Japanese Encephalitis Vaccine Acceptance and Strategies for Travelers: Insights from a Scoping Review and Practitioners in Endemic Countries
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
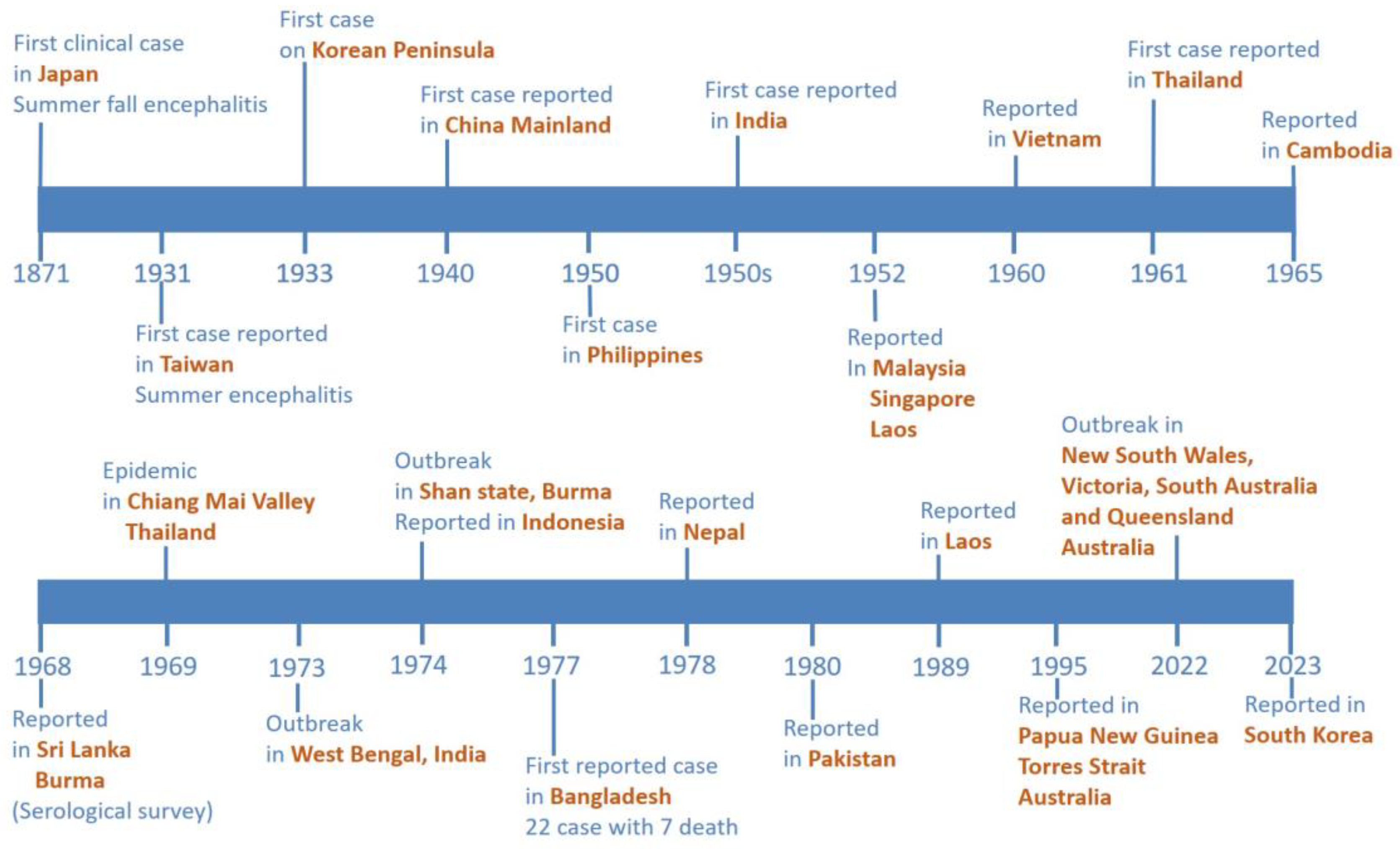
3.1. A Comprehensive Update from 2017 to 2023 for Local Residents and Travelers
3.2. Japanese Encephalitis Vaccine Implications for Travelers Visiting JE-Endemic Areas
3.2.1. Inactivated JE Vaccine
3.2.2. Live Attenuated JE Vaccine
3.3. Vaccines under Development
3.4. Time Taken for the JE Vaccine to Become Effective
| Vaccine Type | Substrate | Trade Name | Manufacturer | Vaccine Strains | License | Regimen | Efficacy Study | Prices (In USD) | Country |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Inactivated MB-JEV | Mouse brain | BIKEN®, JE-VAX, Sanofi Pasteur | BIKEN, Osaka, Japan (Research Foundation for Microbial Diseases of Osaka University) | Nakayama strain Beijing-1 strain | Japan in 1954 | Days 0, 7, 28 at 12–24 months of age; booster after 12 months, then every 3–5 years | In Thailand, 84.8–100% [45] 85.59% after 1 dose [43] 91.07% after 2 doses [43] 98.51% after 3 doses [43] | - | European Union, United States, India, Japan, Malaysia, North Korea, South Korea, Sri Lanka, Taiwan, Thailand, Vietnam |
| Inactivated | Hamster kidney cells | - | China | Beijing-3 or P-3 | China in 1968 | - | - | - | China |
| Inactivated (Freeze dried) | Vero cells | JEBIK® | BIKEN, Japan (JEBIK-V) | Beijing-1 | Japan in 2009 | Days 0, 7, 28 at 12–24 months of age; booster after 12 months, then every 3–5 years | - | Japan | |
| Vero cells | ENCEVAC® | KAKETSUKEN, Kumamoto, Japan (ENCEVAC, JEIMMUGEN) | Beijing-1 | Japan in 2011 | Days 0, 7, 28 at 12–24 months of age; booster after 12 months, then every 3–5 years | SPRs 100% after 2 doses and 3 doses [47] | Japan and South Korea | ||
| Vero cells | JEVACTM | Liaoning Cheng Da Biotechnology Co., Ltd., Shenyang, China | Beijing P-3 strain | China in 2008 | Day 0, 1–4 weeks and a booster vaccination at one year | SPRs 83% after 2 doses and SPRs 100% after booster [48] | - | China | |
| Inactivated JE-VC | Vero cells | IXIARO® (USA, EU); JESPECT® (AUS, NZ); JEEV® | Valneva Scotland Ltd., Livingston, UK; Biological E, Telangana, India | SA-14-14-2 | USA, Australia, and Europe in 2009 | Days 0, 28 as early as 2 months of age; booster after 1 year; accelerated schedule: Days 0,7 | SPRs 86–98% [51,53] | 96–339 [68,69] | European Union, United States, Canada, Latin America, Australia, New Zealand, Japan, Hong Kong, South Korea, Singapore, India, Nepal, Bangladesh, Bhutan, Pacific Islands, Papua New Guinea |
| Inactivated | Vero cells | JENVAC® | Bharat Biotech International Ltd., Telangana, India | Kolar-821564XY | India in 2014 | Days 0, 28 as early as 6 months of age | SPRs 61.7–99.8% [56,57] | 8–15 [70] | India |
| Live attenuated | Hamster kidney cells | CD.JEVAX® | Chengdu Institute of Biological Products (CDIBD), Chengdu, China | SA-14-14-2 | China in 1988 | A single dose at the age of 8 month and older; if needed, booster at 3–12 month | 78–99.3% after single dose [42,58,66,71,72] | 13.84–36.6 [73] | Japan, South Korea, China, Hong Kong, India, Nepal, Sri Lanka, Thailand |
