Homologous or Heterologous COVID-19 Booster Regimens Significantly Impact Sero-Neutralization of SARS-CoV-2 Virus and Its Variants
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cell Line and Virus
2.2. Microneutralization Assay
2.3. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Demographic Data of Participants
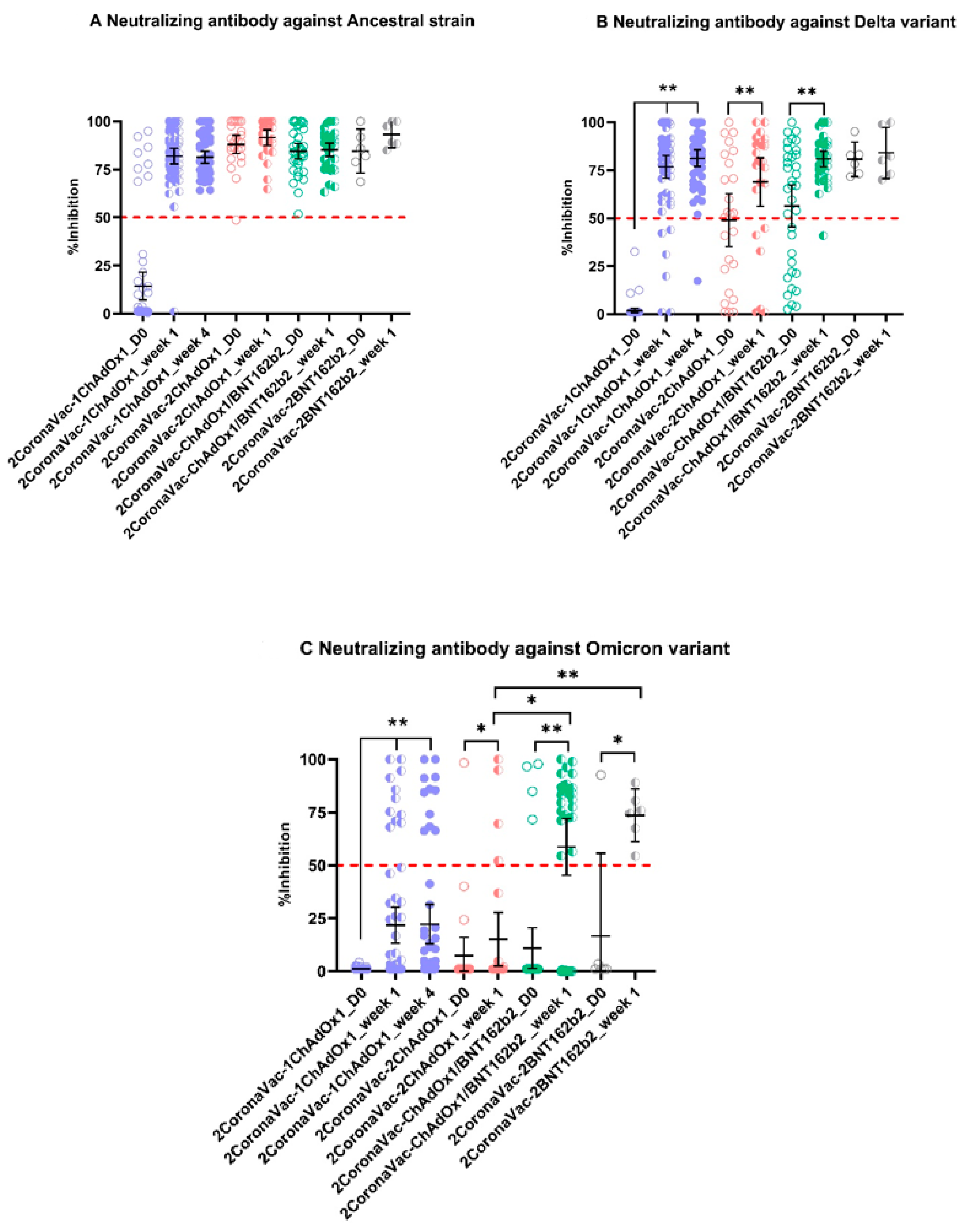
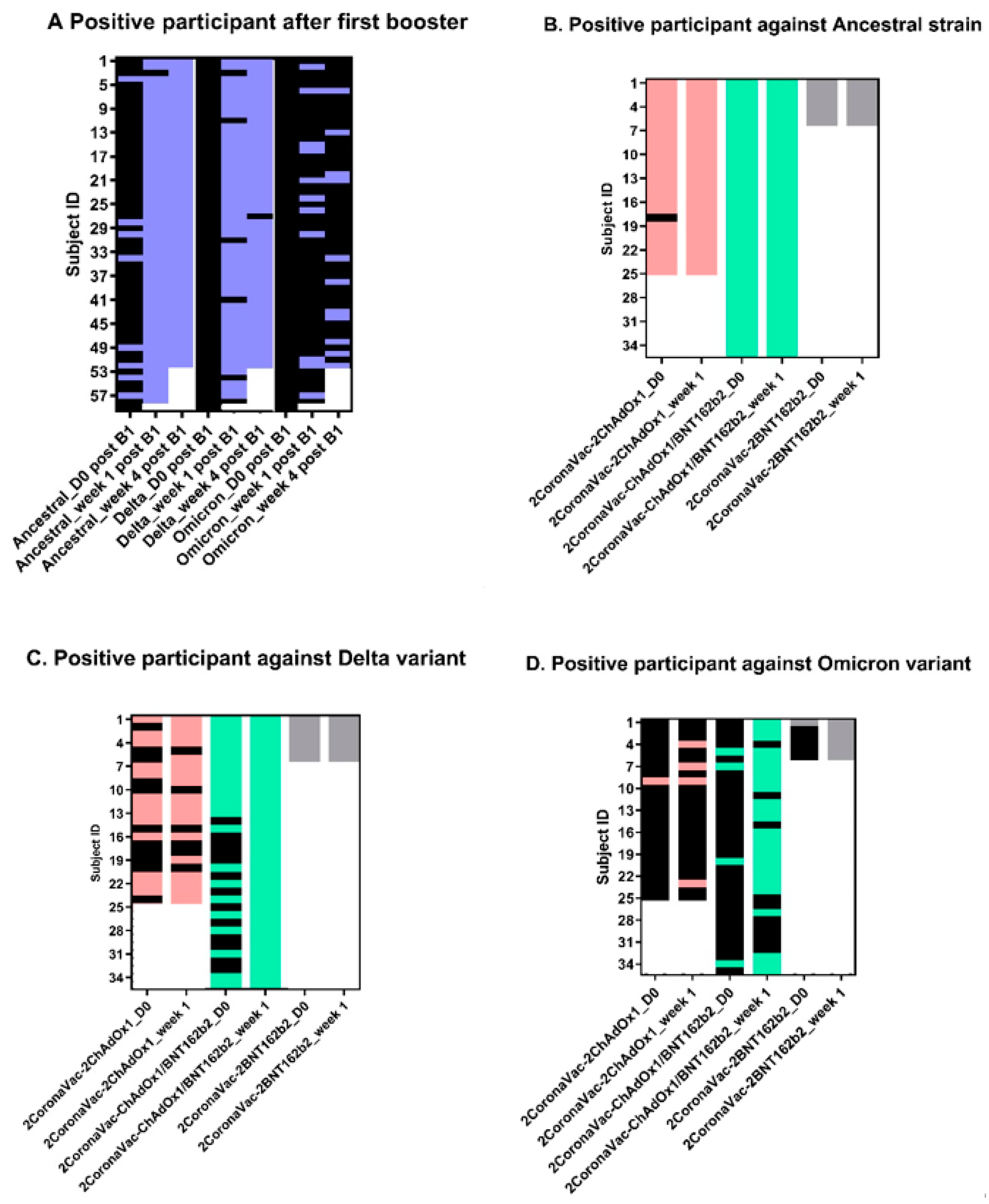
3.2. Neutralizing Antibodies against SARS-CoV-2 Ancestral Strain, Delta, and Omicron VOCs
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kucharski, A.J.; Russell, T.W.; Diamond, C.; Liu, Y.; Edmunds, J.; Funk, S.; Eggo, R.M.; Sun, F.; Jit, M.; Munday, J.D.; et al. Early Dynamics of Transmission and Control of COVID-19: A Mathematical Modelling Study. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2020, 20, 553–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krammer, F. SARS-CoV-2 Vaccines in Development. Nature 2020, 586, 516–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosenberg, E.S.; Dorabawila, V.; Easton, D.; Bauer, U.E.; Kumar, J.; Hoen, R.; Hoefer, D.; Wu, M.; Lutterloh, E.; Conroy, M.B.; et al. COVID-19 Vaccine Effectiveness in New York State. N. Engl. J. Med. 2022, 386, 116–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eyre, D.W.; Taylor, D.; Purver, M.; Chapman, D.; Fowler, T.; Pouwels, K.B.; Walker, A.S.; Peto, T.E.A. Effect of COVID-19 Vaccination on Transmission of Alpha and Delta Variants. N. Engl. J. Med. 2022, 386, 744–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Britton, A.; Fleming-Dutra, K.E.; Shang, N.; Smith, Z.R.; Dorji, T.; Derado, G.; Accorsi, E.K.; Ajani, U.A.; Miller, J.; Schrag, S.J.; et al. Association of COVID-19 Vaccination With Symptomatic SARS-CoV-2 Infection by Time Since Vaccination and Delta Variant Predominance. JAMA 2022, 327, 