Prediction of SARS-CoV-2 Omicron Variant Immunogenicity, Immune Escape and Pathogenicity, through the Analysis of Spike Protein-Specific Core Unique Peptides
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Methods
2.2. Databases
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Mapping the C/H-CrUPs Landscape of Spike Protein of the SARS-CoV-2 Omicron Variant
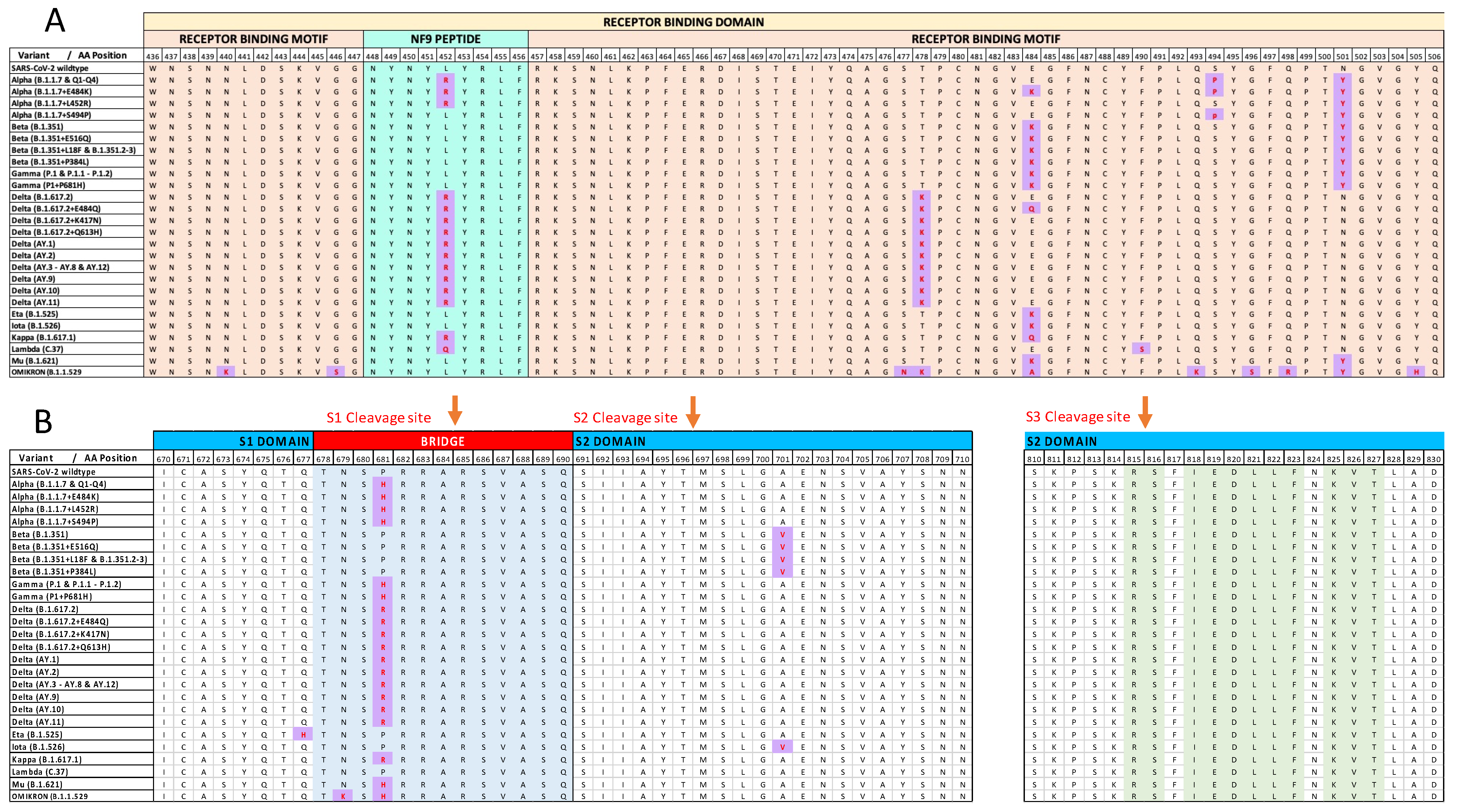
3.2. Omicron-Specific C/H-CrUPs That belong to the Receptor Binding Domain
3.3. C/H-CrUPs Altered Architecture around the Spike-Cleavage Site(s) of the Omicron Variant
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
References
- Pierros, V.; Kontopodis, E.; Stravopodis, D.J.; Tsangaris, G.T. Unique Peptide Signatures of SARS-CoV-2 Against Human Proteome Reveal Variants’ Immune Escape and Infectiveness. bioRxiv 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Cheng, G. Sequence analysis of the emerging SARS-CoV-2 variant Omicron in South Africa. J. Med. Virol. 2022, 94, 11728–11733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kontopodis, E.; Pierros, V.; Anagnostopoulos, A.; Stravopodis, D.J.; Papassideri, I.; Vorgias, C.; Tsangaris, G.T. Data Processing Approach for the Construction and Evaluation of an Organism’s UNIQUOME with Comparative Analysis for the Human, Rat and Mouse Uniquomes. In Proceedings of the XIII. Annual Congress of the European Proteomics Association: From Genes via Proteins and their Interactions to Functions, Potsdam, Germany, 24–28 March 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Shang, J.; Ye, G.; Shi, K.; Wan, Y.; Luo, C.; Aihara, H.; Geng, Q.; Auerbach, A.; Li, F. Structural basis of receptor recognition by SARS-CoV-2. Nature 2020, 581, 221–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hatmal, M.M.; Alshaer, W.; Al-Hatamleh, M.A.I.; Hatmal, M.; Smadi, O.; Taha, M.O.; Oweida, A.J.; Boer, J.C.; Mohamud, R.; Plebanski, M. Comprehensive Structural and Molecular Comparison of Spike Proteins of SARS-CoV-2, SARS-CoV and MERS-CoV, and Their Interactions with ACE2. Cells 2020, 9, 2638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Zhang, Y.N.; Yan, R.; Wang, G.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, Z.-R.; Li, Y.; Ou, J.; Chu, W.; Liang, Z.; et al. ACE2-targeting monoclonal antibody as potent and broad-spectrum coronavirus blocker. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2021, 6, 315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zahradnik, J.; Marciano, S.; Shemesh, M.; Zoler, E.; Harari, D.; Chiaravalli, J.; Meyer, B.; Rudich, Y.; Li, C.; Marton, I.; et al. SARS-CoV-2 variant prediction and antiviral drug design are enabled by RBD in vitro evolution. Nat. Microbiol. 