Comparison of Immunogenicity and Safety of Diphtheria–Tetanus–Pertussis–Hepatitis B–Haemophilus influenza B (Bio Farma) with Pentabio® Vaccine Primed with Recombinant Hepatitis B at Birth (Using Different Source of Hepatitis B) in Indonesian Infants
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design and Population
2.2. Vaccine
2.3. Study Vaccine
2.4. Immunogenicity Assessment
2.5. Safety Assessment
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Study Population
3.2. Diphtheria
3.3. Tetanus
3.4. Pertussis
3.5. Hepatitis B
3.6. Hemophilus Influenzae Type b
3.7. Safety Assessment
3.8. Local and Systemic Reactions
3.9. Serious Adverse Events
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- SDG UN. Sustainable Development Goals. The Energy Progress Report. Track SDG 2019, 6. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, B.X.; Kjaerulf, F.; Turner, S.; Cohen, L.; Donnelly, P.D.; Muggah, R.; Davis, R.; Realini, A.; Kieselbach, B.; MacGregor, L.S.; et al. Transforming our world: Implementing the 2030 agenda through sustainable development goal indicators. J. Public Health Policy 2016, 37, 13–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization. Global Health Sector Strategy on Viral Hepatitis 2016–2021. Towards Ending Viral Hepatitis; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Waheed, Y.; Siddiq, M.; Jamil, Z.; Najmi, M.H. Hepatitis elimination by 2030: Progress and challenges. World J. Gastroenterol. 2018, 24, 4959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayuningtyas, D.; Hapsari, D.; Rachmalina, R.; Amir, V.; Rachmawati, R.; Kusuma, D. Geographic and socioeconomic disparity in child undernutrition across 514 districts in indonesia. Nutrients 2022, 14, 843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fahriani, M.; Anwar, S.; Yufika, A.; Bakhtiar, B.; Wardani, E.; Winardi, W.; Akel, K.B.; Wagner, A.L.; Harapan, H. Disruption of childhood vaccination during the COVID-19 pandemic in Indonesia. Narra. J. 2021, 1–3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bavdekar, A.; Malshe, N.; Ravichandran, L.; Sapru, A.; Kawade, A.; Lalwani, S.; Palkar, S.; Hanumante, N.; Gunale, B.; Kapse, D.; et al. Clinical study of safety and immunogenicity of pentavalent DTP–HB–Hib vaccine administered by disposable-syringe jet injector in india. Contemp. Clin. Trials Commun. 2019, 14, 100321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rahayu, M.M.; Idris, H. KELENGKAPAN Imunisasi Rutin Pada Anak Usia-9 Bulan Di Indonesia (Analisis Data RISKESDAS 2018). Ph.D. Thesis, Sriwijaya University, Palembang, Indonesia.
- Rachmawati, P.D.; Kurnia, I.D.; Asih, M.N.; Kurniawati, T.W.; Krisnana, I.; Arief, Y.S.; Mani, S.; Dewi, Y.S.; Arifin, H. Determinants of under-five mortality in indonesia: A nationwide study. J. Pediatr. Nurs. 2022, 65, e43–e48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galazka, A.; Dittmann, S. The changing epidemiology of diphtheria in the vaccine era. J. Infect. Dis. 2000, 181, S2–S9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arguni, E.; Karyanti, M.R.; Satari, H.I.; Hadinegoro, S.R. Diphtheria outbreak in jakarta and tangerang, indonesia: Epidemiological and clinical predictor factors for death. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0246301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holipah; Maharani, A.; Kuroda, Y. Determinants of immunization status among 12- to 23-Month-old children in indonesia (2008–2013): A multilevel analysis. B.M.C. Public Health 2018, 18, 288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harapan, H.; Anwar, S.; Dimiati, H.; Hayati, Z.; Mudatsir, M. Diphtheria outbreak in indonesia, 2017: An outbreak of an ancient and vaccine-preventable disease in the third millennium. Clin. Epidemiol. Glob. Health 2019, 7, 26–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization. Maternal and neonatal tetanus elimination in bali and java, indonesia. Wkly. Epidemiol. Rec. Relev. Épidémiologique Hebd. 2010, 85, 47–88. [Google Scholar]
- Aceh Epidemiology Group. Outbreak of tetanus cases following the tsunami in Aceh province, Indonesia. Glob. Public Health 2006, 1, 17–77. [Google Scholar]
- Galles, N.C.; Liu, P.Y.; Updike, R.L.; Fullman, N.; Nguyen, J.; Rolfe, S.; Sbarra, A.N.; Schipp, M.F.; Marks, A.; Abady, G.G.; et al. Measuring routine childhood vaccination coverage in 204 countries and territories, 1980–2019: A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2020, Release 1. Lancet 2021, 398, 503–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Faradita, I.; Sitaresmi, M.N.; Wahab, A. Association between maternal health care and basic immunization completeness in children aged 12–23 months: Analysis of 2017 indonesian demographic and health survey. Open Access Maced. J. Med. Sci. 2022, 10, 26–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nurjannah, N.N.; Najikhah, N. Basic Immunization Coverage Mapping in Indonesia. In Proceedings of the 8th International Conference on Public Health 2021, Surakarta, Indonesia, 17–18 November 2021; Sebelas Maret University: Surakarta, Indonesia, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Kemenkes. Available online: https://www.kemkes.go.id/article/view/22062800003/2-tahun-cakupan-imunisasi-rendah-pemerintah-gelar-bulan-imunisasi-anak-nasional.html (accessed on 28 June 2022).