| Chimera | Vero cells | IMOJEV® | Government Pharmaceutical Organization-Merieux Biological Products Co., Chachoengsao, Thailand; Sanofi Pasteur, Val-de-Reuil, France | JE SA-14-14-2/Yellow fever 17 D | Australia and Thailand in 2012 | A single dose at the age of 9 months and older; booster after 12 to 24 months | SPRs 87–99% [60,61] | 13.32–43 [73] | Australia, South Korea, Thailand |
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Solomon, T. Flavivirus Encephalitis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2004, 351, 370–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Erlanger, T.E.; Weiss, S.; Keiser, J.; Utzinger, J.; Wiedenmayer, K. Past, present, and future of Japanese encephalitis. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2009, 15, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Campbell, G.L.; Hills, S.L.; Fischer, M.; Jacobson, J.A.; Hoke, C.H.; Hombach, J.M.; Marfin, A.A.; Solomon, T.; Tsai, T.F.; Tsu, V.D.; et al. Estimated global incidence of Japanese encephalitis: A systematic review. Bull. World Health Organ. 2011, 89, 766–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- W.H.O. Vaccine-Preventable Communicable Diseases, Japanese Encephalitis Reported Cases by Country. In Global Health Observatory Data Repository; WHO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Lopez, A.L.; Raguindin, P.F.; Aldaba, J.G.; Avelino, F.; Sy, A.K.; Heffelfinger, J.D.; Silva, M.W.T. Epidemiology of Japanese encephalitis in the Philippines prior to routine immunization. Int. J. Infect. Dis. 2021, 102, 344–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taiwan Centers for Disease Control. Japanese Encephalitis; Taiwan Centers for Disease Control: Taipei City, Taiwan, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Moore, S.M. The current burden of Japanese encephalitis and the estimated impacts of vaccination: Combining estimates of the spatial distribution and transmission intensity of a zoonotic pathogen. PLoS Neglected Trop. Dis. 2021, 15, e0009385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Department of Disease Control. Annual Report 2018: Vaccine Preventable Disease Division (VPD); Ministry of Public Health: Bangkok, Thailand, 2018; p. 75.
- Department of Disease Control. Annual Epidemiological Surveillance Report 2019; Ministry of Public Health: Bangkok, Thailand, 2019; p. 802.
- Department of Disease Control. Annual Epidemiological Surveillance Report 2020; Ministry of Public Health: Bangkok, Thailand, 2020.
- Department of Disease Control. Standard Reporting Institution: Immunization; Health Data Center Service: Bangkok, Thailand, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Batchelor, P.; Petersen, K. Japanese encephalitis: A review of clinical guidelines and vaccine availability in Asia. Trop. Dis. Travel Med. Vaccines 2015, 1, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hameed, M.; Wahaab, A.; Nawaz, M.; Khan, S.; Nazir, J.; Liu, K.; Wei, J.; Ma, Z. Potential Role of Birds in Japanese Encephalitis Virus Zoonotic Transmission and Genotype Shift. Viruses 2021, 13, 357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amicizia, D.; Zangrillo, F.; Lai, P.L.; Iovine, M.; Panatto, D. Overview of Japanese encephalitis disease and its prevention. Focus on IC51 vaccine (IXIARO®). J. Prev. Med. Hyg. 2018, 59, E99–E107. [Google Scholar]
