Anthocyanins and Their Metabolites as Therapeutic Agents for Neurodegenerative Disease
Abstract
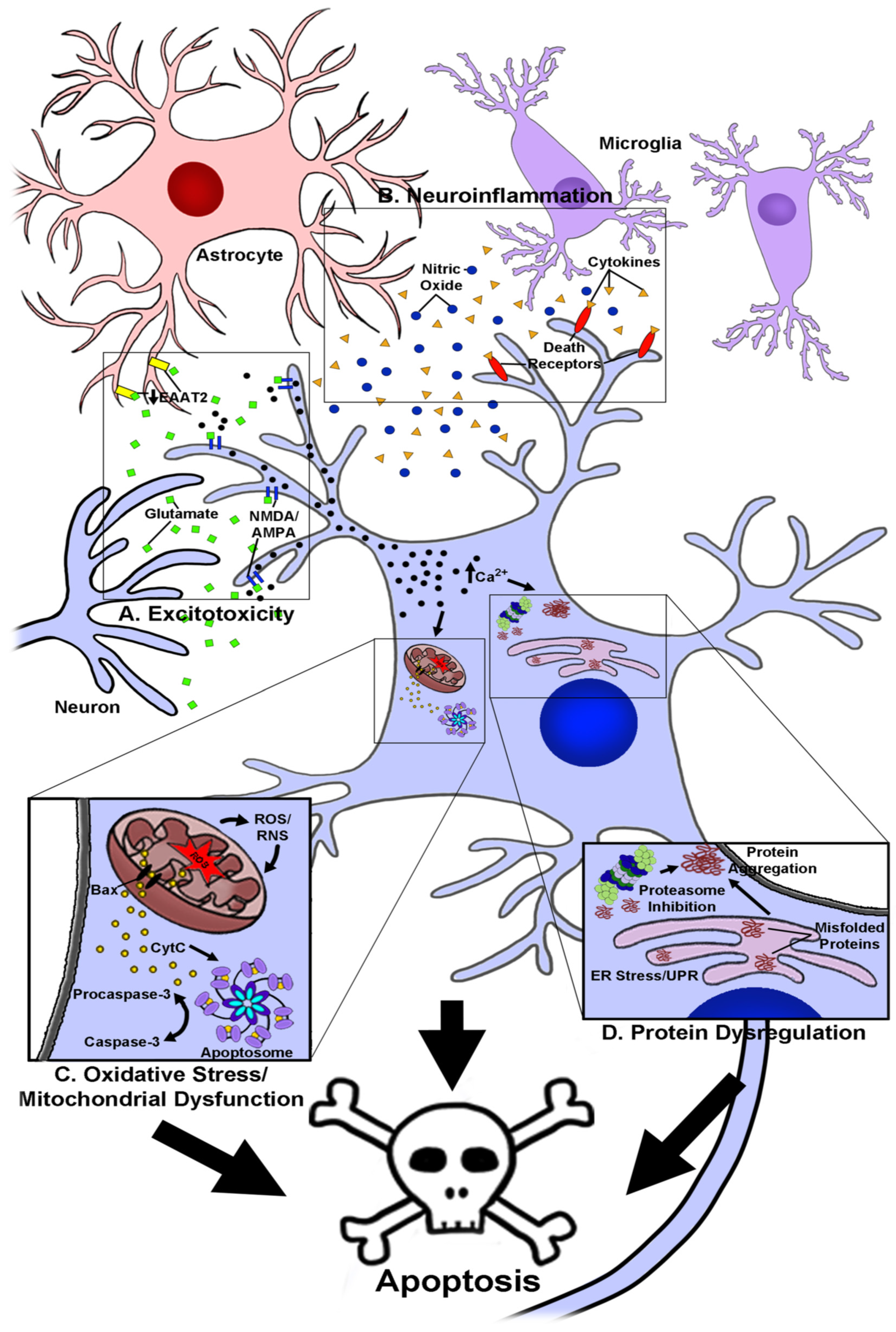
1. Introduction
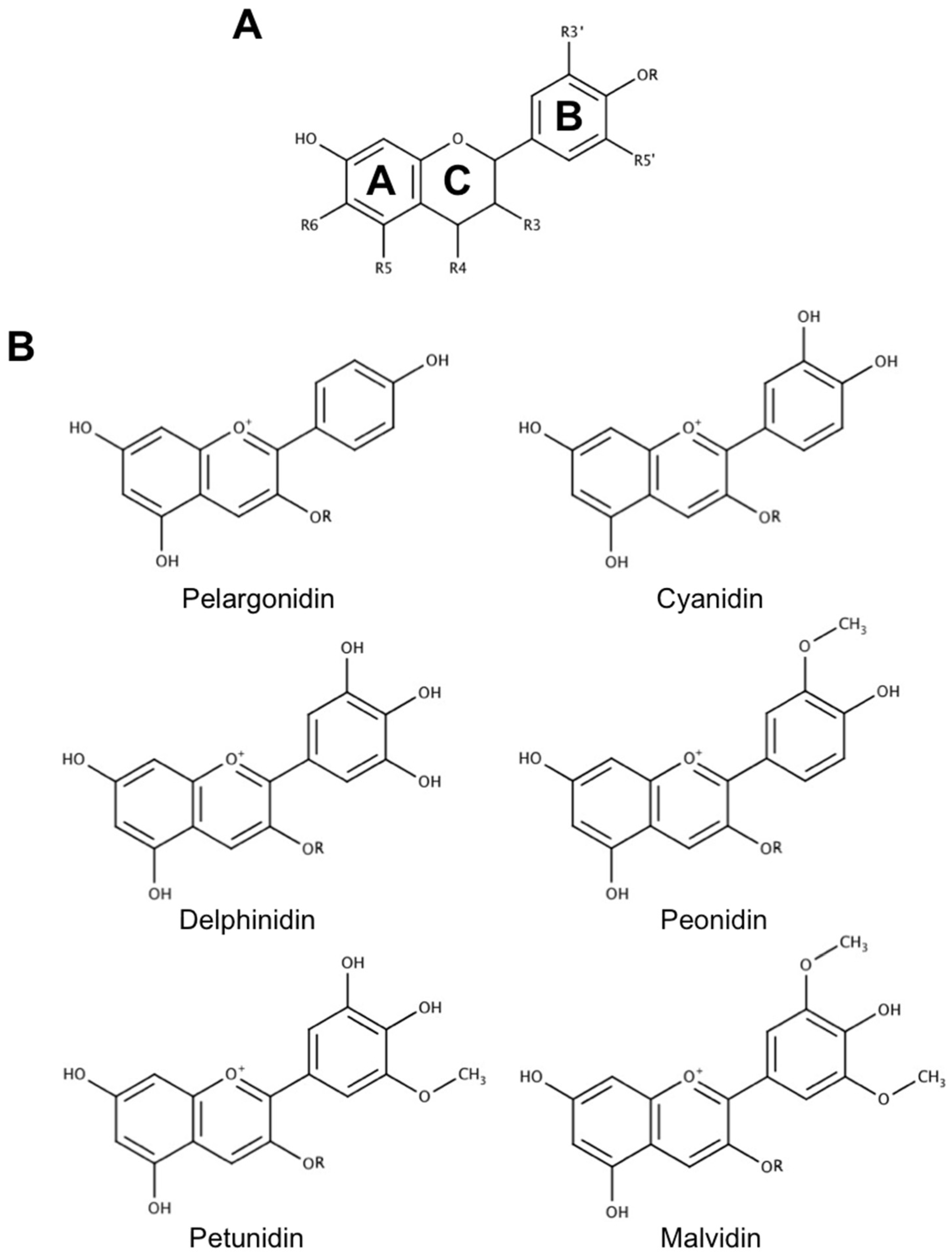
2. The Use of Anthocyanins as Novel Neuroprotective and Therapeutic Agents in Neurodegenerative Disease
2.1. Absorption and Blood–Brain Barrier Permeability of Anthocyanins
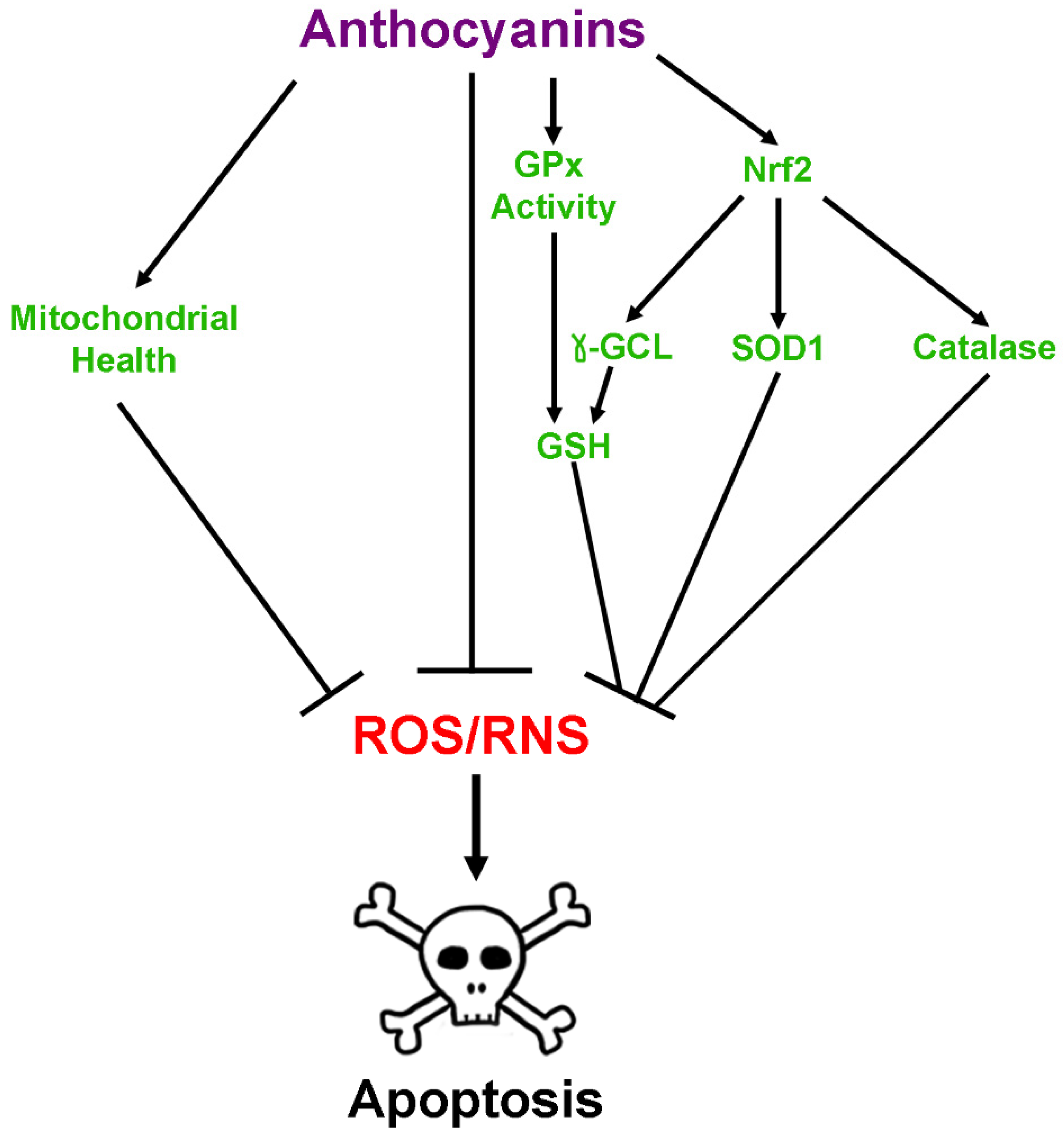
2.2. Antioxidant Effects of Anthocyanins
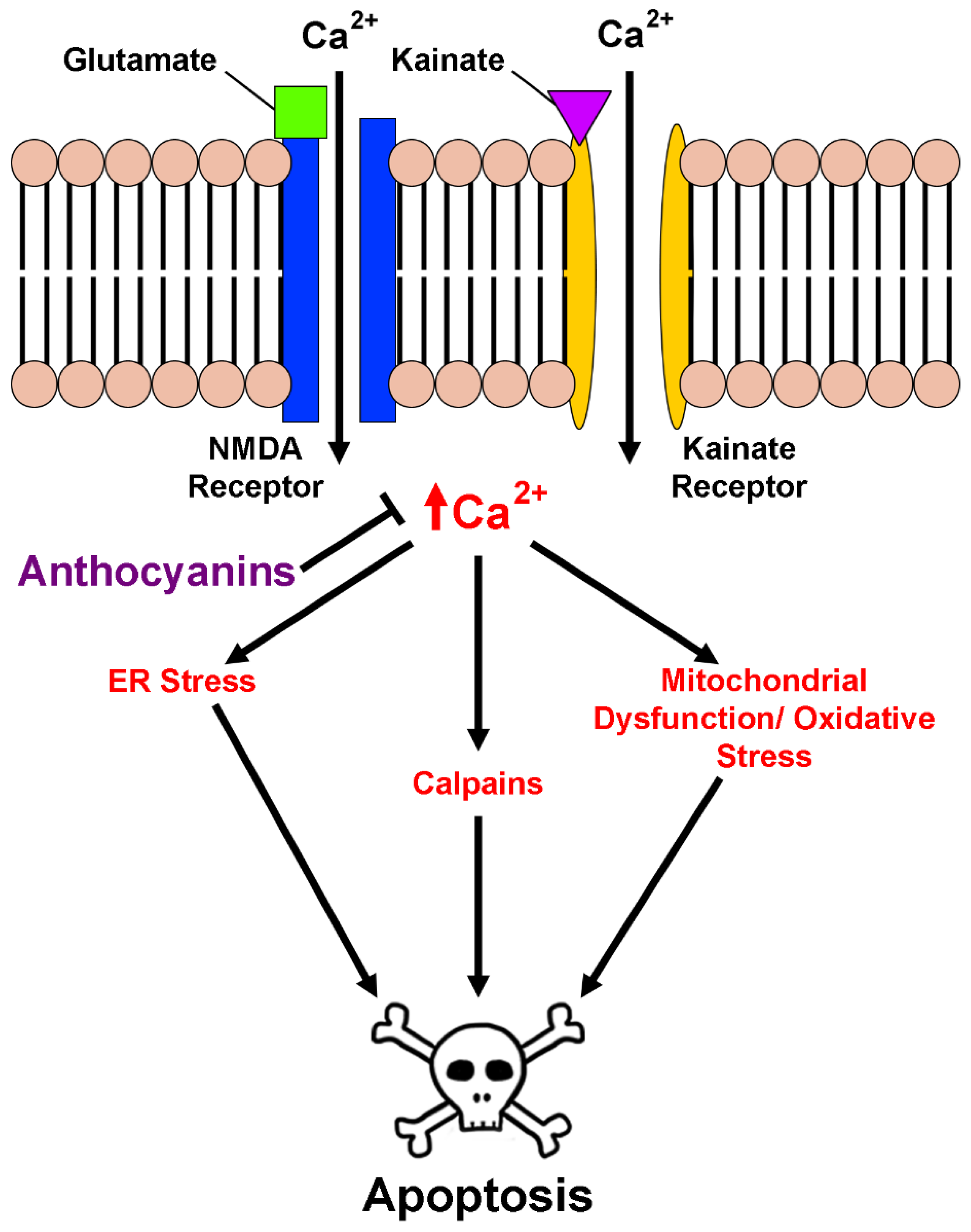
2.3. Anthocyanins in Calcium Homeostasis and Excitotoxicity
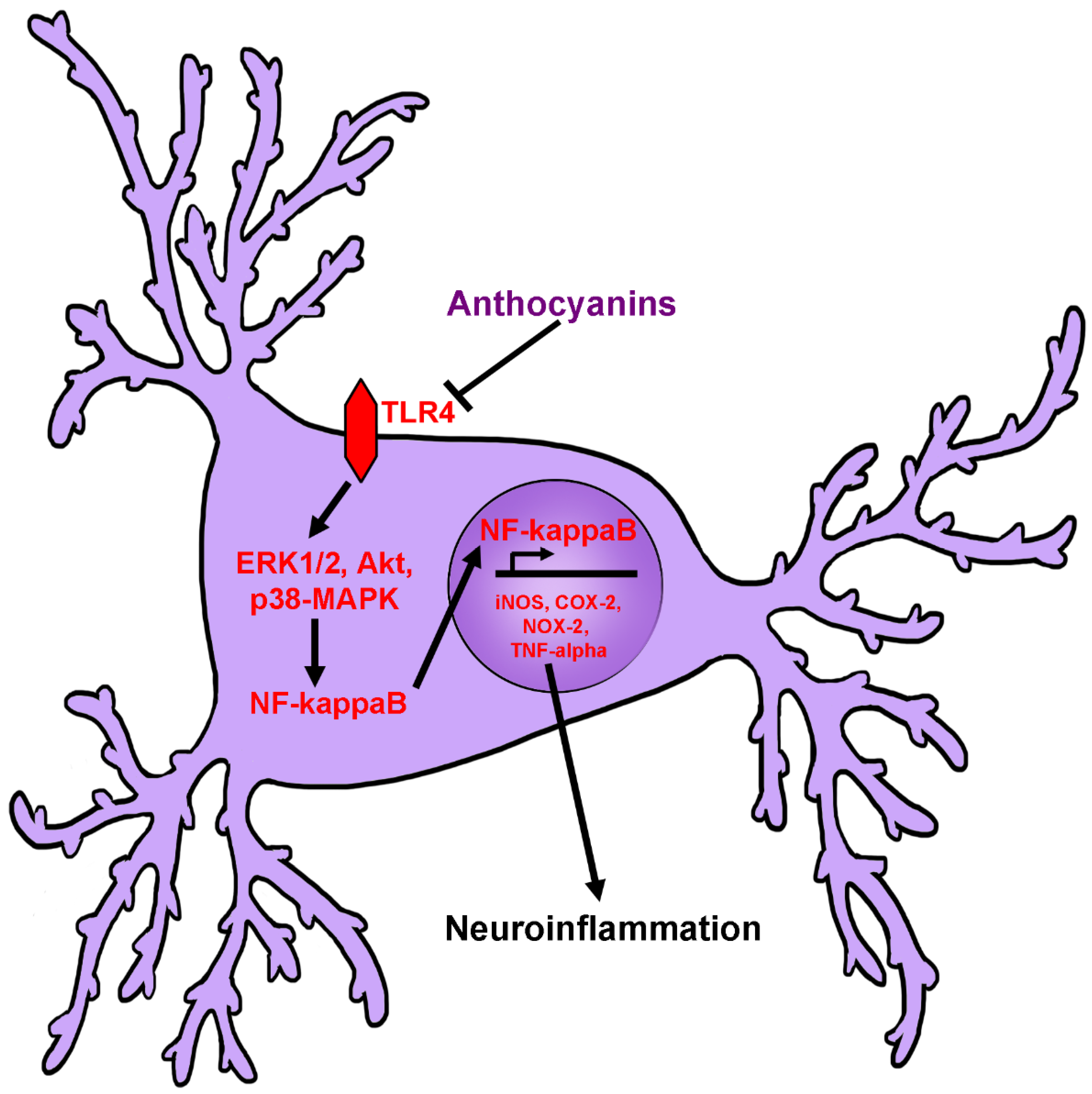
2.4. Anti-Neuroinflammatory Activity of Anthocyanins
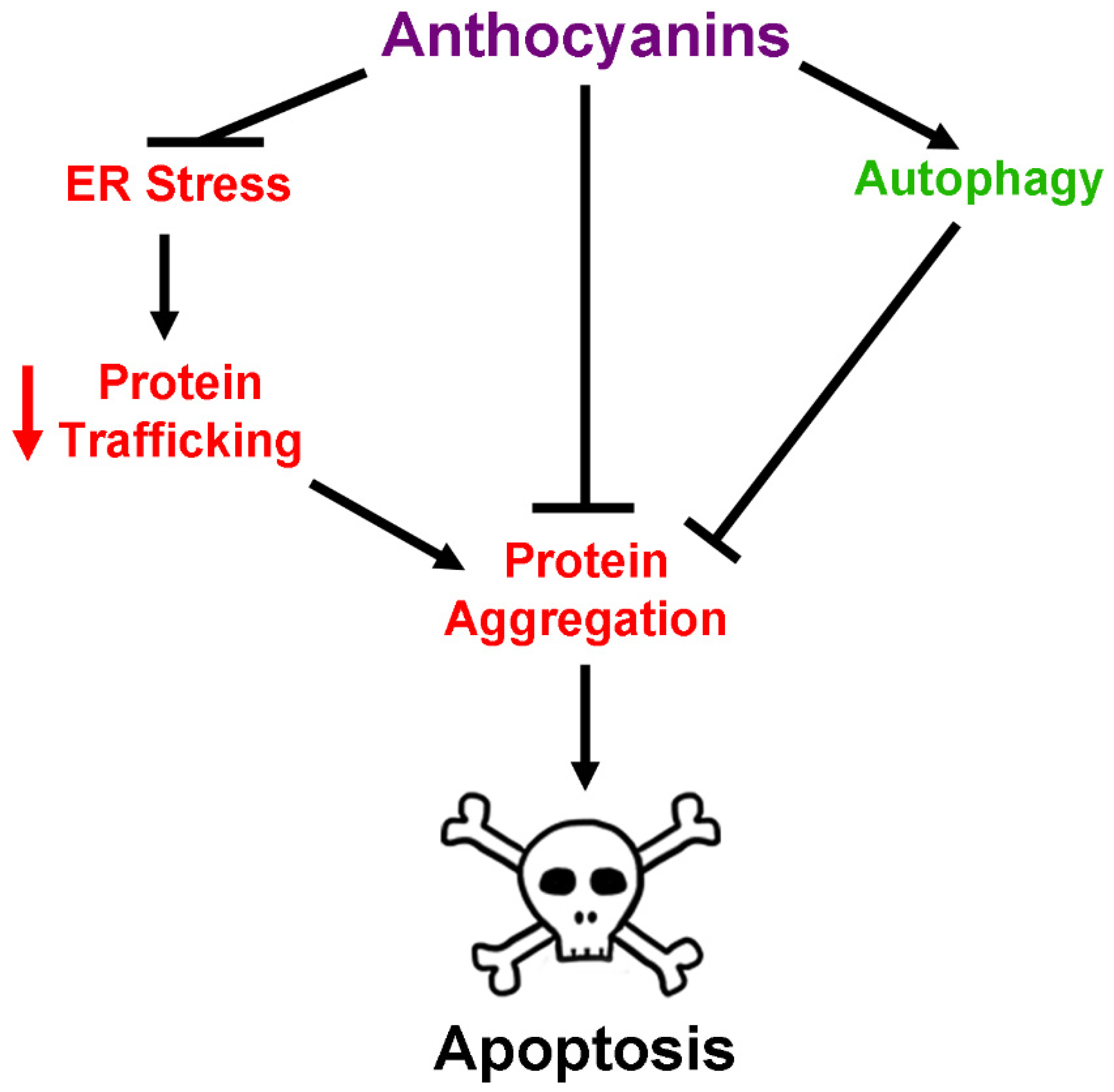
2.5. Anthocyanins and Regulation of Protein Homeostasis
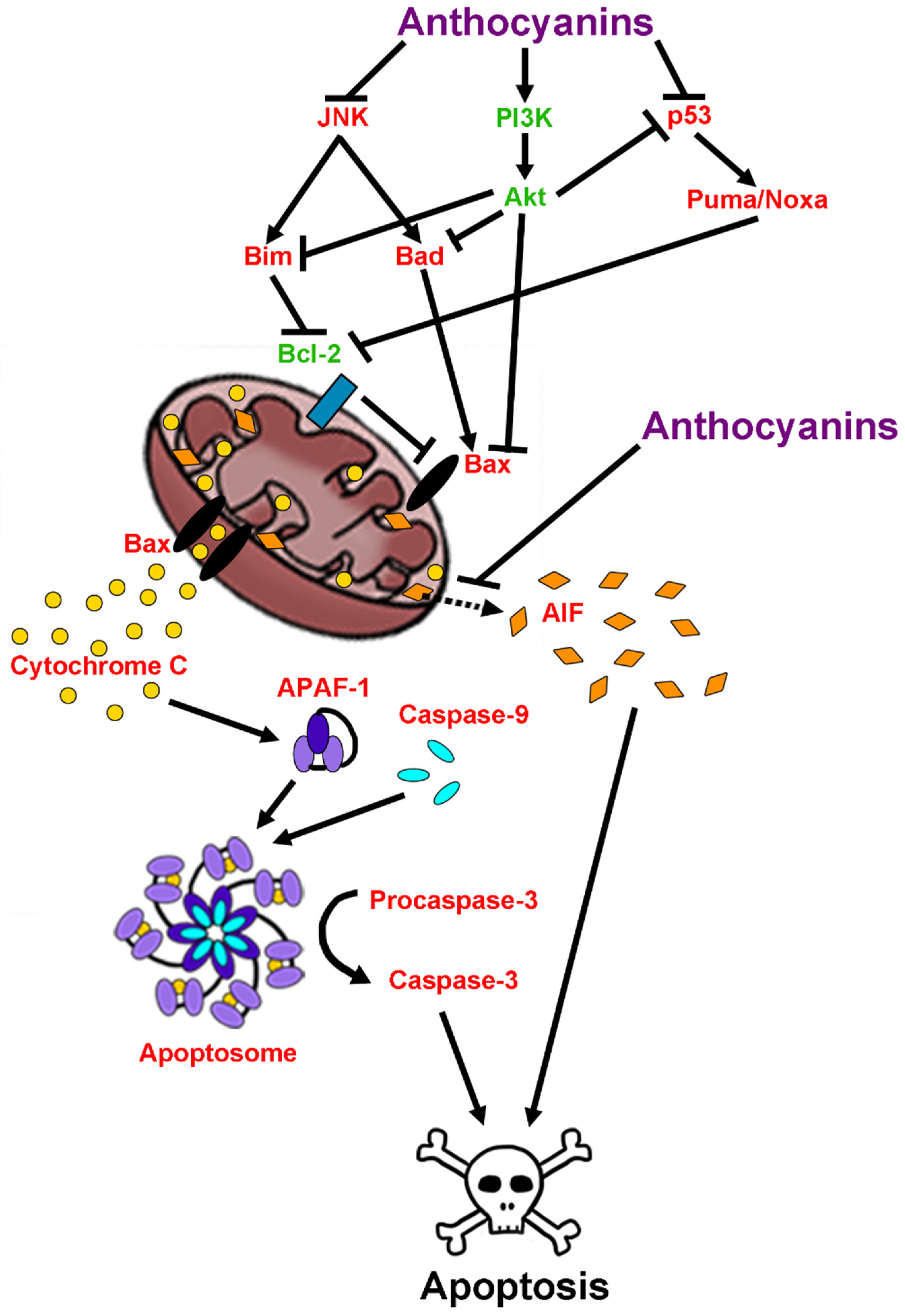
2.6. Anti-Apoptotic Effects of Anthocyanins
2.7. Anthocyanins as Therapeutic Agents in Aging and Neurodegenerative Disease
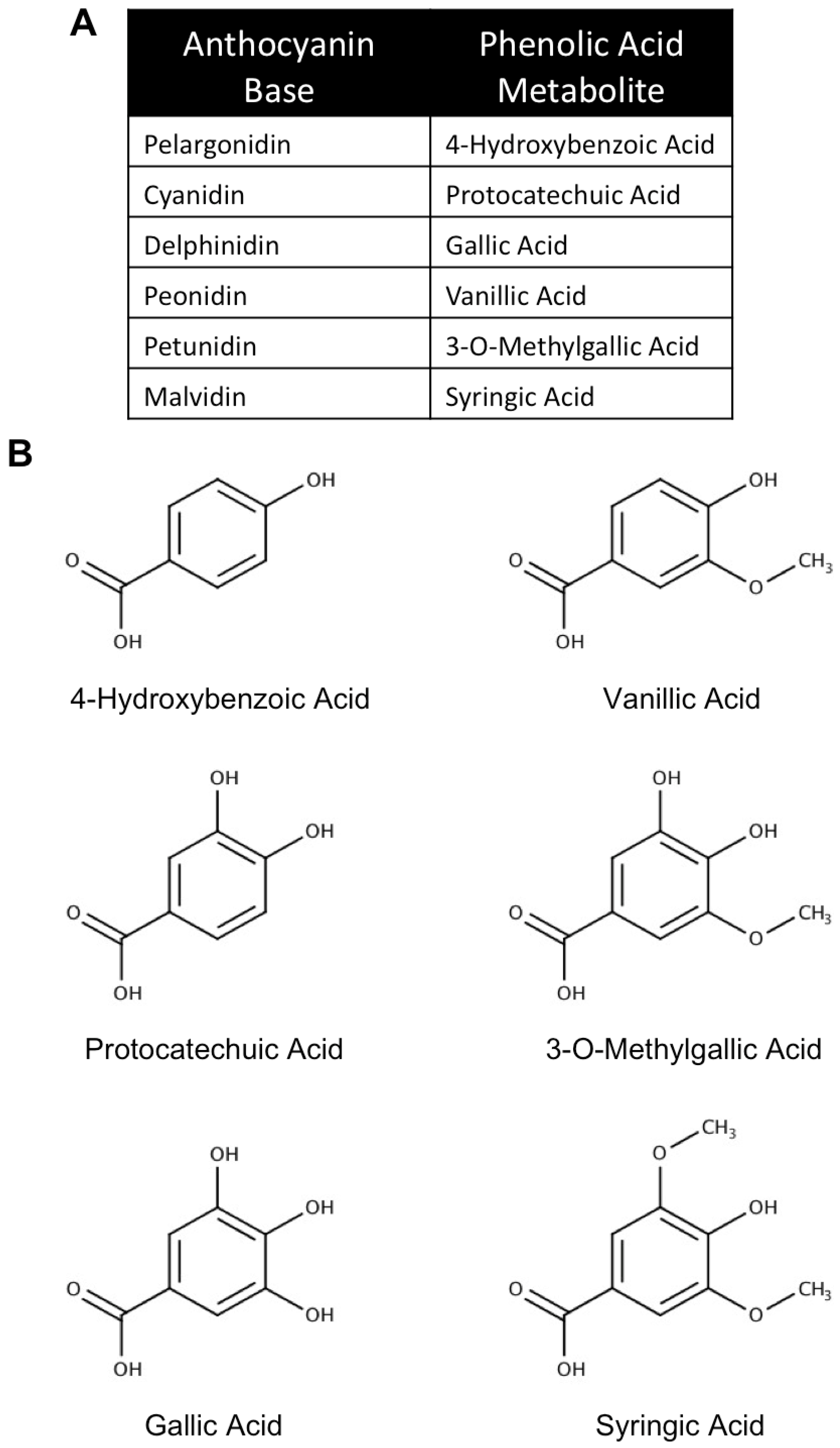
3. The Use of Anthocyanin Metabolites as Novel Neuroprotective and Therapeutic Agents in Neurodegenerative Disease
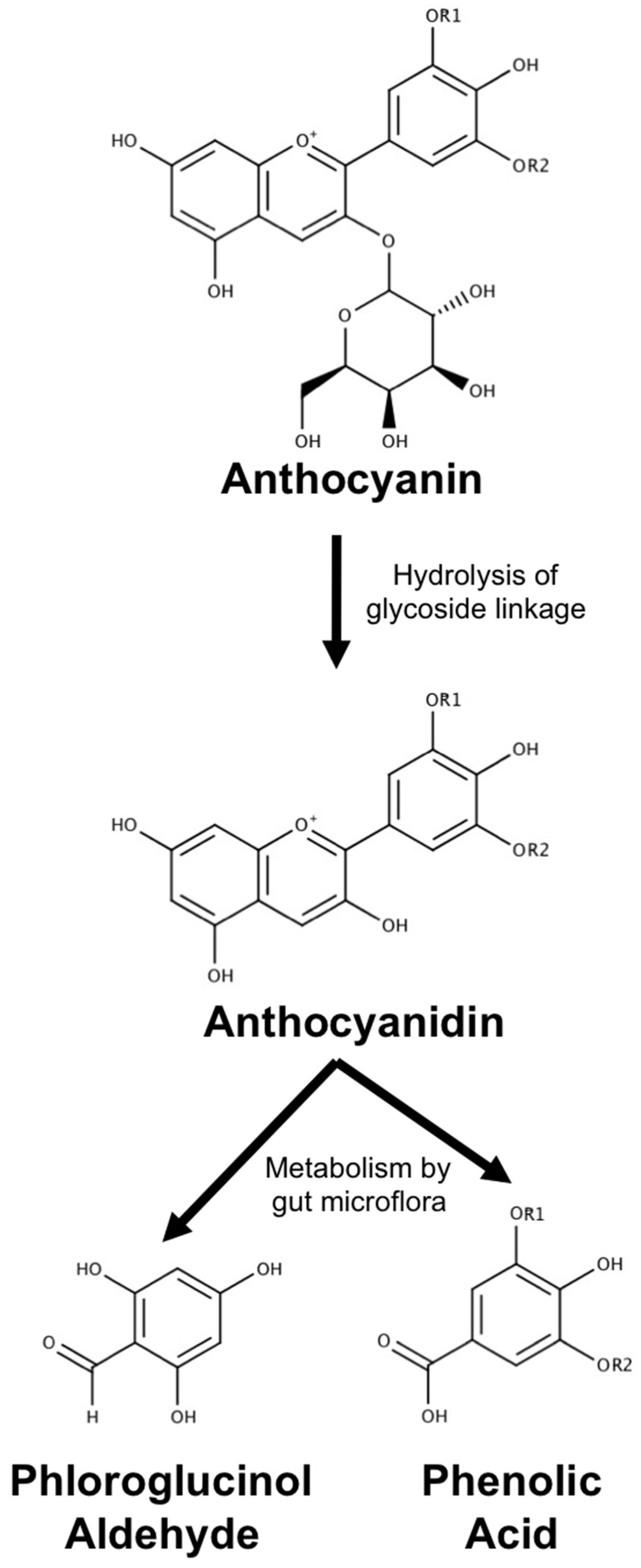
3.1. Metabolism, Absorption and Bioavailability of Anthocyanin Metabolites
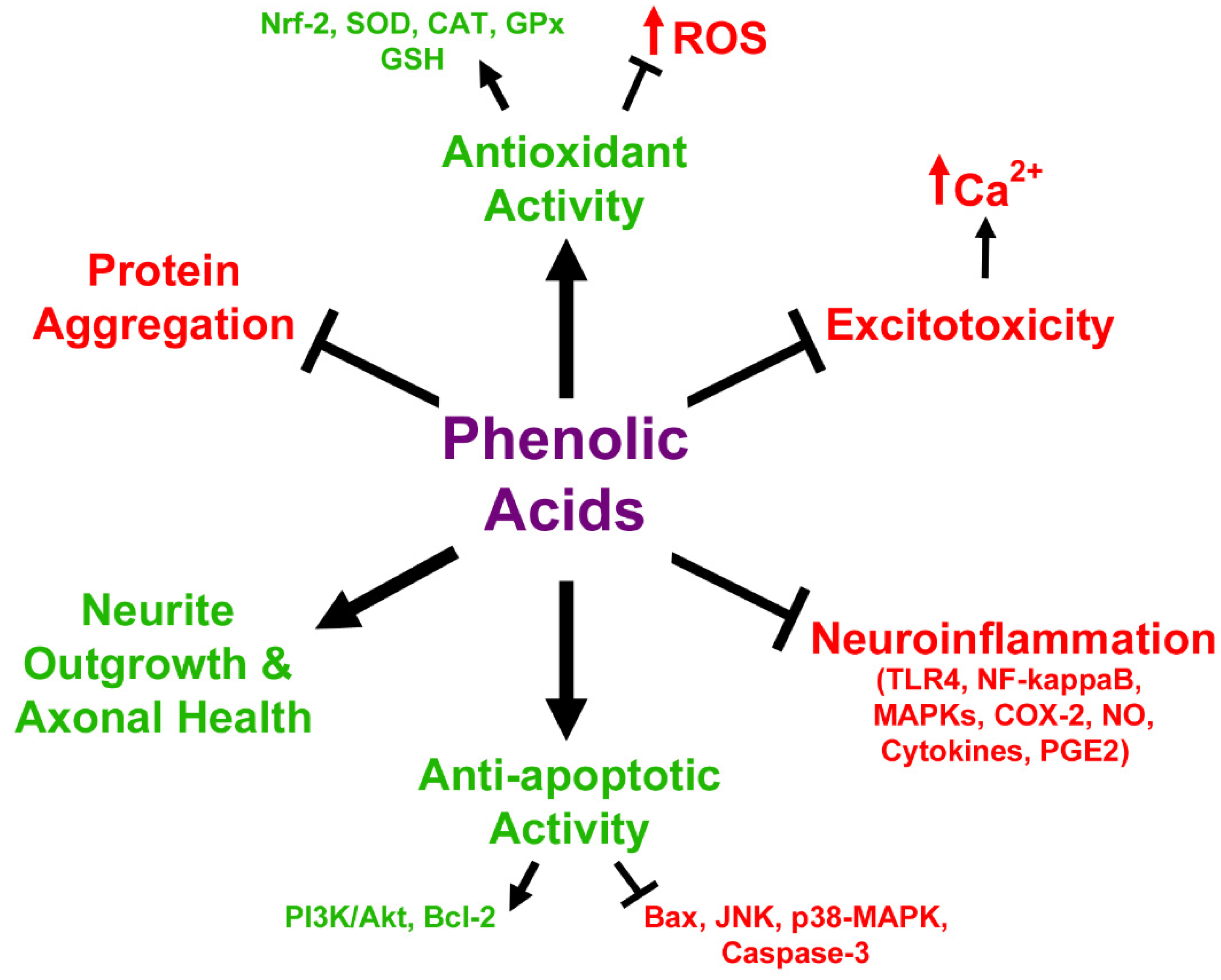
3.2. In Vitro Neuroprotective Effects of Anthocyanin Metabolites
3.3. Anthocyanin Metabolites as Therapeutic Agents in Neurodegeneration and Aging Models
4. Future Considerations
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ilieva, H.; Polymenidou, M.; Cleveland, D.W. Non-cell autonomous toxicity in neurodegenerative disorders: ALS and beyond. J. Cell Biol. 2009, 187, 761–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taylor, J.P.; Brown, R.H., Jr.; Cleveland, D.W. Decoding ALS: From genes to mechanism. Nature 2016, 539, 197–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Magalingam, K.B.; Radhakrishnan, A.; Ping, N.S.; Haleagrahara, N. Current Concepts of Neurodegenerative Mechanisms in Alzheimer’s Disease. Biomed. Res. Int. 2018, 2018, 3740461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeng, X.S.; Geng, W.S.; Jia, J.J.; Chen, L.; Zhang, P.P. Cellular and Molecular Basis of Neurodegeneration in Parkinson Disease. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2018, 10, 109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wallace, T.C. Anthocyanins in cardiovascular disease. Adv. Nutr. 2011, 2, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.S.; Stoner, G.D. Anthocyanins and their role in cancer prevention. Cancer Lett. 2008, 269, 281–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scalbert, A.; Williamson, G. Dietary intake and bioavailability of polyphenols. J. Nutr. 2000, 130, 2073S–2085S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bajda, M.; Guzior, N.; Ignasik, M.; Malawska, B. Multi-target-directed ligands in Alzheimer’s disease treatment. Curr. Med. Chem. 2011, 18, 4949–4975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jalili-Baleh, L.; Babaei, E.; Abdpour, S.; Nasir Abbas Bukhari, S.; Foroumadi, A.; Ramazani, A.; Sharifzadeh, M.; Abdollahi, M.; Khoobi, M. A review on flavonoid-based scaffolds as multi-target-directed ligands (MTDLs) for Alzheimer’s disease. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2018, 152, 570–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kay, C.D.; Kroon, P.A.; Cassidy, A. The bioactivity of dietary anthocyanins is likely to be mediated by their degradation products. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2009, 53, S92–S101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keppler, K.; Humpf, H.U. Metabolism of anthocyanins and their phenolic degradation products by the intestinal microflora. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2005, 13, 5195–5205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Azzini, E.; Vitaglione, P.; Intorre, F.; Napolitano, A.; Durazzo, A.; Foddai, M.S.; Fumagalli, A.; Catasta, G.; Rossi, L.; Venneria, E.; et al. Bioavailability of strawberry antioxidants in human subjects. Br. J. Nutr. 2010, 104, 1165–1173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sandhu, A.K.; Miller, M.G.; Thangthaeng, N.; Scott, T.M.; Shukitt-Hale, B.; Edirisinghe, I.; Burton-Freeman, B. Metabolic fate of strawberry polyphenols after chronic intake in healthy older adults. Food Funct. 2018, 9, 96–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Youdim, K.A.; Dobbie, M.S.; Kuhnle, G.; Proteggente, A.R.; Abbott, N.J.; Rice-Evans, C. Interaction between flavonoids and the blood-brain barrier: In vitro studies. J. Neurochem. 2003, 85, 180–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andres-Lacueva, C.; Shukitt-Hale, B.; Galli, R.L.; Jauregui, O.; Lamuela-Raventos, R.M.; Joseph, J.A. Anthocyanins in aged blueberry-fed rats are found centrally and may enhance memory. Nutr. Neurosci. 2005, 8, 111–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El Mohsen, M.A.; Marks, J.; Kuhnle, G.; Moore, K.; Debnam, E.; Kaila Srai, S.; Rice-Evans, C.; Spencer, J.P. Absorption, tissue distribution and excretion of pelargonidin and its metabolites following oral administration to rats. Br. J. Nutr. 2006, 95, 51–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Williams, C.M.; El Mohsen, M.A.; Vauzour, D.; Rendeiro, C.; Butler, L.T.; Ellis, J.A.; Whiteman, M.; Spencer, J.P. Blueberry-induced changes in spatial working memory correlate with changes in hippocampal CREB phosphorylation and brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) levels. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2008, 45, 295–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fornasaro, S.; Ziberna, L.; Gasperotti, M.; Tramer, F.; Vrhovsek, U.; Mattivi, F.; Passamonti, S. Determination of cyanidin 3-glucoside in rat brain, liver and kidneys by UPLC/MS-MS and its application to a short-term pharmacokinetic study. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 22815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milbury, P.E.; Kalt, W. Xenobiotic metabolism and berry flavonoid transport across the blood-brain barrier. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2010, 58, 3950–3956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanzo, A.; Vrhovsek, U.; Tramer, F.; Mattivi, F.; Passamonti, S. Exceptionally fast uptake and metabolism of cyanidin 3-glucoside by rat kidneys and liver. J. Nat. Prod. 2011, 74, 1049–1054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Passamonti, S.; Vrhovsek, U.; Vanzo, A.; Mattivi, F. The stomach as a site for anthocyanins absorption from food. FEBS Lett. 2003, 544, 210–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maestro, A.; Terdoslavich, M.; Vanzo, A.; Kuku, A.; Tramer, F.; Nicolin, V.; Micali, F.; Decorti, G.; Passamonti, S. Expression of bilitranslocase in the vascular endothelium and its function as a flavonoid transporter. Cardiovasc. Res. 2010, 85, 175–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vanzo, A.; Terdoslavich, M.; Brandoni, A.; Torres, A.M.; Vrhovsek, U.; Passamonti, S. Uptake of grape anthocyanins into the rat kidney and the involvement of bilitranslocase. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2008, 52, 1106–1116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Battiston, L.; Macagno, A.; Passamonti, S.; Micali, F.; Sottocasa, G.L. Specific sequence-directed anti-bilitranslocase antibodies as a tool to detect potentially bilirubin-binding proteins in different tissues of the rat. FEBS Lett. 1999, 453, 351–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ziberna, L.; Tramer, F.; Moze, S.; Vrhovsek, U.; Mattivi, F.; Passamonti, S. Transport and bioactivity of cyanidin 3-glucoside into the vascular endothelium. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2012, 52, 1750–1759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Youdim, K.A.; Shukitt-Hale, B.; Joseph, J.A. Flavonoids and the brain: Interactions at the blood-brain barrier and their physiological effects on the central nervous system. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2004, 37, 1683–1693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Passamonti, S.; Vrhovsek, U.; Vanzo, A.; Mattivi, F. Fast access of some grape pigments to the brain. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2005, 53, 7029–7034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talavera, S.; Felgines, C.; Texier, O.; Besson, C.; Gil-Izquierdo, A.; Lamaison, J.L.; Remesy, C. Anthocyanin metabolism in rats and their distribution to digestive area, kidney, and brain. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2005, 53, 3902–3908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, M.T.; Beal, M.F. Mitochondrial dysfunction and oxidative stress in neurodegenerative diseases. Nature 2006, 443, 787–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hargreaves, I.P.; Lane, A.; Sleiman, P.M. The coenzyme Q10 status of the brain regions of Parkinson’s disease patients. Neurosci. Lett. 2008, 447, 17–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, W.M.; Wilson-Delfosse, A.L.; Mieyal, J.J. Dysregulation of glutathione homeostasis in neurodegenerative diseases. Nutrients 2012, 4, 1399–1440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niedzielska, E.; Smaga, I.; Gawlik, M.; Moniczewski, A.; Stankowicz, P.; Pera, J.; Filip, M. Oxidative Stress in Neurodegenerative Diseases. Mol. Neurobiol. 