnol. 2020, 38, 1073–1078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- U.S. Department of Health and Human Services; Department of Health and Human Services; Food and Drug Administration; CBER. Guidance for Industry Toxicity Grading Scale for Healthy Adult and Adolescent Volunteers Enrolled in Preventive Vaccine Clinical Trials September 2007. Available online: https://www.fda.gov/media/73679/download (accessed on 30 November 2021).
- Zhang, Y.; Zeng, G.; Pan, H.; Li, C.; Hu, Y.; Chu, K.; Han, W.; Chen, Z.; Tang, R.; Yin, W.; et al. Safety, tolerability, and immunogenicity of an inactivated SARS-CoV-2 vaccine in healthy adults aged 18-59 years: A randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase 1/2 clinical trial. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2021, 21, 181–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanriover, M.D.; Doğanay, H.L.; Akova, M.; Güner, H.R.; Azap, A.; Akhan, S.; Köse, Ş.; Erdinç, F.Ş.; Akalın, E.H.; Tabak, Ö.F.; et al. Efficacy and safety of an inactivated whole-virion SARS-CoV-2 vaccine (CoronaVac): Interim results of a double-blind, randomised, placebo-controlled, phase 3 trial in Turkey. Lancet 2021, 398, 213–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cucunawangsih, C.; Wijaya, R.S.; Lugito, N.P.H.; Suriapranata, I. Antibody response after a third dose mRNA-1273 vaccine among vaccinated healthcare workers with two doses of inactivated SARS-CoV-2 vaccine. Int. J. Infect. Dis. 2022, 118, 116–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palgen, J.L.; Feraoun, Y.; Dzangue-Tchoupou, G.; Joly, C.; Martinon, F.; Le Grand, R. Optimize Prime/Boost Vaccine Strategies: Trained Immunity as a New Player in the Game. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 612747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kardani, K.; Bolhassani, A.; Shahbazi, S. Prime-boost vaccine strategy against viral infections: Mechanisms and benefits. Vaccine 2016, 34, 413–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parés-Badell, O.; Martínez-Gómez, X.; Pinós, L.; Borras-Bermejo, B.; Uriona, S.; Otero-Romero, S.; Rodrigo-Pendás, J.Á.; Cossio-Gil, Y.; Agustí, A.; Aguilera, C.; et al. Local and systemic adverse reactions to mRNA COVID-19 vaccines comparing two vaccine types and occurrence of previous COVID-19 infection. Vaccines 2021, 9, 1463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, T.T.; Quach, T.H.T.; Tran, T.M.; Phuoc, H.N.; Nguyen, H.T.; Vo, T.K.; Vo, G.V. Reactogenicity and immunogenicity of heterologous prime-boost immunization with COVID-19 vaccine. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2022, 147, 112650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chalkias, S.; Schwartz, H.; Nestorova, B.; Feng, J.; Chang, Y.; Zhou, H.; Dutko, F.J.; Edwards, D.K.; Montefiori, D.; Pajon, R.; et al. Safety and immunogenicity of a 100 μg mRNA-1273 vaccine booster for severe acute respiratory syndrome Coronavirus-2 (SARS-CoV-2). medRxiv 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