- Vyas, A.; De Jesus, O. Von Economo Encephalitis. In StatPearls; StatPearls Publishing LLC: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Mansfield, K.L.; Hernández-Triana, L.M.; Banyard, A.C.; Fooks, A.R.; Johnson, N. Japanese encephalitis virus infection, diagnosis and control in domestic animals. Vet. Microbiol. 2017, 201, 85–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burchard, G.D.; Caumes, E.; Connor, B.A.; Freedman, D.O.; Jelinek, T.; Jong, E.C.; von Sonnenburg, F.; Steffen, R.; Tsai, T.F.; Wilder-Smith, A.; et al. Expert opinion on vaccination of travelers against Japanese encephalitis. J. Travel Med. 2009, 16, 204–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Liang, G. Epidemiology of Japanese encephalitis: Past, present, and future prospects. Ther. Clin. Risk Manag. 2015, 11, 435–448. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Halstead, S.B.; Jacobson, J. Japanese encephalitis. Adv. Virus Res. 2003, 61, 103–138. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kuttner, A.G.; Ts’un, T. Encephalitis in North China. Results Obtained with Neutralization Tests. J. Clin. Investig. 1936, 15, 525–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okuno, T. An epidemiological review of Japanese encephalitis. World Health Stat. Q. 1978, 31, 120–133. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kono, R.; Kim, K.H. Comparative epidemiological features of Japanese encephalitis in the Republic of Korea, China (Taiwan) and Japan. Bull. World Health Organ. 1969, 40, 263–277. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lincoln, A.F.; Sivertson, S.E. Acute phase of Japanese B encephalitis; Two hundred and one cases in American soldiers, Korea, 1950. J. Am. Med. Assoc. 1952, 150, 268–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gould, D.J.; Edelman, R.; Grossman, R.A.; Nisalak, A.; Sullivan, M.F. Study of Japanese encephalitis virus in Chiangmai Valley, Thailand. IV. Vector studies. Am. J. Epidemiol. 1974, 100, 49–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olsen, S.J.; Supawat, K.; Campbell, A.P.; Anantapreecha, S.; Liamsuwan, S.; Tunlayadechanont, S.; Visudtibhan, A.; Lupthikulthum, S.; Dhiravibulya, K.; Viriyavejakul, A.; et al. Japanese encephalitis virus remains an important cause of encephalitis in Thailand. Int. J. Infect. Dis. 2010, 14, e888–e892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van den Hurk, A.F.; Pyke, A.T.; Mackenzie, J.S.; Hall-Mendelin, S.; Ritchie, S.A. Japanese Encephalitis Virus in Australia: From Known Known to Known Unknown. Trop. Med. Infect. Dis. 2019, 4, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yun, S.I.; Lee, Y.M. Japanese encephalitis: The virus and vaccines. Hum. Vaccin. Immunother. 2014, 10, 263–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Japanese Encephalitis (JE). Vaccine Coverage. 2023. Available online: https://immunizationdata.who.int/pages/coverage/japenc.html (accessed on 25 January 2023).