2021, 6, 1188–1198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hastie, K.M.; Li, H.; Bedinger, D.; Schendel, S.L.; Dennison, S.M.; Li, K.; Rayaprolu, V.; Yu, X.; Mann, C.; Zandonatti, M.; et al. Defining variant-resistant epitopes targeted by SARS-CoV-2 antibodies: A global consortium study. Science 2021, 374, 472–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.; Wang, R.; Gilby, N.B.; Wei, G.-W. Omicron Variant (B.1.1.529): Infectivity, Vaccine Breakthrough, and Antibody Resistance. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 2022, 62, 412–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Liu, J.; Plante, K.S.; Plante, J.A.; Xie, X.; Zhang, X.; Ku, Z.; An, Z.; Scharton, D.; Schindewolf, C.; et al. The N501Y spike substitution enhances SARS-CoV-2 infection and transmission. Nature 2022, 602, 294–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Motozono, C.; Toyoda, M.; Zahradnik, J.; Saito, A.; Nasser, H.; Tan, S.T.; Ngare, I.; Kimura, I.; Uriu, K.; Kosugi, Y.; et al. SARS-CoV-2 spike L452R variant evades cellular immunity and increases infectivity. Cell Host Microbe 2021, 29, 1124–1136.e11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kared, H.; Redd, A.D.; Bloch, E.M.; Bonny, T.S.; Sumatoh, H.; Kairi, F.; Carbajo, D.; Abel, B.; Newell, E.W.; Bettinotti, M.P.; et al. SARS-CoV-2-specific CD8+ T cell responses in convalescent COVID-19 individuals. J. Clin. Investig. 2021, 131, 1124–1136.e11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peacock, T.P.; Goldhill, D.H.; Zhou, J.; Baillon, L.; Frise, R.; Swann, O.C.; Kugathasan, R.; Penn, R.; Brown, J.C.; Sanchez-David, R.Y.; et al. The furin cleavage site in the SARS-CoV-2 spike protein is required for transmission in ferrets. Nat. Microbiol. 2021, 6, 899–909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Whittaker, G.R. SARS-CoV-2 Spike and its Adaptable Furin Cleavage Site. Lancet Microbe 2021, 2, e488–e489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, J.; Wan, Y.; Luo, C.; Ye, G.; Geng, Q.; Auerbach, A.; Li, F. Cell entry mechanisms of SARS-CoV-2. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2020, 117, 11727–11734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoffmann, M.; Kleine-Weber, H.; Schroeder, S.; Krüger, N.; Herrler, Y.; Erichsen, S.; Schiergens, T.S.; Herrler, G.; Wu, N.-H.; Nitsche, A.; et al. SARS-CoV-2 Cell Entry Depends on ACE2 and TMPRSS2 and Is Blocked by a Clinically Proven Protease Inhibitor. Cell 2020, 181, 271–280.e8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoffmann, M.; Kleine-Weber, H.; Pohlmann, S. A Multibasic Cleavage Site in the Spike Protein of SARS-CoV-2 Is Essential for Infection of Human Lung Cells. Mol. Cell 2020, 78, 779–784.e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takeda, M. Proteolytic activation of SARS-CoV-2 spike protein. Microbiol. Immunol. 