Using Dried Blood Spots for a Sero-Surveillance Study of Maternally Derived Antibody against Group B Streptococcus
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design
2.2. Study Population
2.3. Inclusion and Exclusion Criteria
2.4. Control Population
2.5. Sample Size
2.6. Data Collection
2.7. Sample Collection
2.8. Laboratory Methods
2.8.1. DBS Elution
2.8.2. Haematocrit Analysis in DBS
2.8.3. DBS Storage Optimisation
2.8.4. DBS Stability—Freeze Thaw Cycles
2.8.5. Correlation of Antibodies from DBS and Serum
2.8.6. Assessment of GBS Antibodies
2.8.7. Coupling of Antigens to Bead Sets
2.8.8. Multiplex Immunoassay
2.9. Data Processing and Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Case-Control Study
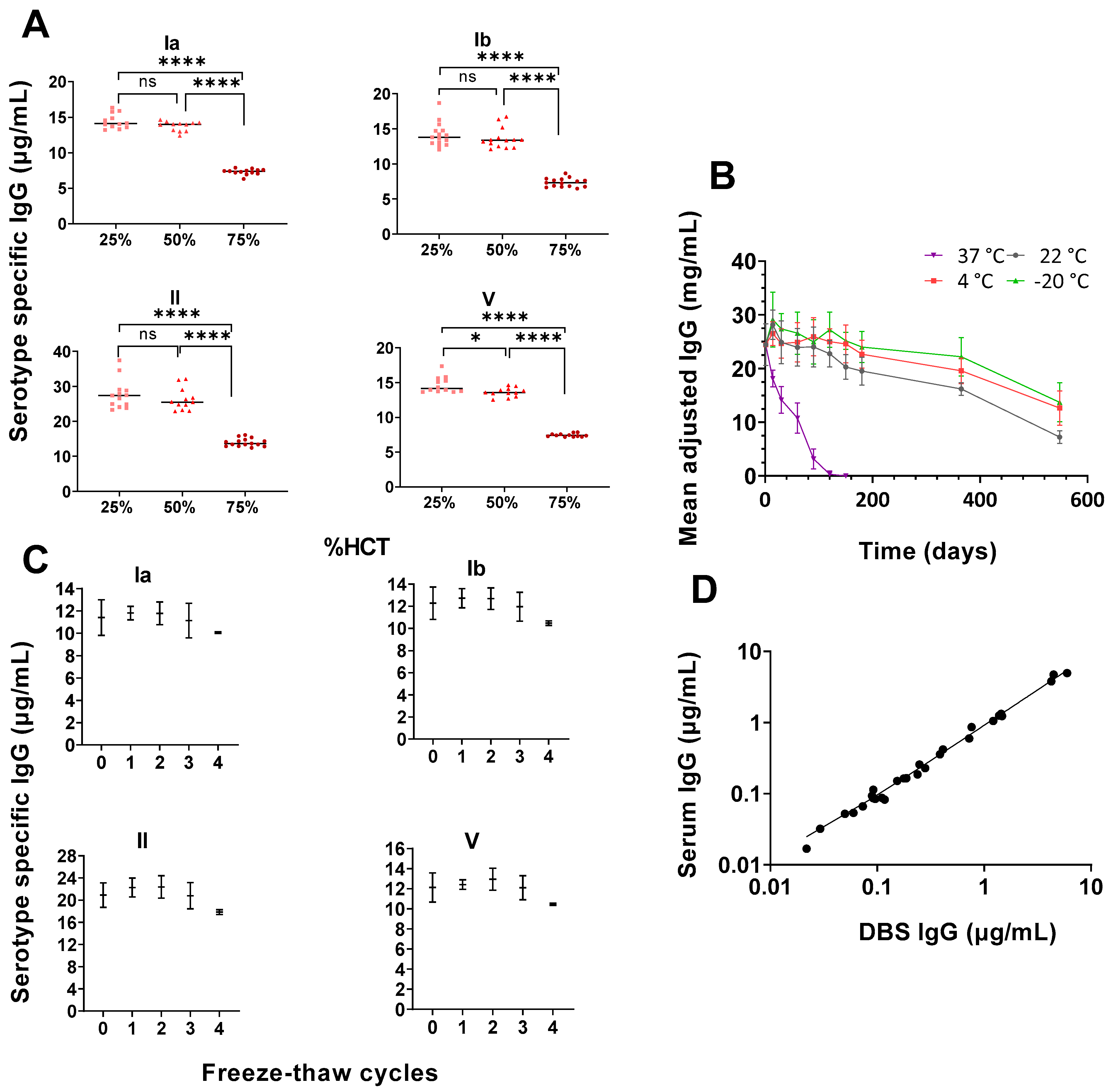
3.2. High Haematocrit May Affect Antibody Concentrations Readouts
3.3. Storage Temperatures Affect Antibody Stability
3.4. Correlation between Freshly Prepared DBS and Paired Serum Samples
3.5. Antibody Concentrations in Invasive GBS Cases and Controls
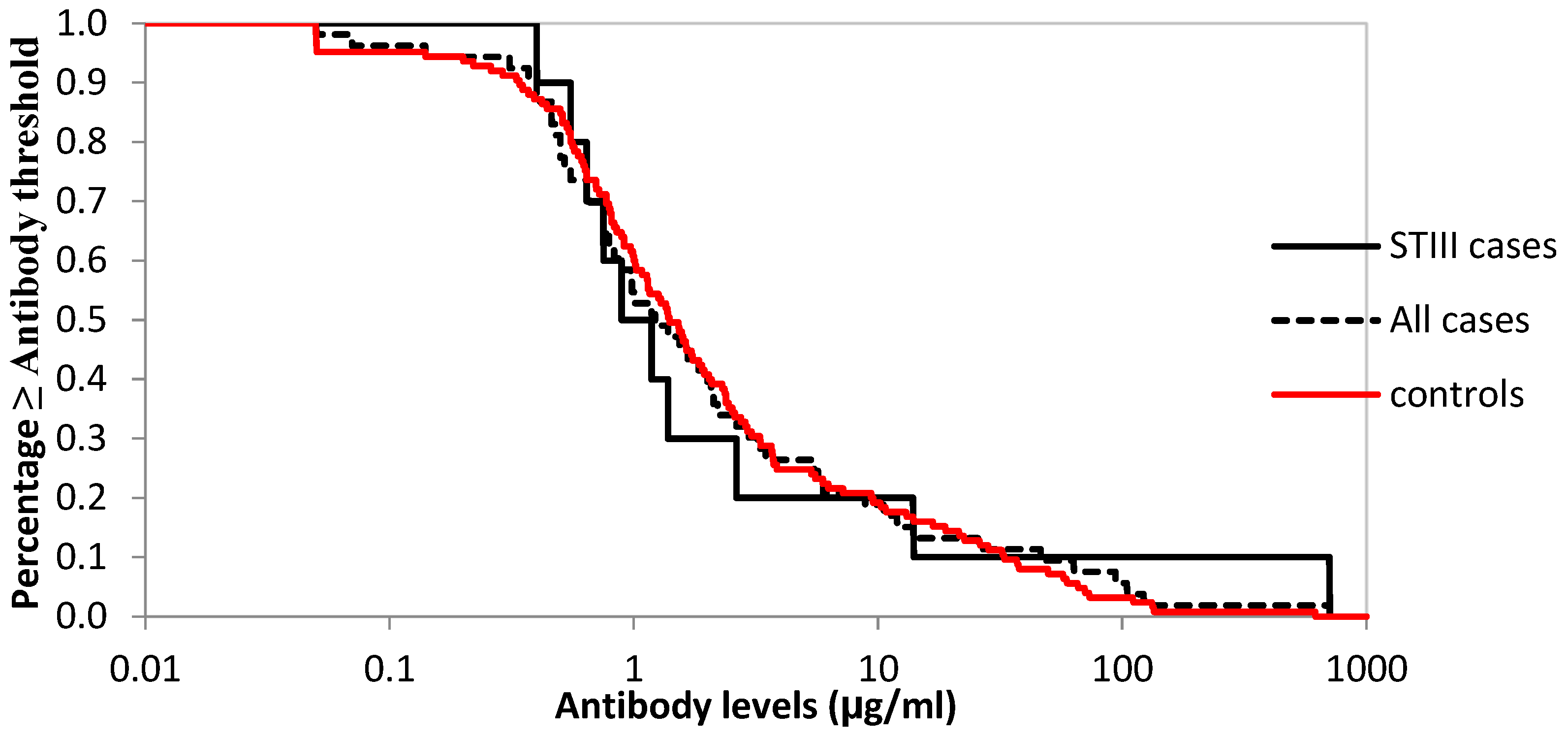
3.6. Logistic Regression to Assess Cut-Offs and Reverse Cumulative Distribution of Antibodies against Serotype III for Cases and Controls
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cozzi, R.; Malito, E.; Lazzarin, M.; Nuccitelli, A.; Castagnetti, A.; Bottomley, M.J.; Margarit, I.; Maione, D.; Rinaudo, C.D. Structure and assembly of group B streptococcus pilus 2b backbone protein. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0125875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seale, A.C.; Bianchi-Jassir, F.; Russell, N.J.; Kohli-Lynch, M.; Tann, C.J.; Hall, J.; Madrid, L.; Blencowe, H.; Cousens, S.; Baker, C.J.; et al. Estimates of the Burden of Group B Streptococcal Disease Worldwide for Pregnant Women, Stillbirths, and Children. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2017, 65, S200–S219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Le Doare, K.; Heath, P.T. An overview of global GBS epidemiology. Vaccine 2013, 31, D7–D12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marchant, A.; Sadarangani, M.; Garand, M.; Dauby, N.; Verhasselt, V.; Pereira, L.; Bjornson, G.; Jones, C.E.; Halperin, S.A.; Edwards, K.M.; et al. Maternal immunisation: Collaborating with mother nature. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2017, 17, E197–E208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baker, C.J.; Kasper, D.L. Correlation of Maternal Antibody Deficiency with Susceptibility to Neonatal Group B Streptococcal Infection. N. Engl. J. Med. 2010, 294, 753–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frasch, C.E.; Borrow, R.; Donnelly, J. Bactericidal antibody is the immunologic surrogate of protection against meningococcal disease. Vaccine 2009, 27, 112–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madhi, S.A.; Dangor, Z. Prospects for preventing infant invasive GBS disease through maternal vaccination. Vaccine 2017, 35, 4457–4460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, M.D. Review article: Dried blood spots for global health diagnostics and surveillance: Opportunities and challenges. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2018, 99, 256–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guthrie, R.S.A. A simple phenylalanine method for detecting phenylketonuria in large populations of newborn infants. Paediatrics 1963, 32, 338–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ostler, M.W.; Porter, J.H.; Buxton, O.M. Dried blood spot collection of health biomarkers to maximize participation in population studies. J. Vis. Exp. 2014, 83, e50973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aabye, M.G.; Eugen-Olse, J.; Werlinrud, A.M.; Holm, L.L.; Tuuminen, T.; Ravn, P.; Ruhwald, M. A simple method to quantitate IP-10 in dried blood and plasma spots. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e39228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iyer, A.S.; Azman, A.S.; Bouhenia, M.; Deng, L.O.; Anderson, C.P.; Graves, M.; Kováč, P.; Xu, P.; Ryan, E.T.; Harris, J.B.; et al. Dried Blood Spots for Measuring Vibrio cholerae-specific Immune Responses. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2018, 12, e0006196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marangoni, A.; Capretti, M.G.; De Angelis, M.; Nardini, P.; Compri, M.; Foschi, C.; Orlandi, A.; Marsico, C.; Righetti, F.; Faldella, G.; et al. Evaluation of a new protocol for retrospective diagnosis of congenital toxoplasmosis by use of guthrie cards. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2014, 52, 2963–2970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anitha, D.; Ganesan, A.; Jacob, S.; Sushi, K. Diagnosis of HIV-1 infection in infants using dried blood spots in Tamil Nadu, South India. Indian J. Sex. Transm. Dis. AIDS 2011, 32, 99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruangturakit, S.; Rojanasuphot, S.; Srijuggravanvong, A.; Duangchanda, S.; Nuangplee, S.; Igarashi, A. Storage stability of dengue IgM and IgG antibodies in whole blood and serum dried on filter paper strips detected by ELISA. Southeast Asian J. Trop. Med. Public Health 1994, 25, 560–564. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Weldon, W.C.; Steven Oberste, M.; Pallansch, M.A. Standardized methods for detection of poliovirus antibodies. In Poliovirus; Methods in Molecular Biology; Martin, J., Ed.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2016; Volume 1387, pp. 145–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, X.; Carlson, B.F.; Wang, X.; Li, X.; Zhang, Y.; Montgomery, J.L.P.; Ding, Y.; Wagner, A.L.; Gillespie, B.; Boulton, M.L. Dried blood spots: An evaluation of utility in the field. J. Infect. Public Health 2018, 11, 373–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Njenga, S.M.; Kanyi, H.M.; Arnold, B.F.; Matendechero, S.H.; Onsongo, J.K.; Won, K.Y.; Priest, J.W. Integrated cross-sectional multiplex serosurveillance of IgG antibody responses to parasitic diseases and vaccines in coastal Kenya. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2020, 102, 164–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamed, S.; Raimondo, A.; Pénaranda, G.; Camus, C.; Ouzan, D.; Ravet, S.; Bourlière, M.; Khiri, H.; Dukan, P.; Olive, D.; et al. Dried Blood Spot Sampling for Hepatitis B Virus Serology and Molecular Testing. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e61077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- UK Newborn Screening Laboratory Network UK Newborn Screening Laboratory Network. Available online: http://newbornscreening.org/site/laboratory-directory.asp (accessed on 17 January 2023).
