Probiotic as Adjuvant Significantly Improves Protection of the Lanzhou Trivalent Rotavirus Vaccine against Heterologous Challenge in a Gnotobiotic Pig Model of Human Rotavirus Infection and Disease
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Vaccine
2.2. Probiotic Bacteria Used as Vaccine Adjuvant
2.3. Challenge Virus
2.4. Experimental Design: Gn Pig Inoculation, Challenge, and Sample Collection
2.5. Clinical Signs and Rotavirus and Probiotic Bacteria Shedding
2.6. Shedding of Vaccine Virus by RT-PCR Typing Primer for G2, G3, and G4
2.7. Extraction of Mononuclear Cells (MNCs)
2.8. Preparation of Sf9 Cell Plates Expressing Rotavirus D VP7 (G1), DS1 VP7 (G2), PV P7 (G3), and ST3 VP7 (G4)
2.9. Immunocytochemical Staining Assay for Detection of Rotavirus G1, G2, G3, and G4 VP7 G-Type-Specific IgA and IgG Antibody Responses in Serum
2.10. ELISPOT Assay for Rotavirus G1, G2, G3, G4 VP7 G-Type-Specific ASC
2.11. Intracellular Cytokine Staining and Flow Cytometry Analysis of IFN-γ-Producing CD4+ and CD8+ T Cells
2.12. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
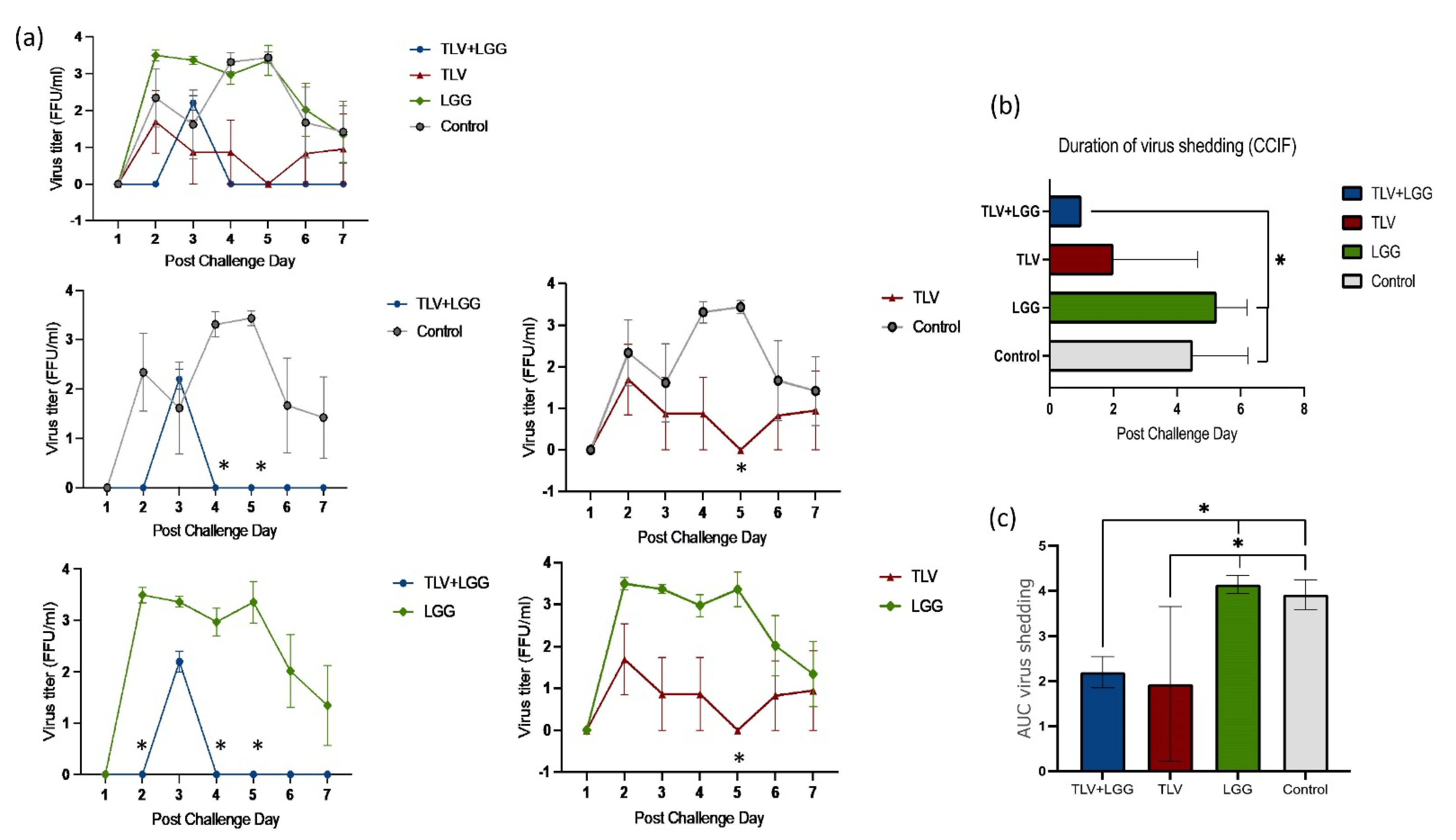
3.1. Vaccine Replication in Gn Pigs: Shedding of G3 and G4 Reassortant Strains was Detected after Oral Inoculations with TLV+LGG
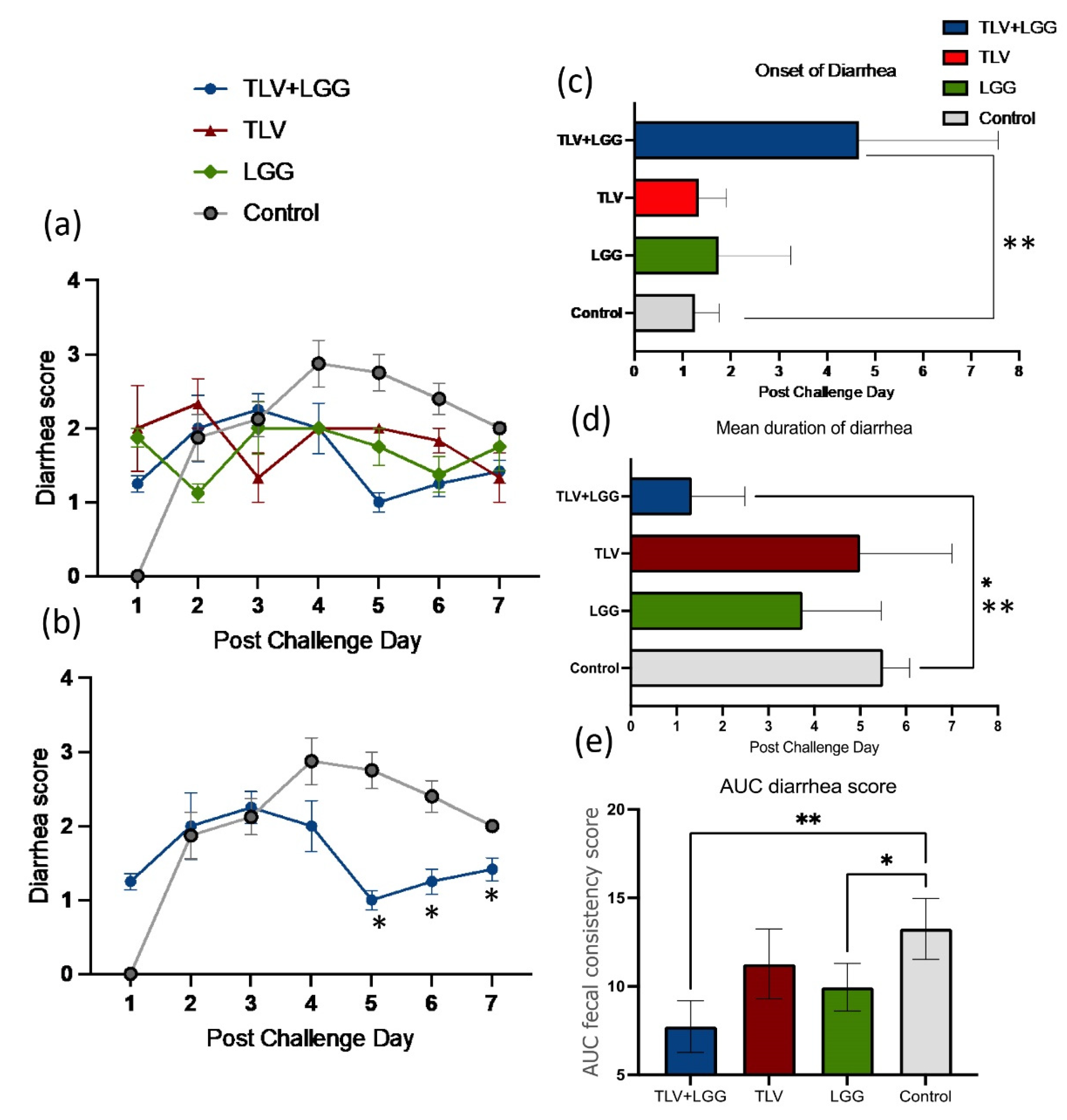
3.2. LGG Enhanced TLV Vaccine’s Protection against Heterotypic Virulent Wa HRV Challenge
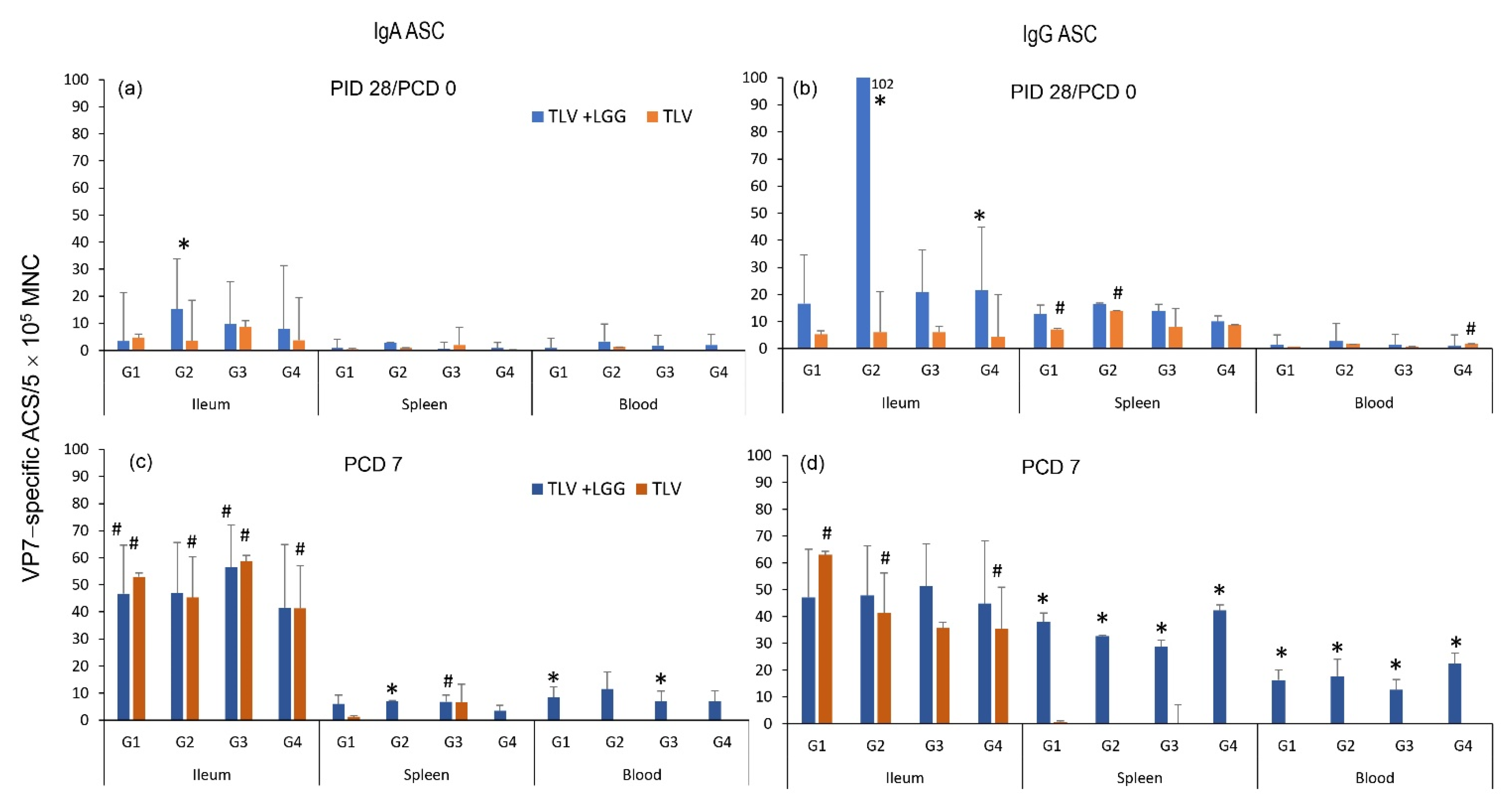
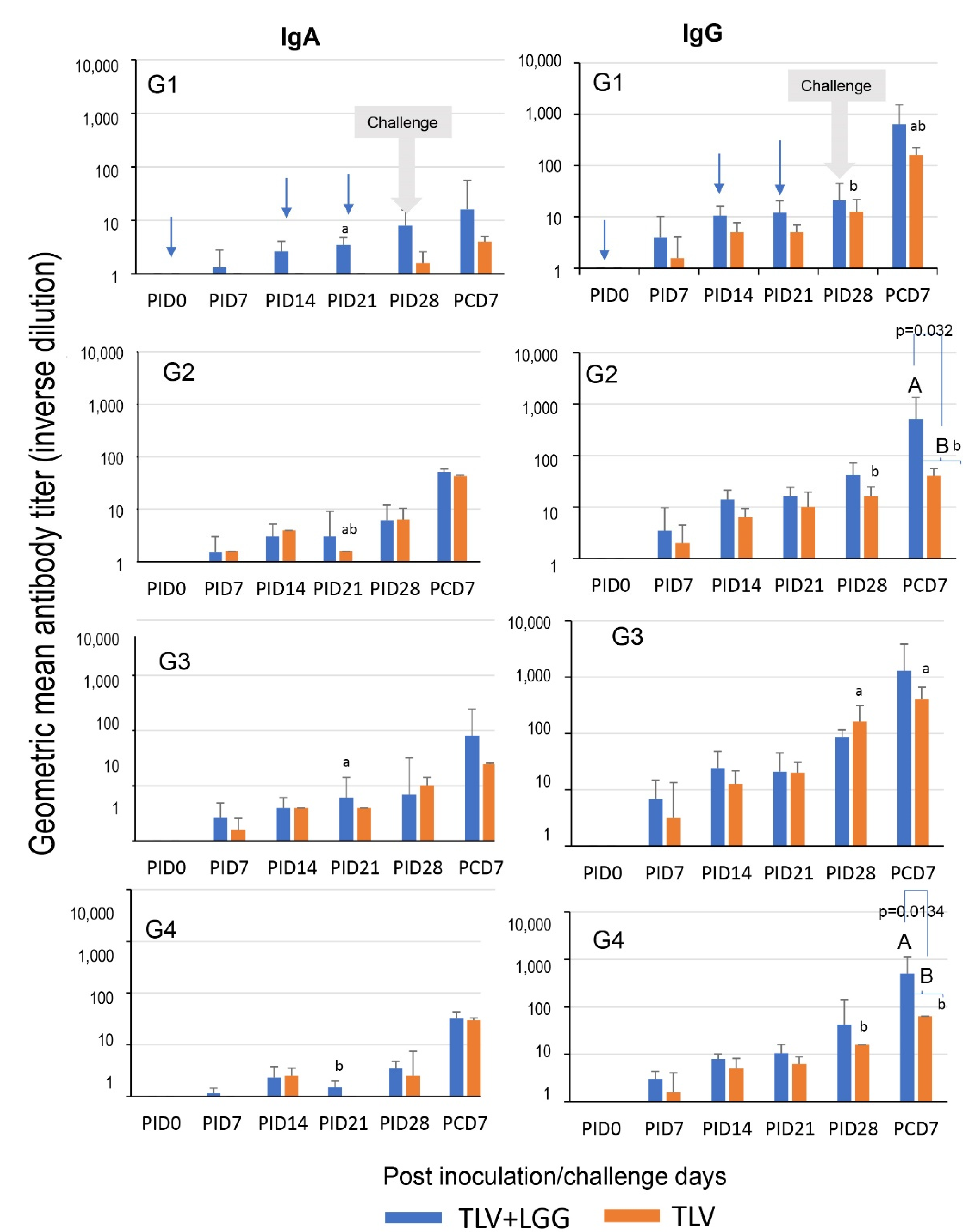
3.3. The TLV Induced Intestinal VP7-Specific IgA and IgG ASC Responses to Homotypic and Heterotypic VP7 G-Types; The Presence of LGG Promoted Stronger Intestinal Vaccine Antigen-Specific ASC Responses
3.4. LGG Adjuvant Enhanced VP7 G-Type Specific IgA and IgG Antibody Responses in Serum Pre- and Postchallenge, including the Cross-Reactive Response to the Heterotypic G1 HRV Challenge Strain
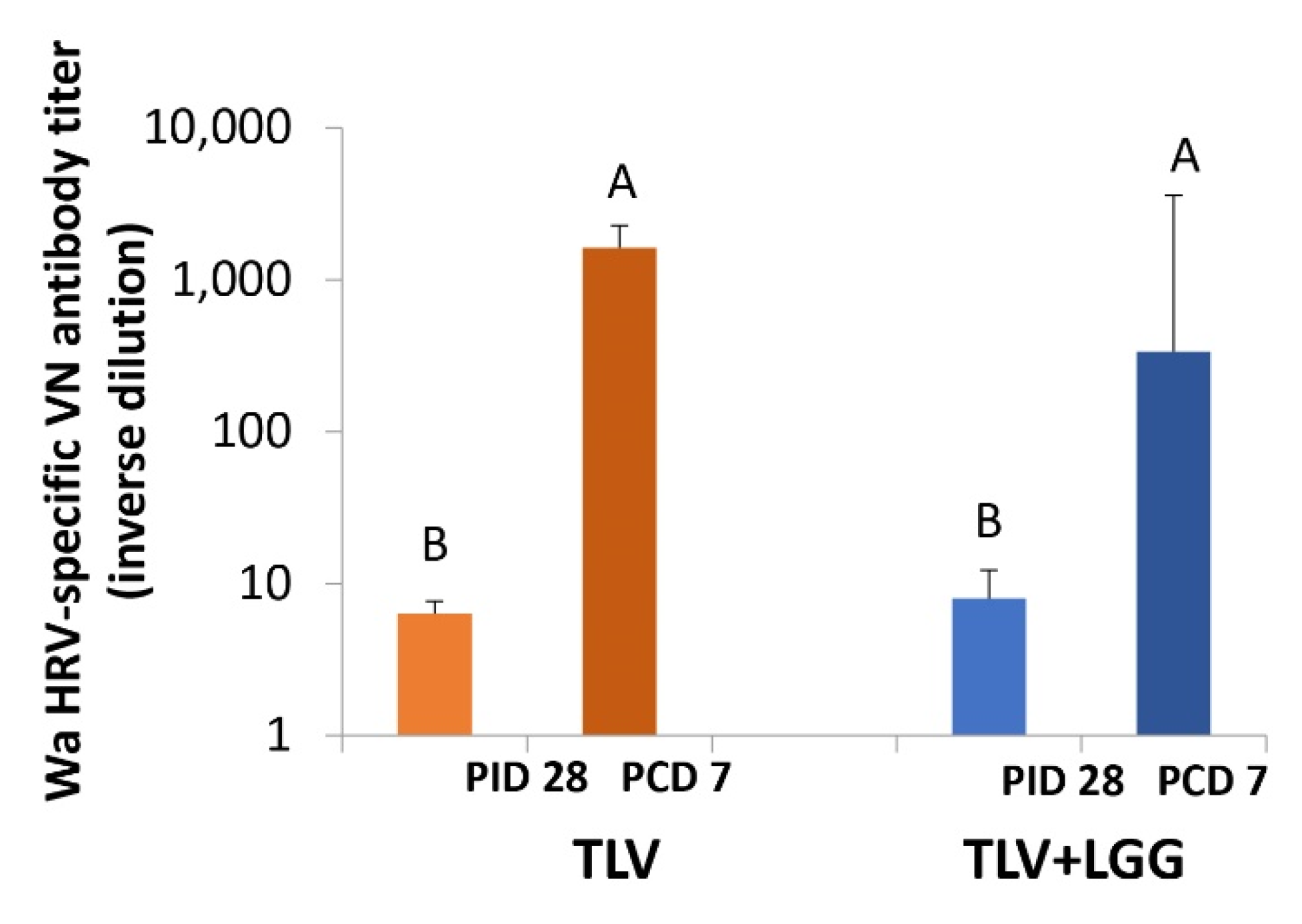
3.5. The TLV Primed for Strong Anamnestic Serum VN Antibody Responses to Heterotypic G1P[8] HRV Post-Challenge with or without LGG
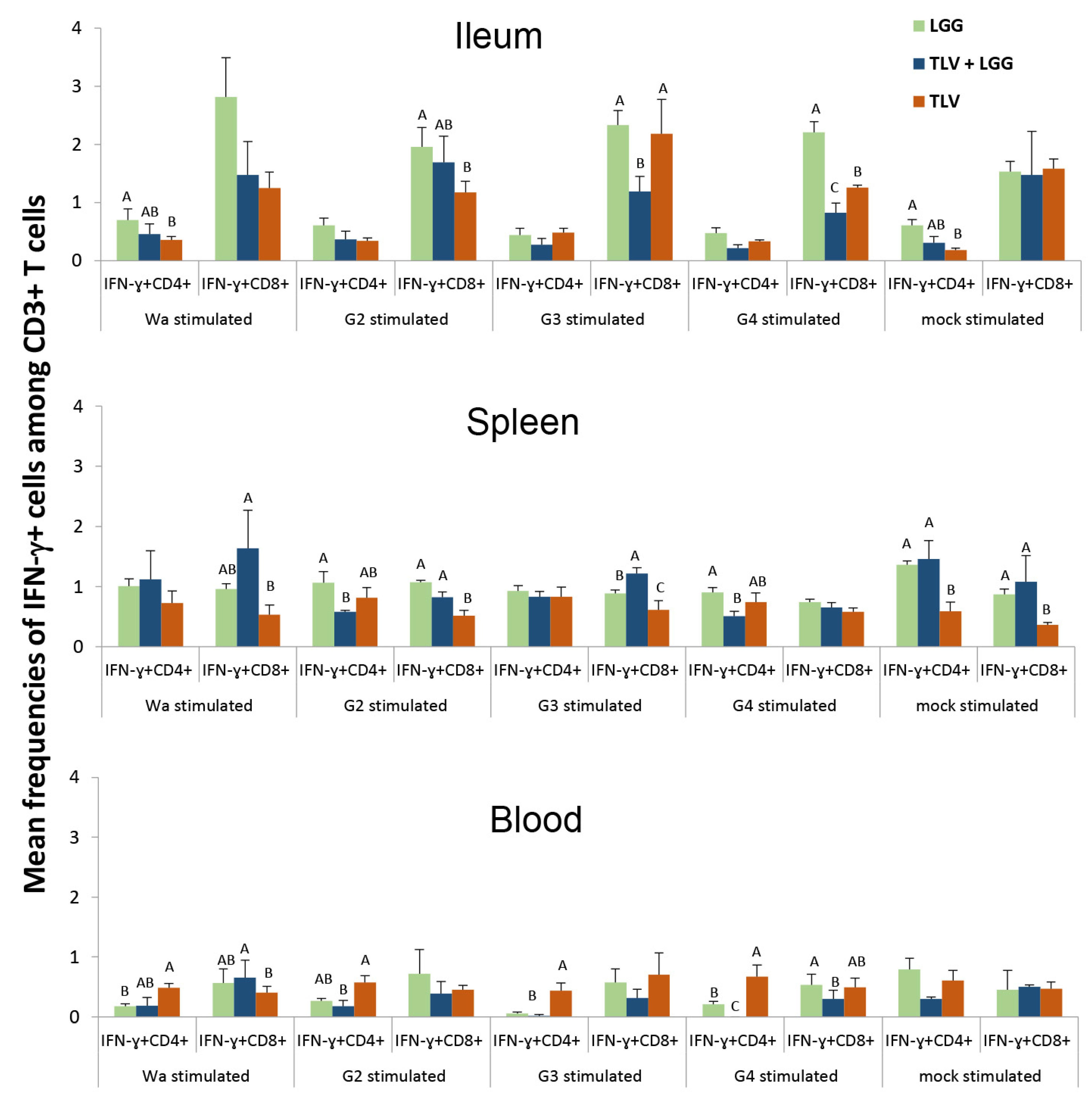
3.6. IFN-γ-Producing CD4+ and CD8+ T Cell Responses in Intestinal and Systemic Lymphoid Tissues
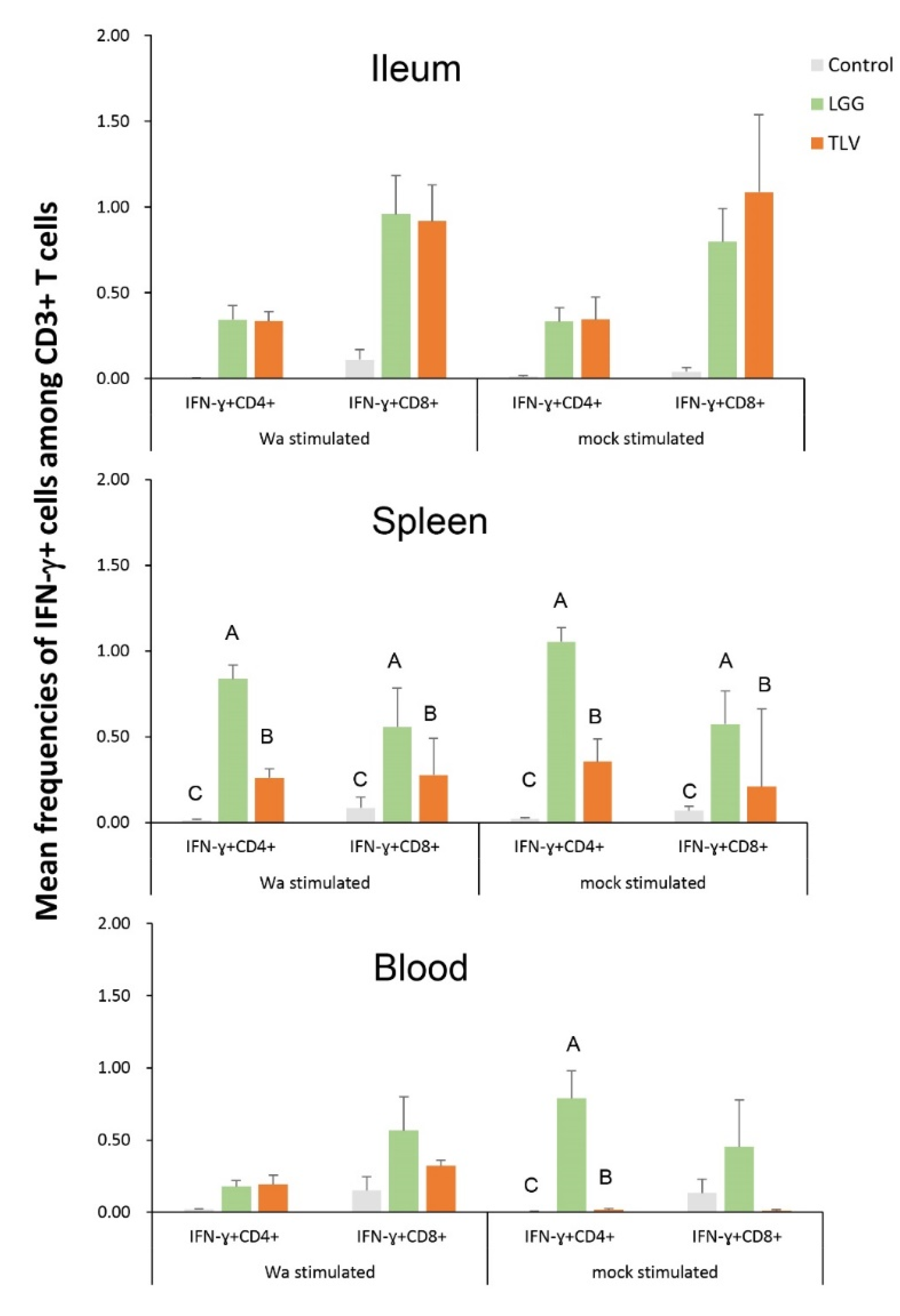
3.6.1. Both LGG and TLV Alone Induced IFN-γ-Producing CD4+ and CD8+ T-Cell Responses in Intestinal and Systemic Lymphoid Tissues
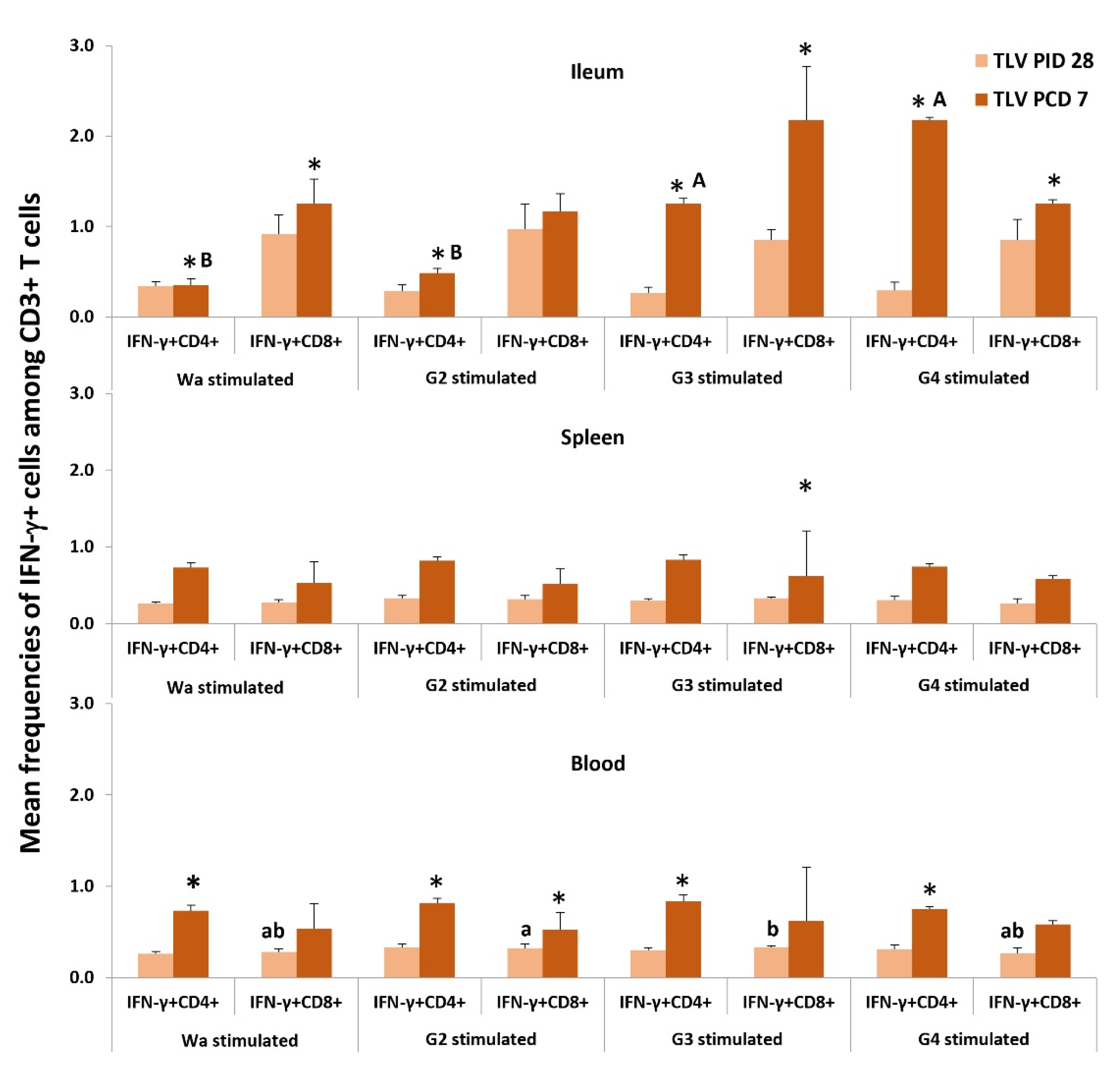