- Rusmil, K.; Fadlyana, E.; Bachtiar, N.S.; Hadyana, H. Safety and immunogenicity of the DTP/HB /Hib combination vaccine: Phase I study. Paediatr. Indones. 2013, 53, 309–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gunardi, H.; Rusmil, K.; Fadlyana, E.; Soedjatmiko; Dhamayanti, M.; Sekartini, R.; Tarigan, R.; Satari, H.I.; Medise, B.E.; Sari, R.M.; et al. DTwP-HB-Hib: Antibody persistence after a primary series, immune response and safety after a booster dose in children 1–4 months old. B.M.C. Pediatr. 2018, 18, 177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bachtiar, N.S.; Rusmil, K.; Sudigdoadi, S.; Kartasasmita, C.B.; Hadyana, H. The Immunogenicity and safety of the new, indonesian DTwP-HB-Hib vaccine compared to the DTwP/HB vaccine given with the hib vaccine. Paediatr. Indones. 2017, 57, 12–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rusmil, K.; Gunardi, H.; Fadlyana, E.; Dhamayanti, M.; Sekartini, R.; Satari, H.I.; Risan, N.A.; Prasetio, D.; Tarigan, R.; Garheni, R.; et al. The immunogenicity, safety, and consistency of an Indonesia combined DTP-HB-Hib vaccine in expanded program on immunization schedule. BMC Pediatr. 2015, 15, 219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Julitasari, S.; Rusmil, K.; Sitaresmi, M.N.; Arhana, D.I.G.G.; Hadinegoro, S.R.; Satari, H.I.; Syafriyal, B.N.S.; Sari, R.M. Profil Keamanan Setelah Pemberian Dosis Primer Vaksin Pentabio Pada Bayi di Indonesia. MKB 2017, 49, 86–93. [Google Scholar]
- Nency, Y.M.; Rahmadi, F.A.; Mulyono; Anantyo, D.T.; Farhanah, N.; Hapsari, R.; Farida, H.; Sadhana, U.; Djagat, H.; Kristina, T.N.; et al. Protectivity and safety following recombinant hepatitis B vaccine with different source of bulk compared to hepatitis B (Bio Farma) vaccine in indonesia. Clin. Exp. Vaccin. Res. 2022, 11, 43–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maman, K.; Zöllner, Y.; Greco, D.; Duru, G.; Sendyona, S.; Remy, V. The value of childhood combination vaccines: From beliefs to evidence. Hum. Vaccin. Immunother. 2015, 11, 2132–2141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bar-On, E.S.; Goldberg, E.; Hellmann, S.; Leibovici, L. Combined DTP-HBV-HIB vaccine versus separately administered DTP-HBV and HIB vaccines for primary prevention of diphtheria, tetanus, pertussis, hepatitis B and haemophilus influenzae B (HIB). Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization (WHO). Tetanus. Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/tetanus (accessed on 9 May 2022).
- World Health Organization (WHO). Hepatitis B. Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/hepatitis-b (accessed on 24 June 2022).