- Overview of the UK Population—Office for National Statistics. Available online: https://www.ons.gov.uk/peoplepopulationandcommunity/populationandmigration/populationestimates/articles/overviewoftheukpopulation/january2021 (accessed on 10 January 2021).
- O’Sullivan, C.P.; Lamagni, T.; Patel, D.; Efstratiou, A.; Cunney, R.; Meehan, M.; Ladhani, S.; Reynolds, A.J.; Campbell, R.; Doherty, L.; et al. Group B streptococcal disease in UK and Irish infants younger than 90 days, 2014–15: A prospective surveillance study. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2019, 19, 83–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carreras-Abad, C.; To, K.N.; Ramkhelawon, L.; Planche, T.; Monahan, I.; Djennad, A.; Chalker, V.; Heath, P.T.; Le Doare, K. Detection of group B streptococcus colonisation in pregnant women: Comparison of two different culture methods and study of antimicrobial resistance patterns. J. Infect. 2021, 82, 186–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angeloni, S.; Das, S.; De Jager, W.; Dunbar, S. xMAP® Cookbook A Collection of Methods and Protocols for Developing Multiplex Assays with xMAP® Technology For Research Use Only. Not for Use in Diagnostic Procedures. Authors. Available online: www.luminexcorp.com%7C (accessed on 12 April 2022).
- Buurman, E.T.; Timofeyeva, Y.; Gu, J.; Kim, J.H.; Kodali, S.; Liu, Y.; Mininni, T.; Moghazeh, S.; Pavliakova, D.; Singer, C.; et al. A Novel Hexavalent Capsular Polysaccharide Conjugate Vaccine (GBS6) for the Prevention of Neonatal Group B Streptococcal Infections by Maternal Immunization. J. Infect. Dis. 2019, 220, 105–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baker, C.J.; Carey, V.J.; Rench, M.A.; Edwards, M.S.; Hillier, S.L.; Kasper, D.L.; Platt, R. Maternal antibody at delivery protects neonates from early onset group B streptococcal disease. J. Infect. Dis. 2014, 209, 781–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amini, F.; Auma, E.; Hsia, Y.; Bilton, S.; Hall, T.; Ramkhelawon, L.; Heath, P.T.; Le Doare, K. Reliability of dried blood spot (DBS) cards in antibody measurement: A systematic review. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0248218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jopling, J.; Henry, E.; Wiedmeier, S.; Christensen, R. Reference Ranges for Hematocrit and Blood Hemoglobin Concentration during the Neonatal Period: Data from a Multihospital Health Care System. Pediatrics 2009, 123, e333–e337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salsbury, D. Anemia of Prematurity. Neonatal Netw. 2001, 20, 13–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christensen, R.D. Hematologic Problems of the Neonate; W. B. Saunders: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2000; pp. 117–136. [Google Scholar]
- Geaghan, S. Normal Blood Values: Selected Reference Values for Neonatal, Pediatric and Adult Populations. In Hematology, Basic Principles and Practice; Hoffman, R., Benz, E.J., Shattil, S.J., Furie, B., Cohen, H.J., Silberstein, L.E., McGlave, P., Eds.; Churchill Livingstone: London, UK, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Chanarin, I. Blood and Its Disease; Churchill Livingstone: London, UK, 1984. [Google Scholar]