3.6.2. The TLV Induced Heterotypic G1- and Homotypic G2-, G3- and G4-Specific IFN-γ-Producing CD4+ and CD8+ T-Cell Responses in Intestinal and Systemic Lymphoid Tissues Pre- and Postchallenge
3.6.3. The LGG Modulates IFN-γ-Producing CD4+ and CD8+ T-Cell Responses Differentially in Intestinal and Systemic Lymphoid Tissues
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Troeger, C.; Khalil, I.A.; Rao, P.C.; Cao, S.; Blacker, B.F.; Ahmed, T.; Armah, G.; Bines, J.E.; Brewer, T.G.; Colombara, D.V.; et al. Rotavirus Vaccination and the Global Burden of Rotavirus Diarrhea Among Children Younger Than 5 Years. JAMA Pediatr. 2018, 172, 958–965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, D.; Yen, C.; Yin, Z.D.; Li, Y.X.; Liu, N.; Liu, Y.M.; Wang, H.Q.; Cui, F.Q.; Gregory, C.J.; Tate, J.E.; et al. The Public Health Burden of Rotavirus Disease in Children Younger Than Five Years and Considerations for Rotavirus Vaccine Introduction in China. Pediatr. Infect. Dis. J. 2016, 35, e392–e398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadiq, A.; Bostan, N.; Jadoon, K.; Aziz, A. Effect of rotavirus genetic diversity on vaccine impact. Rev. Med. Virol. 2022, 32, e2259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, Y.; Liang, Z.; Tian, Y.; Liu, B.; Gao, Z.; Jia, L.; Chen, L.; Wang, Q. Effectiveness of Lanzhou lamb rotavirus vaccine in preventing gastroenteritis among children younger than 5years of age. Vaccine 2019, 37, 3611–3616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xia, S.; Du, J.; Su, J.; Liu, Y.; Huang, L.; Yu, Q.; Xie, Z.; Gao, J.; Xu, B.; Gao, X.; et al. Efficacy, immunogenicity and safety of a trivalent live human-lamb reassortant rotavirus vaccine (LLR3) in healthy Chinese infants: A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Vaccine 2020, 38, 7393–7400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, R.C.; Huang, T.; Li, Y.; Luo, D.; Tao, J.; Fu, B.; Si, G.; Nong, Y.; Mo, Z.; Liao, X.; et al. Human rotavirus vaccine (RIX4414) efficacy in the first two years of life: A randomized, placebo-controlled trial in China. Hum. Vaccines Immunother. 