- Pham, D.; Howard-Jones, A.R.; Hueston, L.; Jeoffreys, N.; Doggett, S.; Rockett, R.J.; Eden, J.S.; Sintchenko, V.; Chen, S.C.A.; O’Sullivan, M.V.; et al. Emergence of Japanese encephalitis in Australia: A diagnostic perspective. Pathology 2022, 54, 669–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Outbreak News Radio. South Korea reports 1st Japanese encephalitis case of 2023. Outbreak News Radio, 9 September 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Orenstein, W.P.O.; Edwards, K.M.; Plotkin, S. Plotkin’s Vaccines, 7th ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2017; Volume 33. [Google Scholar]
- Hills, S.L.; Walter, E.B.; Atmar, R.L.; Fischer, M. Japanese Encephalitis Vaccine: Recommendations of the Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices. MMWR Recomm. Rep. 2019, 68, 1–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lehtinen, V.A.; Huhtamo, E.; Siikamäki, H.; Vapalahti, O. Japanese encephalitis in a Finnish traveler on a two-week holiday in Thailand. J. Clin. Virol. 2008, 43, 93–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buhl, M.R.; Lindquist, L. Japanese encephalitis in travelers: Review of cases and seasonal risk. J. Travel Med. 2009, 16, 217–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hills, S.L.; Griggs, A.C.; Fischer, M. Japanese encephalitis in travelers from non-endemic countries, 1973–2008. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2010, 82, 930–936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erra, E.O.; Kantele, A. The Vero cell-derived, inactivated, SA14-14-2 strain-based vaccine (Ixiaro) for prevention of Japanese encephalitis. Expert Rev. Vaccines 2015, 14, 1167–1179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deshpande, B.R.; Rao, S.R.; Jentes, E.S.; Hills, S.L.; Fischer, M.; Gershman, M.D.; Brunette, G.W.; Ryan, E.T.; LaRocque, R.C.; The Global TravEpiNet, C. Use of Japanese encephalitis vaccine in US travel medicine practices in Global TravEpiNet. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2014, 91, 694–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walker, X.J.; Barnett, E.D.; Wilson, M.E.; Macleod, W.B.; Jentes, E.S.; Karchmer, A.W.; Hamer, D.H.; Chen, L.H. Characteristics of Travelers to Asia Requiring Multidose Vaccine Schedules: Japanese Encephalitis and Rabies Prevention. J. Travel Med. 2015, 22, 403–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hatz, C.; Werlein, J.; Mutsch, M.; Hufnagel, M.; Behrens, R.H. Japanese encephalitis: Defining risk incidence for travelers to endemic countries and vaccine prescribing from the UK and Switzerland. J. Travel Med. 2009, 16, 200–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamer, D.H.; Chen, L.H. Japanese encephalitis: Vaccine options and timing of pre-travel vaccination. J. Travel Med. 2018, 25, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Satchidanandam, V. Japanese Encephalitis Vaccines. Curr. Treat. Options Infect. Dis. 2020, 12, 375–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hegde, N.R.; Gore, M.M. Japanese encephalitis vaccines: Immunogenicity, protective efficacy, effectiveness, and impact on the burden of disease. Hum. Vaccin. Immunother. 