2022, 66, 15–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Spike Protein | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Variant | C/H-CrUPs | Same C/H-CrUPs | % of Same C/H-CrUPs | New C/H-CrUPs | % of New C/H-CrUPs | Lost C/H-CrUPs | % of Lost C/H-CrUPs |
| Wild-type virus | 987 | ||||||
| Alpha (B.1.1.7) + (Q1-Q4) | 982 | 931 | 94.8 | 51 | 5.2 | 56 | 5.7 |
| Alpha (B.1.1.7 + E484K) | 983 | 928 | 94.4 | 55 | 5.6 | 59 | 6.0 |
| Alpha (B.1.1.7 + L452R) | 981 | 936 | 95.4 | 45 | 4.6 | 51 | 5.2 |
| Alpha (B.1.1.7 + S494P) | 981 | 936 | 95.4 | 45 | 4.6 | 51 | 5.2 |
| Beta (B.1.351) | 981 | 954 | 97.2 | 27 | 2.8 | 33 | 3.3 |
| Beta (B.1.351 + E516Q) | 981 | 949 | 96.7 | 32 | 3.3 | 38 | 3.8 |
| Beta (B.1.351 + L18F) (B.1.351.2-3) | 979 | 948 | 96.8 | 31 | 3.2 | 39 | 3.9 |
| Beta (B.1.351 + P384L) | 980 | 949 | 96.8 | 31 | 3.2 | 38 | 3.9 |
| Gamma (P.1) (P.1.1 - P.1.2) | 985 | 930 | 94.4 | 55 | 5.6 | 57 | 5.8 |
| Gamma (P1 + P681H) | 985 | 930 | 94.4 | 55 | 5.6 | 57 | 5.8 |
| Delta (B.1.617.2) | 984 | 948 | 96.3 | 36 | 3.7 | 39 | 4.0 |
| Delta (B.1.617.2 + E484Q) | 984 | 945 | 96.0 | 39 | 3.4 | 42 | 4.3 |
| Delta (B.1.617.2 + K417N) | 984 | 944 | 95.9 | 40 | 4.1 | 43 | 4.4 |
| Delta (B.1.617.2 + Q613H) | 984 | 947 | 96.2 | 37 | 3.8 | 40 | 4.1 |
| Delta (AY.1) | 984 | 944 | 95.9 | 40 | 4.7 | 43 | 4.1 |
| Delta (AY.2) | 985 | 939 | 95.3 | 46 | 4.8 | 48 | 4.9 |
| Delta (AY.3 - AY.8) + (AY.12) | 983 | 951 | 96.7 | 32 | 3.3 | 36 | 3.7 |
| Delta (AY.9) | 983 | 951 | 96.7 | 32 | 3.3 | 36 | 3.6 |
| Delta (AY.10) | 983 | 951 | 96.7 | 32 | 3.3 | 36 | 3.6 |
| Delta (AY.11) | 983 | 951 | 96.7 | 32 | 3.3 | 36 | 3.6 |
| Eta (B.1.525) | 990 | 956 | 96.5 | 34 | 3.4 | 31 | 3.1 |
| Iota (B.1.526) | 984 | 960 | 97.5 | 24 | 2.4 | 27 | 2.7 |
| Kappa (B.1.617.1) | 985 | 964 | 97.8 | 21 | 2.1 | 23 | 2.3 |
| Lambda (C.37) | 982 | 949 | 96.6 | 33 | 3.4 | 38 | 3.9 |
| Mu (B.1.621) | 983 | 953 | 96.9 | 30 | 3.1 | 34 | 3.4 |
| Omicron (B.1.1.529) | 983 | 868 | 88.3 | 115 | 11.7 | 119 | 12.1 |
| Alpha Variant | Delta Variant | |||||||||
| C/H-CrUP | Position | Mutation | New C/H-CrUPs | Position | C/H-CrUP | Position | Mutation | New C/H-CrUPs | Position | |
| GNYNYL | 447 | L452R | GNYNYR | 447 | PGQTGKI | 412 | K417N | |||
| NYNYLY | 448 | GQTGKIA | 413 | GQTGNI | 413 | |||||
| YNYRY | 449 | QTGNIA | 414 | |||||||
| NYLYRL | 450 | NYRYRL | 450 | TGKIAD | 415 | TGNIAD | 415 | |||
| YLYRLF | 451 | YRYRLF | 451 | GKIADY | 416 | GNIADY | 416 | |||
| LYRLFR | 452 | |||||||||