2016, 53, 4094–4125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Houten, B.; Woshner, V.; Santos, J.H. Role of mitochondrial DNA in toxic responses to oxidative stress. DNA Repair (Amst.) 2006, 5, 145–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Brien, E.S.; Nucci, N.V.; Fuglestad, B.; Tommos, C.; Wand, A.J. Defining the Apoptotic Trigger: THE INTERACTION OF CYTOCHROME c AND CARDIOLIPIN. J. Biol. Chem. 2015, 290, 30879–30887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hwang, Y.P.; Choi, J.H.; Yun, H.J.; Han, E.H.; Kim, H.G.; Kim, J.Y.; Park, B.H.; Khanal, T.; Choi, J.M.; Chung, Y.C.; et al. Anthocyanins from purple sweet potato attenuate dimethylnitrosamine-induced liver injury in rats by inducing Nrf2-mediated antioxidant enzymes and reducing COX-2 and iNOS expression. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2011, 49, 93–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shih, P.H.; Yeh, C.T.; Yen, G.C. Anthocyanins induce the activation of phase II enzymes through the antioxidant response element pathway against oxidative stress-induced apoptosis. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2007, 55, 9427–9435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zafra-Stone, S.; Yasmin, T.; Bagchi, M.; Chatterjee, A.; Vinson, J.A.; Bagchi, D. Berry anthocyanins as novel antioxidants in human health and disease prevention. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2007, 51, 675–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, F.; Cai, Y.Z.; Yang, X.; Ke, J.; Corke, H. Anthocyanins, hydroxycinnamic acid derivatives, and antioxidant activity in roots of different chinese purple-fleshed sweetpotato genotypes. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2010, 58, 7588–7596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, J.W.; Kim, E.K.; Lee, S.J.; Kim, Y.S.; Moon, S.H.; Jeon, B.T.; Sung, S.H.; Kim, E.T.; Park, P.J. Antioxidant activity and protective effect of anthocyanin oligomers on H(2)O(2)-triggered G2/M arrest in retinal cells. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2012, 60, 4282–4288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chun, O.K.; Kim, D.O.; Lee, C.Y. Superoxide radical scavenging activity of the major polyphenols in fresh plums. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2003, 51, 8067–8072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aimee, W.N.; Ross, E.K.; Khatter, S.; Miller, K.; Linseman, D.A. Chemical basis for the disparate neurprotective effects of the anthocyanins, callistephin and kuromanin, against nitrosative stress. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2017, 103, 23–24. [Google Scholar]
- Belkacemi, A.; Ramassamy, C. Innovative Anthocyanin/Anthocyanidin Formulation Protects SK-N-SH Cells Against the Amyloid-beta Peptide-Induced Toxicity: Relevance to Alzheimer’s Disease. Cent. Nerv. Syst. Agents Med. Chem. 2015, 16, 37–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Casedas, G.; Gonzalez-Burgos, E.; Smith, C.; Lopez, V.; Gomez-Serranillos, M.P. Regulation of redox status in neuronal SH-SY5Y cells by blueberry (Vaccinium myrtillus L.) juice, cranberry (Vaccinium macrocarpon A.) juice and cyanidin. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2018, 118, 572–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Casedas, G.; Gonzalez-Burgos, E.; Smith, C.; Lopez, V.; Gomez-Serranillos, M.P. Sour cherry (Prunus cerasus L.) juice protects against hydrogen peroxide-induced neurotoxicity by modulating the antioxidant response. J. Funct. Foods 2018, 46, 243–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, D.; McGhie, T.K.; Zhang, J.; Adaim, A.; Skinner, M. Effects of anthocyanins and other phenolics of boysenberry and blackcurrant as inhibitors of oxidative stress and damage to cellular DNA in SH-SY5Y and HL-60 cells. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2006, 86, 678–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heo, H.J.; Lee, C.Y. Strawberry and its anthocyanins reduce oxidative stress-induced apoptosis in PC12 cells. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2005, 53, 1984–1989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, H.; Johnson, S.L.; Liu, W.; DaSilva, N.A.; Meschwitz, S.; Dain, J.A.; Seeram, N.P. Evaluation of Polyphenol Anthocyanin-Enriched Extracts of Blackberry, Black Raspberry, Blueberry, Cranberry, Red Raspberry, and Strawberry for Free Radical Scavenging, Reactive Carbonyl Species Trapping, Anti-Glycation, Anti-beta-Amyloid Aggregation, and Microglial Neuroprotective Effects. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spada, P.D.; Dani, C.; Bortolini, G.V.; Funchal, C.; Henriques, J.A.; Salvador, M. Frozen fruit pulp of Euterpe oleraceae Mart. (Acai) prevents hydrogen peroxide-induced damage in the cerebral cortex, cerebellum, and hippocampus of rats. J. Med. Food 2009, 12, 1084–1088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, J.; Yana, Y.; Ran, L.; Mi, J.; Sun, Y.; Lu, L.; Gao, Y.; Zeng, X.; Cao, Y. Isolation, antioxidant property and protective effect on PC12 cell of the main anthocyanin in fruit of Lycium ruthenicum Murray. J. Funct. Foods 2017, 30, 97–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarozzi, A.; Morroni, F.; Hrelia, S.; Angeloni, C.; Marchesi, A.; Cantelli-Forti, G.; Hrelia, P. Neuroprotective effects of anthocyanins and their in vivo metabolites in SH-SY5Y cells. Neurosci. Lett. 2007, 424, 36–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ereminas, G.; Majiene, D.; Sidlauskas, K.; Jakstas, V.; Ivanauskas, L.; Vaitiekaitis, G.; Liobikas, J. Neuroprotective properties of anthocyanidin glycosides against H2O2-induced glial cell death are modulated by their different stability and antioxidant activity in vitro. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2017, 94, 188–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Masheta, Q.D.; Al-Azzawi, S.K. Antioxidant and Anti-Inflammatory Effects of Delphinidin on Glial Cellsand Lack of Effect on Secretase Enzyme. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2018, 454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Case, A.J.; Agraz, D.; Ahmad, I.M.; Zimmerman, M.C. Low-Dose Aronia melanocarpa Concentrate Attenuates Paraquat-Induced Neurotoxicity. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2016, 2016, 5296271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dani, C.; Pasquali, M.A.; Oliveira, M.R.; Umezu, F.M.; Salvador, M.; Henriques, J.A.; Moreira, J.C. Protective effects of purple grape juice on carbon tetrachloride-induced oxidative stress in brains of adult Wistar rats. J. Med. Food 2008, 11, 55–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rahman, M.M.; Ichiyanagi, T.; Komiyama, T.; Sato, S.; Konishi, T. Effects of anthocyanins on psychological stress-induced oxidative stress and neurotransmitter status. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2008, 56, 7545–7550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhuang, J.; Lu, J.; Wang, X.; Wang, X.; Hu, W.; Hong, F.; Zhao, X.X.; Zheng, Y.L. Purple sweet potato color protects against high-fat diet-induced cognitive deficits through AMPK-mediated autophagy in mouse hippocampus. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2019, 65, 35–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poulose, S.M.; Bielinski, D.F.; Carey, A.; Schauss, A.G.; Shukitt-Hale, B. Modulation of oxidative stress, inflammation, autophagy and expression of Nrf2 in hippocampus and frontal cortex of rats fed with acai-enriched diets. Nutr. Neurosci. 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Belkacemi, A.; Ramassamy, C. Anthocyanins Protect SK-N-SH Cells Against Acrolein-Induced Toxicity by Preserving the Cellular Redox State. J. Alzheimers. Dis. 2016, 50, 981–998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, H.Y.; Weon, J.B.; Ryu, G.; Yang, W.S.; Kim, N.Y.; Kim, M.K.; Ma, C.J. Neuroprotective effect of Aronia melanocarpa extract against glutamate-induced oxidative stress in HT22 cells. BMC Complement. Altern. Med. 2017, 17, 207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelsey, N.; Hulick, W.; Winter, A.; Ross, E.; Linseman, D. Neuroprotective effects of anthocyanins on apoptosis induced by mitochondrial oxidative stress. Nutr. Neurosci. 2011, 14, 249–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neves, D.; Valentão, P.; Bernardo, J.; Oliveira, M.C.; Ferreira, J.M.G.; Pereira, D.M.; Andrade, P.B.; Videira, R.A. A new insight on elderberry anthocyanins bioactivity: Modulation of mitochondrial redox chain functionality and cell redox state. J. Funct. Foods 2019, 56, 145–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pacheco, S.M.; Azambuja, J.H.; de Carvalho, T.R.; Soares, M.S.P.; Oliveira, P.S.; da Silveira, E.F.; Stefanello, F.M.; Braganhol, E.; Gutierres, J.M.; Spanevello, R.M. Glioprotective Effects of Lingonberry Extract Against Altered Cellular Viability, Acetylcholinesterase Activity, and Oxidative Stress in Lipopolysaccharide-Treated Astrocytes. Cell. Mol. Neurobiol. 