2017, 13, 1320–1337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, S.E.; Pan, M.J.; Tseng, H.F.; Liau, M.Y. The efficacy of mouse-brain inactivated Nakayama strain Japanese encephalitis vaccine results from 30 years experience in Taiwan. Vaccine 2006, 24, 2669–2673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoke, C.H.; Nisalak, A.; Sangawhipa, N.; Jatanasen, S.; Laorakapongse, T.; Innis, B.L.; Kotchasenee, S.; Gingrich, J.B.; Latendresse, J.; Fukai, K.; et al. Protection against Japanese encephalitis by inactivated vaccines. N. Engl. J. Med. 1988, 319, 608–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muangchana, C.; Henprasertthae, N.; Nurach, K.; Theppang, K.; Yoocharoen, P.; Varinsathien, P.; Techathawat, S.; Sanohsieng, S.; Anantapreecha, S. Effectiveness of mouse brain-derived inactivated Japanese encephalitis vaccine in Thai National Immunization Program: A case-control study. Vaccine 2012, 30, 361–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyazaki, C.; Okada, K.; Ozaki, T.; Hirose, M.; Iribe, K.; Yokote, H.; Ishikawa, Y.; Togashi, T.; Ueda, K. Phase III clinical trials comparing the immunogenicity and safety of the vero cell-derived Japanese encephalitis vaccine Encevac with those of mouse brain-derived vaccine by using the Beijing-1 strain. Clin. Vaccine Immunol. 2014, 21, 188–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yun, K.W.; Lee, H.J.; Kang, J.H.; Eun, B.W.; Kim, Y.J.; Kim, K.H.; Kim, N.H.; Hong, Y.J.; Kim, D.H.; Kim, H.M.; et al. Safety and immunogenicity of a freeze-dried, Vero cell culture-derived, inactivated Japanese encephalitis vaccine (KD-287, ENCEVAC®) versus a mouse brain-derived inactivated Japanese encephalitis vaccine in children: A phase III, multicenter, double-blinded, randomized trial. BMC Infect. Dis. 2015, 15, 7. [Google Scholar]
- Chanthavanich, P.; Limkittikul, K.; Sirivichayakul, C.; Chokejindachai, W.; Hattasingh, W.; Pengsaa, K.; Surangsrirat, S.; Srisuwannaporn, T.; Kaewma, B.; Yoksan, S.; et al. Immunogenicity and safety of inactivated chromatographically purified Vero cell-derived Japanese encephalitis vaccine in Thai children. Hum. Vaccin. Immunother. 2018, 14, 900–905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Ma, S.J.; Liu, X.; Jiang, L.N.; Zhou, J.H.; Xiong, Y.Q.; Ding, H.; Chen, Q. Immunogenicity and safety of currently available Japanese encephalitis vaccines: A systematic review. Hum. Vaccin. Immunother. 2014, 10, 3579–3593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- U.S. Food and Drug Administration. Ixiaro: Japanese Encephalitis Vaccine [Package Insert]; FDA: Vienna, Austria, 2018.
