Virus-Like Particles Based on the Novel Goose Parvovirus (NGPV) VP2 Protein Protect Ducks against NGPV Challenge
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Material and Methods
2.1. Virus, Plasmid Vector and Cells
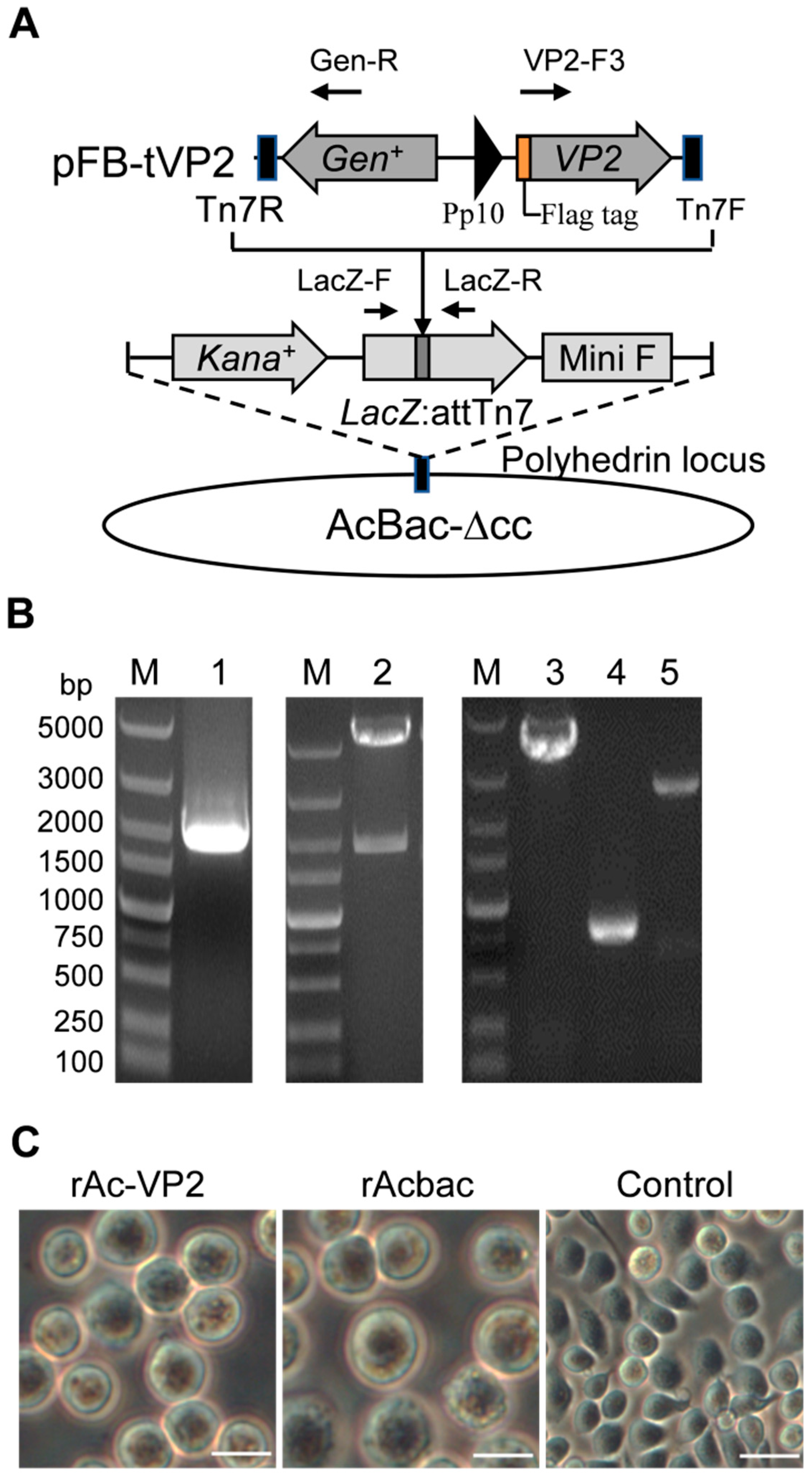
2.2. Construction and Rescue of Recombinant Baculovirus
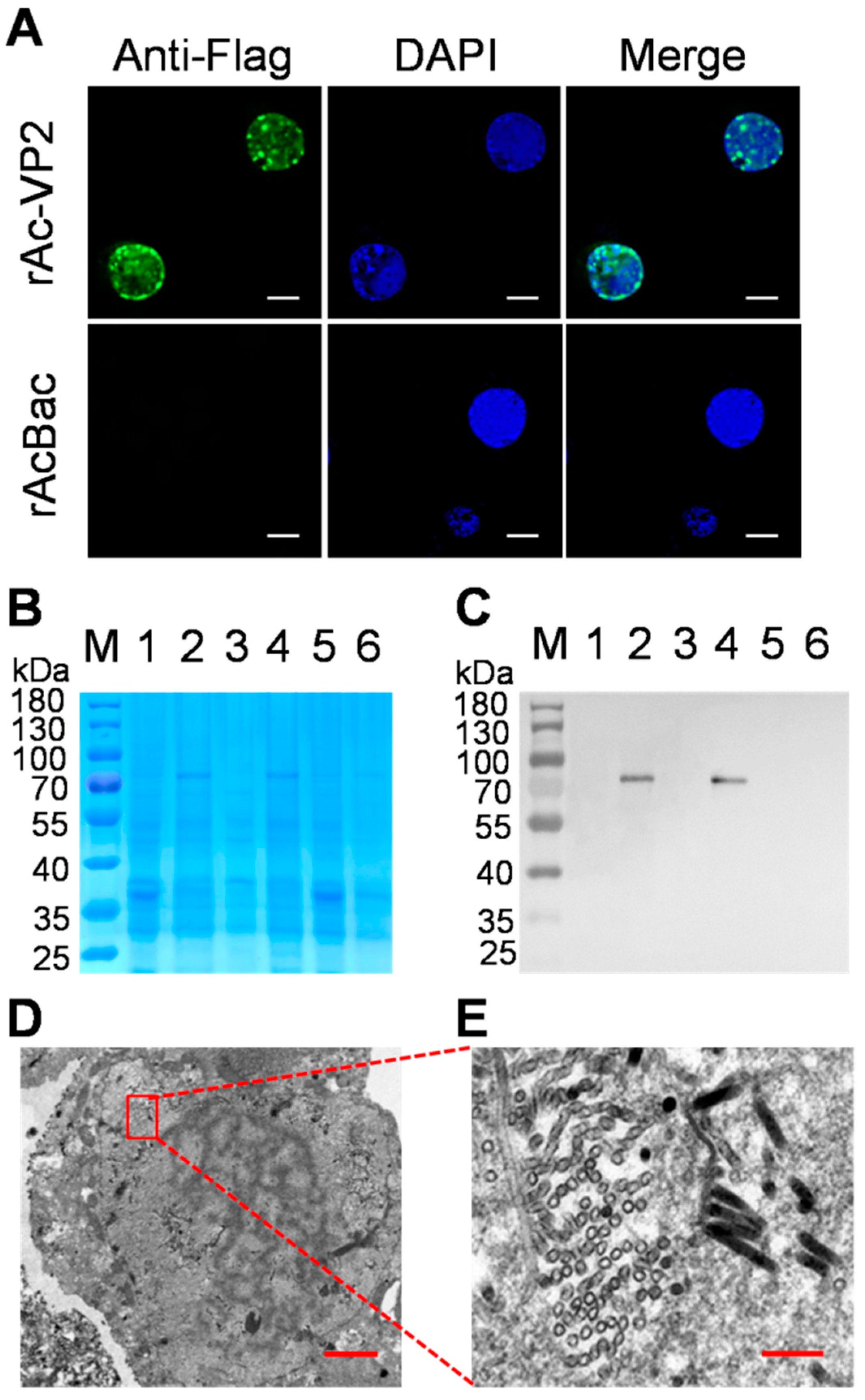
2.3. Indirect Immunofluorescence Assay Analysis
2.4. SDS-PAGE and Western Blotting Analysis
2.5. Transmission Electron Microscopy
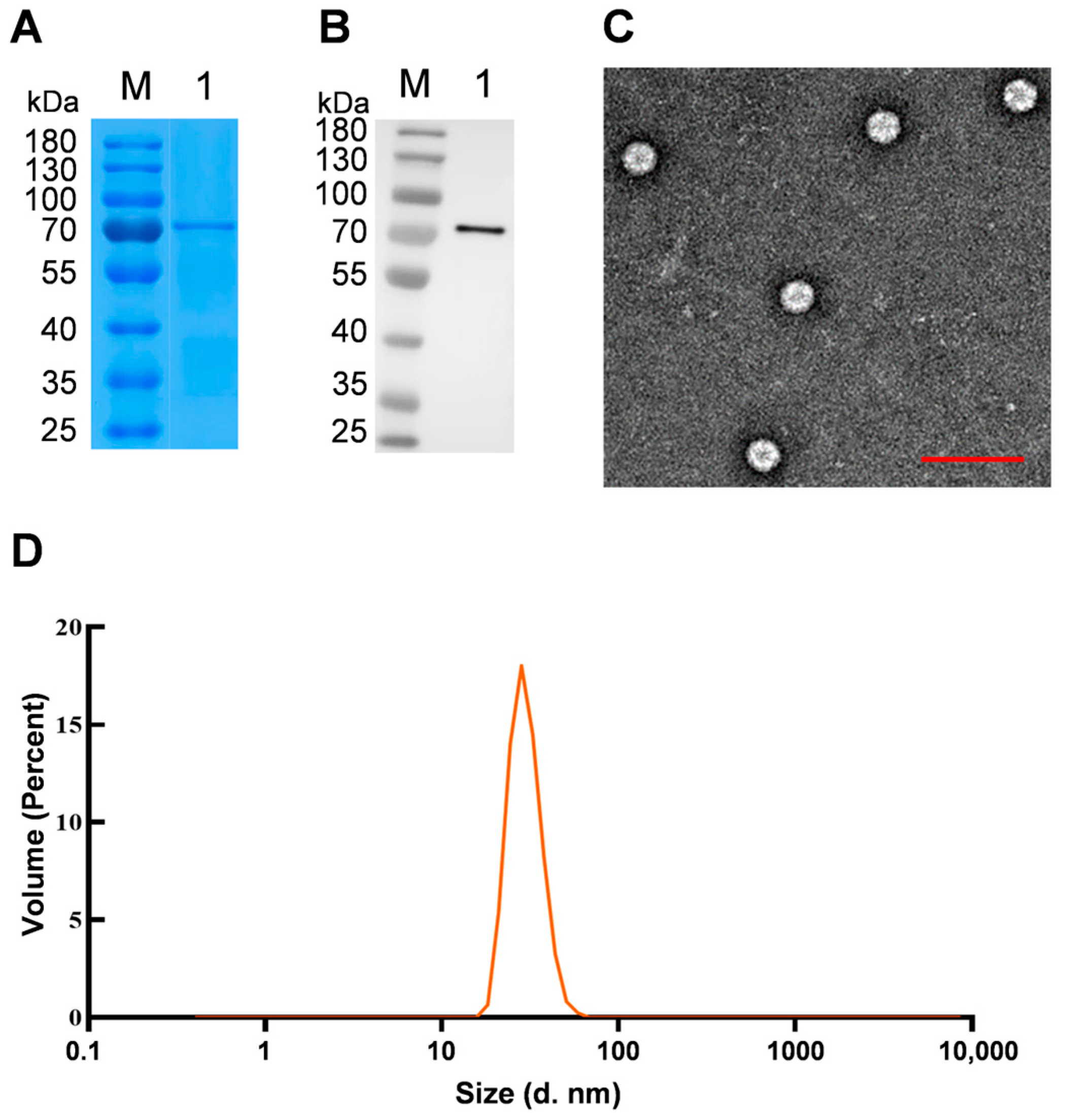
2.6. VLP Purification
2.7. VLP Identification
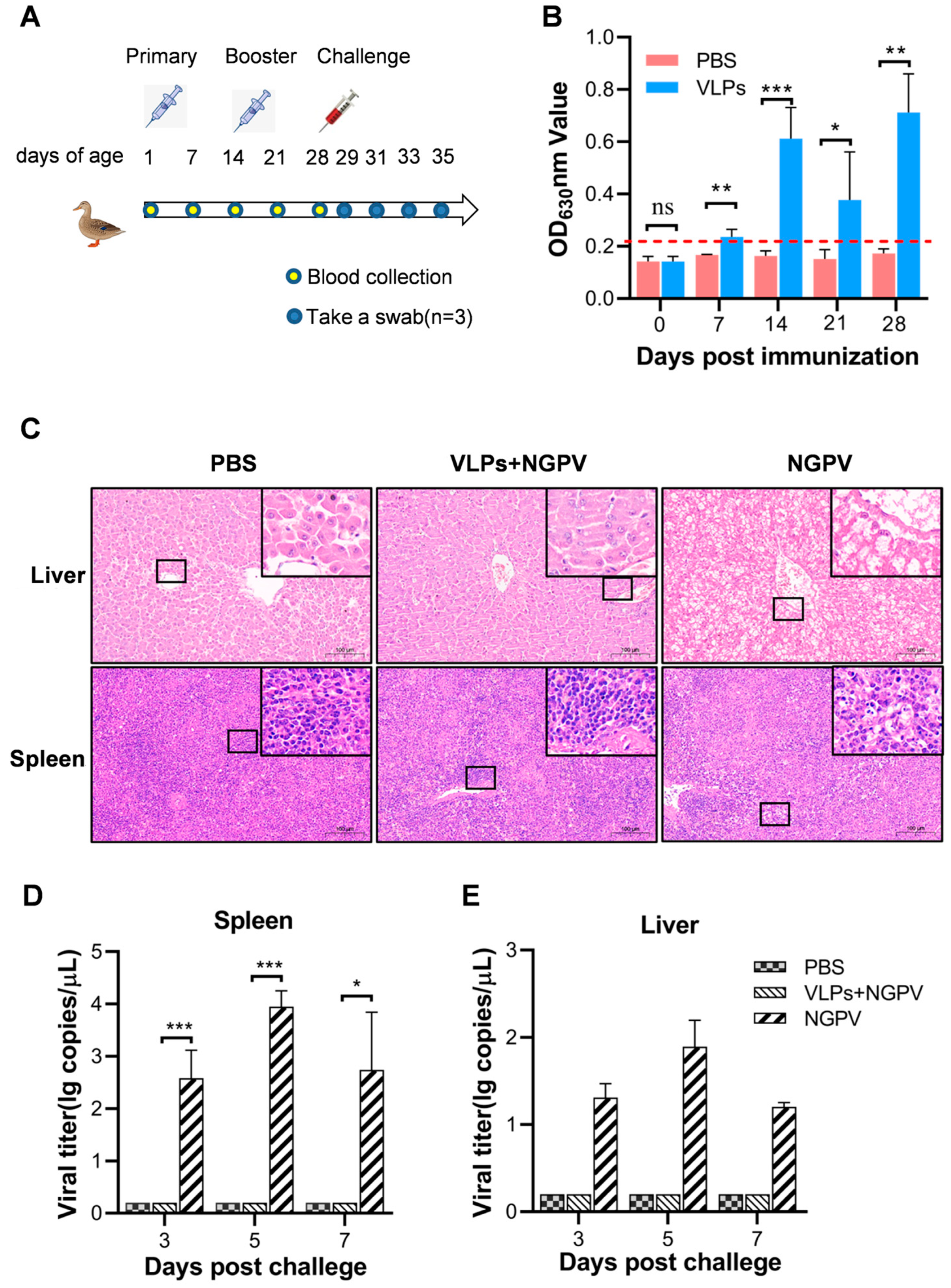
2.8. Animal Experiments
2.9. Quantitative Real-Time PCR
2.10. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Construction and Rescue of Recombinant Baculovirus
3.2. Expression and Identification of tVP2 Protein in Insect Cells
3.3. Observation, Purification and Verification of VLPs
3.4. Serum Antibodies Induced by VLP Vaccine
3.5. Protective Efficacy of VLPs against NGPV Challenge
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bian, G.; Ma, H.; Luo, M.; Gong, F.; Li, B.; Wang, G.; Mohiuddin, M.; Liao, M.; Yuan, J. Identification and Genomic Analysis of Two Novel Duck-Origin GPV-Related Parvovirus in China. BMC Vet. Res. 2019, 15, 88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Wang, Y.; Li, Y.; Gao, Y.; Li, Y.; Jiang, Z.; Zhu, G.; Wang, X. Reproduction and Pathogenesis of Short Beak and Dwarfish Syndrome in Cherry Valley