2018, 38, 1107–1121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Strathearn, K.E.; Yousef, G.G.; Grace, M.H.; Roy, S.L.; Tambe, M.A.; Ferruzzi, M.G.; Wu, Q.L.; Simon, J.E.; Lila, M.A.; Rochet, J.C. Neuroprotective effects of anthocyanin- and proanthocyanidin-rich extracts in cellular models of Parkinsons disease. Brain Res. 2014, 1555, 60–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thummayot, S.; Tocharus, C.; Jumnongprakhon, P.; Suksamrarn, A.; Tocharus, J. Cyanidin attenuates Abeta25-35-induced neuroinflammation by suppressing NF-kappaB activity downstream of TLR4/NOX4 in human neuroblastoma cells. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2018, 39, 1439–1452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parrado-Fernandez, C.; Sandebring-Matton, A.; Rodriguez-Rodriguez, P.; Aarsland, D.; Cedazo-Minguez, A. Anthocyanins protect from complex I inhibition and APPswe mutation through modulation of the mitochondrial fission/fusion pathways. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2016, 1862, 2110–2118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salinska, E.; Danysz, W.; Lazarewicz, J.W. The role of excitotoxicity in neurodegeneration. Folia Neuropathol. 2005, 43, 322–339. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Badshah, H.; Kim, T.H.; Kim, M.O. Protective effects of anthocyanins against amyloid beta-induced neurotoxicity in vivo and in vitro. Neurochem. Int. 2015, 80, 51–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shih, P.H.; Wu, C.H.; Yeh, C.T.; Yen, G.C. Protective effects of anthocyanins against amyloid beta-peptide-induced damage in neuro-2A cells. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2011, 59, 1683–1689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, J.; Meng, X.; Yan, C.; Wang, C. Effect of purple sweet potato anthocyanins on beta-amyloid-mediated PC-12 cells death by inhibition of oxidative stress. Neurochem. Res. 2010, 35, 357–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poulose, S.M.; Fisher, D.R.; Bielinski, D.F.; Gomes, S.M.; Rimando, A.M.; Schauss, A.G.; Shukitt-Hale, B. Restoration of stressor-induced calcium dysregulation and autophagy inhibition by polyphenol-rich acai (Euterpe spp.) fruit pulp extracts in rodent brain cells in vitro. Nutrition 2014, 30, 853–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ullah, I.; Park, H.Y.; Kim, M.O. Anthocyanins protect against kainic acid-induced excitotoxicity and apoptosis via ROS-activated AMPK pathway in hippocampal neurons. CNS Neurosci. Ther. 2014, 20, 327–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, J.S.; Perveen, S.; Ha, T.J.; Kim, S.Y.; Yoon, S.H. Cyanidin-3-glucoside inhibits glutamate-induced Zn2+ signaling and neuronal cell death in cultured rat hippocampal neurons by inhibiting Ca2+-induced mitochondrial depolarization and formation of reactive oxygen species. Brain Res. 2015, 1606, 9–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vyas, P.; Kalidindi, S.; Chibrikova, L.; Igamberdiev, A.U.; Weber, J.T. Chemical analysis and effect of blueberry and lingonberry fruits and leaves against glutamate-mediated excitotoxicity. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2013, 61, 7769–7776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsunaga, N.; Imai, S.; Inokuchi, Y.; Shimazawa, M.; Yokota, S.; Araki, Y.; Hara, H. Bilberry and its main constituents have neuroprotective effects against retinal neuronal damage in vitro and in vivo. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2009, 53, 869–877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duffy, K.B.; Spangler, E.L.; Devan, B.D.; Guo, Z.; Bowker, J.L.; Janas, A.M.; Hagepanos, A.; Minor, R.K.; DeCabo, R.; Mouton, P.R.; et al. A blueberry-enriched diet provides cellular protection against oxidative stress and reduces a kainate-induced learning impairment in rats. Neurobiol. Aging 2008, 29, 1680–1689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chitnis, T.; Weiner, H.L. CNS inflammation and neurodegeneration. J. Clin. Investig. 2017, 127, 3577–3587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, M.S.; Ali, T.; Kim, M.W.; Jo, M.H.; Chung, J.I.; Kim, M.O. Anthocyanins Improve Hippocampus-Dependent Memory Function and Prevent Neurodegeneration via JNK/Akt/GSK3beta Signaling in LPS-Treated Adult Mice. Mol. Neurobiol. 2019, 56, 671–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carey, A.N.; Fisher, D.R.; Rimando, A.M.; Gomes, S.M.; Bielinski, D.F.; Shukitt-Hale, B. Stilbenes and anthocyanins reduce stress signaling in BV-2 mouse microglia. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2013, 61, 5979–5986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeong, J.W.; Lee, W.S.; Shin, S.C.; Kim, G.Y.; Choi, B.T.; Choi, Y.H. Anthocyanins downregulate lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammatory responses in BV2 microglial cells by suppressing the NF-kappaB and Akt/MAPKs signaling pathways. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2013, 14, 1502–1515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lau, F.C.; Bielinski, D.F.; Joseph, J.A. Inhibitory effects of blueberry extract on the production of inflammatory mediators in lipopolysaccharide-activated BV2 microglia. J. Neurosci. Res. 2007, 85, 1010–1017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lau, F.C.; Joseph, J.A.; McDonald, J.E.; Kalt, W. Attenuation of iNOS and COX2 by blueberry polyphenols is mediated through the suppression of NF-κB activation. J. Funct. Foods 2009, 1, 274–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poulose, S.M.; Fisher, D.R.; Larson, J.; Bielinski, D.F.; Rimando, A.M.; Carey, A.N.; Schauss, A.G.; Shukitt-Hale, B. Anthocyanin-rich acai (Euterpe oleracea Mart.) fruit pulp fractions attenuate inflammatory stress signaling in mouse brain BV-2 microglial cells. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2012, 60, 1084–1093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Chen, S.; Liu, T.; Wang, X.; Huang, H.; Liu, W. Callistephin enhances the protective effects of isoflurane on microglial injury through downregulation of inflammation and apoptosis. Mol. Med. Rep. 2019, 20, 802–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shukitt-Hale, B.; Kelly, M.E.; Bielinski, D.F.; Fisher, D.R. Tart Cherry Extracts Reduce Inflammatory and Oxidative Stress Signaling in Microglial Cells. Antioxidants (Basel) 2016, 5, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Bickford, P.C.; Sanberg, P.; Giunta, B.; Tan, J. Blueberry opposes beta-amyloid peptide-induced microglial activation via inhibition of p44/42 mitogen-activation protein kinase. Rejuvenation Res. 2008, 11, 891–901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Casedas, G.; Bennett, A.C.; Gonzalez-Burgos, E.; Gomez-Serranillos, M.P.; Lopez, V.; Smith, C. Polyphenol-associated oxidative stress and inflammation in a model of LPS-induced inflammation in glial cells: Do we know enough for responsible compounding? Inflammopharmacology 2019, 27, 189–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zheng, Y.; Lu, J.; Chen, G.; Wang, X.; Feng, J.; Ruan, J.; Sun, X.; Li, C.; Sun, Q. Purple sweet potato color suppresses lipopolysaccharide-induced acute inflammatory response in mouse brain. Neurochem. Int. 2010, 56, 424–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.S.; Ali, T.; Kim, M.W.; Jo, M.H.; Jo, M.G.; Badshah, H.; Kim, M.O. Anthocyanins protect against LPS-induced oxidative stress-mediated neuroinflammation and neurodegeneration in the adult mouse cortex. Neurochem. Int. 2016, 100, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carvalho, F.B.; Gutierres, J.M.; Bueno, A.; Agostinho, P.; Zago, A.M.; Vieira, J.; Fruhauf, P.; Cechella, J.L.; Nogueira, C.W.; Oliveira, S.M.; et al. Anthocyanins control neuroinflammation and consequent memory dysfunction in mice exposed to lipopolysaccharide. Mol. Neurobiol. 2017, 54, 3350–3367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Shi, Z.; Mi, Y. Purple sweet potato color attenuates high fat-induced neuroinflammation in mouse brain by inhibiting MAPK and NF-kappaB activation. Mol. Med. Rep. 2018, 17, 4823–4831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Z.; Cui, M.; Dai, G.; Yuan, T.; Li, Y.; Ji, T.; Pan, Y. Protective Effect of Anthocyanin on Neurovascular Unit in Cerebral Ischemia/Reperfusion Injury in Rats. Front. Neurosci. 2018, 12, 947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shukitt-Hale, B.; Lau, F.C.; Carey, A.N.; Galli, R.L.; Spangler, E.L.; Ingram, D.K.; Joseph, J.A. Blueberry polyphenols attenuate kainic acid-induced decrements in cognition and alter inflammatory gene expression in rat hippocampus. Nutr. Neurosci. 2008, 11, 172–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glenner, G.G.; Wong, C.W. Alzheimer’s disease and Down’s syndrome: Sharing of a unique cerebrovascular amyloid fibril protein. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1984, 122, 1131–1135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masters, C.L.; Simms, G.; Weinman, N.A.; Multhaup, G.; McDonald, B.L.; Beyreuther, K. Amyloid plaque core protein in Alzheimer disease and Down syndrome. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1985, 82, 4245–4249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Selkoe, D.J.; Abraham, C.R.; Podlisny, M.B.; Duffy, L.K. Isolation of low-molecular-weight proteins from amyloid plaque fibers in Alzheimer’s disease. J. Neurochem. 1986, 46, 1820–1834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bancher, C.; Brunner, C.; Lassmann, H.; Budka, H.; Jellinger, K.; Wiche, G.; Seitelberger, F.; Grundke-Iqbal, I.; Iqbal, K.; Wisniewski, H.M. Accumulation of abnormally phosphorylated tau precedes the formation of neurofibrillary tangles in Alzheimer’s disease. Brain Res. 1989, 477, 90–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baba, M.; Nakajo, S.; Tu, P.H.; Tomita, T.; Nakaya, K.; Lee, V.M.; Trojanowski, J.Q.; Iwatsubo, T. Aggregation of alpha-synuclein in Lewy bodies of sporadic Parkinson’s disease and dementia with Lewy bodies. Am. J. Pathol. 1998, 152, 879–884. [Google Scholar]