- Wierma, S. The Global Burden of Disease of Viral Hepatitis. Viral. Hepat. 2011, 19. [Google Scholar]
- Booy, R.; Aitken, S.J.; Taylor, S.; Tudor-Williams, G.; Macfarlane, J.A.; Moxon, E.R.; Ashworth, L.A.; Mayon-White, R.T.; Griffiths, H.; Chapel, H.M. Immunogenicity of Combined Diphtheria, Tetanus, and Pertussis Vaccine Given at 2, 3, and 4 Months versus 3, 5, and 9 Months of Age. Lancet 1992, 339, 502–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eregowda, A.; Lalwani, S.; Chatterjee, S.; Vakil, H.; Ahmed, K.; Costantini, M.; Lattanzi, M. A Phase III single arm, multicenter, open-label study to assess the immunogenicity and tolerability of a pentavalent DTwP–HepB–Hib vaccine in indian infants. Hum. Vaccin. Immunother. 2013, 9, 190–909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voysey, M.; Kelly, D.F.; Fanshawe, T.R.; Sadarangani, M.; O’Brien, K.L.; Perera, R.; Pollard, A.J. The influence of maternally derived antibody and infant age at vaccination on infant vaccine responses: An individual participant meta-analysis. JAMA Pediatr. 2017, 171, 637–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization. Pertussis vaccines: WHO position paper—August 2015. Wkly. Epidemiol. Rec. Relev. Épidémiologique Hebd. 2015, 90, 433–458. [Google Scholar]
- Purwono, P.B.; Amin, M.; Bramanthi, R.; Resi, E.M.; Wahyuni, R.M.; Yano, Y.; Hotta, H.; Hayashi, Y.; Utsumi, T.; Lusida, M.I. Hepatitis B virus infection in Indonesia 15 years after adoption of a universal infant vaccination program: Possible impacts of low birth dose coverage and a vaccine-escape mutant. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2016, 95, 674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jefferson, T.; Rudin, M.; DiPietrantonj, C. Systematic review of the effects of pertussis vaccines in children. Vaccine 2003, 21, 2003–2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torvaldsen, S.; Simpson, J.M.; McIntyre, P.B. Effectiveness of pertussis vaccination in New South Wales, Australia, 1996–1998. Eur. J. Epidemiol. 