HLA Class II Polymorphism and Humoral Immunity Induced by the SARS-CoV-2 mRNA-1273 Vaccine
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
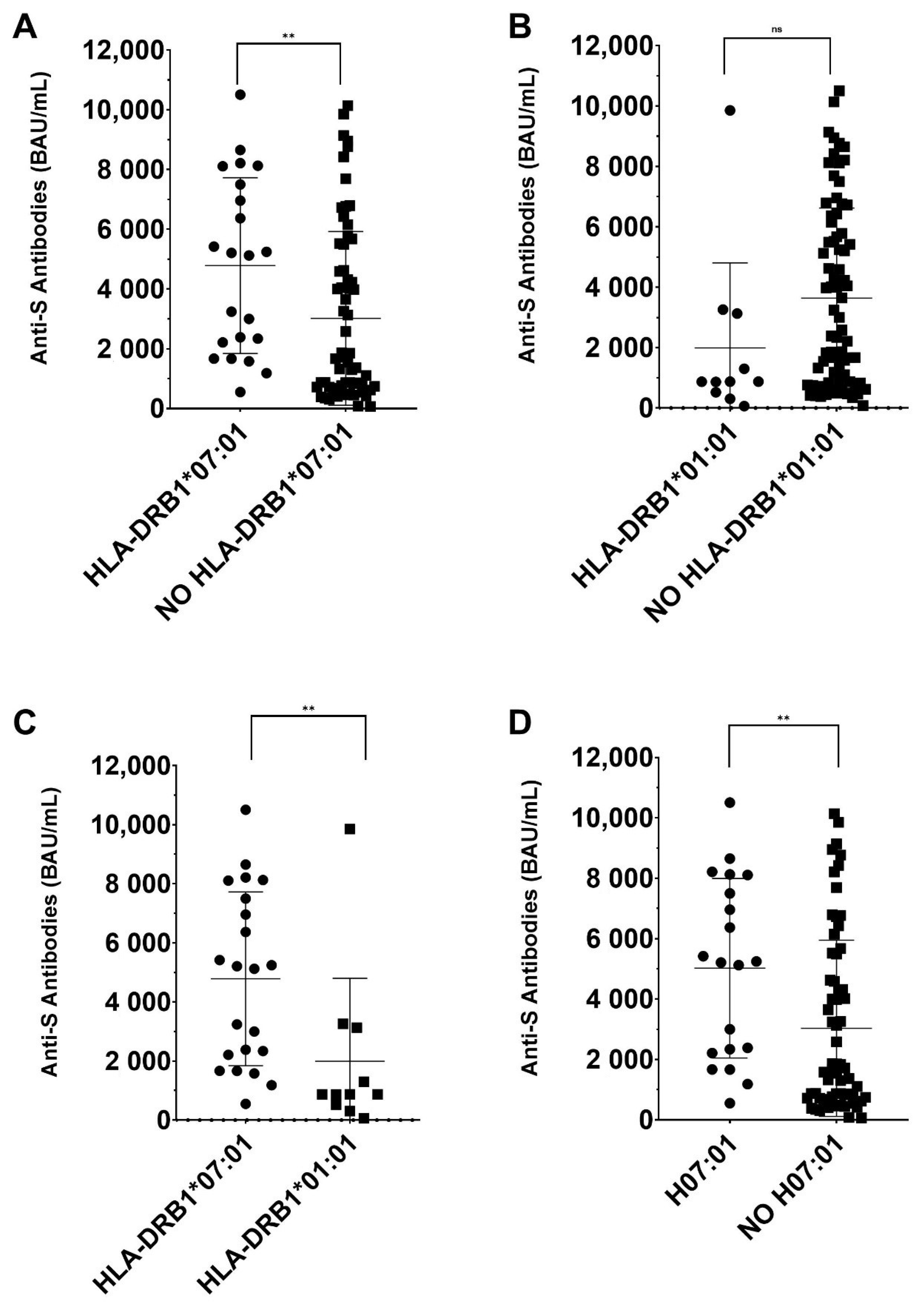
3. Results
- -
- G1 (Low responders) (<1000 BAU/mL): 28 individuals (13 women and 15 men), with an average age of 46.8 years (26–65).
- -
- G2 (Middle responders) (1000–4400 BAU/mL): 29 individuals (14 women and 12 men), with an average age of 49.3 years (28–65).
- -
- G3 (High responders) (>4400 BAU/mL): 30 individuals (14 women and 16 men), with an average age of 48 years (23–65).