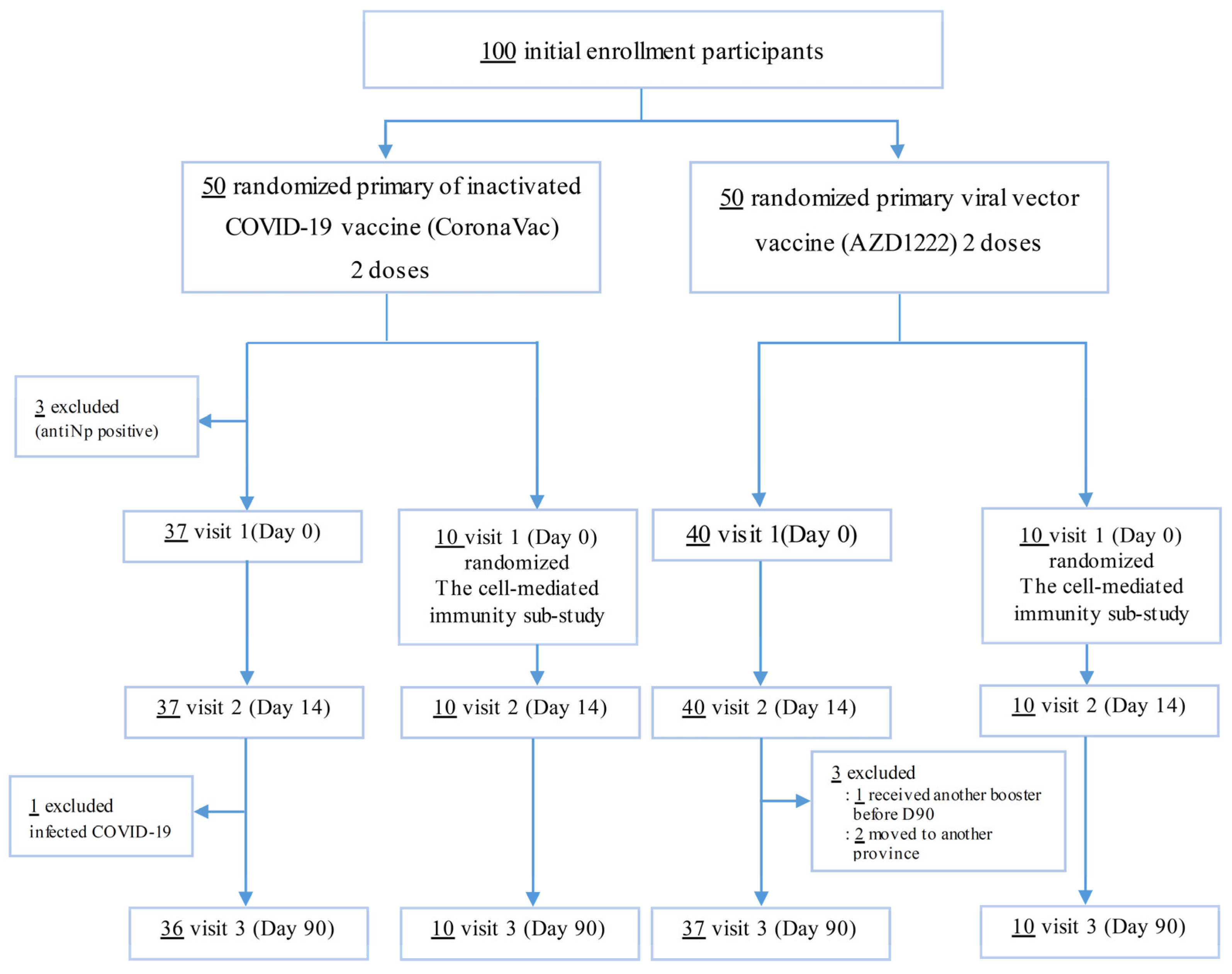


| Baseline Characteristic | Total (n = 97) | Post 2SV (n = 47) | Post 2AZ (n = 50) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age median y (IQR) | 37 (27–47) | 42 (28–49) | 31 (27–46) | 0.033 |
| Female, n (%) | 65 (67.01) | 22 (46.81) | 43 (86.00) | <0.001 |
BMI, median (IQR)
| 22.77 (20.5–25.39) 70 (72.16) 27 (27.84) | 23.51 (21.72–29.32) 31 (65.96) 16 (34.04) | 22.27 (19.61–24.24) 39 (78.00) 11 (22.00) | 0.003 |
Comorbidities, n (%)
| 16 (16.49) 2 (2.06) 3 (3.09) 8 (8.25) 3 (3.09) 1 (1.03) 2 (2.06) | 9 (19.15) 2 (4.26) 3 (6.38) 5 (10.64) 1 (2.13) 0 (0.00) 1 (2.13) | 7 (14.00) 0 (0.00) 0 (0.00) 3 (6.00) 2 (4.00) 1 (2.00) 1 (2.00) | 1.000 0.237 0.113 0.482 1.000 1.000 1.000 |
| Interval between 2nd dose of CoronaVac or AZD1222 to mRNA1273 booster (day); median (IQR) | 155 (143–157) | 143 (138–168) | 155 (155–155) | 0.488 |
| sVNT to Wuhan strain (%inhibition), GM (95%CI) | 22.47 (19.67–25.66) | 18.03 (14.62–22.25) | 27.62 (23.75–32.12) | 0.028 |
| sVNT to Delta variant (%inhibition), GM (95%CI) | 27 (22.86–32.62) | 22.37 (17.44–28.69) | 32.37 (25.21–41.57) | 0.010 |
| Anti-S-RBD IgG (BAU/mL), GM (95%CI) | 36.96 (29.66–46.06) | 23.49 (16.78–32.90) | 56.59 (44.46–72.02) | 0.637 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tangsathapornpong, A.; Nanthapisal, S.; Pontan, K.; Bunjoungmanee, P.; Neamkul, Y.; Boonyarangkul, A.; Wanpen, S.; Fukpho, W.; Jitpokasem, S.; Tharabenjasin, P.; et al. Immunogenicity and Safety of the Third Booster Dose with mRNA-1273 COVID-19 Vaccine after Receiving Two Doses of Inactivated or Viral Vector COVID-19 Vaccine. Vaccines 2023, 11, 553. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines11030553
Tangsathapornpong A, Nanthapisal S, Pontan K, Bunjoungmanee P, Neamkul Y, Boonyarangkul A, Wanpen S, Fukpho W, Jitpokasem S, Tharabenjasin P, et al. Immunogenicity and Safety of the Third Booster Dose with mRNA-1273 COVID-19 Vaccine after Receiving Two Doses of Inactivated or Viral Vector COVID-19 Vaccine. Vaccines. 2023; 11(3):553. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines11030553
Chicago/Turabian StyleTangsathapornpong, Auchara, Sira Nanthapisal, Kanassanan Pontan, Pornumpa Bunjoungmanee, Yamonbhorn Neamkul, Arthit Boonyarangkul, Supattra Wanpen, Waraphon Fukpho, Sumana Jitpokasem, Phuntila Tharabenjasin, and et al. 2023. "Immunogenicity and Safety of the Third Booster Dose with mRNA-1273 COVID-19 Vaccine after Receiving Two Doses of Inactivated or Viral Vector COVID-19 Vaccine" Vaccines 11, no. 3: 553. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines11030553
APA StyleTangsathapornpong, A., Nanthapisal, S., Pontan, K., Bunjoungmanee, P., Neamkul, Y., Boonyarangkul, A., Wanpen, S., Fukpho, W., Jitpokasem, S., Tharabenjasin, P., & Jaru-Ampornpan, P. (2023). Immunogenicity and Safety of the Third Booster Dose with mRNA-1273 COVID-19 Vaccine after Receiving Two Doses of Inactivated or Viral Vector COVID-19 Vaccine. Vaccines, 11(3), 553. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines11030553