| GNYNYL | 447 | L452R | GNYNYR | 447 | ||||||
| CNGVEG | 480 | E484K | CNGVKG | 480 | NYNYLY | 448 | ||||
| NGVEGF | 481 | NGVKGF | 481 | YNYRY | 449 | |||||
| GVEGFN | 482 | GVKGFN | 482 | NYLYRL | 450 | NYRYRL | 450 | |||
| KGFNC | 484 | YLYRLF | 451 | YRYRLF | 451 | |||||
| LYRLFR | 452 | |||||||||
| YFPLQS | 489 | S494P N501Y | YFPLQP | 489 | ||||||
| FPLQSY | 490 | FPLQPY | 490 | YQAGST | 473 | T478K | YQAGSK | 473 | ||
| PLQSYG | 491 | PLQPYG | 491 | QAGSKP | 474 | |||||
| QSYGF | 493 | QPYGF | 493 | AGSTPC | 475 | AGSKPC | 475 | |||
| SYGFQP | 494 | PYGFQP | 494 | GSKPCN | 476 | |||||
| GFQPTN | 496 | STPCN | 477 | |||||||
| FQPTNG | 497 | KPCNG | 478 | |||||||
| QPTNGV | 498 | |||||||||
| QPTΥ | 498 | |||||||||
| PTNGVG | 499 | PTΥG | 499 | |||||||
| TNGVGY | 500 | TΥGV | 500 | |||||||
| NGVGYQ | 501 | ΥGVG | 501 | |||||||
| Omicron variant | ||||||||||
| C/H-CrUP | Position | Mutation | New C/H-CrUPs | Position | C/H-CrUP | Position | Mutation | New C/H-CrUPs | Position | |
| NLCPFG | 334 | G339D | NLCPFD | 334 | IYQAGS | 472 | S477N T478K | |||
| LCPFGE | 335 | LCPFDE | 335 | YQAGST | 473 | YQAGN | 473 | |||
| PFGEVF | 337 | PFDEV | 337 | QAGNKP | 474 | |||||
| FGEVFN | 338 | FDEVFN | 338 | AGSTPC | 475 | |||||
| GEVFNA | 339 | DEVFNA | 339 | STPCN | 477 | NKPCN | 477 | |||
| KPCNG | 478 | |||||||||
| VLYNSA | 367 | S371L S373P S375F | VLYNLAP | 367 | ||||||
| LYNSAS | 368 | CNGVEG | 480 | E484A | CNGVAG | 480 | ||||
| YNSASF | 369 | YNLAPF | 369 | NGVEGF | 481 | NGVAGF | 481 | |||
| NSASFST | 370 | GVEGFN | 482 | GVAGFN | 482 | |||||
| LAPFFT | 371 | VAGFNC | 483 | |||||||
| ASFSTF | 372 | APFFTF | 372 | |||||||
| SFSTFK | 373 | CYFPLQ | 488 | Q493K G496S Q498R N501Y Y505H | CYFPLK | 488 | ||||
| FFTFK | 374 | YFPLQS | 489 | YFPLKS | 489 | |||||
| STFKC | 375 | FTFKCY | 375 | FPLQSY | 490 | FPLKSY | 490 | |||
| PLQSYG | 491 | |||||||||
| PGQTGKI | 412 | K417N | LKSYSF | 492 | ||||||
| GQTGKIA | 413 | GQTGNI | 413 | QSYGF | 493 | KSYSFR | 493 | |||
| QTGNIA | 414 | SYGFQP | 494 | SYSFRP | 494 | |||||
| TGKIAD | 415 | TGNIAD | 415 | YGFQPT | 495 | YSFRPT | 495 | |||
| GKIADY | 416 | GNIADY | 416 | GFQPTN | 496 | |||||
| FQPTNG | 497 | FRPTY | 497 | |||||||
| WNSNN | 436 | N440K G446S | WNSNKL | 436 | QPTNGV | 498 | RPTYGV | 498 | ||
| SNNLDS | 438 | SNKLDS | 438 | PTNGVG | 499 | |||||
| NNLDSK | 439 | NKLDSKV | 439 | TNGVGY | 500 | TYGVGH | 500 | |||
| KLDSKVS | 440 | NGVGYQ | 501 | |||||||
| LDSKVG | 441 | GVGYQP | 502 | GVGHQ | 502 | |||||
| DSKVGG | 442 | DSKVSG | 442 | VGYQPY | 503 | VGHQPY | 503 | |||
| KVGGNY | 444 | KVSGNY | 444 | GYQPYR | 504 | |||||
| VGGNYN | 445 | VSGNYN | 445 | YQPYRV | 505 | HQPYR | 505 | |||
| GGNYNY | 446 | |||||||||