2014, 10, 11–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mo, Z.; Mo, Y.; Li, M.; Tao, J.; Yang, X.; Kong, J.; Wei, D.; Fu, B.; Liao, X.; Chu, J.; et al. Efficacy and safety of a pentavalent live human-bovine reassortant rotavirus vaccine (RV5) in healthy Chinese infants: A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Vaccine 2017, 35, 5897–5904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsieh, M.H. The microbiome and probiotics in childhood. Semin. Reprod. Med. 2014, 32, 23–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gensollen, T.; Iyer, S.S.; Kasper, D.L.; Blumberg, R.S. How colonization by microbiota in early life shapes the immune system. Science 2016, 352, 539–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vitetta, L.; Saltzman, E.T.; Thomsen, M.; Nikov, T.; Hall, S. Adjuvant Probiotics and the Intestinal Microbiome: Enhancing Vaccines and Immunotherapy Outcomes. Vaccines 2017, 5, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zimmermann, P.; Curtis, N. The influence of probiotics on vaccine responses—A systematic review. Vaccine 2018, 36, 207–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Gao, K.; Wen, K.; Allen, I.C.; Li, G.; Zhang, W.; Kocher, J.; Yang, X.; Giri-Rachman, E.; Li, G.H.; et al. Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG modulates innate signaling pathway and cytokine responses to rotavirus vaccine in intestinal mononuclear cells of gnotobiotic pigs transplanted with human gut microbiota. BMC Microbiol. 2016, 16, 109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wen, K.; Li, G.; Bui, T.; Liu, F.; Li, Y.; Kocher, J.; Lin, L.; Yang, X.; Yuan, L. High dose and low dose Lactobacillus acidophilus exerted differential immune modulating effects on T cell immune responses induced by an oral human rotavirus vaccine in gnotobiotic pigs. Vaccine 2012, 30, 1198–1207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, K.; Liu, F.; Li, G.; Bai, M.; Kocher, J.; Yang, X.; Wang, H.; Clark-Deener, S.; Yuan, L. Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG Dosage Affects the Adjuvanticity and Protection Against Rotavirus Diarrhea in Gnotobiotic Pigs. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2015, 60, 834–843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, L. Vaccine Efficacy Evaluation: The Gnotobiotic Pig Model, 1st ed.; Yuan, L., Ed.; CRC Press, Taylor & Francis Group: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2022; p. 189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butler, J.E.; Sinkora, M. The isolator piglet: A model for studying the development of adaptive immunity. Immunol. Res. 2007, 39, 33–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meurens, F.; Summerfield, A.; Nauwynck, H.; Saif, L.; Gerdts, V. The pig: A model for human infectious diseases. Trends Microbiol. 