- Cramer, J.P.; Jelinek, T.; Paulke-Korinek, M.; Reisinger, E.C.; Dieckmann, S.; Alberer, M.; Bühler, S.; Bosse, D.; Meyer, S.; Fragapane, E.; et al. One-year immunogenicity kinetics and safety of a purified chick embryo cell rabies vaccine and an inactivated Vero cell-derived Japanese encephalitis vaccine administered concomitantly according to a new, 1-week, accelerated primary series. J. Travel Med. 2016, 23, taw011. [Google Scholar]
- Schuller, E.; Jilma, B.; Voicu, V.; Golor, G.; Kollaritsch, H.; Kaltenböck, A.; Klade, C.; Tauber, E. Long-term immunogenicity of the new Vero cell-derived, inactivated Japanese encephalitis virus vaccine IC51 Six and 12 month results of a multicenter follow-up phase 3 study. Vaccine 2008, 26, 4382–4386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tauber, E.; Kollaritsch, H.; Korinek, M.; Rendi-Wagner, P.; Jilma, B.; Firbas, C.; Schranz, S.; Jong, E.; Klingler, A.; Dewasthaly, S.; et al. Safety and immunogenicity of a Vero-cell-derived, inactivated Japanese encephalitis vaccine: A non-inferiority, phase III, randomised controlled trial. Lancet 2007, 370, 1847–1853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eder, S.; Dubischar-Kastner, K.; Firbas, C.; Jelinek, T.; Jilma, B.; Kaltenboeck, A.; Knappik, M.; Kollaritsch, H.; Kundi, M.; Paulke-Korinek, M.; et al. Long term immunity following a booster dose of the inactivated Japanese Encephalitis vaccine IXIARO®, IC51. Vaccine 2011, 29, 2607–2612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paulke-Korinek, M.; Kollaritsch, H.; Kundi, M.; Zwazl, I.; Seidl-Friedrich, C.; Jelinek, T. Persistence of antibodies six years after booster vaccination with inactivated vaccine against Japanese encephalitis. Vaccine 2015, 33, 3600–3604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, A.; Mitra, M.; Sampath, G.; Venugopal, P.; Rao, J.V.; Krishnamurthy, B.; Gupta, M.K.; Sri Krishna, S.; Sudhakar, B.; Rao, N.B.; et al. A Japanese Encephalitis Vaccine from India Induces Durable and Cross-protective Immunity Against Temporally and Spatially Wide-ranging Global Field Strains. J. Infect. Dis. 2015, 212, 715–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vadrevu, K.M.; Potula, V.; Khalatkar, V.; Mahantshetty, N.S.; Shah, A.; Ella, R. Persistence of Immune Responses with an Inactivated Japanese Encephalitis Single-Dose Vaccine, JENVAC and Interchangeability with a Live-Attenuated Vaccine. J. Infect. Dis. 2020, 222, 1478–1487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, R.; Tripathi, P.; Rizvi, A. Effectiveness of One Dose of SA 14-14-2 Vaccine against Japanese Encephalitis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2009, 360, 1465–1466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tandan, J.B.; Ohrr, H.; Sohn, Y.M.; Yoksan, S.; Ji, M.; Nam, C.M.; Halstead, S.B. Single dose of SA 14-14-2 vaccine provides long-term protection against Japanese encephalitis: A case-control study in Nepalese children 5 years after immunization. Vaccine 2007, 25, 5041–5045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasveld, P.E.; Ebringer, A.; Elmes, N.; Bennett, S.; Yoksan, S.; Aaskov, J.; McCarthy, K.; Kanesa-thasan, N.; Meric, C.; Reid, M. Long term immunity to live attenuated Japanese encephalitis chimeric virus vaccine: Randomized, double-blind, 5-year phase II study in healthy adults. Hum. Vaccin. 2010, 6, 1038–1046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desai, K.; Coudeville, L.; Bailleux, F. Modelling the long-term persistence of neutralizing antibody in adults after one dose of live attenuated Japanese encephalitis chimeric virus vaccine. Vaccine 2012, 30, 2510–2515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- UNICEF. Japanese Encephalitis Vaccine: Market and Supply Update 2021; UNICEF: New York, NY, USA, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, L.; Xiao, A.; Wang, H.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Li, Y.; Wei, Y.; Liu, W.; Chen, C. A VLP-Based Vaccine Candidate Protects Mice against Japanese Encephalitis Virus Infection. Vaccines 2022, 10, 197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, N.; Zhang, Z.R.; Zhang, Y.N.; Liu, J.; Deng, C.L.; Shi, P.Y.; Yuan, Z.M.; Ye, H.Q.; Zhang, B. A replication-defective Japanese encephalitis virus (JEV) vaccine candidate with NS1 deletion confers dual protection against JEV and West Nile virus in mice. NPJ Vaccines 2020, 5, 73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, X.; Yu, X.; Wang, Y.; Turtle, L.; Cui, M.; Wang, R.; Yin, C. Complete protection for mice conferred by a DNA vaccine based on the Japanese encephalitis virus P3 strain used to prepare the inactivated vaccine in China. Virol. J. 2020, 17, 126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bista, M.B.; Banerjee, M.K.; Shin, S.H.; Tandan, J.B.; Kim, M.H.; Sohn, Y.M.; Ohrr, H.C.; Tang, J.L.; Halstead, S.B. Efficacy of single-dose SA 14-14-2 vaccine against Japanese encephalitis: A case control study. Lancet 2001, 358, 791–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feroldi, E.; Capeding, M.R.; Boaz, M.; Gailhardou, S.; Meric, C.; Bouckenooghe, A. Memory immune response and safety of a booster dose of Japanese encephalitis chimeric virus vaccine (JE-CV) in JE-CV-primed children. Hum. Vaccin. Immunother. 2013, 9, 889–897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- IndiaMART. Vaccine Cost; IndiaMART: Uttar Pradesh, India, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Prices of Ixiaro. 2023. Available online: https://www.goodrx.com (accessed on 27 September 2023).