2003, 18, 63–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, T.; Dalby, T.; Forsyth, K.; Halperin, S.A.; Heininger, U.; Hozbor, D.; Plotkin, S.; Ulloa-Gutierrez, R.; Wirsing von König, C.H. Pertussis across the globe: Recent epidemiologic trends from 2000 to 2013. Pediatr. Infect. Dis. J. 2015, 34, e222–e232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nataprawira, H.M.; Kompiyang Indriyani, S.A.; Olivianto, E. Pertussis in children: Problems in Indonesia. Emerg. Med. 2018, 8, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sunarno, S.; Sofiah, S.N.; Amalia, N.; Hartoyo, Y.; Rizki, A.; Puspandari, N.; Saraswati, R.D.; Febriyana, D.; Febrianti, T.; Susanti, I.; et al. Laboratory and epidemiology data of pertussis cases and close contacts: A 5-year case-based surveillance of pertussis in Indonesia, 2016–2020. PLoS ONE 2022, 17, e0266033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thisyakorn, U.; Tantawichien, T.; Thisyakorn, C.; Buchy, P. Pertussis in the Association of Southeast Asian Nations: Epidemiology and challenges. Int. J. Infect. Dis. 2019, 87, 75–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WHO-Recommended Standards for Surveillance of Selected Vaccine-Preventable Diseases; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2003; Available online: http://www.who.int/vaccinesdocuments/DocsPDF06/843.pdf (accessed on 8 August 2021).
- Jackson, D.W.; Rohani, P. Perplexities of pertussis: Recent global epidemiological trends and their potential causes. Epidemiol. Infect. 2014, 142, 67–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.J.; Narayanan, S.; Tiefenbach, J.; Lukšić, I.; Ale, B.M.; Adeloye, D.; Rudan, I. Estimating the global and regional burden of meningitis in children caused by haemophilus influenzae type b: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Glob. Health 2022, 12, 04014. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Watt, J.P.; Wolfson, L.J.; O’Brien, K.L.; Henkle, E.; Deloria-Knoll, M.; McCall, N.; Lee, E.; Levine, O.S.; Hajjeh, R.; Mulholland, K.; et al. Burden of disease caused by haemophilus influenzae Type b in children younger than 5 Years: Global estimates. Lancet 2009, 374, 903–911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lokida, D.; Farida, H.; Triasih, R.; Mardian, Y.; Kosasih, H.; Naysilla, A.M.; Budiman, A.; Hayuningsih, C.; Anam, M.S.; Wastoro, D.; et al. Epidemiology of community-acquired pneumonia among hospitalised children in indonesia: A multicentre, prospective study. BMJ Open 2022, 12, e057957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabatabaei, S.R.; Karimi, A.; Zahraei, S.M.; Esteghamati, A.; Azimi, L.; Shirvani, F.; Mohammadi, S.; Rajabnejad, M.; Shamshiri, A.; Faghihian, R.; et al. Immunogenicity and safety of three WHO prequalified (DTwP-HB-Hib) pentavalent combination vaccines administered as per iranian national immunization plan in iranian infants: A randomized, phase III study. Indian Pediatr. 2021, 58, 113–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
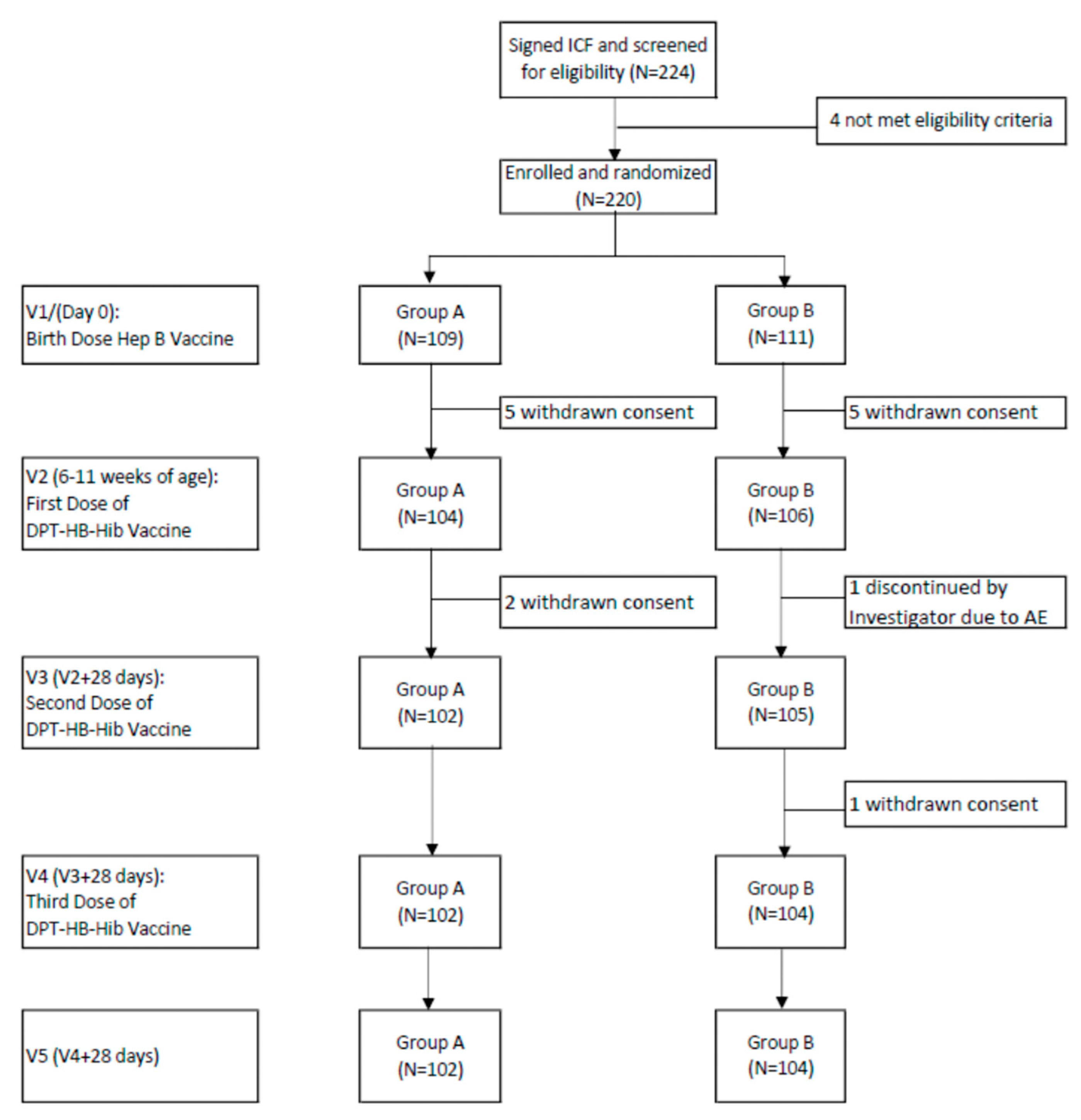
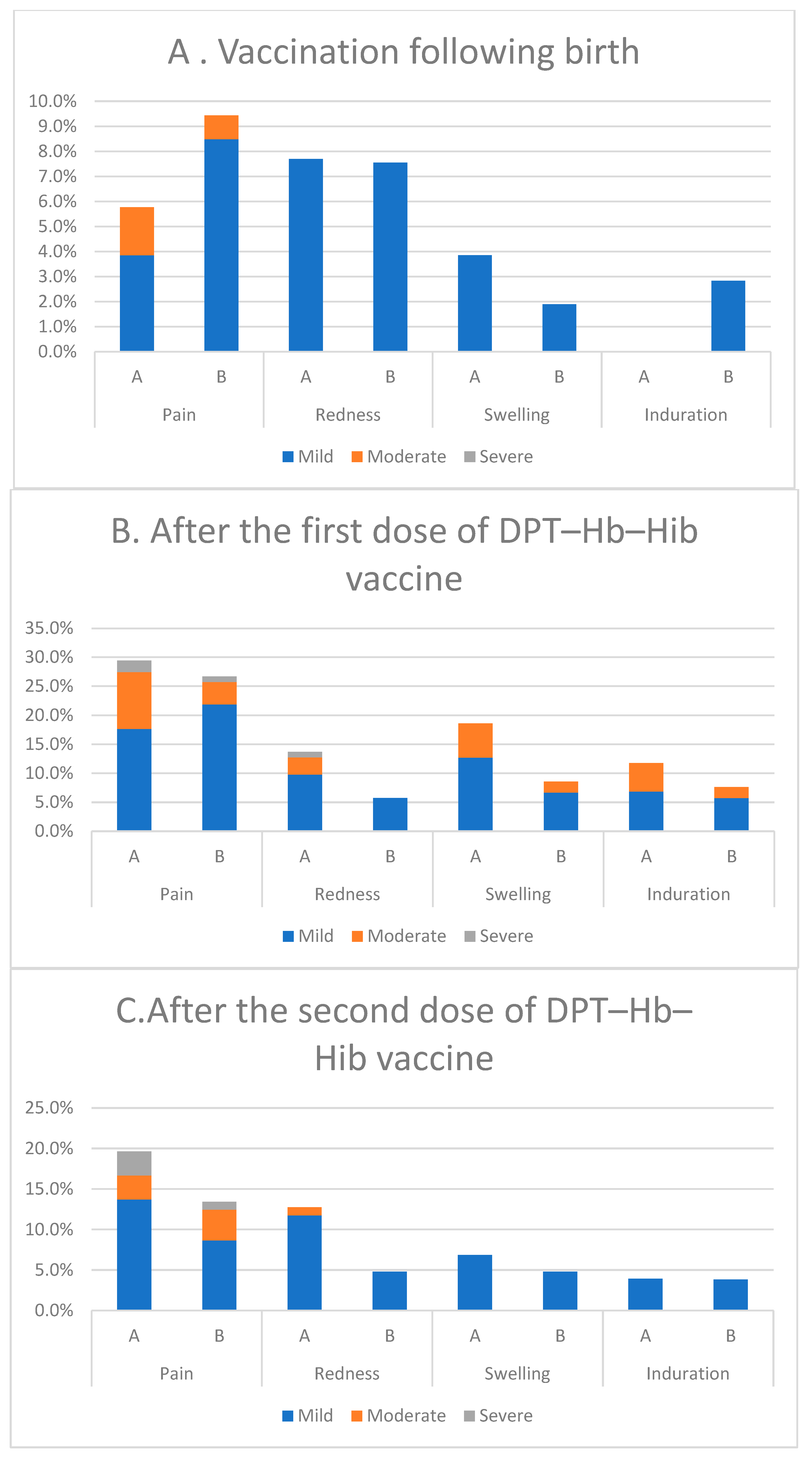

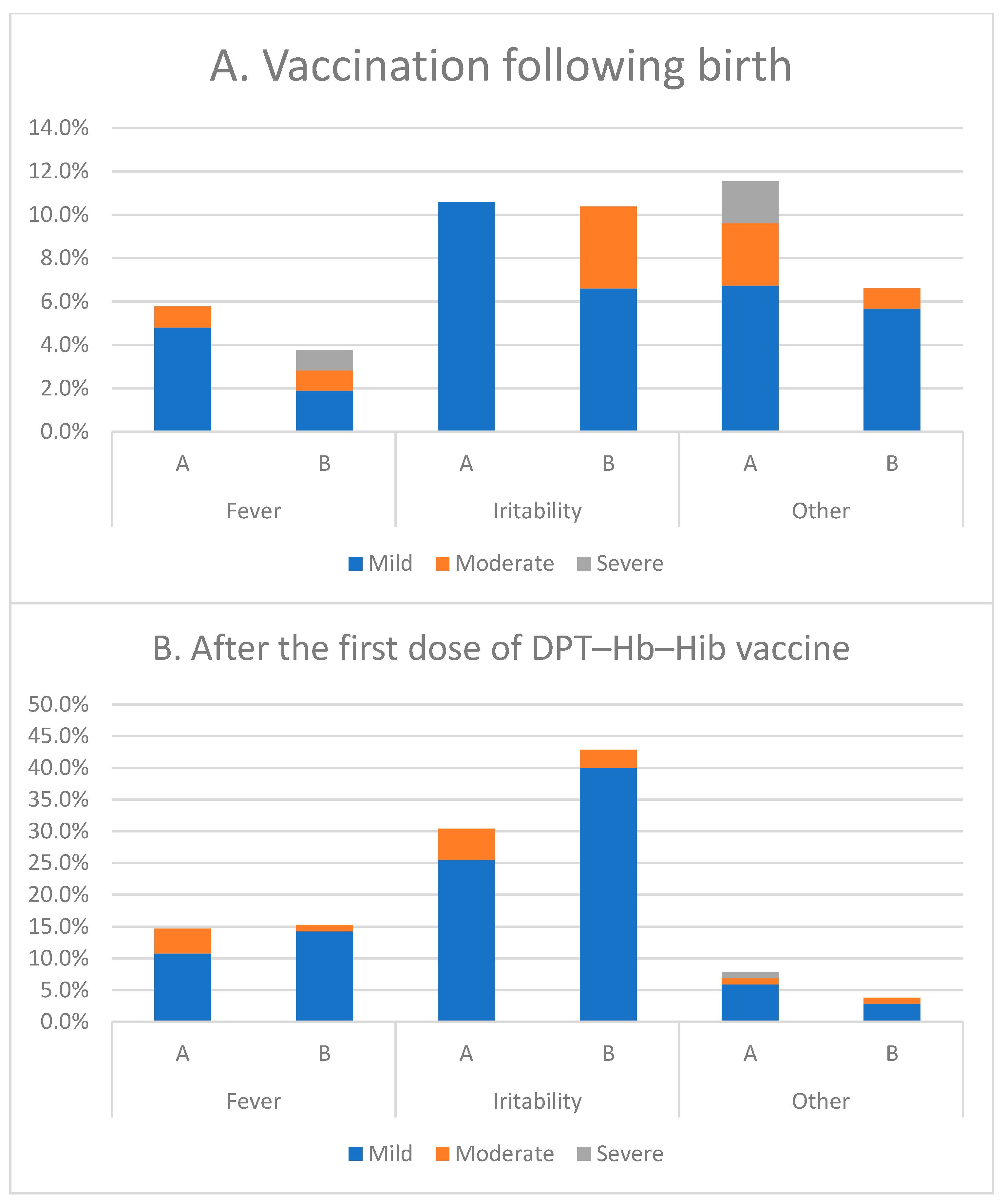
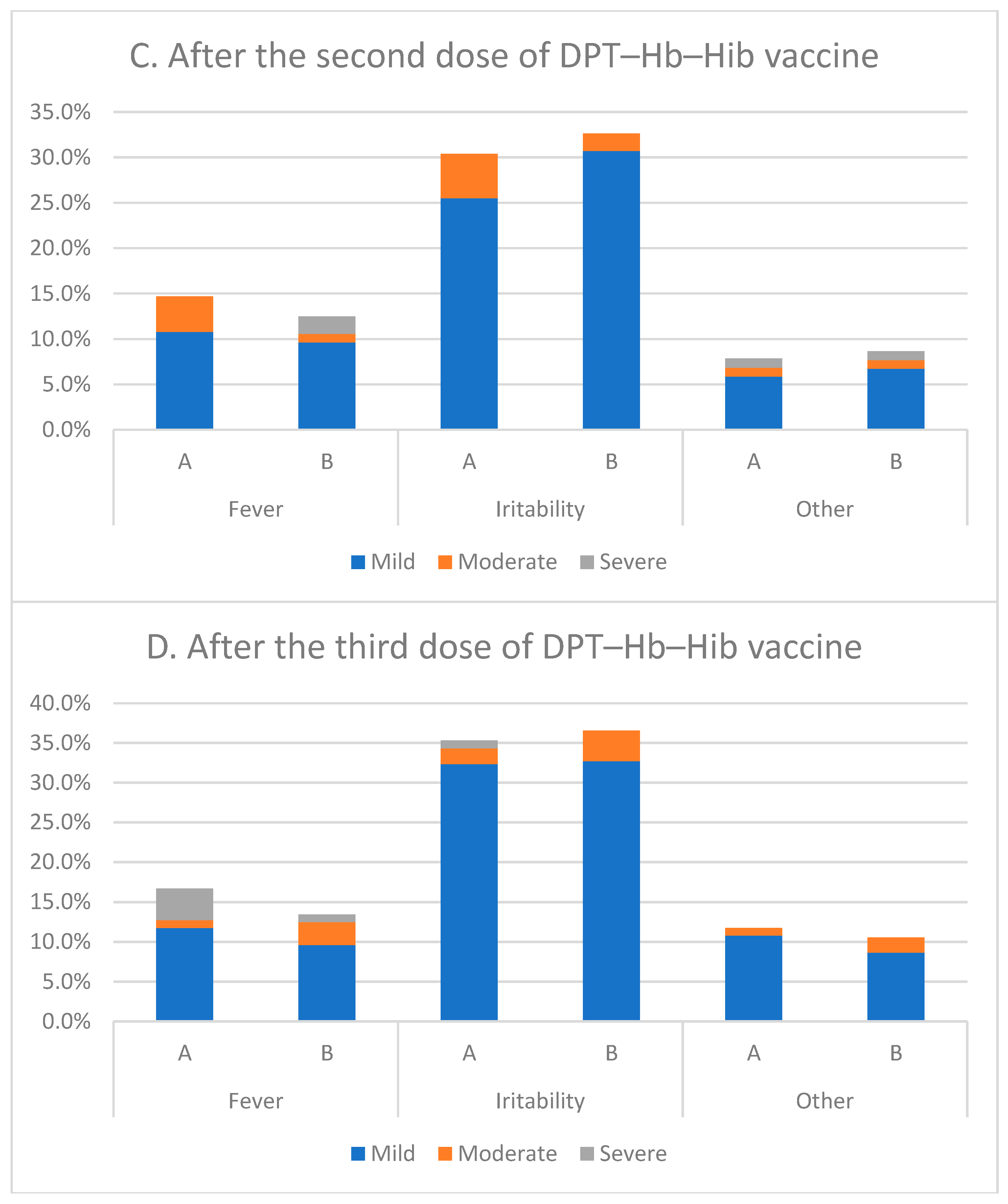
| Age | Group | 0–3 (Days) | 6–11 Weeks | 10–15 Weeks | 14–19 Weeks |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0–3 days | A | Recombinant hepatitis B vaccine using different source | DTP–HB–Hib using different source of hepatitis B bulk | DTP–HB–Hib using different source of hepatitis B bulk | DTP–HB–Hib using different source of hepatitis B bulk |
| B | Recombinant Hepatitis B® vaccine (Bio Farma) | Pentabio® | Pentabio® | Pentabio® |
| Description | Control Product (A) | Investigational Product (B) | Total |
|---|---|---|---|
| N included | 109 | 111 | 220 |