- Mori, K.; Weng, S.M.; Arzberger, T.; May, S.; Rentzsch, K.; Kremmer, E.; Schmid, B.; Kretzschmar, H.A.; Cruts, M.; Van Broeckhoven, C.; et al. The C9orf72 GGGGCC repeat is translated into aggregating dipeptide-repeat proteins in FTLD/ALS. Science 2013, 339, 1335–1338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vance, C.; Rogelj, B.; Hortobagyi, T.; De Vos, K.J.; Nishimura, A.L.; Sreedharan, J.; Hu, X.; Smith, B.; Ruddy, D.; Wright, P.; et al. Mutations in FUS, an RNA processing protein, cause familial amyotrophic lateral sclerosis type 6. Science 2009, 323, 1208–1211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ling, S.C.; Albuquerque, C.P.; Han, J.S.; Lagier-Tourenne, C.; Tokunaga, S.; Zhou, H.; Cleveland, D.W. ALS-associated mutations in TDP-43 increase its stability and promote TDP-43 complexes with FUS/TLS. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 13318–13323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruijn, L.I.; Houseweart, M.K.; Kato, S.; Anderson, K.L.; Anderson, S.D.; Ohama, E.; Reaume, A.G.; Scott, R.W.; Cleveland, D.W. Aggregation and motor neuron toxicity of an ALS-linked SOD1 mutant independent from wild-type SOD1. Science 1998, 281, 1851–1854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bosco, D.A.; Morfini, G.; Karabacak, N.M.; Song, Y.; Gros-Louis, F.; Pasinelli, P.; Goolsby, H.; Fontaine, B.A.; Lemay, N.; McKenna-Yasek, D.; et al. Wild-type and mutant SOD1 share an aberrant conformation and a common pathogenic pathway in ALS. Nat. Neurosci. 2010, 13, 1396–1403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnson, B.S.; Snead, D.; Lee, J.J.; McCaffery, J.M.; Shorter, J.; Gitler, A.D. TDP-43 is intrinsically aggregation-prone, and amyotrophic lateral sclerosis-linked mutations accelerate aggregation and increase toxicity. J. Biol. Chem. 2009, 284, 20329–20339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mackenzie, I.R.; Bigio, E.H.; Ince, P.G.; Geser, F.; Neumann, M.; Cairns, N.J.; Kwong, L.K.; Forman, M.S.; Ravits, J.; Stewart, H.; et al. Pathological TDP-43 distinguishes sporadic amyotrophic lateral sclerosis from amyotrophic lateral sclerosis with SOD1 mutations. Ann. Neurol. 2007, 61, 427–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tarozzi, A.; Morroni, F.; Merlicco, A.; Bolondi, C.; Teti, G.; Falconi, M.; Cantelli-Forti, G.; Hrelia, P. Neuroprotective effects of cyanidin 3-O-glucopyranoside on amyloid beta (25–35) oligomer-induced toxicity. Neurosci. Lett. 2010, 473, 72–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamakawa, M.Y.; Uchino, K.; Watanabe, Y.; Adachi, T.; Nakanishi, M.; Ichino, H.; Hongo, K.; Mizobata, T.; Kobayashi, S.; Nakashima, K.; et al. Anthocyanin suppresses the toxicity of Abeta deposits through diversion of molecular forms in in vitro and in vivo models of Alzheimer’s disease. Nutr. Neurosci. 2016, 19, 32–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Riviere, C.; Richard, T.; Vitrac, X.; Merillon, J.M.; Valls, J.; Monti, J.P. New polyphenols active on beta-amyloid aggregation. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2008, 18, 828–831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, N.; Zhang, L.; Chen, W.; Zhu, H.; Deng, W.; Han, Y.; Guo, J.; Qin, C. Cyanidin 3-O-beta-glucopyranoside activates peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-gamma and alleviates cognitive impairment in the APP(swe)/PS1(DeltaE9) mouse model. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2016, 1862, 1786–1800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thangthaeng, N.; Poulose, S.M.; Gomes, S.M.; Miller, M.G.; Bielinski, D.F.; Shukitt-Hale, B. Tart cherry supplementation improves working memory, hippocampal inflammation, and autophagy in aged rats. Age (Dordr) 2016, 38, 393–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, C.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, H.; Han, F. The role of endoplasmic reticulum stress in neurodegenerative disease. Apoptosis 2017, 22, 1–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thummayot, S.; Tocharus, C.; Suksamrarn, A.; Tocharus, J. Neuroprotective effects of cyanidin against Abeta-induced oxidative and ER stress in SK-N-SH cells. Neurochem. Int. 2016, 101, 15–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ooe, E.; Kuse, Y.; Yako, T.; Sogon, T.; Nakamura, S.; Hara, H.; Shimazawa, M. Bilberry extract and anthocyanins suppress unfolded protein response induced by exposure to blue LED light of cells in photoreceptor cell line. Mol. Vis. 2018, 24, 621–632. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lu, J.; Wu, D.M.; Zheng, Y.L.; Hu, B.; Cheng, W.; Zhang, Z.F. Purple sweet potato color attenuates domoic acid-induced cognitive deficits by promoting estrogen receptor-alpha-mediated mitochondrial biogenesis signaling in mice. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2012, 52, 646–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakamura, O.; Moritoh, S.; Sato, K.; Maekawa, S.; Murayama, N.; Himori, N.; Omodaka, K.; Sogon, T.; Nakazawa, T. Bilberry extract administration prevents retinal ganglion cell death in mice via the regulation of chaperone molecules under conditions of endoplasmic reticulum stress. Clin. Ophthalmol. 2017, 11, 1825–1834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reddivari, L.; Vanamala, J.; Chintharlapalli, S.; Safe, S.H.; Miller, J.C., Jr. Anthocyanin fraction from potato extracts is cytotoxic to prostate cancer cells through activation of caspase-dependent and caspase-independent pathways. Carcinogenesis 2007, 28, 2227–2235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, J.; Wu, D.M.; Zheng, Y.L.; Hu, B.; Zhang, Z.F. Purple sweet potato color alleviates d-galactose-induced brain aging in old mice by promoting survival of neurons via PI3K pathway and inhibiting cytochrome C-mediated apoptosis. Brain Pathol. 2010, 20, 598–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shin, W.H.; Park, S.J.; Kim, E.J. Protective effect of anthocyanins in middle cerebral artery occlusion and reperfusion model of cerebral ischemia in rats. Life Sci. 2006, 79, 130–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Chang, C.F.; Chou, J.; Chen, H.L.; Deng, X.; Harvey, B.K.; Cadet, J.L.; Bickford, P.C. Dietary supplementation with blueberries, spinach, or spirulina reduces ischemic brain damage. Exp. Neurol. 2005, 193, 75–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, H.G.; Ju, M.S.; Shim, J.S.; Kim, M.C.; Lee, S.H.; Huh, Y.; Kim, S.Y.; Oh, M.S. Mulberry fruit protects dopaminergic neurons in toxin-induced Parkinson’s disease models. Br. J. Nutr. 2010, 104, 8–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.; Sun, J.; Jiang, J.; Zhou, J. Cyanidin Protects SH-SY5Y Human Neuroblastoma Cells from 1-Methyl-4-Phenylpyridinium-Induced Neurotoxicity. Pharmacology 2018, 102, 126–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nicklas, W.J.; Vyas, I.; Heikkila, R.E. Inhibition of NADH-linked oxidation in brain mitochondria by 1-methyl-4-phenyl-pyridine, a metabolite of the neurotoxin, 1-methyl-4-phenyl-1,2,5,6-tetrahydropyridine. Life Sci. 1985, 36, 2503–2508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Min, J.; Yu, S.W.; Baek, S.H.; Nair, K.M.; Bae, O.N.; Bhatt, A.; Kassab, M.; Nair, M.G.; Majid, A. Neuroprotective effect of cyanidin-3-O-glucoside anthocyanin in mice with focal cerebral ischemia. Neurosci. Lett. 2011, 500, 157–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gu, P.S.; Moon, M.; Choi, J.G.; Oh, M.S. Mulberry fruit ameliorates Parkinson’s-disease-related pathology by reducing alpha-synuclein and ubiquitin levels in a 1-methyl-4-phenyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridine/probenecid model. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2017, 39, 15–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simola, N.; Morelli, M.; Carta, A.R. The 6-hydroxydopamine model of Parkinson’s disease. Neurotox Res. 2007, 11, 151–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roghani, M.; Niknam, A.; Jalali-Nadoushan, M.R.; Kiasalari, Z.; Khalili, M.; Baluchnejadmojarad, T. Oral pelargonidin exerts dose-dependent neuroprotection in 6-hydroxydopamine rat model of hemi-parkinsonism. Brain Res. Bull. 2010, 82, 279–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stromberg, I.; Gemma, C.; Vila, J.; Bickford, P.C. Blueberry- and spirulina-enriched diets enhance striatal dopamine recovery and induce a rapid, transient microglia activation after injury of the rat nigrostriatal dopamine system. Exp. Neurol. 