2012, 20, 50–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kudo, S.; Zhou, Y.; Cao, X.R.; Yamanishi, S.; Nakata, S.; Ushijima, H. Molecular characterization in the VP7, VP4 and NSP4 genes of human rotavirus serotype 4 (G4) isolated in Japan and Kenya. Microbiol. Immunol. 2001, 45, 167–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Wen, K.; Azevedo, M.S.; Gonzalez, A.; Saif, L.J.; Li, G.; Yousef, A.E.; Yuan, L. Lactic acid bacterial colonization and human rotavirus infection influence distribution and frequencies of monocytes/macrophages and dendritic cells in neonatal gnotobiotic pigs. Veter. Immunol. Immunopathol. 2008, 121, 222–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ward, L.A.; Rosen, B.I.; Yuan, L.; Saif, L.J. Pathogenesis of an attenuated and a virulent strain of group A human rotavirus in neonatal gnotobiotic pigs. J. Gen. Virol. 1996, 77 Pt 7, 1431–1441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; Li, G.; Wen, K.; Bui, T.; Cao, D.; Zhang, Y.; Yuan, L. Porcine small intestinal epithelial cell line (IPEC-J2) of rotavirus infection as a new model for the study of innate immune responses to rotaviruses and probiotics. Viral. Immunol. 2010, 23, 135–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, L.J.; Jobst, P.M.; Weiss, M. Gnotobiotic pigs: From establishing facility to modeling human infectious diseases. In Gnotobiotics, 1st ed.; Schoeb, T.R., Eaton, K.A., Eds.; Acamedic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2017; pp. 349–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Wang, M.; Yu, L.; Ma, C.; Li, X.; Guo, T.; Bao, H.; Kou, K.; Chen, Y.; et al. Establishment of a cell-based quantitative reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction (RT-qPCR) assay for detection of multivalent rotavirus vaccine. J. Med. Virol. 2020, 92, 3157–3164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, L.; Honma, S.; Ishida, S.; Yan, X.Y.; Kapikian, A.Z.; Hoshino, Y. Species-specific but not genotype-specific primary and secondary isotype-specific NSP4 antibody responses in gnotobiotic calves and piglets infected with homologous host bovine (NSP4[A]) or porcine (NSP4[B]) rotavirus. Virology 2004, 330, 92–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Chang, K.O.; Vandal, O.H.; Yuan, L.; Hodgins, D.C.; Saif, L.J. Antibody-secreting cell responses to rotavirus proteins in gnotobiotic pigs inoculated with attenuated or virulent human rotavirus. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2001, 39, 2807–2813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, L.; Wen, K.; Azevedo, M.S.; Gonzalez, A.M.; Zhang, W.; Saif, L.J. Virus-specific intestinal IFN-gamma producing T cell responses induced by human rotavirus infection and vaccines are correlated with protection against rotavirus diarrhea in gnotobiotic pigs. Vaccine 2008, 26, 3322–3331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Gao, X.; Ye, Y.L.; Wan, T.; Zang, H.; Mo, P.H.; Song, C.L. An acute gastroenteritis outbreak associated with person-to-person transmission in a primary school in Shanghai: First report of a GI.5 norovirus outbreak in China. BMC Infect. Dis. 2018, 18, 316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, B.; Kader, M.A.; Colgate, E.R.; Carmolli, M.; Dickson, D.M.; Diehl, S.A.; Alam, M.; Afreen, S.; Mychaleckyj, J.C.; Nayak, U.; et al. Oral rotavirus vaccine shedding as a marker of mucosal immunity. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 21760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; Li, G.; Wen, K.; Wu, S.; Zhang, Y.; Bui, T.; Yang, X.; Kocher, J.; Sun, J.; Jortner, B.; et al. Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG on rotavirus-induced injury of ileal epithelium in gnotobiotic pigs. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2013, 57, 750–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.T.; Xu, H.; Ye, J.Z.; Wu, W.R.; Shi, D.; Fang, D.Q.; Liu, Y.; Li, L.J. Efficacy of Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG in treatment of acute pediatric diarrhea: A systematic review with meta-analysis. World J. Gastroenterol. 2019, 25, 4999–5016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maldonado Galdeano, C.; Cazorla, S.I.; Lemme Dumit, J.M.; Velez, E.; Perdigon, G. Beneficial Effects of Probiotic Consumption on the Immune System. Ann. Nutr. Metab. 2019, 74, 115–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, K.; Tin, C.; Wang, H.; Yang, X.; Li, G.; Giri-Rachman, E.; Kocher, J.; Bui, T.; Clark-Deener, S.; Yuan, L. Probiotic Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG enhanced Th1 cellular immunity but did not affect antibody responses in a human gut microbiota transplanted neonatal gnotobiotic pig model. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e94504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szajewska, H.; Kotowska, M.; Mrukowicz, J.Z.; Armanska, M.; Mikolajczyk, W. Efficacy of Lactobacillus GG in prevention of nosocomial diarrhea in infants. J. Pediatr. 2001, 138, 361–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mastretta, E.; Longo, P.; Laccisaglia, A.; Balbo, L.; Russo, R.; Mazzaccara, A.; Gianino, P. Effect of Lactobacillus GG and breast-feeding in the prevention of rotavirus nosocomial infection. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2002, 35, 527–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Isolauri, E.; Juntunen, M.; Rautanen, T.; Sillanaukee, P.; Koivula, T. A human Lactobacillus strain (Lactobacillus casei sp strain GG) promotes recovery from acute diarrhea in children. Pediatrics 1991, 88, 90–97. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Guandalini, S.; Pensabene, L.; Zikri, M.A.; Dias, J.A.; Casali, L.G.; Hoekstra, H.; Kolacek, S.; Massar, K.; Micetic-Turk, D.; Papadopoulou, A.; et al. Lactobacillus GG administered in oral rehydration solution to children with acute diarrhea: A multicenter European trial. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2000, 30, 54–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Szajewska, H.; Skorka, A.; Ruszczynski, M.; Gieruszczak-Bialek, D. Meta-analysis: Lactobacillus GG for treating acute diarrhoea in children. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2007, 25, 871–881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaila, M.; Isolauri, E.; Soppi, E.; Virtanen, E.; Laine, S.; Arvilommi, H. Enhancement of the circulating antibody secreting cell response in human diarrhea by a human Lactobacillus strain. Pediatr. Res. 1992, 32, 141–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaila, M.; Isolauri, E.; Saxelin, M.; Arvilommi, H.; Vesikari, T. Viable versus inactivated lactobacillus strain GG in acute rotavirus diarrhoea. Arch. Dis. Child. 1995, 72, 51–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorbach, S.L. Probiotics and gastrointestinal health. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2000, 95, S2–S4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isolauri, E.; Joensuu, J.; Suomalainen, H.; Luomala, M.; Vesikari, T. Improved immunogenicity of oral D x RRV reassortant rotavirus vaccine by Lactobacillus casei GG. Vaccine 1995, 13, 310–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mo, Z.; Ma, X.; Luo, P.; Mo, Y.; Kaplan, S.S.; Shou, Q.; Zheng, M.; Hille, D.A.; Arnold, B.A.; Group, V.S.; et al. Immunogenicity of pentavalent rotavirus vaccine in Chinese infants. Vaccine 2019, 37, 1836–1843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ward, R.L.; McNeal, M.M.; Sheridan, J.F. Evidence that active protection following oral immunization of mice with live rotavirus is not dependent on neutralizing antibody. Virology 1992, 188, 57–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ward, R.L.; Knowlton, D.R.; Zito, E.T.; Davidson, B.L.; Rappaport, R.; Mack, M.E. Serologic correlates of immunity in a tetravalent reassortant rotavirus vaccine trial. US Rotavirus Vaccine Efficacy Group. J. Infect. Dis. 1997, 176, 570–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Ward, R.L.; Bernstein, D.I. Lack of correlation between serum rotavirus antibody titers and protection following vaccination with reassortant RRV vaccines. US Rotavirus Vaccine Efficacy Group. Vaccine 1995, 13, 1226–1232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, F.; Polk, D.B. Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG: An Updated Strategy to Use Microbial Products to Promote Health. Funct. Food Rev. 2012, 4, 77–84. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]

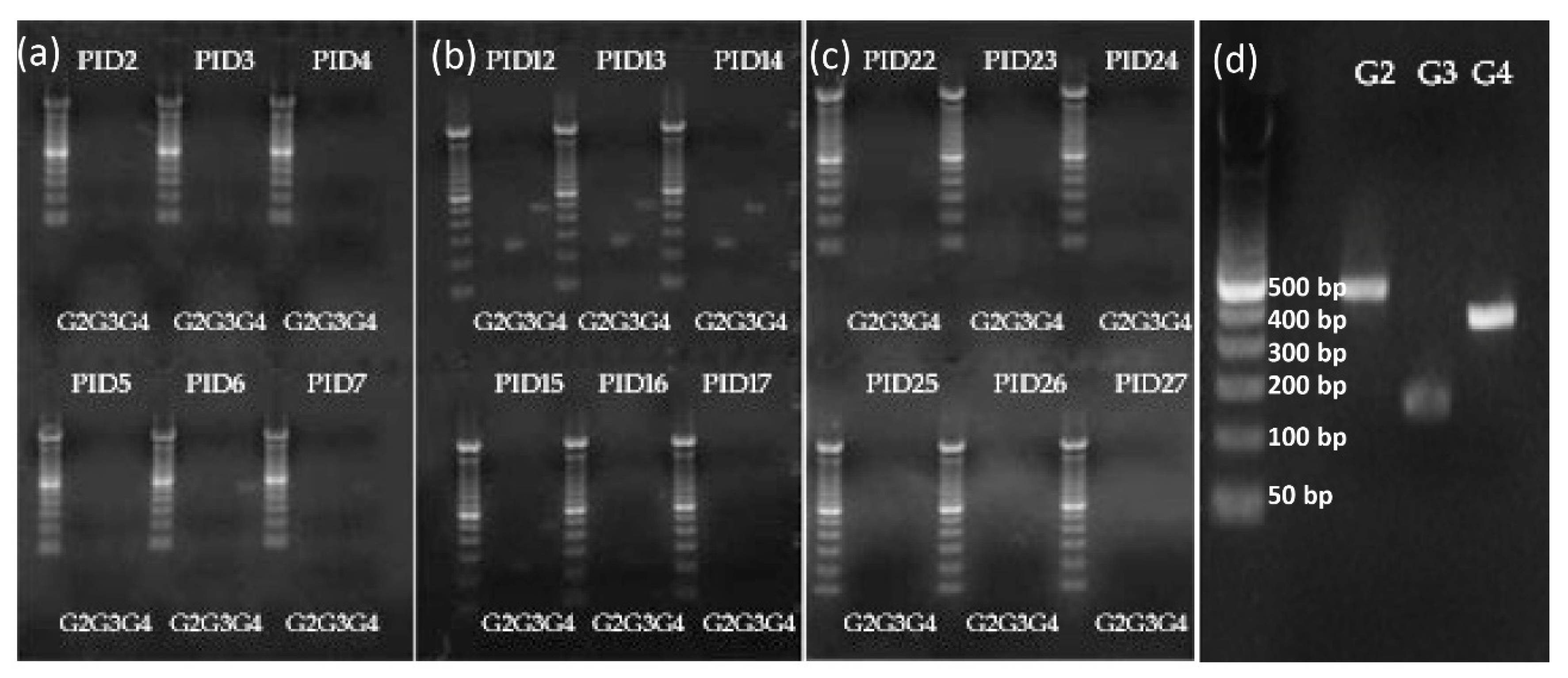

| Primers | Name | Sequence (5′→3′) |
|---|---|---|
| Primers for VP7 gene reverse transcription | VP7-F | tct ggc taa cgg tta gct cc |
| VP7-R | aat act tgc cac cat ttt ttc c | |
| Specific primers for G2 | G2-F | caa tga tat taa cac att ttc tgt |
| G2-R | aat act tgc cac cat ttt ttc c | |
| Specific primers G3 | G3-F | ctt ttg aag aag ttg cga cag |
| G3-R | aat act tgc cac cat ttt ttc c | |
| Specific primers for G4 | G4-F | cgc ttc tgg tga gga gtt g |
| G4-R | aat act tgc cac cat ttt ttc c |
| Treatments | n | Clinical Signs (Diarrhea) | Fecal Virus Shedding | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| % with Diarrhea *,a | Mean Days to Onset **, b | Mean Duration Days ** | Mean AUC of Diarrhea Score c | Mean Cumulative Score ** | % Virus Shedding * | Mean Days to Onset **,b | Mean Duration Days ** | Mean AUC of Virus Shedding d | ||