- TravelDoc. Vaccine Prices. Available online: https://www.travel-doc.com (accessed on 27 September 2023).
- Luo, D.; Yin, H.; Xili, L.; Song, J.; Wang, Z. The efficacy of Japanese encephalitis vaccine in Henan, China: A case-control study. Southeast Asian J. Trop. Med. Public Health 1994, 25, 643–646. [Google Scholar]
- Hennessy, S.; Liu, Z.; Tsai, T.F.; Strom, B.L.; Wan, C.M.; Liu, H.L.; Wu, T.X.; Yu, H.J.; Liu, Q.M.; Karabatsos, N.; et al. Effectiveness of live-attenuated Japanese encephalitis vaccine (SA14-14-2): A case-control study. Lancet 1996, 347, 1583–1586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thai Travel Clinic. Price List of Vaccines. Hospital for Tropical Diseases, Faculty of Tropical Medicine, Mahidol University. Available online: https://www.thaitravelclinic.com (accessed on 27 September 2023).
- Lindquist, L. Recent and historical trends in the epidemiology of Japanese encephalitis and its implication for risk assessment in travellers. J. Travel Med. 2018, 25 (Suppl. S1), S3–S9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sudjaritruk, T.; Kaewpoowat, Q.; Prasarakee, C.; Sarachai, S.; Taurel, A.F.; Sricharoen, N.; Assawawongprom, P.; Saheng, J.; Harris, R.; Nealon, J.; et al. Seroepidemiological study of Japanese encephalitis virus in Chiang Mai: Immunity and susceptibility 28 years after introduction of a vaccination programme. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2022, 16, e0010674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, D.; Chen, X.; Liu, W.; Fu, S.; Li, F.; Liang, G.; Yang, G.; Zheng, H.; Li, J.; Yin, Z.; et al. Emergence of Japanese encephalitis among adults 40 years of age or older in northern China: Epidemiological and clinical characteristics. Transbound Emerg. Dis. 2021, 68, 3415–3423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wirawan, I.M.A. Japanese encephalitis vaccine cost: A major reason to be vaccinated in Bali. J. Travel Med. 2021, 28, taab050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Asawapaithulsert, P.; Ngamprasertchai, T.; Kitro, A. Japanese Encephalitis Vaccine Acceptance and Strategies for Travelers: Insights from a Scoping Review and Practitioners in Endemic Countries. Vaccines 2023, 11, 1683. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines11111683
Asawapaithulsert P, Ngamprasertchai T, Kitro A. Japanese Encephalitis Vaccine Acceptance and Strategies for Travelers: Insights from a Scoping Review and Practitioners in Endemic Countries. Vaccines. 2023; 11(11):1683. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines11111683
Chicago/Turabian StyleAsawapaithulsert, Punyisa, Thundon Ngamprasertchai, and Amornphat Kitro. 2023. "Japanese Encephalitis Vaccine Acceptance and Strategies for Travelers: Insights from a Scoping Review and Practitioners in Endemic Countries" Vaccines 11, no. 11: 1683. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines11111683
APA StyleAsawapaithulsert, P., Ngamprasertchai, T., & Kitro, A. (2023). Japanese Encephalitis Vaccine Acceptance and Strategies for Travelers: Insights from a Scoping Review and Practitioners in Endemic Countries. Vaccines, 11(11), 1683. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines11111683