| WILD-TYPE | OMICRON VARIANT | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Contact Positions | C/H-CrUPs | Mutations | Newly Constructed C/H-CrUPs | |||||||||
| N439 | AWNSN | WNSNN | SNNLDS | NNLDSK | ||||||||
| Y449 | KVGGNY | VGGNYN | GGNYNY | GNYNYL | NYNYLY | |||||||
| Y453 | NYNYLY | NYLYRL | YLYRLF | LYRLFR | YRLFRK | |||||||
| F486 | NGVEGF | GVEGFN | GFNCY | FNCYF | ||||||||
| N487 | GVEGFN | GFNCY | FNCYF | |||||||||
| Y489 | GFNCY | FNCYF | CYFPLQ | YFPLQS | ||||||||
| Q493 | CYFPLQ | YFPLQS | FPLQSY | PLQSYG | QSYGF | Q493K | CYFPLK | YFPLKS | FPLKSY | LKSYSF | KSYSFR | |
| Q498 | SYGFQP | YGFQPT | GFQPTN | FQPTNG | QPTNGV | Q498R | KSYSFR | SYSFRP | YSFRPT | FRPTY | RPTYGV | |
| T500 | YGFQPT | GFQPTN | FQPTNG | QPTNGV | PTNGVG | TNGVGY | ||||||
| N501 | GFQPTN | FQPTNG | QPTNGV | PTNGVG | TNGVGY | NGVGYQ | N501Y | FRPTY | RPTYGV | TYGVGH | ||
| Y505 | TNGVGY | NGVGYQ | GVGYQP | VGYQPY | GYQPYR | YQPYRV | Y505H | TYGVGH | GVGHQ | VGHQPY | HQPYR | |
| Cleavage Site | Mutation | Variant | Position | New C/H-CrUPs |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| R685↓S | P681R | Delta | 680 | SRRRAR↓S |
| P681H | Alpha Omicron | 677 | QTNSH | |
| 678 | TNSHR | |||
| 680 | SHRRAR | |||
| T696↓M | A701V | Beta | None | |
| R815↓S | None | None | None | |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kontopodis, E.; Pierros, V.; Stravopodis, D.J.; Tsangaris, G.T. Prediction of SARS-CoV-2 Omicron Variant Immunogenicity, Immune Escape and Pathogenicity, through the Analysis of Spike Protein-Specific Core Unique Peptides. Vaccines 2022, 10, 357. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines10030357
Kontopodis E, Pierros V, Stravopodis DJ, Tsangaris GT. Prediction of SARS-CoV-2 Omicron Variant Immunogenicity, Immune Escape and Pathogenicity, through the Analysis of Spike Protein-Specific Core Unique Peptides. Vaccines. 2022; 10(3):357. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines10030357
Chicago/Turabian StyleKontopodis, Evangelos, Vasileios Pierros, Dimitrios J. Stravopodis, and George T. Tsangaris. 2022. "Prediction of SARS-CoV-2 Omicron Variant Immunogenicity, Immune Escape and Pathogenicity, through the Analysis of Spike Protein-Specific Core Unique Peptides" Vaccines 10, no. 3: 357. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines10030357
APA StyleKontopodis, E., Pierros, V., Stravopodis, D. J., & Tsangaris, G. T. (2022). Prediction of SARS-CoV-2 Omicron Variant Immunogenicity, Immune Escape and Pathogenicity, through the Analysis of Spike Protein-Specific Core Unique Peptides. Vaccines, 10(3), 357. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines10030357