2005, 196, 298–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Fu, X.T.; Li, D.W.; Wang, K.; Wang, X.Z.; Li, Y.; Sun, B.L.; Yang, X.Y.; Zheng, Z.C.; Cho, N.C. Cyanidin suppresses amyloid beta-induced neurotoxicity by inhibiting reactive oxygen species-mediated DNA damage and apoptosis in PC12 cells. Neural. Regen. Res. 2016, 11, 795–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amin, F.U.; Shah, S.A.; Badshah, H.; Khan, M.; Kim, M.O. Anthocyanins encapsulated by PLGA@PEG nanoparticles potentially improved its free radical scavenging capabilities via p38/JNK pathway against Abeta1-42-induced oxidative stress. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2017, 15, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ali, T.; Kim, T.; Rehman, S.U.; Khan, M.S.; Amin, F.U.; Khan, M.; Ikram, M.; Kim, M.O. Natural Dietary Supplementation of Anthocyanins via PI3K/Akt/Nrf2/HO-1 Pathways Mitigate Oxidative Stress, Neurodegeneration, and Memory Impairment in a Mouse Model of Alzheimer’s Disease. Mol. Neurobiol. 2018, 55, 6076–6093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, M.O. Composition for treating or preventing neurodegenerative brain diseases comprising black bean extract. 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, M.J.; Rehman, S.U.; Amin, F.U.; Kim, M.O. Enhanced neuroprotection of anthocyanin-loaded PEG-gold nanoparticles against Abeta1-42-induced neuroinflammation and neurodegeneration via the NF-KB /JNK/GSK3beta signaling pathway. Nanomedicine 2017, 13, 2533–2544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vepsalainen, S.; Koivisto, H.; Pekkarinen, E.; Makinen, P.; Dobson, G.; McDougall, G.J.; Stewart, D.; Haapasalo, A.; Karjalainen, R.O.; Tanila, H.; et al. Anthocyanin-enriched bilberry and blackcurrant extracts modulate amyloid precursor protein processing and alleviate behavioral abnormalities in the APP/PS1 mouse model of Alzheimer’s disease. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2013, 24, 360–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Essa, M.M.; Subash, S.; Akbar, M.; Al-Adawi, S.; Guillemin, G.J. Long-term dietary supplementation of pomegranates, figs and dates alleviate neuroinflammation in a transgenic mouse model of Alzheimer’s disease. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0120964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qin, L.; Zhang, J.; Qin, M. Protective effect of cyanidin 3-O-glucoside on beta-amyloid peptide-induced cognitive impairment in rats. Neurosci. Lett. 2013, 534, 285–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ali, T.; Kim, M.J.; Rehman, S.U.; Ahmad, A.; Kim, M.O. Anthocyanin-Loaded PEG-Gold Nanoparticles Enhanced the Neuroprotection of Anthocyanins in an Abeta1-42 Mouse Model of Alzheimer’s Disease. Mol. Neurobiol. 2017, 54, 6490–6506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, X.L.; Li, X.X.; Jia, S.L.; Gao, Z.L.; Lu, Z.; Dai, X.L.; Sun, Y.X. Memory Enhancing and Antioxidant Activities of Lycium ruthenicum Murray Anthocyanin Extracts in an Aβ42-Induced Rat Model of Dementia. Mod. Food Sci. Technol. 2017, 33, 29–34. [Google Scholar]
- Shih, P.H.; Chan, Y.C.; Liao, J.W.; Wang, M.F.; Yen, G.C. Antioxidant and cognitive promotion effects of anthocyanin-rich mulberry (Morus atropurpurea L.) on senescence-accelerated mice and prevention of Alzheimer’s disease. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2010, 21, 598–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gutierres, J.M.; Carvalho, F.B.; Schetinger, M.R.; Marisco, P.; Agostinho, P.; Rodrigues, M.; Rubin, M.A.; Schmatz, R.; da Silva, C.R.; de, P.C.G.; et al. Anthocyanins restore behavioral and biochemical changes caused by streptozotocin-induced sporadic dementia of Alzheimer’s type. Life Sci. 2014, 96, 7–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pacheco, S.M.; Soares, M.S.P.; Gutierres, J.M.; Gerzson, M.F.B.; Carvalho, F.B.; Azambuja, J.H.; Schetinger, M.R.C.; Stefanello, F.M.; Spanevello, R.M. Anthocyanins as a potential pharmacological agent to manage memory deficit, oxidative stress and alterations in ion pump activity induced by experimental sporadic dementia of Alzheimer’s type. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2018, 56, 193–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krikorian, R.; Boespflug, E.L.; Fleck, D.E.; Stein, A.L.; Wightman, J.D.; Shidler, M.D.; Sadat-Hossieny, S. Concord grape juice supplementation and neurocognitive function in human aging. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2012, 60, 5736–5742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krikorian, R.; Nash, T.A.; Shidler, M.D.; Shukitt-Hale, B.; Joseph, J.A. Concord grape juice supplementation improves memory function in older adults with mild cognitive impairment. Br. J. Nutr. 2010, 103, 730–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krikorian, R.; Shidler, M.D.; Nash, T.A.; Kalt, W.; Vinqvist-Tymchuk, M.R.; Shukitt-Hale, B.; Joseph, J.A. Blueberry supplementation improves memory in older adults. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2010, 58, 3996–4000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kent, K.; Charlton, K.; Roodenrys, S.; Batterham, M.; Potter, J.; Traynor, V.; Gilbert, H.; Morgan, O.; Richards, R. Consumption of anthocyanin-rich cherry juice for 12 weeks improves memory and cognition in older adults with mild-to-moderate dementia. Eur. J. Nutr. 2017, 56, 333–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Winter, A.N.; Ross, E.K.; Wilkins, H.M.; Stankiewicz, T.R.; Wallace, T.; Miller, K.; Linseman, D.A. An anthocyanin-enriched extract from strawberries delays disease onset and extends survival in the hSOD1(G93A) mouse model of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Nutr. Neurosci. 2018, 21, 414–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, D.M.; Lu, J.; Zheng, Y.L.; Zhou, Z.; Shan, Q.; Ma, D.F. Purple sweet potato color repairs d-galactose-induced spatial learning and memory impairment by regulating the expression of synaptic proteins. Neurobiol. Learn Mem. 2008, 90, 19–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shan, Q.; Lu, J.; Zheng, Y.; Li, J.; Zhou, Z.; Hu, B.; Zhang, Z.; Fan, S.; Mao, Z.; Wang, Y.J.; et al. Purple sweet potato color ameliorates cognition deficits and attenuates oxidative damage and inflammation in aging mouse brain induced by d-galactose. J. Biomed. Biotechnol. 2009, 2009, 564737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, X.; Zhou, Y.; Wu, T.; Hao, L. Ameliorative effect of black rice anthocyanin on senescent mice induced by d-galactose. Food Funct. 2014, 5, 2892–2897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coban, J.; Dogan-Ekici, I.; Aydin, A.F.; Betul-Kalaz, E.; Dogru-Abbasoglu, S.; Uysal, M. Blueberry treatment decreased d-galactose-induced oxidative stress and brain damage in rats. Metab. Brain Dis. 2015, 30, 793–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rehman, S.U.; Shah, S.A.; Ali, T.; Chung, J.I.; Kim, M.O. Anthocyanins Reversed d-Galactose-Induced Oxidative Stress and Neuroinflammation Mediated Cognitive Impairment in Adult Rats. Mol. Neurobiol. 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, J.; Zhang, G.; Zhang, X.; Xu, D.; Gao, J.; Fan, J.; Zhou, Z. Anthocyanins from Black Chokeberry (Aronia melanocarpa Elliot) Delayed Aging-Related Degenerative Changes of Brain. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2017, 65, 5973–5984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, S.; Zhou, H.; Zhang, G.; Meng, J.; Deng, K.; Zhou, W.; Wang, H.; Wang, Z.; Hu, N.; Suo, Y. Anthocyanins from Lycium ruthenicum Murr. Ameliorated d-Galactose-Induced Memory Impairment, Oxidative Stress, and Neuroinflammation in Adult Rats. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2019, 67, 3140–3149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harris, C.S.; Cuerrier, A.; Lamont, E.; Haddad, P.S.; Arnason, J.T.; Bennett, S.A.; Johns, T. Investigating wild berries as a dietary approach to reducing the formation of advanced glycation endproducts: Chemical correlates of in vitro antiglycation activity. Plant Foods Hum. Nutr. 2014, 69, 71–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beracochea, D.; Krazem, A.; Henkouss, N.; Haccard, G.; Roller, M.; Fromentin, E. Intake of Wild Blueberry Powder Improves Episodic-Like and Working Memory during Normal Aging in Mice. Planta Med. 2016, 82, 1163–1168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carey, A.N.; Miller, M.G.; Fisher, D.R.; Bielinski, D.F.; Gilman, C.K.; Poulose, S.M.; Shukitt-Hale, B. Dietary supplementation with the polyphenol-rich acai pulps (Euterpe oleracea Mart. and Euterpe precatoria Mart.) improves cognition in aged rats and attenuates inflammatory signaling in BV-2 microglial cells. Nutr. Neurosci. 2017, 20, 238–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malin, D.H.; Lee, D.R.; Goyarzu, P.; Chang, Y.H.; Ennis, L.J.; Beckett, E.; Shukitt-Hale, B.; Joseph, J.A. Short-term blueberry-enriched diet prevents and reverses object recognition memory loss in aging rats. Nutrition 2011, 27, 338–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rendeiro, C.; Vauzour, D.; Rattray, M.; Waffo-Teguo, P.; Merillon, J.M.; Butler, L.T.; Williams, C.M.; Spencer, J.P. Dietary levels of pure flavonoids improve spatial memory performance and increase hippocampal brain-derived neurotrophic factor. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e63535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shukitt-Hale, B.; Bielinski, D.F.; Lau, F.C.; Willis, L.M.; Carey, A.N.; Joseph, J.A. The beneficial effects of berries on cognition, motor behaviour and neuronal function in ageing. Br. J. Nutr. 2015, 114, 1542–1549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shukitt-Hale, B.; Carey, A.; Simon, L.; Mark, D.A.; Joseph, J.A. Effects of Concord grape juice on cognitive and motor deficits in aging. Nutrition 2006, 22, 295–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shukitt-Hale, B.; Cheng, V.; Joseph, J.A. Effects of blackberries on motor and cognitive function in aged rats. Nutr. Neurosci. 2009, 12, 135–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Youdim, K.A.; Shukitt-Hale, B.; Martin, A.; Wang, H.; Denisova, D.; Bickford, P.C.; Joseph, J.A. Short-Term Dietary Supplementation of Blueberry Polyphenolics: Beneficial Effects on Aging Brain Performance and Peripheral Tissue Function. Nutr. Neurosci. 2000, 3, 383–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joseph, J.A.; Shukitt-Hale, B.; Denisova, N.A.; Bielinski, D.; Martin, A.; McEwen, J.J.; Bickford, P.C. Reversals of age-related declines in neuronal signal transduction, cognitive, and motor behavioral deficits with blueberry, spinach, or strawberry dietary supplementation. J. Neurosci. 1999, 19, 8114–8121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coultrap, S.J.; Bickford, P.C.; Browning, M.D. Blueberry-enriched diet ameliorates age-related declines in NMDA receptor-dependent LTP. Age (Dordr) 2008, 30, 263–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Bowtell, J.L.; Aboo-Bakkar, Z.; Conway, M.E.; Adlam, A.R.; Fulford, J. Enhanced task-related brain activation and resting perfusion in healthy older adults after chronic blueberry supplementation. Appl. Physiol. Nutr. Metab. 2017, 42, 773–779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miller, M.G.; Hamilton, D.A.; Joseph, J.A.; Shukitt-Hale, B. Dietary blueberry improves cognition among older adults in a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Eur. J. Nutr. 2018, 57, 1169–1180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Whyte, A.R.; Cheng, N.; Fromentin, E.; Williams, C.M. A Randomized, Double-Blinded, Placebo-Controlled Study to Compare the Safety and Efficacy of Low Dose Enhanced Wild Blueberry Powder and Wild Blueberry Extract (ThinkBlue) in Maintenance of Episodic and Working Memory in Older Adults. Nutrients 2018, 10, 660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Del Rio, D.; Borges, G.; Crozier, A. Berry flavonoids and phenolics: Bioavailability and evidence of protective effects. Br. J. Nutr. 2010, 104 (Suppl. 3), S67–S90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Woodward, G.; Kroon, P.; Cassidy, A.; Kay, C. Anthocyanin stability and recovery: Implications for the analysis of clinical and experimental samples. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2009, 57, 5271–5278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fleschhut, J.; Kratzer, F.; Rechkemmer, G.; Kulling, S.E. Stability and biotransformation of various dietary anthocyanins in vitro. Eur. J. Nutr. 2006, 45, 7–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Forester, S.C.; Waterhouse, A.L. Gut metabolites of anthocyanins, gallic acid, 3-O-methylgallic acid, and 2,4,6-trihydroxybenzaldehyde, inhibit cell proliferation of Caco-2 cells. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2010, 58, 5320–5327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gonthier, M.P.; Cheynier, V.; Donovan, J.L.; Manach, C.; Morand, C.; Mila, I.; Lapierre, C.; Remesy, C.; Scalbert, A. Microbial aromatic acid metabolites formed in the gut account for a major fraction of the polyphenols excreted in urine of rats fed red wine polyphenols. J. Nutr. 2003, 133, 461–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manach, C.; Williamson, G.; Morand, C.; Scalbert, A.; Remesy, C. Bioavailability and bioefficacy of polyphenols in humans. I. Review of 97 bioavailability studies. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2005, 81, 230S–242S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Day, A.J.; Canada, F.J.; Diaz, J.C.; Kroon, P.A.; McLauchlan, R.; Faulds, C.B.; Plumb, G.W.; Morgan, M.R.; Williamson, G. Dietary flavonoid and isoflavone glycosides are hydrolysed by the lactase site of lactase phlorizin hydrolase. FEBS Lett. 2000, 468, 166–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gee, J.M.; DuPont, M.S.; Day, A.J.; Plumb, G.W.; Williamson, G.; Johnson, I.T. Intestinal transport of quercetin glycosides in rats involves both deglycosylation and interaction with the hexose transport pathway. J. Nutr. 2000, 130, 2765–2771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Woodward, G.M.; Needs, P.W.; Kay, C.D. Anthocyanin-derived phenolic acids form glucuronides following simulated gastrointestinal digestion and microsomal glucuronidation. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2011, 55, 378–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsuda, T.; Horio, F.; Osawa, T. Absorption and metabolism of cyanidin 3-O-beta-d-glucoside in rats. FEBS Lett. 1999, 449, 179–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.J.; Wu, L.; Zhang, Q.L.; Li, J.; Yin, F.X.; Yuan, Y. Pharmacokinetics of phenolic compounds of Danshen extract in rat blood and brain by microdialysis sampling. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2011, 136, 129–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferruzzi, M.G.; Lobo, J.K.; Janle, E.M.; Cooper, B.; Simon, J.E.; Wu, Q.L.; Welch, C.; Ho, L.; Weaver, C.; Pasinetti, G.M. Bioavailability of gallic acid and catechins from grape seed polyphenol extract is improved by repeated dosing in rats: Implications for treatment in Alzheimer’s disease. J. Alzheimers. Dis. 2009, 18, 113–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Winter, A.N.; Brenner, M.C.; Punessen, N.; Snodgrass, M.; Byars, C.; Arora, Y.; Linseman, D.A. Comparison of the Neuroprotective and Anti-Inflammatory Effects of the Anthocyanin Metabolites, Protocatechuic Acid and 4-Hydroxybenzoic Acid. Oxid. Med. Cell Longev. 2017, 2017, 6297080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, L.J.; Guan, S.; Shi, G.F.; Bao, Y.M.; Duan, Y.L.; Jiang, B. Protocatechuic acid from Alpinia oxyphylla against MPP+-induced neurotoxicity in PC12 cells. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2006, 44, 436–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, S.; Bao, Y.M.; Bo, J.; An, L.J. Protective effect of protocatechuic acid from Alpinia oxyphylla on hydrogen peroxide-induced oxidative PC12 cell death. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2006, 538, 73–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, G.F.; An, L.J.; Jiang, B.; Guan, S.; Bao, Y.M. Alpinia protocatechuic acid protects against oxidative damage in vitro and reduces oxidative stress in vivo. Neurosci. Lett. 2006, 403, 206–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.L.; Lin, C.C.; Jeng, K.C.; Yao, P.W.; Chuang, L.T.; Kuo, S.L.; Hou, C.W. Fresh green tea and gallic acid ameliorate oxidative stress in kainic acid-induced status epilepticus. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2012, 60, 2328–2336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maya, S.; Prakash, T.; Madhu, K. Assessment of neuroprotective effects of Gallic acid against glutamate-induced neurotoxicity in primary rat cortex neuronal culture. Neurochem. Int. 2018, 121, 50–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nuzzo, D.; Presti, G.; Picone, P.; Galizzi, G.; Gulotta, E.; Giuliano, S.; Mannino, C.; Gambino, V.; Scoglio, S.; Di Carlo, M. Effects of the Aphanizomenon flos-aquae Extract (Klamin(R)) on a Neurodegeneration Cellular Model. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2018, 2018, 9089016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gay, N.H.; Phopin, K.; Suwanjang, W.; Songtawee, N.; Ruankham, W.; Wongchitrat, P.; Prachayasittikul, S.; Prachayasittikul, V. Neuroprotective Effects of Phenolic and Carboxylic Acids on Oxidative Stress-Induced Toxicity in Human Neuroblastoma SH-SY5Y Cells. Neurochem. Res. 2018, 43, 619–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ben Othman, S.; Katsuno, N.; Kitayama, A.; Fujimura, M.; Kitaguchi, K.; Yabe, T. Water-soluble fractions from defatted sesame seeds protect human neuroblast cells against peroxyl radicals and hydrogen peroxide-induced oxidative stress. Free Radic. Res. 2016, 50, 949–958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ben Othman, S.; Katsuno, N.; Kitayama, A.; Fujimura, M.; Kitaguchi, K.; Yabe, T. White sesame seed water-soluble fraction enhances human neuroblast cell viability via an anti-apoptotic mechanism. Nutr. Res. 2016, 36, 1130–1139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schulz, M.; Gonzaga, L.V.; de Souza, V.; Farina, M.; Vitali, L.; Micke, G.A.; Costa, A.C.O.; Fett, R. Neuroprotective effect of jucara (Euterpe edulis Martius) fruits extracts against glutamate-induced oxytosis in HT22 hippocampal cells. Food Res. Int. 2019, 120, 114–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, M.; Du, Z.; Lu, G.; Li, P.; Wang, L. Syringic acid protects retinal ganglion cells against H2O2-induced apoptosis through the activation of PI3K/Akt signaling pathway. Cell Mol. Biol. (Noisy-le-grand) 2016, 62, 50–54. [Google Scholar]