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Joyce, K.E.; Weaver, S.R.; Lucas, S.J.E. Geographic components of SARS-CoV-2 expansion: A hypothesis. J. Appl. Physiol. 2020, 129, 257–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lotfi, M.; Hamblin, M.R.; Rezaei, N. COVID-19: Transmission, prevention, and potential therapeutic opportunities. Clin. Chim. Acta 2020, 508, 254–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anderson, E.J.; Rouphael, N.G.; Widge, A.T.; Jackson, L.A.; Roberts, P.C.; Makhene, M.; Chappell, J.D.; Denison, M.R.; Stevens, L.J.; Pruijssers, A.J.; et al. Safety and Immunogenicity of SARS-CoV-2 mRNA-1273 Vaccine in Older Adults. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 383, 2427–2438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Polack, F.P.; Thomas, S.J.; Kitchin, N.; Absalon, J.; Gurtman, A.; Lockhart, S.; Perez, J.L.; Pérez Marc, G.; Moreira, E.D.; Zerbini, C.; et al. Safety and Efficacy of the BNT162b2 mRNA COVID-19 Vaccine. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 383, 2603–2615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barouch, D.H.; Stephenson, K.E.; Sadoff, J.; Yu, J.; Chang, A.; Gebre, M.; McMahan, K.; Liu, J.; Chandrashekar, A.; Patel, S.; et al. Durable Humoral and Cellular Immune Responses 8 Months after Ad26.COV2.S Vaccination. N. Engl. J. Med. 2021, 385, 951–953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richards, N.E.; Keshavarz, B.; Workman, L.J.; Nelson, M.R.; Platts-Mills, T.A.E.; Wilson, J.M. Comparison of SARS-CoV-2 Antibody Response by Age Among Recipients of the BNT162b2 vs the mRNA-1273 Vaccine. JAMA Netw. Open 2021, 4, e2124331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oliveira-Silva, J.; Reis, T.; Lopes, C.; Batista-Silva, R.; Ribeiro, R.; Marques, G.; Pacheco, V.; Rodrigues, T.; Afonso, A.; Pinheiro, V.; et al. Humoral response to the SARS-CoV-2 BNT162b2 mRNA vaccine: Real-world data from a large cohort of healthcare workers. Vaccine 2022, 40, 650–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Favresse, J.; Bayart, J.-L.; Mullier, F.; Elsen, M.; Eucher, C.; Van Eeckhoudt, S.; Roy, T.; Wieers, G.; Laurent, C.; Dogné, J.-M.; et al. Antibody titres decline 3-month post-vaccination with BNT162b2. Emerg. Microbes Infect. 2021, 10, 1495–1498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kotsias, F.; Cebrian, I.; Alloatti, A. Antigen processing and presentation. Int. Rev. Cell Mol. Biol. 2019, 348, 69–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crotty, S. T follicular helper cell differentiation, function, and roles in disease. Immunity 2014, 41, 529–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nutt, S.L.; Hodgkin, P.D.; Tarlinton, D.M.; Corcoran, L.M. The generation of antibody-secreting plasma cells. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2015, 15, 160–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krensky, A.M.; Clayberger, C. Structure of HLA molecules and immunosuppressive effects of HLA derived peptides. Int. Rev. Immunol. 1996, 13, 173–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ragone, C.; Meola, S.; Fiorillo, P.C.; Penta, R.; Auriemma, L.; Tornesello, M.L.; Miscio, L.; Cavalcanti, E.; Botti, G.; Buonaguro, F.M.; et al. HLA Does Not Impact on Short-Medium-Term Antibody Response to Preventive Anti-SARS-CoV-2 Vaccine. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 734689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ozaki, Y.; Suzuki, S.; Shigenari, A.; Okudaira, Y.; Kikkawa, E.; Oka, A.; Ota, M.; Mitsunaga, S.; Kulski, J.K.; Inoko, H. HLA-DRB1,-DRB3,-DRB4 and-DRB5 genotyping at a super-high resolution level by long range PCR and high-throughput sequencing. Tissue Antigens 2014, 83, 10–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suan, D.; Sundling, C.; Brink, R. Plasma cell and memory B cell differentiation from the germinal center. Curr. Opin. Immunol. 2017, 45, 97–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savage, P.A.; Klawon, D.E.J.; Miller, C.H. Regulatory T Cell Development. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2020, 38, 421–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- van der Helm-van Mil, A.H.M.; Huizinga, T.W.J.; Schreuder, G.M.T.; Breedveld, F.C.; de Vries, R.R.P.; Toes, R.E.M. An independent role of protective HLA class II alleles in rheumatoid arthritis severity and susceptibility. Arthritis Rheum. 2005, 52, 2637–2644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadegh-Nasseri, S.; Kim, A. Selection of immunodominant epitopes during antigen processing is hierarchical. Mol. Immunol. 2019, 113, 115–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garrido, P.; Ruiz-Cabello, F.; Bárcena, P.; Sandberg, Y.; Cantón, J.; Lima, M.; Balanzategui, A.; González, M.; López-Nevot, M.A.; Langerak, A.W.; et al. Monoclonal TCR-Vβ13.1+/CD4+/NKa+/CD8−/+dim T-LGL lymphocytosis: Evidence for an antigen-driven chronic T-cell stimulation origin. Blood 2007, 109, 4890–4898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chai, H.C.; Phipps, M.E.; Chua, K.H. Genetic risk factors of systemic lupus erythematosus in the Malaysian population: A minireview. Clin. Dev. Immunol. 2012, 2012, 963730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Castro-Santos, P.; Olloquequi, J.; Verdugo, R.A.; Gutiérrez, M.A.; Pinochet, C.; Quiñones, L.A.; Díaz-Peña, R. HLA-DRB1*07:01 and *08:02 Alleles Confer a Protective Effect Against ACPA-Positive Rheumatoid Arthritis in a Latin American Admixed Population. Biology 2020, 9, 467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernandez, C.A.; Smith, C.; Yang, W.; Daté, M.; Bashford, D.; Larsen, E.; Bowman, W.P.; Liu, C.; Ramsey, L.B.; Chang, T.; et al. HLA-DRB1*07:01 is associated with a higher risk of asparaginase allergies. Blood 2014, 124, 1266–1276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kutszegi, N.; Yang, X.; Gézsi, A.; Schermann, G.; Erdélyi, D.J.; Semsei, Á.F.; Gábor, K.M.; Sági, J.C.; Kovács, G.T.; Falus, A.; et al. HLA-DRB1*07:01-HLA-DQA1*02:01-HLA-DQB1*02:02 haplotype is associated with a high risk of asparaginase hypersensitivity in acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Haematologica 2017, 102, 1578–1586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Debes, A.K.; Xiao, S.; Colantuoni, E.; Egbert, E.R.; Caturegli, P.; Gadala, A.; Milstone, A.M. Association of Vaccine Type and Prior SARS-CoV-2 Infection With Symptoms and Antibody Measurements Following Vaccination Among Health Care Workers. JAMA Intern. Med. 2021, 181, 1660–1662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Locus | Allele | Frequency | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| G1 | G2 | G3 | ||
| HLA-DRB1 | 01:01 | 0.125 | 0.052 | 0.017 |
| HLA-DRB1 | 01:02 | 0.107 | 0.034 | 0 |
| HLA-DRB1 | 01:03 | 0.018 | 0 | 0.033 |
| HLA-DRB1 | 03:01 | 0.071 | 0.172 | 0.067 |
| HLA-DRB1 | 04:01 | 0 | 0.034 | 0.050 |
| HLA-DRB1 | 04:02 | 0 | 0.034 | 0 |
| HLA-DRB1 | 04:03 | 0.036 | 0 | 0.017 |
| HLA-DRB1 | 04:04 | 0.054 | 0.052 | 0.017 |
| HLA-DRB1 | 04:05 | 0.054 | 0 | 0.050 |
| HLA-DRB1 | 04:06 | 0 | 0 | 0.017 |
| HLA-DRB1 | 04:07 | 0.036 | 0 | 0 |