1032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hunsawong, T.; Fernandez, S.; Buathong, R.; Khadthasrima, N.; Rungrojchareonkit, K.; Lohachanakul, J.; Suthangkornkul, R.; Tayong, K.; Huang, A.T.; Klungthong, C.; et al. Limited and Short-Lasting Virus Neutralizing Titers Induced by Inactivated SARS-CoV-2 Vaccine. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2021, 27, 3178–3180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jantarabenjakul, W.; Chantasrisawad, N.; Puthanakit, T.; Wacharapluesadee, S.; Hirankarn, N.; Ruenjaiman, V.; Paitoonpong, L.; Suwanpimolkul, G.; Torvorapanit, P.; Pradit, R.; et al. Short-Term Immune Response after Inactivated SARS-CoV-2 (CoronaVac®, Sinovac) and ChAdOx1 NCoV-19 (Vaxzevria®, Oxford-AstraZeneca) Vaccinations in Health Care Workers. Asian Pac. J. Allergy Immunol. 2021; online ahead of print. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Hou, L.; Guo, X.; Jin, P.; Wu, S.; Zhu, J.; Pan, H.; Wang, X.; Song, Z.; Wan, J.; et al. Heterologous AD5-NCOV plus CoronaVac versus Homologous CoronaVac Vaccination: A Randomized Phase 4 Trial. Nat. Med. 2022, 28, 401–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cele, S.; Gazy, I.; Jackson, L.; Hwa, S.-H.; Tegally, H.; Lustig, G.; Giandhari, J.; Pillay, S.; Wilkinson, E.; Naidoo, Y.; et al. Escape of SARS-CoV-2 501Y.V2 from Neutralization by Convalescent Plasma. Nature 2021, 593, 142–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McCallum, M.; Walls, A.C.; Sprouse, K.R.; Bowen, J.E.; Rosen, L.E.; Dang, H.V.; De Marco, A.; Franko, N.; Tilles, S.W.; Logue, J.; et al. Molecular Basis of Immune Evasion by the Delta and Kappa SARS-CoV-2 Variants. Science 2021, 374, 1621–1626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wibmer, C.K.; Ayres, F.; Hermanus, T.; Madzivhandila, M.; Kgagudi, P.; Oosthuysen, B.; Lambson, B.E.; de