| Gender Male n (%) Female n (%) | 53 (48.6%) 56 (51.4%) | 57 (51.4%) 54 (48.6%) | 110 110 |
| Age (days) | |||
| Mean ± SD * | 0.51 ± 0.55 | 0.54 ± 0.57 | 0.53 ± 0.56 |
| Min; Max | 0; 3 | 0; 2 | 0; 3 |
| Antibody Response | Pre-Vaccination/V2 (n = 103) | Post-Vaccination/V5 (n = 103) |
|---|---|---|
| Anti-D ≥ 0.01 IU/mL n (%) | 63 (61.2) | 103 (100) |
| Anti-T ≥ 0.01 IU/mL n (%) | 101 (98.1) | 103 (100) |
| Anti-PRP-T ≥ 0.15 μg/mL n (%) | 83 (80.6) | 99 (96.1) |
| Anti-pertussis ≥ 40 1/dil n (%) | 1 (1.0) | 85 (82.5) |
| Pre-vaccination/V0 (n = 104) | Post-vaccination/V5 (n= 103) | |
| Anti-HBsAg ≥ 10 mIU/mL n (%) | 18 (17.3) | 103 (100) |
| Antibody | Assessment | Criterion | Group A | Group B | p-Value | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| N | %NSP | 95% CI | N | %NSP | 95% CI | ||||
| Diphtheria | Pre-vaccination/V2 | ≥0.01 IU/mL | 55 | 53.9 | 44.3–63.3 | 63 | 61.2 | 51.5–70.0 | 0.294 |
| ≥0.1 IU/mL | 31 | 30.4 | 22.3–39.9 | 37 | 35.9 | 27.3–45.5 | 0.400 | ||
| Post-vaccination/V5 | ≥0.01 IU/mL | 99 | 97.1 | 91.7–99.0 | 103 | 100 | 96.4–100 | 0.080 | |
| ≥0.1 IU/mL | 90 | 97.4 | 79.6–92.5 | 90 | 87.4 | 79.6–92.5 | 0.529 | ||
| Tetanus | Pre-vaccination/V2 | ≥0.01 IU/mL | 100 | 98 | 93.1–99.5 | 101 | 98.1 | 93.2–99.5 | 1.000 |
| ≥0.01 IU/mL | 93 | 91.2 | 84.1–95.3 | 99 | 96.1 | 90.4–98.4 | 0.147 | ||
| Post-vaccination/V5 | ≥0.1 IU/mL | 102 | 100 | 96.4–100 | 103 | 100 | 96.4–100 | 1.000 | |
| ≥0.01 IU/mL | 102 | 100 | 96.4–100 | 103 | 100 | 96.4–100 | 1.000 | ||
| Pertussis | Pre-vaccination/V2 | >40 1/dil | 4 | 3.9 | 1.5–9.6 | 1 | 1.0 | 0.17–5.3 | 0.212 |
| >80 1/dil | 1 | 1.0 | 0.17–5.35 | 1 | 1.0 | 0.17–5.3 | 1.000 | ||
| >160 1/dil | 0 | 0 | 0–3.63 | 1 | 1.0 | 0.17–5.3 | 1.000 | ||
| >320 1/dil | 0 | 0 | – | 0 | 0 | – | - | ||
| Post-vaccination/V5 | >40 1/dil | 94 | 92.2 | 85.3–96.0 | 85 | 82.5 | 74.1–88.6 | 0.038 * | |
| >80 1/dil | 86 | 84.3 | 76.0–90.1 | 79 | 76.7 | 67.7–83.3 | 0.169 | ||