Pekin Ducks Infected with the Rescued Novel Goose Parvovirus. Virulence 2022, 13, 844–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palya, V.; Zolnai, A.; Benyeda, Z.; Kovács, E.; Kardi, V.; Mató, T. Short Beak and Dwarfism Syndrome of Mule Duck Is Caused by a Distinct Lineage of Goose Parvovirus. Avian Pathol. 2009, 38, 175–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, Y.S.; Lin, D.F.; Lee, Y.L.; Liao, Y.K.; Tsai, H.J. Infectious Bill Atrophy Syndrome Caused by Parvovirus in a Co-Outbreak with Duck Viral Hepatitis in Ducklings in Taiwan. Avian Dis. 1993, 37, 591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, H.; Dou, Y.; Tang, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Zheng, X.; Niu, X.; Yang, J.; Yu, X.; Diao, Y. Isolation and Genomic Characterization of a Duck-Origin GPV-Related Parvovirus from Cherry Valley Ducklings in China. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0140284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soliman, M.A.; Erfan, A.M.; Samy, M.; Mahana, O.; Nasef, S.A. Detection of Novel Goose Parvovirus Disease Associated with Short Beak and Dwarfism Syndrome in Commercial Ducks. Animals 2020, 10, 1833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matczuk, A.K.; Chmielewska-Władyka, M.; Siedlecka, M.; Bednarek, K.J.; Wieliczko, A. Short Beak and Dwarfism Syndrome in Ducks in Poland Caused by Novel Goose Parvovirus. Animals 2020, 10, 2397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Li, C.; Tang, A.; Li, H.; Yu, Z.; Chen, Z.; Guo, X.; Liu, G. Immunogenicity of an Inactivated Novel Goose Parvovirus Vaccine for Short Beak and Dwarfism Syndrome in Cherry Valley Ducks. Arch. Virol. 