Oliveira, T.; Vermeulen, M.; van der Berg, K.; et al. SARS-CoV-2 501Y.V2 Escapes Neutralization by South African COVID-19 Donor Plasma. Nat. Med. 2021, 27, 622–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bar-On, Y.M.; Goldberg, Y.; Mandel, M.; Bodenheimer, O.; Amir, O.; Freedman, L.; Alroy-Preis, S.; Ash, N.; Huppert, A.; Milo, R. Protection by a Fourth Dose of BNT162b2 against Omicron in Israel. N. Engl. J. Med. 2022, 386, 1712–1720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, J.; Peng, P.; Cao, X.; Wu, K.; Chen, J.; Wang, K.; Tang, N.; Huang, A.-L. Increased Immune Escape of the New SARS-CoV-2 Variant of Concern Omicron. Cell. Mol. Immunol. 2022, 19, 293–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Regev-Yochay, G.; Gonen, T.; Gilboa, M.; Mandelboim, M.; Indenbaum, V.; Amit, S.; Meltzer, L.; Asraf, K.; Cohen, C.; Fluss, R.; et al. Efficacy of a Fourth Dose of COVID-19 MRNA Vaccine against Omicron. N. Engl. J. Med. 2022, 386, 1377–1380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manenti, A.; Maggetti, M.; Casa, E.; Martinuzzi, D.; Torelli, A.; Trombetta, C.M.; Marchi, S.; Montomoli, E. Evaluation of SARS-CoV-2 Neutralizing Antibodies Using a CPE-Based Colorimetric Live Virus Micro-Neutralization Assay in Human Serum Samples. J. Med. Virol. 2020, 92, 2096–2104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Evans, J.P.; Zeng, C.; Carlin, C.; Lozanski, G.; Saif, L.J.; Oltz, E.M.; Gumina, R.J.; Liu, S.-L. Neutralizing Antibody Responses Elicited by SARS-CoV-2 MRNA Vaccination Wane over Time and Are Boosted by Breakthrough Infection. Sci. Transl. Med. 2022, 14, eabn8057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caniels, T.G.; Bontjer, I.; van der Straten, K.; Poniman, M.; Burger, J.A.; Appelman, B.; Lavell, A.H.A.; Oomen, M.; Godeke, G.