- Cao, Y.; Zhang, L.; Sun, S.; Yi, Z.; Jiang, X.; Jia, D. Neuroprotective effects of syringic acid against OGD/R-induced injury in cultured hippocampal neuronal cells. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2016, 38, 567–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, S.; Jiang, B.; Bao, Y.M.; An, L.J. Protocatechuic acid suppresses MPP+-induced mitochondrial dysfunction and apoptotic cell death in PC12 cells. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2006, 44, 1659–1666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.N.; An, C.N.; Xu, M.; Guo, D.A.; Li, M.; Pu, X.P. Protocatechuic acid inhibits rat pheochromocytoma cell damage induced by a dopaminergic neurotoxin. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2009, 32, 1866–1869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.M.; Jiang, B.; Bao, Y.M.; An, L.J. Protocatechuic acid inhibits apoptosis by mitochondrial dysfunction in rotenone-induced PC12 cells. Toxicol. In Vitro 2008, 22, 430–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.; Li, G.; Szeto, S.S.W.; Chong, C.M.; Quan, Q.; Huang, C.; Cui, W.; Guo, B.; Wang, Y.; Han, Y.; et al. Examining the neuroprotective effects of protocatechuic acid and chrysin on in vitro and in vivo models of Parkinson disease. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2015, 84, 331–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, Z.; Nie, G.; Belton, P.S.; Tang, H.; Zhao, B. Structure-activity relationship analysis of antioxidant ability and neuroprotective effect of gallic acid derivatives. Neurochem. Int. 2006, 48, 263–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chandrasekhar, Y.; Phani Kumar, G.; Ramya, E.M.; Anilakumar, K.R. Gallic Acid Protects 6-OHDA Induced Neurotoxicity by Attenuating Oxidative Stress in Human Dopaminergic Cell Line. Neurochem. Res. 2018, 43, 1150–1160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ban, J.Y.; Cho, S.O.; Jeon, S.Y.; Bae, K.; Song, K.S.; Seong, Y.H. 3,4-dihydroxybenzoic acid from Smilacis chinae rhizome protects amyloid beta protein (25–35)-induced neurotoxicity in cultured rat cortical neurons. Neurosci. Lett. 2007, 420, 184–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, M.; Chen, X.; Liu, J.; Ma, Q.; Zhuo, Z.; Chen, H.; Zhou, L.; Yang, S.; Zheng, L.; Ning, C.; et al. Gallic acid disruption of Abeta1-42 aggregation rescues cognitive decline of APP/PS1 double transgenic mouse. Neurobiol. Dis. 2019, 124, 67–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bastianetto, S.; Yao, Z.X.; Papadopoulos, V.; Quirion, R. Neuroprotective effects of green and black teas and their catechin gallate esters against beta-amyloid-induced toxicity. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2006, 23, 55–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amin, F.U.; Shah, S.A.; Kim, M.O. Vanillic acid attenuates Abeta1-42-induced oxidative stress and cognitive impairment in mice. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 40753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.J.; Seong, A.R.; Yoo, J.Y.; Jin, C.H.; Lee, Y.H.; Kim, Y.J.; Lee, J.; Jun, W.J.; Yoon, H.G. Gallic acid, a histone acetyltransferase inhibitor, suppresses beta-amyloid neurotoxicity by inhibiting microglial-mediated neuroinflammation. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2011, 55, 1798–1808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.Y.; Wang, H.; Wang, J.H.; Wang, Q.; Ma, Q.F.; Chen, Y.Y. Protocatechuic Acid Inhibits Inflammatory Responses in LPS-Stimulated BV2 Microglia via NF-kappaB and MAPKs Signaling Pathways. Neurochem. Res. 2015, 40, 1655–1660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siddiqui, S.; Kamal, A.; Khan, F.; Jamali, K.S.; Saify, Z.S. Gallic and vanillic acid suppress inflammation and promote myelination in an in vitro mouse model of neurodegeneration. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2019, 46, 997–1011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hornedo-Ortega, R.; Alvarez-Fernandez, M.A.; Cerezo, A.B.; Richard, T.; Troncoso, A.M.A.; Garcia-Parrilla, M.A.C. Protocatechuic Acid: Inhibition of Fibril Formation, Destabilization of Preformed Fibrils of Amyloid-beta and alpha-Synuclein, and Neuroprotection. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2016, 64, 7722–7732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weinberg, R.P.; Rha, C.; ASinskey, A.J.; Tan, Y.A.; Sambanthamurthi, R. Protective effects of oil palm composition on Alzheimer’s disease. U.S. Patent Application No. 15/028,265, 1 September 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Panzella, L.; Eidenberger, T.; Napolitano, A. Anti-Amyloid Aggregation Activity of Black Sesame Pigment: Toward a Novel Alzheimer’s Disease Preventive Agent. Molecules 2018, 23, 676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Carver, J.A.; Calabrese, A.N.; Pukala, T.L. Gallic acid interacts with alpha-synuclein to prevent the structural collapse necessary for its aggregation. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2014, 1844, 1481–1485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, A.N.; Hassan, M.N.; Khan, R.H. Gallic acid: A naturally occurring bifunctional inhibitor of amyloid and metal induced aggregation with possible implication in metal-based therapy. J. Mol. Liq. 2019, 285, 27–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adefegha, S.A.; Oboh, G.; Omojokun, O.S.; Adefegha, O.M. Alterations of Na(+)/K(+)-ATPase, cholinergic and antioxidant enzymes activity by protocatechuic acid in cadmium-induced neurotoxicity and oxidative stress in Wistar rats. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2016, 83, 559–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kangtao, Y.; Bais, S. Neuroprotective Effect of Protocatechuic Acid Through MAO-B Inhibition in Aluminium Chloride Induced Dementia of Alzheimer’s Type in Rats. Int. J. Pharmacol. 2018, 14, 879–888. [Google Scholar]
- Maya, S.; Prakash, T.; Goli, D. Evaluation of neuroprotective effects of wedelolactone and gallic acid on aluminium-induced neurodegeneration: Relevance to sporadic amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2018, 835, 41–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maya, S.; Prakash, T.; Goli, D. Effect of wedelolactone and gallic acid on quinolinic acid-induced neurotoxicity and impaired motor function: Significance to sporadic amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Neurotoxicology 2018, 68, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kho, A.R.; Choi, B.Y.; Lee, S.H.; Hong, D.K.; Lee, S.H.; Jeong, J.H.; Park, K.H.; Song, H.K.; Choi, H.C.; Suh, S.W. Effects of Protocatechuic Acid (PCA) on Global Cerebral Ischemia-Induced Hippocampal Neuronal Death. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 1420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khoshnam, S.E.; Farbood, Y.; Fathi Moghaddam, H.; Sarkaki, A.; Badavi, M.; Khorsandi, L. Vanillic acid attenuates cerebral hyperemia, blood-brain barrier disruption and anxiety-like behaviors in rats following transient bilateral common carotid occlusion and reperfusion. Metab. Brain Dis. 2018, 33, 785–793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khoshnam, S.E.; Sarkaki, A.; Khorsandi, L.; Winlow, W.; Badavi, M.; Moghaddam, H.F.; Farbood, Y. Vanillic acid attenuates effects of transient bilateral common carotid occlusion and reperfusion in rats. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2017, 96, 667–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khoshnam, S.E.; Sarkaki, A.; Rashno, M.; Farbood, Y. Memory deficits and hippocampal inflammation in cerebral hypoperfusion and reperfusion in male rats: Neuroprotective role of vanillic acid. Life Sci. 2018, 211, 126–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Guo, Y.; Zhang, S.Y. Vanillic Acid Improve Neural Function after Focal Cerebral Ischemia-reperfusion Rats. Int. J. Pharmacol. 2018, 14, 488–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guven, M.; Aras, A.B.; Topaloglu, N.; Ozkan, A.; Sen, H.M.; Kalkan, Y.; Okuyucu, A.; Akbal, A.; Gokmen, F.; Cosar, M. The protective effect of syringic acid on ischemia injury in rat brain. Turk. J. Med. Sci. 2015, 45, 233–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.N.; An, C.N.; Zhang, H.N.; Pu, X.P. Protocatechuic acid inhibits neurotoxicity induced by MPTP in vivo. Neurosci. Lett. 2010, 474, 99–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, H.C.; Liu, K.F.; Teng, C.J.; Lai, S.C.; Yang, S.E.; Ching, H.; Wu, C.R. Sophora Tomentosa Extract Prevents MPTP-Induced Parkinsonism in C57BL/6 Mice Via the Inhibition of GSK-3beta Phosphorylation and Oxidative Stress. Nutrients 2019, 11, 252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rekha, K.R.; Selvakumar, G.P.; Sivakamasundari, R.I. Effects of syringic acid on chronic MPTP/probenecid induced motor dysfunction, dopaminergic markers expression and neuroinflammation in C57BL/6 mice. Biomed. Aging Pathol. 