| HLA-DRB1 | 07:01 | 0.018 | 0.172 | 0.250 |
| HLA-DRB1 | 07:02 | 0 | 0 | 0.017 |
| HLA-DRB1 | 08:01 | 0.018 | 0 | 0 |
| HLA-DRB1 | 09:01 | 0.018 | 0.017 | 0 |
| HLA-DRB1 | 10:01 | 0 | 0.017 | 0.017 |
| HLA-DRB1 | 11:01 | 0.054 | 0.052 | 0.033 |
| HLA-DRB1 | 11:02 | 0.018 | 0.034 | 0 |
| HLA-DRB1 | 11:03 | 0.036 | 0 | 0 |
| HLA-DRB1 | 11:04 | 0 | 0.052 | 0.050 |
| HLA-DRB1 | 12:01 | 0.054 | 0 | 0 |
| HLA-DRB1 | 13:01 | 0.071 | 0.069 | 0.100 |
| HLA-DRB1 | 13:02 | 0.036 | 0.034 | 0.050 |
| HLA-DRB1 | 13:03 | 0.018 | 0.017 | 0.017 |
| HLA-DRB1 | 14:01 | 0.018 | 0 | 0 |
| HLA-DRB1 | 14:54 | 0.018 | 0.034 | 0.017 |
| HLA-DRB1 | 15:01 | 0.071 | 0.103 | 0.167 |
| HLA-DRB1 | 16:01 | 0.054 | 0.017 | 0.017 |
| HLA-DQB1 | 02:01 | 0.071 | 0.155 | 0.083 |
| HLA-DQB1 | 02:02 | 0.036 | 0.121 | 0.200 |
| HLA-DQB1 | 02:05 | 0 | 0.017 | 0 |
| HLA-DQB1 | 02:10 | 0 | 0.017 | 0 |
| HLA-DQB1 | 03:01 | 0.196 | 0.155 | 0.117 |
| HLA-DQB1 | 03:02 | 0.179 | 0.103 | 0.117 |
| HLA-DQB1 | 03:03 | 0 | 0.052 | 0.050 |
| HLA-DQB1 | 03:19 | 0.018 | 0.034 | 0 |
| HLA-DQB1 | 04:02 | 0.018 | 0 | 0.017 |
| HLA-DQB1 | 05:01 | 0.232 | 0.086 | 0.067 |
| HLA-DQB1 | 05:02 | 0.054 | 0.017 | 0.017 |
| HLA-DQB1 | 05:03 | 0.036 | 0.034 | 0.017 |
| HLA-DQB1 | 06:01 | 0 | 0.034 | 0 |
| HLA-DQB1 | 06:02 | 0.071 | 0.069 | 0.150 |
| HLA-DQB1 | 06:03 | 0.054 | 0.086 | 0.117 |
| HLA-DQB1 | 06:04 | 0.018 | 0.017 | 0.017 |
| HLA-DQB1 | 06:09 | 0.018 | 0 | 0.033 |
| Allele | Frequency | P | Pc | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Low Responders | High Responders | |||
| HLA-DRB1*01:01 | 0.125 | 0.017 | 0.028 | n.s |
| HLA-DQB1*05:01 | 0.232 | 0.067 | 0.016 | n.s |
| HLA-DRB1*07:01 | 0.018 | 0.250 | 2.3 × 10−4 | 3.1 × 10−3 |
| HLA-DQB1*02:02 | 0.036 | 0.200 | 0.008 | n.s |
| Haplotype | Frequency in Low Responders | Frequency in High Responders | P | Pc |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| HLA-DRB1*01:01~DQA1*01:01~DQB1*05:01 | 0.107 | 0.017 | n.s | n.s |
| HLA-DRB1*07:01~DQA1*02:01~DQB1*02:02 | 0.018 | 0.200 | 2.1× 10−3 | 0.028 |
| HLA-DRB1*15:01~DQA1*01:02~DQB1*06:02 | 0.054 | 0.133 | n.s | n.s |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gutiérrez-Bautista, J.F.; Sampedro, A.; Gómez-Vicente, E.; Rodríguez-Granger, J.; Reguera, J.A.; Cobo, F.; Ruiz-Cabello, F.; López-Nevot, M.Á. HLA Class II Polymorphism and Humoral Immunity Induced by the SARS-CoV-2 mRNA-1273 Vaccine. Vaccines 2022, 10, 402. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines10030402
Gutiérrez-Bautista JF, Sampedro A, Gómez-Vicente E, Rodríguez-Granger J, Reguera JA, Cobo F, Ruiz-Cabello F, López-Nevot MÁ. HLA Class II Polymorphism and Humoral Immunity Induced by the SARS-CoV-2 mRNA-1273 Vaccine. Vaccines. 2022; 10(3):402. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines10030402
Chicago/Turabian StyleGutiérrez-Bautista, Juan Francisco, Antonio Sampedro, Esther Gómez-Vicente, Javier Rodríguez-Granger, Juan Antonio Reguera, Fernando Cobo, Francisco Ruiz-Cabello, and Miguel Ángel López-Nevot. 2022. "HLA Class II Polymorphism and Humoral Immunity Induced by the SARS-CoV-2 mRNA-1273 Vaccine" Vaccines 10, no. 3: 402. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines10030402
APA StyleGutiérrez-Bautista, J. F., Sampedro, A., Gómez-Vicente, E., Rodríguez-Granger, J., Reguera, J. A., Cobo, F., Ruiz-Cabello, F., & López-Nevot, M. Á. (2022). HLA Class II Polymorphism and Humoral Immunity Induced by the SARS-CoV-2 mRNA-1273 Vaccine. Vaccines, 10(3), 402. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines10030402