-J.; Valle, C.; et al. Emerging SARS-CoV-2 Variants of Concern Evade Humoral Immune Responses from Infection and Vaccination. Sci. Adv. 2021, 7, eabj5365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Campos, G.R.F.; Almeida, N.B.F.; Filgueiras, P.S.; Corsini, C.A.; Gomes, S.V.C.; de Miranda, D.A.P.; de Assis, J.V.; de Souza Silva, T.B.; Alves, P.A.; da Rocha Fernandes, G.; et al. Booster Dose of BNT162b2 after Two Doses of CoronaVac Improves Neutralization of SARS-CoV-2 Omicron Variant. Commun. Med. 2022, 2, 76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
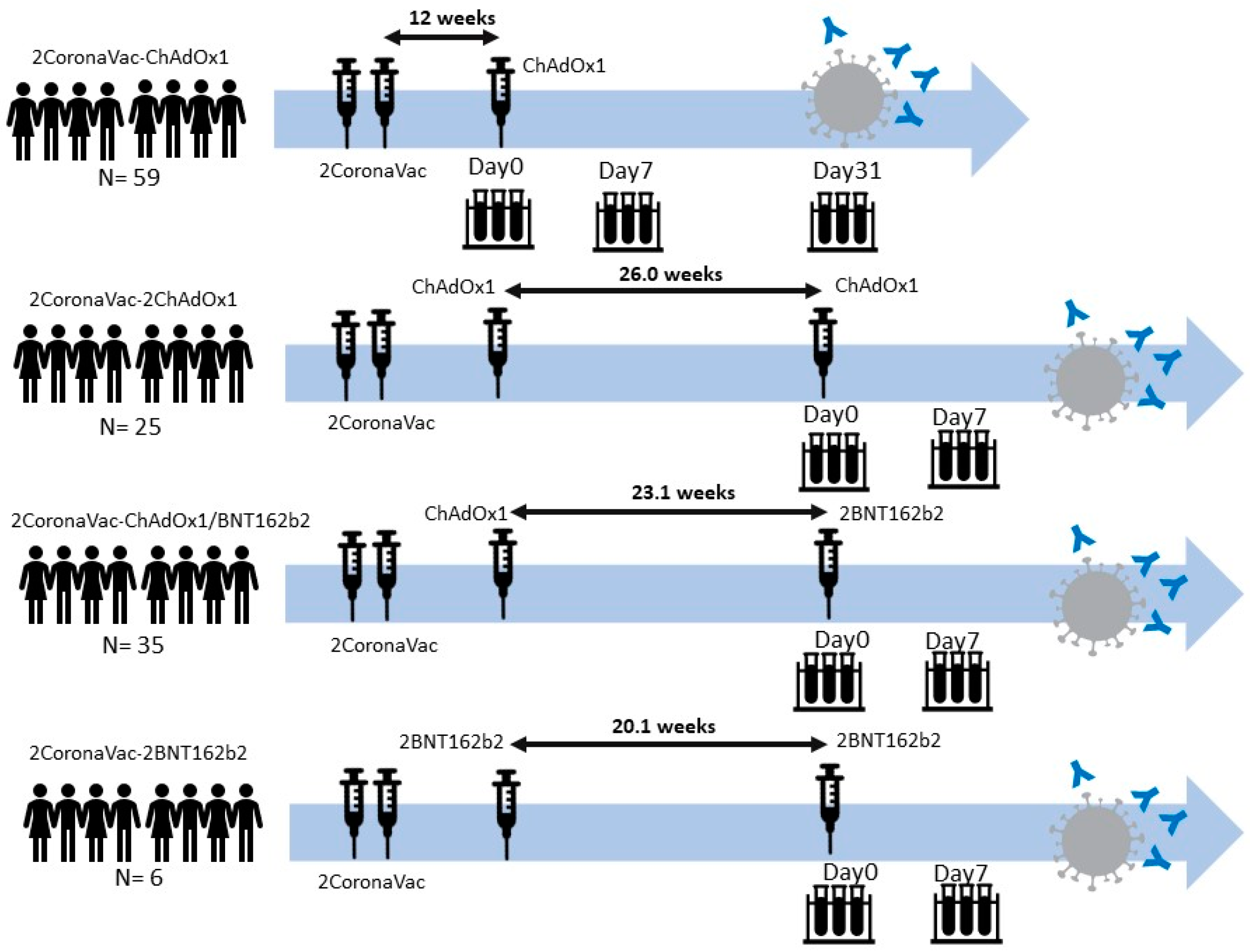
| Number of Participants | 59 |
|---|---|
| Age, median (years) | 40 |
| IQR | 32.5–52.5 |
| 20–30 years | 11 |
| 31–40 years | 19 |
| 41–50 years | 13 |
| 51–60 years | 15 |
| 61–70 years | 1 |
| BMI, median | 22.2 |
| IQR | 20.9–26.3 |
| Range | 16.1–33.2 |
| Duration between 2CoronaVac and ChAdOx1, median (weeks) | 14.1 |
| Characteristics | 2CoronaVac-2ChAdOx1 | 2CoronaVac-ChA-dOx1/BNT162b2 | 2CoronaVac-2BNT162b2 | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Number of participants | 25 | 35 | 6 | |
| Age, median (years) | 42 | 35 | 33 | 0.370 |
| IQR | 36–54 | 2.5–49 | 29.5–44 | |
| Range | 22–62 | 23–60 | 28–57 | |
| Age group, n | ||||
| 20–30 years | 5 | 11 | 2 | |
| 31–40 years | 6 | 9 | 2 | |
| 41–50 years | 6 | 7 | 1 | |
| 51–60 years | 7 | 8 | 1 | |
| 61–70 years | 1 | 0 | 0 | |
| Sex (% Male) | 32.0 | 42.9 | 66.7 | 0.283 |
| BMI, median | 21.5 | 24.0 | 25.4 | 0.489 |
| IQR | 19.4–27.5 | 20.9–25.91 | 24.15–26.36 | |
| Range | 16.0–33.2 | 16.37–30.32 | 21.97–27.51 | |
| Duration between 2CoronaVac and the first booster, median (weeks) | 14.5 | 16.7 | 19.3 | 0.0212 |
| Duration between the first and the second booster, median (weeks) | 26.0 | 23.1 | 20.1 | 0.0047 |
| IQR | 21.4–26.5 | 21.4–26.6 | 20.1–20.2 | |