2014, 4, 95–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mansouri, M.T.; Farbood, Y.; Sameri, M.J.; Sarkaki, A.; Naghizadeh, B.; Rafeirad, M. Neuroprotective effects of oral gallic acid against oxidative stress induced by 6-hydroxydopamine in rats. Food Chem. 2013, 138, 1028–1033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; Cui, T.; Xie, N.; Zhang, X.; Qian, Z.; Liu, J. Protocatechuic acid improves cognitive deficits and attenuates amyloid deposits, inflammatory response in aged AbetaPP/PS1 double transgenic mice. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2014, 20, 276–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Subash, S.; Essa, M.M.; Al-Asmi, A.; Al-Adawi, S.; Vaishnav, R.; Guillemin, G.J. Effect of dietary supplementation of dates in Alzheimer’s disease APPsw/2576 transgenic mice on oxidative stress and antioxidant status. Nutr. Neurosci. 2015, 18, 281–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Subash, S.; Essa, M.M.; Braidy, N.; Awlad-Thani, K.; Vaishnav, R.; Al-Adawi, S.; Al-Asmi, A.; Guillemin, G.J. Diet rich in date palm fruits improves memory, learning and reduces beta amyloid in transgenic mouse model of Alzheimer’s disease. J. Ayurveda. Integr. Med. 2015, 6, 111–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hajipour, S.; Sarkaki, A.; Farbood, Y.; Eidi, A.; Mortazavi, P.; Valizadeh, Z. Effect of Gallic Acid on Dementia Type of Alzheimer Disease in Rats: Electrophysiological and Histological Studies. Basic Clin. Neurosci. 2016, 7, 97–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naghizadeh, B.; Mansouri, M.T. Protective Effects of Gallic Acid against Streptozotocin-induced Oxidative Damage in Rat Striatum. Drug Res. (Stuttg) 2015, 65, 515–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, J.C.; Kakalij, R.M.; Kshirsagar, R.P.; Kumar, B.H.; Komakula, S.S.; Diwan, P.V. Cognitive effects of vanillic acid against streptozotocin-induced neurodegeneration in mice. Pharm. Biol. 2015, 53, 630–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsai, S.J.; Yin, M.C. Anti-glycative and anti-inflammatory effects of protocatechuic acid in brain of mice treated by d-galactose. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2012, 50, 3198–3205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turgut, N.H.; Mert, D.G.; Kara, H.; Egilmez, H.R.; Arslanbas, E.; Tepe, B.; Gungor, H.; Yilmaz, N.; Tuncel, N.B. Effect of black mulberry (Morus nigra) extract treatment on cognitive impairment and oxidative stress status of d-galactose-induced aging mice. Pharm. Biol. 2016, 54, 1052–1064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zha, J.; Koffas, M.A.G. Production of anthocyanins in metabolically engineered microorganisms: Current status and perspectives. Synth. Syst. Biotechnol. 2017, 2, 259–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, J.E.; Kelly, M.F. Inhibition of lipid peroxidation by anthocyanins, anthocyanidins and their phenolic degradation products. Eur. J. Lipid Sci. Tech. 2007, 106, 66–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faria, A.; Meireles, M.; Fernandes, I.; Santos-Buelga, C.; Gonzalez-Manzano, S.; Duenas, M.; de Freitas, V.; Mateus, N.; Calhau, C. Flavonoid metabolites transport across a human BBB model. Food Chem. 2014, 149, 190–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anand, P.; Singh, B. A review on cholinesterase inhibitors for Alzheimer’s disease. Arch. Pharm. Res. 2013, 36, 375–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dezsi, L.; Vecsei, L. Monoamine Oxidase B Inhibitors in Parkinson’s Disease. CNS Neurol. Disord. Drug Targets 2017, 16, 425–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutierres, J.M.; Carvalho, F.B.; Schetinger, M.R.; Agostinho, P.; Marisco, P.C.; Vieira, J.M.; Rosa, M.M.; Bohnert, C.; Rubin, M.A.; Morsch, V.M.; et al. Neuroprotective effect of anthocyanins on acetylcholinesterase activity and attenuation of scopolamine-induced amnesia in rats. Int. J. Dev. Neurosci. 2014, 33, 88–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maeda-Yamamoto, M.; Saito, T.; Nesumi, A.; Tokuda, Y.; Ema, K.; Honma, D.; Ogino, A.; Monobe, M.; Murakami, A.; Murakami, A.; et al. Chemical analysis and acetylcholinesterase inhibitory effect of anthocyanin-rich red leaf tea (cv. Sunrouge). J. Sci. Food Agric. 2012, 92, 2379–2386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Papandreou, M.A.; Dimakopoulou, A.; Linardaki, Z.I.; Cordopatis, P.; Klimis-Zacas, D.; Margarity, M.; Lamari, F.N. Effect of a polyphenol-rich wild blueberry extract on cognitive performance of mice, brain antioxidant markers and acetylcholinesterase activity. Behav. Brain Res. 2009, 198, 352–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pervin, M.; Hasnat, M.A.; Lee, Y.M.; Kim, D.H.; Jo, J.E.; Lim, B.O. Antioxidant activity and acetylcholinesterase inhibition of grape skin anthocyanin (GSA). Molecules 2014, 19, 9403–9418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adedara, I.A.; Fasina, O.B.; Ayeni, M.F.; Ajayi, O.M.; Farombi, E.O. Protocatechuic acid ameliorates neurobehavioral deficits via suppression of oxidative damage, inflammation, caspase-3 and acetylcholinesterase activities in diabetic rats. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2019, 125, 170–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kobus-Cisowska, J.; Szymanowska, D.; Maciejewska, P.; Kmiecik, D.; Gramza-Michałowska, A.; Kulczyński, B.; Cielecka-Piontek, J. In vitro screening for acetylcholinesterase and butyrylcholinesterase inhibition and antimicrobial activity of chia seeds (Salvia hispanica). Electron. J. Biotech. 2019, 37, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neagu, E.; Radu, G.L.; Albu, C.; Paun, G. Antioxidant activity, acetylcholinesterase and tyrosinase inhibitory potential of Pulmonaria officinalis and Centarium umbellatum extracts. Saudi J. Biol. Sci. 2018, 25, 578–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dreiseitel, A.; Korte, G.; Schreier, P.; Oehme, A.; Locher, S.; Domani, M.; Hajak, G.; Sand, P.G. Berry anthocyanins and their aglycons inhibit monoamine oxidases A and B. Pharm. Res. 2009, 59, 306–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Watson, A.W.; Haskell-Ramsay, C.F.; David, O.; Kennedy, D.O.; Cooney, J.M.; Trower, T.; Scheepens, A. Acute supplementation with blackcurrant extracts modulates cognitive functioning and inhibits monoamine oxidase-B in healthy young adults. J. Funct. Foods 2015, 17, 524–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.H.; Kim, G.H.; Hwang, K.H. Monoamine Oxidase and Dopamine beta-Hydroxylase Inhibitors from the Fruits of Gardenia jasminoides. Biomol. Ther. (Seoul) 2012, 20, 214–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, A.; Narayanan, K.; Chaudhary, R.K.; Mishra, S.; Kumar, S.; Vinoth, K.J.; Padmanabhan, P.; Gulyas, B. Current Perspective of Stem Cell Therapy in Neurodegenerative and Metabolic Diseases. Mol. Neurobiol. 2017, 54, 7276–7296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guan, S.; Ge, D.; Liu, T.Q.; Ma, X.H.; Cui, Z.F. Protocatechuic acid promotes cell proliferation and reduces basal apoptosis in cultured neural stem cells. Toxicol. In Vitro 2009, 23, 201–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, S.; Zhang, X.L.; Ge, D.; Liu, T.Q.; Ma, X.H.; Cui, Z.F. Protocatechuic acid promotes the neuronal differentiation and facilitates survival of phenotypes differentiated from cultured neural stem and progenitor cells. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2011, 670, 471–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGuire, S.O.; Sortwell, C.E.; Shukitt-Hale, B.; Joseph, J.A.; Hejna, M.J.; Collier, T.J. Dietary supplementation with blueberry extract improves survival of transplanted dopamine neurons. Nutr. Neurosci. 2006, 9, 251–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Neurodegenerative Disease | Major Constituents of Protein Aggregates | Reference |
|---|---|---|
| Alzheimer’s Disease | Amyloid Beta Peptide (from APP) | Glenner and Wong, [93] |
| Masters et al. [94] | ||
| Selkoe et al. [95] | ||
| Hyperphosphorylated Tau | Bancher et al. [96] | |
| Parkinson’s Disease | α-synuclein | Baba et al. [97] |
| ALS | C9orf72 | Mori et al. [98] |
| FUS | Vance et al. [99] | |
| Ling et al. [100] | ||
| SOD1 | Bruijn et al. [101] | |
| Bosco et al. [102] | ||
| TDP-43 | Johnson et al. [103] | |
| Mackenzie et al. [104] |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Winter, A.N.; Bickford, P.C. Anthocyanins and Their Metabolites as Therapeutic Agents for Neurodegenerative Disease. Antioxidants 2019, 8, 333. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox8090333
Winter AN, Bickford PC. Anthocyanins and Their Metabolites as Therapeutic Agents for Neurodegenerative Disease. Antioxidants. 2019; 8(9):333. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox8090333
Chicago/Turabian StyleWinter, Aimee N., and Paula C. Bickford. 2019. "Anthocyanins and Their Metabolites as Therapeutic Agents for Neurodegenerative Disease" Antioxidants 8, no. 9: 333. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox8090333
APA StyleWinter, A. N., & Bickford, P. C. (2019). Anthocyanins and Their Metabolites as Therapeutic Agents for Neurodegenerative Disease. Antioxidants, 8(9), 333. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox8090333