| >160 1/dil | 68 | 66.7 | 57.1–75.1 | 60 | 58.3 | 48.6–67.3 | 0.214 | ||
| >320 1/dil | 31 | 30.4 | 22.5–33.9 | 36 | 35.0 | 26.4–44.6 | 0.487 | ||
| Hepatitis B | Pre-vaccination/V0 | ≥10 mIU/mL | 19 | 18.1 | 11.9–26.5 | 11 | 10.5 | 5.9–17.8 | 0.115 |
| Pre-vaccination/V2 | ≥10 mIU/mL | 27 | 26.0 | 18.5–35.1 | 18 | 17.3 | 11.2–25.7 | 0.130 | |
| Post-vaccination/V5 | ≥10 mIU/mL | 101 | 99.0 | 94.6–99.8 | 103 | 100 | 96.4–100 | 0.498 | |
| PRP (Hib) | Pre-vaccination/V2 | ≥0.15 µg/mL | 77 | 75.7 | 66.3–82.8 | 83 | 80.6 | 71.9–87.1 | 0.378 |
| ≥1.0 µg/mL | 5 | 4.9 | 2.1–11.0 | 4 | 3.9 | 1.5–9.6 | 0.748 | ||
| Post-vaccination/V5 | ≥0.15 µg/mL | 101 | 99.0 | 94.6–99.8 | 99 | 96.1 | 90.4–98.5 | 0.369 | |
| ≥1.0 µg/mL | 81 | 79.4 | 70.6–86.1 | 84 | 81.6 | 73.0–87.9 | 0.699 | ||
| Antibody | Assessment | Group A | Group B | p-Value | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GMT, IU/mL | 95% CI | GMT, IU/mL | 95% CI | |||
| Diphtheria | Pre-vaccination/V2 | 0.1465 | 0.0088–0.2431 | 0.0201 | 0.0122–0.03323 | 0.440 |
| Post-vaccination/V5 | 0.3260 | 0.2419–0.4393 | 0.4215 | 0.3380–0.5256 | 0.270 | |
| Tetanus | Pre-vaccination/V2 | 0.5950 | 0.4557–0.7770 | 0.6414 | 0.4944–0.8320 | 0.678 |
| Post-vaccination/V5 | 1.0268 | 0.8929–1.1808 | 1.2653 | 1.0691–1.4976 | 0.065 | |
| Pertussis | Pre-vaccination/V2 | 5.8462 | 5.2944–6.4570 | 5.606 | 5.128–6.117 | 0.596 |
| Post-vaccination/V5 | 133.179 | 106.346–166.783 | 105.419 | 80.868–137.423 | 0.407 | |
| Hepatitis B | Pre-vaccination/V0 | 0.3347 | 0.1551–0.72 | 0.1986 | 0.100–0.394 | 0.491 |
| Pre-vaccination/V2 | 1.4824 | 0.823–2.669 | 0.5458 | 0.280–1.063 | 0.076 | |
| Post-vaccination/V5 | 533.303 | 415.090–85.184 | 2372.378 | 1905.03–2956.87 | 0.001 * | |
| PRP-Hib | Pre-vaccination/V2 | 0.1643 | 0.1156–0.2336 | 0.2075 | 0.1529–0.2816 | 0.252 |