| Range | 21.4–27.4 | 13.0–28.0 | 16.0–20.2 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Buathong, R.; Hunsawong, T.; Wacharapluesadee, S.; Guharat, S.; Jirapipatt, R.; Ninwattana, S.; Thippamom, N.; Jitsatja, A.; Jones, A.R.; Rungrojchareonkit, K.; et al. Homologous or Heterologous COVID-19 Booster Regimens Significantly Impact Sero-Neutralization of SARS-CoV-2 Virus and Its Variants. Vaccines 2022, 10, 1321. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines10081321
Buathong R, Hunsawong T, Wacharapluesadee S, Guharat S, Jirapipatt R, Ninwattana S, Thippamom N, Jitsatja A, Jones AR, Rungrojchareonkit K, et al. Homologous or Heterologous COVID-19 Booster Regimens Significantly Impact Sero-Neutralization of SARS-CoV-2 Virus and Its Variants. Vaccines. 2022; 10(8):1321. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines10081321
Chicago/Turabian StyleBuathong, Rome, Taweewun Hunsawong, Supaporn Wacharapluesadee, Suriya Guharat, Ratthapat Jirapipatt, Sasiprapa Ninwattana, Nattakarn Thippamom, Anusara Jitsatja, Anthony R. Jones, Kamonthip Rungrojchareonkit, and et al. 2022. "Homologous or Heterologous COVID-19 Booster Regimens Significantly Impact Sero-Neutralization of SARS-CoV-2 Virus and Its Variants" Vaccines 10, no. 8: 1321. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines10081321
APA StyleBuathong, R., Hunsawong, T., Wacharapluesadee, S., Guharat, S., Jirapipatt, R., Ninwattana, S., Thippamom, N., Jitsatja, A., Jones, A. R., Rungrojchareonkit, K., Lohachanakul, J., Suthangkornkul, R., Tayong, K., Klungthong, C., Fernandez, S., & Putcharoen, O. (2022). Homologous or Heterologous COVID-19 Booster Regimens Significantly Impact Sero-Neutralization of SARS-CoV-2 Virus and Its Variants. Vaccines, 10(8), 1321. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines10081321