- Plotkin, S.A. Correlates of vaccine-induced immunity. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2008, 47, 401–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chase, B.A.; Johnston, S.A.; Legutki, J.B. Evaluation of biological sample preparation for immunosignature-based diagnostics. Clin. Vaccine Immunol. 2012, 19, 352–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hardelid, P.; Williams, D.; Dezateux, C.; Cubitt, W.D.; Peckham, C.S.; Tookey, P.A.; Cortina-Borja, M. Agreement of rubella IgG antibody measured in serum and dried blood spots using two commercial enzyme-linked immunosorbent assays. J. Med. Virol. 2008, 80, 360–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Characteristics | Case, n (%) | Controls, n (%) | Total, n (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| DBS analysed | 61 (32.79%) | 125 (67.20%) | 186 (100) |
| Male | 33 (32.04%) | 70 (67.96%) | 103 (55.38) |
| Female | 26 (33.77%) | 51 (66.23%) | 77 (41.40) |
| Missing | 2 (16.67%) | 4 (83.33%) | 6 (3.23%) |
| Mean gestation age (weeks) | 38.58 (37–41) | 38.90 (38–41) |
| Serotype | Ia | Ib | II | III | IV | V |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cases, homotypic serotype | 183.01 * | NA ** | NA ** | 2.29 *** (0.46–11.47) | NA ** | NA ** |
| Case, any serotype | 1.71 (0.75–3.92) | 1.03 (0.55–1.94) | 5.42 (2.36–12.45) | 1.92 (1.19–3.12) | 0.02 (0.02–0.02) | 1.37 (0.70–2.69) |
| Controls | 2.89 (1.58–5.30) | 1.00 (0.64–1.59) | 5.55 (3.26–9.47) | 2.00 (1.45–2.80) | 0.02 (0.02–0.02) | 1.05 (0.67–1.66) |
| Cut-Off | Case Inclusion | Cases | Controls | Odds ≥ Cut in Cases vs. Controls | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| <Cut-Off | ≥Cut-Off | <Cut-Off | ≥Cut-Off | Conditional OR (95% CI) | p-Value | ||
| 0.3 | STIII | 0 | 10 | 11 | 114 | n/a | |
| STIII and ST not known | 3 | 50 | 11 | 114 | 1.61 (0.39–6.59) | 0.51 | |
| All | 3 | 56 | 11 | 114 | 1.81 (0.46–7.17) | 0.40 | |
| 1 | STIII | 5 | 5 | 49 | 76 | 0.78 (0.15–4.20) | 0.77 |
| STIII and ST not known | 23 | 30 | 49 | 76 | 0.66 (0.29–1.48) | 0.31 | |
| All | 27 | 32 | 49 | 76 | 0.67 (0.32–1.41) | 0.29 | |
| 3 | STIII | 8 | 2 | 86 | 39 | 0.67 (0.07–6.41) | 0.73 |
| STIII and ST not known | 37 | 16 | 86 | 39 | 0.93 (0.45–1.95) | 0.85 | |
| All | 42 | 17 | 86 | 39 | 0.86 (0.43–1.74) | 0.68 | |
| 10 | STIII | 8 | 2 | 101 | 24 | 1.00 (0.09–11.03) | 1.00 |
| STIII and ST not known | 44 | 9 | 101 | 24 | 0.78 (0.32–1.94) | 0.60 | |
| All | 49 | 10 | 101 | 24 | 0.77 (0.33–1.77) | 0.54 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Auma, E.; Hall, T.; Chopra, S.; Bilton, S.; Ramkhelawon, L.; Amini, F.; Calvert, A.; Amirthalingam, G.; Jones, C.E.; Andrews, N.; et al. Using Dried Blood Spots for a Sero-Surveillance Study of Maternally Derived Antibody against Group B Streptococcus. Vaccines 2023, 11, 357. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines11020357
Auma E, Hall T, Chopra S, Bilton S, Ramkhelawon L, Amini F, Calvert A, Amirthalingam G, Jones CE, Andrews N, et al. Using Dried Blood Spots for a Sero-Surveillance Study of Maternally Derived Antibody against Group B Streptococcus. Vaccines. 2023; 11(2):357. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines11020357
Chicago/Turabian StyleAuma, Erick, Tom Hall, Simran Chopra, Sam Bilton, Laxmee Ramkhelawon, Fahimah Amini, Anna Calvert, Gayatri Amirthalingam, Christine E. Jones, Nick Andrews, and et al. 2023. "Using Dried Blood Spots for a Sero-Surveillance Study of Maternally Derived Antibody against Group B Streptococcus" Vaccines 11, no. 2: 357. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines11020357
APA StyleAuma, E., Hall, T., Chopra, S., Bilton, S., Ramkhelawon, L., Amini, F., Calvert, A., Amirthalingam, G., Jones, C. E., Andrews, N., Heath, P. T., & Le Doare, K. (2023). Using Dried Blood Spots for a Sero-Surveillance Study of Maternally Derived Antibody against Group B Streptococcus. Vaccines, 11(2), 357. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines11020357