| Post-vaccination/V5 | 3.4965 | 2.6706–4.7936 | 2.9457 | 2.0478–4.2372 | 0.974 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Fadlyana, E.; Rusmil, K.; Dhamayanti, M.; Tarigan, R.; Kartasasmita, C.B.; Sari, R.M.; Putra, M.G.D.; Sukandar, H. Comparison of Immunogenicity and Safety of Diphtheria–Tetanus–Pertussis–Hepatitis B–Haemophilus influenza B (Bio Farma) with Pentabio® Vaccine Primed with Recombinant Hepatitis B at Birth (Using Different Source of Hepatitis B) in Indonesian Infants. Vaccines 2023, 11, 498. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines11030498
Fadlyana E, Rusmil K, Dhamayanti M, Tarigan R, Kartasasmita CB, Sari RM, Putra MGD, Sukandar H. Comparison of Immunogenicity and Safety of Diphtheria–Tetanus–Pertussis–Hepatitis B–Haemophilus influenza B (Bio Farma) with Pentabio® Vaccine Primed with Recombinant Hepatitis B at Birth (Using Different Source of Hepatitis B) in Indonesian Infants. Vaccines. 2023; 11(3):498. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines11030498
Chicago/Turabian StyleFadlyana, Eddy, Kusnandi Rusmil, Meita Dhamayanti, Rodman Tarigan, Cissy B. Kartasasmita, Rini Mulia Sari, Muhammad Gilang Dwi Putra, and Hadyana Sukandar. 2023. "Comparison of Immunogenicity and Safety of Diphtheria–Tetanus–Pertussis–Hepatitis B–Haemophilus influenza B (Bio Farma) with Pentabio® Vaccine Primed with Recombinant Hepatitis B at Birth (Using Different Source of Hepatitis B) in Indonesian Infants" Vaccines 11, no. 3: 498. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines11030498
APA StyleFadlyana, E., Rusmil, K., Dhamayanti, M., Tarigan, R., Kartasasmita, C. B., Sari, R. M., Putra, M. G. D., & Sukandar, H. (2023). Comparison of Immunogenicity and Safety of Diphtheria–Tetanus–Pertussis–Hepatitis B–Haemophilus influenza B (Bio Farma) with Pentabio® Vaccine Primed with Recombinant Hepatitis B at Birth (Using Different Source of Hepatitis B) in Indonesian Infants. Vaccines, 11(3), 498. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines11030498