2022, 167, 881–889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Li, Q.; Chen, Z.; Liu, G. Novel Duck Parvovirus Identified in Cherry Valley Ducks (Anas Platyrhynchos Domesticus), China. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2016, 44, 278–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Liu, P.; Wu, Y.; Wang, M.; Jia, R.; Zhu, D.; Liu, M.; Yang, Q.; Wu, Y.; Zhao, X.; et al. Growth Characteristics of the Novel Goose Parvovirus SD15 Strain in Vitro. BMC Vet. Res. 2019, 15, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kheirvari, M.; Liu, H.; Tumban, E. Virus-like Particle Vaccines and Platforms for Vaccine Development. Viruses 2023, 15, 1109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ju, H.; Wei, N.; Wang, Q.; Wang, C.; Jing, Z.; Guo, L.; Liu, D.; Gao, M.; Ma, B.; Wang, J. Goose Parvovirus Structural Proteins Expressed by Recombinant Baculoviruses Self-Assemble into Virus-like Particles with Strong Immunogenicity in Goose. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2011, 409, 131–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohsen, M.O.; Bachmann, M.F. Virus-like Particle Vaccinology, from Bench to Bedside. Cell Mol. Immunol. 2022, 19, 993–1011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, S.; Wang, M.; Shen, S.; Hu, Z.; Wang, H.; Deng, F. The FP25K Acts as a Negative Factor for the Infectivity of AcMNPV Budded Virus. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0128471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaba, S.A.; Salcedo, A.M.; Wafula, P.O.; Vlak, J.M.; Van Oers, M.M. Development of a Chitinase and V-Cathepsin Negative Bacmid for Improved Integrity of Secreted Recombinant Proteins. J. Virol. Methods 2004, 122, 113–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, H.; Dou, Y.; Tang, Y.; Zheng, X.; Niu, X.; Yang, J.; Yu, X.; Diao, Y. Experimental Reproduction of Beak Atrophy and Dwarfism Syndrome by Infection in Cherry Valley Ducklings with a Novel Goose Parvovirus-Related Parvovirus. Vet. Microbiol. 2016, 183, 16–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Le Gall-Reculé, G.; Jestin, V. Biochemical and Genomic Characterization of Muscovy Duck Parvovirus. Arch. Virol. 1994, 139, 121–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhat, T.; Cao, A.; Yin, J. Virus-like Particles: Measures and Biological Functions. Viruses 2022, 14, 383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, R.; Arora, K.; Roy, S.S.; Joseph, A.; Rastogi, R.; Arora, N.M.; Kundu, P.K. Platforms, Advances, and Technical Challenges in Virus-like Particles-Based Vaccines. Front. Immunol. 