| TLV+LGG | 3 | 100 A | 4.7 (1.7) fA | 1.3 (0.7) B | 7.7 (0.8) C | 9.3 (0.8) B | 100 A | 2.0 (0.3) A | 1.0 (0) B | 2.2 (0.2) B |
| TLV | 3 | 67 A | 1.3 (0.3) B | 5.0(1.2) A | 11.3 (1.1) AB | 12.8 (1.6) A | 100 A | 1.7 (0.3) A | 3.3 (0.7) AB | 1.9 (0.9) B |
| LGG | 4 | 100 A | 1.8 (0.8) B | 3.8 (0.9) A | 9.9 (0.7) B | 11.9 (0.8) A | 100 A | 2.0 (0) A | 5.3 (0.5) A | 4.2 (0.1) A |
| Mock control | 4 | 100 A | 1.3 (0.3) B | 5.5 (0.3) A | 13.2 (0.9) A | 16.9 (1.3) A | 100 A | 2.0 (0.3) A | 4.5 (0.9) A | 3.9 (0.2) A |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Parreno, V.; Bai, M.; Liu, F.; Jing, J.; Olney, E.; Li, G.; Wen, K.; Yang, X.; Castellucc, T.B.; Kocher, J.F.; et al. Probiotic as Adjuvant Significantly Improves Protection of the Lanzhou Trivalent Rotavirus Vaccine against Heterologous Challenge in a Gnotobiotic Pig Model of Human Rotavirus Infection and Disease. Vaccines 2022, 10, 1529. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines10091529
Parreno V, Bai M, Liu F, Jing J, Olney E, Li G, Wen K, Yang X, Castellucc TB, Kocher JF, et al. Probiotic as Adjuvant Significantly Improves Protection of the Lanzhou Trivalent Rotavirus Vaccine against Heterologous Challenge in a Gnotobiotic Pig Model of Human Rotavirus Infection and Disease. Vaccines. 2022; 10(9):1529. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines10091529
Chicago/Turabian StyleParreno, Viviana, Muqun Bai, Fangning Liu, Jiqiang Jing, Erika Olney, Guohua Li, Ke Wen, Xingdong Yang, Tammy Bui Castellucc, Jacob F. Kocher, and et al. 2022. "Probiotic as Adjuvant Significantly Improves Protection of the Lanzhou Trivalent Rotavirus Vaccine against Heterologous Challenge in a Gnotobiotic Pig Model of Human Rotavirus Infection and Disease" Vaccines 10, no. 9: 1529. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines10091529
APA StyleParreno, V., Bai, M., Liu, F., Jing, J., Olney, E., Li, G., Wen, K., Yang, X., Castellucc, T. B., Kocher, J. F., Zhou, X., & Yuan, L. (2022). Probiotic as Adjuvant Significantly Improves Protection of the Lanzhou Trivalent Rotavirus Vaccine against Heterologous Challenge in a Gnotobiotic Pig Model of Human Rotavirus Infection and Disease. Vaccines, 10(9), 1529. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines10091529