2023, 14, 1123805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bogani, G.; Raspagliesi, F.; Ditto, A.; de la Fuente, J. The Adoption of Viral Capsid-Derived Virus-Like Particles (VLPs) for Disease Prevention and Treatments. Vaccines 2020, 8, 432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Syomin, B.V.; Ilyin, Y.V. Virus-Like Particles as an Instrument of Vaccine Production. Mol. Biol. 2019, 53, 323–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crisci, E.; Bárcena, J.; Montoya, M. Virus-like Particle-Based Vaccines for Animal Viral Infections. Inmunología 2013, 32, 102–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crisci, E.; Bárcena, J.; Montoya, M. Virus-like Particles: The New Frontier of Vaccines for Animal Viral Infections. Vet. Immunol. Immunopathol. 2012, 148, 211–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohsen, M.O.; Gomes, A.C.; Vogel, M.; Bachmann, M.F. Interaction of Viral Capsid-Derived Virus-Like Particles (VLPs) with the Innate Immune System. Vaccines 2018, 6, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nooraei, S.; Bahrulolum, H.; Hoseini, Z.S.; Katalani, C.; Hajizade, A.; Easton, A.J.; Ahmadian, G. Virus-like Particles: Preparation, Immunogenicity and Their Roles as Nanovaccines and Drug Nanocarriers. J. Nanobiotechnology 2021, 19, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le, D.T.; Müller, K.M. In Vitro Assembly of Virus-Like Particles and Their Applications. Life 2021, 11, 334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chaves, L.C.S.; Ribeiro, B.M.; Blissard, G.W. Production of GP64-Free Virus-like Particles from Baculovirus-Infected Insect Cells. J. Gen. Virol. 2018, 99, 265–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Jia, J.; Mi, Q.; Li, Y.; Gao, Y.; Zhu, G.; Wang, J. Molecular Characteristics and Phylogenetic Analysis of Novel Goose Parvovirus Strains Associated with Short Beak and Dwarfism Syndrome. Arch. Virol. 2021, 166, 2495–2504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minkner, R.; Park, E.Y. Purification of Virus-like Particles (VLPs) Expressed in the Silkworm Bombyx Mori. Biotechnol. Lett. 2018, 40, 659–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, S.; Wang, S.; Jiang, D.; Cheng, X.; Zhu, X.; Lin, F.; Yu, B.; Dong, H.; Wang, X.; Munir, M.; et al. VP2 Virus-like Particles Elicit Protective Immunity against Duckling Short Beak and Dwarfism Syndrome in Ducks. Transbound. Emerg. Dis. 2022, 69, 570–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Name | Primer Sequences (5’–3’) |
|---|---|
| FH-F1 | TTCTCGAGGCCACCATGGACTATAAGGACGACGATGATTACCACCATCACCATCATCAT (Xho I) |
| FH-R1 | AGCTTCCCTGTATTTTTTTTTGCAGGTGCCGTATGATGATGGTGATGGTGGTAATCATC |
| VP2-F2 | CCTGCAAAAAAAAATACAGGGAAGCT |
| VP2-F3 | TTCTCGAGGCCACCATGGACTATAA (Xho I) |
| VP2-R2 | TTGCATGCTTACAGATTTTGAGTTAGATATCTGGTTCCAAT (Sph I) |
| LacZ-F | TCACACAGGAAACAGCTATGACCATG |
| LacZ-R | CTCTTCGCTATTACGCCAGCTGG |
| Gen-R | TGCTGCCTTCGACCAAGAAGC |
| Group | Cloacal Swabs | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 dpc | 3 dpc | 5 dpc | 7 dpc | |
| PBS | 0/10 | 0/10 | 0/10 | 0/10 |
| VLPs + NGPV | 0/10 | 0/10 | 0/10 | 0/10 |
| NGPV | 0/10 | 2/10 | 4/10 | 2/10 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shang, Y.; Ma, Y.; Tang, S.; Chen, X.; Feng, H.; Li, L.; Wang, H.; Zeng, Z.; Yao, L.; Zhang, T.; et al. Virus-Like Particles Based on the Novel Goose Parvovirus (NGPV) VP2 Protein Protect Ducks against NGPV Challenge. Vaccines 2023, 11, 1768. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines11121768
Shang Y, Ma Y, Tang S, Chen X, Feng H, Li L, Wang H, Zeng Z, Yao L, Zhang T, et al. Virus-Like Particles Based on the Novel Goose Parvovirus (NGPV) VP2 Protein Protect Ducks against NGPV Challenge. Vaccines. 2023; 11(12):1768. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines11121768
Chicago/Turabian StyleShang, Yu, Yao Ma, Sheng Tang, Xing Chen, Helong Feng, Li Li, Hongcai Wang, Zhe Zeng, Lun Yao, Tengfei Zhang, and et al. 2023. "Virus-Like Particles Based on the Novel Goose Parvovirus (NGPV) VP2 Protein Protect Ducks against NGPV Challenge" Vaccines 11, no. 12: 1768. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines11121768
APA StyleShang, Y., Ma, Y., Tang, S., Chen, X., Feng, H., Li, L., Wang, H., Zeng, Z., Yao, L., Zhang, T., Zeng, C., Luo, Q., & Wen, G. (2023). Virus-Like Particles Based on the Novel Goose Parvovirus (NGPV) VP2 Protein Protect Ducks against NGPV Challenge. Vaccines, 11(12), 1768. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines11121768





